Topics
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- TOPICS
- Topics
- Topics
-
- Adolescence Medicine (4)
- Allergy (61)
- Cardiology (79)
- Critical Care Medicine (10)
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine (24)
- Emergency Medicine (5)
- Endocrinology (60)
- Gastroenterology (65)
- General Pediatrics (46)
- Genetics and Metabolism (24)
- Hematology (15)
- Immunology (15)
- Infection (73)
- Neonatology (Perinatology) (119)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary) (52)
- Neurology (94)
- Nutrition (30)
- Oncology (16)
- Neurobehavior (12)
- Pulmonology (30)
- Rheumatology (3)
- Other (36)
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Barriers to and enablers of kangaroo mother care
- Soon Min Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):431-432. Published online October 10, 2019
-
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Undescended testis: importance of a timely referral to a surgical specialist
- Su Jin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):429-430. Published online March 23, 2020
-
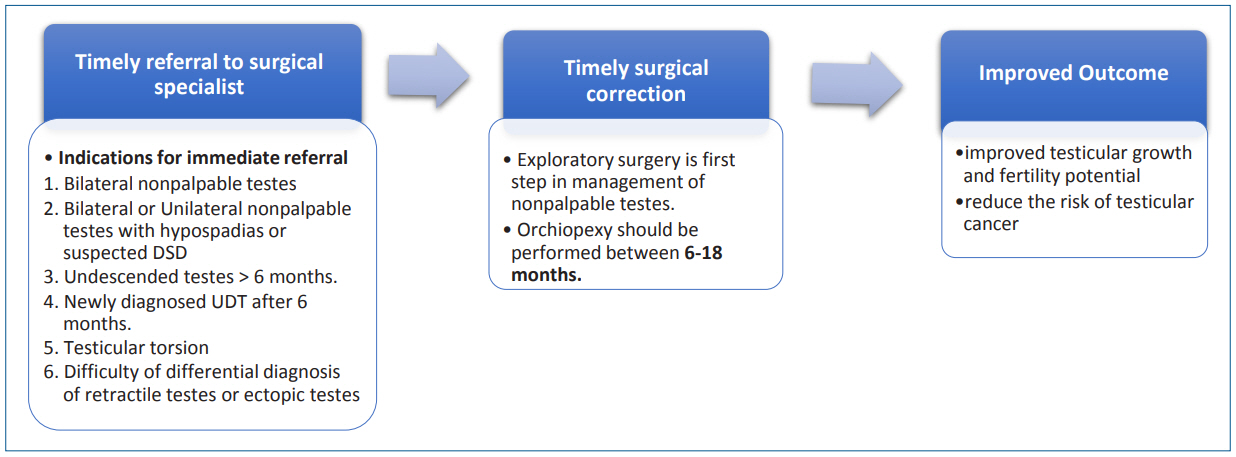
Undescended testes (UDT) is the most common congenital genitourinary abnormality in male infants and associated with decreased fertility and a higher future malignancy risk, especially in cases of delayed orchiopexy after puberty. It is important to timely referral to a surgical specialist and timely surgical correction of UDT to improve fertility and decrease the risk of malignancy.
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Health effects of electromagnetic fields on children
- Jin-Hwa Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):422-428. Published online May 26, 2020
-
· The nervous systems of children are more vulnerable to the effects of electromagnetic waves than adults.
· The exposure to electromagnetic fields (EMFs) among children should be minimized.
· According to International Agency for Research on Cancer EMFs are possibly carcinogenic, it should not be overlooked or interpreted with bias.
