Most viewed
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most viewed
"Most viewed" Articles are from the articles published in 2023 during the last six month.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Quantifying myelin in neonates using magnetic resonance imaging: a systematic literature review (3,660 times)
- Nabila Hanem Arshad, Hasyma Abu Hassan, Nur Farhayu Omar, Zurina Zainudin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):371-385. Published online December 6, 2023
-

Question: This systematic review attempts to discover the best magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique for myelin quantification in neonates by evaluating various MRI parameters and their reproducibility.
Finding: Since the benefits of using synthetic MRI for quantifying myelin in neonates outweigh the very minor draw- backs, it is recommended.
Meaning: The findings suggest the importance of identifying noninvasive MRI techniques available to assess myelin tissue in neonates, which aid in diagnosing neurodevelopmental disorders.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Trends and determinants in breastfeeding among Korean infants (2007–2021): a nationwide study using the National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children (3,657 times)
- Minwoong Kang, Eui Kyung Choi, Jeung Min Lee, Hye-Jung Shin, Woo Ryoung Lee, Son Moon Shin; Korean Society of Breastfeeding Medicine
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):772-780. Published online July 4, 2025
-
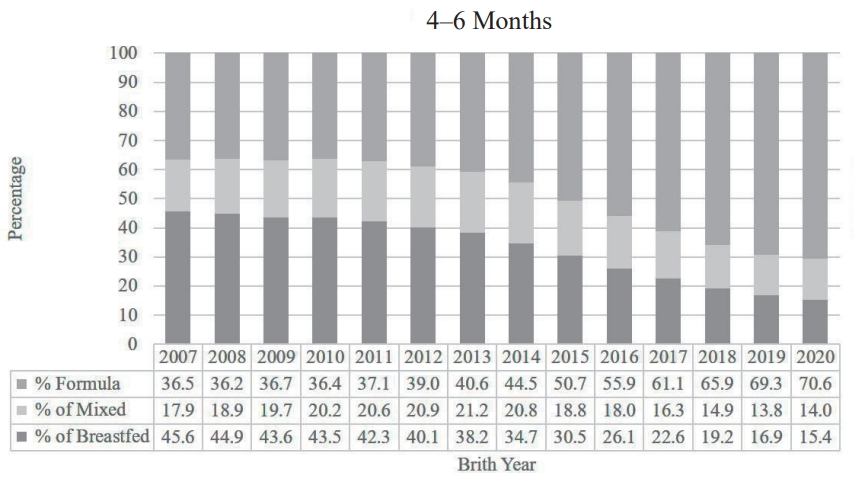
Question: What are the recent trends and determinants of breastfeeding in South Korea?
Finding: Breastfeeding rates in South Korea declined significantly from 2007 to 2021, with lower rates observed in preterm, low-birthweight, and multiple-birth infants as well as rural or lower-income households.
Meaning: Targeted interventions, including prenatal education, postnatal support, and community-based programs, are required to address disparities and improve breastfeeding rates.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Comorbidities of allergic rhinitis in children (3,653 times)
- Yong Ju Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):675-676. Published online July 31, 2024
-
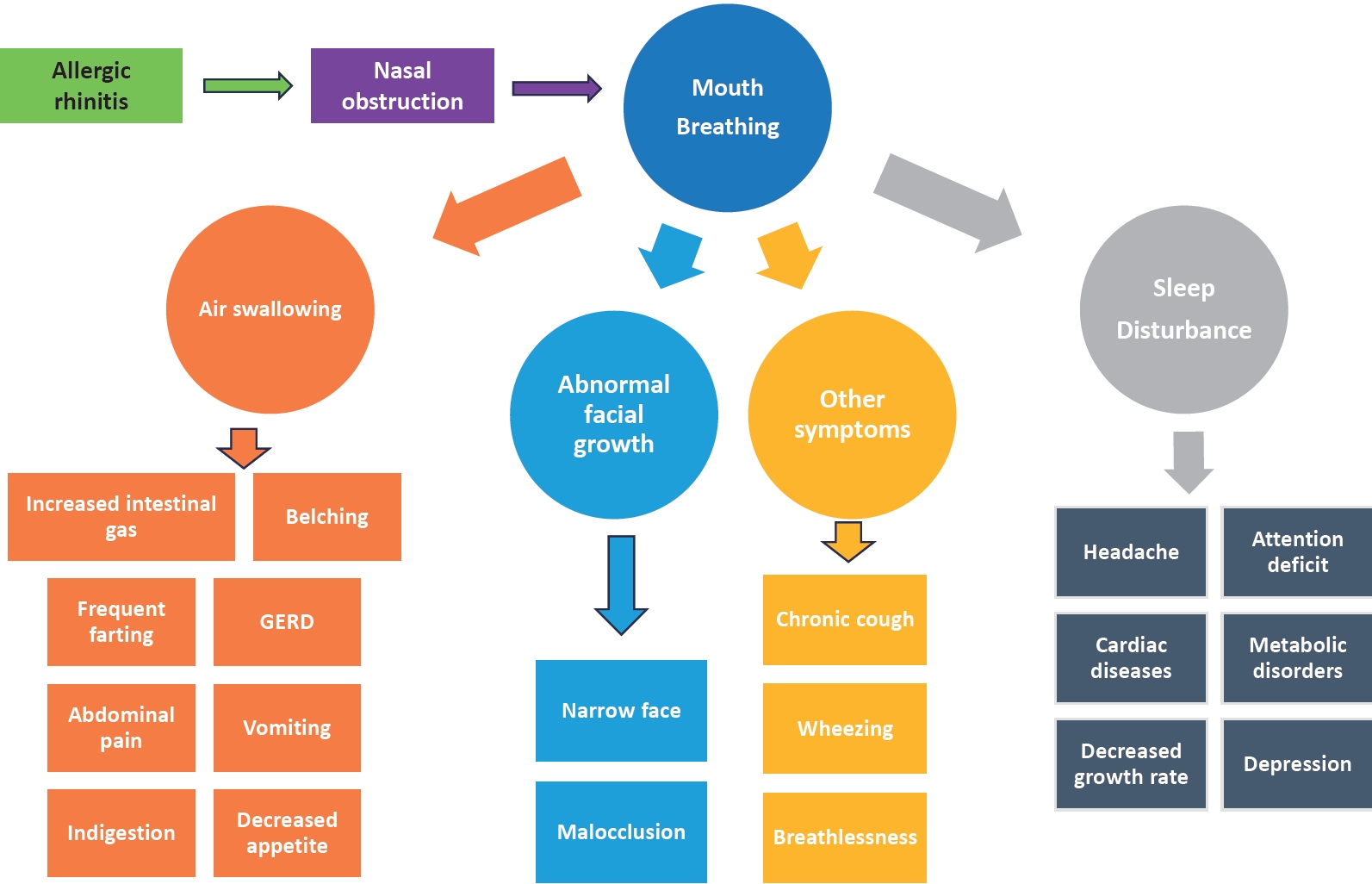
· Allergic rhinitis in children often goes undiagnosed or untreated, with significant systemic complications like sleep disorders, growth issues, and gastrointestinal symptoms linked to nasal obstruction.
· A patient-centered action plan that considers symptom severity, preferences, and comprehensive management of associated complications is essential for effective treatment.
