Original article
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Original article
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Risk factors of prolonged diarrhea in children under 2 years old
- Dedy Rahmat, Agus Firmansyah, Ina S. Timan, Saptawati Bardosono, Joedo Prihartono, Pramita Gayatri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):538-544. Published online November 16, 2023
-
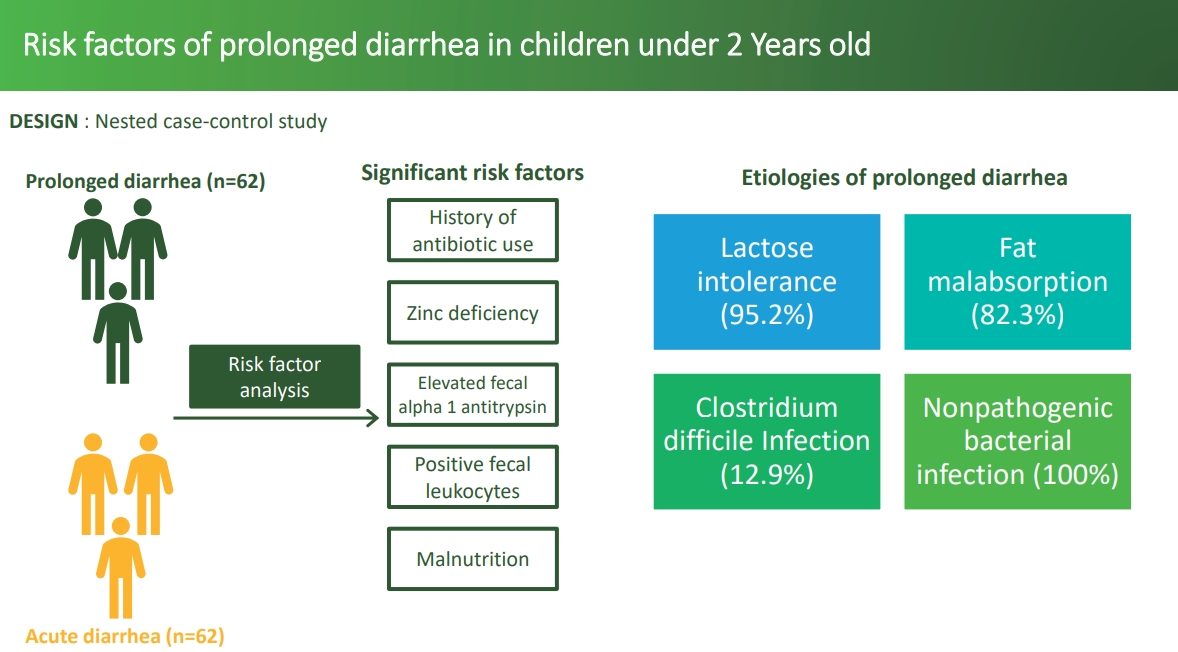
Question: What are the risk factors for prolonged diarrhea in children under 2 years old?
Finding: History of antibiotic use, zinc deficiency, and elevated fecal alpha-1 antitrypsin levels were the main risk factors of prolonged diarrhea in children under 2 years old with acute diarrhea.
Meaning: Rational antibiotic usage is necessary as well as thorough testing of serum zinc level and fecal alpha-1 antitrypsin levels.
- General Pediatrics
- Virtual reality for pain reduction during intravenous injection in pediatrics: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Amir Mohammad Salehi, Masoud Rafiee, Mozhdeh Bashirian
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):533-537. Published online June 14, 2023
-
Question: This is the first meta-analysis to examine published evidence of the effectiveness of virtual reality at reducing pain during pediatric intravenous injections.
Finding: Our results suggest that virtual reality effectively reduces pain associated with intravenous injections in pediatric patients.
Meaning: These findings suggest the importance of virtual reality in decreasing the pain of intravenous injections among children.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Association between maternal coronavirus disease 2019 and transient tachypnea of the newborn: a single-center study
- Sung Hee Lee, Ju Hyun Jin, Jong Ha Yoo, Shin Won Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):493-500. Published online October 24, 2023
-
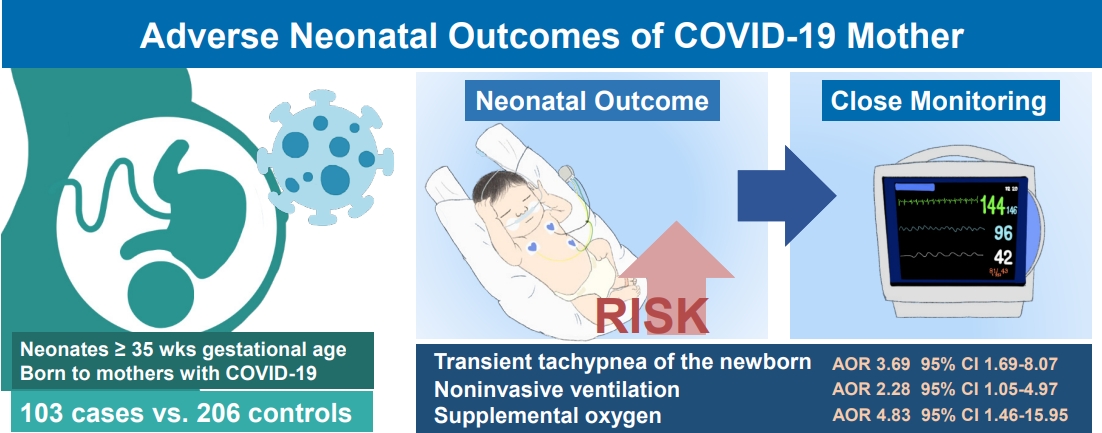
Question: What are the adverse clinical outcomes of neonates of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)–infected mothers?
Finding: Infants of mothers with COVID-19 were at significantly increased risk of transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN), use of noninvasive ventilation, and need for supplemental oxygen (P<0.05).
Meaning: Neonates of mothers with COVID-19 are at risk of TTN and require respiratory support. Close monitoring is essential to ensuring timely intervention if required.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Attention-deficit/hyperactive-impulsive disorder symptoms among grade 1 students with reading disorder in Thailand
- Patcharapun Sarisuta, Issarapa Chunsuwan, Tippawan Hansakunachai, Paskorn Sritipsukho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):485-492. Published online October 24, 2023
-
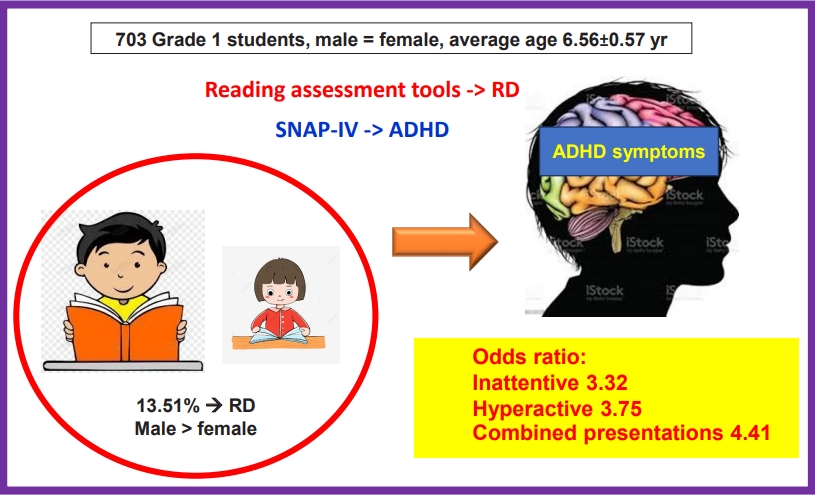
Question: Would students with reading disorder have a significantly higher prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactiveimpulsive disorder (ADHD) symptoms than neurotypical students?
