Review article
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Review article
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Neonatal seizures: diagnostic updates based on new definition and classification
- Eun-Hee Kim, Jeongmin Shin, Byoung Kook Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):387-397. Published online April 4, 2022
-
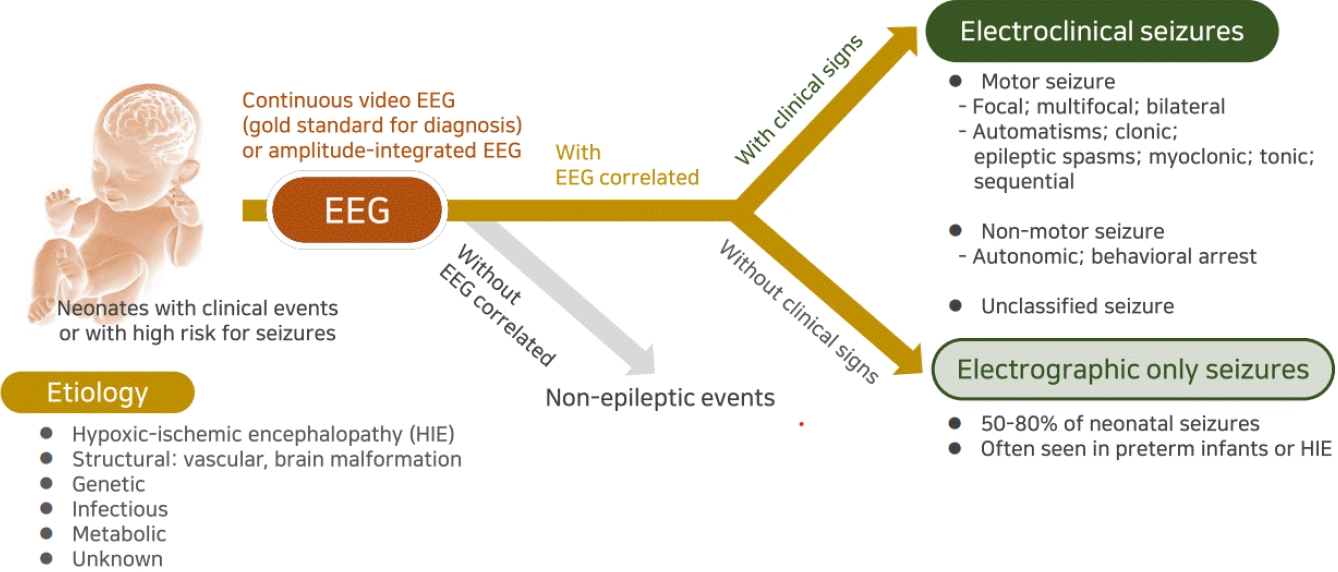
· Neonatal seizures are often electrographic-only seizures without clinical signs; therefore, the identification of electrical seizure activity on electroencephalography is the gold standard for diagnosis.
· Clinical signs of neonatal seizures are divided into motor or nonmotor seizures, and motor seizures are mostly focal or multifocal.
· Most neonatal seizures are caused by acute symptomatic etiologies, but in cases of intractable seizures, structural, genetic, or metabolic etiologies should be investigated.
- Infection
- Therapeutics for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 in children and adolescents
- Soo-Han Choi, Jae Hong Choi, Ki Wook Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):377-386. Published online June 27, 2022
-
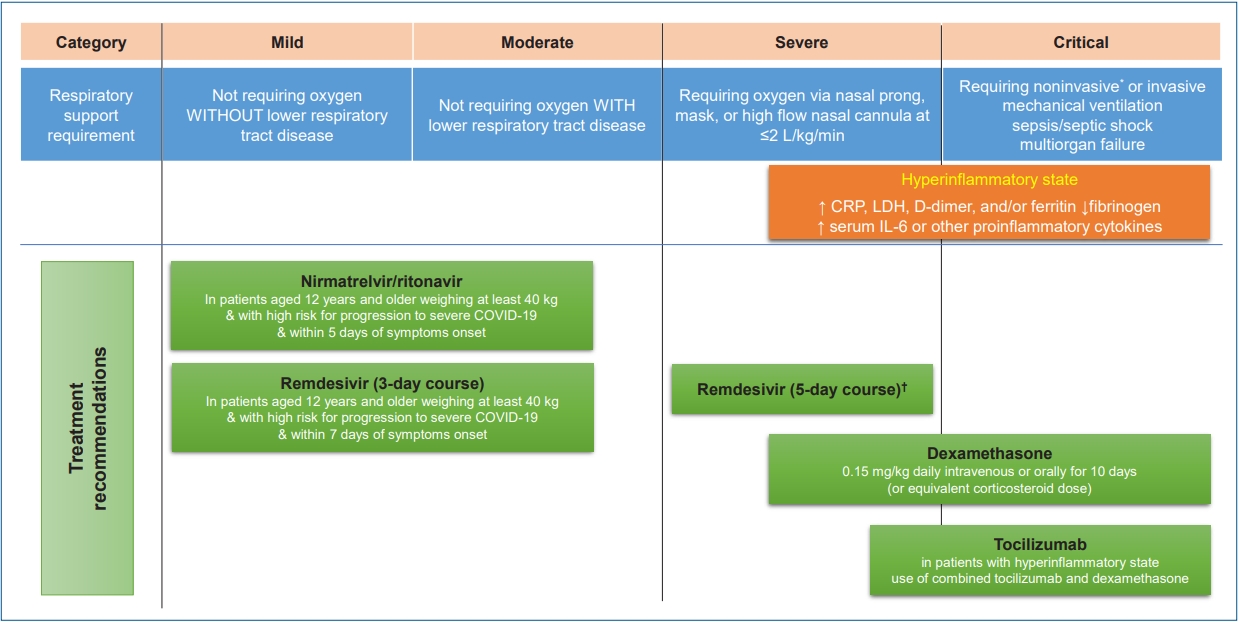
· Children and adolescents with high risks for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) should be identified and proper treatment should be provided promptly according to the patient’s condition.
· Remdesivir can be considered for pediatric patients of all ages with COVID-19 who have an emergent or increase in supplemental oxygen.
· The use of corticosteroids is not recommended for patients with nonsevere COVID-19. Corticosteroids are recommended in children and adolescents with severe and critical COVID-19.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Neonatal hypertension: concerns within and beyond the neonatal intensive care unit
- Kathleen Altemose, Janis M. Dionne
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):367-376. Published online May 30, 2022
-
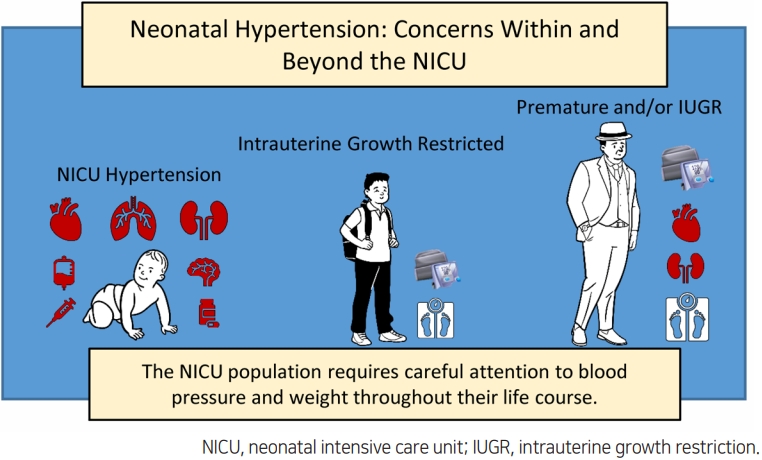
Some neonates, especially those who are premature, may experience hypertension while in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). The most common causes are prematurity-related and the hypertension usually resolves over the first 1–2 years of life. Unfortunately, the increasing population of NICU graduates is at risk for later cardiovascular and kidney disease in childhood and adulthood. This population requires careful attention to blood pressure and weight throughout their life course.