- Review Article
- Immunology
- Systemic autoinflammatory disorders (3,629 times)
- Dae Chul Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):432-438. Published online June 14, 2023
-
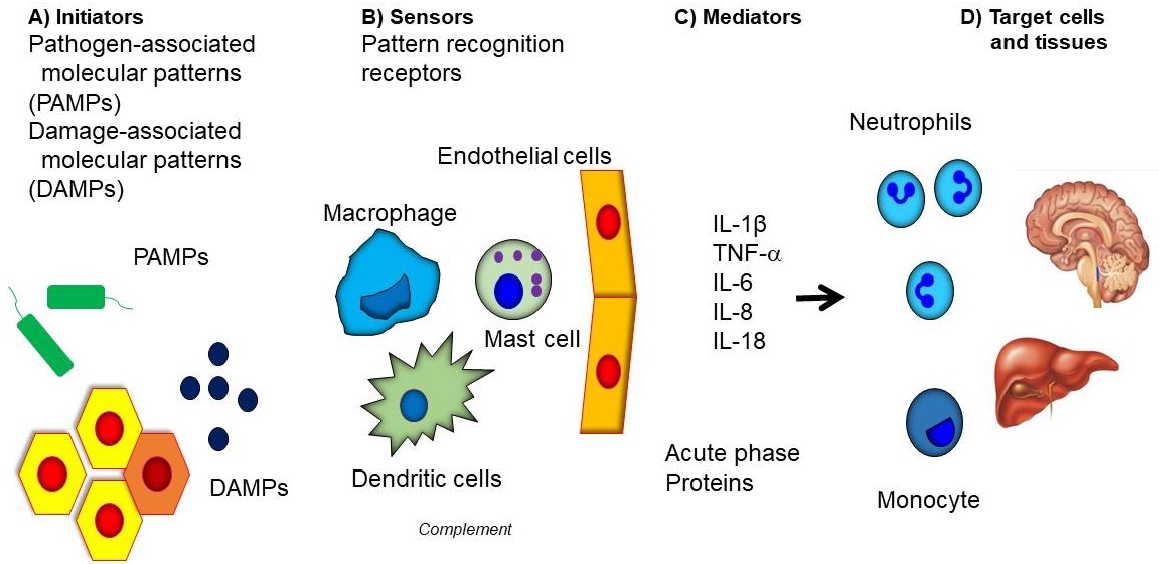
· Systemic autoinflammatory disorders (SAID) are disorders caused by dysregulation of the innate immunity with genetic background, leading to recurrent episodes of systemic inflammation.
· SAID is characterized by recurrent acute inflammatory responses including fever or skin manifestations, unrelated with infection or malignancy.
· Diagnosis is based on family and long-term history with detailed clinical and laboratory manifestations during febrile periods.
- Original Article
- Other
- Balance assessment with decreased base of support for children with disabilities (3,624 times)
- Guilherme M. Cesar, Madison Giebler, Thad W. Buster, Judith M. Burnfield
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):718-724. Published online November 11, 2024
-
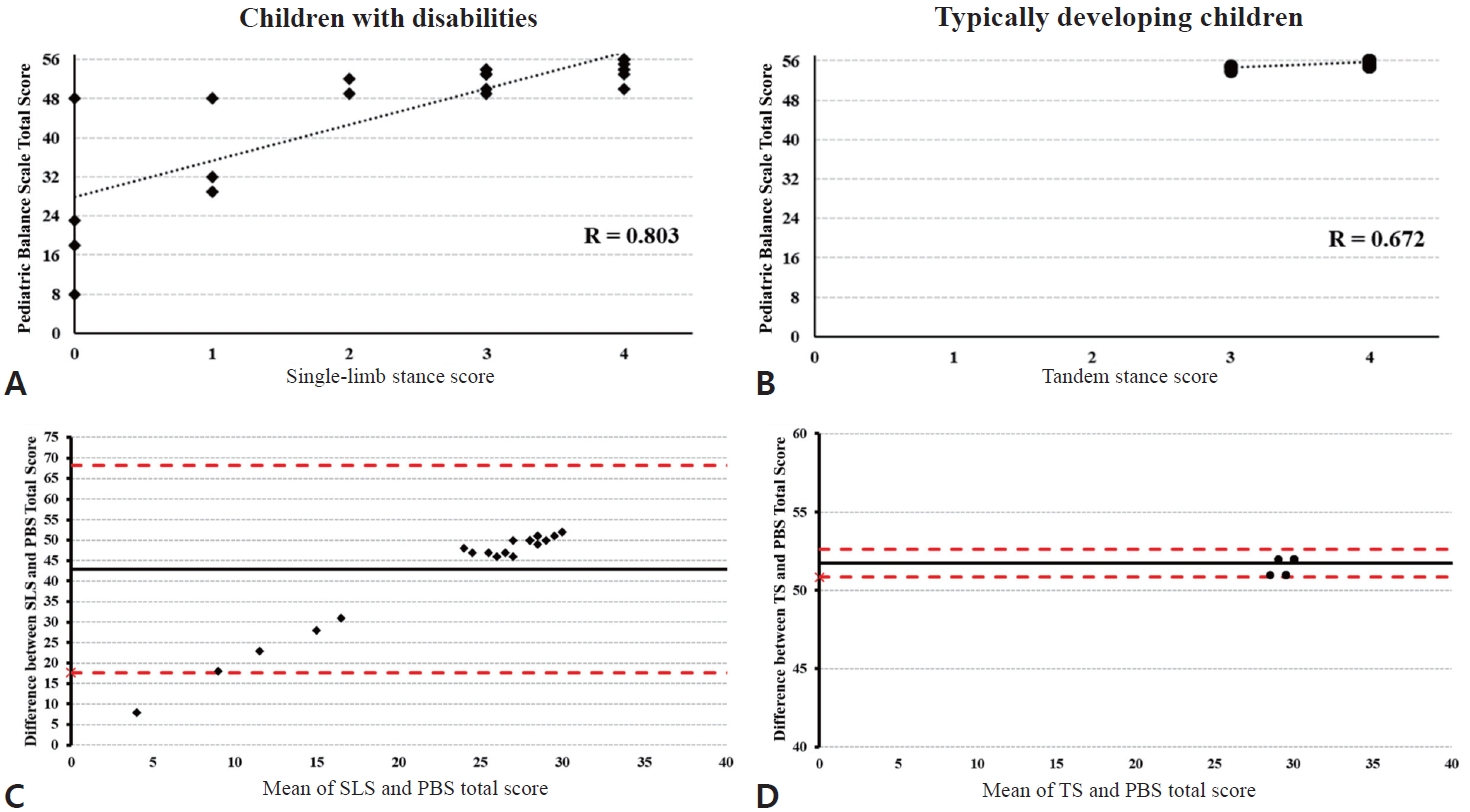
Question: Can a balance task with narrowed base of support indicate overall functional balance control in children with disabilities?
Finding: While single-limb standing could explain overall balance control for children with disabilities, it was unrelated with balance control for typically developing children.
Meaning: One balance task with narrowed base of support can be used as practical assessment of balance abilities for children with disabilities when allocated session time is of concern.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccines: February 26, 2021, To June 4, 2022, Republic of Korea (3,604 times)
- Yeon-Kyeng Lee, Yunhyung Kwon, Yesul Heo, Eun Kyoung Kim, Seung Yun Kim, Hoon Cho, Seontae Kim, Mijeong Ko, Dosang Lim, Soon-Young Seo, Enhi Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):415-423. Published online June 13, 2023
-
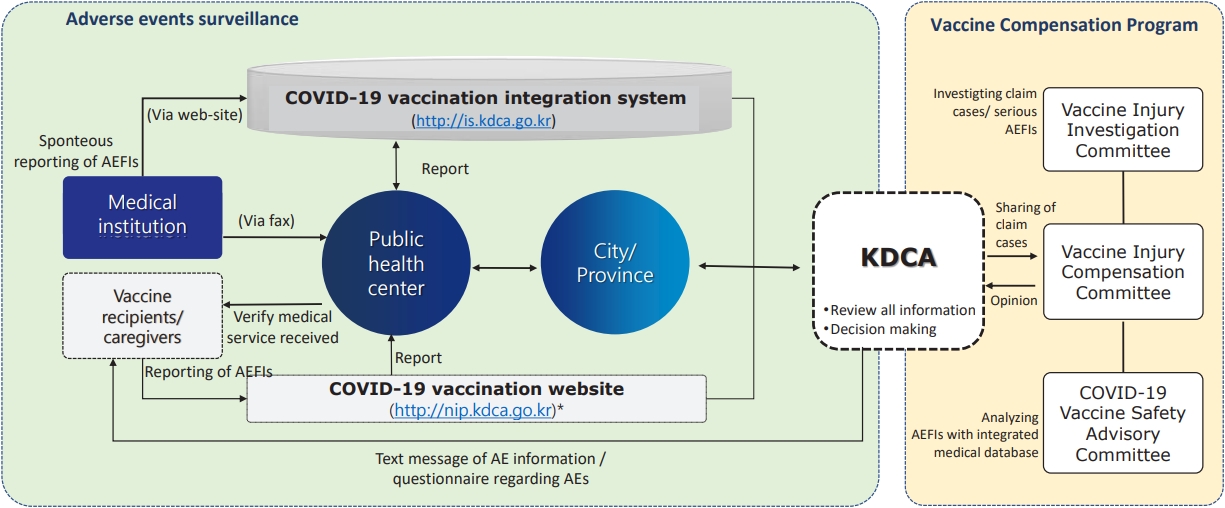
· Enhanced safety monitoring system of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines were implemented to detect signals rapidly as part of the national COVID-19 vaccination program.
