Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- TOPICS
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Topics
-
- Adolescence Medicine (4)
- Allergy (64)
- Cardiology (81)
- Critical Care Medicine (16)
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine (24)
- Emergency Medicine (5)
- Endocrinology (65)
- Gastroenterology (77)
- General Pediatrics (62)
- Genetics and Metabolism (27)
- Hematology (20)
- Immunology (16)
- Infection (82)
- Neonatology (Perinatology) (127)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary) (55)
- Neurology (98)
- Nutrition (33)
- Oncology (19)
- Neurobehavior (12)
- Pulmonology (35)
- Rheumatology (4)
- Other (44)
- Case Report
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- De novo mutations in COL4A5 identified by whole exome sequencing in 2 girls with Alport syndrome in Korea
- Kyoung Hee Han, Jong Eun Park, Chang-Seok Ki
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(5):193-197. Published online November 26, 2018
-
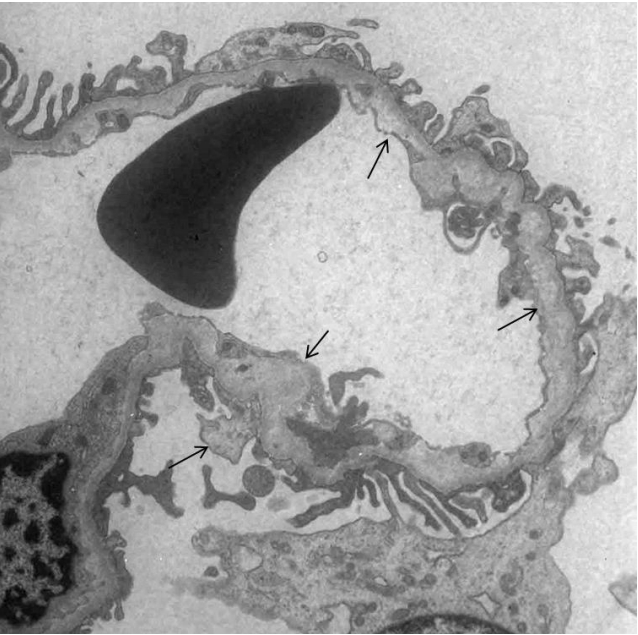
Alport syndrome (ATS) is an inherited glomerular disease caused by mutations in one of the type IV collagen novel chains (α3, α4, and α5). ATS is characterized by persistent microscopic hematuria that starts during infancy, eventually leading to either progressive nephritis or end-stage renal disease. There are 3 known genetic forms of ATS, namely X-linked ATS, autosomal recessive ATS, and...
- Editorial
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Genetic diagnosis of Alport syndrome
- Hae Il Cheong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(5):164-165. Published online January 3, 2019
-
- Original Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Changes in the thyroid hormone profiles in children with nephrotic syndrome
- Sun Hee Jung, Jeong Eun Lee, Woo Yeong Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(3):85-89. Published online October 4, 2018