- Gastroenterology
- Clinical importance of immunonutrition in infants: a review of the recent literature
- Ji Sook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):337-343. Published online February 17, 2022
-

Nutrients are important in the developing immune system. Human milk supplies diverse bioactives to prevent acute infection or chronic inflammation. Immunoglobulins, lactoferrin, and glutamine in human milk decrease gastrointestinal and respiratory infection. Human milk oligosaccharides promote the growth of intestinal microbiota, the gut barrier, and antimicrobial or antiviral activity. Micronutrients act as anti-inflammatory immunonutrients, too. However, the toxicity of some nutrients from an overdose should be considered.
- Other
- Epidemiology of pediatric fractures before versus during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic
- Chi Hoon Oh, Siyeong Yoon, Kyung Rae Ko, Young Woo Kwon, Kyeong Mi Kim, Hyun Seo Park, Hogyeong Kang, Inseok Jang, Soonchul Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):330-336. Published online June 3, 2022
-

∙ The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was first reported in December 2019 as a cluster outbreak in Wuhan, since then, national lockdowns have included school closures, stay-at-home orders.
∙ The characteristics of adolescent fractures were often related to physical activity such as sports-related injury.
∙ During the COVID-19 pandemic, both in the East and the West, the incidence of fractures in children and adolescents is showing a decreasing trend worldwide.
∙ Fractures in children and adolescents were significantly reduced in the proportion of relatively low-energy damage, and the incidence of fractures in adolescents with greater activity compared to children was reduced.
∙ If COVID-19 pandemic ends, normal academic and sports activities increase due to the easing of lockdown policies, the number of trauma patients related to increased activity may increase rapidly, and clinics should prepare for this change.
- Neurobehavior
- Jeopardized mental health of children and adolescents in coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic
- Bohyun Jin, Sohee Lee, Un Sun Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):322-329. Published online June 3, 2022
-
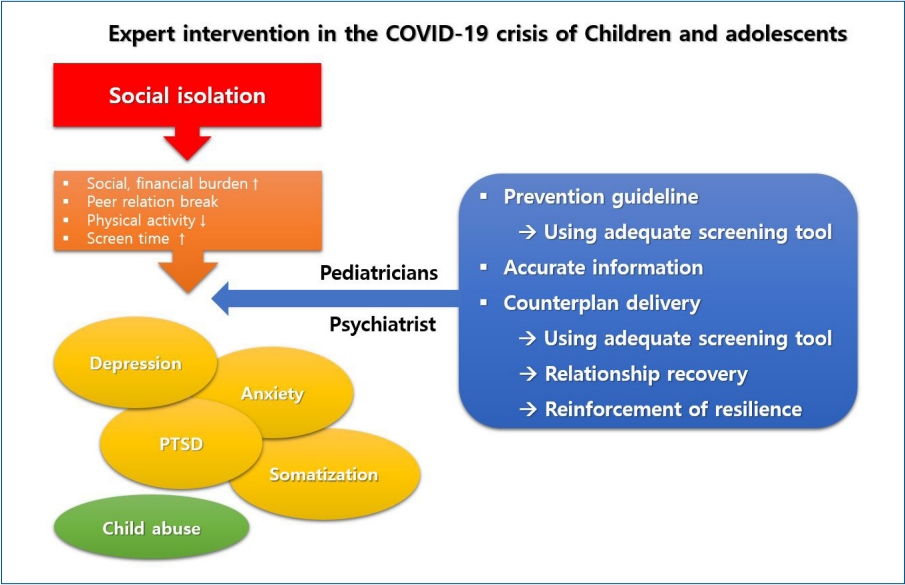
∙ The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has required preventive measures like self-quarantine, school closures, and lockdown, which ultimately make youth directly and indirectly vulnerable to depression, anxiety, posttraumatic stress disorder, and somatization.
∙ Child abuse is more common in the COVID-19 era than previously.
∙ Pediatricians should carefully examine parental and child mental health to directly and indirectly aid their physical and mental health.
- Neurology
- Recent trends of healthcare information and communication technologies in pediatrics: a systematic review
- Se young Jung, Keehyuck Lee, Hee Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):291-299. Published online December 15, 2021
-
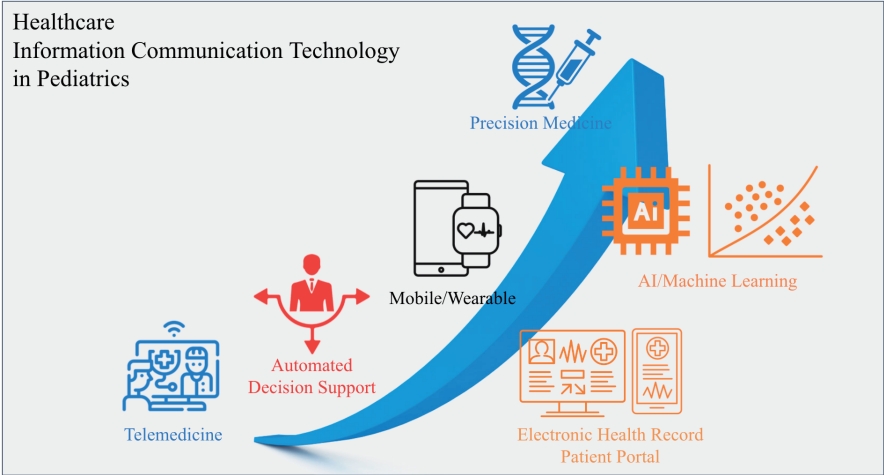
· The innovation of healthcare information communication technology (ICT) was accelerated with the adoption of electronic health records (EHRs).
· Telemedicine currently has no technical barriers.
· EHRs and personal health records are being connected, and mobile/wearable technologies are being integrated into them.
· Conventional rule-based clinical decision support systems have already been implemented and used in EHRs and PHRs. Artificial intelligence/machine learning improves precision and accuracy.
