Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Clinical course of children with postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans with versus without comorbid bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Lamia Medghoul, Julien Grosjean, Christophe Marguet, Hortense Petat
-
Background: Post-infectious bronchiolitis obliterans (PIBO) is a rare chronic obstructive pulmonary disease that occurs after a respiratory infection. Its diagnosis is generally based on clinical history, respiratory symptoms, and computed tomography (CT) findings.
Purpose: Here we evaluated the frequency of exacerbations, clinical progress, and inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) usage in children diagnosed with PIBO with or without comorbid bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). Methods:... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.00122 [Accepted]
- Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in pediatric patients with type VI mucopolysaccharidosis
- Vedat Uygun, Koray Yalçın, Hayriye Daloğlu, Seda Öztürkmen, Suna Çelen, Suleimen Zhumatayev, Gülsün Karasu, Akif Yeşilipek
-
Background: It is uncertain whether hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), versus standard enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), is effective for type VI mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS VI).
Purpose: New related advances in HSCT prompted an examination of the transplant procedures performed in a recent cohort. Methods: This single-center retrospective study reviewed the medical records of 17 pediatric patients with MPS VI who underwent allogeneic... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.02033 [Accepted]
- Somatic symptom severity during acute illnesses among children with functional gastrointestinal disorders
- Rattanachart Sirinil, Anundorn Wongteerasut
-
Background: Functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) are associated with various gastrointestinal (GI) and non-GI symptoms, risk factors for which commonly include psychosocial and physical stresses.
Purpose: This study aimed to compare somatic symptom severity between children with FGIDs and healthy controls during acute illnesses. Methods: This was a prospective descriptive cross-sectional study whose inclusion criterion was age 4–18 years. Children were... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.01795 [Accepted]
- Nonlinear association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and asthma in children and adolescents in the USA: a cross-sectional study
- Chuhan Cheng, Liyan Zhang
-
Background: The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is a marker of systemic inflammation associated with various diseases including respiratory conditions. However, the relationship between NLR and asthma in the pediatric population remains underexplored.
Purpose: This study aimed to explore the association between NLR and asthma in children and adolescents and assess its potential role as a predictive biomarker for pediatric asthma. Methods: We... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.01844 [Accepted]
- Serum amyloid A and proadrenomedullin as early markers in critically ill children with sepsis
- Nagwan Saleh, Wafaa Abo El Fotoh, Mona Habib, Salem Deraz
-
Background: Pro-adrenomedullin (pro-ADM), the most stable part of ADM, serves as an indirect marker of ADM levels. Serum amyloid A (SAA) is a protein produced primarily in the liver during acute inflammation.
Purpose: To assess the role of SAA and pro-ADM, individually and in combination, as diagnostic and prognostic markers in pediatric sepsis. Methods: This prospective case-control cohort study included... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.01928 [Accepted]
- Review Article
- The Korea Infant Physical Growth Examination Survey (KIPGroS): a study protocol
- Jong Woo Hahn, MinSoo Shin, Jin Gyu Lim, Yoon-Joo Kim, Ki Soo Kang, Narae Lee, Seong Hee Jeong, Mun Hui Jeong, Yeoun Joo Lee, Eui Kyung Choi, Jung Ok Shim, Jee Yoon Park, Chan-Wook Park, Joo Young Kim, Su Jin Jeong, Young Hwa Jung, Jae Hyun Kim, Chang Won Choi, Ju Whi Kim, Seung Han Shin, Yun Jeong Lee, Young Ah Lee, Choong-Ho Shin, Seung-sik Hwang, Young Eun Kim
-
Growth charts are important tools used to evaluate the growth status of children and estimate the nutritional and health status of the general population. In Korea, the national standardized growth charts were updated in 2017. However, the growth charts developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) are being adopted for children under 3 years of age despite a lack of... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.00297 [Accepted]
- Original Article
- COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus
- Karnchanit Sausukpaiboon, Nuanpan Penboon, Pornpimol Rianthavorn
-
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination remains an essential strategy for reducing disease burden. Specific guidelines for vaccinating children with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are currently unavailable, highlighting the gap in tailored recommendations for this population.
Purpose: This study aimed to estimate parental intention to vaccinate children with SLE against COVID-19 and identify factors associated with this intention. It also explored... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.01340 [Accepted]
- Differential effects of dietary and physical activity interventions on adiposity of children with obesity
- Anekchoke Tangtongsoong, Chonnikant Visuthranukul, Yuda Chongpison, Sirinuch Chomtho
-
Background: Managing obesity in children remains challenging. In addition to body mass index (BMI), incorporating body composition into evaluations of post-obesity interventions would help assess changes in adiposity.
