Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Kidney complications associated with COVID-19 infection and vaccination in children and adolescents: a brief review
- Hee Sun Baek, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):424-431. Published online June 28, 2023
-
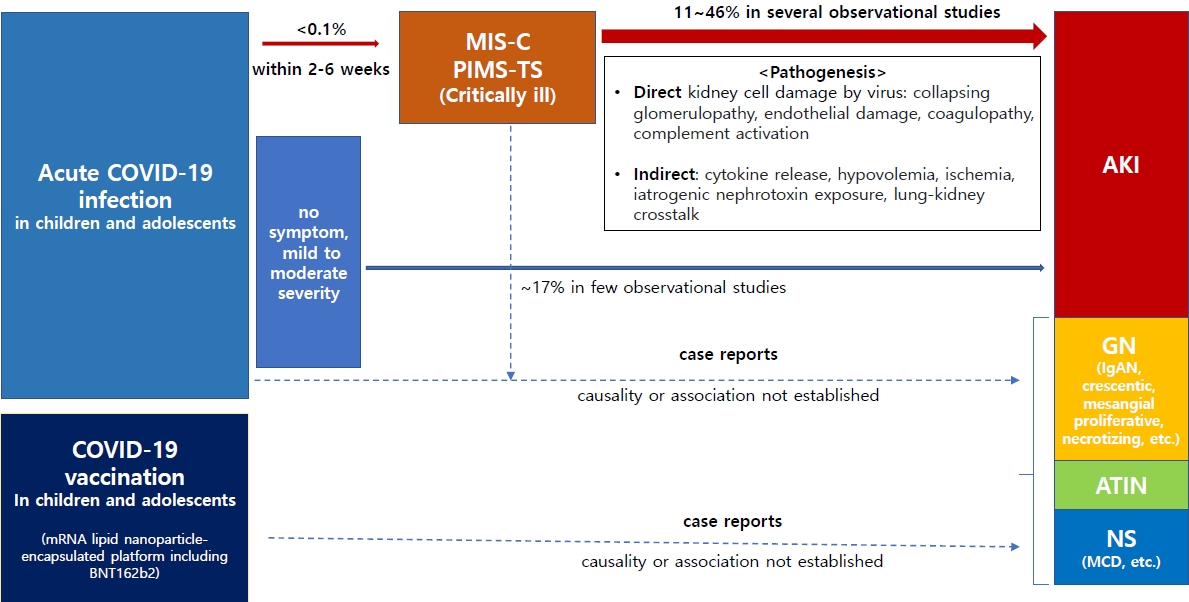
Several observational studies have shown that acute kidney injury affects up to 46% of children and adolescents who develop severe postinflammatory responses, such as multisystem inflammatory syndrome in childhood, due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Although causality has not been established, some cases of glomerulopathy or nephrotic syndrome occurring after COVID-19 infection or vaccination have been reported. Therefore, kidney complications associated with these conditions in children and adolescents warrant attention.
- Original Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Expression profiling of cultured podocytes exposed to nephrotic plasma reveals intrinsic molecular signatures of nephrotic syndrome
- Stuti Panigrahi, Varsha Chhotusing Pardeshi, Karthikeyan Chandrasekaran, Karthik Neelakandan, Hari PS, Anil Vasudevan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(7):355-363. Published online November 1, 2020
-
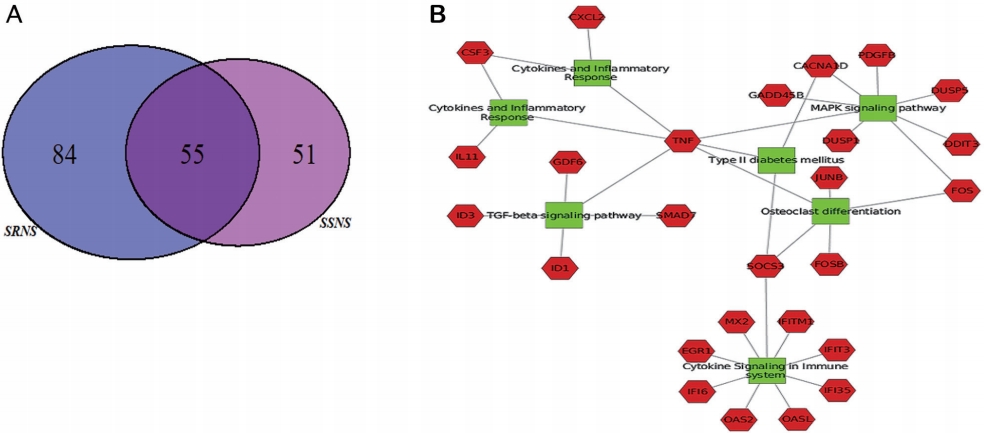
Question: Is it possible to classify nephrotic syndrome (NS) through gene expression profiling of podocytes exposed to NS plasma?