-
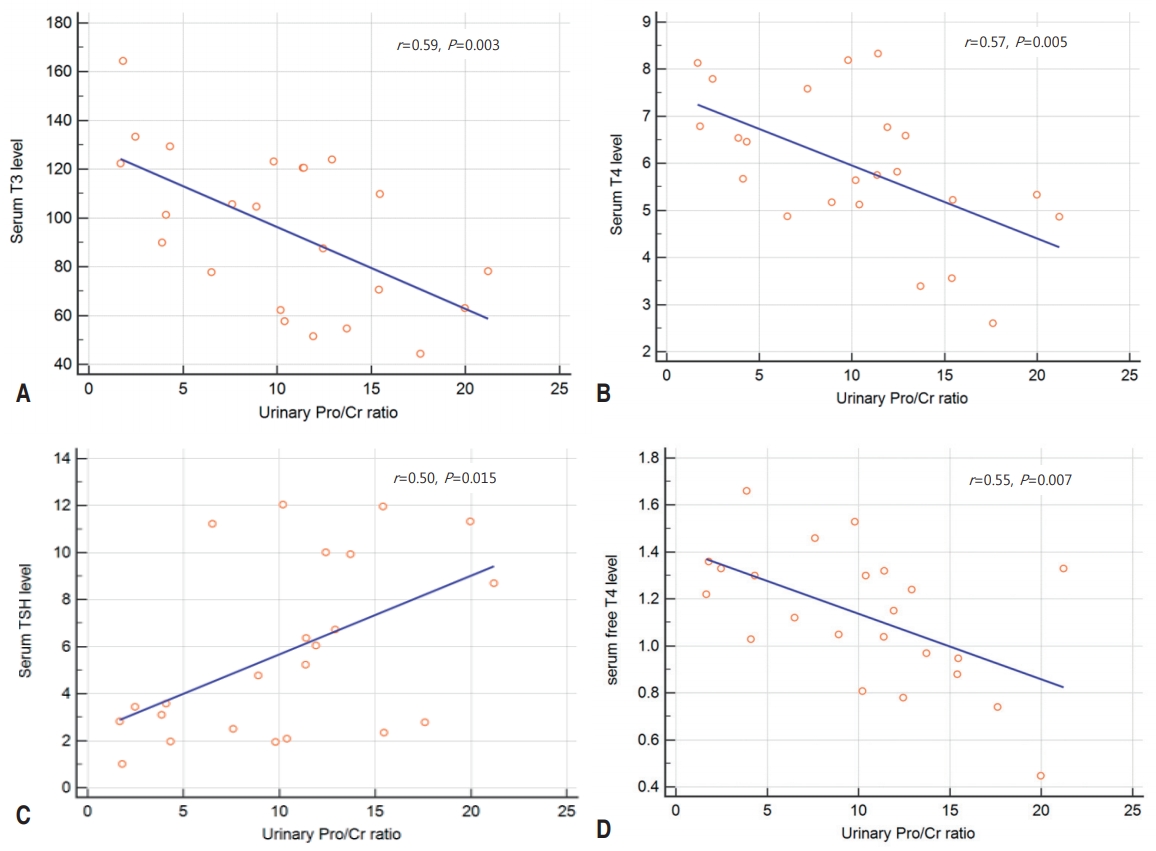
Purpose: We compared thyroid hormone profiles in children with nephrotic syndrome (NS) during the nephrotic phase and after remission. Methods: This study included 31 pediatric NS patients. The thyroid hormone profiles included serum levels of triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and free T4. Results: Of the 31 patients, 16 (51.6%) showed abnormal thyroid hormone profiles: 6 had overt hypothyroidism, 8...
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Renal replacement therapy in neonates with an inborn error of metabolism
- Heeyeon Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(2):43-47. Published online November 7, 2018
-
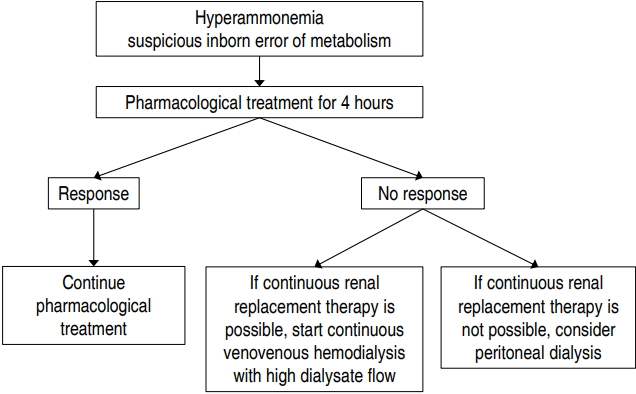
Hyperammonemia can be caused by several genetic inborn errors of metabolism including urea cycle defects, organic acidemias, fatty acid oxidation defects, and certain disorders of amino acid metabolism. High levels of ammonia are extremely neurotoxic, leading to astrocyte swelling, brain edema, coma, severe disability, and even death. Thus, emergency treatment for hyperammonemia must be initiated before a precise diagnosis is...
- Acute kidney injury and continuous renal replacement therapy in children; what pediatricians need to know
- Myung Hyun Cho, Hee Gyung Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(11):339-347. Published online October 23, 2018
-
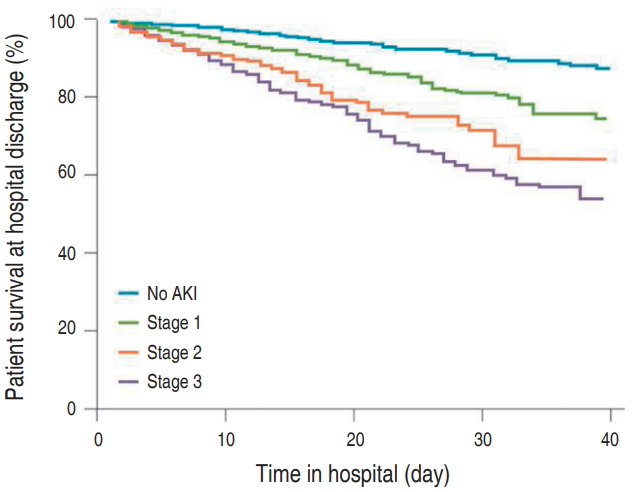
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is characterized by abrupt deterioration of renal function, and its diagnosis relies on creatinine measurements and urine output. AKI is associated with higher morbidity and mortality, and is a risk factor for development of chronic kidney disease. There is no proven medication for AKI. Therefore, prevention and early detection are important. Physicians should be aware of...
