Cardiology
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- TOPICS
- Cardiology
- Topics
-
- Adolescence Medicine (4)
- Allergy (60)
- Cardiology (79)
- Critical Care Medicine (10)
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine (24)
- Emergency Medicine (5)
- Endocrinology (60)
- Gastroenterology (63)
- General Pediatrics (45)
- Genetics and Metabolism (24)
- Hematology (15)
- Immunology (14)
- Infection (72)
- Neonatology (Perinatology) (119)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary) (52)
- Neurology (94)
- Nutrition (28)
- Oncology (16)
- Neurobehavior (12)
- Pulmonology (30)
- Rheumatology (3)
- Other (35)
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Iron deficiency anemia as a predictor of coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki disease
- Sohyun Kim, Lucy Youngmin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(8):301-306. Published online February 8, 2019
-
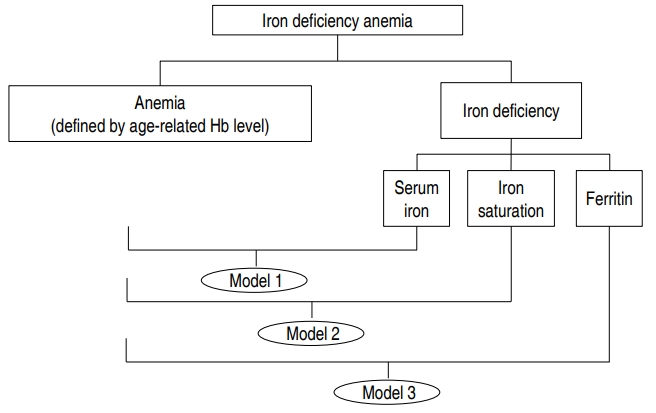
Purpose: Coronary artery abnormalities (CAA) are the most important complications of Kawasaki disease (KD). Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) is a prevalent micronutrient deficiency and its association with KD remains unknown. We hypothesized that presence of IDA could be a predictor of CAA. Methods: This retrospective study included 173 KD patients, divided into 2 groups according to absence (group 1) and presence...
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- Can iron be a risk factor for coronary lesions in Kawasaki disease?
- Kyung Lim Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(8):297-298. Published online June 7, 2019
-
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Reality of Kawasaki disease epidemiology
- Gi Beom Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(8):292-296. Published online July 9, 2019
-
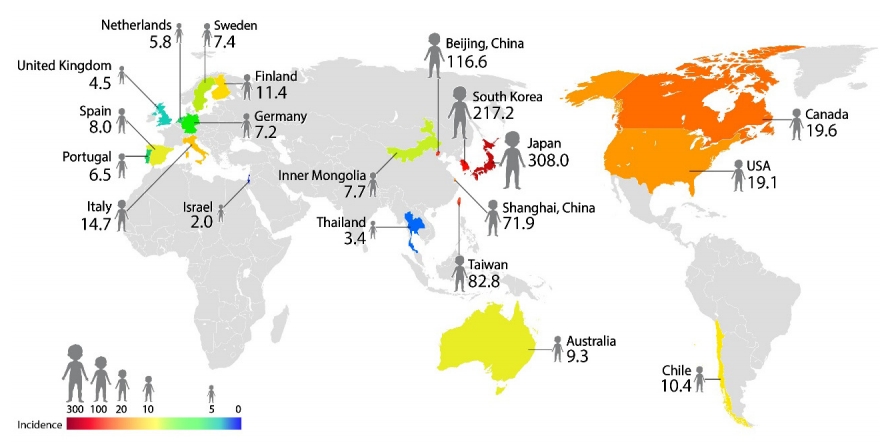
Epidemiologic studies of Kawasaki disease (KD) have shown a new pattern or change of its occurrence suggestive of its pathophysiology or risk factors from the first patient with KD reported in 1961. The incidence of KD in Northeast Asian countries including Japan, South Korea, China, and Taiwan is 10–30 times higher than that in the United States and Europe. Knowing...
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Change of coronary artery indices according to coronary dominance pattern in early childhood
- Yoon jin Lee, Kyoung Soo Park, Hong Ryang Kil
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):240-243. Published online November 22, 2018
-

