- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Recent advances in epigenetic mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment of pediatric gastrointestinal allergic disorders
- Eell Ryoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):250-251. Published online May 19, 2023
-

· Epigenetic mechanisms are involved in rapidly increasing food allergy.
· There is still no definitive way to diagnose food allergy.
· Early introduction of peanuts, eggs, and cow’s milk reduces food allergy incidence.
· Administration of probiotics such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Bifidobacterium bifidum can partially reduce the occurrence of allergic symptoms.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Update on eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease beyond eosinophilic esophagitis in children
- Hye Ran Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):233-239. Published online January 3, 2023
-

· Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease (EGID) is uncommon, with a prevalence of 1–30/100,000 in the general population; however, it is increasing worldwide.
· The diagnosis of EGID is based on histopathological findings of endoscopic mucosal biopsy in which tissue eosinophils are counted in each gastrointestinal tract segment of patients with chronic or recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms.
· Individualized treatment strategies, including adequate dietary and pharmacological therapy, may help improve outcomes of children with EGID.
- Role of social media use in onset of functional gastrointestinal disorders in children
- Mauro Cinquetti, Vanessa Dargenio, Michele Fingerle, Carolina Marchiotto, Marco Biasin, Massimo Pettoello Mantovani, Flavia Indrio
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):226-232. Published online December 21, 2022
-
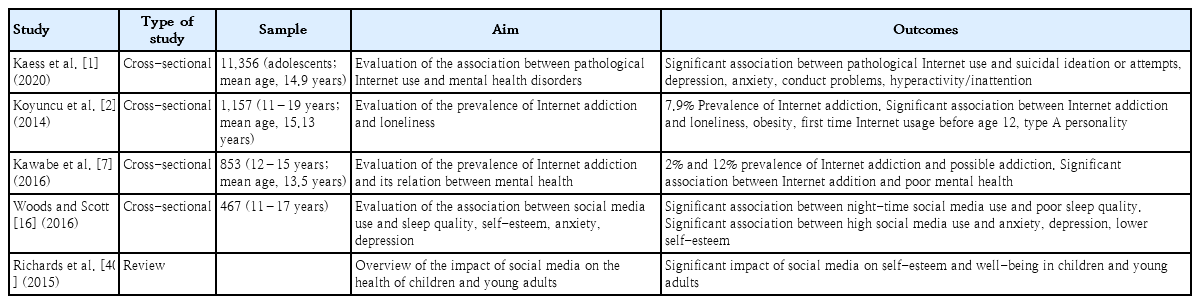
· Social media use can cause adverse health outcomes, including gastrointestinal disorders, in children and adolescents.
· Recent findings have shown a high prevalence of social media use and decreased well-being in patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders.
· The biopsychosocial nature of functional gastrointestinal disorders and the clear influence of social media on the psychosocial lives of children suggests the likely involvement of social media in their development.
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Is there a link between social media usage and functional gastrointestinal disorders in children?
- Hae Jeong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):169-170. Published online March 23, 2023
-
Social media use has potential benefits and risks, including links to adverse health problems in children such as functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs). Screen time control, emotional support, and parental guidance can help children navigate social media safely and reduce the risk of developing FGIDs.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- High-resolution esophageal manometry in children
- Yogesh Waikar
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):155-160. Published online October 17, 2022
-

High-resolution esophageal manometry can be safely performed in children where recurrent vomiting and persistent dysphagia is the working diagnosis after excluding nonluminal and structural obstructive pathologies using pediatric upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Normal manometry values are available. Clinical picture, biochemical tests, radiological interpretation, and endoscopic findings with manometry completes the analysis of patients with recurrent vomiting and dysphagia.
- Liver fibrosis in children: a comprehensive review of mechanisms, diagnosis, and therapy
- Elif Ozdogan, Cigdem Arikan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):110-124. Published online December 19, 2022
-
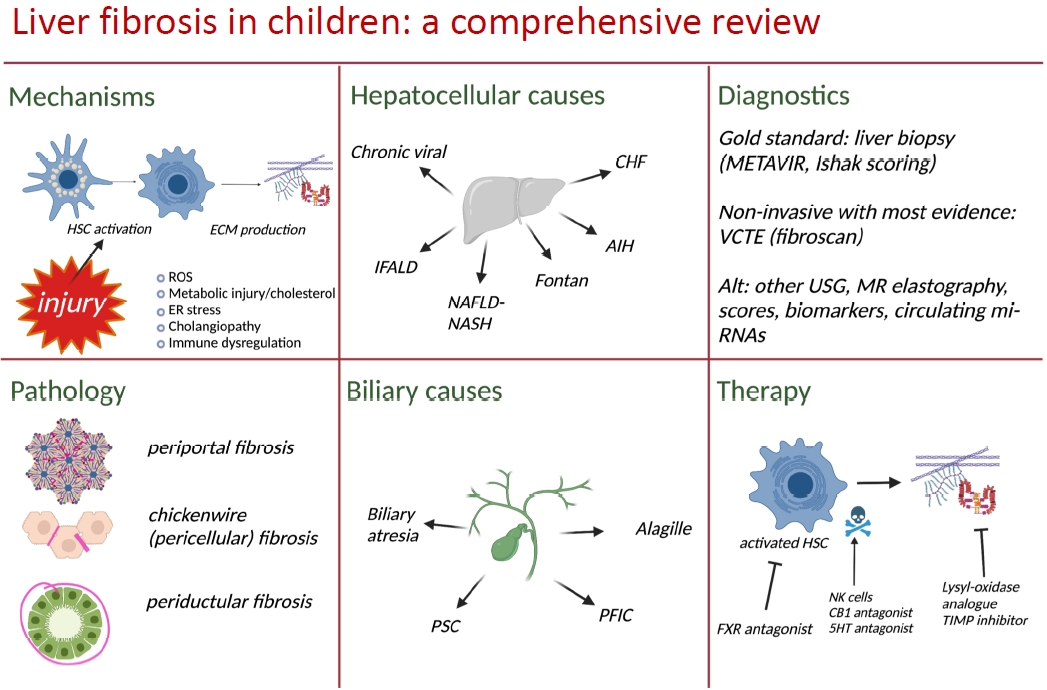
· Chronic liver diseases in children are heterogenous but converge in the common pathway of fibrosis.