· As of June 4, 2023, reported adverse events after COVID-19 vaccination was 0.38% among 125,107,883 doses of COVID- 19 vaccines administered.
· Most reported adverse reactions after COVID-19 vaccinations have shown nonserious and mild intensity.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone score changes in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency (3,602 times)
- Pattara Wiromrat, Yutapong Raruenrom, Phanpaphorn Namphaisan, Nantaporn Wongsurawat, Ouyporn Panamonta, Chatlert Pongchaiyakul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):238-246. Published online November 13, 2024
-
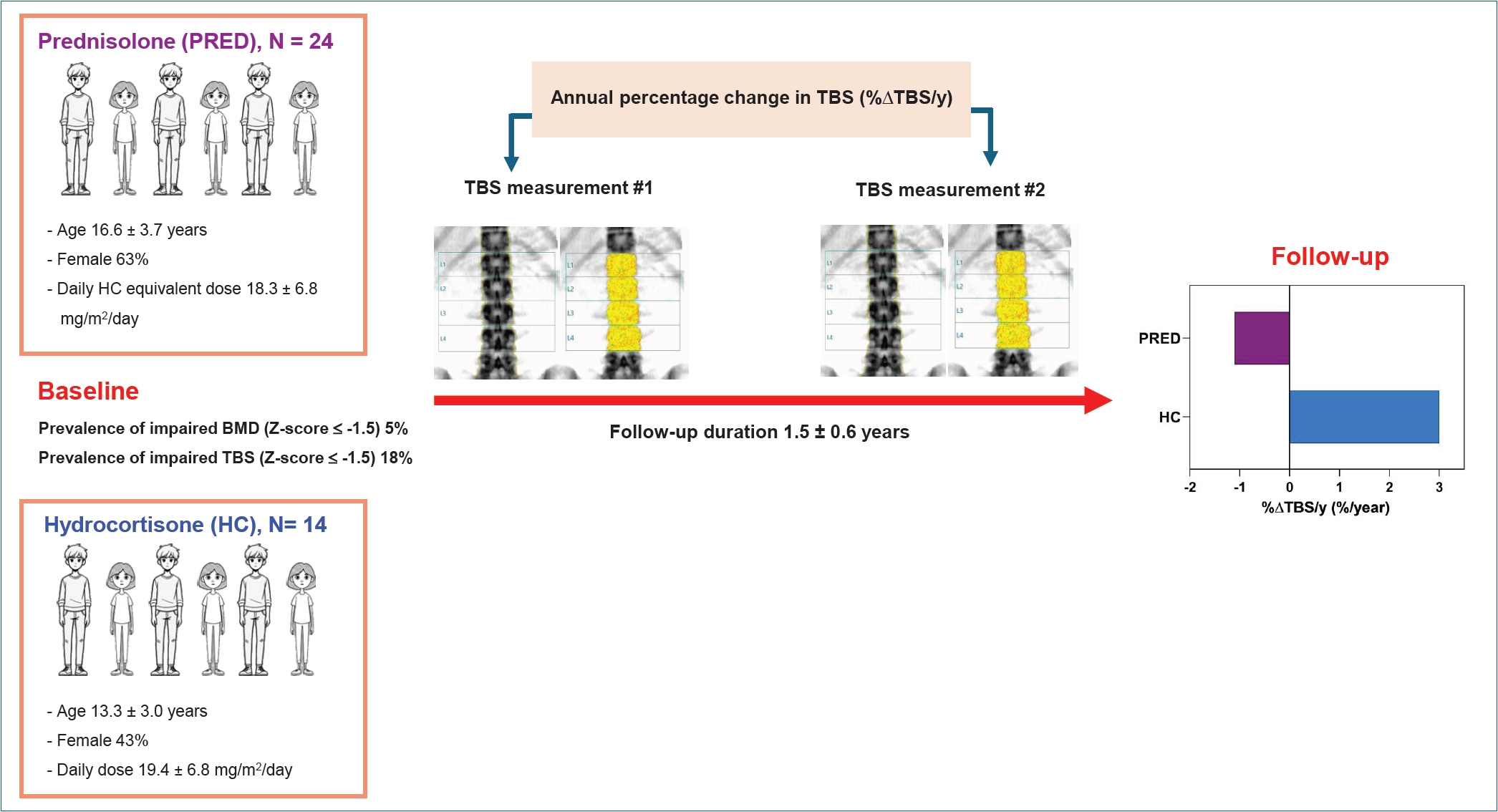
Question: What is the prevalence of an impaired trabecular bone score (TBS), a measure of bone microarchitecture, in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency (21OHD)? Do prednisolone and hydrocortisone affect TBS differently in this patient population?
Finding: Impaired TBS was observed in 18% of participants. Prednisolone use negatively impacted TBS change.
Meaning: Impaired TBS is prevalent among adolescents with 21OHD. Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone microarchitecture development.
- Cardiology
- Echocardiographic reference z scores of right ventricular dimension and systolic function of children aged 5–12 years (3,547 times)
- Alaba Busola Oladimeji, Moriam Omolola Lamina, Peter Odion Ubuane, Motunrayo Oluwabukola Adekunle, Omolara Adeolu Kehinde, Barakat Adeola Animasahun, Olisamedua FidelisNjokanma
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):215-222. Published online April 18, 2023
-

Question: Z score reference values for right ventricular size and systolic function in children using echocardiography are available in several countries. Despite the high burden of diseases involving the right ventricle in Nigeria, these reference values have limited applicability.
Finding: The right ventricular sizes of Nigerian children differed from those published elsewhere.
Meaning: These reference values will aid the treatment, monitoring, and pre- and postintervention for Nigerian children.
- Gastroenterology
- Inferior vena cava to aorta ratio in dehydrated pediatric patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis (3,546 times)
- Gilbert Sterling Octavius, Michelle Imanuelly, Johan Wibowo, Nadia Khoirunnisa Heryadi, Melanie Widjaja
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):477-484. Published online June 14, 2023
-
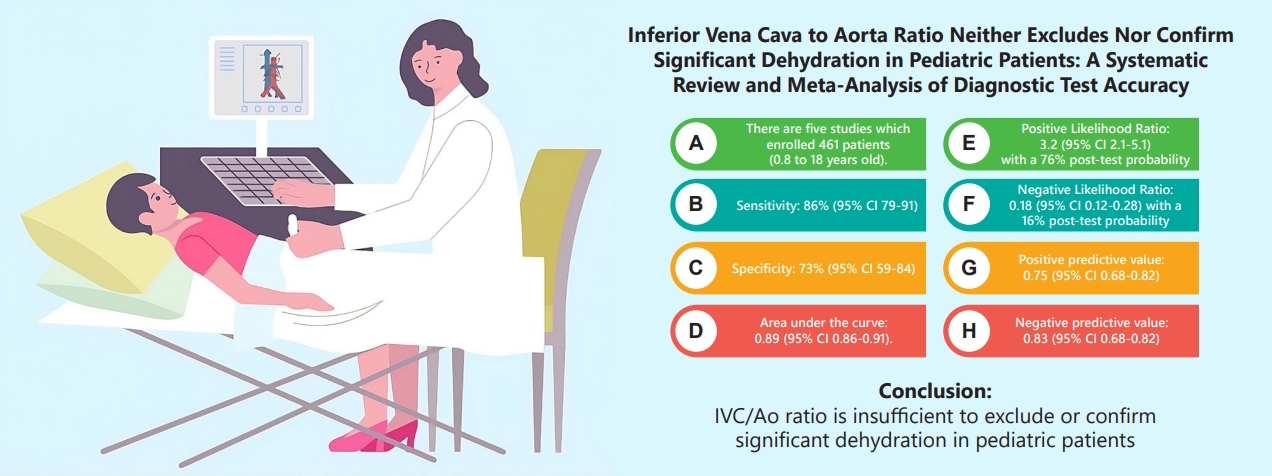
Question: The inferior vena cava to aorta (IVC/Ao) ratio measured via ultrasound has been touted as a promising noninvasive technique to assess clinically significant dehydration in pediatric patients.