Finding: Our data showed different expression profiles in podocytes exposed to nephrotic plasma from different clinical groups, suggesting the molecular stratification of patients into intrinsic subtypes.
Meaning: Transcriptome profiling of podocytes treated with NS plasma can stratify patients into intrinsic subtypes and provide insight into the molecular mechanisms of podocyte injury.
- Changes in the thyroid hormone profiles in children with nephrotic syndrome
- Sun Hee Jung, Jeong Eun Lee, Woo Yeong Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(3):85-89. Published online October 4, 2018
-
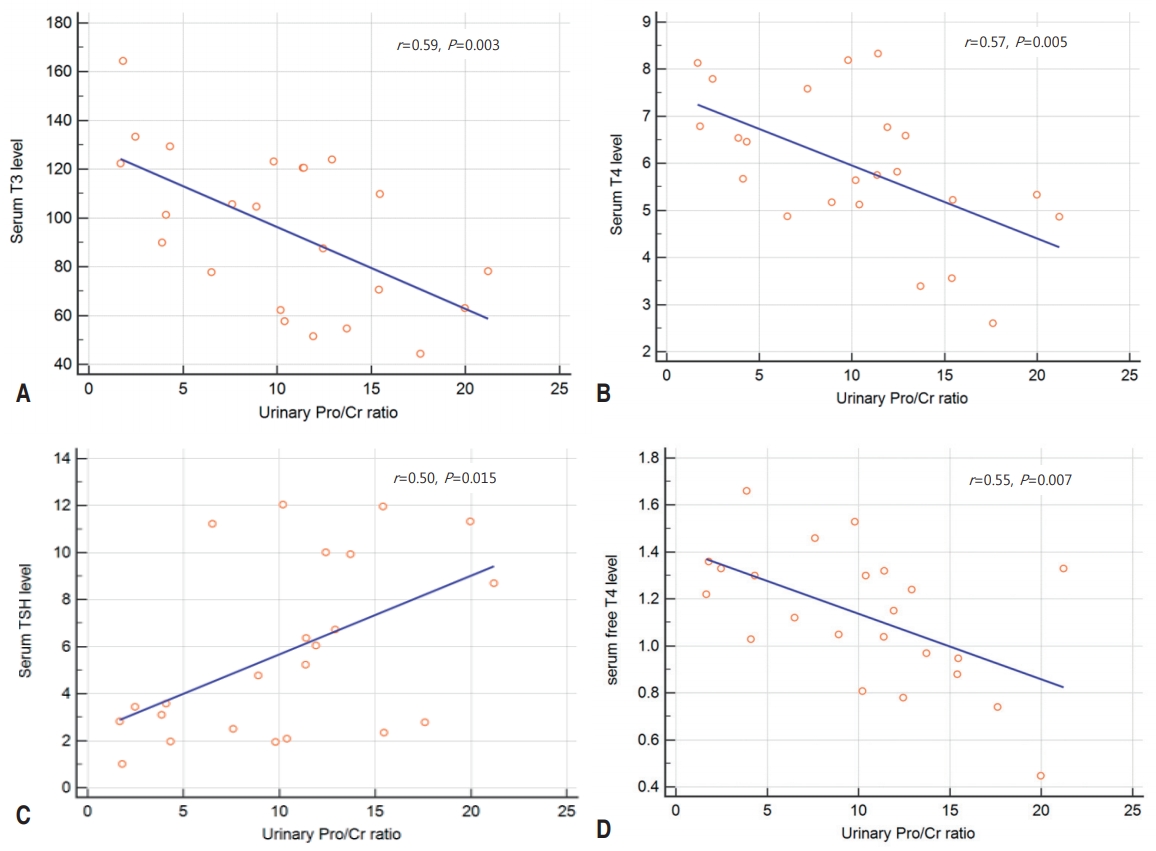
Purpose: We compared thyroid hormone profiles in children with nephrotic syndrome (NS) during the nephrotic phase and after remission. Methods: This study included 31 pediatric NS patients. The thyroid hormone profiles included serum levels of triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and free T4. Results: Of the 31 patients, 16 (51.6%) showed abnormal thyroid hormone profiles: 6 had overt hypothyroidism, 8...
