Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Rheumatology
- Double-negative T cells in pediatric rheumatic diseases
- Dimitri Poddighe, Tilektes Maulenkul, Kuanysh Dossybayeva, Gulsamal Zhubanova, Zaure Mukusheva, Lyudmila Akhmaltdinova
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):632-640. Published online September 12, 2024
-
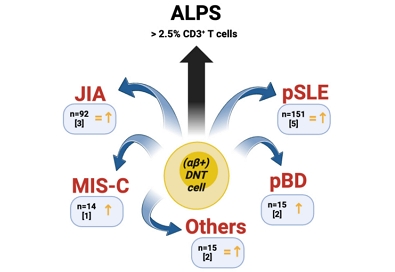
Double-negative T (DNT) cells appear to be increased in several pediatric rheumatic diseases and this finding may be correlated with disease activity to some extent. However, due to significant heterogeneity in several methodological aspects, further investigations in rheumatic children are needed to assess the potential relevance of DNT cells as biomarkers and clarify their immunopathological role.
- Original Article
- Other
- Risk factors and screening timing for developmental dysplasia of the hip in preterm infants
- Ga Won Jeon, Hye Jung Choo, Yong Uk Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):262-268. Published online November 5, 2021
-

Question: When is the best screening timing and what is the risk factor for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) in preterm infants?
Finding: Ultrasonography performed earlier than 38 weeks of postmenstrual age caused unnecessary subsequent ultrasonography. DDH did not occur predominantly on the left side or in breech infants.
Meaning: The screening timing, etiology, and risk factors for DDH in preterm infants are somewhat different from those in term infants.
- Case Report
Candida tropicalis arthritis of the elbow in a patient with Ewing's sarcoma that successfully responded to itraconazole- Seung Youn Kim, Jung Sub Lim, Dong Hwan Kim, Hyeon Jeong Lee, Joong Bum Cho, Jun Ah Lee, Dong Ho Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(9):385-388. Published online September 30, 2011
-
Fungal infections are rarely responsible for arthritis. Few cases of fungal arthritis have been reported, even in immunocompromised hosts susceptible to low-virulence organisms. Herein, the authors report the first case of
Candida tropicalis arthritis in a child with a solid tumor. A 13-year-old boy with Ewing's sarcoma developed arthritis in his elbow during the neutropenic period after chemotherapy. Despite treatment...
- A case of reactive arthritis after
Salmonella enteritis in in a 12-year-old boy - Peter Chun, Young Jin Kim, Young Mi Han, Young Mi Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(7):313-315. Published online July 31, 2011
-
Reactive arthritis comprises a subgroup within infection-associated arthritides in genetically susceptible hosts. Researchers and clinicians recognize two clinical forms of reactive arthritis which occurs after genitourinary tract infection and after gastrointestinal tract infection. Chlamydia infection has been implicated as the most common agent associated with post-venereal reactive arthritis. Studies have proposed Shigella infection,
Salmonella infection, orYersinia infection as the...
- Review Article
- Treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Kwang Nam Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(11):936-941. Published online November 30, 2010
-
The systematic approach to pharmacologic treatment is typically to begin with the safest, simplest, and most conservative measures. It has been realized that the more rapidly inflammation is under control, the less likely it is that there will be permanent sequelae. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the mainstay of initial treatment for inflammation. In addition, the slow-acting antirheumatic drugs (SAARDs)...
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Diagnosis and differential diagnosis
- Ki Hwan Kim, Dong Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(11):931-935. Published online November 30, 2010
-
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is comprised of a heterogeneous group of several disease subtypes that are characterized by the onset of arthritis before the age of 16 years and has symptoms lasting at least 6 weeks. The previous classification of JIA included seven different categories, whereas its current classification was compiled by the International League of the Association for Rheumatology,...
- Pathogenesis and clinical manifestations of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Youn-Soo Hahn, Joong-Gon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(11):921-930. Published online November 30, 2010
-
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) is the most common rheumatic childhood disease; its onset is before 16 years of age and it persists for at least 6 weeks. JRA encompasses a heterogeneous group of diseases that is classified according to 3 major presentations: oligoarthritis, polyarthritis, and systemic onset diseases. These presentations may originate from the same or different causes that involve...
