- Review Articles
- Rheumatology
- Double-negative T cells in pediatric rheumatic diseases
- Dimitri Poddighe, Tilektes Maulenkul, Kuanysh Dossybayeva, Gulsamal Zhubanova, Zaure Mukusheva, Lyudmila Akhmaltdinova
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):632-640. Published online September 12, 2024
-
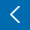
Double-negative T (DNT) cells appear to be increased in several pediatric rheumatic diseases and this finding may be correlated with disease activity to some extent. However, due to significant heterogeneity in several methodological aspects, further investigations in rheumatic children are needed to assess the potential relevance of DNT cells as biomarkers and clarify their immunopathological role.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Screen time among preschoolers: exploring individual, familial, and environmental factors
- Sangha Lee, Donghee Kim, Yunmi Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):641-650. Published online September 12, 2024
-
This systematic review examined the correlation between screen time and various factors in preschoolers. Findings suggest that media parenting, including setting appropriate media limits, is crucial in protecting against excessive screen exposure. However, limited research has been done on the impact of family and personal factors, particularly with the increasing use of portable devices among young children.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Strategies to support language development in neonatal intensive care unit: a narrative review
- Ju Sun Heo, Ee-Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):651-663. Published online November 6, 2024
-
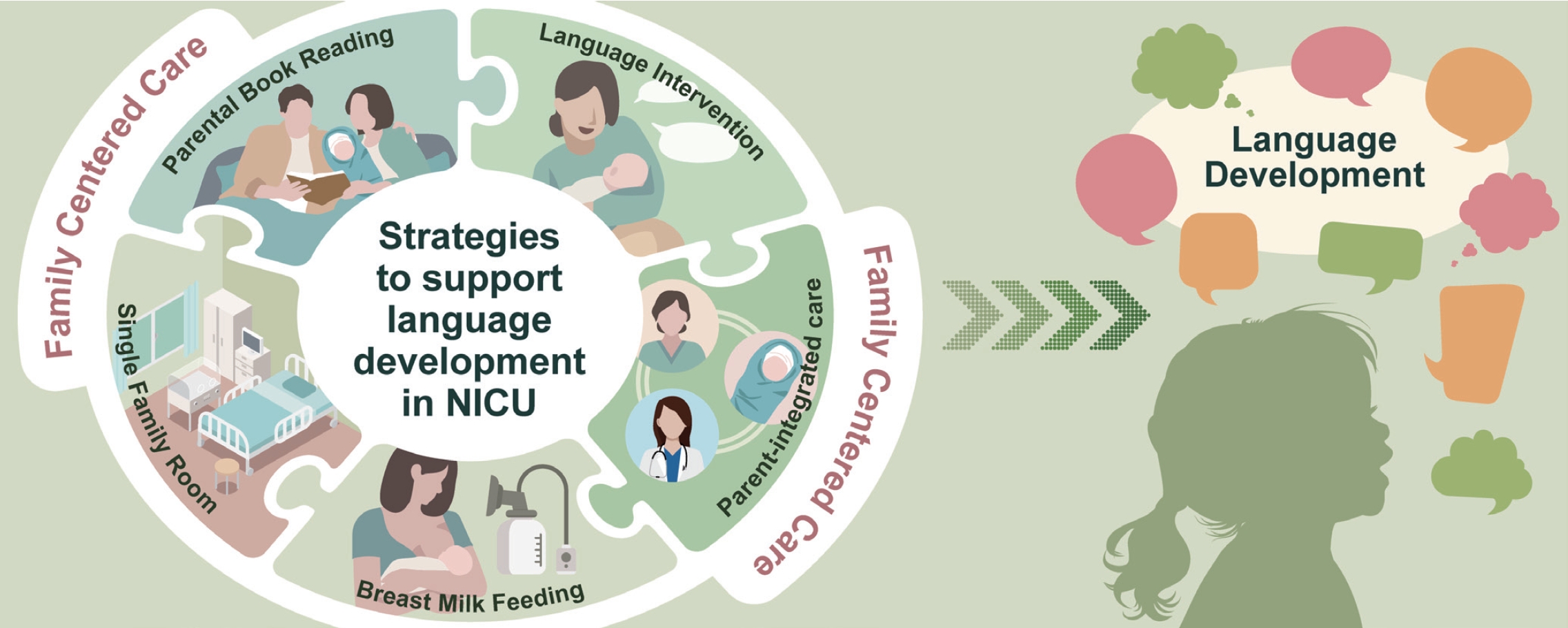
· Preterm infants often experience speech and language development delays during early childhood, impacting children's ultimate outcomes.