- Other
- Comparison of diagnostic and treatment guidelines for undescended testis
- Jaeho Shin, Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):415-421. Published online March 23, 2020
-
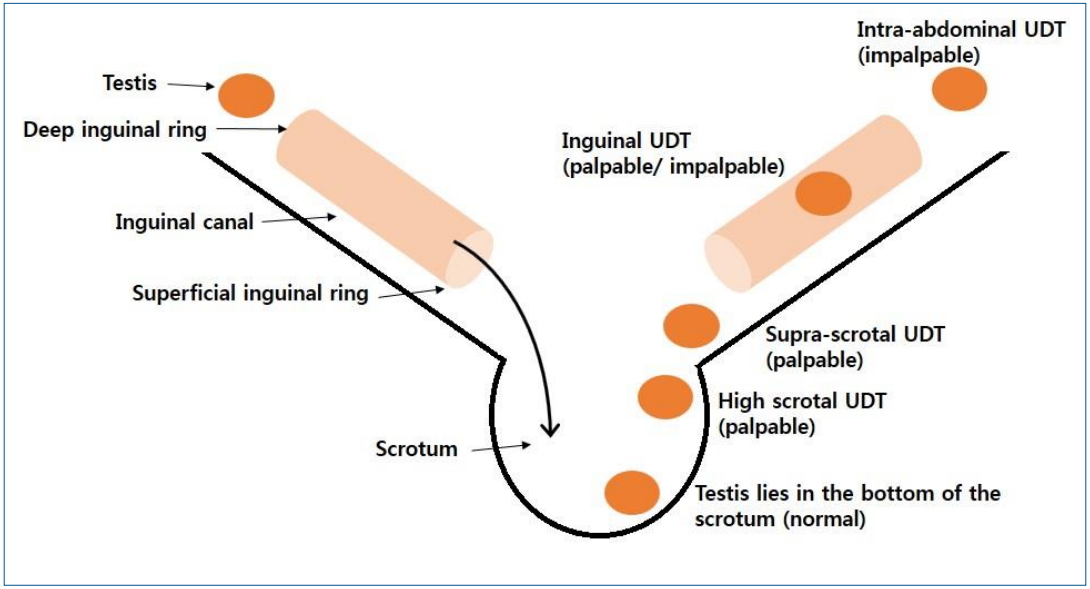
Primary caregivers should consider surgical specialist referral of patients with undescended testis if no descent occurs by 6 months, undescended testis is newly diagnosed after 6 months of age, or testicular torsion is suspected. Orchiopexy is recommended between 6 and 18 months at the latest. The original location of the testes and the age at orchiopexy are predictive factors for infertility and malignancy later in life.
- Clinical Note
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- First episode of nephrotic syndrome with acute abdominal pain
- Samridhi Goyal, Rachita Singh Dhull, Bobbity Deepthi, Abhijeet Saha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):411-414. Published online July 21, 2020
-
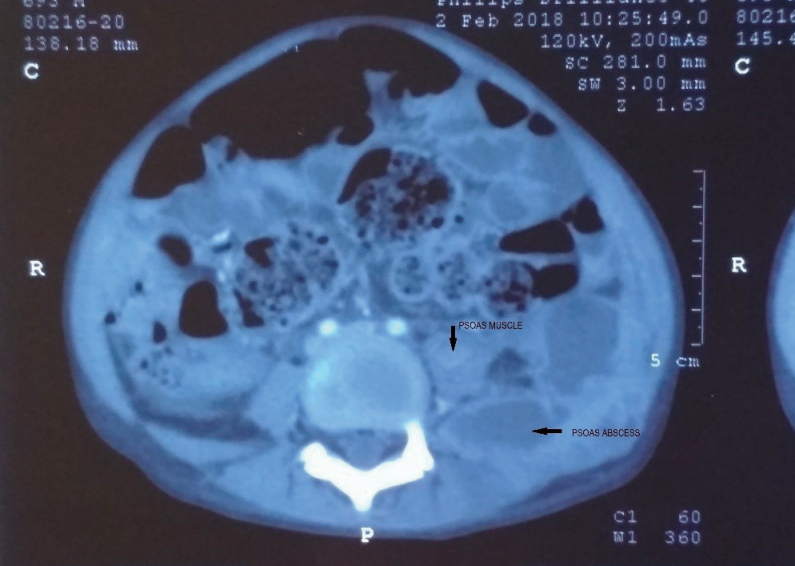
Question: What are the likely causes of pain abdomen in Nephrotic syndrome?
Finding: Severe hypovolemia leading to mesenteric ischemia, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, gastroenteritis, adverse effect of corticosteroids leading to gastritis, mesenteric ischemia due to thromboembolism, acute appendicitis, intussusception due to severe gut wall oedema and rarely Psoas abscess.