Finding: Students at risk of reading disorder exhibited significant ADHD symptoms compared with those not at risk of reading disorder according to all presentations of teacher assessments versus only for predominantly inattentive presentations of the parental assessments.
Meaning: Students with reading disorder have a significantly higher prevalence of ADHD symptoms than neurotypical students. Sex, parental education level, average family income, and children’s school affiliation significantly influenced reading disorder prevalence.
- Gastroenterology
- Inferior vena cava to aorta ratio in dehydrated pediatric patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Gilbert Sterling Octavius, Michelle Imanuelly, Johan Wibowo, Nadia Khoirunnisa Heryadi, Melanie Widjaja
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):477-484. Published online June 14, 2023
-
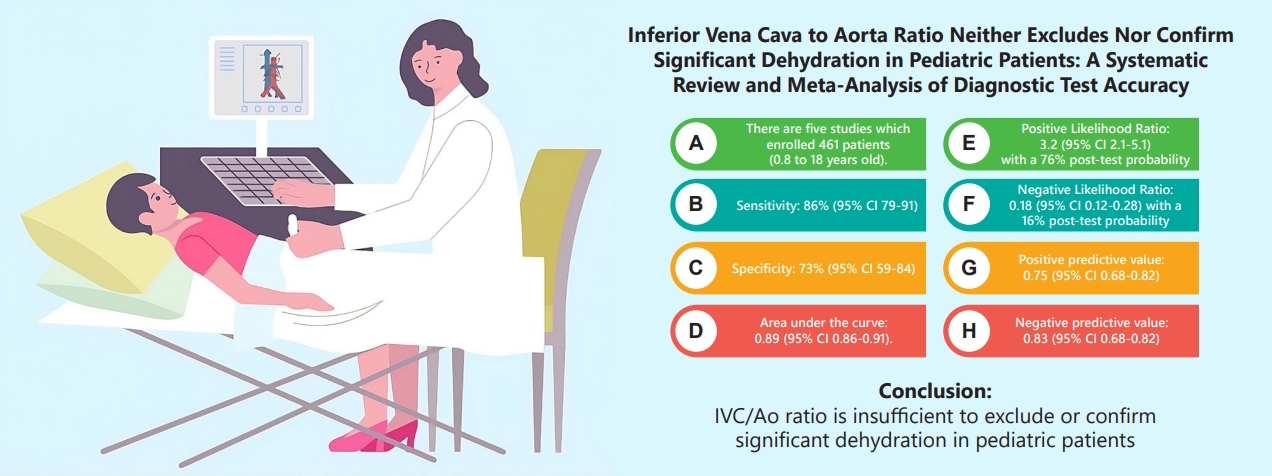
Question: The inferior vena cava to aorta (IVC/Ao) ratio measured via ultrasound has been touted as a promising noninvasive technique to assess clinically significant dehydration in pediatric patients.
Finding: Our meta-analysis found that IVC/Ao ratio had a positive likelihood ratio of 3.2 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.1–5.1) and negative likelihood ratio of 0.18 (95% CI, 0.12–0.28).
Meaning: Hence, IVC/Ao ratio is insufficient to exclude or confirm significant dehydration in pediatric patients.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Impact of short and intensive art-based intervention on symptomatology and social interactions among children with autism spectrum disorder
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Bayar Mohammed Omar Abdulla, Pranee Liamputtong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):447-454. Published online September 14, 2023
-

Question: Does a short and intensive art-based intervention affect symptoms and social interactions among children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Finding: The short and intensive art-based intervention did not affect symptoms in children with ASD level 2 or 3, including social awareness, social cognition, social communication, social motivation, and autistic mannerisms.
Meaning: The short and intensive art-based intervention did not improve the symptoms of patients with ASD.
- Neonatal risk factors associated with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: an umbrella review
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Erfan Ayubi, Sajjad Farashi, Saeid Bashirian, Fereshteh Mehri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):441-446. Published online July 14, 2023
-
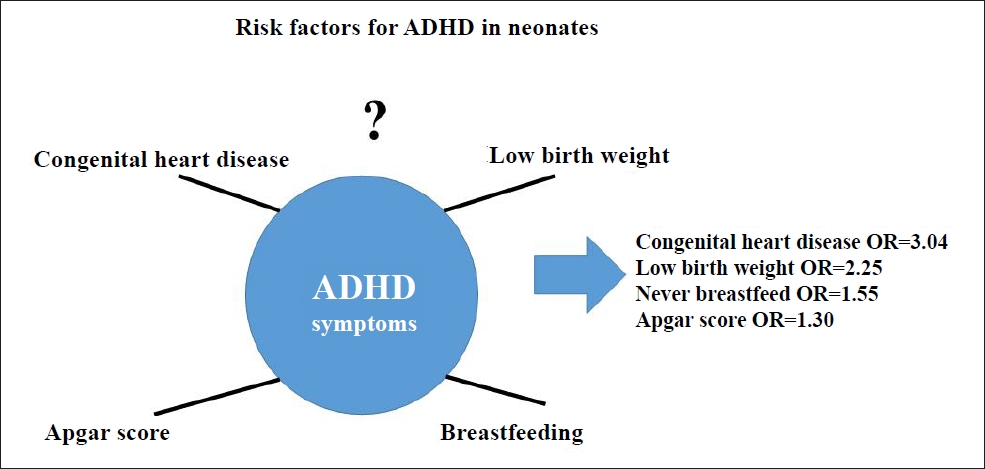
Question: The risk factors for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), such as breastfeeding, congenital heart disease, and low birth weight, in neonates are not well understood.
Finding: This umbrella review obtained significant effect sizes for ADHD for congenital heart disease (odds ratio [OR], 3.04), low birth weight (OR, 2.25), never breastfed (OR, 1.55), and Apgar score (OR, 1.30).
Meaning: Congenital heart disease, low birth weight, lack of breastfeeding, and Apgar scores were significant factors for ADHD.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Timing of parenteral nutrition initiation in critically ill children: a randomized clinical trial
- Nagwan Y. Saleh, Hesham M. Aboelghar, Nehad B. Abdelaty, Mohamed I. Garib, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):403-411. Published online June 14, 2023
-
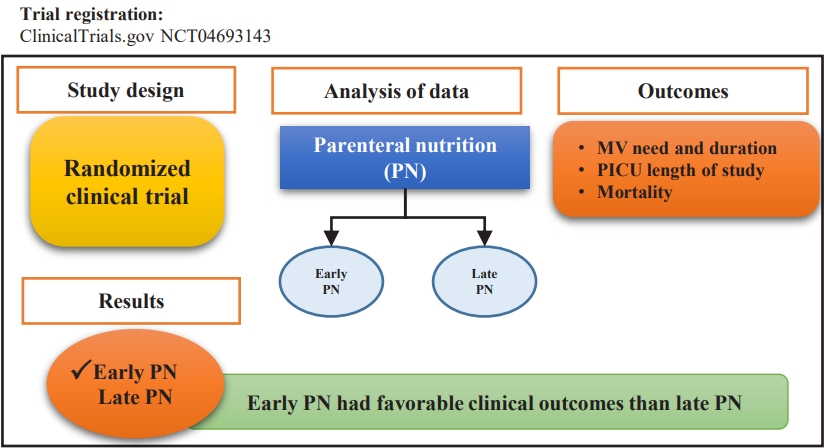
Question: What is the ideal initiation timing of parenteral nutrition for critically ill children?