Finding: Our meta-analysis found that IVC/Ao ratio had a positive likelihood ratio of 3.2 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.1–5.1) and negative likelihood ratio of 0.18 (95% CI, 0.12–0.28).
Meaning: Hence, IVC/Ao ratio is insufficient to exclude or confirm significant dehydration in pediatric patients.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Role of social media use in onset of functional gastrointestinal disorders in children (3,543 times)
- Mauro Cinquetti, Vanessa Dargenio, Michele Fingerle, Carolina Marchiotto, Marco Biasin, Massimo Pettoello Mantovani, Flavia Indrio
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):226-232. Published online December 21, 2022
-
· Social media use can cause adverse health outcomes, including gastrointestinal disorders, in children and adolescents.
· Recent findings have shown a high prevalence of social media use and decreased well-being in patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders.
· The biopsychosocial nature of functional gastrointestinal disorders and the clear influence of social media on the psychosocial lives of children suggests the likely involvement of social media in their development.
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Evaluation of pediatric migraine triggers: a single-center study (3,528 times)
- Hey-Joon Son, Joo-Ok Jin, Kon-Hee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):163-169. Published online November 11, 2024
-
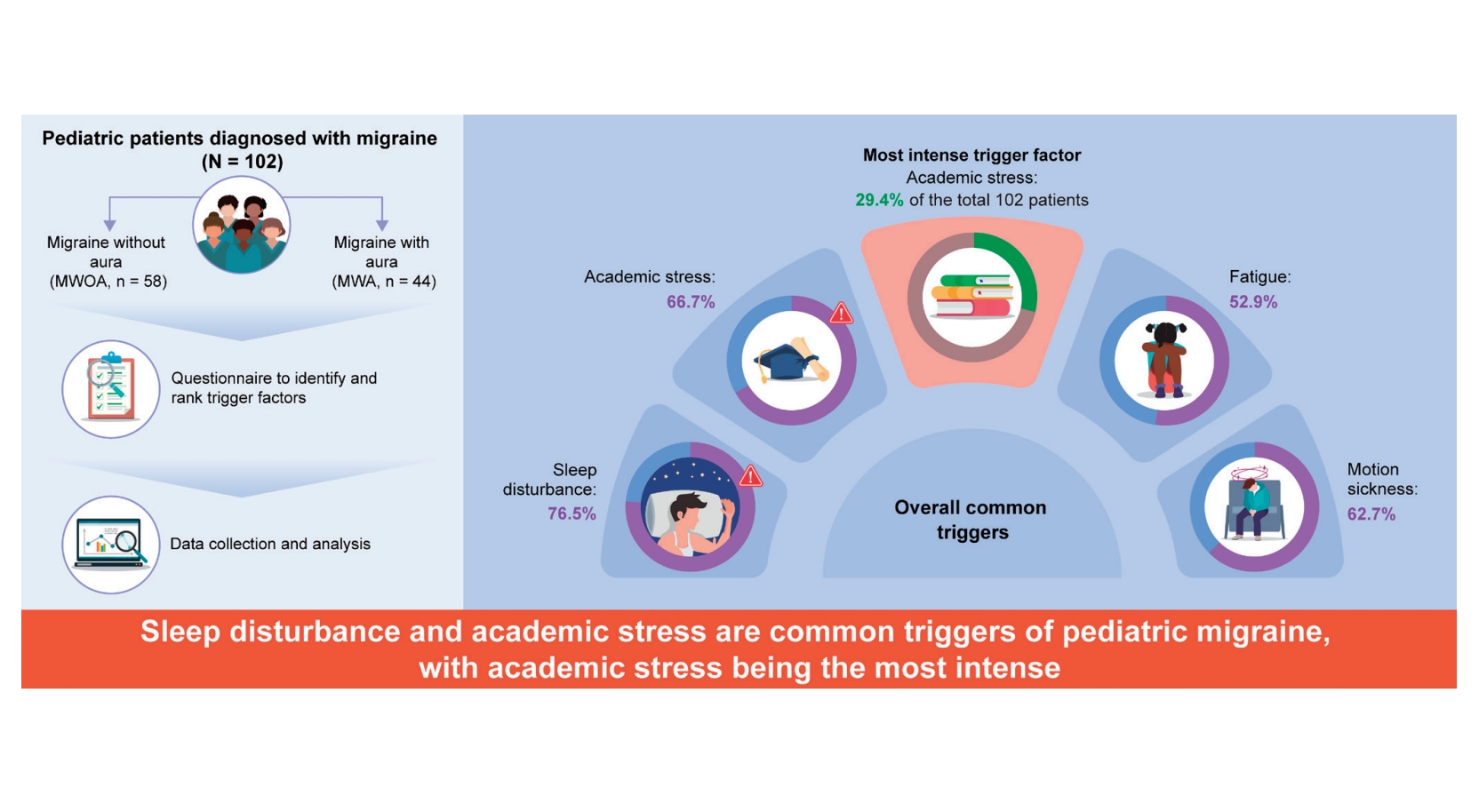
Question: What are the primary triggers for pediatric migraines, and how do they impact clinical management?
Finding: Common triggers for pediatric migraines include sleep disturbances, academic stress, and motion sickness, with academic stress identified as the most intense.
Meaning: Recognizing and addressing specific triggers like sleep disturbance and academic stress is crucial to effectively managing pediatric migraines with emphasis on personalized care to improve outcomes.
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Arrhythmia and COVID-19 in children (3,513 times)
- Mi Kyoung Song, Bryan Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):190-200. Published online April 18, 2023
-
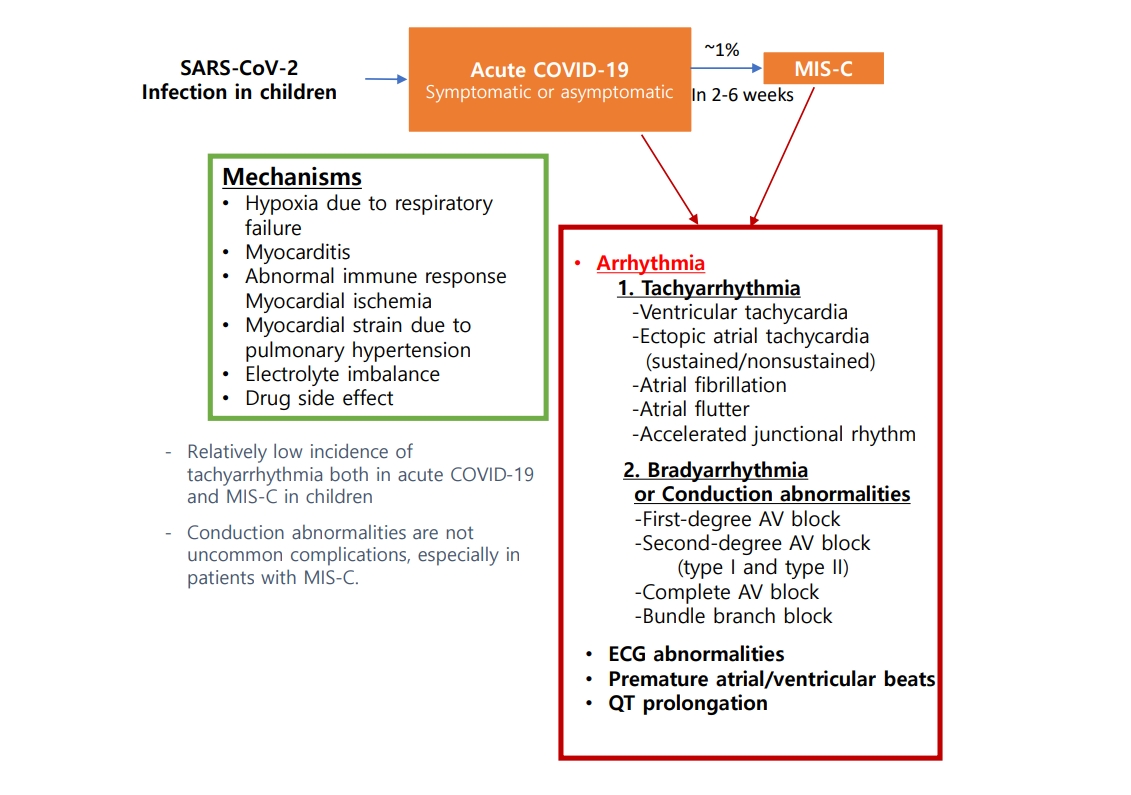
· Pediatric patients have a relatively low incidence of tachyarrhythmia both in acute coronavirus disease 2019 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), but it was associated with an increased risk of poor outcomes.