· Promoting breastfeeding, increasing parent-infant interactions in a single-family room, promoting a nurturing language environment by parental book reading and language interventions, and parent-integrated interventions in the neonatal intensive care unit could potentially enhance children's language development.
· Integrating these strategies through family-centered care is essential.
- Adolescence Medicine
- Diet-related behaviors affecting health and substance use among children and adolescents
- Ji-Hyun Seo, Sochung Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):664-671. Published online October 31, 2024
-
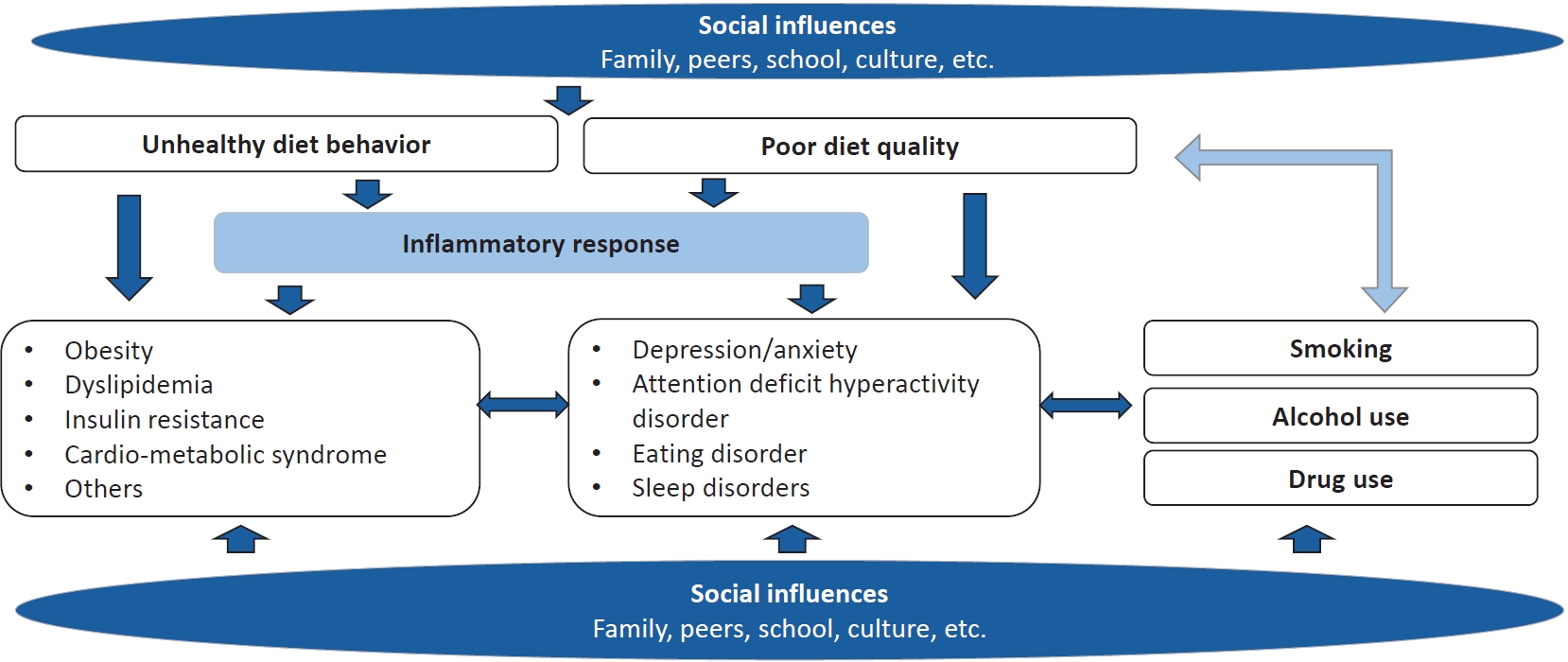
· Diet behaviors in children and adolescents are influenced by environmental and sociocultural factors.