· Much of the literature on mechanisms of fibrogenesis focus on adults but pediatric physiology has documented differences.
· Understanding of these distinctions are necessary to define, treat, and prevent fibrosis.
· Current management of liver fibrosis relies heavily on liver biopsy. Multiple tools have shown high diagnostic performance in pediatric and adult populations. Large, multicenter studies are needed for validation.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Association between maternal weight gain during pregnancy and child’s body mass index at preschool age
- Jeewon Shin, Yoowon Kwon, Ju Hee Kim, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):76-81. Published online November 30, 2022
-
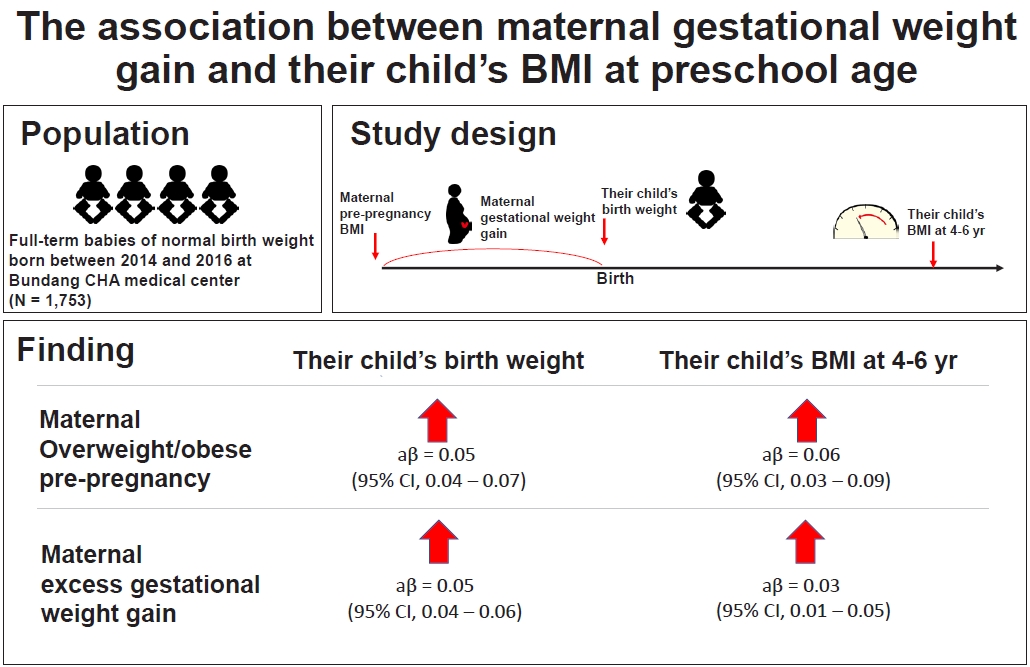
Question: What are the risk factors of newborn birth weight? Does gestational weight gain and prepregnancy body mass index affect childhood weight?
Finding: Excess maternal weight gain increases the risk of overweight/obesity, newborn birth weight, and child body mass index at 4–6 years.
Meaning: Maternal weight control before and during pregnancy should be well controlled.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Current diagnosis and image-guided reduction for intussusception in children
- Jisun Hwang, Hee Mang Yoon, Pyeong Hwa Kim, Ah Young Jung, Jin Seong Lee, Young Ah Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):12-21. Published online July 4, 2022
-
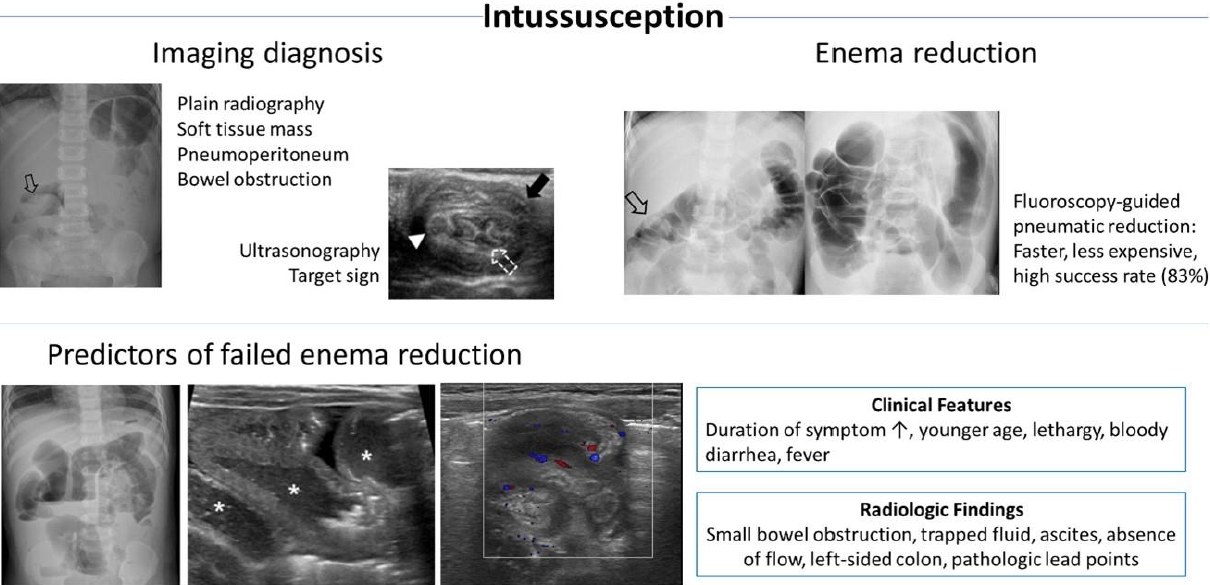
· Intussusception, the most common cause of small bowel obstruction in young children, has an overall incidence in Korea of 28.3 cases per 100,000 person-years.