Meaning: Clinical suspicion and careful investigation is warranted to diagnose rare cause of pain abdomen like Psoas abscess.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Risk-based maternal group B Streptococcus screening strategy is compatible with the implementation of neonatal early-onset sepsis calculator
- Niek B. Achten, J. Wendelien Dorigo-Zetsma, Annemarie M.C. van Rossum, Rianne Oostenbrink, Frans B. Plötz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):406-410. Published online April 16, 2020
-
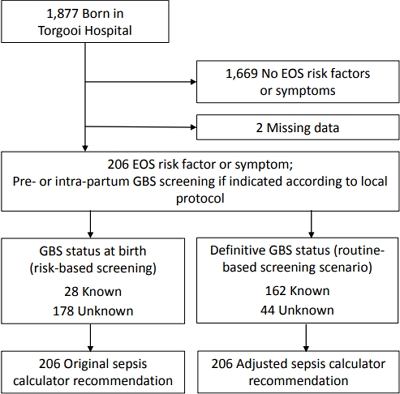
Question: To what extent does risk-based Group B Streptococcus (GBS) screening influence management recommendations by the early-onset sepsis (EOS) calculator?
Finding: In 97% of the newborn infants, the EOS calculator recommendation remained unchanged after the GBS status at birth was updated to the definitive GBS status.
Meaning: Risk-based GBS screening results are compatible with EOS calculator recommendations.
- Endocrinology
- Zinc transporter 8 autoantibody in the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in children
- Nur Rochmah, Muhammad Faizi, Siti Wahyu Windarti
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):402-405. Published online October 6, 2020
-
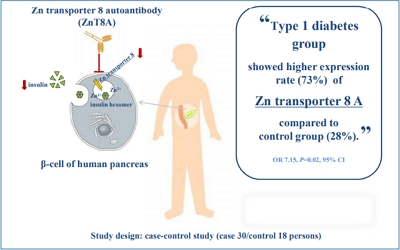
Question: Can zinc transporter 8 autoantibody (ZnT8A) be used for diagnosing type 1 diabetes (T1D)?
Finding: Twenty-two of 30 subjects with type 1 diabetes (73.3 %) were positive for ZnT8A compared to 5 of 18 controls (27.8%).
Meaning: ZnT8A has potential for clinical applications in the diagnosis of T1D.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- New modified version of the Risk Adjustment for Congenital Heart Surgery category and mortality in premature infants with critical congenital heart disease
- Young Mi Yoon, Seong Phil Bae, Yoon-Joo Kim, Jae Gun Kwak, Woong-Han Kim, Mi Kyoung Song, Seung Han Shin, Ee-Kyung Kim, Han-Suk Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):395-401. Published online July 15, 2020
-
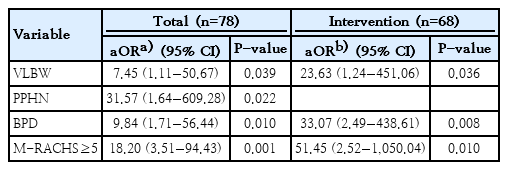
Questions: This study aimed to describe the survival of premature infants with critical congenital heart disease (CHD) and to identify the risk factors including the new modified version of the Risk Adjustment for Congenital Heart Surgery (M-RACHS) associated with mortality.
Finding: For premature infants with critical CHD, survival rate was 76.9% and very low birth weight (VLBW), persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN), bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), and M-RACHS 5 or more were associated with in-hospital mortality.
Meaning: VLBW, PPHN and BPD, as well as M-RACHS≥5, were risk factors for mortality among premature infants with critical CHD.
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Utility of neonatal early-onset sepsis calculator in risk-based group B Streptococcus screening approach
- Myo-Jing Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):393-394. Published online May 22, 2020
-
· Evaluation of the risk factors for early-onset sepsis (EOS) is important to optimal prevention and treatment.
· The EOS calculator is still valid as part of the risk-based group B Streptococcus (GBS) screening approach.
· The risk factor assessment using the EOS calculator is worth use before the introduction of universal GBS screening.
