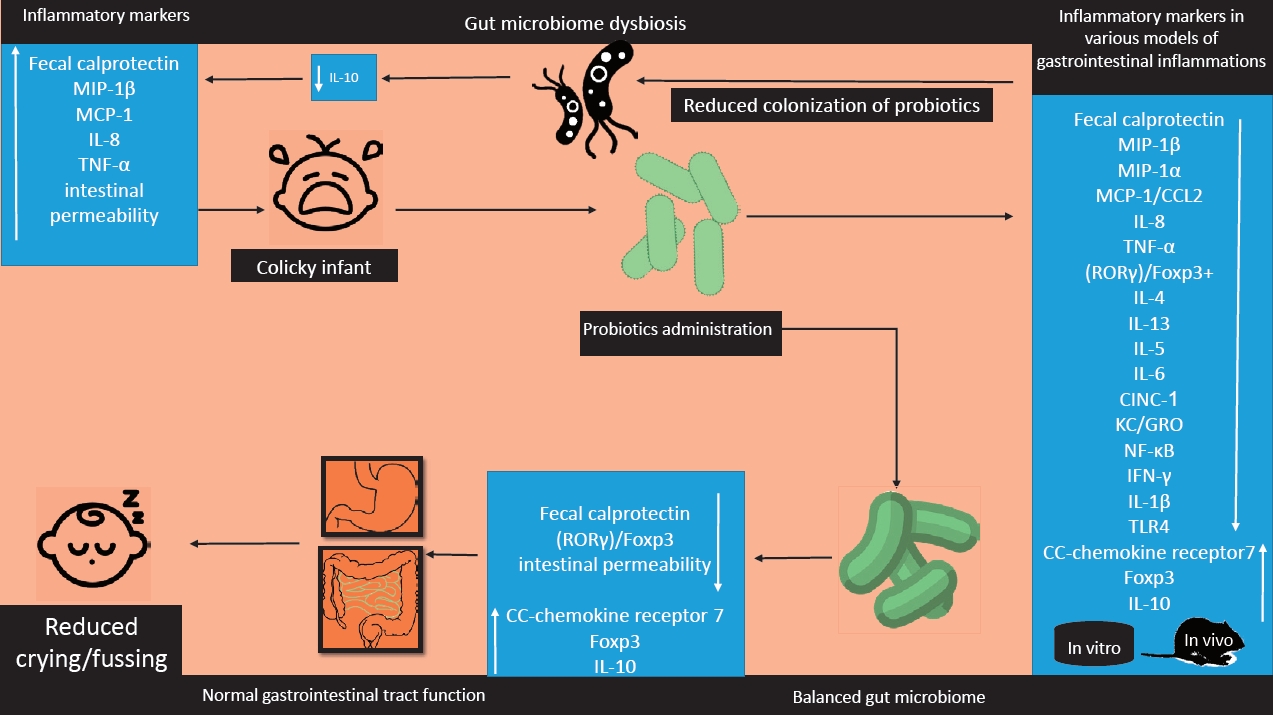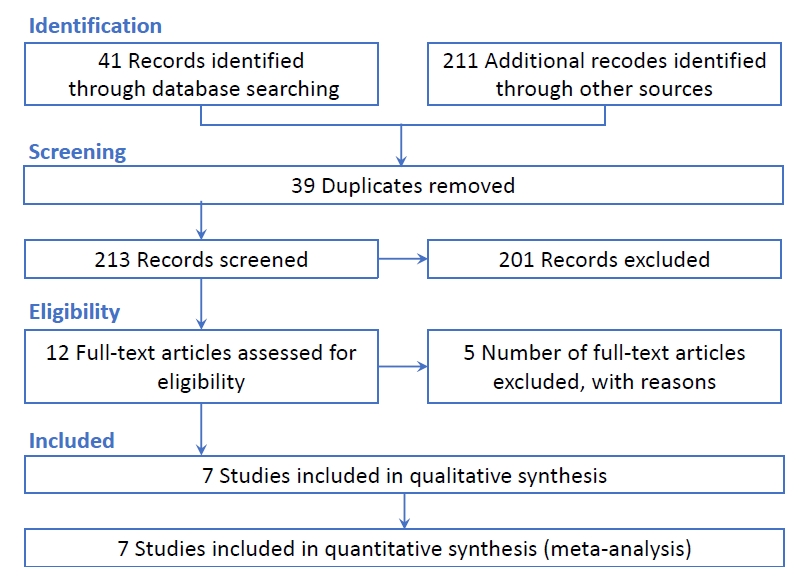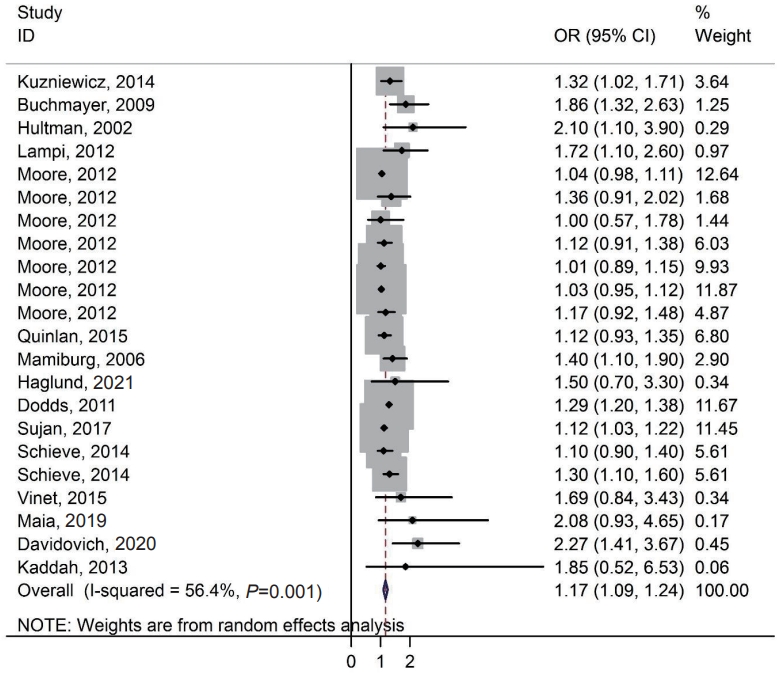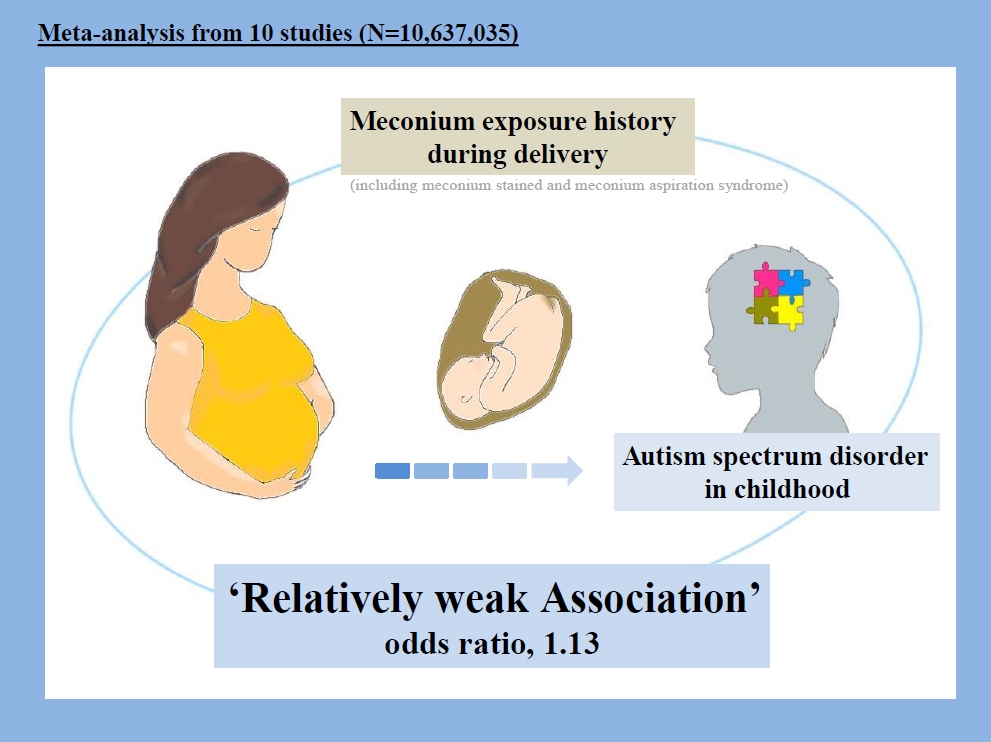
|
Question: Have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) increased risk of having an offspring with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)?