Purpose: Coronary arterial lesion assessment in children can be difficult, depending on the coronary dominance pattern. Although it is easier to determine coronary dominance with echocardiography in children than in adults, it is still difficult. This study aimed to examine the coronary dominance pattern according to the objective coronary artery (CA) indices. Methods: The CA diameter, aortic valve annulus, and abdominal...
- High antistreptolysin O titer is associated with coronary artery lesions in patients with Kawasaki disease
- Dong Eun Min, Do Hee Kim, Mi Young Han, Sung Ho Cha, Kyung Lim Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):235-239. Published online November 7, 2018
-
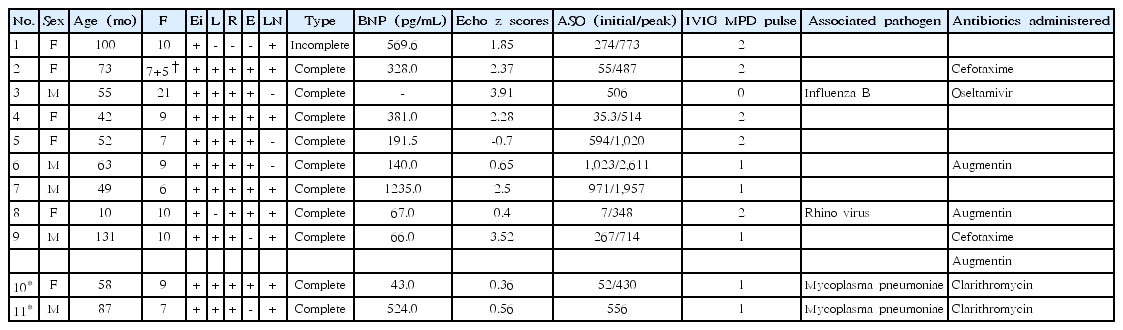
Purpose: In Kawasaki disease (KD) patients, coronary artery complications, incomplete and refractory types occur more frequently in patients with streptococcal or other bacterial/viral infections. Recently, we observed a higher incidence of coronary lesions in KD patients with high anti-streptolysin O (ASO) titer. Therefore, we hypothesized that KD patients diagnosed with concurrent streptococcal infection have poor prognosis, with respect to treatment...
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- Importance of coronary artery dominance in children to determine coronary artery dilatation
- Hee Joung Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):215-216. Published online May 3, 2019
-
- Does any specific infection cause Kawasaki disease?
- Dong Seok Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):213-214. Published online May 3, 2019
-
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Changes of Bax, Bcl-2, CCR-2, MCP-1, and TGF-β1 genes in the left ventricle of spontaneously hypertensive rat after losartan treatment
- Hyeryon Lee, Kwan Chang Kim, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(3):95-101. Published online October 24, 2018
-

Purpose: Increased apoptosis was recently found in the hypertrophied left ventricle of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs). Although the available evidence suggests that apoptosis can be induced in cardiac cells by various insults including pressure overload, cardiac apoptosis appears to result from an exaggerated local production of angiotensin in adult SHRs. Altered expressions of Bcl associated X (Bax), Bcl-2, chemokine receptor...
- Outcomes of transcatheter closure of ductus arteriosus in infants less than 6 months of age: a single-center experience
- Gwang-Jun Choi, Jinyoung Song, Yi-Seul Kim, Heirim Lee, June Huh, I-Seok Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(12):397-402. Published online September 19, 2018
-
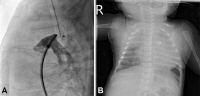
Purpose: Transcatheter device closure of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is challenging in early infancy. We evaluated PDA closure in infants less than 6 months old. Methods: We performed a retrospective review of infants less than 6 months of age who underwent attempted transcatheter device closure in our institution since 2004. To compare clinical outcomes between age groups, infants aged 6–12 months...
- The improvement of right ventricular function after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea
- Dong Yeop Kim, Kyung Ok Ko, Jae Woo Lim, Jung Min Yoon, Young Hwa Song, Eun Jeong Cheon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(12):392-396. Published online October 26, 2018
-
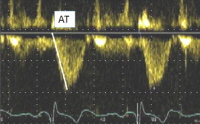
Purpose: Adenotonsillar hypertrophy (ATH) that causes upper airway obstruction might lead to chronic hypoxemic pulmonary vasoconstriction and right ventricular (RV) dysfunction. We aimed to evaluate whether adenotonsillectomy (T&A) in children suffering from obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) due to severe ATH could improve RV function. Methods: Thirty-seven children (boy:girl=21:16; mean age, 9.52±2.20 years), who underwent T&A forsleep apnea due to ATH, were...
- The change of QRS duration after pulmonary valve replacement in patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot and pulmonary regurgitation
- Yuni Yun, Yeo Hyang Kim, Jung Eun Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(11):362-365. Published online October 24, 2018
-
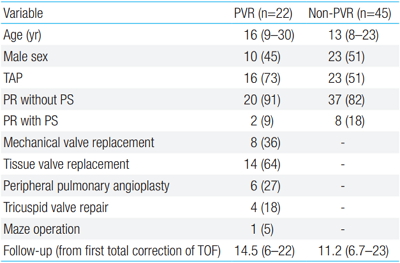
Purpose: This study aimed to analyze changes in QRS duration and cardiothoracic ratio (CTR) following pulmonary valve replacement (PVR) in patients with tetralogy of Fallot (TOF). Methods: Children and adolescents who had previously undergone total repair for TOF (n=67; median age, 16 years) who required elective PVR for pulmonary regurgitation and/or right ventricular out tract obstruction were included in this study....
- Change of voltage-gated potassium channel 1.7 expressions in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension rat model
- Hyeryon Lee, Kwan Chang Kim, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(9):271-278. Published online September 15, 2018
-