· Unhealthy diet behaviors and poor diet quality are the main contributing factors to noncommunicable diseases and mental health problems during childhood and adolescence.
· Smoking and alcohol drinking in children and adolescents may be associated with unhealthy diet behavior or poor diet quality.
- Editorials
- Allergy
- Advancements in food allergen immunotherapy: improving quality of life and reducing risks
- Jihyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):672-674. Published online July 31, 2024
-
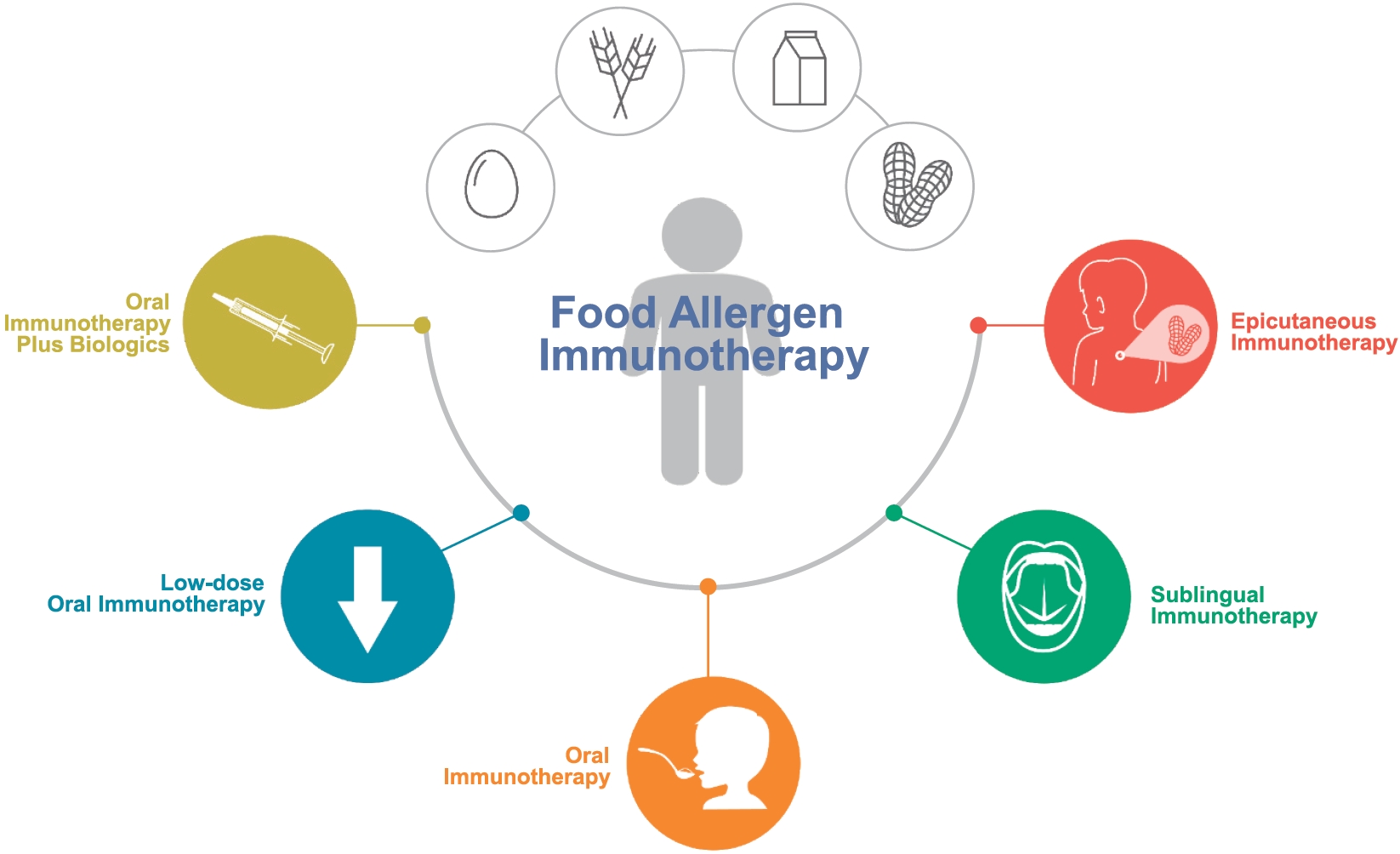
· Pediatric food allergies considerably impair patient and family quality of life, particularly those with persistent allergies to common food allergens.
