Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Treatment of congenital cytomegalovirus infection
- Gyu Hong Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):384-394. Published online December 28, 2022
-
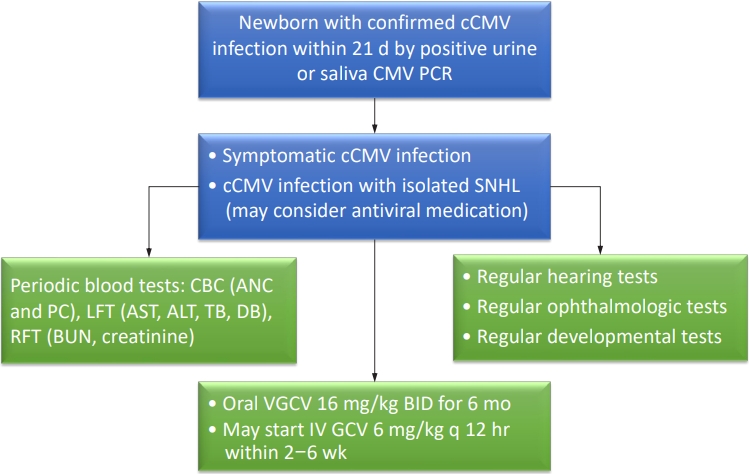
· Congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is among the most common causes of nongenetic sensorineural hearing loss.
· Congenital CMV is initially treated with intravenous ganciclovir for 2–6 weeks and switched to oral valganciclovir, or with oral valganciclovir for the entire 6-month period.
· Infants with congenital CMV require periodic monitoring of absolute neutrophil count, platelet count, and blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, liver function tests, audiological, ophthalmological, and developmental tests during antiviral medication.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Seroprevalence of maternal peripartum human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the Nigerian literature
- Abdulrasheed Usman, Muhammad Hamis Musa, Bukhari Isah Shuaib, Olayemi Balogun, Mukhtar Adeiza
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):307-316. Published online December 22, 2022
-
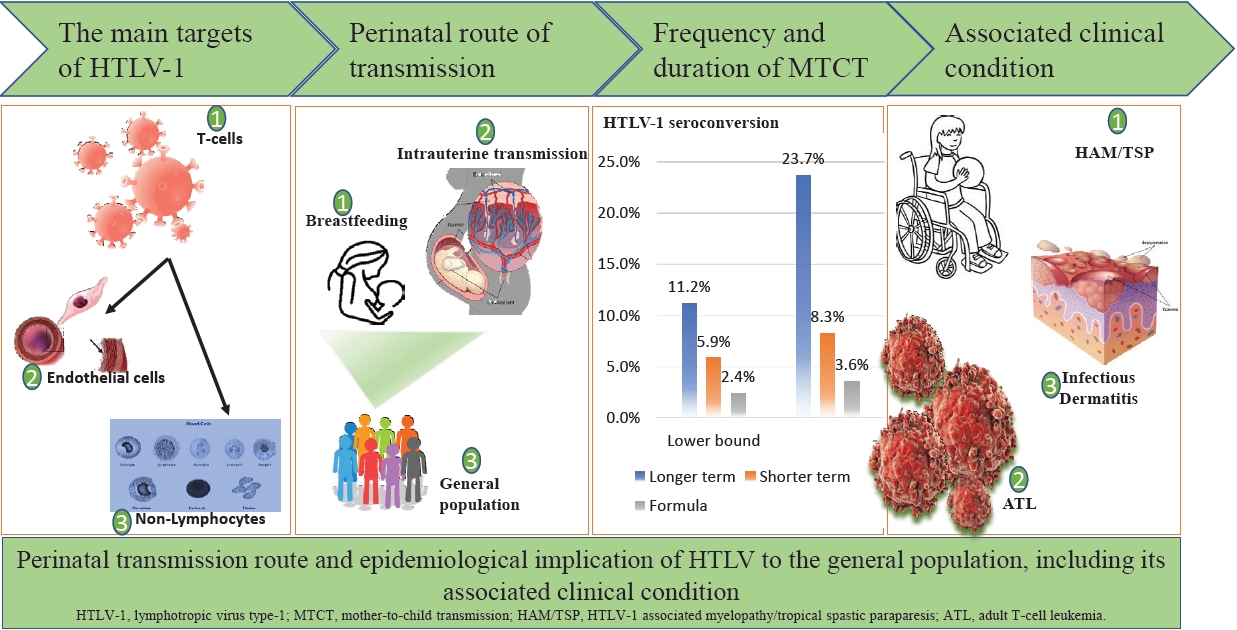
The peripartum period is an important transmission time for human T-cell lymphotropic virus-1 (HTLV-1) infection, mainly via breastfeeding and partly through the placental tissues of carrier mothers. Although most HTLV-1–infected individuals are asymptomatic, fetal and childhood infections often result in several diseases with disappointing treatment outcomes. An estimated HTLV-1 burden in Nigeria among perinatal women must be determined to enable rational planning of a comprehensive health care intervention.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST): development, applications, and implications for future early childhood development interventions
- Dooyoung Kim, Young June Choe, Bilal Aurang Zeb Durrani, EunYoung Kim, Junghye Byeon, Baik-Lin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):288-293. Published online December 22, 2022
-

· This review discusses the development and application of the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST) for ensuring early childhood development.
· Various studies have demonstrated the integral role of the K-DST in facilitating the detection of developmental delays and delivery of timely interventions.