- Risk factors for in-hospital mortality in premature infants with critical congenital heart disease
- Jeonghee Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):391-392. Published online October 6, 2020
-
The incidence and mortality rates of critical congenital heart disease (CHD) are higher in preterm than in term infants. The risk factors for in-hospital mortality in premature infants with critical CHD are unclear. However, the mortality of preterm infants with critical CHD may be related to CHD complexity as well as gestational age, birth weight, the presence of prematurity-associated comorbidities, and the treatment itself.
- Allergy
- Should we prescribe montelukast to allergic pediatric patients?
- Yong Mean Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):389-390. Published online August 24, 2020
-
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Air pollution and childhood obesity
- Moon Young Seo, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):382-388. Published online March 27, 2020
-
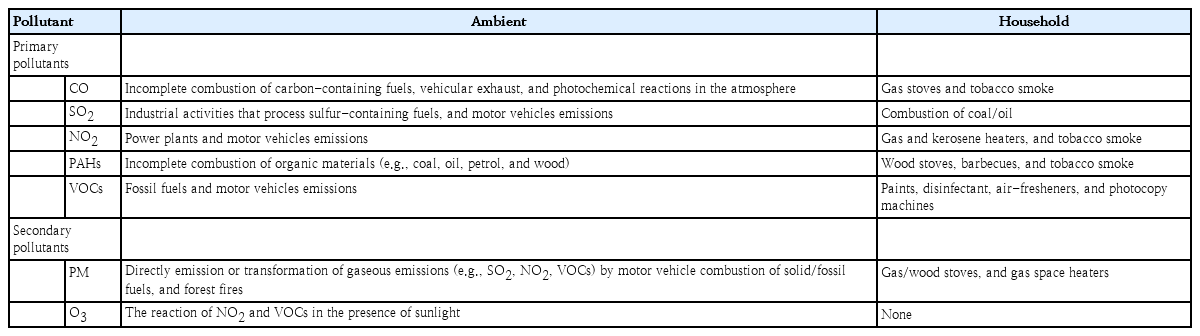
Questions: What are the possible effects of air pollution on the occurrence of childhood obesity and what are the mechanisms?
Finding: Epidemiologic studies suggest that air pollutants might act as obesogens in the pediatric population, and their possible mechanisms include oxidative stress, physical inactivity, and epigenetic modulation.
Meaning: This paper reviews updated information on air pollution, one of the modifiable environmental factors in childhood obesity.
- Allergy
- Montelukast use over the past 20 years: monitoring of its effects and safety issues
- Yong Ju Lee, Chang-Keun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):376-381. Published online February 5, 2020
-
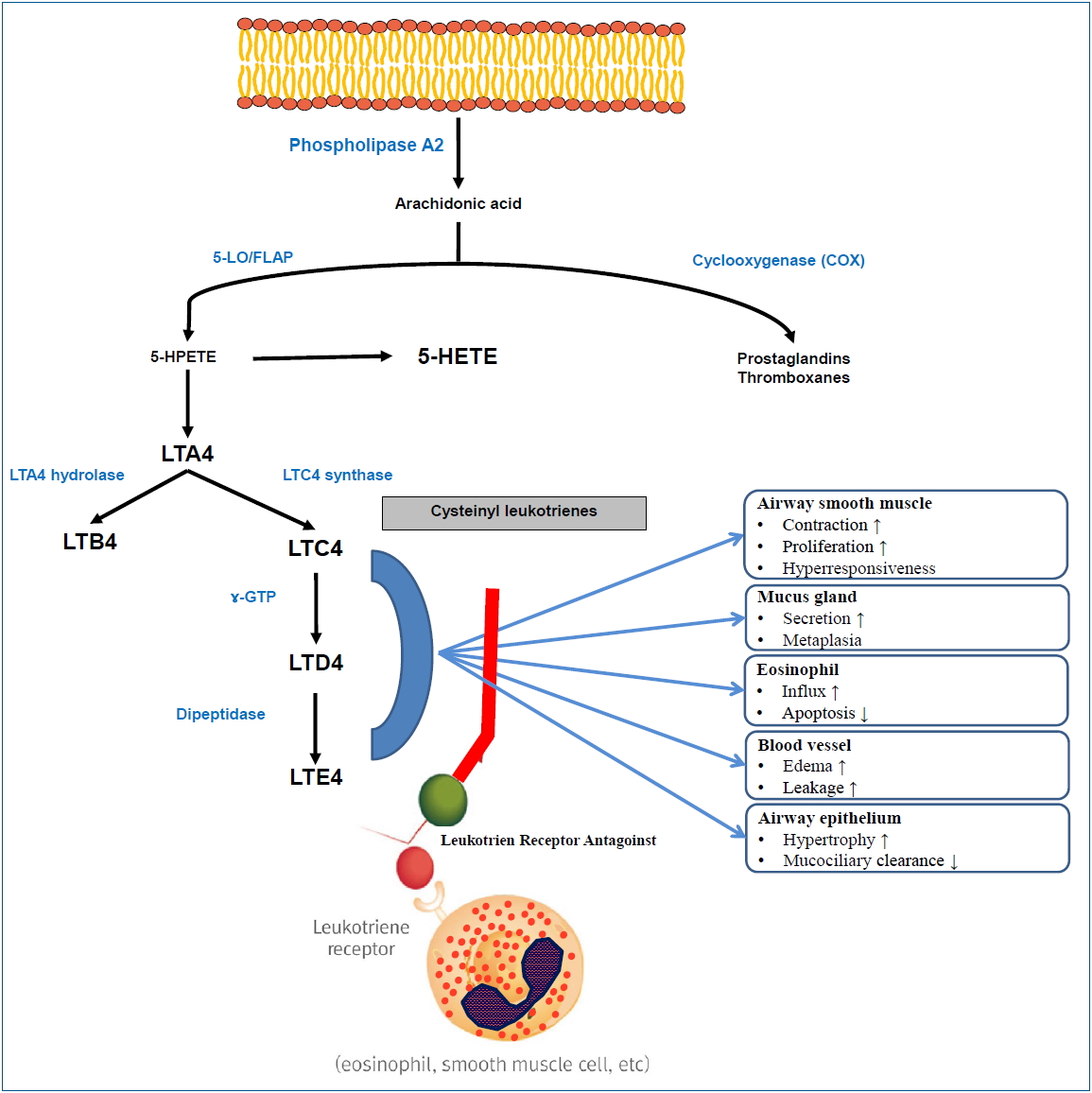
Although the efficacy of montelukast is inferior to that of ICS, both physicians and parents prefer montelukast to ICSs.