· Recent research has focused on developing diverse approaches to food allergen immunotherapy, showing promising outcomes of oral, sublingual, and epicutaneous immuno therapies.
· Critical considerations in immunotherapy candidate selection underscore the need for personalized approaches and reliable biomarkers in future studies to improve treatment outcomes.
- Comorbidities of allergic rhinitis in children
- Yong Ju Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):675-676. Published online July 31, 2024
-
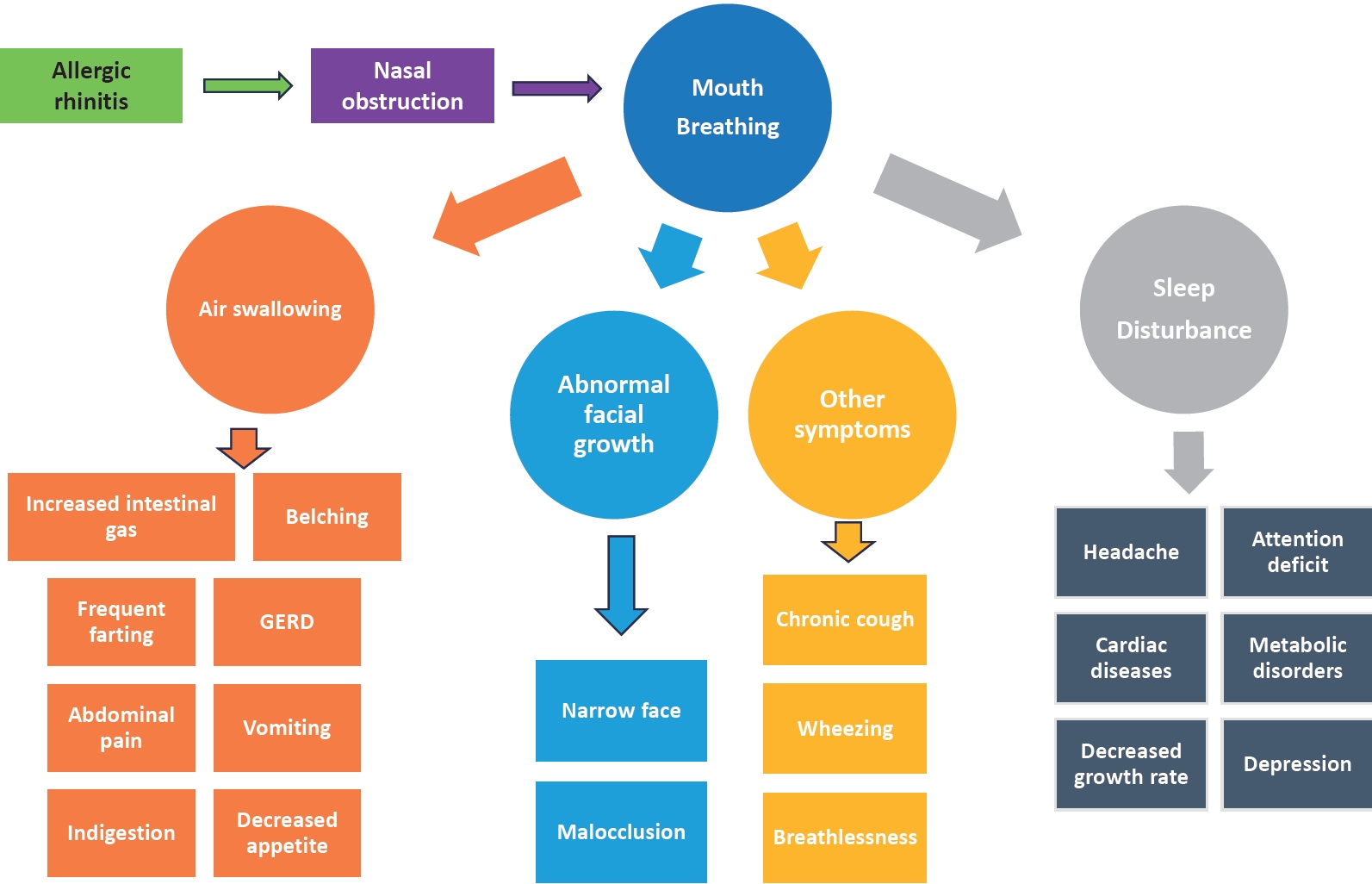
· Allergic rhinitis in children often goes undiagnosed or untreated, with significant systemic complications like sleep disorders, growth issues, and gastrointestinal symptoms linked to nasal obstruction.
· A patient-centered action plan that considers symptom severity, preferences, and comprehensive management of associated complications is essential for effective treatment.
- Original Articles
- General Pediatrics
- Nonpharmacological interventions for managing postoperative pain and anxiety in children: a randomized controlled trial