· The tailoring of the K-DST to Korean infants and children suggests that other countries may further translate and adapt it.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Predicting COVID-19 transmission in a student population in Seoul, South Korea, 2020–2021
- Young Hwa Lee, Han Ho Kim, Young June Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):173-178. Published online December 22, 2022
-
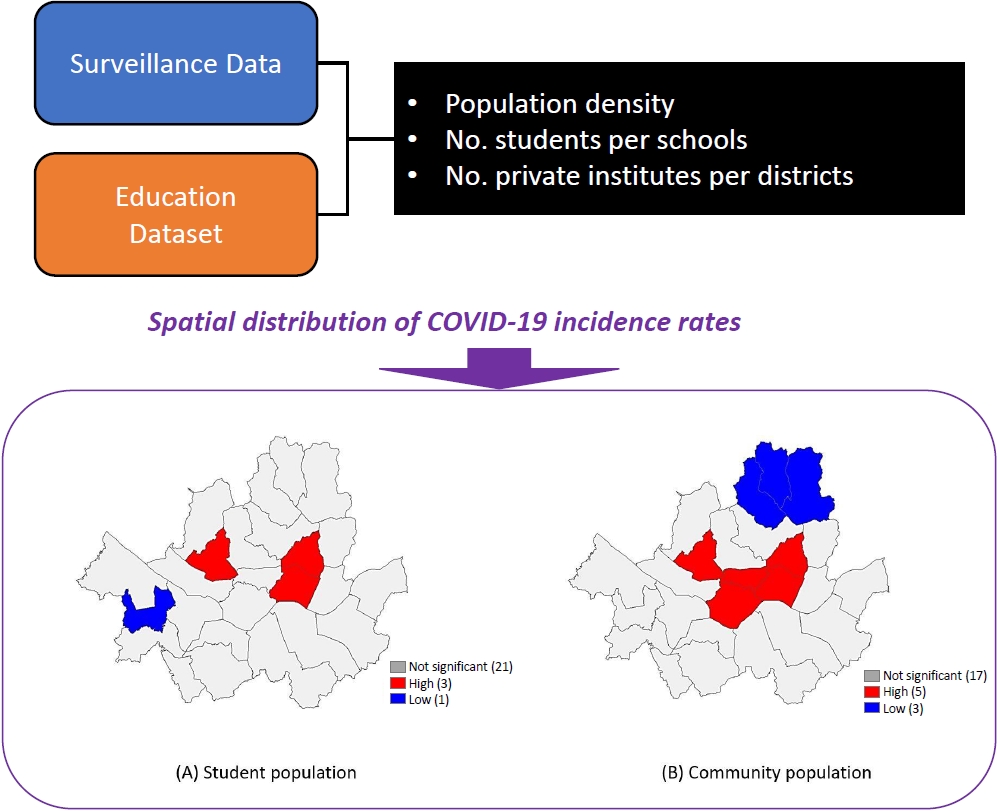
Question: What is the spatial distribution and determinants of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection among students in Korea?
Finding: The community population was closely associated with the risk of COVID-19, and the number of students per school class were inversely associated with COVID-19 rates in students.
Meaning: Our finding suggests that controlling the community-level burden of COVID-19 can help prevent sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in school-aged children.
- Clinical characteristics of pediatric patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus common human coronaviruses: a national multicenter study
- In Suk Sol, Eun Lee, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Yong Ju Lee, Hye Yung Yum, Mi-Hee Lee, Mi Ae Chu, Hui Jeong Moon, Hyo-Bin Kim, Ju Hee Seo, Jung Yeon Shim, Ji Young Ahn, Yoon Young Jang, Hai Lee Chung, Eun Hee Chung, Kyunghoon Kim, Bong-Seong Kim, Cheol Hong Kim, Yang Park, Meeyong Shin, Kyung Suk Lee, Man Yong Han, Soo-Jong Hong, Eun Kyeong Kang, Chang Keun Kim; on behalf of The Pneumonia & Respiratory Disease Study Group of Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):134-141. Published online December 22, 2022
-

Question: The clinical differences between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and human coronaviruses (HCoV) in children remain unknown.
Finding: This study compared the clinical findings of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus HCoV. Its findings suggest that children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 have a milder clinical course than those with HCoV.
Meaning: The clinical course of children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 should be closely monitored during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Role of social media use in onset of functional gastrointestinal disorders in children
- Mauro Cinquetti, Vanessa Dargenio, Michele Fingerle, Carolina Marchiotto, Marco Biasin, Massimo Pettoello Mantovani, Flavia Indrio
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):226-232. Published online December 21, 2022
-
· Social media use can cause adverse health outcomes, including gastrointestinal disorders, in children and adolescents.
· Recent findings have shown a high prevalence of social media use and decreased well-being in patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders.
· The biopsychosocial nature of functional gastrointestinal disorders and the clear influence of social media on the psychosocial lives of children suggests the likely involvement of social media in their development.
- Liver fibrosis in children: a comprehensive review of mechanisms, diagnosis, and therapy
- Elif Ozdogan, Cigdem Arikan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):110-124. Published online December 19, 2022
-
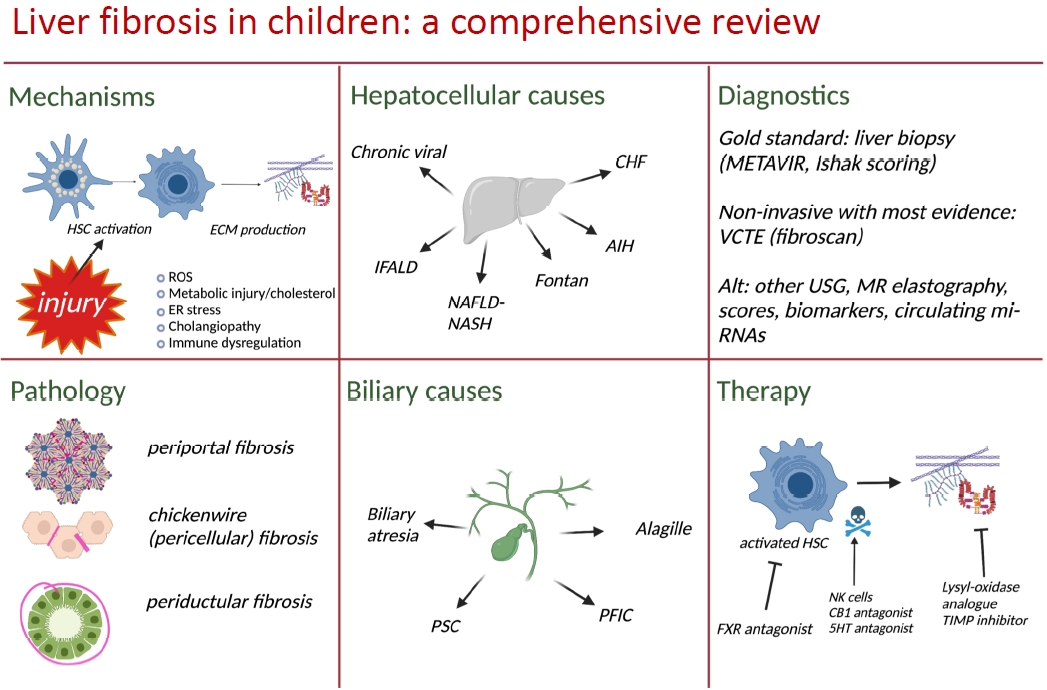
· Chronic liver diseases in children are heterogenous but converge in the common pathway of fibrosis.