EDN may be a useful biomarker for the treatment and monitoring of preschool children with asthma.
The US FDA requires boxed warning about serious neuropsychiatric events of montelukast, therefore, physicians should consider the benefits and risks of montelukast before prescribing it.
- Clinical Note
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Management of the first newborn delivered by a mother with COVID-19 in South Korea
- Eun-Kyung Lee, Won Duck Kim, Dong won Lee, Sang-Ah Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):373-375. Published online July 13, 2020
-
Question: How to manage the newborn born to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pregnant?
Finding: Medical staff managed the delivery and neonatal care of a COVID-19 pregnant patient was based on the “Guidelines for COVID-19 response.”
Meaning: We desire that our management will help treat for subsequent patients and there should be updated continuously the prevention and control consensus strategies for newborn COVID-19.
- Original Article
- Neurobehavior
- Association between assisted reproductive technology and autism spectrum disorders in Iran: a case-control study
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Mahdieh Seyedi, Ronak Hamzehei, Saeid Bashirian, Mohammad Rezaei, Katayoon Razjouyan, Salman Khazaei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):368-372. Published online March 27, 2020
-

Background: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder defined by impairments in social interaction and verbal and nonverbal communication.
Purpose: Determine the association between use of assisted reproduction technology (ART) and the risk of ASD among children. Methods: This case-control study included 300 participants (100 cases, 200 controls). The control group included women with a child aged 2–10 years without ASD,...
