Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Neonatal hypertension: concerns within and beyond the neonatal intensive care unit
- Kathleen Altemose, Janis M. Dionne
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):367-376. Published online May 30, 2022
-
Some neonates, especially those who are premature, may experience hypertension while in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). The most common causes are prematurity-related and the hypertension usually resolves over the first 1–2 years of life. Unfortunately, the increasing population of NICU graduates is at risk for later cardiovascular and kidney disease in childhood and adulthood. This population requires careful attention to blood pressure and weight throughout their life course.
- Original Article
- Other
- Plastic bottle feeding produces changes in biochemical parameters in human infants – A pilot study
- Mahendra K. Pant, Abul. H. Ahmad, Manisha Naithani, Jayanti Pant
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):459-465. Published online May 19, 2022
-

Question: Plastic feeding bottles are used commonly to feed infants who cannot be breastfeed. Does plastic bottle feeding produce biochemical changes in infants?
Finding: The plastic bottles leach out endocrine disruptors and affects bodily functions in terms of biochemical alterations like increased blood urea, raised creatine-kinase–MB levels, and altered lipid profile in infants exposed to bottle feeding.
Meaning: Plastic bottles feeding alters bodily functions in infants.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Growth patterns of preterm infants in Korea
- Joohee Lim, So Jin Yoon, Soon Min Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):1-9. Published online July 8, 2021
-
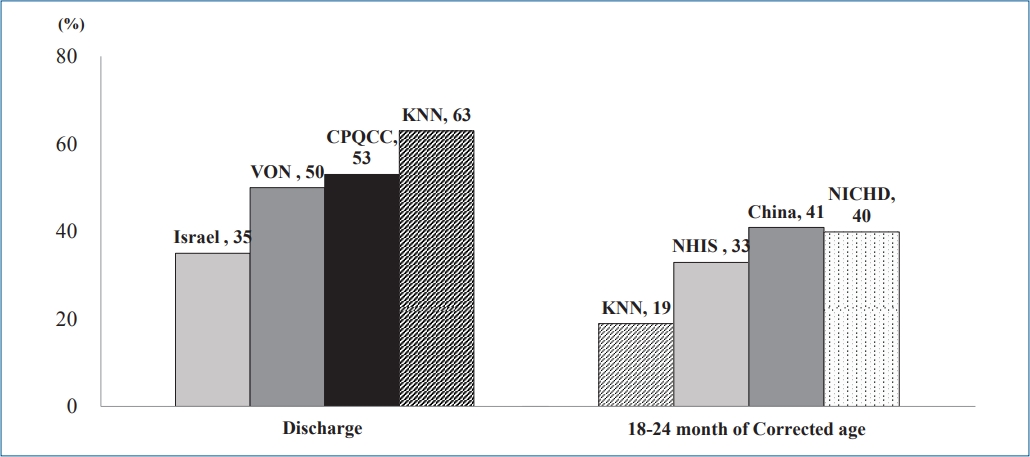
∙ The growth of preterm infants is a main focus of neonatology.
∙ Preterm infants in Korea, especially those with a very low birth weight, achieve retarded growth.
∙ Careful growth monitoring and early intervention will contribute to better development outcomes and quality of life for preterm infants and improve public health.
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes of very low birth weight infants in the Neonatal Research Network of Japan: importance of neonatal intensive care unit graduate follow-up
- Yumi Kono; on behalf of the Neonatal Research Network of Japan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(7):313-321. Published online November 9, 2020
-

· Very low birth weight infants remain at high risk of developing neurodevelopmental impairments in early childhood.
· It is important to establish a network follow-up protocol and complete assessments with fewer dropouts to enable clarification of the outcomes of registered infants.