· Much of the literature on mechanisms of fibrogenesis focus on adults but pediatric physiology has documented differences.
· Understanding of these distinctions are necessary to define, treat, and prevent fibrosis.
· Current management of liver fibrosis relies heavily on liver biopsy. Multiple tools have shown high diagnostic performance in pediatric and adult populations. Large, multicenter studies are needed for validation.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- A thickened formula reduces feeding-associated oxygen desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants
- Gayoung Lee, Juyoung Lee, Ga Won Jeon, Yong Hoon Jun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):32-37. Published online December 15, 2022
-
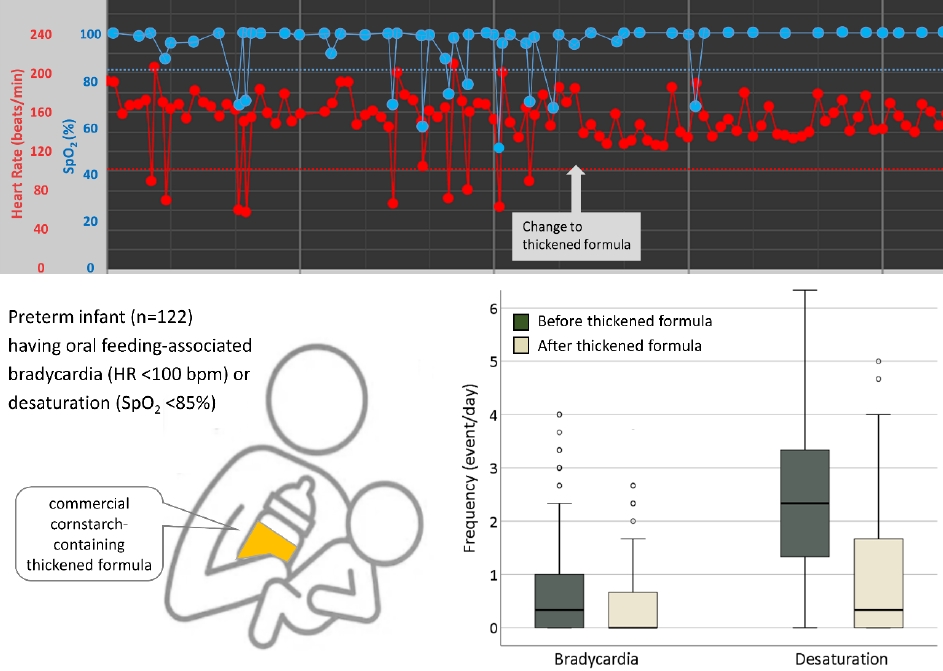
Question: Is a commercial thickened formula able to alleviate oral feeding-associated desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants?
Finding: Thickened formula feeding significantly reduced oral feeding-associated desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants.
Meaning: Thickened formula feeding stabilizes oxygen saturation and heart rate during oral feeding among preterm infants with feeding difficulties.
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Lumbar puncture or not: when does febrile seizure require a neurodiagnostic evaluation?
- Seung Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):68-69. Published online December 9, 2022
-
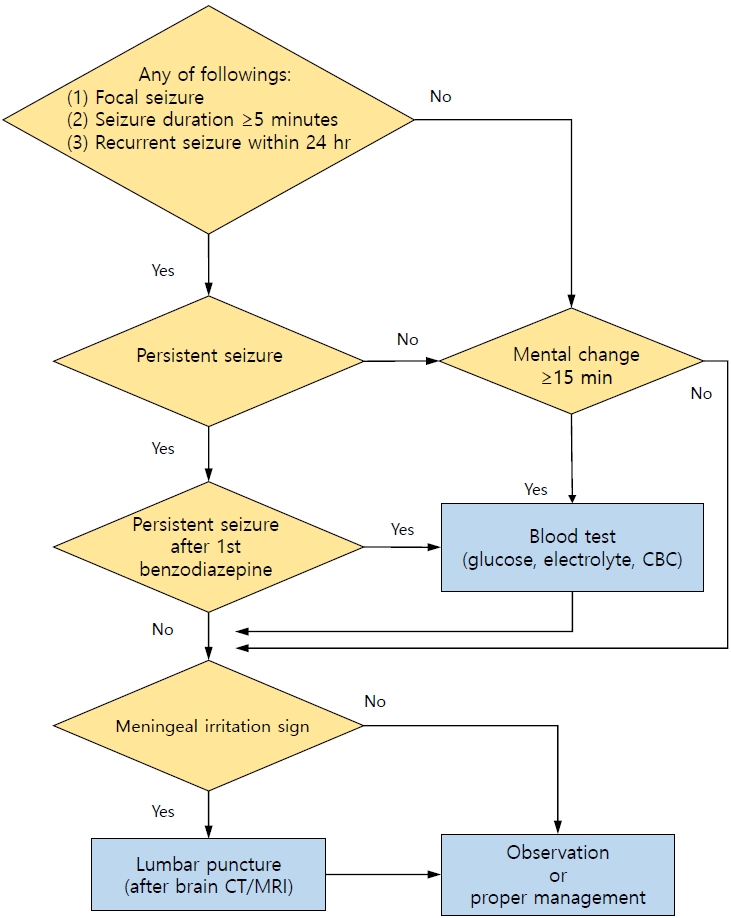
· A neurodiagnostic evaluation (lumbar puncture, blood tests, electroencephalography, and neuroimaging) is not indicated in most patients with simple febrile seizures.
· A lumbar puncture is indicated when a central nervous system infection is suspected in any patient with febrile seizures.
· Blood tests (glucose, electrolytes, and complete blood count) are indicated in patients with persistent seizure after benzodiazepine treatment, prolonged loss of consciousness, poor general condition, or signs of dehydration.