· Its cause is idiopathic inmost cases, although viral or bacterial gastroenteritis has beenpostulated as a cause. Approximately 4% of children have pathological lead points for intussusception, and Meckel’s diverticulum is the most common cause.
· Intussusception in preterm infants is extremely rare. Older children (>5 years of age) are at increased risk of pathological lead points.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Ability of polymicrobial probiotic and mono-strain probiotic to reduce functional abdominal pain in children: a randomized clinical trial
- Seyed Sajad Jafari, Seyed Mojtaba Hashemi, Bahman Sadeghi, Amir Almasi-Hashiani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):589-594. Published online October 31, 2022
-
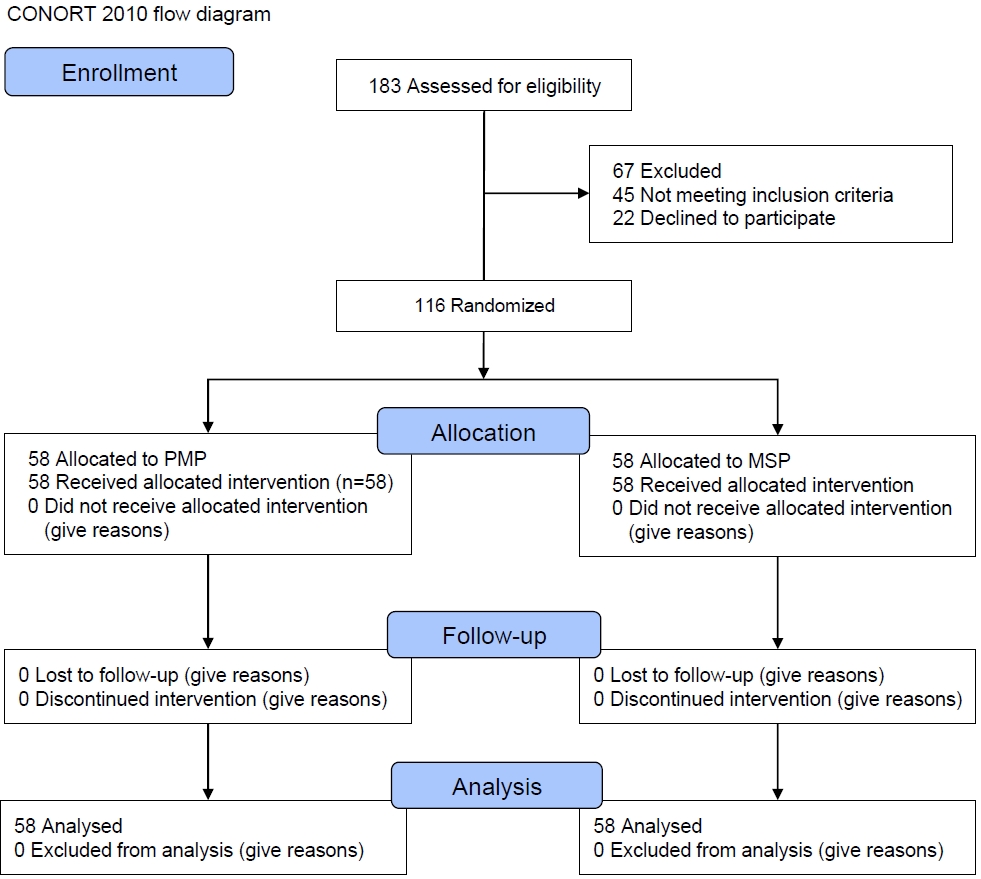
· This study compared the ability of 2 probiotics to reduce and improve functional abdominal pain (FAP) in children.
· In the polymicrobial probiotic (PMP) group, 10.34% of children reported no pain; in the mono-strain probiotic (MSP) group, all patients reported low-degree pain. The mean pain score decreased significantly over time in both groups.
· The use of both PMP and MSP is recommended to reduce pain in patients with FAP.
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Ability of probiotics to reduce functional abdominal pain in children
- Ji Sook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):585-586. Published online October 6, 2022
-
· The ability of probiotics to relieve pain caused by functional abdominal pain disorders (FAPD) in children is unclear.
· Lactobacillus reuteri may effectively reduce pain caused by childhood FAPD.
· Since the routine use of probiotics cannot be recommended due to a lack of clinical evidence, research into probiotic mixtures or symbiotics remains necessary.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Probiotics added to maternal nutrition affect ınfantile colic symptoms and fecal microbiota profile: a single-blind randomized controlled study
- Aysu Yıldız Karaahmet, Gülümser Dolgun, Metehan Özen
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):547-554. Published online September 23, 2022
-

Question: Do probiotics added to maternal nutrition affect infantile colic symptoms and intestinal microbiota?
Finding: Infants whose mothers ingested probiotics demonstrated decreased crying frequency and intensity and significantly increased bacterial diversity in the stools. The bacterial variety was substantially affected by the added probiotic product.