Finding: This randomized clinical trial of 140 children examined the effects of an early or late start of parenteral nutrition on mechanical ventilation need (primary outcome) and length of stay and mortality (secondary outcomes).
Meaning: Children who received early versus late parenteral nutrition had lower mechanical ventilation need and duration.
- Gastroenterology
- Relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hyperandrogenemia in adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome
- Ozlem Kara, Hanife Aysegul Arsoy, Murat Keskin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):395-402. Published online June 14, 2023
-

Question: Is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) a risk factor for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in adolescents?
Finding: The frequency of NAFLD did not increase in adolescents with PCOS. However, hyperandrogenemia was a risk factor for NAFLD.
Meaning: Adolescents with PCOS and hyperandrogenemia should be closely monitored for hepatic steatosis.
- Allergy
- Association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children: a systematic review and multicenter cohort study using a common data model
- Ji Eun Lim, Hye Min Kim, Ju Hee Kim, Hey Sung Baek, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):357-365. Published online June 14, 2023
-
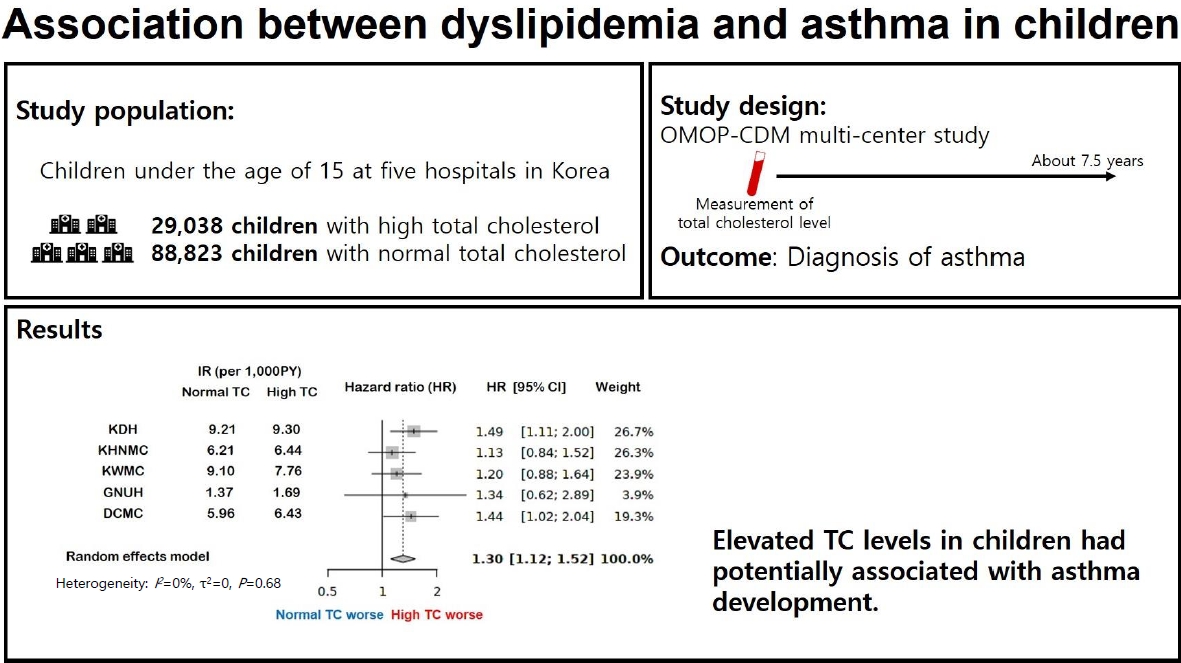
Question: Is dyslipidemia a risk factor for asthma in children?
Finding: This was a comprehensive systematic review and retrospective multicenter study of the association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children. In a multicenter cohort analysis using the Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership Common Data Model, elevated total cholesterol levels were associated with increased risk of asthma development.
Meaning: These findings suggest an association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children.
- Neurology
- Need for palliative care from birth to infancy in pediatric patients with neurological diseases
- Raffaele Falsaperla, Silvia Marino, Carla Moscheo, Lucia Giovanna Tardino, Simona Domenica Marino, Concetta Sciuto, Piero Pavone, Giovanna Vitaliti, Federica Sullo, Martino Ruggieri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):350-356. Published online June 14, 2023
-
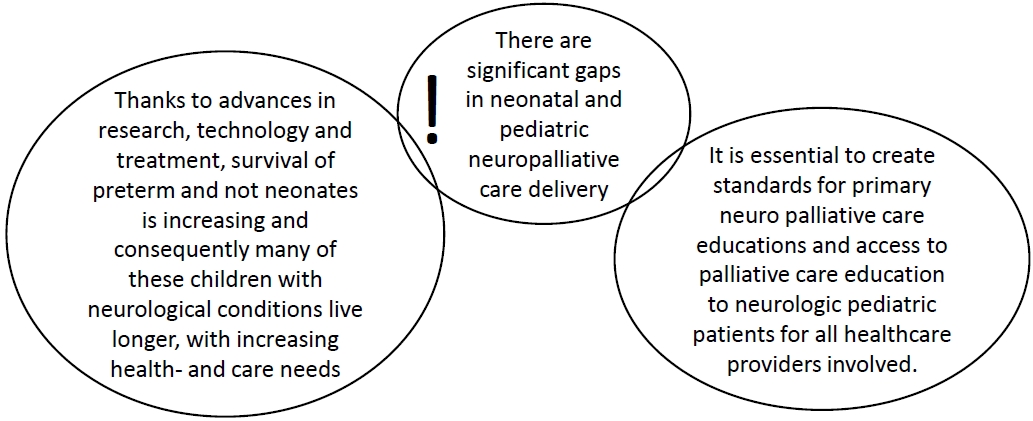
Question: What are the current palliative care protocols, palliative course, and implementable palliative care programs for hospitalized pediatric patients with neurological diseases in Italy?
Finding: We studied 34 newborns with nervous system diseases, all of whom had a poor prognosis.
Meaning: Despite current legislation in Italy, no palliative care network has been implemented. Given the vast number of patients with neurological conditions, standardized palliative care guidelines and protocols are required.