· All possible strategies should be employed to maintain good compliance after neonatal intensive care unit discharge.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Fluconazole prophylaxis against invasive candidiasis in very low and extremely low birth weight preterm neonates: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Mahmoud Robati Anaraki, Masoud Nouri-Vaskeh, Shahram Abdoli Oskoei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(4):172-179. Published online May 14, 2020
-
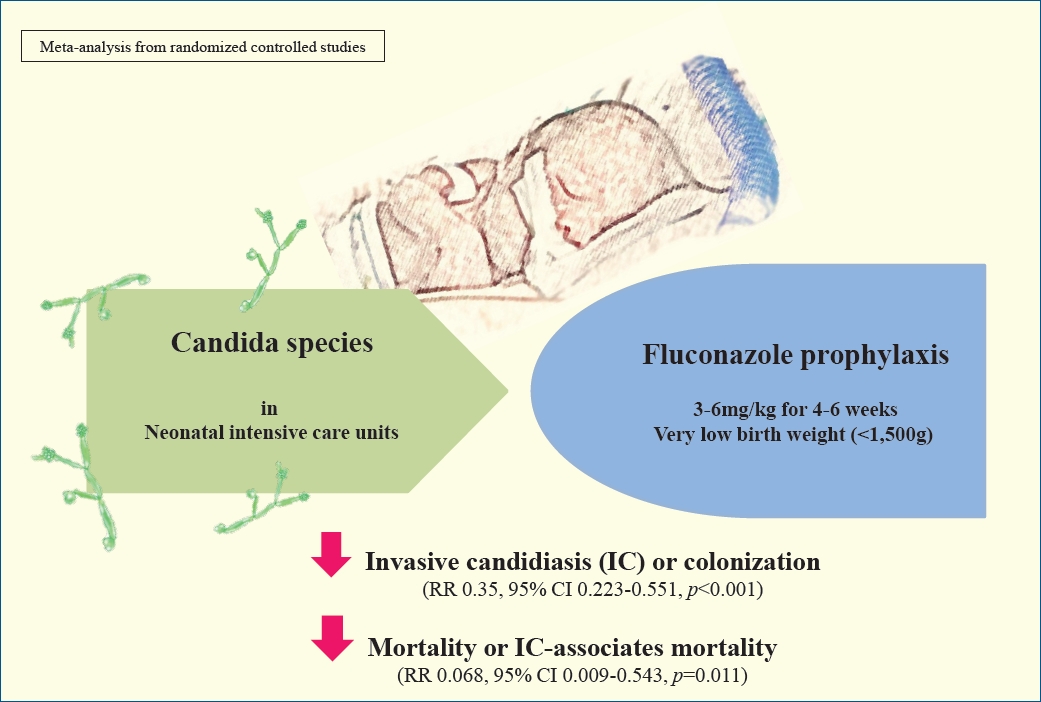
· Mortality is decreased significantly in meta-analysis of studies in different regimen of fluconazole prophylaxis.
· Significant decrease was seen in incidence of invasive candidiasis-associated mortality in extremely low birth weight infants in same schedules of prophylaxis.
· More studies required to relief the concerns.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Development of the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST)
- Hee Jung Chung, Donghwa Yang, Gun-Ha Kim, Sung Koo Kim, Seoung Woo Kim, Young Key Kim, Young Ah Kim, Joon Sik Kim, Jin Kyung Kim, Cheongtag Kim, In-Kyung Sung, Son Moon Shin, Kyung Ja Oh, Hee-Jeong Yoo, Hee Joon Yu, Seoung-Joon Lim, Jeehun Lee, Hae-Ik Jeong, Jieun Choi, Jeong-Yi Kwon, Baik-Lin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):438-446. Published online May 14, 2020
-
Question: Can the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST) be a useful screening tool for infants and children in Korea?
Finding: The K-DST has high reliability (internal consistency of 0.73–0.93, test-retest reliability of 0.77–0.88) and a high discriminatory ability with a sensitivity of 0.833 and specificity of 0.979.
Meaning: The K-DST is an effective and reliable screening tool for infants and children with neurodevelopmental disorders in Korea.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Short- and long-term outcomes of very low birth weight infants in Korea: Korean Neonatal Network update in 2019
- Jang Hoon Lee, YoungAh Youn, Yun Sil Chang; Korean Neonatal Network
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):284-290. Published online February 5, 2020
-

The Korean Neonatal Network (KNN) has collected population-based data for very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs) born in Korea since 2013. The survival rate of all VLBWIs was 86% in Korea. The overall prevalence of cerebral palsy was 6.2%–6.6%. Bilateral blindness and hearing loss were reported in 0.2%–0.3%, 0.8%–1.9%, respectively. The KNN has published annual reports and papers for facilitating the improvement of VLBWIs outcome in Korea.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Placental histopathology in late preterm infants: clinical implications
- Kristina Ericksen, Joshua Fogel, Rita P. Verma
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(2):48-51. Published online August 19, 2019
-

Question: Placental histopathology and its clinical implications in late preterm infants.