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Genetics of hereditary nephrotic syndrome: a clinical review
- Tae-Sun Ha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):55-63. Published online March 27, 2017
-
Advances in podocytology and genetic techniques have expanded our understanding of the pathogenesis of hereditary steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS). In the past 20 years, over 45 genetic mutations have been identified in patients with hereditary SRNS. Genetic mutations on structural and functional molecules in podocytes can lead to serious injury in the podocytes themselves and in adjacent structures, causing sclerotic...
- Case Report
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Eosinophilic gastroenteritis in an 18-year-old male with prolonged nephrotic syndrome
- Da Min Choi, Jung Eun Pyun, Hyung Eun Yim, Kee Hwan Yoo, Jung Ok Shim, Eun Jung Lee, Nam Hee Won
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S72-S75. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis is a rare disease characterized by prominent eosinophilic tissue infiltration of the gastrointestinal tract. Here, we report a case of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in an 18-year-old patient with prolonged nephrotic syndrome who presented with abdominal pain and peripheral hypereosinophilia. During the previous 2 years, he had visited local Emergency Department several times because of epigastric pain and nausea. He...
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Pathogenesis of minimal change nephrotic syndrome: an immunological concept
- Seong Heon Kim, Se Jin Park, Kyoung Hee Han, Andreas Kronbichler, Moin A. Saleem, Jun Oh, Beom Jin Lim, Jae Il Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(5):205-211. Published online May 31, 2016
-
Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS) in children is characterized by massive proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia. Minimal change nephrotic syndrome (MCNS) is the most common form of INS in children. The pathogenesis of MCNS still remains unclear, however, several hypotheses have been recently proposed. For several decades, MCNS has been considered a T-cell disorder, which causes the impairment of the glomerular filtration barrier...
- Nephrotic syndrome: what's new, what's hot?
- Hee Gyung Kang, Hae Il Cheong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(8):275-282. Published online August 21, 2015
-
While the incidence of nephrotic syndrome (NS) is decreasing in Korea, the morbidity of difficult-to-treat NS is significant. Efforts to minimize treatment toxicity showed that prolonged treatment after an initial treatment for 2-3 months with glucocorticosteroids was not effective in reducing frequent relapses. For steroid-dependent NS, rituximab, a monoclonal antibody against the CD20 antigen on B cells, was proven to...
- Original Article
- Initial steroid regimen in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome can be shortened based on duration to first remission
- Hee Sun Baek, Ki-Soo Park, Hee Gyung Kang, Cheol Woo Ko, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(6):206-210. Published online June 22, 2015
-
Purpose The use of a 12-week steroid regimen (long-term therapy, LT) for the first episode of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (NS) reportedly induces a more sustained remission and lower relapse rate than previous regimens, including an 8-week steroid regimen (short-term therapy, ST). Here, we assessed the potential for selective application of 2 steroid regimens (LT vs. ST) based on the days to...
- Case Report
- Cystic fibrosis of pancreas and nephrotic syndrome: a rare association
- Selvi Kelekçi, Müsemma Karabel, Aydın Ece, Velat Şen, Ali Güneş, İlyas Yolbaş, Cahit Şahin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(10):456-458. Published online October 31, 2013
-
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disease with autosomal recessive inheritance and is common in Caucasian people. The prevalence of this disease is between 1/2,000 and 1/3,500 live births, and the incidence varies between populations. Although the CF transmembrane conductance regulator gene is expressed in the kidneys, renal involvement is rare. With advances in the treatment of CF, life expectancy...
- Review Article
- Complications of nephrotic syndrome
- Se Jin Park, Jae Il Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(8):322-328. Published online August 31, 2011
-
Nephrotic syndrome (NS) is one of the most common glomerular diseases that affect children. Renal histology reveals the presence of minimal change nephrotic syndrome (MCNS) in more than 80% of these patients. Most patients with MCNS have favorable outcomes without complications. However, a few of these children have lesions of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, suffer from severe and prolonged proteinuria, and...