- Infection
- Seroprevalence of maternal peripartum human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the Nigerian literature
- Abdulrasheed Usman, Muhammad Hamis Musa, Bukhari Isah Shuaib, Olayemi Balogun, Mukhtar Adeiza
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):307-316. Published online December 22, 2022
-
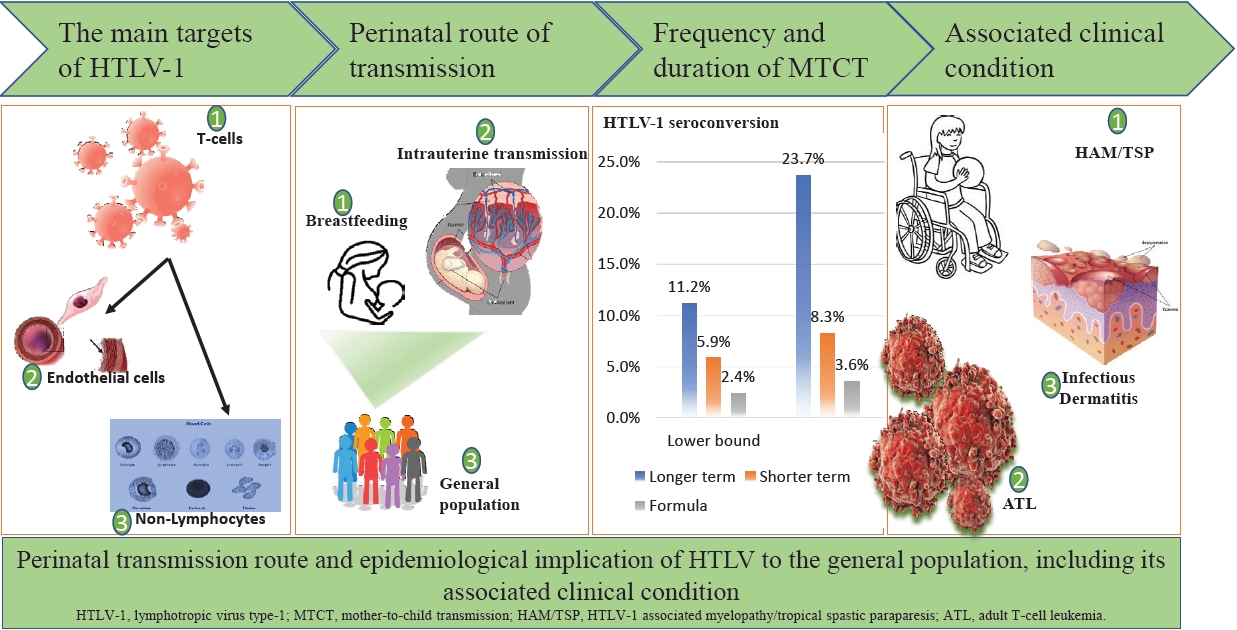
The peripartum period is an important transmission time for human T-cell lymphotropic virus-1 (HTLV-1) infection, mainly via breastfeeding and partly through the placental tissues of carrier mothers. Although most HTLV-1–infected individuals are asymptomatic, fetal and childhood infections often result in several diseases with disappointing treatment outcomes. An estimated HTLV-1 burden in Nigeria among perinatal women must be determined to enable rational planning of a comprehensive health care intervention.
- Gastroenterology
- Assessing indicators and clinical differences between functional and organic childhood constipation: a retrospective study in pediatric gastroenterology clinics
- Hasan M. Isa, Fatema A. Alkharsi, Fatema A. Salman, Maryam S. Ali, Zahra K. Abdulnabibi, Afaf M. Mohamed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):296-306. Published online June 14, 2023
-
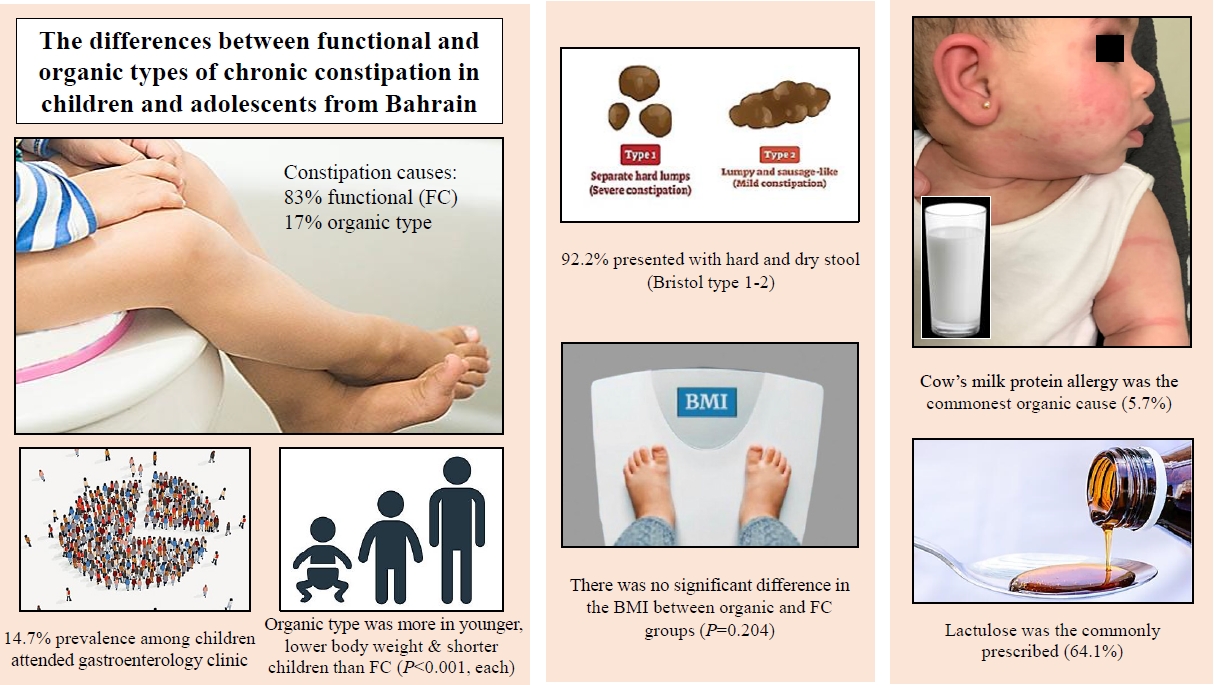
Question: What causes childhood constipation, and what can predict organic constipation?
Finding: Constipation represents 14.7% of gastroenterology visits. Functional constipation is more common among constipation types, while organic constipation is more common in young children and those with a low body weight, stunted growth, mucus in the stool, and associated diseases.
Meaning: Younger children and those with lower growth or mucus in the stool should be assessed for underlying organic causes of constipation.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Efficacy of body position on gastric residual in preterm infant: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Kurvatteppa Halemani, Alwin Issac, Sanjay Dhiraaj, Prabhaker Mishra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):262-270. Published online November 30, 2022
-
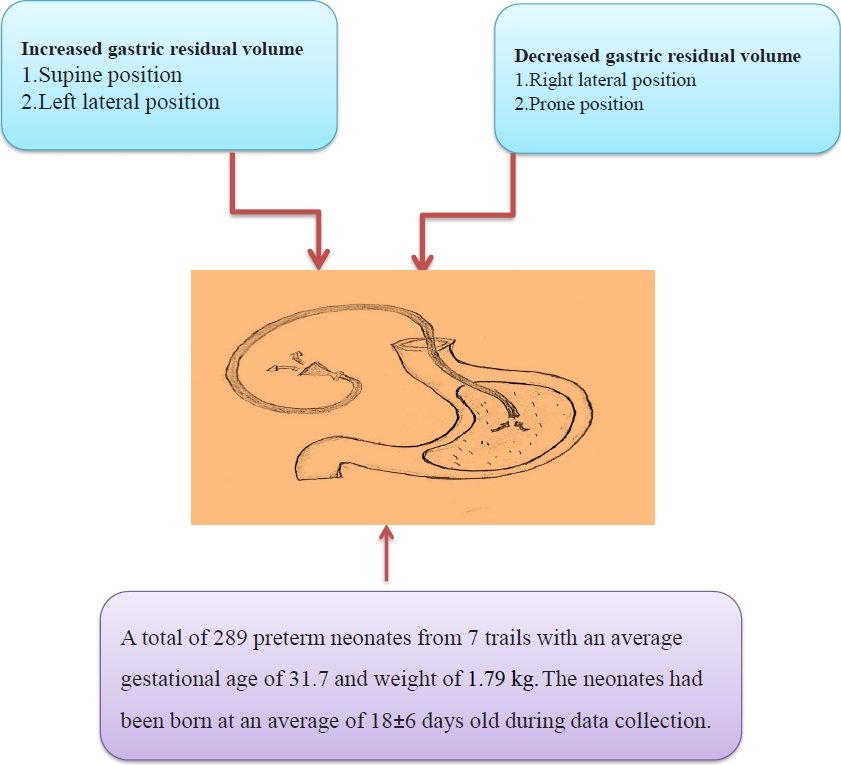
