Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Gross motor dysfunction and balance impairments in children and adolescents with Down syndrome: a systematic review
- Preyal D. Jain, Akshatha Nayak, Shreekanth D. Karnad, Kaiorisa N. Doctor
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):142-149. Published online June 11, 2021
-
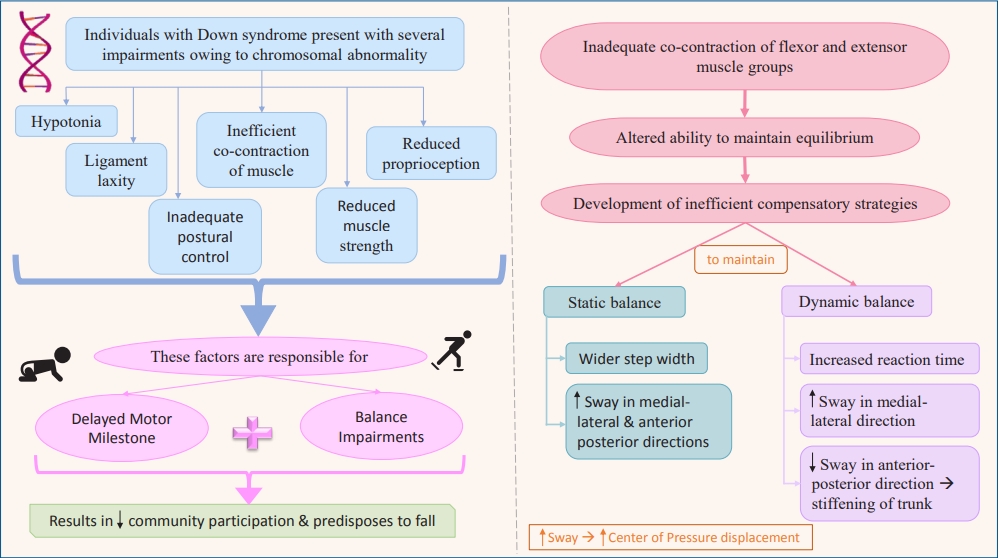
Question: What are the primary motor and balance dysfunctions in children with Down syndrome?
Finding: These individuals have gross delays, altered balance, and inefficient compensatory mechanisms.
Meaning: Neuromuscular and musculoskeletal impairments due to the chromosomal abnormality lead to developmental delay. These children also exhibit poor balance with greater instability and inefficient compensatory mechanisms including altered center of pressure displacement and trunk stiffening that predisposes them to falls.
- Case Report
- Asymptomatic moyamoya syndrome, atlantoaxial subluxation and basal ganglia calcification in a child with Down syndrome
- Kyung Yeon Lee, Kun-Soo Lee, Young Cheol Weon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(12):540-543. Published online December 20, 2013
-
Down syndrome, the most common chromosomal abnormality, may be associated with various neurologic complications such as moyamoya syndrome, cervical spinal cord compression due to atlantoaxial subluxation, and basal ganglia damage, as well as epileptic seizures and stroke. Many cases of Down syndrome accompanied by isolated neurologic manifestations have been reported in children; however, Down syndrome with multiple neurologic conditions is...