· Conduction abnormalities were not uncommon, especially in those with MIS-C. Most patients recovered to normal sinus rhythm; however, some progressed to advanced atrioventricular block and rarely required permanent pacemaker implantation.
- Infection
- Incidence, causative organisms, and risk factors of bloodstream infections in pediatric liver transplant patients: a systematic review (3,497 times)
- Mohamad Shieb, Rand Hasanain, Zara Arshad, Faisal A. Nawaz, Rahul Kashyap, Eric J. Stern
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):427-434. Published online April 5, 2024
-

The overall incidence of bloodstream infections was 23.5%. Gram-negative organisms occur at a much higher rate in pediatric liver transplant recipients then that the general pediatric population. However, when comparing pediatric and adult liver transplant recipients Gram-positive organisms occur with a much higher rate in the pediatric population highlighting the importance of early and broad spectrum antimicrobial coverage when bloodstream infections are suspected.
- Endocrinology
- Applications of genomic research in pediatric endocrine diseases (3,477 times)
- Ja Hye Kim, Jin-Ho Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):520-530. Published online June 14, 2023
-
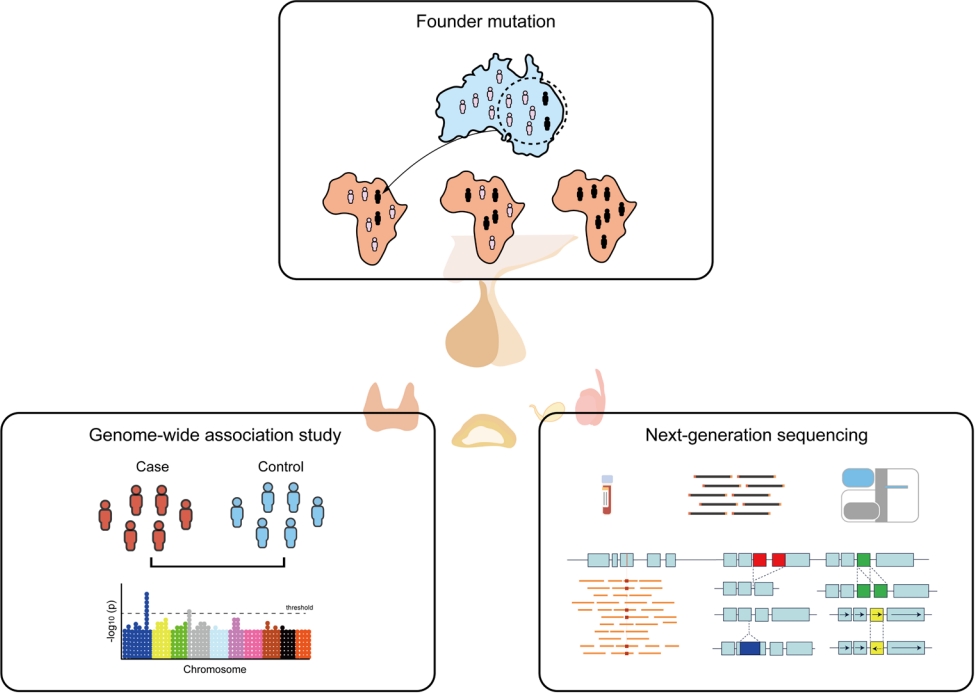
· Recent advances in molecular genetics have improved our understanding of pediatric endocrine disorders and are now used in mainstream medical practice.
· Genome-wide association studies can increase our understanding of the biological mechanisms of disease and inform new therapeutic options.
· The identification of founder mutations leads to the efficient localization of the genes underlying Mendelian disorders.
· Next-generation sequencing technologies benefit clinical practice and research of pediatric endocrinology.
- Other
- Peripheral nerve sheath tumors in the head and neck in patients with APC gene deletion mutations: a case report and scoping review of the literature (3,469 times)
- Koral M. Blunt, Monirah Albathi, Miriam Conces, Tendy Chiang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):428-433. Published online January 13, 2025
-
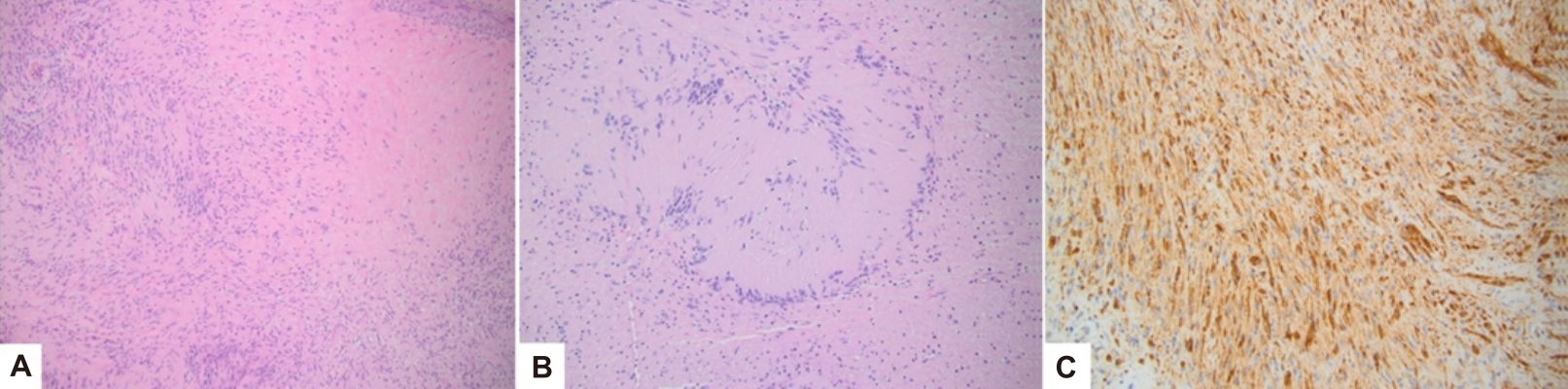
