Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Diagnosis of coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki disease: recent guidelines and z score systems
- Sung Hye Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):430-438. Published online December 17, 2021
-
∙ Kawasaki disease is the leading cause of acquired heart disease among children in the developed countries, and Korea has the second-highest incidence in the world.
∙ Early diagnosis and proper treatment are imperative to prevent coronary complication, and evaluation of coronary artery abnormalities is fundamental.
∙ Recent guidelines have adapted z score system for the diagnosis of coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki disease.
∙ Applying z score in diagnosis of coronary abnormalities has better correlation with clinical outcomes than absolute cutoff values.
∙ Calculated z scores could be different according to the z score formula, which might influence the treatment plan.
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Iron deficiency anemia as a predictor of coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki disease
- Sohyun Kim, Lucy Youngmin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(8):301-306. Published online February 8, 2019
-
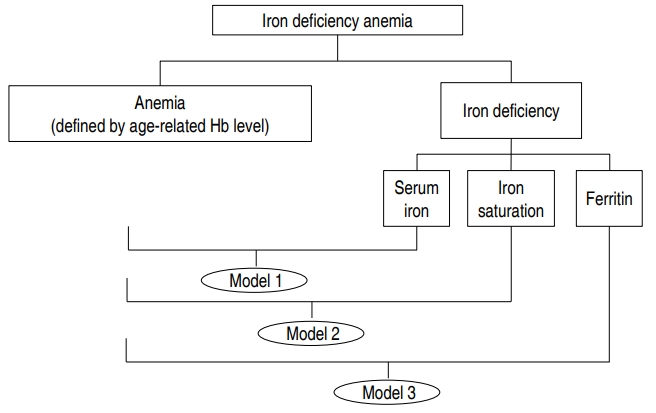
Purpose: Coronary artery abnormalities (CAA) are the most important complications of Kawasaki disease (KD). Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) is a prevalent micronutrient deficiency and its association with KD remains unknown. We hypothesized that presence of IDA could be a predictor of CAA. Methods: This retrospective study included 173 KD patients, divided into 2 groups according to absence (group 1) and presence...
- Change of coronary artery indices according to coronary dominance pattern in early childhood
- Yoon jin Lee, Kyoung Soo Park, Hong Ryang Kil
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):240-243. Published online November 22, 2018
-

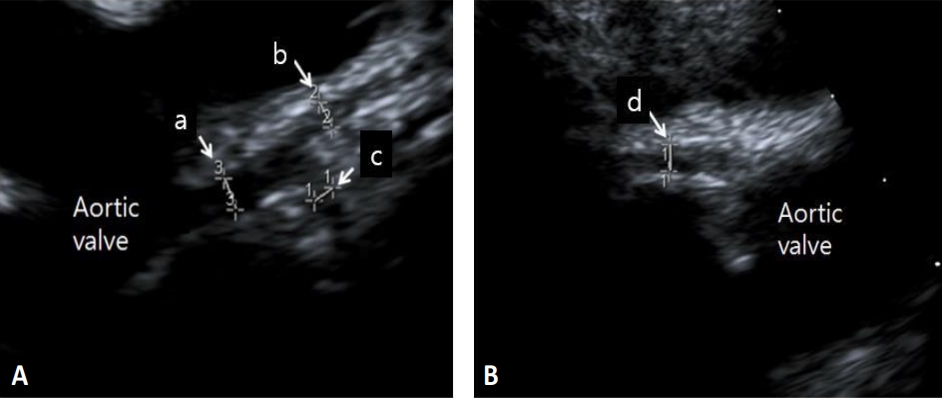
Purpose: Coronary arterial lesion assessment in children can be difficult, depending on the coronary dominance pattern. Although it is easier to determine coronary dominance with echocardiography in children than in adults, it is still difficult. This study aimed to examine the coronary dominance pattern according to the objective coronary artery (CA) indices. Methods: The CA diameter, aortic valve annulus, and abdominal...