- Treatment of steroid-resistant pediatric nephrotic syndrome
- Hee Gyung Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(8):317-321. Published online August 31, 2011
-
Children who suffer from steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS) require aggressive treatment to achieve remission. When intravenous high-dose methylprednisolone fails, calcineurin inhibitors, such as cyclosporine and tacrolimus, are used as the first line of treatment. A significant number of patients with SRNS progress to end-stage renal disease if remission is not achieved. For these children, renal replacement therapy can also be...
- Case Report
- A case of steroid-induced psychosis in a child having nephrotic syndrome with toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Sae Yoon Kim, Jae Min Lee, Yong Hoom Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(3):437-441. Published online March 15, 2010
-
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS) are rare, life-threatening mucocutaneous diseases, usually attributable to drugs and infections. Corticosteroids have been used in the management of TEN for the last 30 years. This remains controversial and is still much debated. TEN can occur despite administration of high doses of systemic corticosteroids. The psychiatric side effects of corticosteroids can include... -
- Original Article
- Polymorphisms of the NR3C1 gene in Korean children with nephrotic syndrome
- Hee Yeon Cho, Hyun Jin Choi, So Hee Lee, Hyun Kyung Lee, Hee Kyung Kang, Il Soo Ha, Yong Choi, Hae Il Cheong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(11):1260-1266. Published online November 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (NS) can be clinically classified as steroid-sensitive and steroid-resistant. The detailed mechanism of glucocorticoid action in NS is currently unknown. Methods : In this study, we investigated 3 known single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (ER22/23EK, N363S, and BclI) of the glucocorticoid receptor gene (the NR3C1 gene) in 190 children with NS using polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment... -
- Is routine screening examination necessary for detecting thromboembolism in childhood nephrotic syndrome?
- Mun Sub Kim, Ja Wook Koo, Soung Hee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(7):736-741. Published online July 15, 2008
-
Purpose : The incidence of thromboembolic episodes in children with nephrotic syndrome (NS) is low; however, these episodes are often severe. Moreover, both pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) and renal vein thrombosis (RVT) rarely show clinical symptoms. This study was performed to determine the benefits of routine screening in the detection of thrombosis in childhood NS. Methods : Among 62 children with... -
- Therapeutic response of cyclosporine and outcome in steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome
- Hyung Soon Choi, Joo Hoon Lee, Young Seo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(3):293-298. Published online March 15, 2008
-
Purpose : The aim of our study was to evaluate the therapeutic response to cyclosporine, time to remission and side effects in steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS). Methods : This study included 22 children with idiopathic SRNS who were treated with cyclosporine between June 1989 and August 2006. Medical records were reviewed retrospectively. Results : The mean age of patients at diagnosis... -
- Effects of puromycin aminonucleoside on the cytoskeletal changes of glomerular epithelial cells
- Jun Ho Lee, Tae Sun Ha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(1):54-61. Published online January 15, 2008
-
of microvilli, but also separated the intercellular gaps and linear ZO-1. PAN induced oxidative stresses in time and dose dependent manners and increases of intercellular permeability in anti-oxidants inhibitable manners. High concentration of PAN induced not only actin polymerization and disorganization, but also the conglomerulation and internal dislocation of α-actinin protein. The intensities of fluorescences of ZO-1 protein were diminished... -
- Clinical Lecture
- Can We Predict How Often Nephrotic Syndrome will Relapse into the Patients?