In this report, we describe our experience with a patient with an APC-related genetic syndrome who presented with a rare palatal lesion with characteristics of a schwannoma. We discuss the role of immunohistochemical staining in discerning the differential diagnosis.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Clinical characteristics and associated factors of pediatric acute necrotizing encephalopathy: a retrospective study (3,458 times)
- Huiling Zhang, Yilong Wang, Qianyun Ding, Xuekun Li, Sheng Ye
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):153-162. Published online November 11, 2024
-
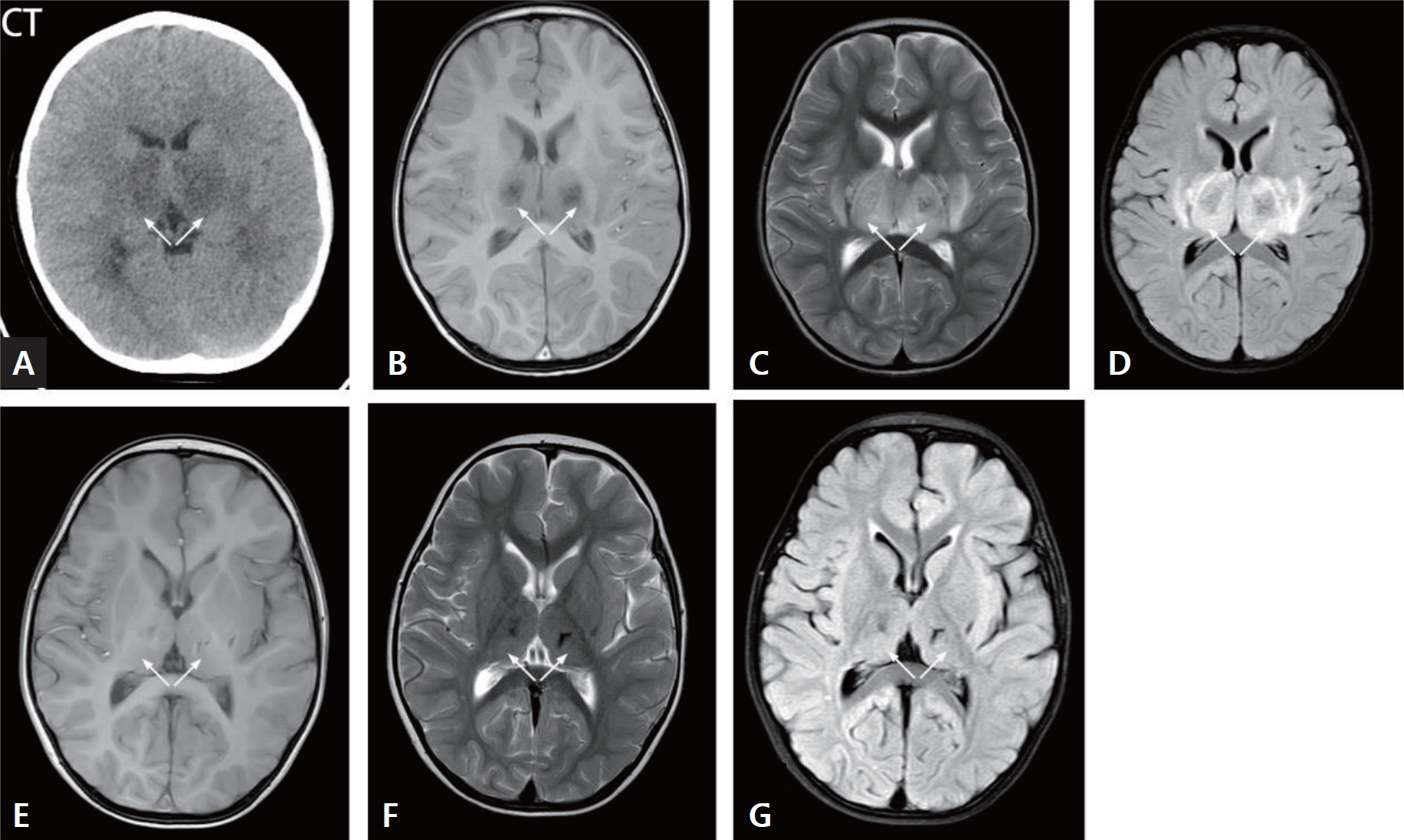
· The mortality rate of acute necrotizing encephalopathy was high.
· Laboratory tests revealed that the fatal group had higher creatinine, lactate, activated partial thromboplastin time, thrombin time, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, creatine kinase, and D-dimer than survivors.
· The fatal group displayed lower Glasgow Coma Scale scores and arterial pH.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Association between maternal coronavirus disease 2019 and transient tachypnea of the newborn: a single-center study (3,429 times)
- Sung Hee Lee, Ju Hyun Jin, Jong Ha Yoo, Shin Won Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):493-500. Published online October 24, 2023
-
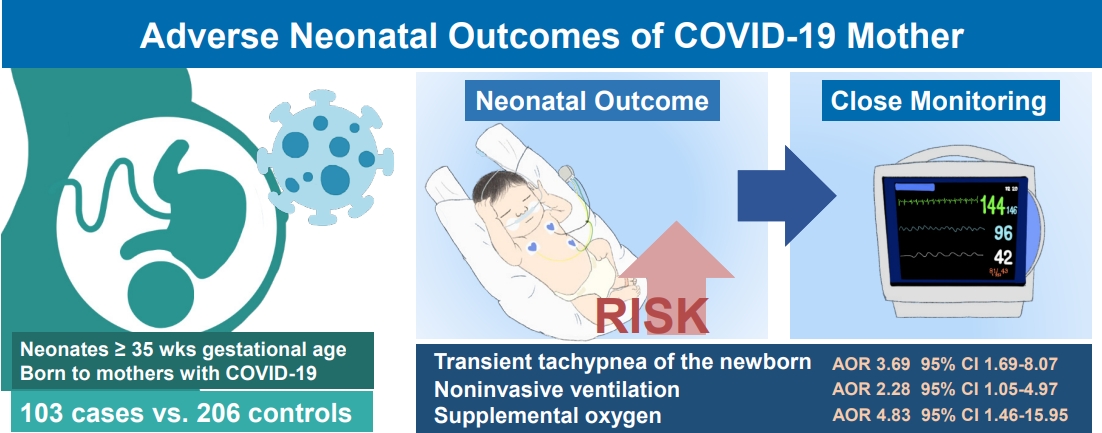
Question: What are the adverse clinical outcomes of neonates of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)–infected mothers?
Finding: Infants of mothers with COVID-19 were at significantly increased risk of transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN), use of noninvasive ventilation, and need for supplemental oxygen (P<0.05).
Meaning: Neonates of mothers with COVID-19 are at risk of TTN and require respiratory support. Close monitoring is essential to ensuring timely intervention if required.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Parenting stress and interactive engagement behaviors in children with developmental delay (3,419 times)
- Jung Sook Yeom, Rock Bum Kim, Jae Young Cho, Ji Sook Park, Eun Sil Park, Ji-Hyun Seo, Jae-Young Lim, Hyang-Ok Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):252-261. Published online May 19, 2023
-
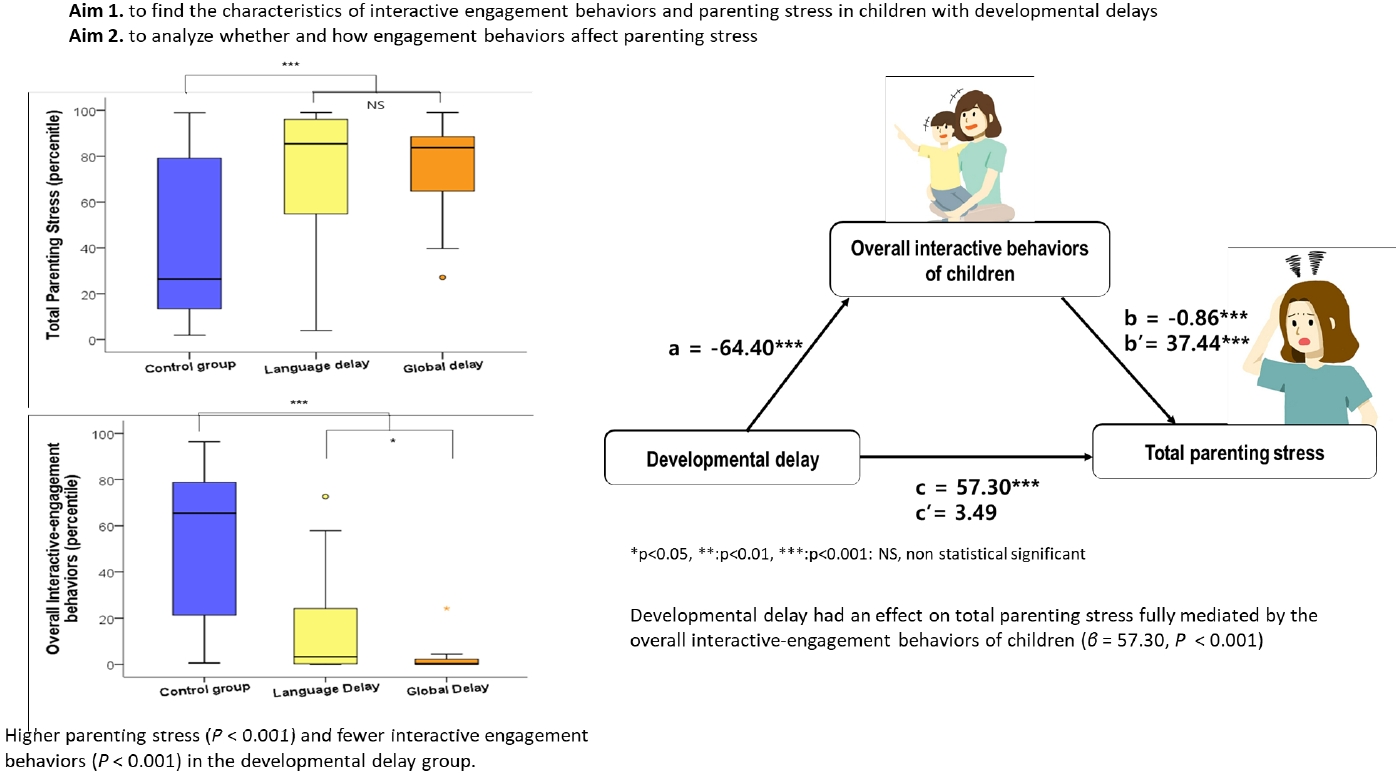
· Question: What level of parenting stress is experienced by parents of children with developmental delays (DDs) without autism spectrum disorder, and what factors contribute to it?