- Case Report
- A case of postoperative nasopharyngeal reflux associated with retropharyngeal lymphangioma in newborn infant
- Ah Reum Kwon, Eun Jung Park, Ki Hwan Kim, Dong Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(2):262-266. Published online February 15, 2010
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is a major proinflammatory cytokine involved in the pathophysiology of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Etanercept is an effective inhibitor of TNF-α and has shown a beneficial effect in patients with JRA. However, the most important cause of concern related to etanercept administration is infection. We report a case of encephalitis in a JRA patient receiving long-term treatment... -
- Review Article
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Dong Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(12):1173-1179. Published online December 15, 2007
-
The diagnosis of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) is based on patient's age at disease onset, symptom duration, gender, and clinical manifestations. JRA is of unknown origin, begins under the age of 16, and persists for a minimum of 6 weeks. JRA is categorized into three principal types, systemic, oligoarticular and polyarticular. Infection, other connective tissue diseases, malignancy, trauma, and immunodeficiency... -
- Original Article
- Clinical observations of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Joo Hoon Lee, Jeong Min Ryu, Young Seo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(4):424-430. Published online April 15, 2006
-
Purpose : Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis(JRA) is one of the most common rheumatic diseases of childhood and is an important cause of short- and long-term disability. The purpose of this study was to determine the disease course and outcome in childhood patients with JRA. Methods : Fifty nine patients with JRA who were diagnosed and treated in the Department of Pediatrics, Asan... -
- Clinical Features of Septic Arthritis in Neonates
- Min Jung Kwak, Su Eun Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(11):1161-1166. Published online November 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Septic arthritis is uncommon in neonates, and the diagnosis of septic arthritis in newborns is difficult because of non-specific laboratory findings and paucity of signs and symptoms. When appropriate treatment is delayed, permanant sequelae are inevitable. We report a retrospective study of 22 neonates who were diagnosed with septic arthritis. Methods : We reviewed 22 patients, who were diagnosed... -
- Effect of Histone H1 on Collagen Induced Arthritis in Mice
- Jae Ho Yang, Kyung Mi Shin, Dong Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(7):779-788. Published online July 15, 2004
-
Objective : Besides the functions of histones in the nucleus of the cells, there is growing evidence that histones have many other extra-cellular or extra-nuclear functions, such as stabilizing axonemal microtubule of sea urchin sperm flagella. This microtule assembly function of the histone is similar to that of taxol, which has an effect of controlling joint inflammation. In this study,... -
- Effect of a Flavon Extracted from Artemisia absinthium on Collagen Induced Arthritis in Mice
- Kyong Min Choi, Dae Hwan Hwang, Kyung Mi Shin, Do-Young Yoon, Dong Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(6):677-684. Published online June 15, 2004
-
Purpose : In this study, a possible suppressive effect of a flavon extracted from Artemisia absinthium on a mouse collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model was investigated. Methods : DBA/1 mice were injected intradermally with emulsified chicken type II collagen. Three weeks after immunization, a flavon was introduced p.o. everyday. Clinical incidences of arthritis and arthritis index were measured. Measurement of anti-collagen antibodies... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Multiple Septic Arthritis by Streptococcus pneumoniae in Kawasaki Disease
- Jae-Hoon Choe, In-Gyu Lee, Kyung-Bae Park, Joon-Soo Park, Young Chang Kim, Hwa-Yong Song, Byung-Heum Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(5):579-582. Published online May 15, 2004
-
In Kawasaki disease, arthritis may occur, generally affecting the hands, knees, ankles, or hips. Operations have not usually been needed. We report a case of Kawasaki Disease with multiple septic arthritis which was caused by S. pneumoniae and which needed athrotomy with drainage for both hips, both knees, and both ankle joints. A two year, ten-month-old girl was admitted to... -
-
- Arthritis in the Subacute Stage of Kawasaki Disease after Responding to Intravenous Immunoglobulin Treatment
- Kyung-Yil Lee, Jin-Hee Oh, Dea-Kyun Koh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(11):1124-1127. Published online November 15, 2003
-
We evaluated the clinical and laboratory characteristics of five children with Kawasaki disease who had showed arthritis after responding to intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) treatment. Age distribution was between 13 months and six years of age(mean 3.2?.6 years). There were two males and three females. Arthritis occurred when acute symptoms were subsiding, with the average onset on day 5.8?.8 after final IVIG... -
- Original Article
- Etiologic Agents and Clinical Features of Acute Pyogenic Osteoarthritis in Children
- Young Ho Kwak, Su Eun Park, Jung Youn Hong, He Sun Jung, Jin Young Park, Jung Hwan Choi, Hoan Jong Lee, In Ho Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(4):506-513. Published online April 15, 2000
-
Purpose : Though acute pyogenic infections of musculoskeletal system are infrequent in children, delayed diagnosis or inadequate management may cause serious chronic sequelae. We analysed 40 cases of children who were affected by acute septic osteomyelitis and/or septic arthritis to find etiologic agents and to establish proper initial antimicrobial therapy. Methods : Medical records of 40 cases of microbiologically confirmed acute... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Septic Arthritis due to Haemophilus influenzae associated with Atypical Kawasaki Disease
- Sun Mi Yang, Jun Yun, Hea Kyoung Lee, Young Hee Yu, Hyun Sook Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(10):1441-1445. Published online October 15, 1999
-
We report a case of septic arthritis due to H. influenzae associated with atypical Kawasaki disease. A 2-year-old boy was admitted to our orthopedic department due to limping gait of the right leg. CT finding of right hip joint revealed fluid collection. He was diagnosed as transient synovitis and septic arthritis. He was treated with antibiotics, but no incision nor... -
- Original Article
- The Effect of Acanthopanax koreanum Extract on the Induction of Collagen Induced Arthritis for DBA/1J Mice