- Pulmonology
- Wheezing in infants and preschoolers: phenotypes and treatment options
- Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):26-27. Published online December 6, 2022
-
· Knowing who will develop into asthma or who will not is important to impose proper treatment and early intervention in a child with the first episode of wheezing.
· Phenotypes of severe bronchiolitis in less than 2-year-old children with first episode of wheezing were suggested for different treatment options
· RV-induced and/or atopy-associated severe wheezing in preschool children may benefit from early intervention of asthma treatment.
- Letter to the Editor
- Critical Care Medicine
- Role of serum bilirubin-to-albumin ratio as a prognostic index in critically ill children
- You Min Kang, Ga Eun Kim, Mireu Park, Jong Deok Kim, Min Jung Kim, Yoon Hee Kim, Kyung Won Kim, Myung Hyun Son, Soo Yeon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):85-87. Published online December 5, 2022
-
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Efficacy of body position on gastric residual in preterm infant: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Kurvatteppa Halemani, Alwin Issac, Sanjay Dhiraaj, Prabhaker Mishra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):262-270. Published online November 30, 2022
-
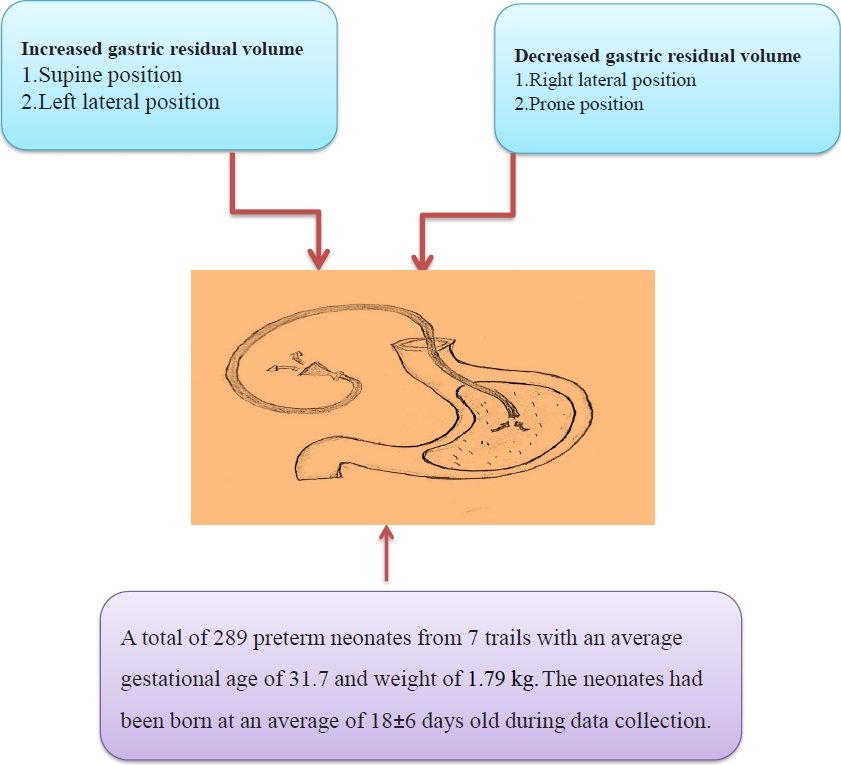
Breastfeeding and it's tolerance are the positive indicators for preterm babies. Placing the preterm infant in the right lateral or prone position after feed had lesser gastric residual volume compared to placing them in left lateral or supine positions. The post-feed position is a vital element in enhancing feeding tolerance, mechanical functions of the gastrointestinal tract and the overall development of preterm infants.
- Gastroenterology
- Association between maternal weight gain during pregnancy and child’s body mass index at preschool age
- Jeewon Shin, Yoowon Kwon, Ju Hee Kim, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):76-81. Published online November 30, 2022
-
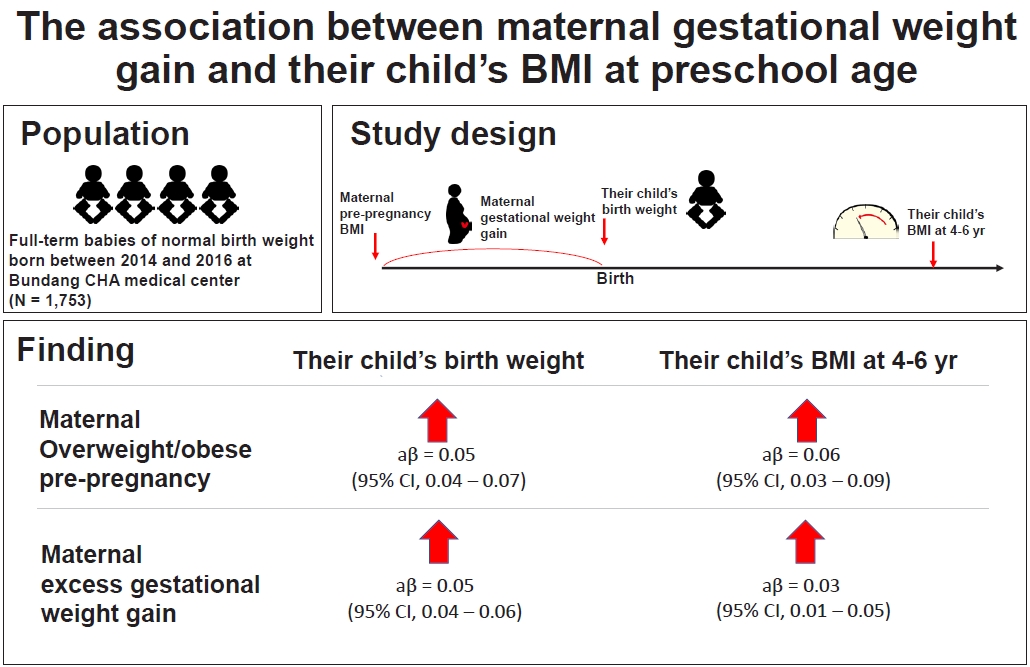
Question: What are the risk factors of newborn birth weight? Does gestational weight gain and prepregnancy body mass index affect childhood weight?