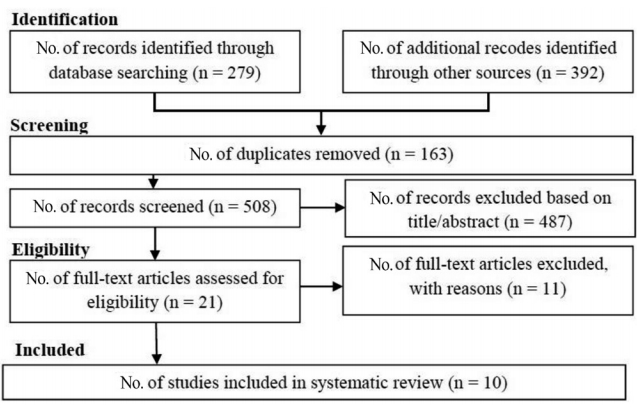
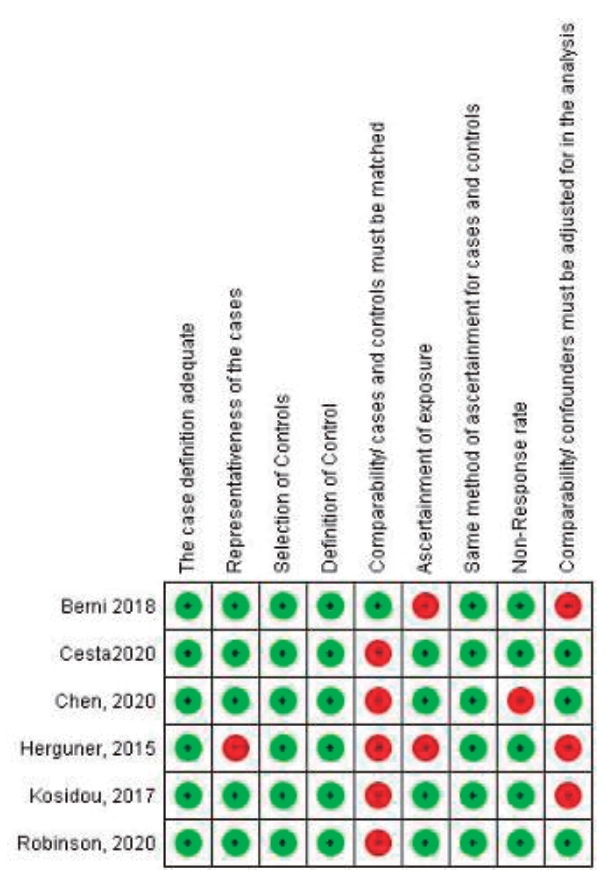
Finding: Six articles (3 cohort and 3 case-control studies; 401,413 total ADHD cases) met the study criteria. Maternal PCOS was associated with an increased risk of ADHD in the offspring based on odds ratio (OR) and relative ratio (RR) (OR, 1.42; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.27–1.57) and (RR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.35–1.51), respectively.
Meaning: Our study showed that maternal PCOS is a risk factor for ADHD. |