- Endocrinology
- Pediatric hypertension based on Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines (JSH 2019) with actual school blood pressure screening data in Japan
- Toru Kikuchi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):283-290. Published online November 26, 2021
-
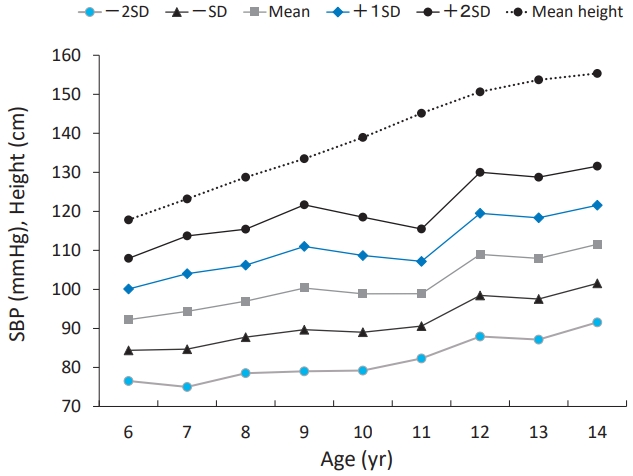
The prevalence of Japanese pediatric hypertension is 0.9% based on proper measurement protocols. Hypertensive children tend to be hypertensive adults. Pediatric essential hypertension is characterized by an absence of symptoms, obesity, a family history of hypertension, and a low birth weight. The most common causes of pediatric secondary hypertension are renal parenchymal and renovascular diseases. Important factors controlling pediatric hypertension include healthy lifestyle modifications and pharmacotherapy.
- Neurology
- Big data analysis and artificial intelligence in epilepsy – common data model analysis and machine learning-based seizure detection and forecasting
- Yoon Gi Chung, Yonghoon Jeon, Sooyoung Yoo, Hunmin Kim, Hee Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):272-282. Published online November 26, 2021
-
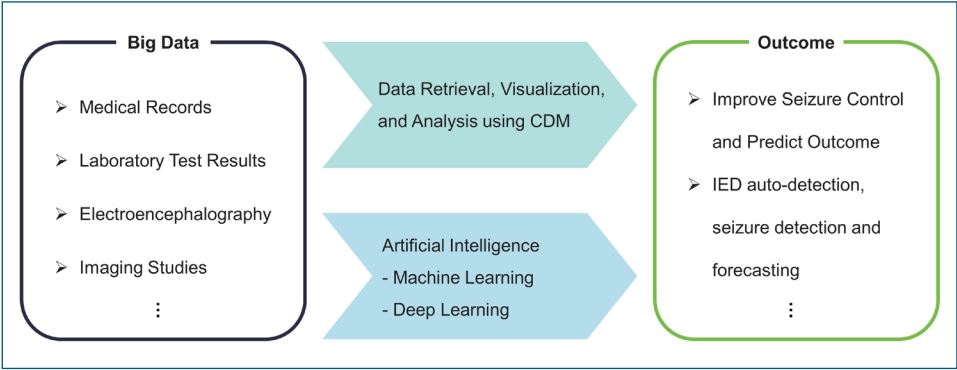
· Big data analysis, such as common data model and artificial intelligence, can solve relevant questions and improve clinical care.
· Recent deep learning studies achieved 0.887–0.996 areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve for automated interictal epileptiform discharge detection.
· Recent deep learning studies achieved 62.3%–99.0% accuracy for interictal-ictal classification in seizure detection and 75.0%– 87.8% sensitivity with a 0.06–0.21/hr false positive rate in seizure forecasting.
- Other
- Knowledge-guided artificial intelligence technologies for decoding complex multiomics interactions in cells
- Dohoon Lee, Sun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):239-249. Published online November 26, 2021
-
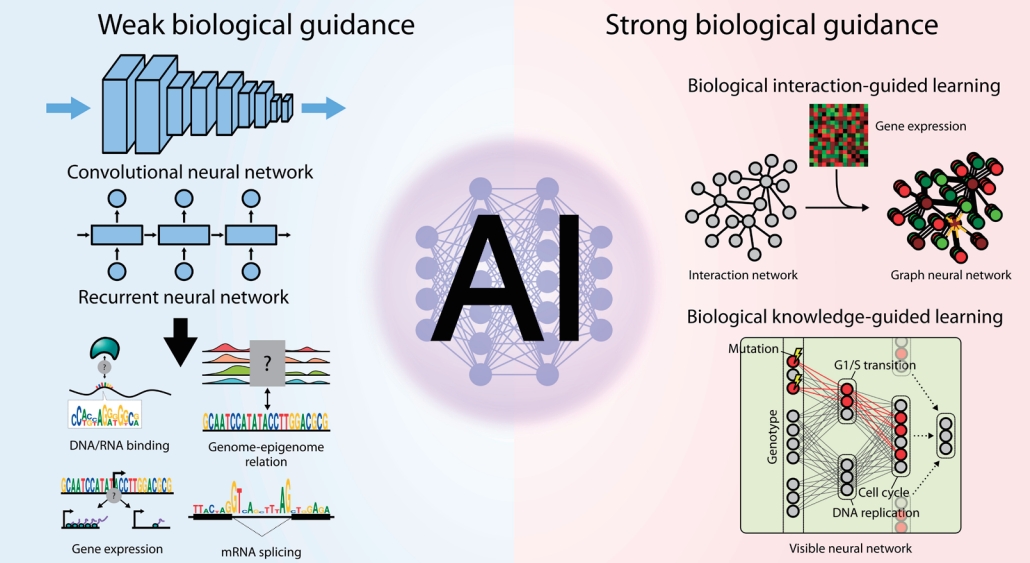
· The need for data-driven modeling of multiomics interactions was recently highlighted.
· Many artificial intelligence-driven models have been developed, but only a few have incorporated biological domain knowledge within model architectures or training procedures.
· Here we provide a comprehensive review of deep learning models to decipher complex multiomics interactions regarding the biological guidance imposed upon them to facilitate further development of biological knowledge-guided deep learning models.
- Cardiology
- Implication of microRNA as a potential biomarker of myocarditis
- Jin-Hee Oh, Gi Beom Kim, Heeyoung Seok
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):230-238. Published online March 2, 2022
-
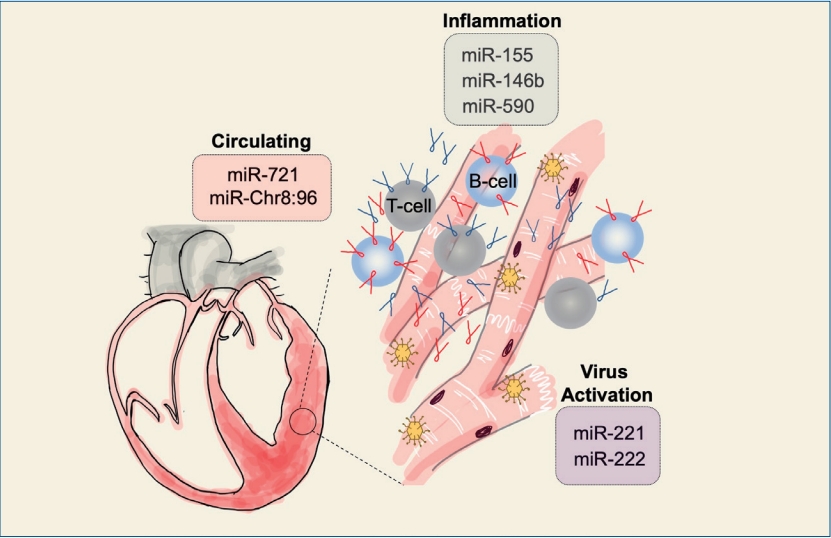
· Myocarditis was recently examined quantitatively as inflammation of the heart muscle based on endomyocardial biopsy, and its noninvasive diagnosis remains unsatisfactory.