Finding: Excess maternal weight gain increases the risk of overweight/obesity, newborn birth weight, and child body mass index at 4–6 years.
Meaning: Maternal weight control before and during pregnancy should be well controlled.
- Neurology
- Long-term neurological cognitive, behavioral, functional, and quality of life outcomes after fetal myelomeningocele closure: a systematic review
- Andre Marolop Pangihutan Siahaan, Martin Susanto, Sarma Nursani Lumbanraja, Dwi Herawati Ritonga
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):38-45. Published online November 30, 2022
-
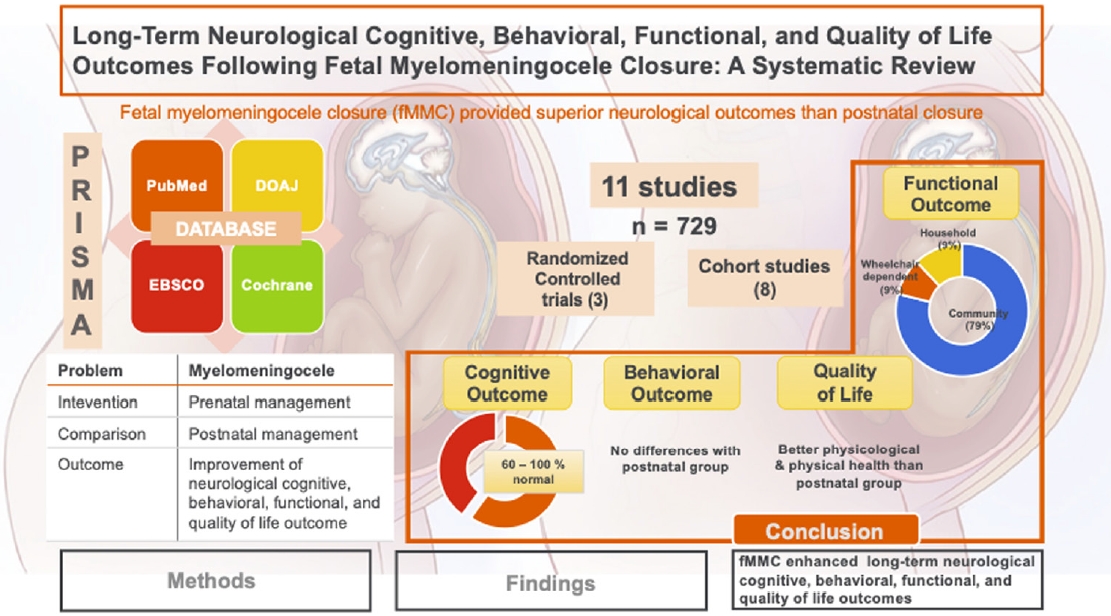
· Fetal myelomeningocele closure significantly improved long-term neurological cognitive, behavioral, functional, and quality of life outcomes, most likely by reducing hydrocephalus rates.
· However, fetal myelomeningocele closure is associated with a significant risk of pregnancy complications, especially premature rupture of membranes and preterm delivery.
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Does cord blood cortisol have a mediating effect on maternal prepregnancy body mass index and birth weight?
- Gyu Hong Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):24-25. Published online November 30, 2022
-

· A high prepregnancy body mass index (pre-BMI) is associated with large for gestational age (LGA) and macrosomia, whereas a low pre-BMI is associated with small for gestational age (SGA) and low birth weight (LBW).
· The identification of the role of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis in the effect of pre-BMI and maternal gestational weight gain on birth weight could reduce the frequency of LGA, macrosomia, SGA, or LBW through maternal diet optimization.
- Allergy
- Clinical considerations and practical issues of allergic diseases in COVID-19 era
- Sungsu Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):587-588. Published online November 29, 2022
-
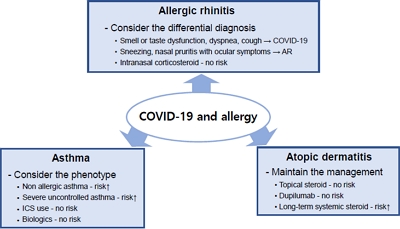
The risk of sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection and severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outcomes is not elevated in patients with the type 2 phenotype and well-controlled asthma. Inhaled corticosteroids, intranasal corticosteroids, and topical steroids can be safely used in COVID-19 patients. Biologics can be safely used by patients with allergic diseases without concern about antibody responses.
- Review Article
- Nutrition
- Association of gut microbiota with obesity in children and adolescents
- Ky Young Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):148-154. Published online November 16, 2022
-

The gut microbiota is an emerging factor in the development of pediatric obesity, which is affected by renowned risk factors such as diet, lifestyle, and socioeconomic status. This review aimed to describe the association between the gut microbiota and childhood obesity.
- Editorial
- Pulmonology
- Community-acquired pneumonia in Korean children: time to read between the lines
- Dong In Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):22-23. Published online November 10, 2022
-
· Various studies have reported the etiology of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in Korean children
· Factors other than etiology are equally important to a compre hensive understanding of CAP
· Knowledge from archived reports is no longer directly applicable to the current CAP and requires careful modification
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Gut microbiota affects brain development and behavior
- Gun-Ha Kim, Jung-Ok Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):274-280. Published online November 8, 2022
-

· The gut microbiota can alter a host’s brain development and behavior.
· Gut bacteria communicate with the brain via the microbiota-gut-brain axis.
· Fecal microbial transplantation is a promising treatment strategy for autism spectrum disorder.