Meaning: The addition of probiotics to maternal nutrition in early infancy could play an important role in preventing infantile colic.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Factors influencing development of the infant microbiota: from prenatal period to early infancy
- Sujin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):439-447. Published online December 23, 2021
-
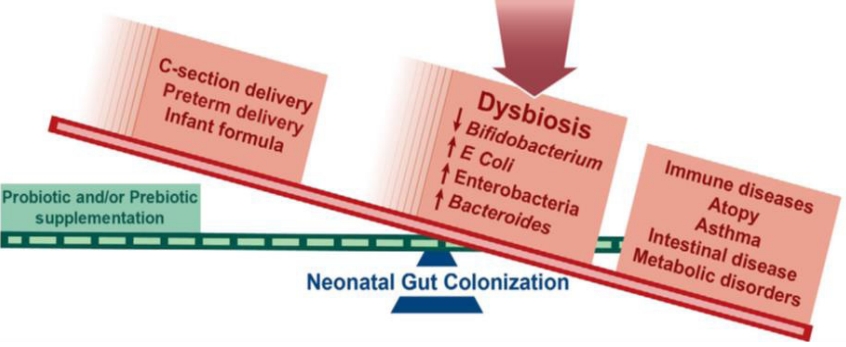
∙ Microbial colonization primarily occurs after birth but there may be some colonization in utero, although this remains highly controversial.
∙ Maternal factors during pregnancy affect the infant microbiota: diet, weight, gestational weight gain, and antibiotic usage.
∙ Microbes are passed from mother-to-infant during and after birth. Delivery mode, breastfeeding, early life antibiotic, and proton pump inhibitor treatment have the largest effects on microbial composition in early life.
∙ The early life gut microbiome plays an important role in the development of the immune system and metabolism.
- Clinical importance of immunonutrition in infants: a review of the recent literature
- Ji Sook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):337-343. Published online February 17, 2022
-

Nutrients are important in the developing immune system. Human milk supplies diverse bioactives to prevent acute infection or chronic inflammation. Immunoglobulins, lactoferrin, and glutamine in human milk decrease gastrointestinal and respiratory infection. Human milk oligosaccharides promote the growth of intestinal microbiota, the gut barrier, and antimicrobial or antiviral activity. Micronutrients act as anti-inflammatory immunonutrients, too. However, the toxicity of some nutrients from an overdose should be considered.
- Upper gastrointestinal tract involvement of Crohn disease: clinical implications in children and adolescents
- Eun Sil Kim, Mi Jin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):21-28. Published online September 10, 2021
-
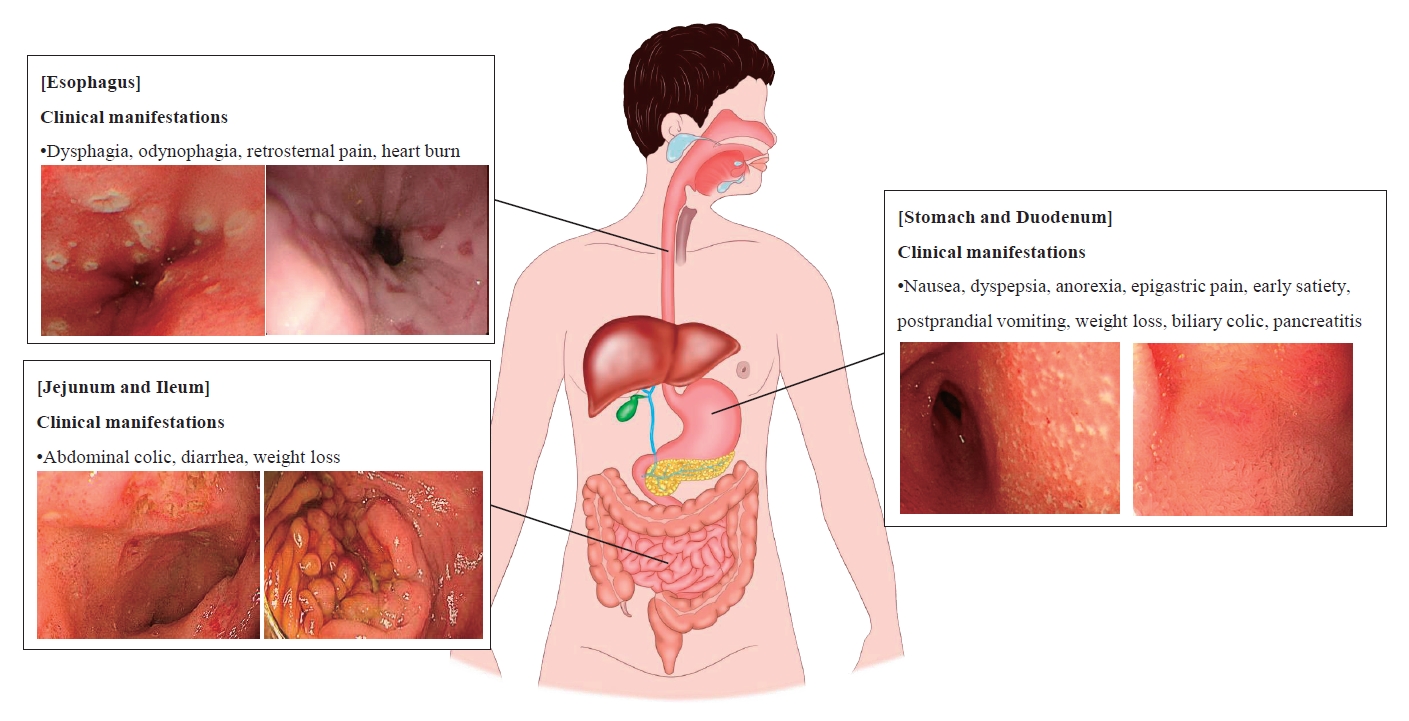
· Clinical manifestations of upper gastrointestinal (UGI) tract involvement in Crohn's disease (CD) are common but often clinically underestimated.
· Diagnosing CD by confirming inflammation of the UGI tract histologically is challenging because macroscopic and microscopic findings overlap with those of other diseases.
· Ongoing efforts are needed to enable a standardized assessment of UGI CD in the future.