· Findings: Parents of children with DDs experienced high parenting stress that were significantly mediated by their children’s low interactive behaviors.
· Meaning: The interactive behaviors of children with DDs mediate parenting stress.
- Endocrinology
- Kisspeptin and DLK1 levels for monitoring treatment of girls with central precocious puberty (3,408 times)
- Witchuwan Onsoi, Nattakarn Numsriskulrat, Suphab Aroonparkmongkol, Vichit Supornsilchai, Khomsak Srilanchakon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):296-302. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Questions: Can the serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 be potential biomarkers for monitoring the treatments for central precocious puberty (CPP)?
Findings: There were no significant differences in the baseline serum kisspeptin and DLK1 levels in CPP girls compared to girls with premature thelarche (PT). After 6 months of GnRH analogue treatment in CPP girls, median serum kisspeptin levels decreased, while median serum DLK1 levels increased compared to baseline.
Meanings: Serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 may serve as novel biomarkers for monitoring the efficacy of treatments for CPP.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Impact of short and intensive art-based intervention on symptomatology and social interactions among children with autism spectrum disorder (3,356 times)
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Bayar Mohammed Omar Abdulla, Pranee Liamputtong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):447-454. Published online September 14, 2023
-

Question: Does a short and intensive art-based intervention affect symptoms and social interactions among children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Finding: The short and intensive art-based intervention did not affect symptoms in children with ASD level 2 or 3, including social awareness, social cognition, social communication, social motivation, and autistic mannerisms.
Meaning: The short and intensive art-based intervention did not improve the symptoms of patients with ASD.
- Infection
- Clinical, biochemical, and genetic study of TACE/TNF-α/ACE signaling pathway in pediatric COVID-19 infection (3,345 times)
- Ahmed El-Abd Ahmed, Sawsan M.A. Abuhamdah, Mohammed H. Hassan, Nagwan I. Rashwan, Eman A. Abd-Elmawgood, Haggagy Mansour, Hoda S. Sherkawy, Shymaa G. Rizk
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):704-717. Published online November 27, 2024
-
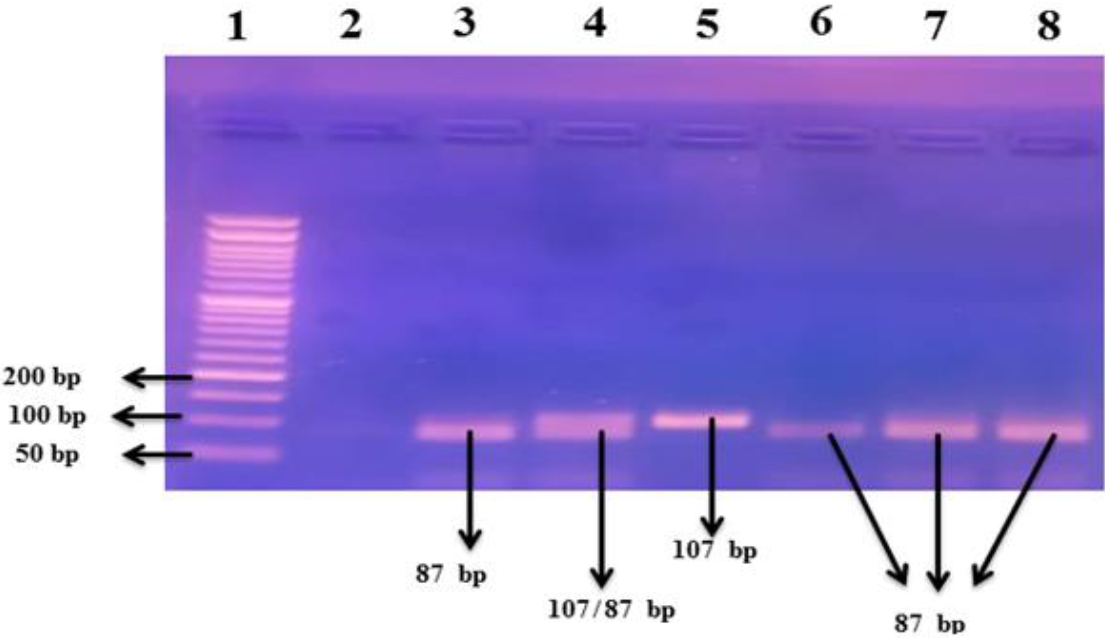
Question: Is the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathway (TNF-α-converting enzyme [TACE]/TNF-α/angiotensin converting enzyme [ACE]) involved in pediatric coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection?
Finding: Significantly increased circulating TACE/TNF-α and decreased ACE2 levels were noted. TNF-α-308G/A plays a significant role in susceptibility to COVID-19 infection among children. The ACE (I/D) (rs4646994) and ACE2 (rs2285666) single nucleotide polymorphisms lack significant associations with pediatric COVID-19 infection.
Meaning: The TNF signaling pathway participates in pediatric COVID-19 infection.
- Clinical Note
- Gastroenterology
- Abdominal pain in a young girl: a twist in the tale (3,339 times)
- Upasana Ghosh, Ankit Agrawal, Umesh Shukla, Vikas Jain, Deeksha Bhalla
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):395-397. Published online March 11, 2025
-
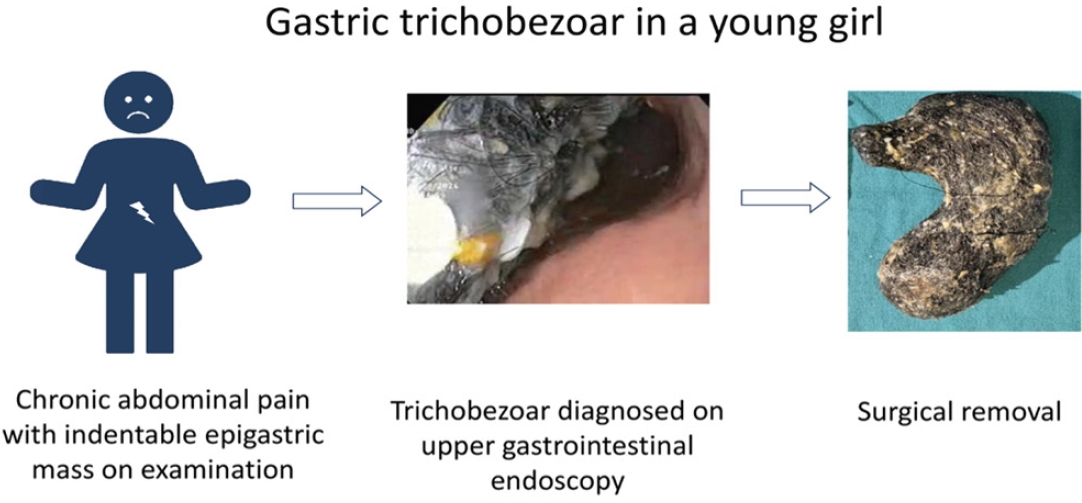
· Chronic abdominal pain caused by a gastric trichobezoar is extremely rare among children.
· An indentable epigastric mass is characteristic and upper gastrointestinal endoscopy is diagnostic of a gastric trichobezoar.
· Symptomatic large trichobezoars usually require surgery.
· Neuropsychiatric disorders are often associated with gastric trichobezoar, making a psychiatric evaluation of paramount importance.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Oligohydramnios affects pulmonary functional/structural abnormalities in school-aged children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (3,333 times)
- Jeong Eun Shin, Soon Min Lee, Mi-Jung Lee, Jungho Han, Joohee Lim, Haerin Jang, Ho Seon Eun, Min Soo Park, Soo Yeon Kim, Myung Hyun Sohn, Ji Ye Jung, Kyung Won Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):257-266. Published online April 16, 2024
-

Question: Is bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) associated with functional/structural abnormalities later in life?