- Edlin Glane Mathias, Mamatha Shivananda Pai, Vijay Kumar, Dinesh Narayanakurup, Malavika Kulkarni, Vasudeva Guddattu, Ann-Cathrine Bramhagen, Baby S Nayak, Anice George
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):677-685. Published online October 31, 2024
-
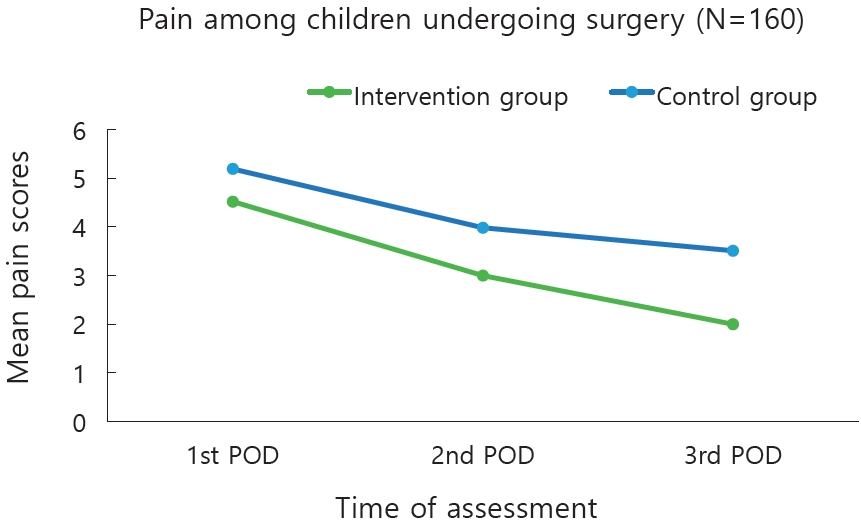
Question: What is the effect of nonpharmacological interventions on postoperative pain and anxiety among children.
Finding: Nurse-provided distraction interventions reduce pain and anxiety among pediatric surgical patients.
Meaning: The findings suggest that nonpharmacological interventions provided postoperatively to children reduce their pain and anxiety levels.
- Role of proper postnatal care in continued exclusive breastfeeding among young Indonesian mothers
- Wahyu Triadmajani, Shinta Prawitasari, Abdul Wahab
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):686-693. Published online September 12, 2024
-
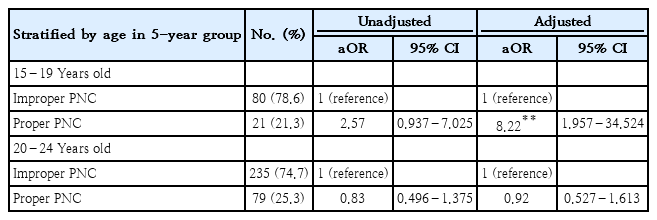
Question: Is proper postnatal care (PNC) associated with exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) practice among young Indonesian mothers?