- Original Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Renal involvement in children and adolescents with inflammatory bowel disease
- Hea Min Jang, Hee Sun Baek, Jung-Eun Kim, Ju Young Kim, Yeon Hee Lee, Hee Yeon Cho, Yon Ho Choe, Ben Kang, Byung-Ho Choe, Bong Seok Choi, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(10):327-331. Published online September 12, 2018
-

Purpose: The incidence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is rapidly increasing, and several reports have described the renal complications of IBD. We sought to evaluate the clinical manifestations of renal complications in children with IBD in order to enable early detection and prompt treatment of the complications. Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 456 children and adolescents aged <20...
- Erratum
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Erratum: Pediatric kidney transplantation is different from adult kidney transplantation
- Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(8):264-264. Published online August 15, 2018
-
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Pediatric kidney transplantation is different from adult kidney transplantation
- Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(7):205-209. Published online July 15, 2018
-
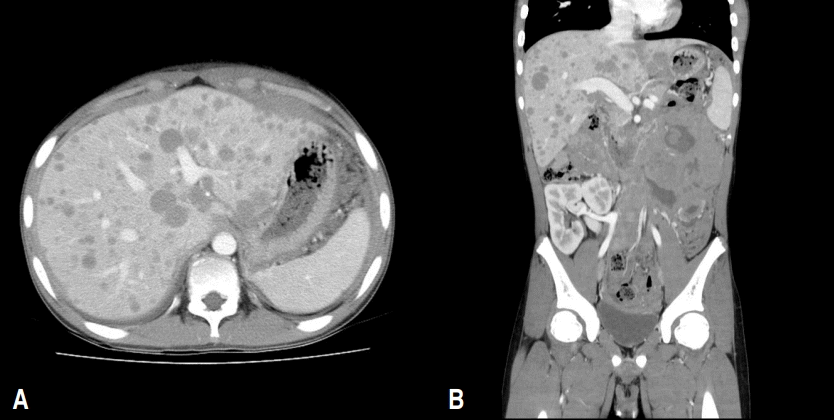
Kidney transplantation (KT) is the gold standard for renal replacement therapy in pediatric patients with end-stage renal disease. Recently, it has been observed that the outcome of pediatric KT is nearly identical to that in adults owing to the development and application of a variety of immunosuppressants and newer surgical techniques. However, owing to several differences in characteristics between children...
- Original Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Hypercalciuria and febrile convulsion in children under 5 years old
- Vahid Seddighi Gorabi, Bahram Nikkhoo, Obeidollah Faraji, Mona Mohammadkhani, Sattar Mirzaee, Mohammad Aziz Rasouli, Abdorrahim Afkhamzadeh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(4):129-131. Published online April 23, 2018
-
Purpose The association between hypercalciuria and febrile convulsion is controversial. The present study aimed to investigate the statistical association between hypercalciuria and childhood febrile convulsions.
Methods Overall, 160 children aged 6 months to 5 years, including 80 children with febrile convulsion and 80 febrile children without convulsion (comparison group), were recruited. All laboratory tests, including 24-hour urine calcium, were undertaken in an academic...
- Acute kidney injury in pediatric patients with rhabdomyolysis
- Young Shin Lim, Heeyeon Cho, Sang Taek Lee, Yeonhee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(3):95-100. Published online March 19, 2018
-
Purpose This study aimed to evaluate the clinical findings in pediatric rhabdomyolysis and the predictive factors for acute kidney injury (AKI) in Korean children.
Methods Medical records of 39 Korean children, who were newly diagnosed with rhabdomyolysis from January 2008 to December 2015, were retrospectively analyzed. The diagnosis was made from the medical history, elevated serum creatinine kinase level >1,000 IU/L, and plasma...