Breastfeeding and it's tolerance are the positive indicators for preterm babies. Placing the preterm infant in the right lateral or prone position after feed had lesser gastric residual volume compared to placing them in left lateral or supine positions. The post-feed position is a vital element in enhancing feeding tolerance, mechanical functions of the gastrointestinal tract and the overall development of preterm infants.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Parenting stress and interactive engagement behaviors in children with developmental delay
- Jung Sook Yeom, Rock Bum Kim, Jae Young Cho, Ji Sook Park, Eun Sil Park, Ji-Hyun Seo, Jae-Young Lim, Hyang-Ok Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):252-261. Published online May 19, 2023
-
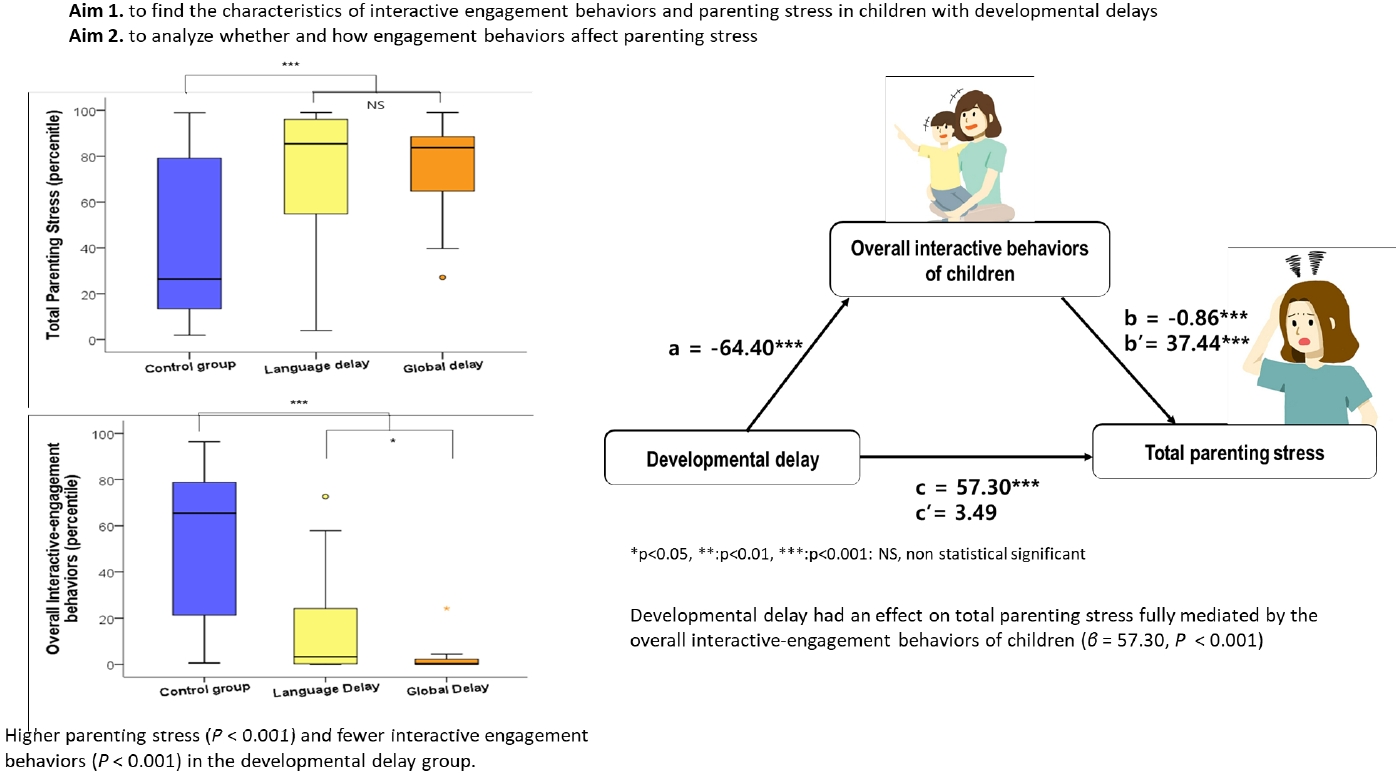
· Question: What level of parenting stress is experienced by parents of children with developmental delays (DDs) without autism spectrum disorder, and what factors contribute to it?
· Findings: Parents of children with DDs experienced high parenting stress that were significantly mediated by their children’s low interactive behaviors.
· Meaning: The interactive behaviors of children with DDs mediate parenting stress.
- Cardiology
- Echocardiographic reference z scores of right ventricular dimension and systolic function of children aged 5–12 years
- Alaba Busola Oladimeji, Moriam Omolola Lamina, Peter Odion Ubuane, Motunrayo Oluwabukola Adekunle, Omolara Adeolu Kehinde, Barakat Adeola Animasahun, Olisamedua FidelisNjokanma
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):215-222. Published online April 18, 2023
-

Question: Z score reference values for right ventricular size and systolic function in children using echocardiography are available in several countries. Despite the high burden of diseases involving the right ventricle in Nigeria, these reference values have limited applicability.
Finding: The right ventricular sizes of Nigerian children differed from those published elsewhere.
Meaning: These reference values will aid the treatment, monitoring, and pre- and postintervention for Nigerian children.
- Infection
- Predicting COVID-19 transmission in a student population in Seoul, South Korea, 2020–2021
- Young Hwa Lee, Han Ho Kim, Young June Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):173-178. Published online December 22, 2022
-
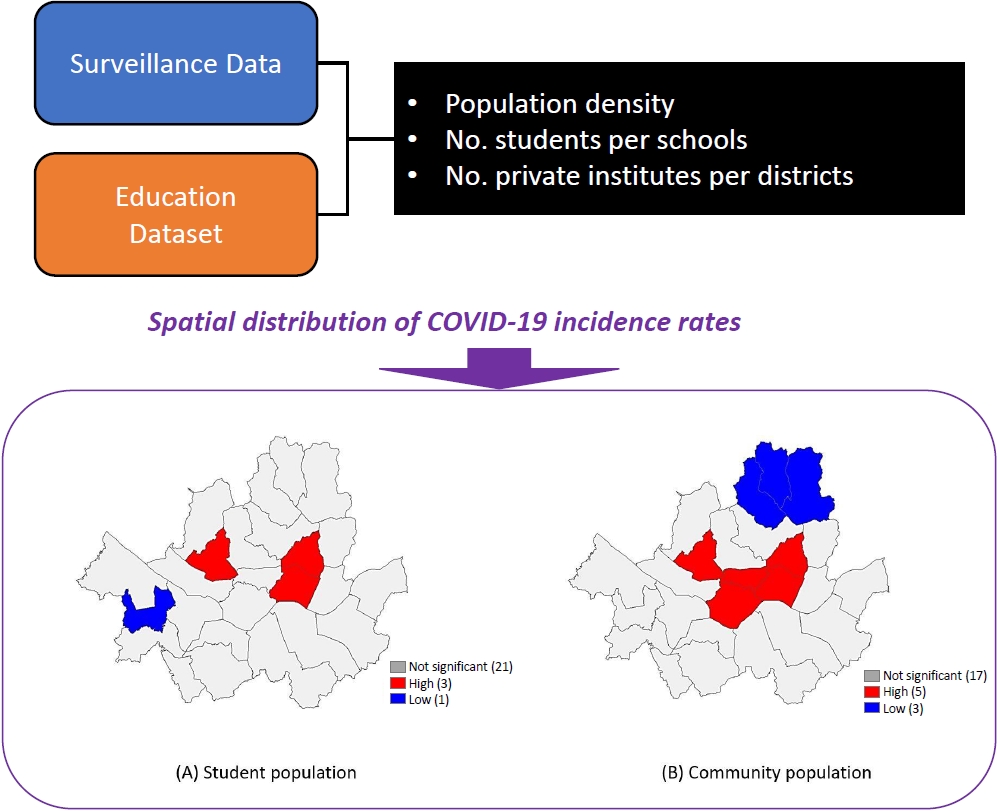
Question: What is the spatial distribution and determinants of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection among students in Korea?