Purpose: Abnormal potassium channels expression affects vessel function, including vascular tone and proliferation rate. Diverse potassium channels, including voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels, are involved in pathological changes of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Since the role of the Kv1.7 channel in PAH has not been previously studied, we investigated whether Kv1.7 channel expression changes in the lung tissue of a monocrotaline...
- Outcome of neonatal palliative procedure for pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect or tetralogy of Fallot with severe pulmonary stenosis: experience in a single tertiary center
- Tae Kyoung Jo, Hyo Rim Suh, Bo Geum Choi, Jung Eun Kwon, Hanna Jung, Young Ok Lee, Joon Yong Cho, Yeo Hyang Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(7):210-216. Published online July 15, 2018
-

Purpose: The present study aimed to evaluate progression and prognosis according to the palliation method used in neonates and early infants aged 3 months or younger who were diagnosed with pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect (PA VSD) or tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with severe pulmonary stenosis (PS) in a single tertiary hospital over a period of 12 years. Methods: Twenty...
- The outcome of percutaneous stent implantation in congenital heart disease: experience of a single institute
- Moon Sun Kim, Ja Kyoung Yoon, Seong Ho Kim, Ji Seok Bang, So Ick Jang, Sang Yoon Lee, Eun Young Choi, Su Jin Park, Hye Won Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(6):187-193. Published online June 25, 2018
-

Purpose The efficacy of percutaneous stent implantation for congenital heart disease (CHD) in Korea, where stent availability is limited, has not been determined. This study evaluated the acute and midterm results of stent implantation in different CHD subgroups.
Methods Stents were implanted in 75 patients with 81 lesions: (1) pulmonary artery stenosis (PAS) group, 56 lesions in 51 patients; (2) coarctation of the...
- Differentiation between incomplete Kawasaki disease and secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis following Kawasaki disease using N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide
- Jung Eun Choi, Yujin Kwak, Jung Won Huh, Eun-Sun Yoo, Kyung-Ha Ryu, Sejung Sohn, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(5):167-173. Published online May 28, 2018
-

Purpose Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a hyperinflammatory syndrome with many causes, including Kawasaki disease (KD). The purpose of this study was to identify the laboratory tests needed to easily differentiate KD with HLH from incomplete KD alone.
Methods We performed a retrospective study on patients diagnosed with incomplete KD and incomplete KD with HLH (HLH-KD) between January 2012 and March 2015. We compared...
- Clinical implications in laboratory parameter values in acute Kawasaki disease for early diagnosis and proper treatment
- Yu-Mi Seo, Hyun-Mi Kang, Sung-Churl Lee, Jae-Won Yu, Hong-Ryang Kil, Jung-Woo Rhim, Ji-Whan Han, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(5):160-166. Published online May 28, 2018
-
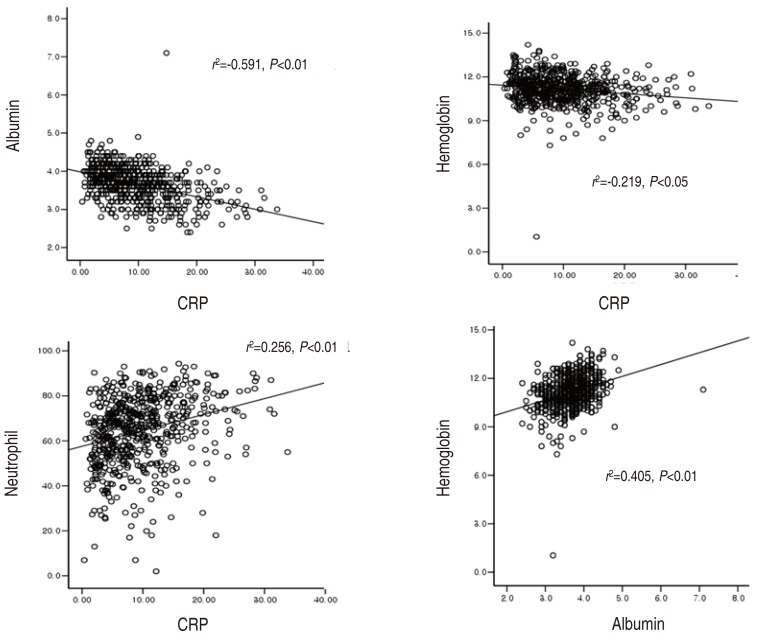
Purpose This study aimed to analyse laboratory values according to fever duration, and evaluate the relationship across these values during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease (KD) to aid in the early diagnosis for early-presenting KD and incomplete KD patients.
Methods Clinical and laboratory data of patients with KD (n=615) were evaluated according to duration of fever at presentation, and were compared between...
- Cardiac function associated with home ventilator care in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Sangheun Lee, Heeyoung Lee, Lucy Youngmin Eun, Seung Woong Gang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(2):59-63. Published online February 28, 2018
-