· Additionally, numerous miRNAs (miR-155, miR-146b, miR-590, miR-221, miR-222, etc.) coupled with inflammation or viral activation have been examined in myocarditis patients or mouse models.
· The recent identification of mmu-miR-721 (has-miR-Chr8: 96), a myocarditis-specific microRNA, demonstrated its potential as an acute myocarditis biomarker.
- Neurobehavior
- Psychological aspects in children and parents of children with chronic kidney disease and their families
- Alemsungla Aier, Priya Pais, Vijaya Raman
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):222-229. Published online November 10, 2021
-
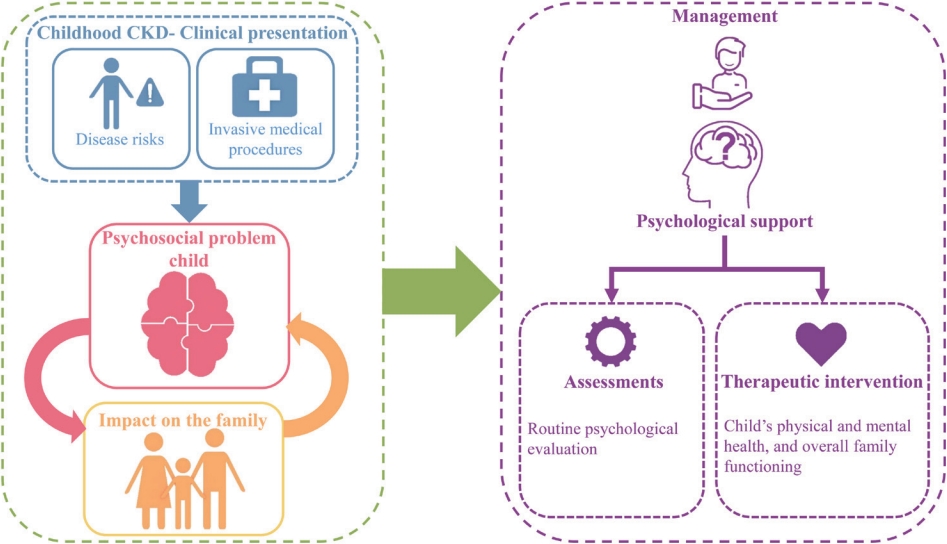
· Childhood chronic kidney disease (CKD) is complex and requires lifetime medical treatment.
· Children with CKD are at risk for emotional, behavioral, social, and academic difficulties that significantly affect their quality of life.
· Caring for children with CKD is stressful for families.
· These unique challenges are crucial and can negatively impact treatment outcomes.
· Awareness of and addressing these evolving psychosocial issues can foster their developing needs.
- Infection
- Four months of rifampicin monotherapy for latent tuberculosis infection in children
- Chi Eun Oh, Dick Menzies
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):214-221. Published online October 29, 2021
-
· Recently, the importance of a short-term treatment regimen including rifamycin has been highlighted in the treatment of latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI).
· Four prospective or retrospective studies in children consistently reported that a 4-month daily rifampicin regimen (4R) had a higher completion rate than and comparable safety to a nine-month daily isoniazid regimen.
· We suggest rifampicin 20–30 mg/kg/day for children aged 0–2 years and 15–20 mg/kg/day for children aged 2–10 years in 4R to treat LTBI.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Pathophysiology, classification, and complications of common asymptomatic thrombocytosis in newborn infants
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):182-187. Published online October 18, 2021
-
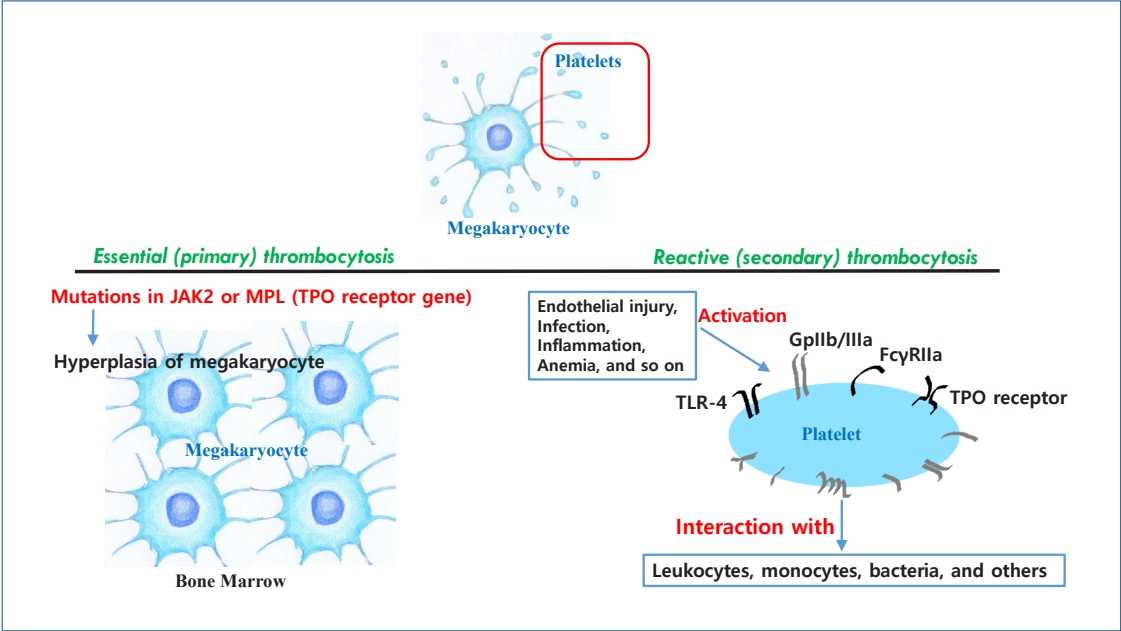
· Thrombocytosis, common in newborns and infants (<2 years) (3%–13%), is caused by elevated thrombopoietin (TPO) concentrations.
· Serum TPO levels are significantly higher immediately to 1 month postnatal and decrease with age.
· Platelet counts are positively correlated with gestational age at birth and postnatal age.
· Thrombocytosis is more common in preterm than in term infants.
· Thrombocytosis in newborns is reactive and resolves spontaneously without complications.