Finding: Placental vascular anomalies are more, and placental inflammation less common in late preterm infants compared to term. Higher maternal age, magnesium sulfate therapy and hypertension are clinical risk factors associated with late preterm delivery.
Meaning: Prevention and aggressive management of hypertension, and conception before 30 years of age might be effective in preventing late preterm births.
- Association between vitamin D level at birth and respiratory morbidities in very-low-birth-weight infants
- Ian Kim, Sung Shin Kim, Jee In Song, Seock Hwa Yoon, Ga Young Park, Yong-Wha Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(5):166-172. Published online October 24, 2018
-
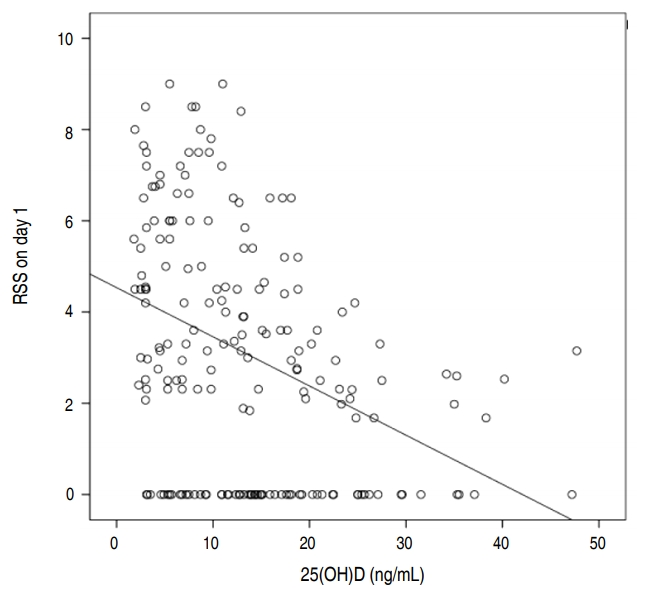
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate vitamin D status at birth in very-low-birth-weight infants (VLBWIs: <1,500 g) and to determine the association between vitamin D level and respiratory morbidity. Methods: A retrospective study was conducted at Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital between November 2013 and November 2017. We collected blood samples and data on respiratory morbidity from 230 VLBWIs on the first...
- Transient intubation for surfactant administration in the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome in extremely premature infants
- Ji Won Koh, Jong-Wan Kim, Young Pyo Chang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(10):315-321. Published online September 16, 2018
-
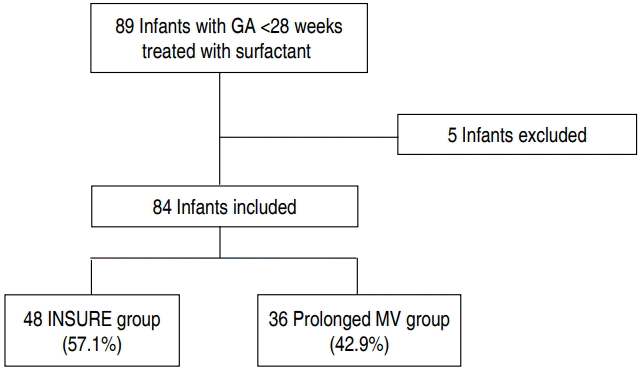
Purpose: To investigate the effectiveness of transient intubation for surfactant administration and extubated to nasal continuous positive pressure (INSURE) for treatment of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and to identify the factors associated with INSURE failure in extremely premature infants. Methods: Eighty-four infants with gestational age less than 28 weeks treated with surfactant administration for RDS for 8 years were included. Perinatal...