Finding: The community population was closely associated with the risk of COVID-19, and the number of students per school class were inversely associated with COVID-19 rates in students.
Meaning: Our finding suggests that controlling the community-level burden of COVID-19 can help prevent sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in school-aged children.
- Clinical characteristics of pediatric patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus common human coronaviruses: a national multicenter study
- In Suk Sol, Eun Lee, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Yong Ju Lee, Hye Yung Yum, Mi-Hee Lee, Mi Ae Chu, Hui Jeong Moon, Hyo-Bin Kim, Ju Hee Seo, Jung Yeon Shim, Ji Young Ahn, Yoon Young Jang, Hai Lee Chung, Eun Hee Chung, Kyunghoon Kim, Bong-Seong Kim, Cheol Hong Kim, Yang Park, Meeyong Shin, Kyung Suk Lee, Man Yong Han, Soo-Jong Hong, Eun Kyeong Kang, Chang Keun Kim; on behalf of The Pneumonia & Respiratory Disease Study Group of Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):134-141. Published online December 22, 2022
-

Question: The clinical differences between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and human coronaviruses (HCoV) in children remain unknown.
Finding: This study compared the clinical findings of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus HCoV. Its findings suggest that children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 have a milder clinical course than those with HCoV.
Meaning: The clinical course of children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 should be closely monitored during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.
- Hematology
- Changes and correlations of T-cell coinhibitory molecule programmed death-1 and interferon-γ in pediatric immune thrombocytopenia
- Fady Mohamed El-Gendy, Amira M.F. Shehata, Esam Awad Abd El-Kawy, Mahmoud Ahmed El-Hawy
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):127-133. Published online February 24, 2023
-

Question: What are the PD-1+ CD4+ T cells percentages and serum interferon gamma (IFN-γ) levels of pediatric patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP)?
Finding: Compared with healthy controls, the PD-1+ CD4+ T cells percentages and IFN-γ levels were significantly higher in ITP patients before and 1 month after therapy.
Meaning: Our findings suggest that PD-1+ CD4+ T cells and IFN-γ are involved in the pathophysiological process of ITP.
- Gastroenterology
- Association between maternal weight gain during pregnancy and child’s body mass index at preschool age
- Jeewon Shin, Yoowon Kwon, Ju Hee Kim, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):76-81. Published online November 30, 2022
-
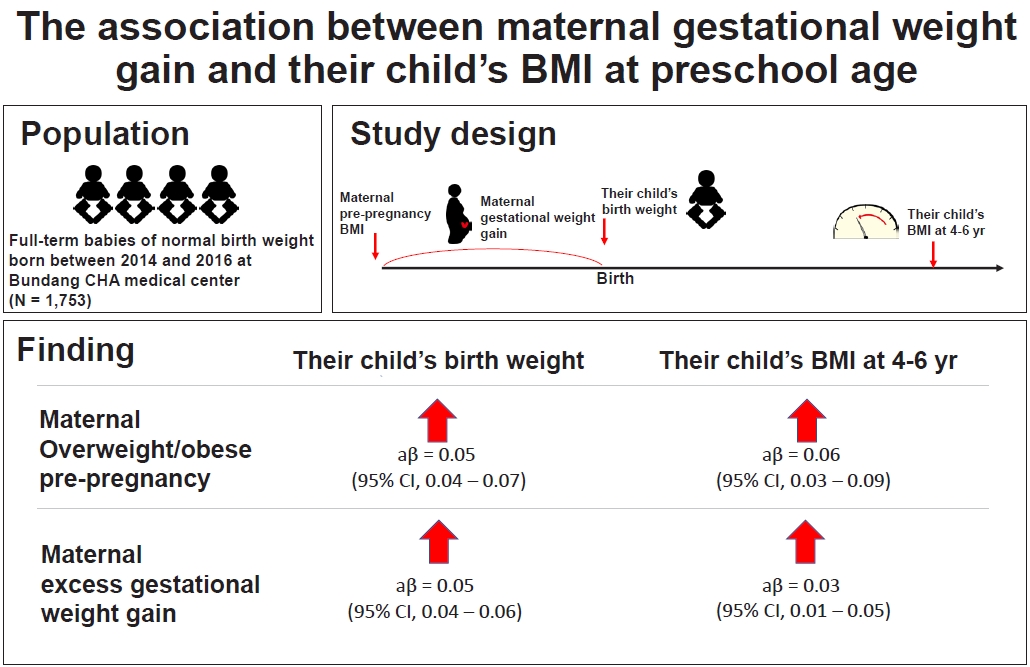
Question: What are the risk factors of newborn birth weight? Does gestational weight gain and prepregnancy body mass index affect childhood weight?
Finding: Excess maternal weight gain increases the risk of overweight/obesity, newborn birth weight, and child body mass index at 4–6 years.
Meaning: Maternal weight control before and during pregnancy should be well controlled.
- Neurobehavior
- Association between previous abortion history and risk of autism spectrum disorders among offspring: a meta-analysis
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Erfan Ayubi, Saeid Bashirian, Mahdieh Seyedi, Mohammad Rezaei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):70-75. Published online August 17, 2022
-
Question: This study aimed to determine whether there is an association between previous abortion history and the risk of autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) among children.
Finding: We found that the risk of ASD associated with previous abortion history had an odds ratio of 1.64 (95% confidence interval, 1.28–2.0; I2=61.7%).
Meaning: These findings suggest a positive and significant association between history of previous abortion and risk of ASD in children.
- Neurology
- Long-term neurological cognitive, behavioral, functional, and quality of life outcomes after fetal myelomeningocele closure: a systematic review
- Andre Marolop Pangihutan Siahaan, Martin Susanto, Sarma Nursani Lumbanraja, Dwi Herawati Ritonga
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):38-45. Published online November 30, 2022
-
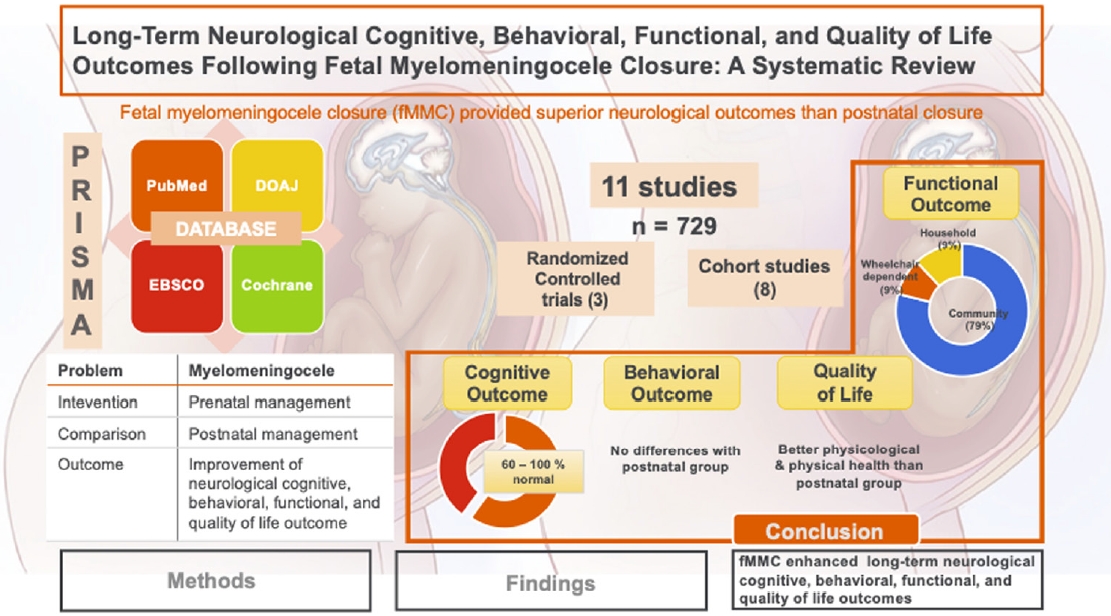
· Fetal myelomeningocele closure significantly improved long-term neurological cognitive, behavioral, functional, and quality of life outcomes, most likely by reducing hydrocephalus rates.