- Letter to the Editor
- Gastroenterology
- Functional gastrointestinal disorders and smartphone use in adolescents
- Mauro Cinquetti, Marco Biasin, Marco Ventimiglia, Linda Balanzoni, Denise Signorelli, Angelo Pietrobelli
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(9):494-496. Published online November 9, 2020
-
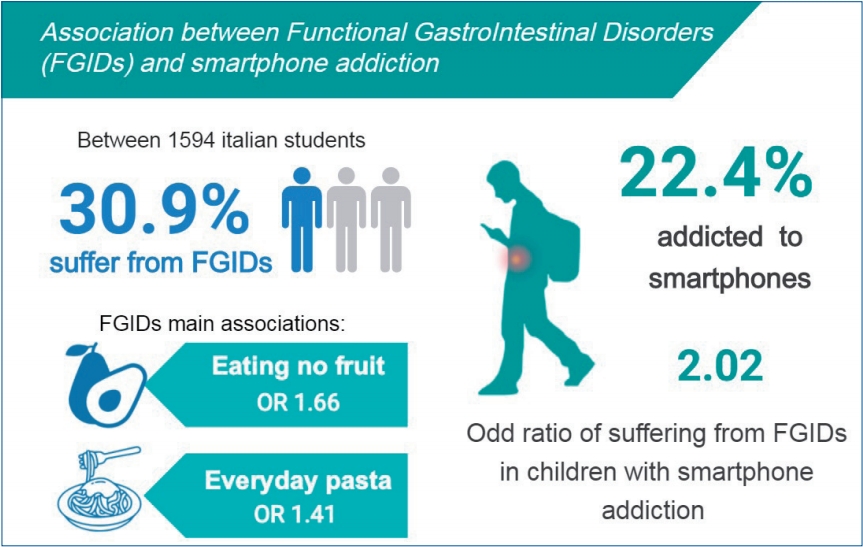
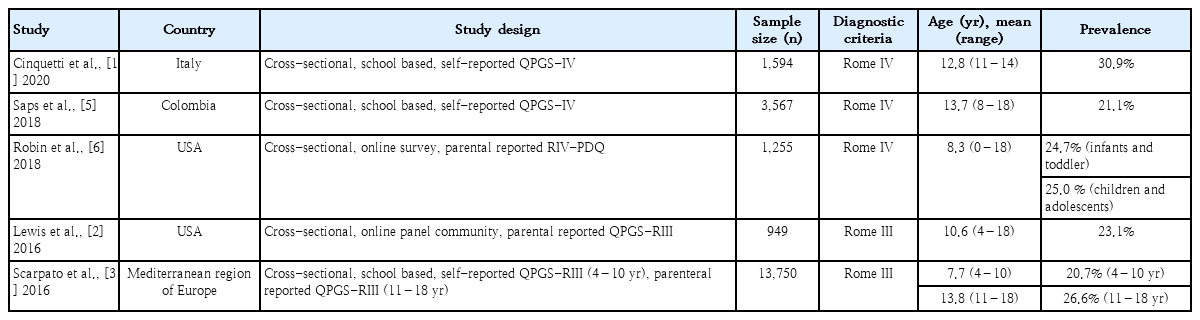
Question: Are functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) common in Italy? If so, what are the associated risk factors?
Finding: In this cross-sectional study of 1,594 adolescents, the prevalence of FGIDs was 30.9% and was mainly associated with smartphone addiction.
Meaning: Smartphone use and dietary habits should be monitored in children with FGIDs.
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Does smartphone overuse affect functional gastrointestinal disorders?
- Jee Hyun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(9):471-472. Published online December 28, 2020
-
Functional gastrointestinal disorders are common disorders characterized by persistent and recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms. Pathophysiological mechanisms have been suggested, including intestinal microbiota, altered intestinal permeability and motility, dietary effects, sensory abnormalities, and brain-gut dysregulation. Lifestyle factors such as diet, sleep, affect, and physical activity might function as moderators.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Celiac disease in children: Increasing prevalence and changing clinical presentations
- Hasan M. Isa, Eman Farid, Jaafar J. Makhlooq, Afaf M. Mohamed, Jumana G. Al-Arayedh, Fawzeya A. Alahmed, Shima Medani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(6):301-309. Published online October 17, 2020
-
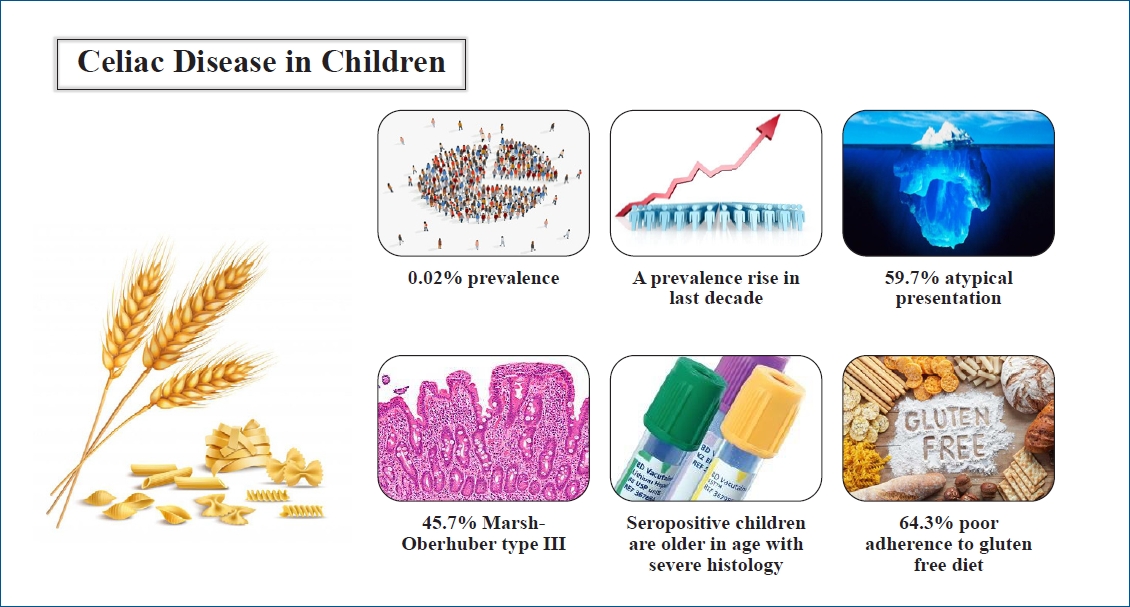
Question: What are the prevalence and clinical characteristics of celiac disease (CD) in children in Bahrain?