- Infection
- Global varicella vaccination programs
- Young Hwa Lee, Young June Choe, Jia Lee, Eunseong Kim, Jae Young Lee, Kwan Hong, Yoonsun Yoon, Yun-Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):555-562. Published online November 2, 2022
-
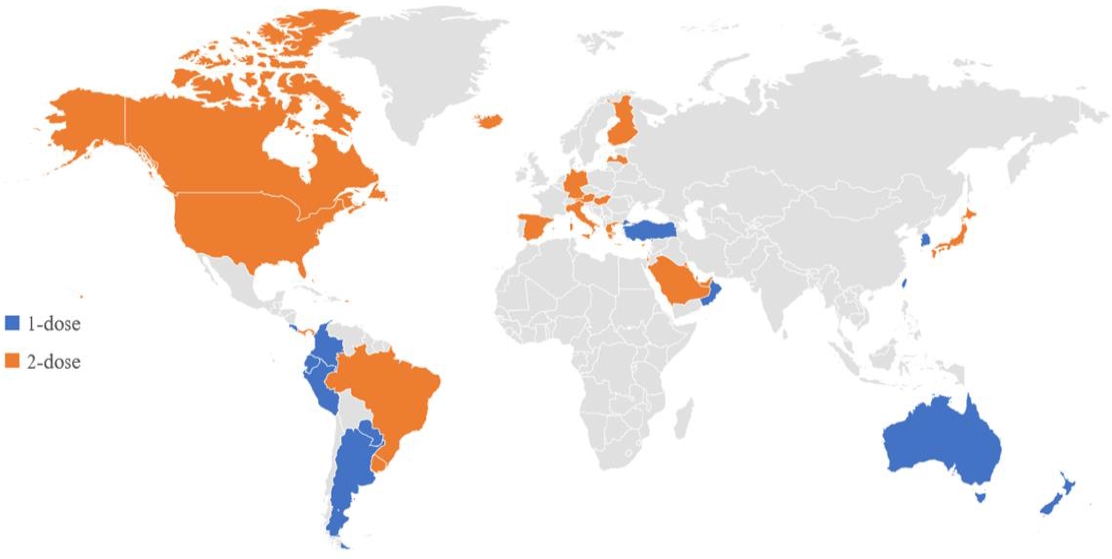
It is important to evaluate its effectiveness at the national level and to determine the varicella vaccine schedule based on the evidence generated through the studies.
- Nutrition
- Protein substitutions as new-generation pharmanutrition approach to managing phenylketonuria
- Fatma Nur Keskin, Teslime Özge Şahin, Raffaele Capasso, Duygu Ağagündüz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):320-331. Published online November 1, 2022
-
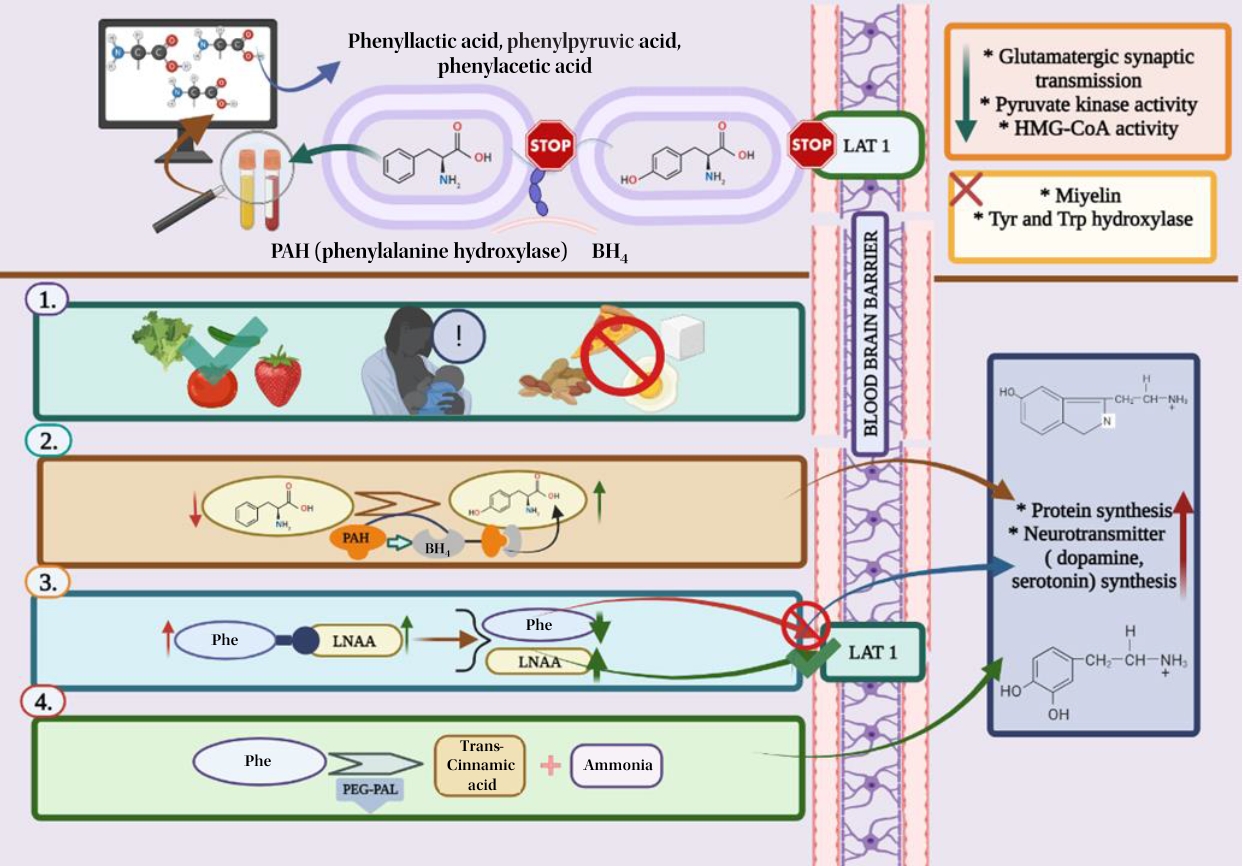
Phenylketonuria, an autosomal recessive disease that results from the inability to metabolize phenylalanine, is currently treated with medical nutrition therapy. New treatment approaches such as tetrahydrobiopterin, glycomacropeptide, large neutral amino acids, pegvaliase, and gene therapy significantly impact disease management and dietary enrichment. This article also reviews animal and human studies that have evaluated the efficacy and safety of these new protein substitutes.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Predictors of high-flow nasal cannula failure in pediatric patients with acute respiratory distress
- Kantara Saelim, Busawan Thirapaleka, Kanokpan Ruangnapa, Pharsai Prasertsan, Wanaporn Anuntaseree
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):595-601. Published online November 1, 2022
-

SpO2/FiO2 ratio ≤166, pediatric respiratory rate-oxygenation index <132, and clinical respiratory score ≥6 at 12 hours after high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) initiation were useful bedside predictors for HFNC failure in pediatric patients.