· However, fetal myelomeningocele closure is associated with a significant risk of pregnancy complications, especially premature rupture of membranes and preterm delivery.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- A thickened formula reduces feeding-associated oxygen desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants
- Gayoung Lee, Juyoung Lee, Ga Won Jeon, Yong Hoon Jun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):32-37. Published online December 15, 2022
-
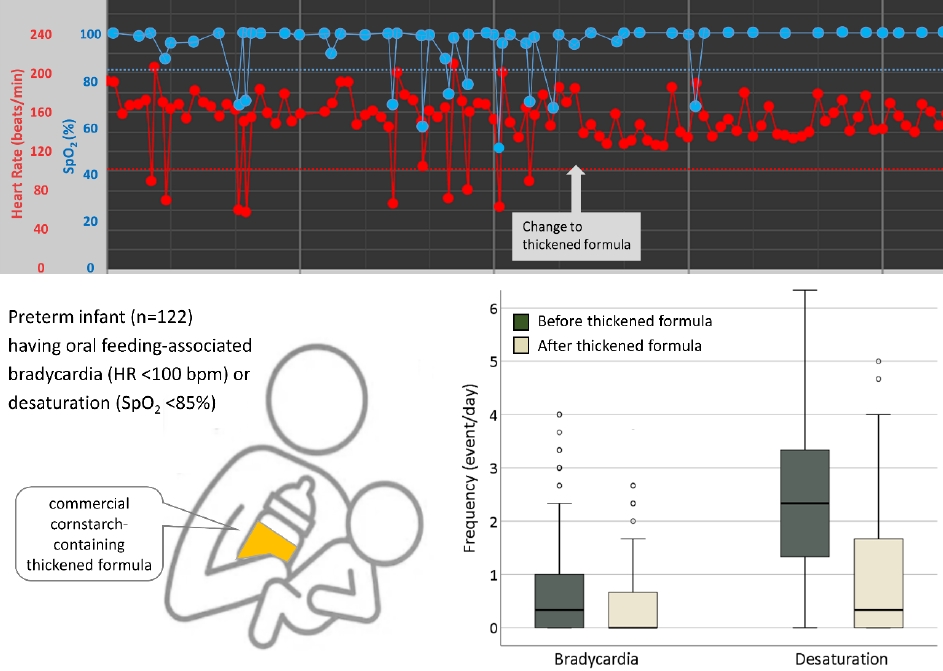
Question: Is a commercial thickened formula able to alleviate oral feeding-associated desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants?
Finding: Thickened formula feeding significantly reduced oral feeding-associated desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants.
Meaning: Thickened formula feeding stabilizes oxygen saturation and heart rate during oral feeding among preterm infants with feeding difficulties.
- Nutrition
- Not breastfeeding and risk of autism spectrum disorders among children: a meta-analysis
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Amir Mohammad Salehi, Salman Khazaei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):28-31. Published online July 19, 2022
-
This study aimed to determine whether there is an association between not breastfeeding (versus breastfeeding) and the risk of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) among children. We found that the risk of ASD associated with not breastfeeding had an odds ratio of 1.81 (95% confidence interval, 1.35–2.27; I2=0 %). These findings suggest the importance of breastfeeding in decreasing the risk of ASD among children.
- Pulmonology
- Predictors of high-flow nasal cannula failure in pediatric patients with acute respiratory distress
- Kantara Saelim, Busawan Thirapaleka, Kanokpan Ruangnapa, Pharsai Prasertsan, Wanaporn Anuntaseree
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):595-601. Published online November 1, 2022
-

SpO2/FiO2 ratio ≤166, pediatric respiratory rate-oxygenation index <132, and clinical respiratory score ≥6 at 12 hours after high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) initiation were useful bedside predictors for HFNC failure in pediatric patients.
- Gastroenterology
- Ability of polymicrobial probiotic and mono-strain probiotic to reduce functional abdominal pain in children: a randomized clinical trial
- Seyed Sajad Jafari, Seyed Mojtaba Hashemi, Bahman Sadeghi, Amir Almasi-Hashiani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):589-594. Published online October 31, 2022
-
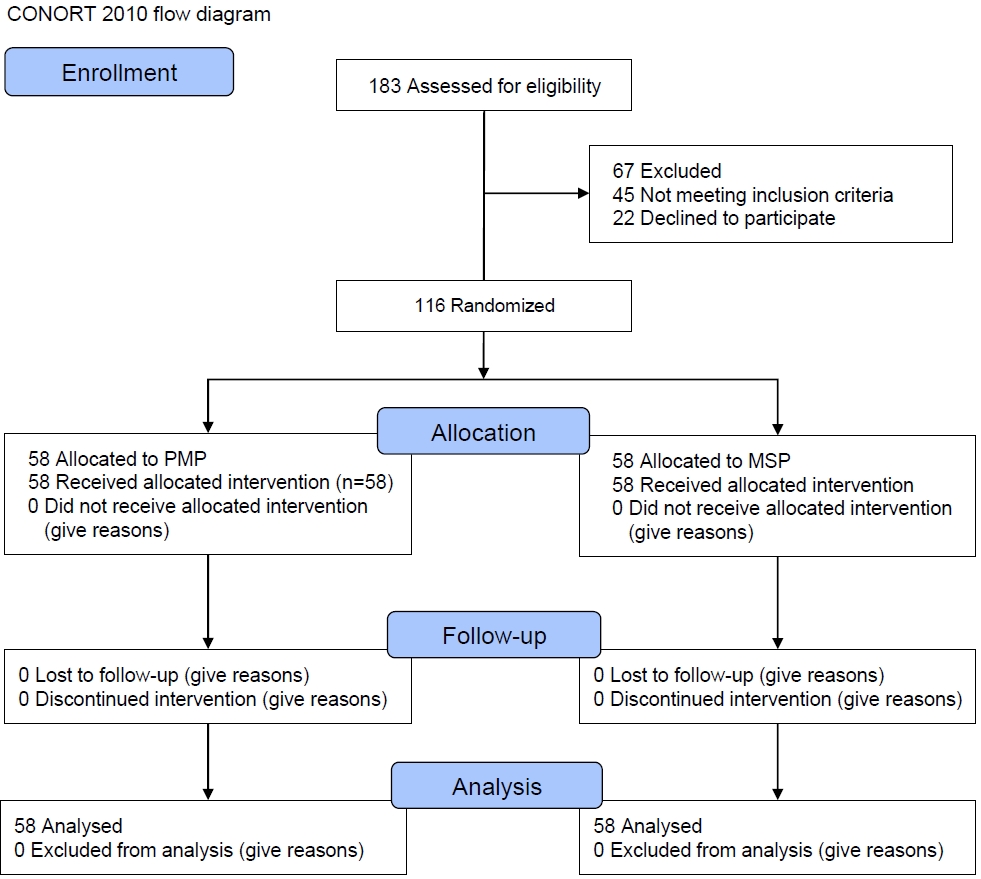
· This study compared the ability of 2 probiotics to reduce and improve functional abdominal pain (FAP) in children.