- Endocrinology
- Genetic factors in precocious puberty
- Young Suk Shim, Hae Sang Lee, Jin Soon Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):172-181. Published online October 18, 2021
-
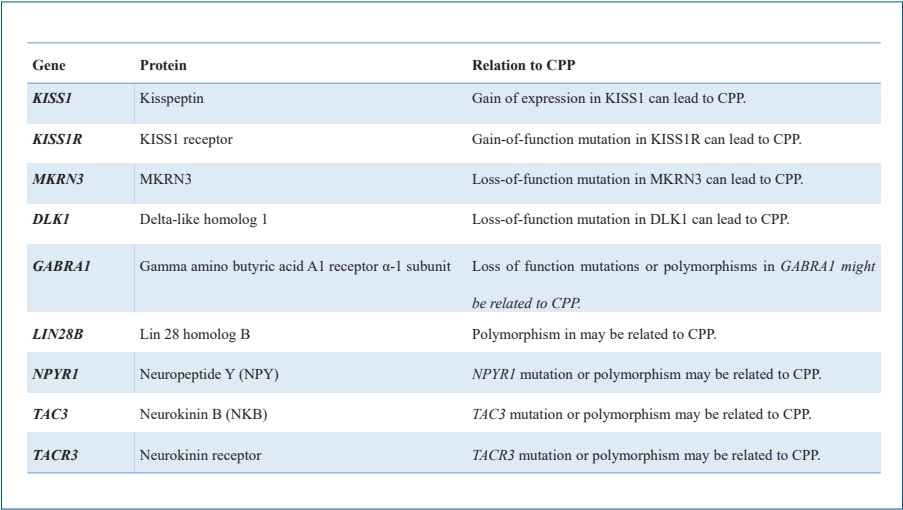
· Mutations in the kisspeptin (KISS1), kisspeptin receptor (KISS1R), makorin ring finger protein 3 (MKRN3), and delta-like homolog 1 (DLK1) genes are associated with idiopathic central precocious puberty (ICPP).
· A few genes related to pubertal onset have been implicated in ICPP.
· Epigenetic factors such as DNA methylation, histone posttranslational modifications, and noncoding ribonucleic acids may be related to ICPP
- Infection
- Epidemiological changes in infectious diseases during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in Korea: a systematic review
- Jong Gyun Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):167-171. Published online November 30, 2021
-
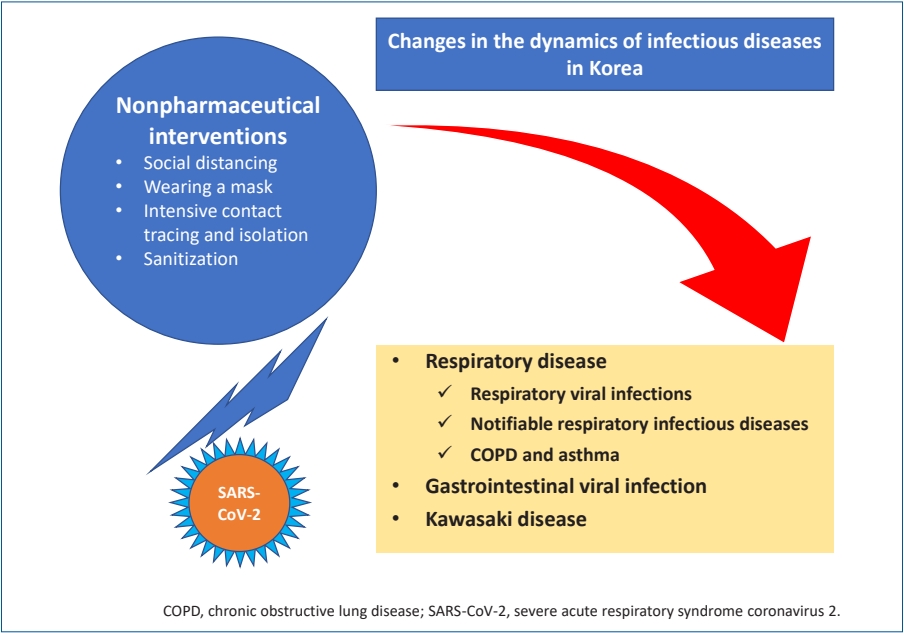
· Nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) have had a major impact on the epidemiology of various infectious diseases in Korea.
· Respiratory diseases and gastrointestinal viral diseases were significantly reduced during the NPI period.
· The decrease in Kawasaki disease after the introduction of NPI is an unintended result.
· Infectious diseases that decreased during NPI use may re-emerge.
· We must continuously monitor the epidemiology of various infectious diseases during the coronavirus era
- Etiological and pathophysiological enigmas of severe coronavirus disease 2019, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, and Kawasaki disease
- Jung-Woo Rhim, Jin-Han Kang, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):153-166. Published online November 23, 2021
-
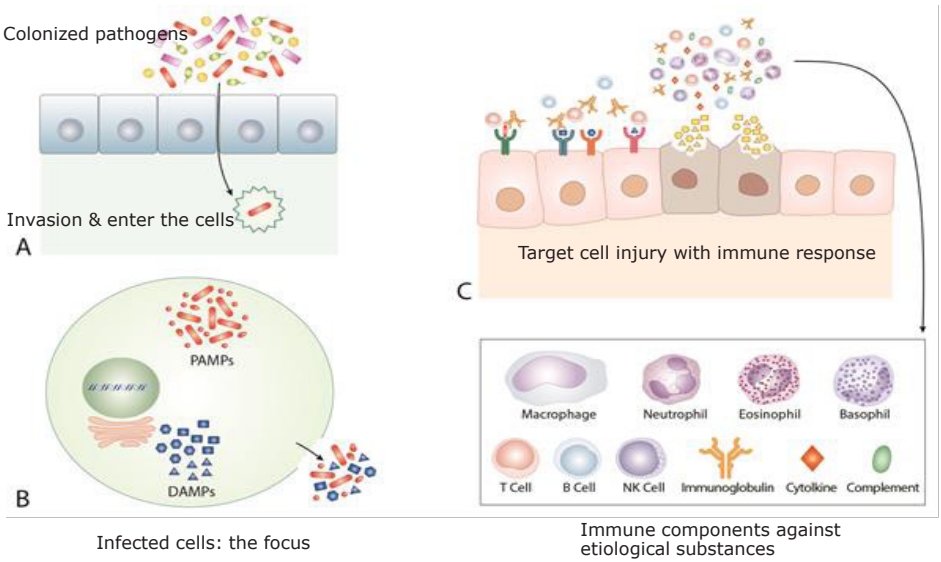
· Severe cases of coronavirus disease, Kawasaki disease (KD), and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) share similar findings: a protracted clinical course, multiorgan involvement, and similar activated biomarkers.
· Here we propose etiological agents in KD and MIS-C as species in the microbiota and introduce a common pathogenesis through the protein-homeostasis-system hypothesis.