- Other
- Evaluation of goodness of fit of semiparametric and parametric models in analysis of factors associated with length of stay in neonatal intensive care unit
- Fatemeh Kheiry, Sadegh Kargarian-Marvasti, Sima Afrashteh, Abolfazl Mohammadbeigi, Nima Daneshi, Salma Naderi, Seyed Hossein Saadat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):361-367. Published online June 10, 2020
-

Question: Hospitalization in neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) is associated with life-threatening hazards. What factors associated with neonatal length of stay (LOS) in the NICU?
Finding: Breastfeeding, phototherapy, acute renal failure (ARF), mechanical ventilation, and central venous catheter (CVC) access were identified as factors associated with NICU length of stay.
Meaning: Protective effects of breastfeeding and CVC access, whereas increase effects of phototherapy, ARF, and mechanical ventilation in LOS can be supporting evidence to establish effective interventions to reduce length of NICU stay.
- Editorial
- Infection
- What are considerations for neonates at risk for COVID-19?
- Soo-Han Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):359-360. Published online July 17, 2020
-

- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Survival model application for analysis of neonatal length of stay
- Eun Joo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):357-358. Published online May 14, 2020
-
- Gastroenterology
- Dietary role in the development and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease
- Jae Young Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):355-356. Published online July 13, 2020
-

Although the precise pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is unclear, dietary factors seem to play a significant role. Dietary modifications including enteral nutrition and the Crohn disease exclusion, specific carbohydrate, and anti-inflammatory diets show a potential ability to downregulate gut inflammation. These nutritional interventions have various degree of efficacies with limited side effects profile for treating pediatric IBD, but data from randomized prospective studies are lacking, and further studies are warranted.
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- Overview of management of children with COVID-19
- Dyah Kanya Wati, Arya Krisna Manggala
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):345-354. Published online July 17, 2020
-
The specific treatments for COVID-19 in children remain inconclusive and debatable despite effectively decreasing its signs and symptoms.
The need for clinical trials and reports should be investigated.
- Gastroenterology
- Increasing incidence of inflammatory bowel disease in children and adolescents: significance of environmental factors
- Sowon Park, Yunkoo Kang, Hong Koh, Seung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):337-344. Published online December 6, 2019
-
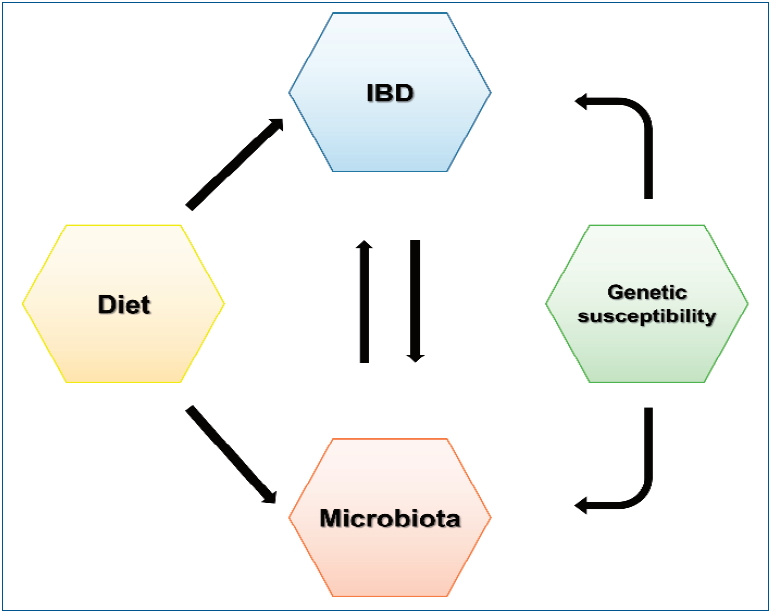
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic relapsing immune-mediated disease of the intestinal tract. Although its prevalence is reportedly lower in Asia than in Western countries, the rapid increase in the incidence of IBD has drawn attention to its etiology, including genetic susceptibility and environmental factors. Specifically, recent studies concerning dietary treatments and intestinal microbiota suggest that these factors may...
- Perspective
- Infection
- Can we get a clue for the etiology of Kawasaki disease in the COVID-19 pandemic?