· In the polymicrobial probiotic (PMP) group, 10.34% of children reported no pain; in the mono-strain probiotic (MSP) group, all patients reported low-degree pain. The mean pain score decreased significantly over time in both groups.
· The use of both PMP and MSP is recommended to reduce pain in patients with FAP.
- Probiotics added to maternal nutrition affect ınfantile colic symptoms and fecal microbiota profile: a single-blind randomized controlled study
- Aysu Yıldız Karaahmet, Gülümser Dolgun, Metehan Özen
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):547-554. Published online September 23, 2022
-

Question: Do probiotics added to maternal nutrition affect infantile colic symptoms and intestinal microbiota?
Finding: Infants whose mothers ingested probiotics demonstrated decreased crying frequency and intensity and significantly increased bacterial diversity in the stools. The bacterial variety was substantially affected by the added probiotic product.
Meaning: The addition of probiotics to maternal nutrition in early infancy could play an important role in preventing infantile colic.
- Nutrition
- Survey of Korean pediatrician’s perceptions of barriers to and improvements in breastfeeding
- Seong Phil Bae, Woo Ryoung Lee, Won-Ho Hahn, Hye-Jung Shin, Young Min Ahn, Son Moon Shin, Yong Joo Kim, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim, Youn Jeong Shin, Dae Yong Yi, Soon Min Lee, Juyoung Lee, Jin A Lee, Sung-Hoon Chung, Euiseok Jung, Eui Kyung Choi, Ju Sun Heo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):540-546. Published online July 29, 2022
-
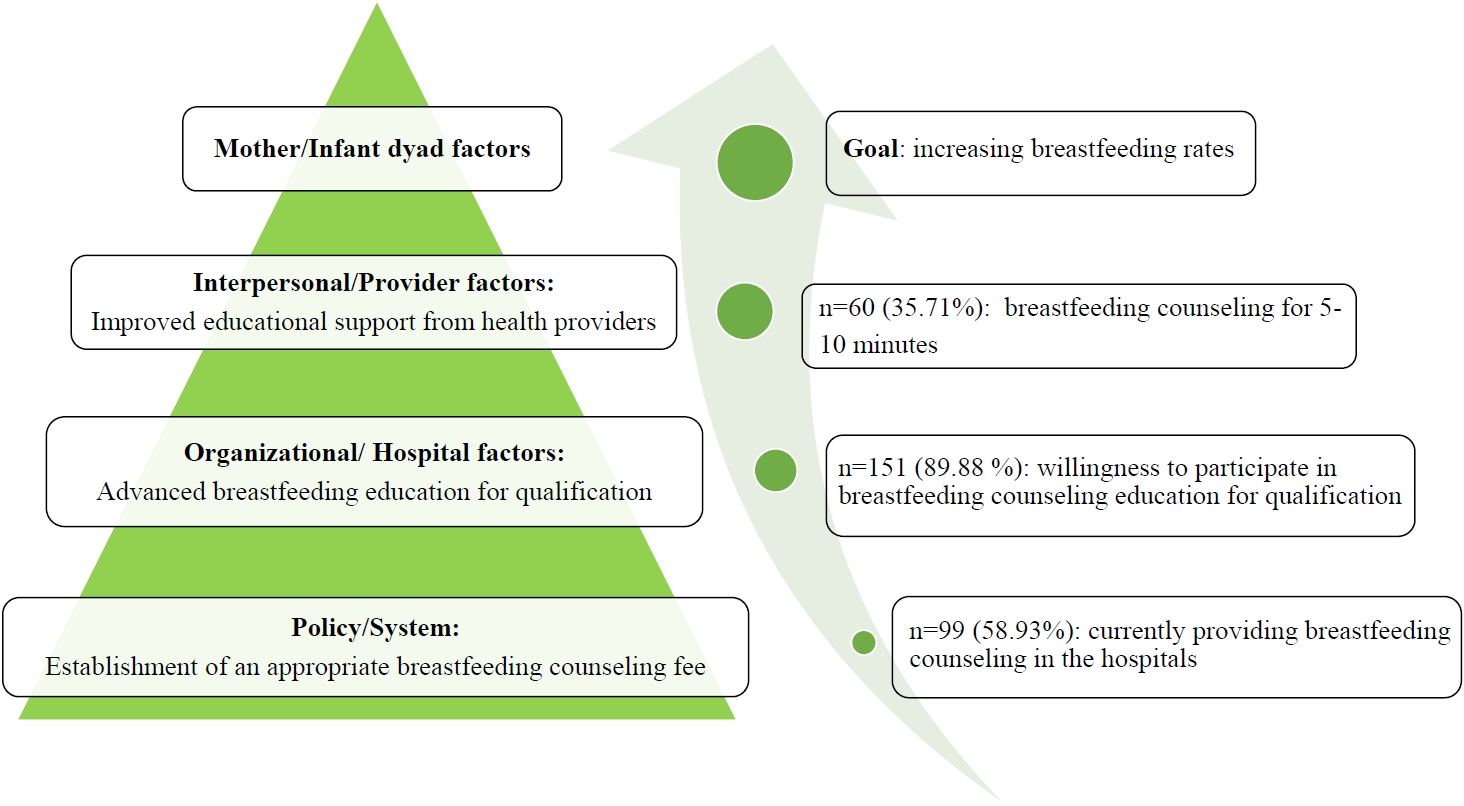
Question: What barriers to breastfeeding do Korean pediatricians perceive?
Finding: Regardless of medical institution, breastfeeding counseling for parents is currently limited, and breastfeeding is commonly discontinued due to various maternal and neonatal factors.
Meaning: To promote breastfeeding, increasing pediatrician participation in breastfeeding counseling with the establishment of appropriate breastfeeding counseling fees and the expansion of practical and high-quality breastfeeding education for medical staff should be considered.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Mediation effect of cord blood cortisol levels between maternal prepregnancy body mass index and birth weight: a hospital-based cross-sectional study
- Nisanth Selvam, Jayashree K, Prasanna Mithra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):500-506. Published online July 29, 2022
-

Question: What is the association between cord blood cortisol and maternal weight, birth weight, and cord blood lipid profile?
Finding: Cord blood cortisol levels did not influence the relationship between maternal weight changes or birth weight. Maternal weight changes, birth weight, and cortisol levels altered the cord blood lipid profile.
Meaning: Our findings may aid United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 3 (Good Health and Well-Being) achievement by 2030.
- Other
- Plastic bottle feeding produces changes in biochemical parameters in human infants – A pilot study
- Mahendra K. Pant, Abul. H. Ahmad, Manisha Naithani, Jayanti Pant
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):459-465. Published online May 19, 2022
-

Question: Plastic feeding bottles are used commonly to feed infants who cannot be breastfeed. Does plastic bottle feeding produce biochemical changes in infants?
Finding: The plastic bottles leach out endocrine disruptors and affects bodily functions in terms of biochemical alterations like increased blood urea, raised creatine-kinase–MB levels, and altered lipid profile in infants exposed to bottle feeding.
Meaning: Plastic bottles feeding alters bodily functions in infants.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