Finding: We found a significant increase in CD prevalence over the last decade (P=0.0001). A male predominance was noted. Atypical presentations were common. Most patients had poor adherence to a gluten-free diet.
Meaning: CD is an underdiagnosed condition. Atypical symptoms should be considered to prevent missing patients with CD.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Causes of acute gastroenteritis in Korean children between 2004 and 2019
- Eell Ryoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(6):260-268. Published online September 18, 2020
-
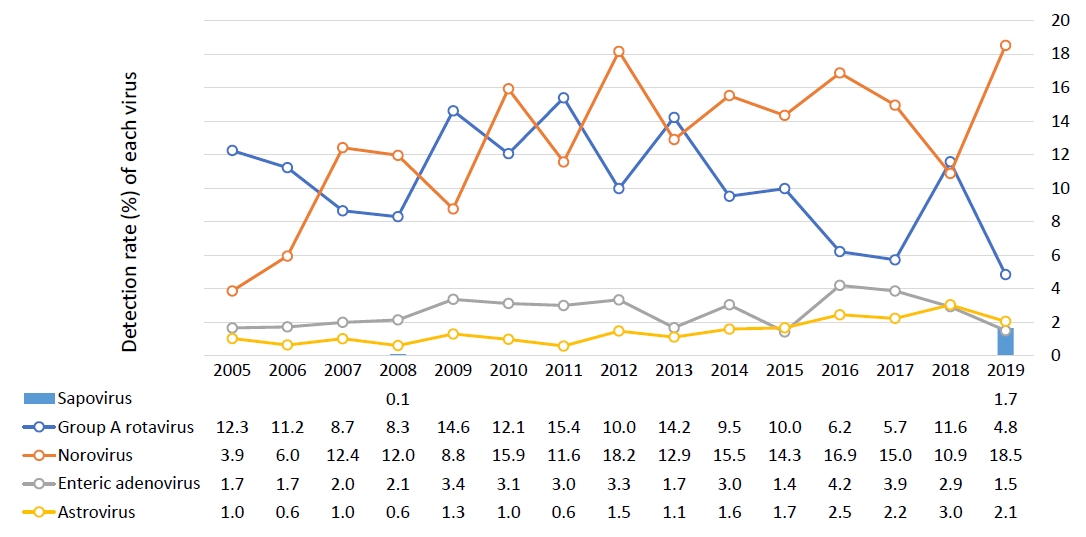
· Norovirus is the most common virus in Korean children with acute gastroenteritis.
· Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. are the most common cause of bacterial gastroenteritis in Korean children, with a detection rate of 3%–20%.
· Uncommon bacterial and parasitic gastroenteritis require attention because of increasing international exchange and overseas travel.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Value of the International Classification of Diseases code for identifying children with biliary atresia
- Pornthep Tanpowpong, Chatmanee Lertudomphonwanit, Pornpimon Phuapradit, Suporn Treepongkaruna
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(2):80-85. Published online August 24, 2020
-
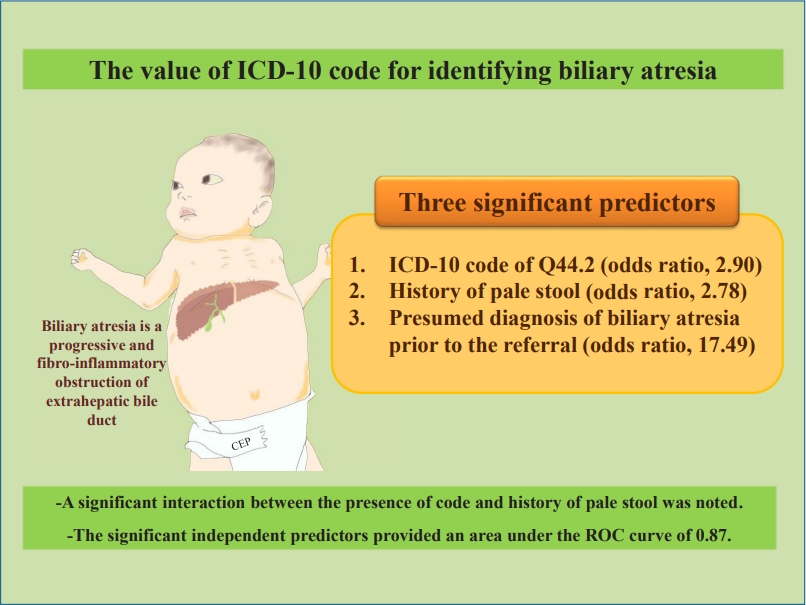
Question: What is the value of the diagnostic code in identifying cases of biliary atresia in a large administrative database?
Finding: The diagnostic code’s accuracy and sensitivity are acceptable for identifying algorithm-defined cases. A history of pale stool and a presumed diagnosis of biliary atresia prior to referral added value.
Meaning: The addition of clinical data to the diagnostic code significantly increased the diagnostic yield.