- Mee Kyung Namgoong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(10):1033-1037. Published online October 15, 2005
-
Pediatric nephrotic syndrome is a well-known illness for its high relapsing rate. If we can predict the relapsing rate and the responses to the steroid therapy of individual patients with nephrotic syndrome, the predictability will be helpful in building a therapeutic plan. Here is my review of research articles on the risk factors for the prediction of relapsing nephrotic syndrome. -
- Original Article
- Pharmacokinetics of Cyclosporine A and Its Therapeutic Effect in Children with Renal Diseases
- Woo Sung Chun, Min-Soo Park, Jae Seung Lee, Juyun Yu, Moon Sung Park, Ki-Soo Pa
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(2):193-203. Published online February 15, 2004
-
Purpose : To know the body handling properties and anti-proteinuric effect of cyclosporine A(CsA) in children with renal diseases, 34 patients with nephrotic syndrome or glomerular diseases were included to treatment trials and evaluated. Methods : Microemulsion formula CsA, 5 mg/kg/day was administered orally in two divided doses for 9.3?.6 months. Pharmacokinetic studies of CsA were done twice at beginning and... -
- Risk Factors for the First-Year Relapse in Children with Nephrotic Syndrome
- Hye Kyoung Shin, Ji Hee Kim, Kee Hwan Yoo, Young Sook Hong, Joo Won Lee, Soon Kyum Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(9):889-892. Published online September 15, 2003
-
Purpose : This study aimed to evaluate risk factors of the first year relapse in children with nephrotic syndrome(NS) without the need for biopsy. Methods : We reviewed, retrospectively, 78 children diagnosed with steroid responsive nephrotic syndrome between July 1997 and June 2002. Median years to follow up were 4.4 years(range : 1-5 years). We divided the patients into two groups(group... -
- Clinical Study of the Correlation of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha and the Proteinuria of Henoch-Schönlein Nephritis and Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome
- Dong-Ho Jeong, Jeong-Hyun Park, Hye-Cheon Jeong, Hyun-Hoe Koo, Jun-Ho Lee, Tae-Sun Ha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(2):240-246. Published online February 15, 2002
-
Purpose : It is not clear that the development of glomerular injury and aggravation by tumor necrosis factor alpha(TNF-α) is related to intrarenal or serum concentration of TNF-α. So, we studied the relationship between the concentration of TNF-α and aggravation of glomerular damage in the Henoch-Schönlein nephritis(HSN) and idiopathic nephrotic syndrome(INS). Methods : We collected the sera and urines of... -
- Case Report
- Galloway-Mowat Syndrome in Two Siblings
- Hae-Sung Jung, Eun-Young Cho, Jae-Young Lim, Ji-Hyeoan Seo, Myoung-Bum Choi, Chan-Ho Park, Hang-Ok Woo, Hee-Shang Youn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(9):1081-1084. Published online September 15, 2001
-
We report on two Korean siblings with multiple congenital anomalies : microcephaly, gyral abnormality, minor facial anomalies, and congenital nephrotic syndrome. The first infant developed proteinuria at age 3 days. This condition appeared similar to that described by Galloway and Mowat and reviewed by Cooperstone, et al, especially the presence of abnormal gyral patterns. She died at 19 months. The second infant; the brother... -
- Two Cases of Thin Basement Membrane Nephropathy presented with Minimal Change Nephrotic Syndrome
- Young Mee Seo, Jae Gul Chung, En Sil Yu, Jin Yeong Jeong, Young Seo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(7):978-982. Published online July 15, 2000
-
Thin basement membrane nephropathy(TBMN) is defined histologically as follows : 1) By light microscopy only minor abnormalities are detected in the glomeruli at most minor mesangial widening. 2) By electron microscopy, diffuse thinning of glomerular basement membrane is demonstrated. 3) By immunofluorescence, absence of immunoglobulins and complement components is demonstrated. 4) Alport`s syndrome and systemic diseases that may affect the... -
- A Childhood Case of Nephrotic Syndrome Complicated with Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Followed by Left Popliteal Artery Thrombosis
- Si-Eun Lee, Sue-Jin Lee, Yang-Suk Jung, Jae-Young Lim, Chan-Hoo Park, Hyang-Ok Woo, Jin-Jong Yoo, Hee-Shang Youn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(7):1019-1025. Published online July 15, 1999
-
We report a 10-year-old male with steroid-responsive nephrotic syndrome which was complicated by cerebral venous sinus thrombosis including superior sagittal sinus and left popliteal artery thrombosis following 5 months later. At each thrombotic episode, he suffered from relapse of massive proteinuria with hypovolemic crisis, and from hemoconcentration with dehydration due to vomiting or diarrhea. Brain MR angiography confirmed thromboses of... -