- The impact of a quality improvement effort in reducing admission hypothermia in preterm infants following delivery
- Han Saem Choi, Soon Min Lee, Hoseon Eun, Minsoo Park, Kook-In Park, Ran Namgung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(8):239-244. Published online August 15, 2018
-
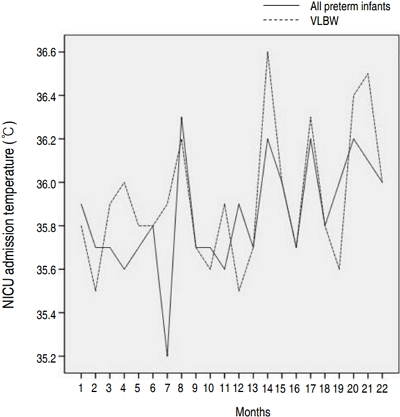
Purpose: Hypothermia at admission is associated with increased mortality and morbidity in preterm infants. We performed a quality improvement (QI) effort to determine the impact of a decrease in admission hypothermia in preterm infants. Methods: The study enrolled very low birth weight (VLBW) infants born at Gangnam Severance Hospital between January 2013 and December 2016. This multidisciplinary QI effort included the...
- Augmentation of respiratory muscle activities in preterm infants with feeding desaturation
- Dong Rak Kwon, Gi Young Park, Ji Eun Jeong, Woo Taek Kim, Eun Joo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(3):78-83. Published online March 19, 2018
-
Purpose Frequent desaturation due to immature incoordination of suck-swallow-breathing in preterm infants can influence multiple organs such as the heart, lungs, and brain, which can then affect growth and development. Most notably in preterm infants, feeding desaturation may even affect pulmonary function during gavage feeding. Because respiratory muscle activities may reflect the work required during respiration, we evaluated the differences in...
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Fetal and preterm infant microbiomes: a new perspective of necrotizing enterocolitis
- Yong-Sung Choi, In Gyu Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(10):307-311. Published online October 20, 2017
-
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating condition of hospitalized preterm infants. Numerous studies have attempted to identify the cause of NEC by examining the immunological features associated with pathogenic microorganisms. No single organism has proven responsible for the disease; however, immunological studies are now focused on the microbiome. Recent research has investigated the numerous bacterial species residing in the body...
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effects of cord blood vitamin D levels on the risk of neonatal sepsis in premature infants
- Birgul Say, Nurdan Uras, Suzan Sahin, Halil Degirmencioglu, Serife Suna Oguz, Fuat Emre Canpolat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(8):248-253. Published online August 14, 2017
-
Purpose Vitamin D plays a key role in immune function. Vitamin D deficiency may play a role in the pathogenesis of infections, and low levels of circulating vitamin D are strongly associated with infectious diseases. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the effects of low vitamin D levels in cord blood on neonatal sepsis in preterm infants.
Methods One hundred seventeen premature...
- Low levels of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 at birth may be associated with subsequent development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants
- Choae Lee, Jaewoo An, Ji Hee Kim, Eun Sun Kim, Soo Hyun Kim, Yeon Kyung Cho, Dong Hyun Cha, Man Yong Han, Kyu Hyung Lee, Youn Ho Sheen
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(11):415-420. Published online November 22, 2015
-
Purpose Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is characterized by inflammation with proteolytic damage to the lung extracellular matrix. The results from previous studies are inconsistent regarding the role of proteinases and antiproteinases in the development of BPD. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-8, MMP-9, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-2, and TIMP-1 levels in the serum of...
- Validity of bag urine culture for predicting urinary tract infections in febrile infants: a paired comparison of urine collection methods
- Geun-A Kim, Ja-Wook Koo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(5):183-189. Published online May 22, 2015
-
Purpose Catheter urine (CATH-U) and suprapubic aspiration (SPA) are reliable urine collection methods for confirming urinary tract infections (UTI) in infants. However, noninvasive and easily accessible collecting bag urine (CBU) is widely used, despite its high contamination rate. This study investigated the validity of CBU cultures for diagnosing UTIs, using CATH-U culture results as the gold standard.
Methods We retrospectively analyzed 210 infants,...