Purpose: This study aimed to identify the relationship between dietary intake, physical activity, and changes in BMI z-scores and adiposity among children with obesity. Methods: Children aged 7–15 years with obesity received monthly dietary... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.01347 [Accepted]
- Enteric pathogens implicated in acute infectious diarrhea among young children in resource-limited region with rapidly growing population: a hospital-based cross-sectional study
- Aseel Al-Mashahedah, Randa Dhahi
-
Background: Acute infectious diarrhea is among the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide, particularly in developing countries and among children younger than 5 years of age.
Purpose: To determine the causative microorganisms in diarrhea and elucidate their epidemiological trajectory among children younger than 5 years of age to establish successful preventive measures. Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted in Al-Musayyib... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.01333 [Accepted]
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- C3 glomerulopathy in children: experience at a resource-limited center
- Soumya Reddy, Abhishek Ghante, Mahesha Vankalakunti, Anil Vasudevan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):311-318. Published online November 28, 2024
-

Question: What are the clinicopathological features and outcomes of pediatric C3 glomerulopathy (C3G) in resource-limited settings?
Finding: Children with C3G in resource-limited settings have significant morbidities, and most experience kidney sequelae despite treatment. Electron microscopy was performed in only 50% of our patients, while none received complement assays or genetic testing.
Meaning: Pediatric C3G presentation, management, and kidney outcomes vary. Its thorough evaluation and management are challenging in resource-limited settings.
- Neurology
- Occurrence of stroke in children and young adults in Indonesia: a multicenter private hospital study
- Jeanne Leman, Veli Sungono, Yosua Timotius Haryono, Muhammad Adam Mudzakir, Dewi Lestari Rahmawati, Callistus Bruce Henfry Sulay, Gilbert Sterling Octavius
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):303-310. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: What is the occurrence of pediatric stroke in Indonesia?
Finding: This multicenter study identified 1,074 stroke cases, predominantly hemorrhagic (83.4%), with males and older children at higher risk. Accidents were the primary cause (73.2%).
Meaning: Pediatric stroke in Indonesia shows critical epidemiological trends, highlighting the need for targeted prevention efforts, particularly for high-risk groups like males and accident victims.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Practical concepts and strategies for early diagnosis and management of eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders in East-Asian children
- Byung-Ho Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):185-198. Published online November 13, 2024
-
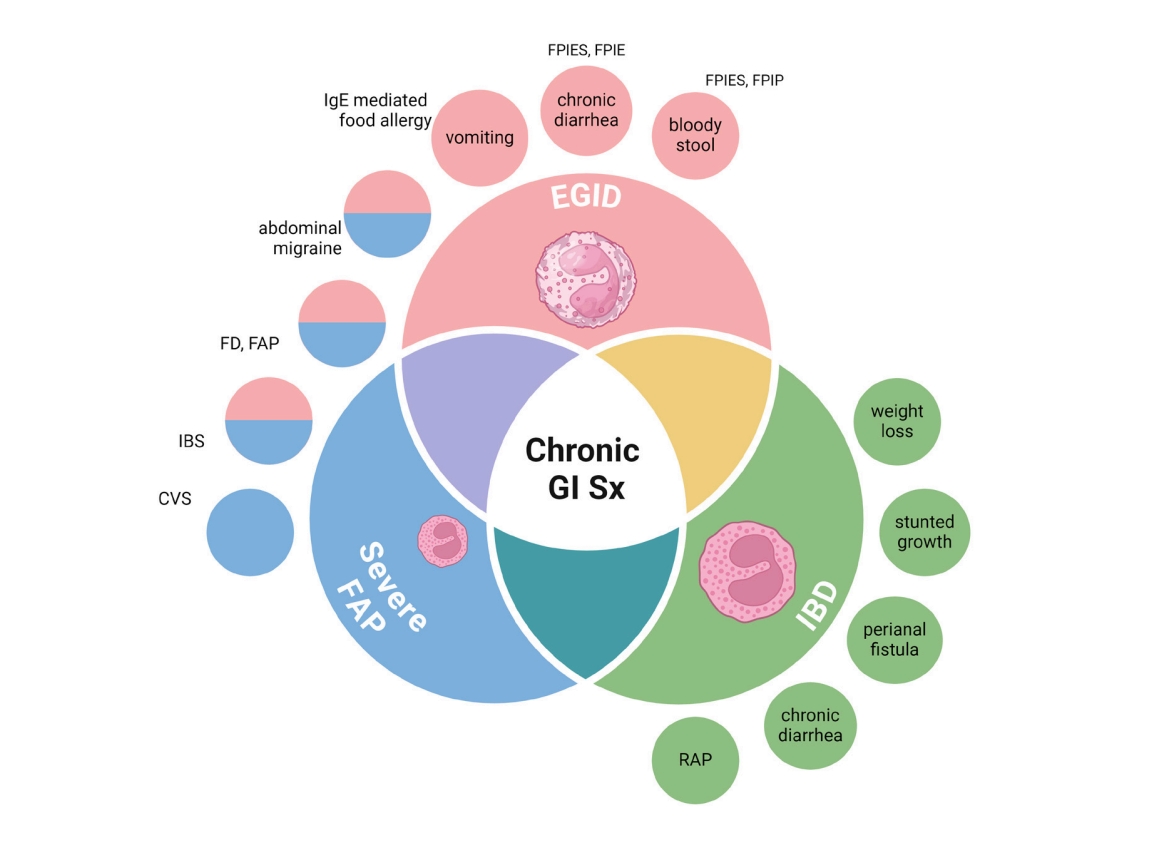
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs) often coexist with functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) and other IgE or non-IgE mediated GI diseases. Diagnosing EGIDs requires a high index of suspicion and a comprehensive approach to differentiate them from conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. Tests such as fecal calprotectin and biopsies aid in severe cases. Maintaining a food diary helps identify triggers for long-term elimination. Awareness and education are key to effective management.