- Jong-Woon Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):335-336. Published online July 13, 2020
-
A new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been spreading globally since December 2019. Children with a Kawasaki disease (KD)-like illness related with COVID-19 have been reported in Europe and the United States. They presented with symptoms of KD with or without cardiac abnormalities or shock, showing manifestations of hyperactive proinflammatory cytokine reactions like KD. Such cases may provide the opportunity for us to learn more about the etiology and pathogenesis of KD.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Evaluation of the role of ischemia modified albumin in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Mohamed A. Talat, Rabab M. Saleh, Mohammed M. Shehab, Naglaa A. Khalifa, Maha Mahmoud Hamed Sakr, Walaa M. Elmesalamy
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):329-334. Published online August 15, 2020
-
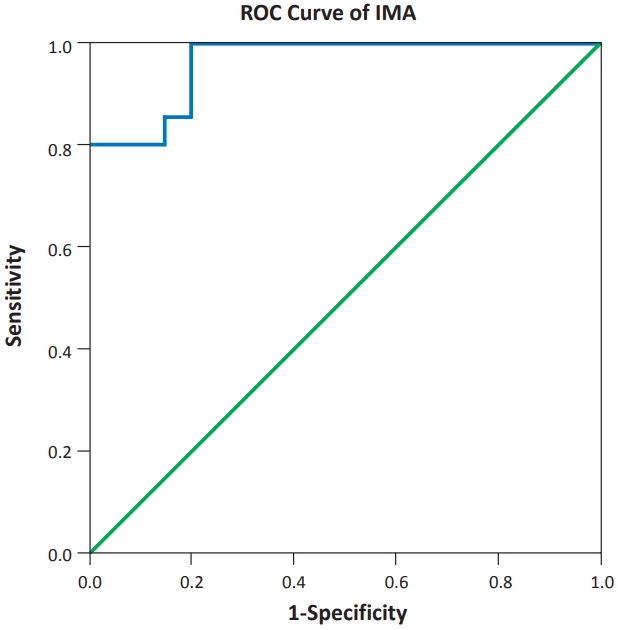
Question: What is the value of ischemia modified albumin (IMA) as a diagnostic marker for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)?
Finding: IMA levels were significantly higher (nearly double elevation) in hypoxic than healthy newborns in the first few hours after birth in the full-term neonates.
Meaning: IMA can be a reliable marker for the early diagnosis of neonatal HIE and can be a predictor of injury severity.
- Cardiology
- Age-, sex-, and height-based blood pressure reference charts, Yazd children 6–18 years, Iran
- Nastaran ahmadi, Seyedeh Mahdieh Namayandeh, Seyed Mahmood Sadr Bafghi, Mohammad Reza Mohammadi, Masoud Mirzaei, Mohammadtaghi Sarebanhassanabadi, Amir Houshang Mehrparvar, Reza Faraji, Neda Nilforoshan, Ahmad Karimi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):321-328. Published online July 21, 2020
-
Question: What is the 90th, 95th, 99th percentile of blood pressure based on height as the cut point for diagnosis of hypertension in children of our province?
Finding: We used blood pressure of 456 males and 579 females in 6–18 years old in “Iranian Children and Adolescents' Psychiatric Disorders survey.
Meaning: The 90th, 95th, 99th percentiles of systolic and diastolic blood pressure in both sex based on age and 10-cm height intervals were developed in Yazd.
- Hematology
- Effects of α-tocopherol on hemolysis and oxidative stress markers on red blood cells in β-thalassemia major
- Nora Sovira, Munar Lubis, Pustika Amalia Wahidiyat, Franciscus D. Suyatna, Djajadiman Gatot, Saptawati Bardosono, Mohammad Sadikin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):314-320. Published online August 15, 2020
-

Question: Is the α-tocopherol as an exogenous antioxidant supplementation effective in improving hemolysis and oxidative stress on β-thalassemia major?
Finding: We found significant enhancements in plasma haptoglobin were noted in the α-tocopherol group (3.01 mg/dL; range, 0.60–42.42 mg/dL; P=0.021).
Meaning: The α-tocopherol can improve hemolysis by increasing the haptoglobin level as hemolysis marker.