- Gastroenterology
- Ability of polymicrobial probiotic and mono-strain probiotic to reduce functional abdominal pain in children: a randomized clinical trial
- Seyed Sajad Jafari, Seyed Mojtaba Hashemi, Bahman Sadeghi, Amir Almasi-Hashiani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):589-594. Published online October 31, 2022
-
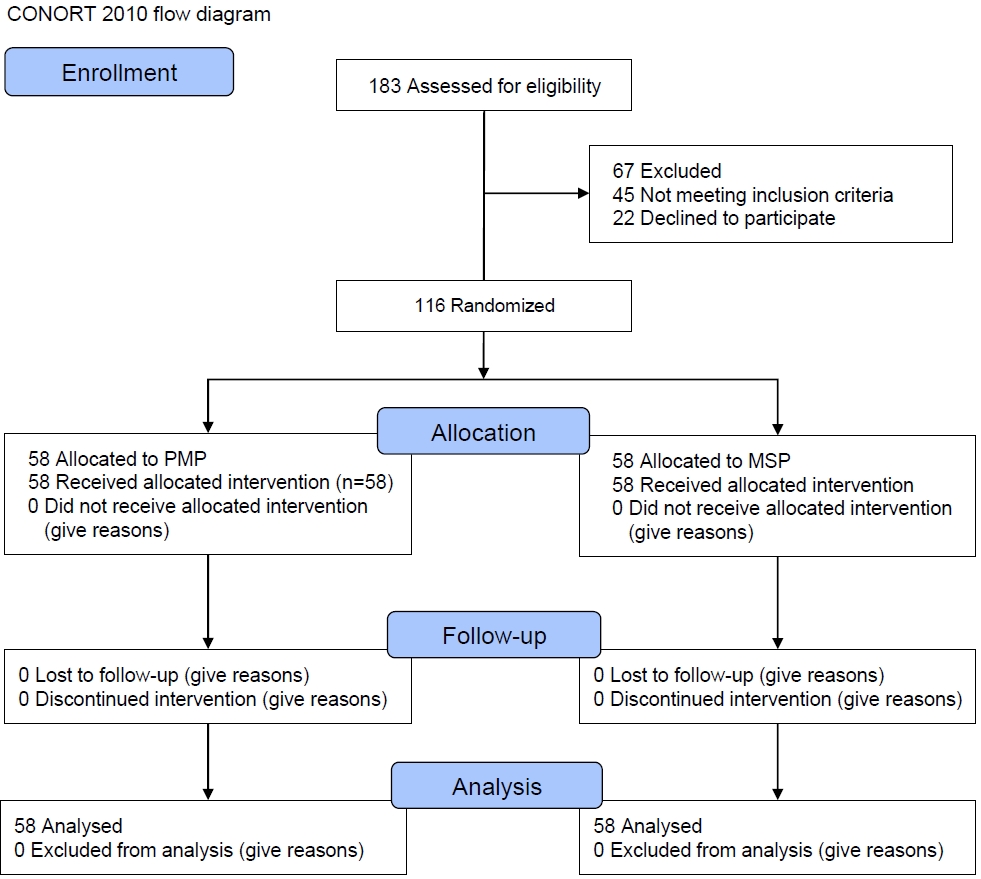
· This study compared the ability of 2 probiotics to reduce and improve functional abdominal pain (FAP) in children.
· In the polymicrobial probiotic (PMP) group, 10.34% of children reported no pain; in the mono-strain probiotic (MSP) group, all patients reported low-degree pain. The mean pain score decreased significantly over time in both groups.
· The use of both PMP and MSP is recommended to reduce pain in patients with FAP.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- New approaches to immunotherapy in house dust mite allergy
- In Sik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):161-168. Published online October 25, 2022
-
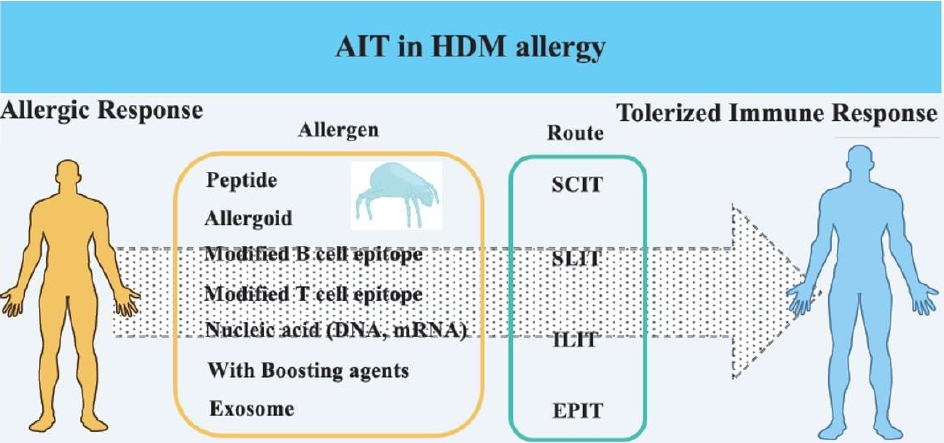
Allergen immunotherapy (AIT) has developed over the last few decades and has emerged as a promising treatment. House dust mite (HDM) is a target allergen in AIT, and various modified HDM allergens have been improved for their efficacy. Moreover, clinical trials have proved their significantly therapeutic effects in allergy. This article review focuses on HDM allergens developed for AIT efficacy,...
- Gastroenterology
- High-resolution esophageal manometry in children
- Yogesh Waikar
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):155-160. Published online October 17, 2022
-

High-resolution esophageal manometry can be safely performed in children where recurrent vomiting and persistent dysphagia is the working diagnosis after excluding nonluminal and structural obstructive pathologies using pediatric upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Normal manometry values are available. Clinical picture, biochemical tests, radiological interpretation, and endoscopic findings with manometry completes the analysis of patients with recurrent vomiting and dysphagia.
- Nutrition
- Total energy expenditure measured by doubly labeled water method in children and adolescents: a systematic review
- Nahyun Kim, Jonghoon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):54-65. Published online October 17, 2022
-
This systematic review summarizes convincing evidence that total energy expenditure (TEE) measured using the doubly labeled water technique increased with age from 1 to 18 years, while fat-free mass (FFM) increased with growth. TEE and in normal-weight participants, while physical activity level did not differ from that of normal-weight participants.