Purpose Cardiomyopathy is becoming the leading cause of death in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy because mechanically assisted lung ventilation and assisted coughing have helped resolve respiratory complications. To clarify cardiopulmonary function, we compared cardiac function between the home ventilator-assisted and non-ventilator-assisted groups.
Methods We retrospectively reviewed patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy from January 2010 to March 2016 at Gangnam Severance Hospital. Demographic...
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/kjp.2018.61.2.59 Correction in: Clin Exp Pediatr 2019;62(6):244
- Discrimination of Kawasaki disease with concomitant adenoviral detection differentiating from isolated adenoviral infection
- Jong Han Kim, Hye Ree Kang, Su Yeong Kim, Ji-Eun Ban
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(2):43-48. Published online February 28, 2018
-
Purpose Human adenovirus infection mimics Kawasaki disease (KD) but can be detected in KD patients. The aim of this study was to determine the clinical differences between KD with adenovirus infection and only adenoviral infection and to identify biomarkers for prediction of adenovirus-positive KD from isolated adenoviral infection.
Methods A total of 147 patients with isolated adenovirus were identified by quantitative polymerase chain...
- C-reactive protein and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide discrepancy: a differentiation of adenoviral pharyngoconjunctival fever from Kawasaki disease
- Jung Eun Choi, Hee Won Kang, Young Mi Hong, Sejung Sohn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(1):12-16. Published online January 22, 2018
-
Purpose To differentiate adenoviral pharyngoconjunctival fever (PCF) from acute Kawasaki disease (KD) using laboratory tests before results of virus-real time polymerase chain reaction and ophthalmologic examination are obtained.
Methods Baseline patient characteristics and laboratory measurements were compared between 40 patients with adenovirus infection and 123 patients with KD.
Results The patients with adenovirus infection were generally older than those with KD (median: 3.9 years vs....
- Radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia in children and adolescents: a single center experience
- Myung Chul Hyun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(12):390-394. Published online December 22, 2017
-
Purpose Atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia (AVNRT) is less common in pediatric patients than in adult patients. Thus, data for pediatric AVNRT patients are insufficient. Hence, we aimed to analyze the patient characteristics, treatment, and any recurrences in pediatric AVNRT patients.
Methods We reviewed the records of 50 pediatric AVNRT patients who had undergone radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) between January 1998 and December 2016...
- A comparative study of established
z score models for coronary artery diameters in 181 healthy Korean children - Kyungguk Ryu, Jeong Jin Yu, Hyun Ok Jun, Eun Jung Shin, Young Hee Heo, Jae Suk Baek, Young-Hwue Kim, Jae-Kon Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(11):373-378. Published online November 27, 2017
-
Purpose The aim of this study was to investigate the statistical properties of four previously developed pediatric coronary artery
z score models in healthy Korean children.Methods The study subjects were 181 healthy Korean children, whose age ranged from 1 month to 15 years. The diameter of each coronary artery was measured using 2-dimensional echocardiography and converted to the
z score in the...
- Apoptosis and remodeling in adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy rat model
- Young Mi Hong, Hyeryon Lee, Min-Sun Cho, Kwan Chang Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(11):365-372. Published online November 27, 2017
-
Purpose The mechanism for the pathogenesis of adriamycin (ADR)-induced cardiomyopathy is not yet known. Different hypotheses include the production of free radicals, an interaction between ADR and nuclear components, and a disruption in cardiac-specific gene expression. Apoptosis has also been proposed as being involved in cardiac dysfunction. The purpose of this study was to determine if apoptosis might play a role...
- Subtle inflammation: a possible mechanism of future cardiovascular risk in obese children
- Watchareewan Sontichai, Prapai Dejkhamron, Peraphan Pothacharoen, Prachya Kongtaweelert, Kevalee Unachak, Nuthapong Ukarapol
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(11):359-364. Published online November 27, 2017
-
Purpose The risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) has been shown to be associated with systemic inflammation in obese adults with metabolic syndrome (MetS). The aims of this study were to evaluate the prevalence of MetS and its relation to inflammatory markers in obese Thai children.
Methods A cross-sectional study was conducted. Children with history of endogenous obesity, chronic diseases, drug ingestion, and any...
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Neonatal arrhythmias: diagnosis, treatment, and clinical outcome
- Ji-Eun Ban
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(11):344-352. Published online November 27, 2017
-