- Review Article
- Necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns: update in pathophysiology and newly emerging therapeutic strategies
- Young Youn Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(12):505-513. Published online December 31, 2014
-
While the survival of extremely premature infants with respiratory distress syndrome has increased due to advanced respiratory care in recent years, necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) remains the leading cause of neonatal mortality and morbidity. NEC is more prevalent in lower gestational age and lower birth weight groups. It is characterized by various degrees of mucosal or transmural necrosis of the intestine....
- Original Article
- The relationship between eosinophilia and bronchopulmonary dysplasia in premature infants at less than 34 weeks' gestation
- Joo Yun Yang, Jihei Cha, So-Yeon Shim, Su Jin Cho, Eun Ae Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(4):171-177. Published online April 30, 2014
-
Purpose Eosinophilia is common in premature infants, and its incidence increases with a shorter gestation period. We investigated the clinical significance of eosinophilia in premature infants born at <34 weeks gestation.
Methods We analyzed the medical records of premature infants born at <34 weeks gestation who were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit at Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital between January 2003...
- Analysis of the association between necrotizing enterocolitis and transfusion of red blood cell in very low birth weight preterm infants
- Seon-Yeong Bak, Sihyoung Lee, Jae-Hong Park, Kyu-Hee Park, Ji-Hyun Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(3):112-115. Published online March 18, 2013
-
Purpose To investigate the association between necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) and red blood cell transfusions in very low birth weight (VLBW) preterm infants.
Methods We studied were 180 VLBW preterm infants who were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit of CHA Gangnam Hospital from January of 2006 to December of 2009. The subjects were divided into 2 groups: an NEC group (greater than...
- Effect of early postnatal neutropenia in very low birth weight infants born to mothers with pregnancy-induced hypertension
- Yang Hee Park, Gyung Min Lee, Jung Min Yoon, Enn Jung Cheon, Kyung Ok Ko, Yung Hyuk Lee, Jae Woo Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(12):462-469. Published online December 20, 2012
-
Purpose In this study, we aimed to investigate the perinatal clinical conditions of very low birth weight (VLBW) infants born to mothers with pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) focusing on the effects of early postnatal neutropenia.
Methods We reviewed the medical records of 191 VLBW infants who were born at Konyang University Hospital, between March 2003 and May 2011. We retrospectively analyzed the clinical characteristics...
- Case Report
- PHACE association with intracranial, oropharyngeal hemangiomas, and an atypical patent ductus arteriosus arising from the tortuous left subclavian artery in a premature infant
- Do-Hyun Kim, Jang Hwan Choi, Jung Ha Lee, Hee Sup Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(1):29-33. Published online January 31, 2012
-
PHACE association is a rare neurocutaneous condition in which facial hemangiomas associate with a spectrum of posterior fossa malformations, arterial cerebrovascular anomalies, cardiovascular anomalies, and eye anomalies. We reported a case of PHACE association in a premature infant showing facial, intracranial, and oropharyngeal hemangiomas with evidence of the Dandy-Walker variant and complicated cardiovascular anomalies, including a right-sided aortic arch and...
- Original Article
- Outcomes of small for gestational age micropremies depending on how young or how small they are
- Hee Joon Yu, Eun Sun Kim, Jin Kyu Kim, Hye Soo Yoo, So Yoon Ahn, Yun Sil Chang, Won Soon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(6):246-252. Published online June 30, 2011
-
Purpose The outcomes of small for gestational age (SGA) infants especially in extremely low birth weight infants (ELBWIs) are controversial. This study evaluated the mortality and morbidity of ELBWIs, focusing on whether or not they were also SGA.
Methods The medical records of 415 ELBWIs (birth weight <1,000 g), who were inborn and admitted to the Samsung Medical Center neonatal intensive care unit...
- A study on the measurement of the nucleated red blood cell (nRBC) count based on birth weight and its correlation with perinatal prognosis in infants with very low birth weights
- Tae Hwan Kil, Ji Yeon Han, Jun Bum Kim, Gyeong Ok Ko, Young Hyeok Lee, Kil Young Kim, Jae Woo Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(2):69-78. Published online February 28, 2011
-
Purpose The aim of this study was conducted to investigate the mean nRBC count in very low births weight infants (VLBWIs) and to determine the usefulness of the nRBC as an independent prognostic factors of perinatal complications in VLBWIs.