Finding: Proper PNC elevates the likelihood of EBF among Indonesian adolescent mothers aged 15–19 years.
Meaning: Breastfeeding services should be provided during the early postnatal period to support EBF practice among adolescent mothers. High-quality PNC is a tailored intervention for vulnerable populations.
- Cardiology
- Comparative analysis of adolescent hypertension definitions for predicting early adulthood carotid artery intima-media thickness: Tehran lipid and glucose study
- Maryam Barzin, Shirin Yaghoobpoor, Maryam Mahdavi, Behnaz Abiri, Majid Valizadeh, Fereidoun Azizi, Pooneh Dehghan, Farhad Hosseinpanah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):694-703. Published online September 12, 2024
-
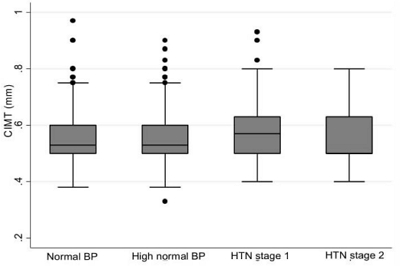
Question: What is the prevalence of HTN among adolescents enrolled in the TLGS according to 3 different accepted definitions (4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG). Also, what is the ability of each of these definitions in predicting early adulthood CIMT, as a surrogate for cardiovascular disease events?
Finding: The highest and lowest prevalence of stage 1 HTN was observed with the AAP-CPG (17.7%) and ESH (8.8%), respectively. Similarly, the highest and lowest prevalence of stage 2 HTN was noted with the AAP-CPG (1.5%) and ESH (0.8%), respectively. The highest to lowest predictive abilities belonged to the 4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG, respectively.
Meaning: Among the various definitions of pediatric HTN, the 4th report offered the best ability to predict a high CIMT during early adulthood, followed by the ESH and AAP-CPG.
- Infection
- Clinical, biochemical, and genetic study of TACE/TNF-α/ACE signaling pathway in pediatric COVID-19 infection
- Ahmed El-Abd Ahmed, Sawsan M.A. Abuhamdah, Mohammed H. Hassan, Nagwan I. Rashwan, Eman A. Abd-Elmawgood, Haggagy Mansour, Hoda S. Sherkawy, Shymaa G. Rizk
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):704-717. Published online November 27, 2024
-
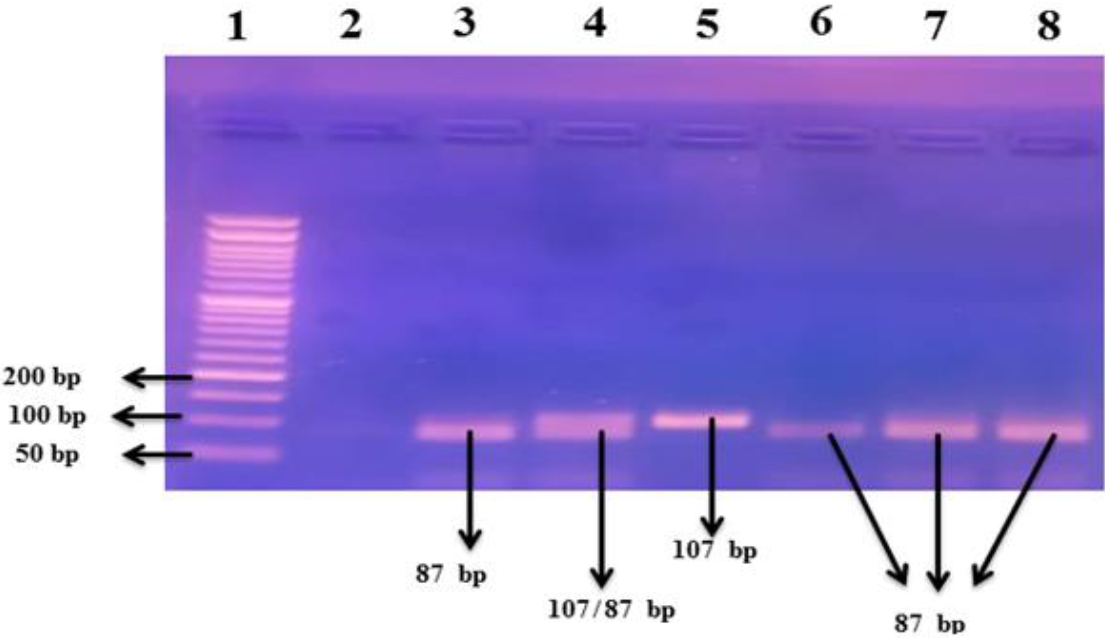
Question: Is the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathway (TNF-α-converting enzyme [TACE]/TNF-α/angiotensin converting enzyme [ACE]) involved in pediatric coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection?