- Editorial
- Nutrition
- Pivotal roles of prolactin and other hormones in lactogenesis and the nutritional composition of human milk
- Yong Joo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):312-313. Published online August 15, 2020
-
- Neurology
- Commentary on "Autoimmune encephalitis and epilepsy: evolving definition and clinical spectrum"
- Jieun Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):310-311. Published online August 15, 2020
-
- Review Article
- Nutrition
- Components of human breast milk: from macronutrient to microbiome and microRNA
- Su Yeong Kim, Dae Yong Yi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):301-309. Published online March 23, 2020
-
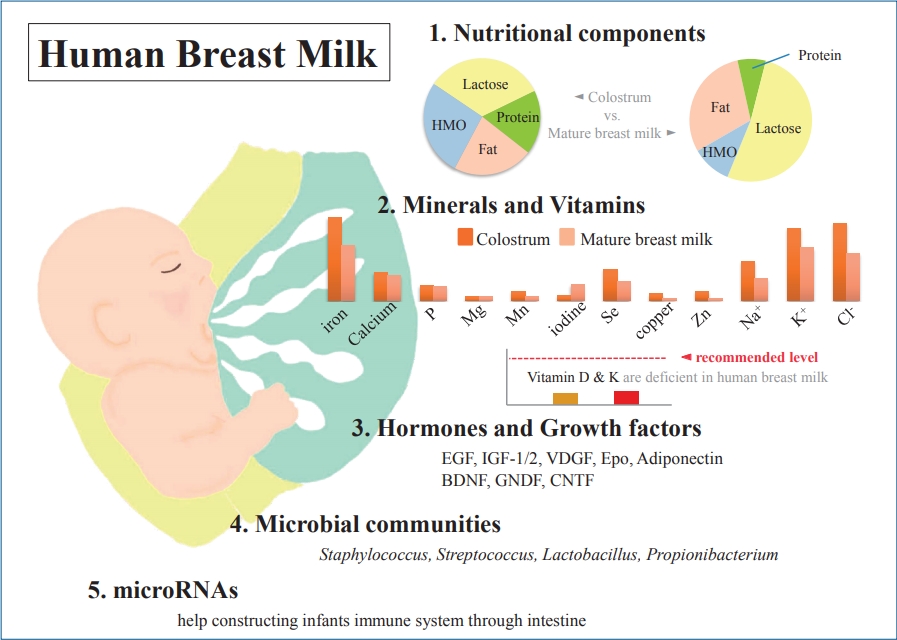
Human breast milk (HBM) is essential for the infant’s growth and development right after birth and is an irreplaceable source of nutrition for early human survival. Various infant formulas have many similarities to HBM in many components, but there is no perfect substitute for HBM. Recently, various breast milk components and their roles have been studied according to the development...
- Neurology
- Autoimmune encephalitis and epilepsy: evolving definition and clinical spectrum
- Joo Hee Seo, Yun-Jin Lee, Ki Hyeong Lee, Elakkat Gireesh, Holly Skinner, Michael Westerveld
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):291-300. Published online August 16, 2019
-
Advances in autoimmune encephalitis studies in the past 10 years have led to the identification of new syndromes and biomarkers that have transformed the diagnostic approach to the disorder. The disorder or syndrome has been linked to a wide variety of pathologic processes associated with the neuron-specific autoantibodies targeting intracellular and plasma membrane antigens. However, current criteria for autoimmune encephalitis...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Short- and long-term outcomes of very low birth weight infants in Korea: Korean Neonatal Network update in 2019
- Jang Hoon Lee, YoungAh Youn, Yun Sil Chang; Korean Neonatal Network
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):284-290. Published online February 5, 2020
-

The Korean Neonatal Network (KNN) has collected population-based data for very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs) born in Korea since 2013. The survival rate of all VLBWIs was 86% in Korea. The overall prevalence of cerebral palsy was 6.2%–6.6%. Bilateral blindness and hearing loss were reported in 0.2%–0.3%, 0.8%–1.9%, respectively. The KNN has published annual reports and papers for facilitating the improvement of VLBWIs outcome in Korea.
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