- Clinical implications in laboratory parameter values in acute Kawasaki disease for early diagnosis and proper treatment
- Yu-Mi Seo, Hyun-Mi Kang, Sung-Churl Lee, Jae-Won Yu, Hong-Ryang Kil, Jung-Woo Rhim, Ji-Whan Han, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(5):160-166. Published online May 28, 2018
-
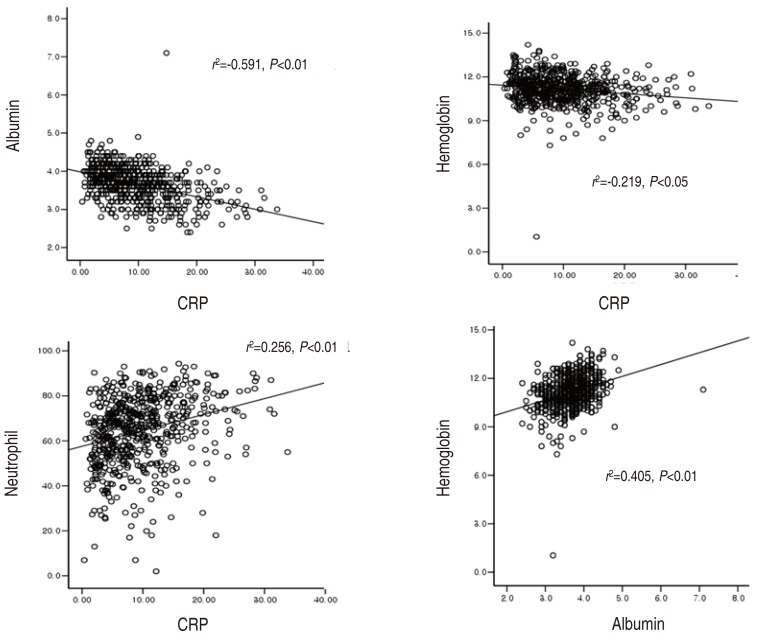
Purpose This study aimed to analyse laboratory values according to fever duration, and evaluate the relationship across these values during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease (KD) to aid in the early diagnosis for early-presenting KD and incomplete KD patients.
Methods Clinical and laboratory data of patients with KD (n=615) were evaluated according to duration of fever at presentation, and were compared between...
- A comparative study of established
z score models for coronary artery diameters in 181 healthy Korean children - Kyungguk Ryu, Jeong Jin Yu, Hyun Ok Jun, Eun Jung Shin, Young Hee Heo, Jae Suk Baek, Young-Hwue Kim, Jae-Kon Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(11):373-378. Published online November 27, 2017
-
Purpose The aim of this study was to investigate the statistical properties of four previously developed pediatric coronary artery
z score models in healthy Korean children.Methods The study subjects were 181 healthy Korean children, whose age ranged from 1 month to 15 years. The diameter of each coronary artery was measured using 2-dimensional echocardiography and converted to the
z score in the...
- Predictive factors of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin and coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease
- Hye Young Lee, Min Seob Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(12):477-482. Published online December 31, 2016
-
Purpose We conducted a study to determine which factors may be useful as predictive markers in identifying Kawasaki disease (KD) patients with a high risk of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and developing coronary artery lesions (CAL).
Methods We enrolled 287 patients in acute phase of KD at a single center. The demographic, clinical and laboratory data were collected retrospectively.
Results There were 34 patients...
- Age-adjusted plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide level in Kawasaki disease
- Heul Jun, Kyung Ok Ko, Jae Woo Lim, Jung Min Yoon, Gyung Min Lee, Eun Jung Cheon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(7):298-302. Published online July 31, 2016
-
Purpose Recent reports showed that plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) could be a useful biomarker of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) unresponsiveness and coronary artery lesion (CAL) development in Kawasaki disease (KD). The levels of these peptides are critically influenced by age; hence, the normal range and upper limits for infants and children are different. We performed an age-adjusted analysis of plasma...
- Prediction of nonresponsiveness to medium-dose intravenous immunoglobulin (1 g/kg) treatment: an effective and safe schedule of acute treatment for Kawasaki disease
- Kyung Pil Moon, Beom Joon Kim, Kyu Jin Lee, Jin Hee Oh, Ji Whan Han, Kyung Yil Lee, Soon Ju Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(4):178-182. Published online April 30, 2016
-
Purpose Medium-dose (1 g/kg) intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is effective in the majority of patients with Kawasaki disease (KD) but some patients who do not respond to medium-dose IVIG are at high risk for the development of coronary artery lesions (CALs). The purpose of this study was to identify the clinical predictors associated with unresponsiveness to medium-dose IVIG and the development of...
- Usefulness of anterior uveitis as an additional tool for diagnosing incomplete Kawasaki disease
- Kyu Jin Lee, Hyo Jin Kim, Min Jae Kim, Ji Hong Yoon, Eun Jung Lee, Jae Young Lee, Jin Hee Oh, Soon Ju Lee, Kyung Yil Lee, Ji Whan Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(4):174-177. Published online April 30, 2016
-
Purpose There are no specific tests for diagnosing Kawasaki disease (KD). Additional diagnostic criteria are needed to prevent the delayed diagnosis of incomplete Kawasaki disease (IKD). This study compared the frequency of coronary artery lesions (CALs) in IKD patients with and without anterior uveitis (AU) and elucidated whether the finding of AU supported the diagnosis of IKD.