Finding: Significantly increased circulating TACE/TNF-α and decreased ACE2 levels were noted. TNF-α-308G/A plays a significant role in susceptibility to COVID-19 infection among children. The ACE (I/D) (rs4646994) and ACE2 (rs2285666) single nucleotide polymorphisms lack significant associations with pediatric COVID-19 infection.
Meaning: The TNF signaling pathway participates in pediatric COVID-19 infection.
- Other
- Balance assessment with decreased base of support for children with disabilities
- Guilherme M. Cesar, Madison Giebler, Thad W. Buster, Judith M. Burnfield
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):718-724. Published online November 11, 2024
-
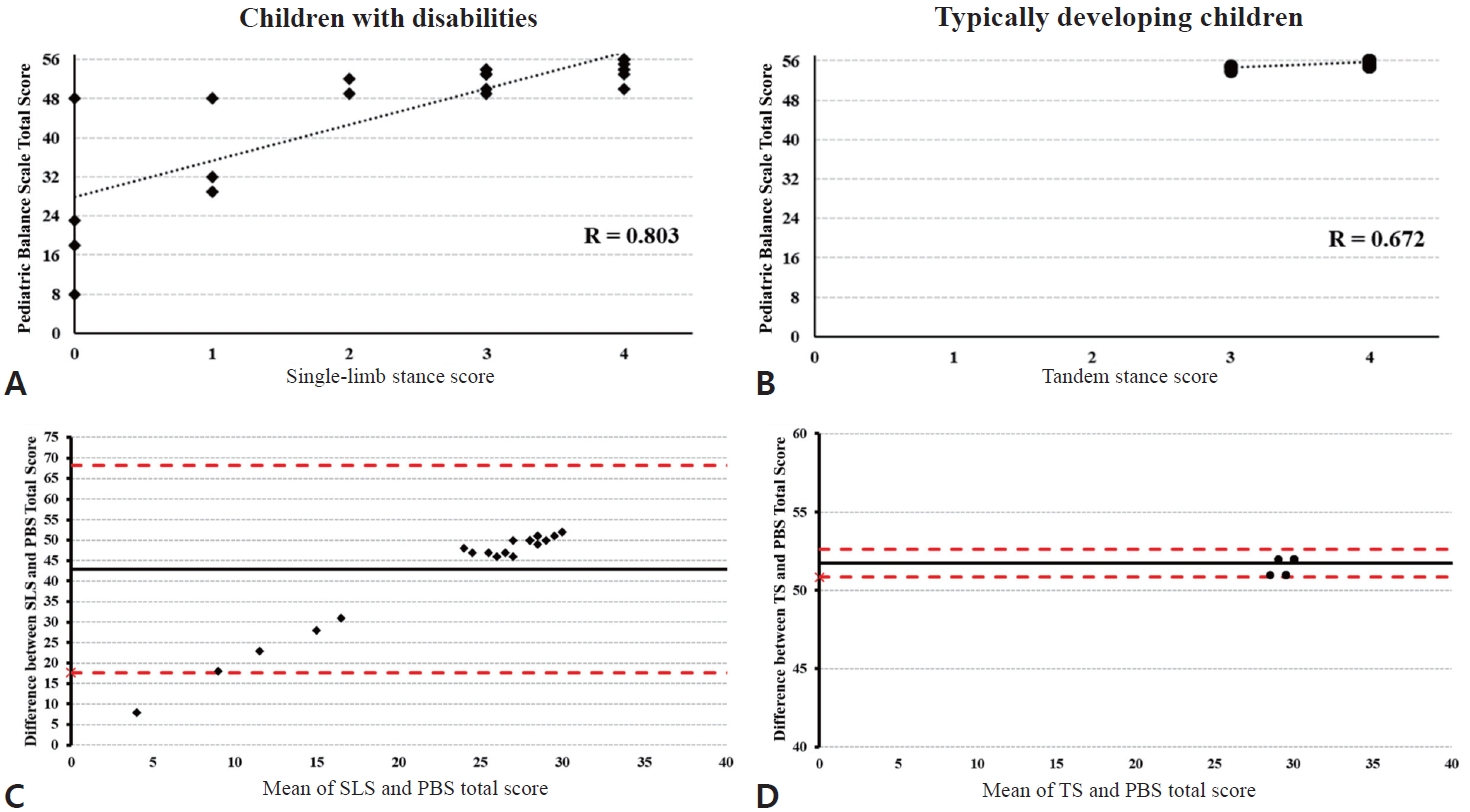
Question: Can a balance task with narrowed base of support indicate overall functional balance control in children with disabilities?