- Original Article
- Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase C677T and A1298C Polymorphisms and Risk of Down Syndrome
- Kyu Young Chae, Jin Hee Han, Ji Yeong Seo, Min Jung Cho, Sehyun Kim, Nam Keun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(10):1053-1057. Published online October 15, 2004
-
Purpose : The C677T polymorphism of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase(MTHFR) has been suggested as a risk factor of maternal meiotic nondisjunction for Down syndrome. Recently, a second genetic polymorphism in MTHFR at position 1298 was reported. However, a positive association between the A1298C MTHFR polymorphism and Down syndrome has not been reported. Therefore, this study was undertaken to determine which polymorphism... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Nonsyndromic Paucity of Interlobular Bile Ducts in Down Syndrome
- Chun Hyuk Chang, Jun Ho Kim, Sun Ju Le, Dong Seok Lee, Doo Kwun Kim, Sung Min Choi, Woo Taek Kim, Tae Jung Jang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(6):858-862. Published online June 15, 1999
-
The nonsyndromic paucity of interlobular bile ducts, which belongs to intrahepatic biliary atresia, is characterized by conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, suggesting cholestasis in newborn infants it has little relationship with extrahepatic congenital abnormalities. Pathologic findings through percutaneous liver biopsy show portal changes(duct paucity and fibrosis) and lobular changes(cholestasis, giant cell transformation, extramedullary hematopoiesis and perisinusoidal fibrosis). The overall incidence of intrahepatic biliary... -
- A Case of Acute Myeloblastic Leukemia Transformed from Transient Myeloproliferative Disorder with Down Syndrome
- Jae Eun Lee, Seung Woo Baeck, Wan Seob Kim, Chun Hee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(1):128-132. Published online January 15, 1999
-
Individuals with Down syndrome have a high incidence of hematologic diseases such as transient myeloproliferative disorder(TMD) & acute leukemia. Because it is difficult to distinguish TMD from acute myeloblastic leukemia, the diagnosis in neonate, who have Down syndrome, should be made with extreme caution. TMD usually undergoes spontaneous remission within a few months, but acute leukemia can develope after remission... -
- A Case of Unusual (1q;21q) Translocation Down Syndrome Inherited from a t(1q;21q) Balanced Carrier Mother
- Dong Hoon Yi, Jae Ock Park, Sang Mann Shin, You Kyoung Lee, Won Bae Kim, Won Bae Lee, Sung Sup Park, Han-Ik Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(8):1156-1161. Published online August 15, 1997
-
Down syndrome is the most common autosomal syndrome in man. The incidence of trisomy 21 due to translocation is about 3.5-5%. Translocations are usually centric fusions between a 21 and a D group (54.2%) or a G group (40.9%) chromosome. Since the short arm of 21 carries no phenotypically active genes, even if the short arm of 21 is lost, usually there is... -
- Original Article
- Extrachromosome 21 in Korean with Down Syndrome Using DNA Haplotyping
- Jin-Sung Lee, Won Kyu Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(7):917-924. Published online July 15, 1997
-
Purpose : Down syndrome, the most common single cause of mental retardation, is usually due to meiotic nondisjunction leading to trisomy 21. In order to understand the mechanisms of meiotic nondisjunction including parental origin of an extrachromosome and the meiotic stage of nondisjunction, we have studied DNA polymorphisms at loci on the long arm of chromosome 21 in 36 families with free trisomy 21. Methods... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Congenital Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia with Down Syndrome
- Nan Yee Kye, Kon Hee Lee, Jae Kook Cha, Hye Sun Yoon, Won Keun Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(4):578-583. Published online April 15, 1997
-
We experienced a case of congenital acute megakaryoblastic leukemia with Down syndrome. The patient was admitted due to characteristic facial figure of Down syndrome and abdominal distension. Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia was diagnosed with abundant megakaryoblast in peripheral blood smear, severe myelofibrosis in bone marrow biopsy and positive platelet glycoprotein Ⅲa receptor. On third hospital day, the patient expired due to DIC... -
- Original Article
- The Pelvic Changes of Patients with Down Syndrome in Korea
- Jong Park, Kwan Cheol Oh, Kyoung Sim Kim, Ki Bok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(2):159-166. Published online February 15, 1997
-
Purpose : Since Caffey et al. first described the anomaly in pelvis among the Down patients, decreased iliac and pelvic indexes have been helpful in diagnosing the syndrome. For Korean cases, however, no definitive data are available as yet, prompting us to evaluate the pelvic changes in Korean Down's patients. Methods : Subjected to this study were 68 children with Down's syndrome. As... -
- Changes in MaternalAge and the Incidence of Down Syndrome
- Chang Weon Oh, Sung Su Lim, Ki Bok Kim, Won Jin Kee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1996;39(11):1512-1519. Published online November 15, 1996
-
Purpose : The incidence of Down syndrome, the most common chromosoaml anomaly, increases with the advanced maternal age. Recently, however, the incidence of Down symdrome was reported to have decreased with wide acceptance of prenatal diagnosis and planned parenthood, prompting us to re-evaluate the incidence of Down syndrome in relation to changes in maternal age. Methods : Subjected to study were 296 Down cases: 26... -