Finding: School-aged children with severe BPD had abnormalities on pulmonary function tests and lung computed tomography despite no subjective respiratory symptoms; however, only prenatal oligohydramnios and prolonged ventilator use were associated with abnormal lung function.
Meaning: Long-term monitoring of preterm infants’ lung health is essential, especially for those with prenatal oligohydramnios or prolonged ventilator use.
- Gastroenterology
- Adenosine deaminase and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist genetic polymorphisms among obese children with versus without metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (3,328 times)
- Hala M. Sakhr, Mohammed H. Hassan, Azza Mohamed Taha, Ali Helmi Bakri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):808-818. Published online May 29, 2025
-
Question: Is there an association between adenosine deaminase (ADA) G22A and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RN) genetic polymorphisms and pediatric metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)?
Finding: The GG genotype and G allele of ADA G22A were significantly associated with obesity but not pediatric MAFLD, while the *1/*2 genotype of the IL-1RN gene was significantly associated with obesity and pediatric MAFLD.
Meaning: The IL-1RN gene may contribute to pediatric MAFLD.
- Adolescence Medicine
- Relationship between inflammatory biomarkers and insulin resistance in excess-weight Latin children (3,293 times)
- Mariano Nicolás Aleman, María Constanza Luciardi, Emilce Romina Albornoz, María Cristina Bazán, Adela Victoria Abregú
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):37-45. Published online December 21, 2023
-
Question: What is the prevalence of insulin resistance (IR) in excess-weight Latin children, and can proinflammatory biomarkers predict it?
Finding: IR prevalence was elevated and tumor necrosis factor- α, interleukin-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein- 1, soluble CD40 ligand, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels were increased in excess-weight Latin children. However, none predicted IR status.
Meaning: These inflammatory biomarkers were unable to predict IR status. Therefore, further investigations are necessary.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effectiveness of online responsive teaching in young children with developmental disabilities: a pilot study (3,288 times)
- Jung Sook Yeom, Jeongmee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):303-311. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Question: Does online responsive teaching (RT) impact children's and parents’ emotions and behaviors, and do parents find it satisfactory?
Finding: Online RT significantly improved children's pivotal and problem behaviors, decreased parenting stress, and enhanced parental interactive styles with high satisfaction.
Meaning: This pilot study's findings suggest that online RT can enhance child outcomes, offering accessible interventions amid challenges such as limited access and pandemics.
- Infection
- Clinical characteristics of pediatric patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus common human coronaviruses: a national multicenter study (3,229 times)
- In Suk Sol, Eun Lee, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Yong Ju Lee, Hye Yung Yum, Mi-Hee Lee, Mi Ae Chu, Hui Jeong Moon, Hyo-Bin Kim, Ju Hee Seo, Jung Yeon Shim, Ji Young Ahn, Yoon Young Jang, Hai Lee Chung, Eun Hee Chung, Kyunghoon Kim, Bong-Seong Kim, Cheol Hong Kim, Yang Park, Meeyong Shin, Kyung Suk Lee, Man Yong Han, Soo-Jong Hong, Eun Kyeong Kang, Chang Keun Kim; on behalf of The Pneumonia & Respiratory Disease Study Group of Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):134-141. Published online December 22, 2022
-

Question: The clinical differences between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and human coronaviruses (HCoV) in children remain unknown.
Finding: This study compared the clinical findings of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus HCoV. Its findings suggest that children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 have a milder clinical course than those with HCoV.
Meaning: The clinical course of children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 should be closely monitored during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Oral administration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates intestinal injury in necrotizing enterocolitis (3,229 times)
- Yeong Seok Lee, Yong Hoon Jun, Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):152-160. Published online February 19, 2024
-
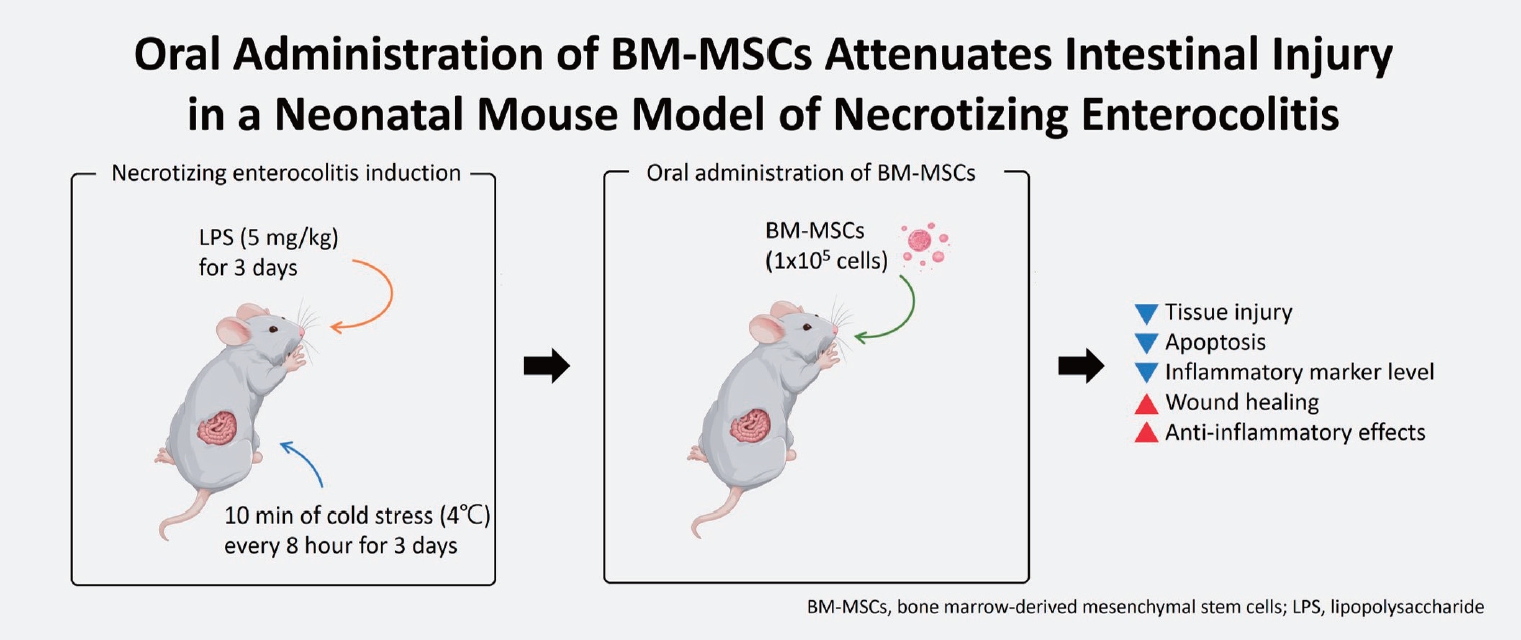
Question: What is the optimal dose of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) for treating necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), and is orally administered BM-MSC effective?
Findings: High (1×106 cells) or multiple BM-MSC doses showed similar effects as low (1×105 cells) doses of intraperitoneally administered BM-MSCs. Furthermore, orally administered BM-MSCs were as effective as intraperitoneally administered BM-MSCs.
Meaning: Orally administered low-dose BM-MSCs are a potential treatment for NEC.
- Letter to the Editor
- Critical Care Medicine
- Role of serum bilirubin-to-albumin ratio as a prognostic index in critically ill children (3,227 times)
- You Min Kang, Ga Eun Kim, Mireu Park, Jong Deok Kim, Min Jung Kim, Yoon Hee Kim, Kyung Won Kim, Myung Hyun Son, Soo Yeon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):85-87. Published online December 5, 2022
-
- Clinical Note
- Immunology
- Comparative analysis of rare periodic fever syndromes including the first Korean case of hyperimmunoglobulinemia D and periodic fever syndrome (3,220 times)
- Yoonsun Yoon, Hyun Seo Kim, Jung Ok Shim, JungHwa Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):550-552. Published online September 24, 2024
-

-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