- Pulmonology
- Epidemiology and surveillance implications of community-acquired pneumonia in children
- Eui Jeong Roh, Jung Yeon Shim, Eun Hee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):563-573. Published online October 17, 2022
-
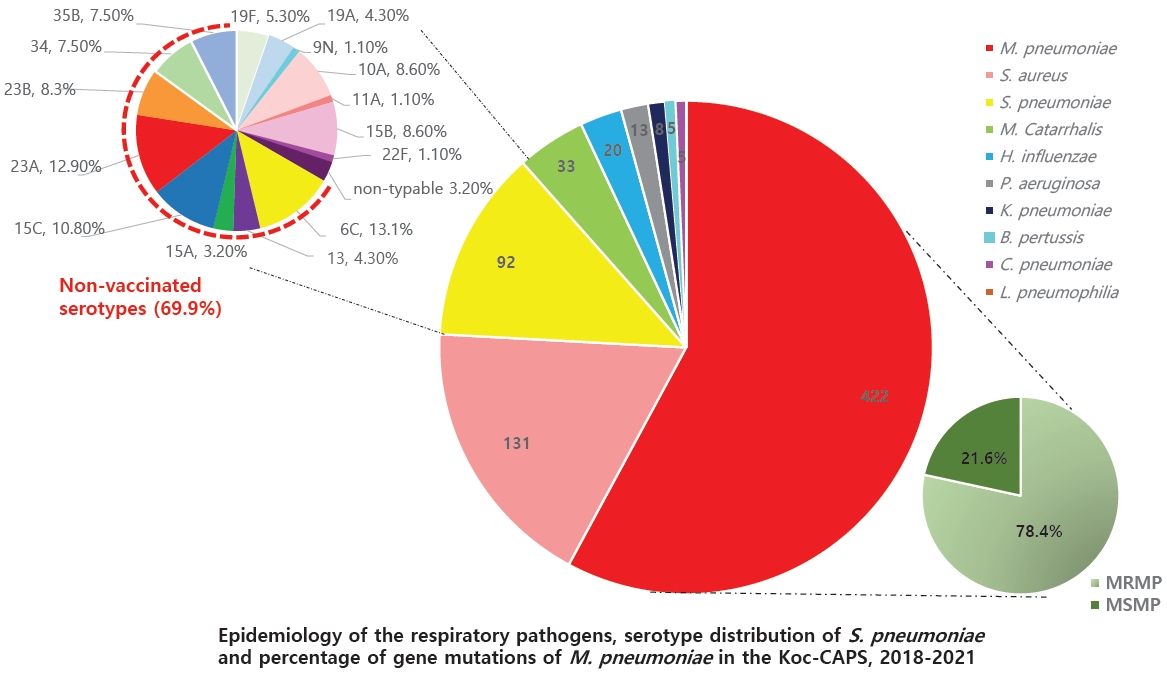
The identification of the causative pathogens of community-acquired pneumonia and appropriate treatment and prevention can reduce mortality and the socioeconomic burden by reducing the medical expenses. The world has been in the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic since 2020, and there is always a risk of continuous emergence and epidemic of new respiratory infectious diseases. Therefore, it is important to sustain a monitoring system for respiratory infectious diseases including pneumonia.
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Ability of probiotics to reduce functional abdominal pain in children
- Ji Sook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):585-586. Published online October 6, 2022
-
· The ability of probiotics to relieve pain caused by functional abdominal pain disorders (FAPD) in children is unclear.
· Lactobacillus reuteri may effectively reduce pain caused by childhood FAPD.
· Since the routine use of probiotics cannot be recommended due to a lack of clinical evidence, research into probiotic mixtures or symbiotics remains necessary.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Probiotics added to maternal nutrition affect ınfantile colic symptoms and fecal microbiota profile: a single-blind randomized controlled study
- Aysu Yıldız Karaahmet, Gülümser Dolgun, Metehan Özen
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):547-554. Published online September 23, 2022
-

Question: Do probiotics added to maternal nutrition affect infantile colic symptoms and intestinal microbiota?
Finding: Infants whose mothers ingested probiotics demonstrated decreased crying frequency and intensity and significantly increased bacterial diversity in the stools. The bacterial variety was substantially affected by the added probiotic product.
Meaning: The addition of probiotics to maternal nutrition in early infancy could play an important role in preventing infantile colic.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Management of patients with allergic diseases in the era of COVID-19
- Eun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):529-535. Published online September 23, 2022
-
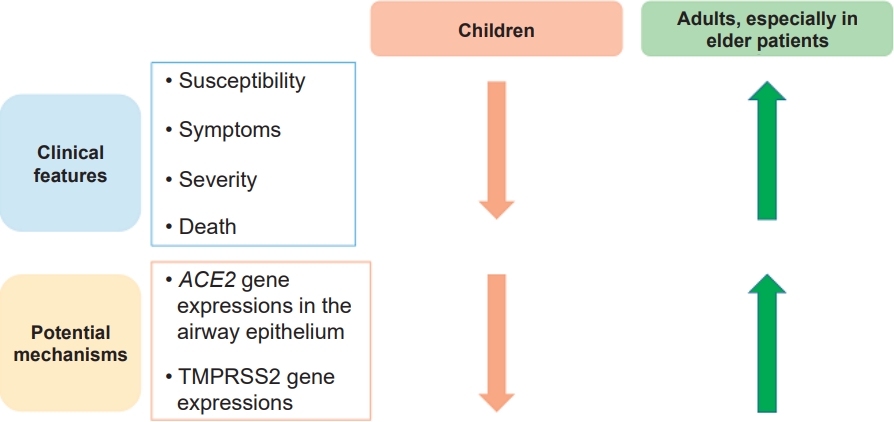
In the early days of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, allergic diseases, especially asthma, were considered to be risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, hospitalization, and death. These concerns stemmed from the idea that individuals with allergic diseases are generally more susceptible to respiratory virus infections, which are major causes of exacerbation of allergic diseases. However, epidemiologic data with...
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