- Levamisole-Induced Reversible Agranulocytosis in Children with Steroid Dependent Nephrotic Syndrome
- Su Jin Lee, Su Ja Hwan, Eun Seon Yoo, Seung Joo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(4):576-579. Published online April 15, 1999
-
Levamisole has been used for nephrotic syndrome due to its immunostimulating, immunomodulating, and steroid-sparing effects. Agranulocytosis, a serious side effect of levamisole, was rare and mostly associated with autoimmune disease, neoplastic disease and HLA B27 except one case in a nephrotic syndrome who was treated with high-dose(5mg/kg QOD) levamisole. This 15 year-old girl with steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome, who was... -
- Original Article
- The Effect of Long-term Steroid Therapy on Cardiac Function in Nephrotic Syndrome
- Jae-Goo Lee, Hong-Ryang Gil, Jae-Ho Lee, Yong-Hun Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(1):102-107. Published online January 15, 1999
-
Purpose : The aim of this study is to assess the cardiac effect of long-term steroid therapy in nephrotic syndrome and the validity of LV functional parameters as an early predictor of subclinical cardiac dysfunction. Methods : The study group was composed of 21 patients diagnosed as minimal change nephrotic syndrome(NS), being managed with prednisone over 6 months or within 6... -
- Long-term Follow-up Study of Children with Minimal Change Nephrotic Syndrome
- Jung Sue Kim, Hae Il Cheong, Hyun Soon Lee, Yong Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(12):1675-1684. Published online December 15, 1998
-
Purpose : Most of childhood MCNS has a long disease course with frequent relapses. This study was designed to analyze the long-term clinical course of childhood MCNS, focusing at relapsing pattern, treatment response and complications. Mothods : The medical records of 137 children with biopsy-proven MCNS observed during 1976 ti 1996 were analyzed retrospectively. They were classified as initial responders(111 patients,... -
- The Effect of Steroid Therapy on Growth and Bone Density in Children with Nephrotic Syndrome
- Seong Hoi Jeon, Ae Yeon Lim, Young Kook Kim, Hae Won Cheon, Kee Hwan Yoo, Young Sook Hong, Joo Won Lee, Soon Kyum Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(10):1396-1402. Published online October 15, 1998
-
Purpose : Long-term steroid therapy for various glomerular disorders in children has been known to decrease serum Vit D3 level and develop osteomalacia. The aim of this study was to observe the effect of long-term steroid therapy on growth and bone density in children with nephrotic syndrome. Methods : Bone density of 17 steroid-treated nephrotic syndrome was compared with that of... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Congenital Nephrotic Syndrome due to Diffuse Mesangial Sclerosis
- Jung-Jin Yu, Dong Kyu Jin, Hae Il Cheong, Hyun Soon Lee, Yong Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(3):415-419. Published online March 15, 1998
-
Diffuse mesangial sclerosis(DMS) is one of the underlying pathology of congenital and infantile nephrotic syndrome. Infants with DMS develop nephrotic syndrome before 2 years of age and progress to end stage renal disease within 3 years of age. The authors experienced a case of isolated DMS in a 4-month-old male infant who had nephrotic syndrome for 1 month. The diagnosis... -
- Original Article
- A Study of Serum Cytokines in Nephrotic Syndrome
- Mea Young Chang, Jae Ho Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(12):1701-1706. Published online December 15, 1997
-
Purpose : It has been reported that patients with nephrotic syndrome have high serum IgE value and IL-4 involve in IgE synthesis, IL-6 is an autocrine growth factor for the proliferation of mesangial cells. We studied association between serum cytokines and of nephrotic syndrome. Methods : We measured serum IL-6, IL-4, IFN-Υ, CD23 in 14 children with nephrotic syndrome and 3 healthy children by... -
- Prediction of Steroid Responsiveness in the Primary Nephrotic Syndrome Using Urinary β2-Microglobulin Level and N-Acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase Activity
- Kwang In Lee, In Seok Lim, Eung Sang Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(9):1285-1292. Published online September 15, 1997
-
Purpose : Considering that renal biopsy is not routinely indicated in nephrotic syndrome in children and the risk of the procedure, we studied that it is possible to predict steroid responsiveness in nephrotic syndrome and the difference in responsivenss is related with the histopathologic type using urinary β2-microglobulin and N-Acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase activity as a safe and noninvasive method. Methods : We measured serum creatinine, albumin, cholesterol... -
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