- Dong Soo Kim, Chang Ho Song, Soo Kon Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(2):247-254. Published online February 15, 1998
-
Purpose : It is well known that the Acanthopanax koreanum extract has an anti-inflammatory action without any adverse effects reported. We conducted this study to see whether the Acanthopanax koreanum extract has a preventive effect on the development of collagen induced arthritis in DBA/1J mice. Methods : Three groups of BDA/1J mice were immunized by intradermal injection of 2mg/kg bovine type... -
- Case Report
- A Fatal Case of Systemic Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis with Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
- Eun Young Park, Sung Hee Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(1):129-134. Published online January 15, 1998
-
Disseminated intravascular coagulation(DIC) occurs rarely but can cause death in patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis(JRA), especially in the systemic type. The reports of DIC complicating JRA have increased recently. We experienced a 13 - year - old female patient with systemic JRA who died of DIC. The patient had been managed with aspirin, steroid, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug for 7 years,... -
- Original Article
- The Clinical Aspects of Septic Arthritis in Children
- Milim Koo, Dongsoo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(12):1731-1744. Published online December 15, 1997
-
Purpose : Acute septic arthritis in infancy and childhood is uncommon. Delay of diagnosis and inappropriate treatment of septic arthritis results in permanent physical sequelae. We studied the initial treatment, clinical manifestations, involved sites, and etiologic organisms of septic arthritis. Methods : We reviewed 74 patients who were diagnosed septic arthritis in Departments of Pediatrics and Orthopedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine from July 1986... -
- A Clinical Study on Pauciarticular Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis(JRA)
- Youn Soon Hahn, Jeoong Gon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1995;38(3):386-396. Published online March 15, 1995
-
Purpose : The purpose of this study was to analyse clinical and laboratory patterns in patients in Korea with juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis(JRA), pauciarticular type and to know the characteristics of pauciarticular JRA in Korea. Methods : Twenty-three cases of pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis(JRA) who were diagnosed in the department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University hospital (from june 1988 to May 1994)... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Poststreptococcal Reactive Polyarthralgia
- Sung Ho Cha, Byong Soo Cho, Taekyu Hame
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(11):1635-1637. Published online November 15, 1993
-
Poststreptococcal reactive arthritis/arthralgia is characterized as an evidence of group A beta hemolytic streptococcal infection and does not fulfill the modified Jones criteria for a diagnosis of acute rheumatic fever. We had used to meet the patients with incomplete acute rheumatic fever who had more than 3 items of minor Jones criteria, or arthralgia or arthritis with one or two... -
- Original Article
- Clinical Significance of Rheumatoid Factor in Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Ki Joong Kim, Bo Young Yun, Joong Gon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(5):639-645. Published online May 15, 1992
-
Rheumatoid factor is a commonly used laboratory test by clinicians to assess the children with possible juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. To assess its diagnositc value and clinical significance we reviewed the case histories of the patients in whom latex agglutinating rheumatoid factor was tested during November 1988 to April 1991 at Seoul National University Children's Hospital. There were 61 patients with... -
- Clinical observation on juvenile theumatoid arthritis.
- Sung Sub Shim, Chan Yung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(8):1123-1131. Published online August 31, 1991
-
The authors analyzed the clinical features, and the therapeutic responses in 29 patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis who were diagnosed and followed at Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University Hospital from 1980. 1 to 1990. 6. The following results were obtained 1) Of the total 29 patients, 12cases (41.4%) were pauciarticular type II and 7cases (24.2%) were polyarticular RF(—) type. Seventeen cases (58.7%) were 8-11 yrs... -
- Acute pyogenic arthritis of hip in neonate and infant.
- Mi Jung Kim, Young Ah Lee, Young Pyo Chang, Hoan Jong Lee, Jung Hwan Choi, Chong Ku Yun, Hak Jin Min, In Ho Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(2):197-205. Published online February 28, 1991
-
Acute pyogenic arthritis of hip is a serious infection that can lead to truly devastating complica- tions especially in neonatal period and infancy. Clinical survey on twelve neonates and infants (14 hip joints) with acute pyogenic arthritis of hip who were admitted to the Departments of Pediatrics and Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital from Jan. 1980 to Dec. 1989 were done. The results... -
- A Case of Systemic-Onset Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis with Multiple Complications.
- Jong Deok Kim, Dong Joo Na, Jin Han Kang, Kyong Su Lee, Ki Yeal Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1988;31(7):948-952. Published online July 31, 1988
-
We recently experienced a case of systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis with protracted and variable clinical course with multiple complications and sequeles including pericarditis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, severe ankylosis and bony fusion of neural arches of C2 through C6 vertebrae, and multiple chronic arthritis causing joint deformities at relatively young age of nine. A brief review of related literatures is also presented. -
- Clinical Observation on Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis.
- Won Soon Park, Kwang Wook Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1986;29(2):152-162. Published online February 28, 1986
-
A clinical observation on 70 patients of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis who were admitted to S.N.U.H. during the 6 year period from Jan. 1979 to Dec. 1984, was assessed. The results were as follows; 1) On type classification, systemic type(37.2%) was most frequent, followed by RF negative polyarticular type, pauciarticular type H, RF positive polyarticular type and pauciarticular type I in order of frequency. The... -
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