Methods This study was conducted on 112 VLBWIs who were hospitalized in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) of the author's hospital within the...
- Predictive factors for severe infection among febrile infants younger than three months of age
- Eun Young Cho, Hwa Song, Ae Suk Kim, Sun Ju Lee, Dong Seok Lee, Doo Kwun Kim, Sung Min Choi, Kwan Lee, Byoung Chan Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(8):898-903. Published online August 15, 2009
-
Purpose:This study investigated the predictive factors for identifying infection-prone febrile infants younger than three months. Methods:We conducted a retrospective study of 167 infants younger than three months with an axillary temperature >38℃ who were hospitalized between 2006 and 2008. If they met any of the following criteria, positive blood culture, CSF WBC ≥ 11/mm3 or positive CSF culture, urinalysis WBC ≥6/HPF and positive... -
- A comparative study on iron deficiency anemia based on feeding patterns of nine-month-old infants
- Hyun Jin Yun, Eun Jeong Choi, Eun Jin Choi, Su Young Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(8):820-826. Published online August 15, 2008
-
Purpose : This study was conducted to evaluate the red cell indices and frequency of iron deficiency anemia based on the feeding patterns of nine-month-old infants. Methods : Blood tests were performed on 253 nine-month-old infants, who visited Il Sin Christian Hospital for health check- ups from January to December 2007. Their parents answered telephonic questions regarding their feeding patterns... -
- Growth and clinical efficacy of fortified human milk and premature formula on very low birth weight infants
- Heewon Chueh, Myo Jing Kim, Young-A Lee, Jin-A Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(7):704-712. Published online July 15, 2008
-
Purpose : A prospective, controlled trial was conducted to evaluate growth, efficacy, safety and nutritional status for very low birth weight infants fed with human milk fortified with Maeil human milk fortifier (Maeil HMF ; Maeil Dairies Co., Ltd.). Methods : We enrolled 45 premature infants with a birth weight <1,500 g and gestational age <33 weeks, who were born at... -
- Review Article
- Changes in birth rates of low birth weight and premature infants in Korea over the past 7 years
- Min Hee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(3):233-236. Published online March 15, 2008
-
In recent years, Korea has experienced a steadily declining birth rate, which is a serious social problem in the country. Although living conditions have improved, the birth rates for low birth weight infants and preterm babies has increased because more and more women choose to give birth later in life and the social environment has changed. The rise in low... -
- Original Article
- Factors influencing birth weight premature infants
- Ji A Aum, Hee Jin Jung, Jae Won Huh, Su Young Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(10):954-958. Published online October 15, 2007
-
Purpose : The purpose of this study was to identify factors influencing premature infants who are small for their gestational ago. Methods : The medical records of 1,010 premature infants of 26 to 35 weeks of gestational age born at Il-Sin Christian Hospital, Busan from January 2000 to August 2006 were reviewed. We collected data on gestational age, birth weight, infant... -
- Platelet count and mean platelet volume in low birth weight infants (≤2,000 g) with sepsis
- Wan-soo Lee, Jin-young Cho, Seung-taek Yoo, Chang-woo Lee, Doo-young Choi, Jong-duck Kim, Yeon-kyun Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(7):643-648. Published online July 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Sepsis is a common complication in Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICU), seen especially in low birth weight (LBW) infants. A recent study showed that fungal or gram-negative sepsis is associated with a greater degree of thrombocytopenia than is seen with gram-positive sepsis. So, this study was undertaken to examine the platelet counts and platelet indices in LBW infants... -
- Fluconazole prophylaxis in high-risk, very low birth weight infants
- Soo Young Kim, Soon Joo Lee, Mi Jeong Kim, Eun Song Song, Young Youn Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(7):636-642. Published online July 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Fluconazole prophylaxis for very low birth weight (VLBW) infants has been shown to reduce invasive fungal infection and its mortality. This study aims to evaluate the effect of fluconazole prophylaxis in VLBW infants on the incidence and mortality of fungal infection. Methods : VLBW infants with endotracheal intubation and central vascular access admitted to the Neonatal Intensive Care... -
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