- Noninvasive markers for esophageal varices in children with cirrhosis
- Parisa Rahmani, Fatemeh Farahmand, Ghobad Heidari, Azadeh Sayarifard
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):31-36. Published online July 21, 2020
-
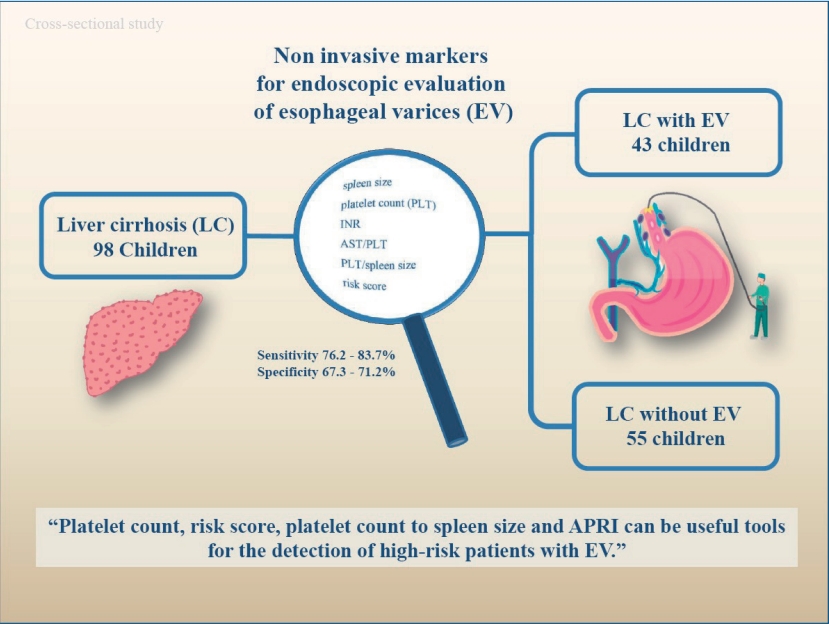
Question: Can noninvasive biomarkers identify esophageal varices among children with esophageal cirrhosis?
Finding: The spleen size, platelet count, international normalized ratio, aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index, platelet count to spleen size ratio, and risk score differed significantly between the patients with and those without esophageal varices.
Meaning: These biological parameters can predict esophageal varices among pediatric patients and indicate the need for esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Changing prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in children and adolescents
- Ji Sook Park, Jin Su Jun, Ji-Hyun Seo, Hee-Shang Youn, Kwang-Ho Rhee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):21-25. Published online July 15, 2020
-
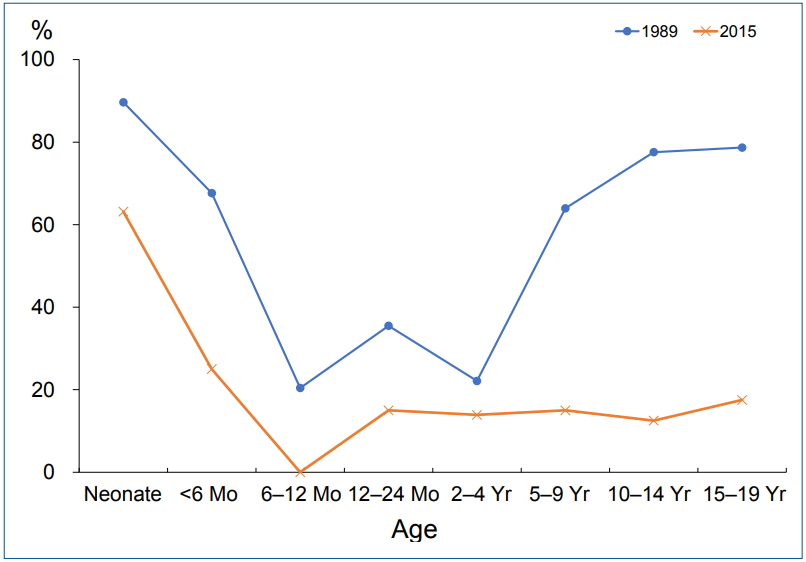
Although Helicobacter pylori infection rate in children is unclear due to diversity and limitation of diagnostic tests unlike in adults, investigation the childhood prevalence is important for predicting H. pylori-related diseases in the future.
H. pylori infection occurred in early childhood, and declined during 30 years in our study.
Change in risk factors of H. pylori transmission and consensus for eradication therapy in children might further reduce the infection rate.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Evaluating the effects of probiotics in pediatrics with recurrent abdominal pain
- Parisa Rahmani, Azin Ghouran-orimi, Farzaneh Motamed, Alireza Moradzadeh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):485-490. Published online July 21, 2020
-
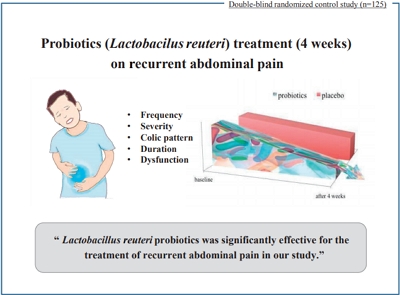
Question: ecurrent abdominal pain (RAP) is a chief complaint among pediatrics and is associated with reduced quality of life, for both parent and child, and economic burden. Does probiotics reduce the frequency of RAP among children?
Finding: This study reported the effects of Lactobacillus reuteri probiotics among children with RAP as a result of multiple etiologies.
Meaning: The administration of probiotic supplements is significantly associated with pain relief among RAP children presented with functional abdominal pain, irritable bowel syndrome, and functional dyspepsia.
- Acquired noncaustic esophageal strictures in children
- Elif Sag, Aysenur Bahadir, Mustafa Imamoglu, Sefa Sag, Gokce Pinar Reis, Erol Erduran, Murat Cakir
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):447-450. Published online October 15, 2020
-
Question: Which clinical findings suggest esophageal structure in children with dysphagia?
Finding: The presence of solid dysphagia, malnutrition, and a comorbid condition is suggestive of esophageal stricture in children with dysphagia.
Meaning: Patients with findings suggestive of noncaustic esophageal stricture should receive early referral to pediatric gastroenterology units.