· Early proper dose of corticosteroids and/or intravenous immunoglobulin may help to reduce morbidity and mortality in these diseases.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Retinopathy of prematurity: a review of epidemiology and current treatment strategies
- Eun Hee Hong, Yong Un Shin, Heeyoon Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):115-126. Published online October 12, 2021
-
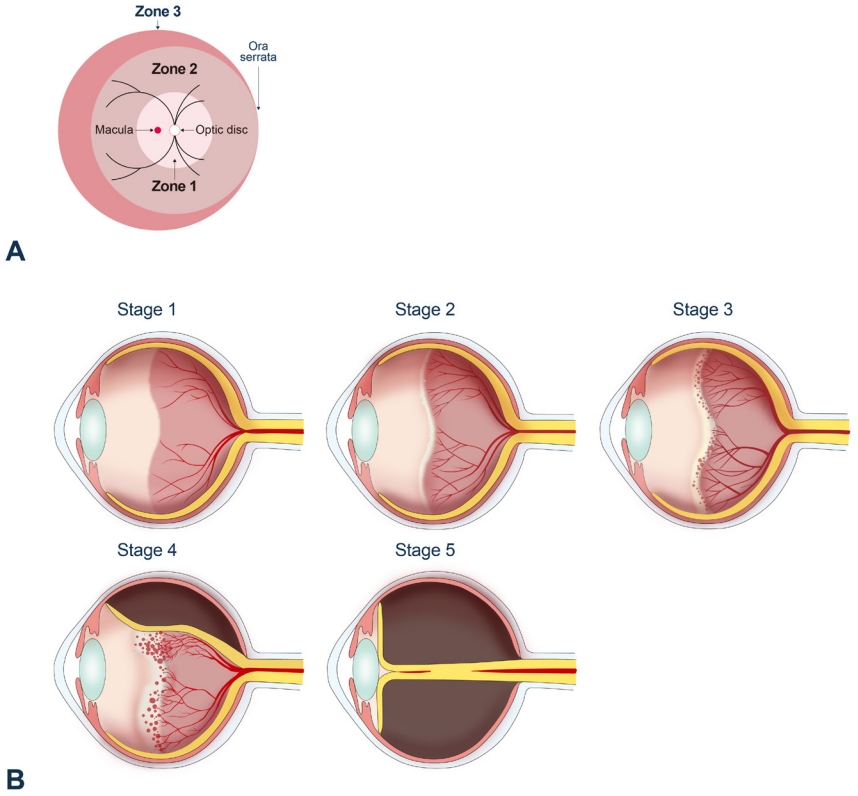
There have been global tri-phasic epidemic periods of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP). In recent years, its incidence has reportedly been 10%–40% depending on country and study population. Current treatment strategies for ROP include laser photocoagulation, surgical treatment, and anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment, the role of which has drawn attention in recent years.
- Infection
- Changes in age-specific seroprevalence of Japanese encephalitis virus and impact of Japanese encephalitis vaccine in Korea
- Byung Ok Kwak, Young Jin Hong, Dong Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):108-114. Published online September 24, 2021
-

Since the introduction of a universal Japanese encephalitis (JE) vaccination program and urbanization, the incidence of JE has dramatically decreased in Korea. However, recent JE cases have occurred, predominantly among unvaccinated adults and with a shift in age distribution. Continuous surveillance of the seroprevalence of JE is required to establish a proper immunization policy in Korea.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Blood pressure measurements and hypertension in infants, children, and adolescents: from the postmercury to mobile devices
- Seon Hee Lim, Seong Heon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):73-80. Published online September 15, 2021
-

· Hypertension is defined as a blood pressure (BP) >90th (elevated) or 95th (hypertension) percentile in children by height, age, and sex and >95th percentile in neonates by age, birth weight, and sex.
· Although the oscillometric method can be used for screenings, the auscultatory method remains the gold standard. The hybrid method employs the auscultatory and electronic methods and can reduce bias.
· BP measurement mobile device applications have a potential for development.
- General Pediatrics
- A new perspective on cholesterol in pediatric health: association of vitamin D metabolism, respiratory diseases, and mental health problems
- Jeana Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):65-72. Published online December 9, 2021
-
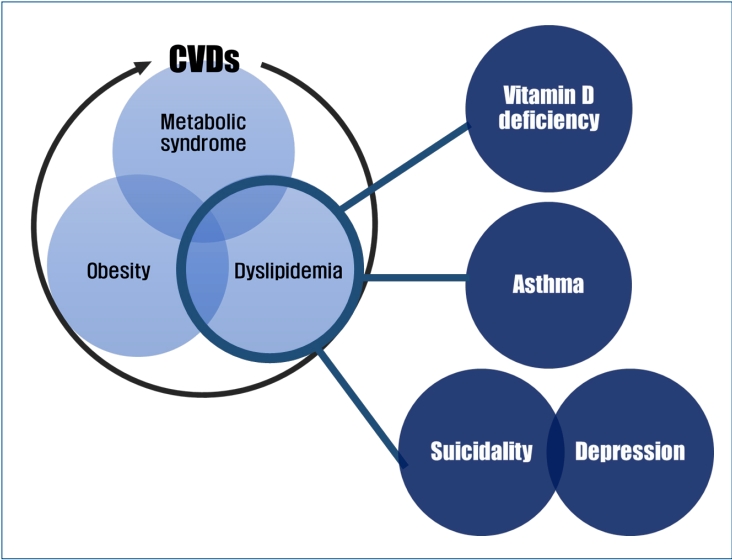
∙ Pediatric dyslipidemia is associated with several health problems besides cardiovascular diseases.
∙ There is a direct association between pediatric dyslipidemia and low serum vitamin D levels, asthma, and mental health problems regardless of body mass index.
∙ More large-scale nationally representative studies are needed to establish the appropriate cutoff points for the definition of dyslipidemia that is a prerequisite for further epidemiological studies in the Korean pediatric population.
- Neurology
- Promising candidate cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of seizure disorder, infection, inflammation, tumor, and traumatic brain injury in pediatric patients
- Seh Hyun Kim, Soo Ahn Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):56-64. Published online August 23, 2021
-
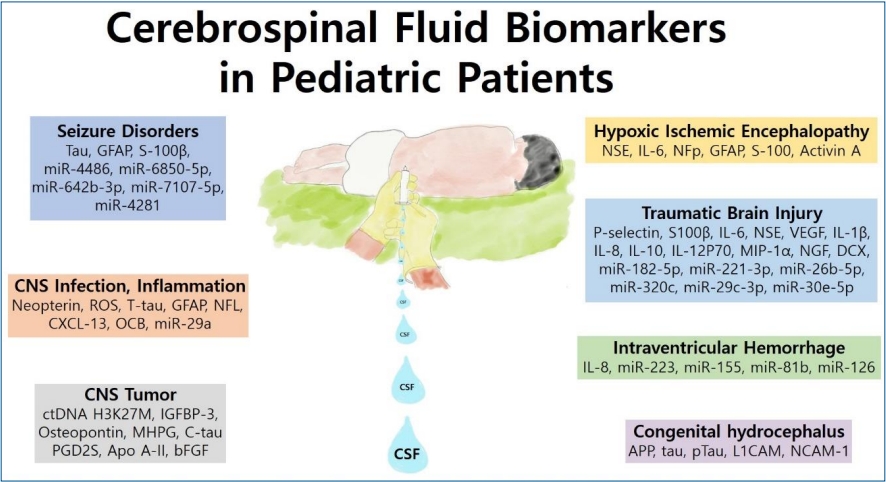
· Pediatric cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) components have been extensively evaluated as biomarkers of various neurologic diseases.
· Several promising candidate CSF biomarkers, including Tau, glial fibrillary acidic protein, neuron-specific enolase, S100β, and interleukins, have been studied in pediatric patients with seizure disorders, central nervous system infections, inflammation, tumors, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, traumatic brain injuries, intraventricular hemorrhage, and congenital hydrocephalus.
· Circulating microRNAs in the CSF are a promising class of biomarkers for various neurological diseases.