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome and eculizumab therapy in children
- Seong Heon Kim, Hye Young Kim, Su Young Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(2):37-42. Published online February 28, 2018
-
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is often encountered in children with acute kidney injury. Besides the well-known shiga toxin-producing
Escherichia coli -associated HUS, atypical HUS (aHUS) caused by genetic complement dysregulation has been studied recently. aHUS is a rare, chronic, and devastating disorder that progressively damages systemic organs, resulting in stroke, end-stage renal disease, and death. The traditional treatment for aHUS is...
- Original Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Diagnostic accuracy of urinary biomarkers in infants younger than 3 months with urinary tract infection
- Nani Jung, Hye Jin Byun, Jae Hyun Park, Joon Sik Kim, Hae Won Kim, Ji Yong Ha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(1):24-29. Published online January 22, 2018
-
Purpose The aim of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of urinary biomarkers, such as neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (uNGAL) and β-2 microglobulin (uB2MG), in early detection of urinary tract infection (UTI) in infants aged <3 months with fever.
Methods A total of 422 infants aged <3 months (male:female=267:155; mean age, 56.4 days), who were admitted for fever, were retrospectively included in...
- Is vaginal reflux associated with urinary tract infection in female children under the age of 36 months?
- Yu Bin Kim, Chih Lung Tang, Ja Wook Koo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(1):17-23. Published online January 22, 2018
-
Purpose To determine the relationship between vaginal reflux (VR) and urinary tract infection (UTI) in female children aged <36 months.
Methods A single center retrospective study was performed for 191 girls aged <36 months, with a diagnosis of febrile UTI, who underwent a voiding cystourethrography (VCUG) for assessment of vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) at Sanggye Paik Hospital. Fifty-one girls, who underwent VCUG for assessment...
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Genetics of hereditary nephrotic syndrome: a clinical review
- Tae-Sun Ha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):55-63. Published online March 27, 2017
-
Advances in podocytology and genetic techniques have expanded our understanding of the pathogenesis of hereditary steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS). In the past 20 years, over 45 genetic mutations have been identified in patients with hereditary SRNS. Genetic mutations on structural and functional molecules in podocytes can lead to serious injury in the podocytes themselves and in adjacent structures, causing sclerotic...
- Case Report
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- A novel mutation of
CLCNKB in a Korean patient of mixed phenotype of Bartter-Gitelman syndrome - Hee-Won Cho, Sang Taek Lee, Heeyeon Cho, Hae Il Cheong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S103-S106. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Bartter syndrome (BS) is an inherited renal tubular disorder characterized by low or normal blood pressure, hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis, and hyperreninemic hyperaldosteronism. Type III BS is caused by loss-of-function mutations in
CLCNKB encoding basolateral ClC-Kb. The clinical phenotype of patients withCLCNKB mutations has been known to be highly variable, and cases that are difficult to categorize as type III...
- Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome caused by presumed Takayasu arteritis
- Ki Wuk Lee, Sang Taek Lee, Heeyeon Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S145-S148. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Takayasu arteritis (TA) is a chronic inflammatory disease of unknown etiology that affects mainly the aorta, main aortic branches, and pulmonary arteries. Diverse neurological manifestations of TA have rarely been reported in children. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is a neuroradiological condition that presents with headache, seizure, visual disturbances, and characteristic lesions on imaging. Inflammatory condition and severe hypertension in...
- Eosinophilic gastroenteritis in an 18-year-old male with prolonged nephrotic syndrome
- Da Min Choi, Jung Eun Pyun, Hyung Eun Yim, Kee Hwan Yoo, Jung Ok Shim, Eun Jung Lee, Nam Hee Won
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S72-S75. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis is a rare disease characterized by prominent eosinophilic tissue infiltration of the gastrointestinal tract. Here, we report a case of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in an 18-year-old patient with prolonged nephrotic syndrome who presented with abdominal pain and peripheral hypereosinophilia. During the previous 2 years, he had visited local Emergency Department several times because of epigastric pain and nausea. He...
- Successful treatment of tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis with steroid and azathioprine in a 12-year-old boy
- Ji Eun Kim, Se Jin Park, Ji Young Oh, Hyeon Joo Jeong, Ji Hong Kim, Jae Il Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S99-S102. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis (TINU) syndrome is a rare disease, often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed in children. We describe the case of a 12-year-old boy who presented to Severance Hospital with a 1-month history of bilateral conjunctival injection. He was first evaluated by an Ophthalmologist in another hospital and diagnosed with panuveitis. Laboratory tests indicated renal failure, and a renal biopsy...