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Dietary role in the development and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease
- Jae Young Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):355-356. Published online July 13, 2020
-

Although the precise pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is unclear, dietary factors seem to play a significant role. Dietary modifications including enteral nutrition and the Crohn disease exclusion, specific carbohydrate, and anti-inflammatory diets show a potential ability to downregulate gut inflammation. These nutritional interventions have various degree of efficacies with limited side effects profile for treating pediatric IBD, but data from randomized prospective studies are lacking, and further studies are warranted.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Increasing incidence of inflammatory bowel disease in children and adolescents: significance of environmental factors
- Sowon Park, Yunkoo Kang, Hong Koh, Seung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):337-344. Published online December 6, 2019
-
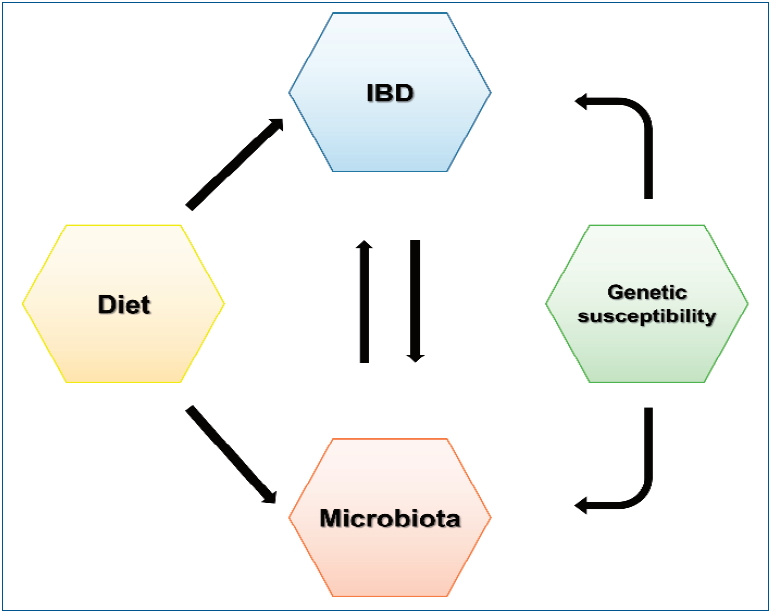
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic relapsing immune-mediated disease of the intestinal tract. Although its prevalence is reportedly lower in Asia than in Western countries, the rapid increase in the incidence of IBD has drawn attention to its etiology, including genetic susceptibility and environmental factors. Specifically, recent studies concerning dietary treatments and intestinal microbiota suggest that these factors may...
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Management of perianal abscess and fistula-in-ano in infants and children
- Jinyoung Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):261-262. Published online March 23, 2020
-
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Thyroid disturbances in children treated with combined pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C
- Yasser K. Rashed, Fatma A. Khalaf, Sobhy E. Kotb
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(2):52-55. Published online September 27, 2019
-

Background: Immunomodulatory properties of interferon (IFN) have been documented. It may induce autoimmune diseases such as autoimmune thyroiditis with hypo- or hyperthyroidism. In addition, it may impair thyroid hormone synthesis through affecting iodide organification in thyroid gland.
Purpose: The aim of this study was to describe thyroid function tests disturbances in children with chronic hepatitis C (CHC) receiving pegylated interferon-alpha (PEG...
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Strategies for treating and managing chronic hepatitis C in children in the direct-acting antiviral era
- Suk-Jin Hong, Byung-Ho Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(2):46-47. Published online February 6, 2020
-

- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Association between Body Mass Index and Hepatitis B antibody seropositivity in children
- Yoowon Kwon, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(11):416-421. Published online August 12, 2019
-
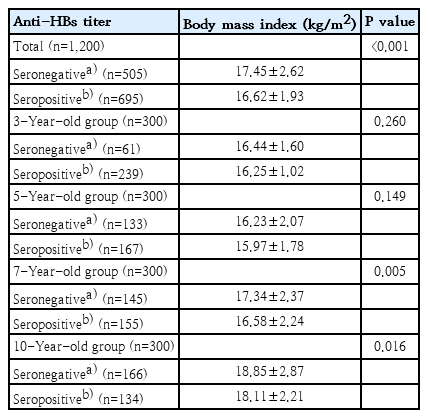
Background: The seropositivity rate of hepatitis B surface antigen (anti-HBs) antibodies is known to be ≥95% after hepatitis B virus vaccination during infancy. However, a low level or absence of anti-HBs in healthy children is discovered in many cases. Recent studies in adults reported that a reduced anti-HBs production rate is related to obesity.
Purpose: To investigate whether body mass index...
- Influence of proton pump inhibitor therapy on intestinal inflammation assessed by fecal calprotectin in pediatric patients
- Su Yeong Kim, Na Mi Lee, Sin Weon Yun, Soo Ahn Chae, In Seok Lim, Eung Sang Choi, Dae Yong Yi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):400-404. Published online July 3, 2019
-
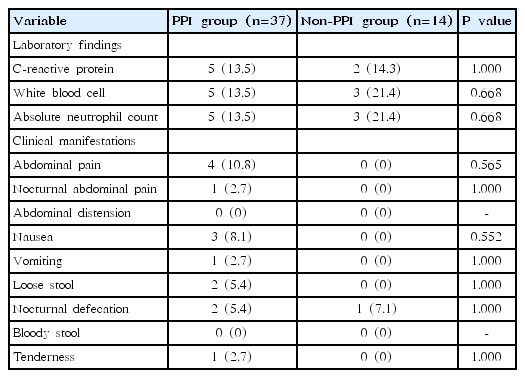
Background: An increase in the numbers of patients with gastrointestinal symptoms has recently been observed.
Purpose: To investigate the effects of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy on intestinal inflammation in children and adolescents as confirmed by clinical manifestations and objectively assessed by fecal calprotectin (FC) level measurement. Methods: Consecutive children (aged 3–18 years) who presented with gastrointestinal symptoms and were treated with...