- Gastroenterology
- Upper gastrointestinal tract involvement of Crohn disease: clinical implications in children and adolescents
- Eun Sil Kim, Mi Jin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):21-28. Published online September 10, 2021
-
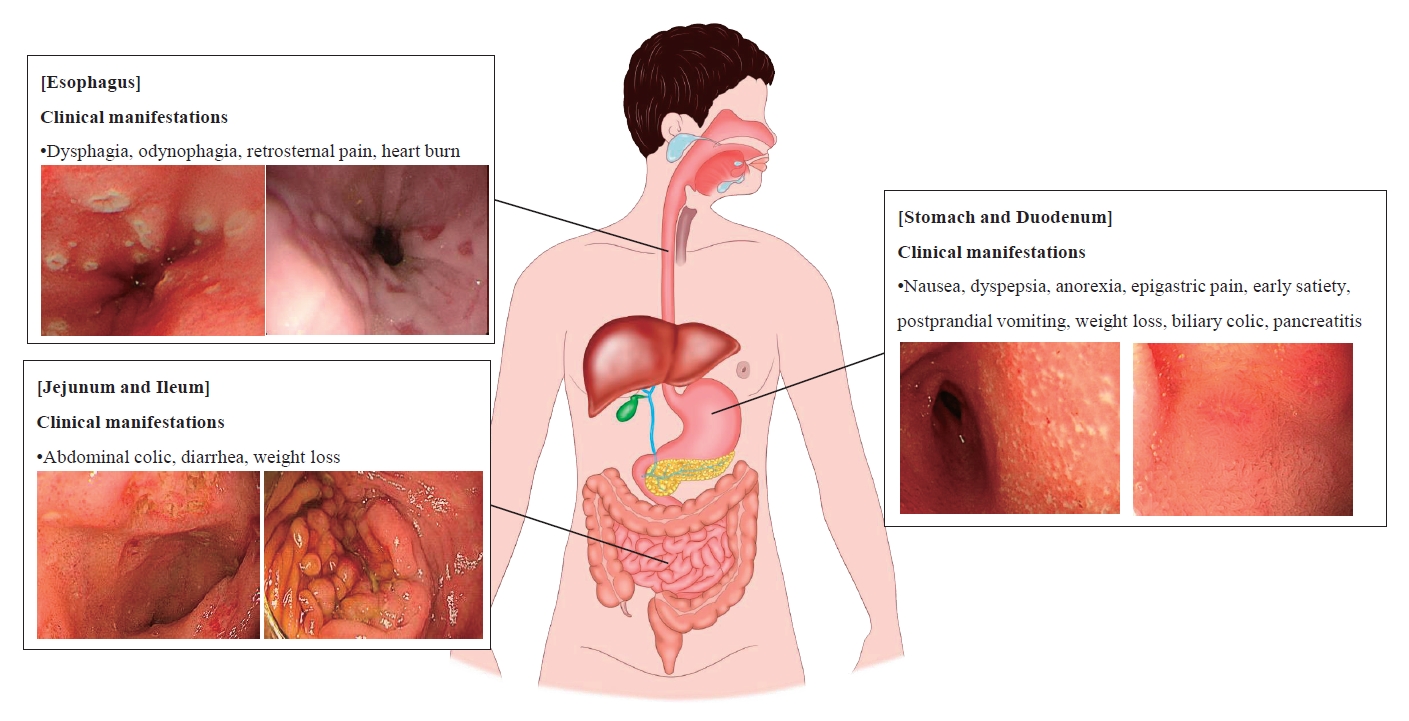
· Clinical manifestations of upper gastrointestinal (UGI) tract involvement in Crohn's disease (CD) are common but often clinically underestimated.
· Diagnosing CD by confirming inflammation of the UGI tract histologically is challenging because macroscopic and microscopic findings overlap with those of other diseases.
· Ongoing efforts are needed to enable a standardized assessment of UGI CD in the future.
- Neurology
- Worldwide national intervention of developmental screening programs in infant and early childhood
- Seunghyo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):10-20. Published online September 30, 2021
-

∙ Prevalence rate of developmental disabilities has been reported from 8% to 15% and its rate is increasing worldwide.
∙ The critical period of intervention for developmental delay is before the child reaches 3 years of age.
∙ All primary care pediatricians should conduct developmental surveillance and screening tests to infants and children at scheduled visits. Through this, they are liable for providing early identification and timely intervention.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Growth patterns of preterm infants in Korea
- Joohee Lim, So Jin Yoon, Soon Min Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):1-9. Published online July 8, 2021
-
∙ The growth of preterm infants is a main focus of neonatology.
∙ Preterm infants in Korea, especially those with a very low birth weight, achieve retarded growth.
∙ Careful growth monitoring and early intervention will contribute to better development outcomes and quality of life for preterm infants and improve public health.
- Endocrinology
- Endocrine comorbidities of pediatric obesity
- Jieun Lee, Jae Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):619-627. Published online August 26, 2021
-

∙ Pediatric obesity can involve endocrine comorbidities such as prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, polycystic ovary syndrome, and central precocious puberty.
∙ Prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in youth aged 10–19 years had a prevalence of 25.9% and 0.6% in 2013–2014, respectively.
∙ Dyslipidemia in Korean adolescents aged 10–18 years had a prevalence of 7.64% (total cholesterol ≥200 mg/dL), 6.09% (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol ≥130 mg/dL), 8.69% (triglyceride ≥150 mg/dL), and 12.52% (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ≤40 mg/dL) in 2007–2018.
∙ Metabolic syndrome in Korean youth has a prevalence of 1.9%–14.7% in males and 1.7%–12.6% in females with wide variation in definitions.
∙ Appropriate comorbidity screening and management and/or specialist referral are necessary for obese children and adolescents.