Methods This study enrolled patients diagnosed...
- Comparison between Kawasaki disease with lymph-node-first presentation and Kawasaki disease without cervical lymphadenopathy
- Jung Ok Kim, Yeo Hyang Kim, Myung Chul Hyun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(2):54-58. Published online February 29, 2016
-
Purpose We evaluated the characteristics of patients with Kawasaki disease (KD) who presented with only fever and cervical lymphadenopathy on admission, and compared them with the characteristics of those who presented with typical features but no cervical lymphadenopathy.
Methods We enrolled 98 patients diagnosed with KD. Thirteen patients had only fever and cervical lymphadenopathy on the day of admission (group 1), 31 had...
- Review Article
- Update of genetic susceptibility in patients with Kawasaki disease
- Kyung Lim Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(3):84-88. Published online March 20, 2015
-
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute systemic vasculitis that predominantly affects children, and can result in coronary artery lesions (CAL). A patient with KD who is resistant to treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) has a higher risk of developing CAL. Incomplete KD has increased in prevalence in recent years, and is another risk factor for the development of CAL. Although...
- Case Report
- A rare type of single coronary artery with right coronary artery originating from the left circumflex artery in a child
- Jong Min Kim, Ok Jeong Lee, I-Seok Kang, June Huh, Jinyoung Song, Geena Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(1):37-40. Published online January 31, 2015
-
The presence of a single coronary artery is a rare congenital anomaly; such patients often present with severe myocardial ischemia. We experienced the case of a 13-year-old girl with the right coronary artery originating from the left circumflex artery. She visited our Emergency Department owing to severe chest pain; her cardiac enzyme levels were elevated, but her initial electrocardiogram (ECG)...
- Original Article
- Epidemiology of Kawasaki disease in infants 3 months of age and younger
- Eun Jung Lee, Yong Won Park, Young Mi Hong, Joon Sung Lee, Ji Whan Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(6):202-205. Published online June 21, 2012
-
Purpose This study investigated the epidemiology of Kawasaki disease (KD) in infants ≤3-month-old.
Methods To study the epidemiology of KD in Korea, data for 27,851 KD patients were collected on a 3-year basis between 2000 and 2008 in a retrospective survey. From this, data for 609 KD patients ≤3-month-old were analyzed and compared with the data for KD patients >3-month-old.
Results The 609 KD patients...
- Transforming growth factor beta receptor II polymorphisms are associated with Kawasaki disease
- Yu Mi Choi, Kye Sik Shim, Kyung Lim Yoon, Mi Young Han, Sung Ho Cha, Su Kang Kim, Joo Ho Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(1):18-23. Published online January 31, 2012
-
Purpose Transforming growth factor beta receptor 2 (
TGFBR2 ) is a tumor suppressor gene that plays a role in the differentiation of striated cells and remodeling of coronary arteries. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of this gene are associated with Marfan syndrome and sudden death in patients with coronary artery disease. Cardiovascular remodeling and T cell activation ofTGFBR2 gene suggest that the...
- Polymorphisms of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase are not a risk factor for Kawasaki disease in the Korean population
- Kyung Lim Yoon, Jin Hee Ko, Kye Shik Shim, Mi Young Han, Sung Ho Cha, Su Kang Kim, Joo Ho Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(8):335-339. Published online August 31, 2011
-
Purpose Hyperhomocysteinemia is known as a risk factor for atherosclerosis. Preclinical arteriosclerosis is noted and premature atherosclerosis is known to be accelerated in Kawasaki disease (KD) patients. Genetic polymorphisms in the 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (
MTHFR ) gene result in elevated plasma homocysteine concentrations and are known to be associated with the development of coronary artery disease. Our hypothesis is that single nucleotide polymorphisms...