Arrhythmias in the neonatal period are not uncommon, and may occur in neonates with a normal heart or in those with structural heart disease. Neonatal arrhythmias are classified as either benign or nonbenign. Benign arrhythmias include sinus arrhythmia, premature atrial contraction, premature ventricular contraction, and junctional rhythm; these arrhythmias have no clinical significance and do not need therapy. Supraventricular tachycardia,...
- Recent advances in pediatric interventional cardiology
- Seong-Ho Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(8):237-244. Published online August 14, 2017
-
During the last 10 years, there have been major technological achievements in pediatric interventional cardiology. In addition, there have been several advances in cardiac imaging, especially in 3-dimensional imaging of echocardiography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and cineangiography. Therefore, more types of congenital heart diseases can be treated in the cardiac catheter laboratory today than ever before. Furthermore, lesions previously...
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Relationship between vitamin D levels and intravenous immunoglobulin resistance in Kawasaki disease
- Jae Sung Jun, Young Kwon Jung, Dong Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(7):216-220. Published online July 31, 2017
-
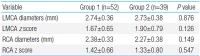
Purpose Vitamin D is associated with various pathological conditions such as cardiovascular diseases and cancer. We investigated the relationship between vitamin D and Kawasaki disease (KD).
Methods We performed a retrospective review of the medical records of patients with KD between February 2013 and March 2016 in Daegu Fatima Hospital. Study participants were grouped according to vitamin D serum concentration. Group 1 included...
- Association of Toll-like receptor 2-positive monocytes with coronary artery lesions and treatment nonresponse in Kawasaki disease
- Soo Jung Kang, Nam Su Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(7):208-215. Published online July 31, 2017
-
Purpose Activation of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) present on circulating monocytes in patients with Kawasaki disease (KD) can lead to the production of proinflammatory cytokines and interleukin-10 (IL-10). We aimed to determine the association of the frequency of circulating TLR2+/CD14+ monocytes (FTLR2%) with the outcomes of KD, as well as to compare FTLR2% to the usefulness of sIL-10.
Methods The FTLR2% in patients...
- The evolution of electrocardiographic changes in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophies
- Woo Hyun Yoo, Min-Jung Cho, Peter Chun, Kwang Hun Kim, Je Sang Lee, Yong Beom Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(6):196-201. Published online June 22, 2017
-
Purpose Myocardial dysfunction and dysrhythmias are inevitable consequences of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. We aimed to evaluate specific trends of electrocardiographic changes that reflect the progress of cardiomyopathy in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Methods Fifty electrocardiograms (ECGs) of 30 patients (ages 1 to 27 years) who had not been prescribed medications for heart failure treatment at the time of examination were retrospectively analyzed...
- Clinical usefulness of serum procalcitonin level in distinguishing between Kawasaki disease and other infections in febrile children
- Na Hyun Lee, Hee Joung Choi, Yeo Hyang Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(4):112-117. Published online April 25, 2017
-
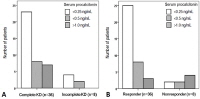
Purpose The aims of this study were to compare serum procalcitonin (PCT) levels between febrile children with Kawasaki disease (KD) and those with bacterial or viral infections, and assess the clinical usefulness of PCT level in predicting KD.
Methods Serum PCT levels were examined in febrile pediatric patients admitted between August 2013 and August 2014. The patients were divided into 3 groups as...
- Relationship between serum sodium level and coronary artery abnormality in Kawasaki disease
- Sora Park, Lucy Youngmin Eun, Ji Hong Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(2):38-44. Published online February 27, 2017
-

Purpose Kawasaki disease (KD) is an immune-related multisystemic vasculitis that occurs in children, especially ensuing from a coronary artery abnormality. Sodium level is known to be related to vascular injury, which could affect the progress of KD. The purpose of this study was to determine the serum sodium levels that could predict the occurrence of cardiac and coronary artery events in...
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