- Clinical Course of Atrioventricular Septal Defect(AVSD) in Down and non Down syndrome
- Un Seok Nho, Myung Chul Hyun, Sang Bum Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1996;39(9):1288-1294. Published online September 15, 1996
-
Purpose : It is well known that 1/3 - 1/2 of Atrioventricular septal defect(AVSD) patients also have Down syndrome which may influence the clinical course of AVSD. To know the anatomic type of AVSD and the effect of Down syndrome on the clinical course of AVSD, we studied 37 cases( Down group: 14 cases, non Down group: 23 cases) who were diagnosed and... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Syndrome Associated with Colonic Atresia
- Si Whan Koh, Joon Soo Park, Kyung Hwan Oh, Dong Hwan Lee, Sang Jhoo Lee, Chul Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(7):1030-1033. Published online July 15, 1993
-
The association of colonic atresia in patients with Down syndrome is a rare anomaly. The incidence of congenital atresia of the gastrointestinal tract has been estimated to be about one in 1500 births. Colonic atresia is rarer still, and is throut to comprise about 5% to 10% of this group. This intestinal atresia occurs in about 30% to 50% of... -
- A Case of Monozygotic Twin with Dwn Syndrome
- Seong Heon Jeon, Choong Hyun Yoon, Young Wook Kim, Ki Bok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(3):434-438. Published online March 15, 1993
-
Down syndrome is the most common autosomal chromosomal abnormality characterized by mental and growth retardation, and by various typical features including prominent epicanthal fold, oblique palpebral fissure, flat nasal bridge, short and broad hand, wide toe interspace, etc. The overall incidence has been shown to be 1:800 deliveries, increasing with advancing maternal age. However, twin cses are extremely rare, and... -
- Original Article
- A Study on the Atlantoaxial Instability in Children with Down syndrome
- Sa Young Kim, Chan Yung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(2):179-184. Published online February 15, 1993
-
To evaluate the atlantoaxial instability in children with Down syndrome, the authors analyzed the 97 children with Down syndrome attending to 2 schools for handicaped children in Pusan. The results of study were as follows; 1) The incidence of atlantoaxial instability in 97 individuals with Down syndrome was 8(8.3%) in neutral position and in 10(10.3%) in flexion, respectively. 2) The mean atlantoaxial gap... -
- The Incidence of Hypothyroidism in Children with Down Syndrome
- Seong Hyeon Jeon, Chun Ho Cho, Kyoung Sim Kim, Ki Bok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(4):534-538. Published online April 15, 1992
-
A review of Thyroid function tests was performed on 32 children with Down syndrome confirmed by cytogenetic examination at the Dept. of Pediatrics, Kwangju Christian Hospital from Jan.1989 to Feb.1990. 1) Twenty among 32 children with Down syndrome were male, with the sex ratio being 1.7 : 1. Their ages ranged from 3 days to 5 years, with the mean age... -
- A case of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia with Down syndrome.
- Sung Jin Chang, Sung Min Sohn, Heung Sik Kim, Chin Moo Kang, Dong Seok Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(12):1730-1735. Published online December 31, 1991
-
We experienced a case of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (M7) with Down syndrome. The patient was admitted due to premature SGA, which revealed characteristic facial figure of Down syndrome. M7 was diagnosed with PB smear which showed abundant megakaryoblast and confirmed by using the monoclonal antiplatelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antibody (J 15). On 25th hospital day, the patient gained weight but discharged without further treatment of M7. Authors... -
- Clinical considerations of acute leukemia or transient myeloprolifo- rative disorder in Down syndrome.
- Eun Sil Dong, Sung Hee Jang, Hong Hoe Koo, Hye Lim Jung, Hee Young Shin, Hyo Seop Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(1):74-82. Published online January 31, 1991
-
Children with Down syndrome have an increased incidence of acute leukemia. Infants with Down syndrome are also at risk of developing a transient myeloproliferative disorder indistinguishable from acute nonlymphocytic leukemia (ANLL) except by its eventual clinical recovery. We observed 11 patients with acute leukemia or transient myeloproliferative disorder in Down syndrome who had admitted to the Departmetn of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children’s Hospital,... -
- A Case of Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in infantwith down Syndrome.
- Jang Sik Moon, Hae Young Hwang, Sejung Sohn, Hak Soo Lee, Heum Rye Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1990;33(10):1441-1446. Published online October 31, 1990
-
Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia is an uncommonly recognized disorder that is characterized by rapidly progressive proliferation of atypical megakaryocytes and their precursor cells, and fatal course. Abnormalities in chromosome 21 may have more than relationship to it. The authors report a case of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia in a 17 day-old male patient who was admitted for evaluation of high fever and dyspnea. The infiltration of atypical megakaryocytes... -
- A Case of (21q 21q) Translocation Down Syndrome Inherited from a t(21q 21q) Balanced Carrier Mother.