- Case Report
- Anomalous origin of left coronary artery arising from the right coronary cusp presenting with chest discomfort and syncope on physical exercise
- Ran Baik, Nam Kyun Kim, Han Ki Park, Young Hwan Park, Byung Won Yoo, Jae Young Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(2):248-252. Published online February 15, 2010
-
Anomalous origins of coronary arteries are a rare type of disease among children. These anomalies can be categorized into 3 types according to the anatomical relationship of the aorta and pulmonary trunks. Among these types, the interarterial type, as observed in our case, needs early diagnosis and treatment, because it can increase the risk for the patient, causing sudden cardiac... -
- Original Article
- Predictive indicators of coronary artery complications in Kawasaki disease
- Min Jee Park, In-sang Jeon, Hann Tchah, Kang Ho Cho, Mi-Jin Jung, Deok Young Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(10):1161-1166. Published online October 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Kawasaki disease—the most common cause of acquired heart disease in children—incidence is increasing yearly. Therefore, we evaluated the predictive indicators of coronary complications of Kawasaki disease based on clinical and laboratory data. Methods : Between January 2005 and March 2008, of the 201 children with Kawasaki disease treated at the Gil Hospital of Gachon University of Medicine and... -
- Case Report
- A case of adolescent Kawasaki disease with Epstein-Barr virus-associated infectious mononucleosis complicated by splenic infarction
- Byeong Sam Choi, Bo Sang Kwon, Gi Beom Kim, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Jung-Eun Cheon, Eun Jung Bae, Chung Il Noh, Jung Yun Choi, Yong Soo Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(9):1029-1034. Published online September 15, 2009
-
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute systemic vasculitis of unknown etiology that affects children. There are few reports that describe the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) as the possible infectious agent of KD. Here, we describe a case of KD in a 15- year-old boy complicated with giant coronary artery aneurysms, pericardial effusion, and splenic infarction. The clinical course of KD was... -
- Original Article
- The relationship between catechol-O-methyltransferase gene polymorphism and coronary artery abnormality in Kawasaki disease
- Hyo Jin Lee, Myung Sook Lee, Ji Sook Kim, Eun Ryoung Kim, Sung Wook Kang, Soo Kang Kim, Joo Ho Chun, Kyung Lim Yoon, Mi Young Han, Seong Ho Cha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(1):87-92. Published online January 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Many gene polymorphisms are associated with coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki disease. Catechol-O- methyltransferase (COMT) plays an important role in the metabolism of catecholamines, catechol estrogen, and catechol drugs. Polymorphisms of the COMT gene are reported to be associated with myocardial infarction and coronary artery abnormalities. The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between COMT... -
- Coronary artery diameter of normal children aged 3 months to 6 years
- Jeong Jin Yu, Suk Kyung Cho, Yong-Mean Park, Ran Lee, Sochung Chung, Sun Hwan Bae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(6):629-633. Published online June 15, 2008
-
Purpose : This study was designed to investigate normal domestic values for the diameter of the left main coronary artery (LCA), the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD) and the right coronary artery (RCA). These data are necessary to define dilatation of coronary arteries in Kawasaki disease cases. Methods : Study subjects were 43 normal healthy children whose ages ranged from... -
- Change of hemostatic markers according to the clinical state in Kawasaki disease
- Yong Beom Kim, You Sook Yoon, Sang Yun Lee, Hong Ryang Kil
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(12):1247-1251. Published online December 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Pathologically, Kawasaki disease (KD) is associated with widespread vascular endothelial damage in the acute phase. The vasculitis induced endothelial injury leads to coagulation abnormalities. Abnormalities of endothelial function, platelet activation, and fibrinolysis are present during acute phase and long after the onset of KD. The aim of study is to evaluate the change of hemostatic markers in the... -
- Serum homocysteine and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels after intravenous gammaglobulin treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease
- Jung Hwa Cha, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(10):1093-1099. Published online October 15, 2006
-
Purpose : Homocysteine is a strong and independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease. The deleterious effects of homocysteine included endothelial dysfunction, arterial intimal-medial thickening, wall stiffness and procoagulant activity. However, the precise mechanism responsible for homocysteine release in children with coronary artery disease is still unknown. The purpose of this study was to investigate serum homocysteine and tumor necrosis factor(TNF)-α... -
- The Change of Serum Soluble E-selectin in Kawasaki Disease
- Jae-Ho Jeong, Eun-Young Cho, Jae-Woo Lim, Eun-Jeong Cheon, Kyong-Og Ko, Kyung-Il Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(5):539-544. Published online May 15, 2005