- Bilateral iliac and popliteal arterial thrombosis in a child with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
- Kyoung Hee Han, Ji Youn Park, Seung-Kee Min, Il-Soo Ha, Hae Il Cheong, Hee Gyung Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(5):242-245. Published online May 31, 2016
-
Thromboembolic complications (TECs) are clinically important sequelae of nephrotic syndrome (NS). The incidence of TECs in children is approximately 2%–5%. The veins are the most commonly affected sites, particularly the deep veins in the legs, the inferior vena cava, the superior vena cava, and the renal veins. Arterial thrombosis, which is less common, typically occurs in the cerebral, pulmonary, and...
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Pathogenesis of minimal change nephrotic syndrome: an immunological concept
- Seong Heon Kim, Se Jin Park, Kyoung Hee Han, Andreas Kronbichler, Moin A. Saleem, Jun Oh, Beom Jin Lim, Jae Il Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(5):205-211. Published online May 31, 2016
-
Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS) in children is characterized by massive proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia. Minimal change nephrotic syndrome (MCNS) is the most common form of INS in children. The pathogenesis of MCNS still remains unclear, however, several hypotheses have been recently proposed. For several decades, MCNS has been considered a T-cell disorder, which causes the impairment of the glomerular filtration barrier...
- Case Report
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Deficiency of antidiuretic hormone: a rare cause of massive polyuria after kidney transplantation
- Kyung Mi Jang, Young Soo Sohn, Young Ju Hwang, Bong Seok Choi, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(4):202-204. Published online April 30, 2016
-
A 15-year-old boy, who was diagnosed with Alport syndrome and end-stage renal disease, received a renal transplant from a living-related donor. On postoperative day 1, his daily urine output was 10,000 mL despite normal graft function. His laboratory findings including urine, serum osmolality, and antidiuretic hormone levels showed signs similar to central diabetes insipidus, so he was administered desmopressin acetate...
- Original Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Acute tubular necrosis as a part of vancomycin induced drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome with coincident postinfectious glomerulonephritis
- Kyung Min Kim, Kyoung Sung, Hea Koung Yang, Seong Heon Kim, Hye Young Kim, Gil Ho Ban, Su Eun Park, Hyoung Doo Lee, Su Young Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(3):145-148. Published online March 31, 2016
-
Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome is a rare and potentially fatal condition characterized by skin rash, fever, eosinophilia, and multiorgan involvement. Various drugs may be associated with this syndrome including carbamazepine, allopurinol, and sulfasalazine. Renal involvement in DRESS syndrome most commonly presents as acute kidney injury due to interstitial nephritis. An 11-year-old boy was referred to...
- Usefulness of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in young children with febrile urinary tract infection
- Song Yi Han, I Re Lee, Se Jin Park, Ji Hong Kim, Jae Il Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(3):139-144. Published online March 31, 2016
-
Purpose Acute pyelonephritis (APN) is a serious bacterial infection that can cause renal scarring in children. Early identification of APN is critical to improve treatment outcomes. The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is a prognostic marker of many diseases, but it has not yet been established in urinary tract infection (UTI). The aim of this study was to determine whether NLR is a...
- Case Report
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Recombinant Human Erythropoietin Therapy for a Jehovah's Witness Child With Severe Anemia due to Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome
- Da Eun Woo, Jae Min Lee, Yu Kyung Kim, Yong Hoon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(2):100-103. Published online February 29, 2016
-
Patients with hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS) can rapidly develop profound anemia as the disease progresses, as a consequence of red blood cell (RBC) hemolysis and inadequate erythropoietin synthesis. Therefore, RBC transfusion should be considered in HUS patients with severe anemia to avoid cardiac or pulmonary complications. Most patients who are Jehovah's Witnesses refuse blood transfusion, even in the face of life-threatening...
- Original Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Impaired angiogenesis in the enalapril-treated neonatal rat kidney
- Hyung Eun Yim, Kee Hwan Yoo, Eun Soo Bae, Young Sook Hong, Joo Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(1):8-15. Published online January 22, 2016
-
Purpose Nephrogenesis is normally accompanied by a tightly regulated and efficient vascularization. We investigated the effect of angiotensin II inhibition on angiogenesis in the developing rat kidney.
Methods Newborn rat pups were treated with enalapril (30 mg/kg/day) or vehicle (control) for 7 days after birth. Renal histological changes were checked using Hematoxylin & Eosin staining. We also investigated the intrarenal expression of vascular...
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