- Neurology
- Cognitive outcomes in late childhood and adolescence of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Bo Lyun Lee, Hannah C. Glass
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):608-618. Published online May 24, 2021
-
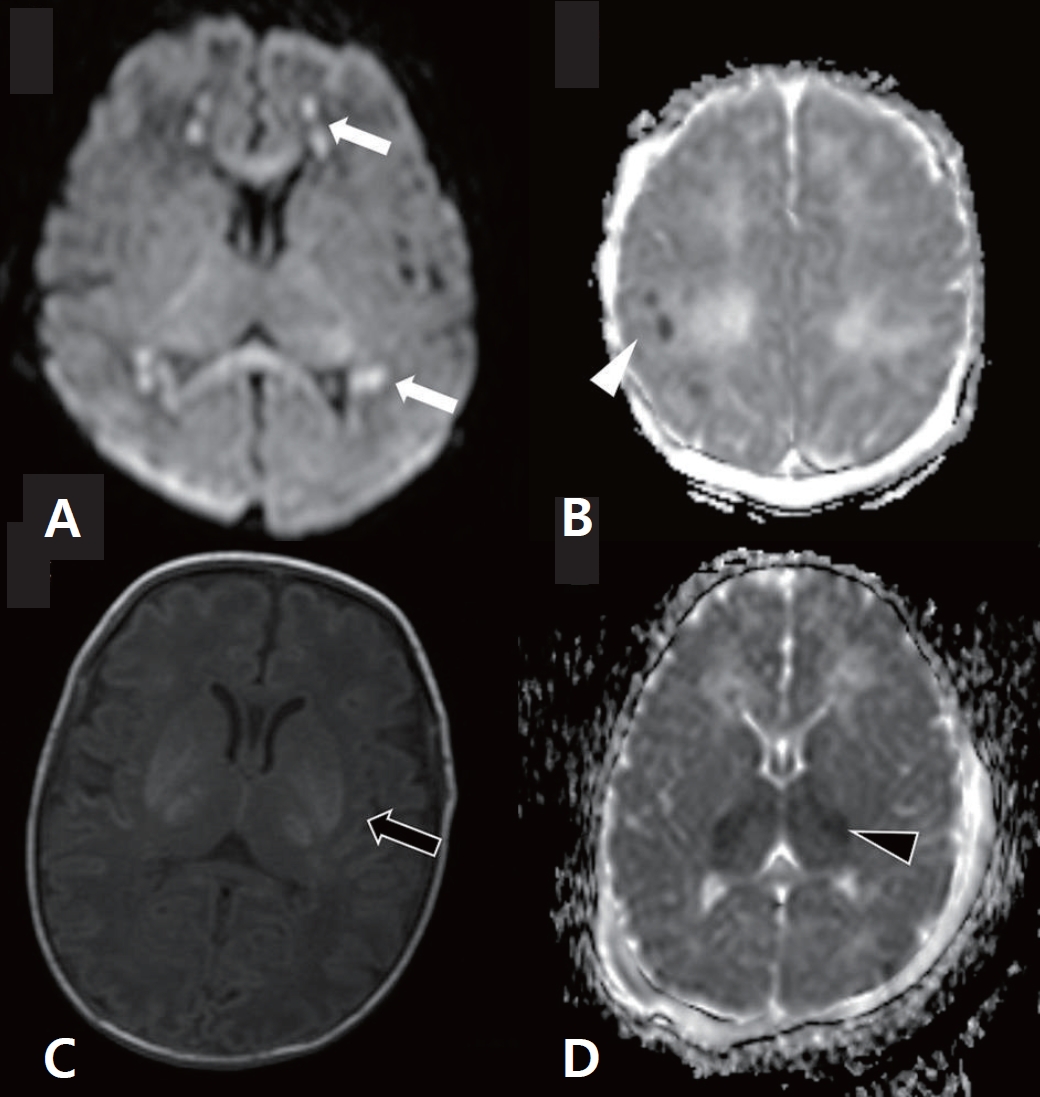
∙ Cognitive impairments occur in children with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) even without neuromotor deficits.
∙ Therapeutic hypothermia has improved neurodevelopmental outcomes of children with HIE; however, 40% of children remain at risk of death/disability or cognitive impairments necessitating the development of adjunctive neuroprotective therapies.
∙ Long-term follow-up until adolescence is required to identify cognitive dysfunction.
∙ A pattern of watershed injury on brain imaging is associated with poor cognitive outcomes.
- Infection
- Recommendation for use of diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis, inactivated poliovirus, Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate, and hepatitis B vaccine in infants
- Hye-Kyung Cho, Su Eun Park, Yae-Jean Kim, Dae Sun Jo, Yun-Kyung Kim, Byung-Wook Eun, Taek-Jin Lee, Jina Lee, Hyunju Lee, Ki Hwan Kim, Eun Young Cho, Jong Gyun Ahn, Eun Hwa Choi; The Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):602-607. Published online June 8, 2021
-
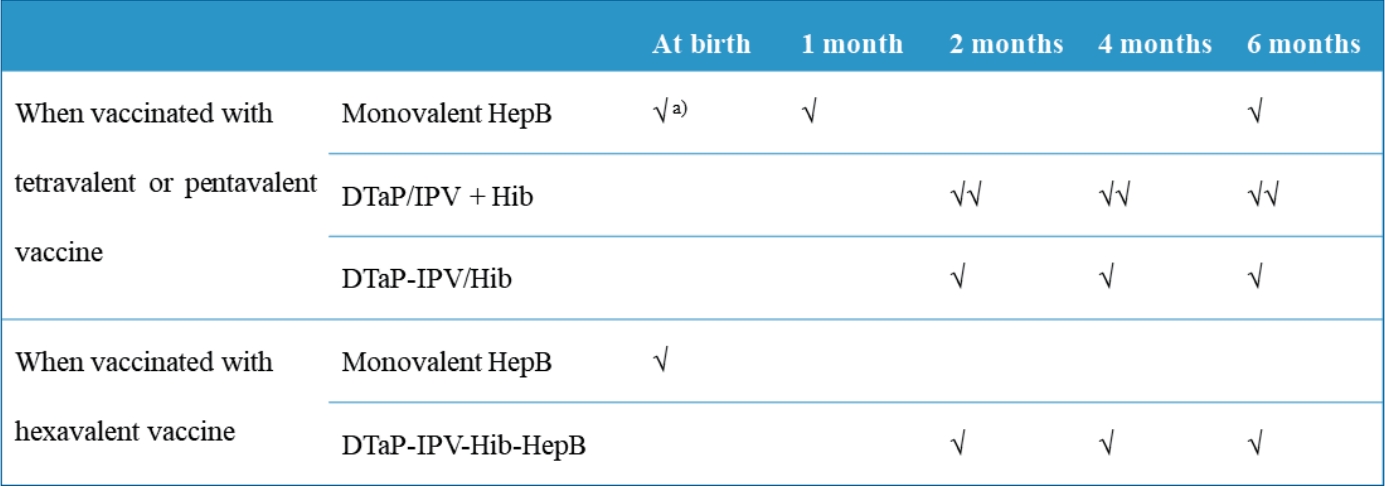
∙ Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis-inactivated poliovirus-Haemophilus influenzae type b-hepatitis B (DTaP-IPV-Hib-HepB) was licensed in Korea in April 2020.
∙ DTaP-IPV-Hib-HepB is indicated as a 3-dose primary series for infants aged 2, 4, and 6 months who received the standalone HepB vaccine at birth.
∙ Infants born to HepB surface antigen-positive mothers are currently recommended to be immunized with HepB immunoglobulin at birth and then monovalent HepB vaccine at 0, 1, and 6 months.
- Oncology
- Update on infantile hemangioma
- Hye Lim Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):559-572. Published online May 26, 2021
-

· Infantile hemangiomas (IHs) are the most common benign vascular tumors, occurring in 5%–10% of infants.
· IHs are characteristically not present at birth but are usually diagnosed at 1–4 weeks of age, rapidly proliferate until 5 months of age, and then spontaneously involute.
· High-risk IHs (10%) require early treatment from 1 month of age.
· Oral propranolol, a nonselective beta-blocker, is the first-line treatment for IHs.
- Nutrition
- Changes in health status of North Korean children and emerging health challenges of North Korean refugee children
- Seong-Woo Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):552-558. Published online May 17, 2021
-

· Among North Korean refugee (NKR) children under 5 years, 61% and 9.3% were underweight in 1998 and 2017, respectively.
· The immunization rate of NKR children exceeded 90% since 2006.
· For NKR children, protein-energy malnutrition was the #1 cause of death in 2009 versus #17 in 2019.
· In 2020, stunting affected 5.4% and 0.9% and obesity affected 10.7% and 2.7% of NKR versus South Korean children, respectively.
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