Finding: While single-limb standing could explain overall balance control for children with disabilities, it was unrelated with balance control for typically developing children.
Meaning: One balance task with narrowed base of support can be used as practical assessment of balance abilities for children with disabilities when allocated session time is of concern.
- Clinical Note
- Oncology
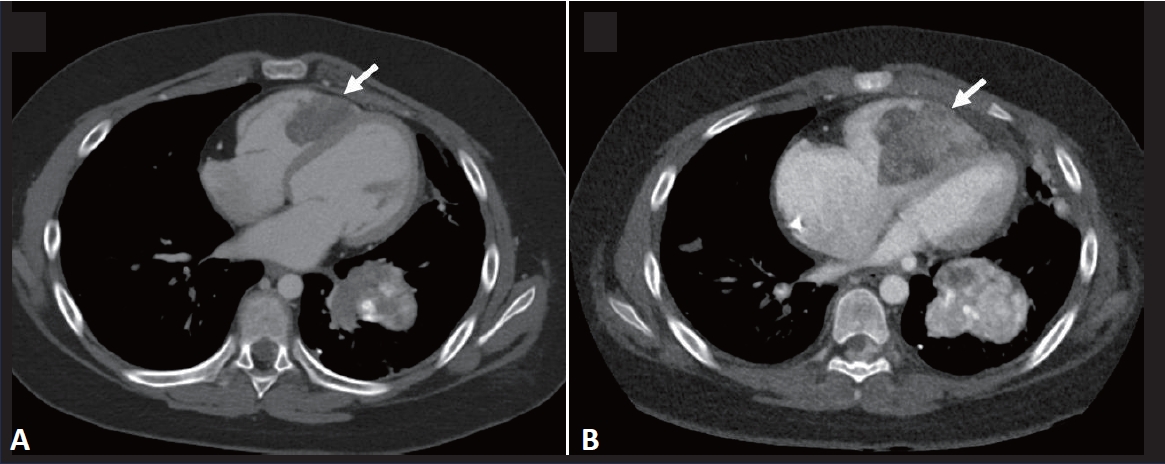
- Right ventricular mass in a 10-year-old girl with osteosarcoma: an unusual case of asymptomatic cardiac metastasis
- Jun Ah Lee, Hyun-Ju Lim, Jong Woong Park, Sang-Hoon Shin, Mi Hyang Kwak
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):725-727. Published online November 26, 2024
-