- Byeong Gie Yeo, Chong Woo Bae, Yong Mook Choi, Chang Il Ahn, Bo Hoon Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1990;33(7):1004-1008. Published online July 31, 1990
-
Vast majority of t(21q 21q) Down syndrome occur de novo and familial cases are extremely rare. In familial translocation Down syndrome, One of the parent show 45 chromosomes. In general, the carrier parent carrying (21q 21q) translocation is phenotypically normal because significant amount of genetic material has not been lost in the translocation process. Homologous Robertsonian translocation can be produced either by abnormal gametogenesis... -
- A Case of Nonimmunologic Hydrops Fetalis Associated with Down Syndrome.
- Sang Eun Lee, Meen Jai Lee, Dong Hwan Lee, Sang Jhoo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1990;33(2):205-211. Published online February 28, 1990
-
We experienced a case of nonimmunologic hydrops fetalis associated with Down syndrome. The patient had generalized edema with severe scrotal swelling and abdominal distension. A roentgenogram showed bilateral pleural effusion and ascites. The chromosomal study revealed 21 trisomy. On autopsy, there were pleural fluid and ascites as well as pericardial fluid. Small ASD and incomplete lobation of the right lung were detected. Chromosomal abnormalities should always... -
- Physical Features, Karyotypes and Dermatoglyphics of 113 Children with Down Syndrome.
- Byung Ho Lim, Kyoung Sim Kim, Ki Bok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1988;31(4):474-481. Published online April 30, 1988
-
The physical features including dermatoglyphic patterns as well as the karyotype patterns were assesed in 113 children with Down Syndrome who had been cytogenetically confirmed in the Department during past 5 years from August 1981. The results are summarized as follows: 1) The sex ratio of the patients was 1.2 male to one female. 2) Cytogenetic examination revealed 21-trisomy in 79% and translocation in 21% of all... -
- Clinical Evaluation of Congenital Heart Disease in Down Syndrome.
- Sang Kyu Park, Young Hoon Kim, Son Moon Shin, Chung Il Noh, Jung Yun Choi, Yong Soo Yun, Cang Yee Hong, Kyoo Wan Choi, Shin Yong Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1986;29(10):1095-1103. Published online October 31, 1986
-
The association of congenital heart disease in patients with Down syndrome has been recognized for nearly 100 years. A wide variety of congenital heart diseases have been identified in these patients. This is the report of clinical evaluation of 105 patients with congenital heart disease in Down syndrome, experienced at the Seoul National University Hospital, during past 6 years from Jan. 1980... -
- Superoxide Dismutase Activity in Down Syndrom.
- Moon Sook Lee, Hae Woon Chang, Kun Soo Lee, Ja Hoon Koo, Kun Young Sohn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1986;29(4):361-374. Published online April 30, 1986
-
Superoxide dismutase activity of erythrocyte in 20 cases of 21-trisomy Down syndrome between 2 months and 15 years old age and 13 cases of age-matched normal children were checked at Department of Pediatrics and Department of Biochemistry, School of Medicine, Kyung-Pook National University. The results were following: Mean superoxide dismutase activity in normal children was 202.25 U/gmHb and in Down syndrome 291.69 U/gmHb, and the ratio... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Trensient Myeloproliferative Disorder with Down Syndrome.
- Dong Gyoon Kim, Jae Ho Lee, Jung Il Noh, Hyo Seop Ahn, Chang Yee Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(10):1024-1028. Published online October 31, 1983
-
Transient myeloproliferative disorder has been reported in infants with Down syndrome. Infants with Down syndrome and this transient myeloproliferative disorder often present with signs and symptoms that are clinically and hematologically indistinguishable from congenital acute myelogenous leukemia. In contrast to congenital AML, complete clinical and hematological recovery occurs within weeks to months of diagnosis without any specific anti- leukemic treatment. A case of transient myeloproliferative disorder... -
- Original Article
- Physical Features of Korean Children of Down Syndrome.
- Hack Joo Cha, You Nam Kim, Ki Bok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1982;25(10):994-1006. Published online October 31, 1982
-
Ths physical features characteristic of Down Syndrome in Korean children were analyzed in 81 patients confirmed by cytogenetic examination in the Department of Pediatrics, Kwangju Christian Hospital, during the period from March, 1974 through July, 1981, and results are- summarized as follows: 1) The sex ratio was 2 males to one female. 2) The frequency of most stigmata found among Down cases were signifi cantly higher than, among... -
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