-
Purpose : The aim of this study was to investigate the pathophysiologic role of serum E-selectin, vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF)-induced cell adhesion mollecule in Kawasaki disease(KD) and to look for the evidence of direct relationship between the plasma levels of soluble E-selectin and the incidence of coronary artery lesion(CAL). Methods : Changes in plasma levels of sE-selectin(n=98) over time were... -
- Follow-Up Method in Patients with Kawasaki Disease who had No Coronary Artery Abnormalities in the Convalescent Period
- Hee Jung Joo, Min Seob Song, Chul Ho Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(2):165-173. Published online February 15, 2005
-
Purpose : We performed the study to evaluate the value of the follow-up echocardiogram performed 6 months to 1 year after the onset of Kawasaki disease(KD), as recommended by American Heart Association(AHA) guidelines, when echocardiograms in the convalescent period were normal. Methods : Patients were selected from 147 cases diagnosed with KD at Pusan Paik hospital from January 2000 to October... -
- Prediction of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Non-responders in Patients with Kawasaki Disease
- Gi Bum Lee, Ji-Won Lee, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(1):90-94. Published online January 15, 2004
-
Purpose : We evaluated the effects of intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) on the levels of laboratory indices examined serially according to the responsiveness to IVIG therapy in children with Kawasaki disease(KD). Methods : Children with KD(n=63) who had been treated with IVIG at a dosage of 2.0 g/kg were classified into two groups : the IVIG-resistant(consistent fever over 48 hours after initiation... -
- Serum Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor as a Predictive Risk Factor for the Occurrence of Coronary Artery Lesions in Kawasaki Disease
- Min Hyuk Park, Hye Lim Jung, Ju Hee Yang, Jung-Yeon Shim, Deok Soo Kim, Jae Won Shim, Moon Soo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(8):811-816. Published online August 15, 2003
-
Purpose : Kawasaki disease is an acute systemic vasculitis of unknown etiology with a predilection for the coronary arteries. Vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF) is a cytokine which promotes vascular permeability and angiogenesis. We investigated serum VEGF(sVEGF) levels in Kawasaki disease to determine whether sVEGF level can be used as a risk factor to predict the occurrence of coronary artery lesions(CAL)... -
- Laboratory Values in Patients with Kawasaki Disease after Intravenous Immunoglobulin : Comparison of Patients with Coronary Artery Lesions to those without Coronary Artery Lesions
- Min-Young Park, Kyung-Yil Lee, Ji-Whan Han, Hyung-Shin Lee, Ja-Hyun Hong, Kyung-Tai Whang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(2):162-166. Published online February 15, 2003
-
Purpose : We evaluated the effects of intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) on level of laboratory parameters examined serially according to the existence of coronary artery lesions in children with Kawasaki disease. Methods : Children with Kawasaki disease(n=63), treated with IVIG at a dose of 2.0 g/kg, were classified as a group with coronary artery lesions(CALs+ group, n=9) or a group without coronary... -
- An Epidemiologic Study of Kawasaki Disease(1987-2000) : Incidence of Coronary Artery Complication in the Acute Stage
- Kyung-Yil Lee, Min-Young Park, Ji-Whan Han, Hyung-Shin Lee, Jin Choi, Kyung-Tai Whang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(6):783-789. Published online June 15, 2002
-
Purpose : We evaluated the epidemiologic characteristics and incidence of coronary artery sequele of children with KD according to treatment. Methods : We retrospectively analyzed 506 medical records of children with KD, who were admitted at Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital from Jan. 1987 to Dec. 2000. Results : The mean annual incidence was 36.1±11.1 cases per year. There was a slightly higher... -
- Clinical Characteristics of Infant Kawasaki Disease
- Yeun Keun Choi, Jung Min Hong, Su Mi Ihn, Hae Kyeung Lim, Hong Ryang Kil
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(1):109-113. Published online January 15, 2002
-
Purpose : To assess the incidence of coronary artery lesion(CAL) and the efficacy of intravenously administered immune globulin(IVGG) and aspirin therapy, identify risk factors for CAL, and analyze clinical characteristics in infants less than 12 months of age with Kawasaki disease. Methods : Retrospective chart review of children less than 12 months of age with Kawasaki disease between 1994 and 1998, diagnosed at Chungnam... -
- Predicting of Aneurysm with Learning Vector Quantization in Patients with Kawasaki Disease
- Jae Hyun Kwon, Myung Kul Yum, Nam Su Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(1):78-84. Published online January 15, 2000
-
Purpose : We applied Learning Vector Quantization(LVQ) in the analysis of data from Kawasaki disease patients with coronary artery aneurysm in an attempt to achieve accurate predictions of outcome for individual patients. Methods : One hundred and seventy-five patients with Kawasaki disease were recruited. First, data of 75 patients(of which 60 patients had no aneurysm and 15 patients had aneurysm) were trained using the network.... -
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