- Value of transabdominal ultrasonography for diagnosing functional constipation in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Duc Long Tran, Phu Nguyen Trong Tran, Paweena Susantitaphong, Phichayut Phinyo, Palittiya Sintusek
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):127-135. Published online November 13, 2024
-
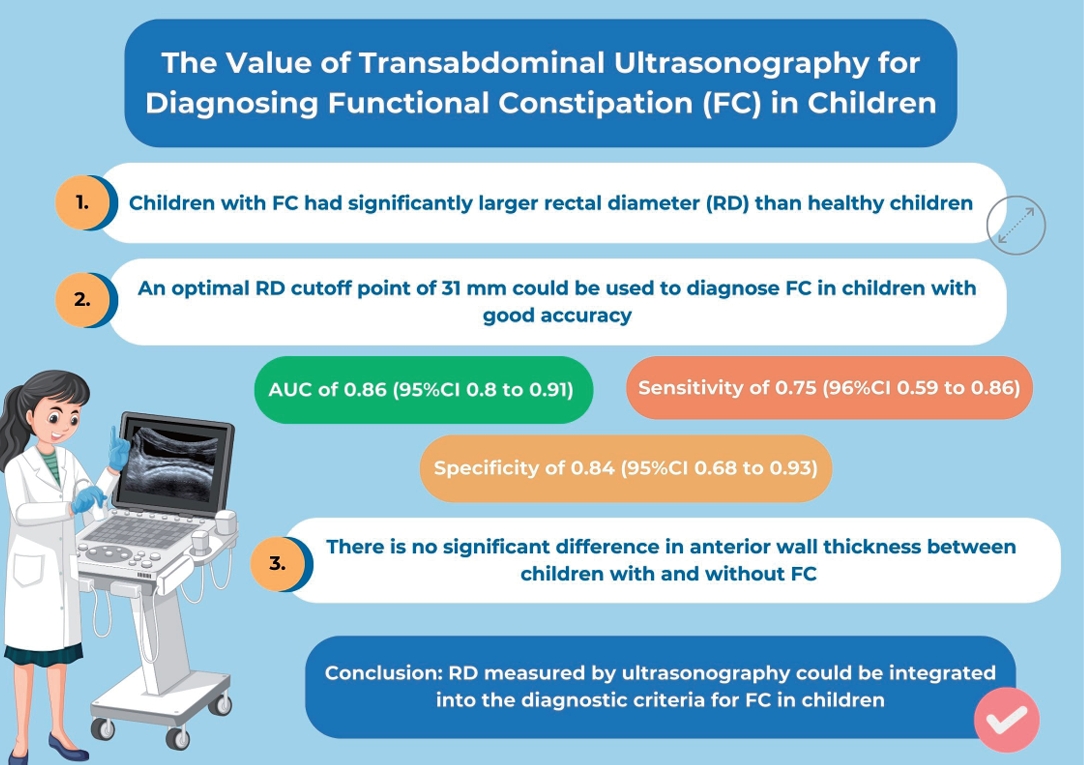
Transabdominal ultrasonography is increasingly used as a novel modality for detecting pediatric functional constipation (FC). This systematic review and metaanalysis aimed to assess the diagnostic parameters of FC including rectal diameter (RD) and anterior rectal wall thickness. A systematic search was conducted of the Ovid MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, and PubMed databases through September 29, 2023, to identify studies comparing RD...
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Evaluation of pediatric migraine triggers: a single-center study
- Hey-Joon Son, Joo-Ok Jin, Kon-Hee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):163-169. Published online November 11, 2024
-
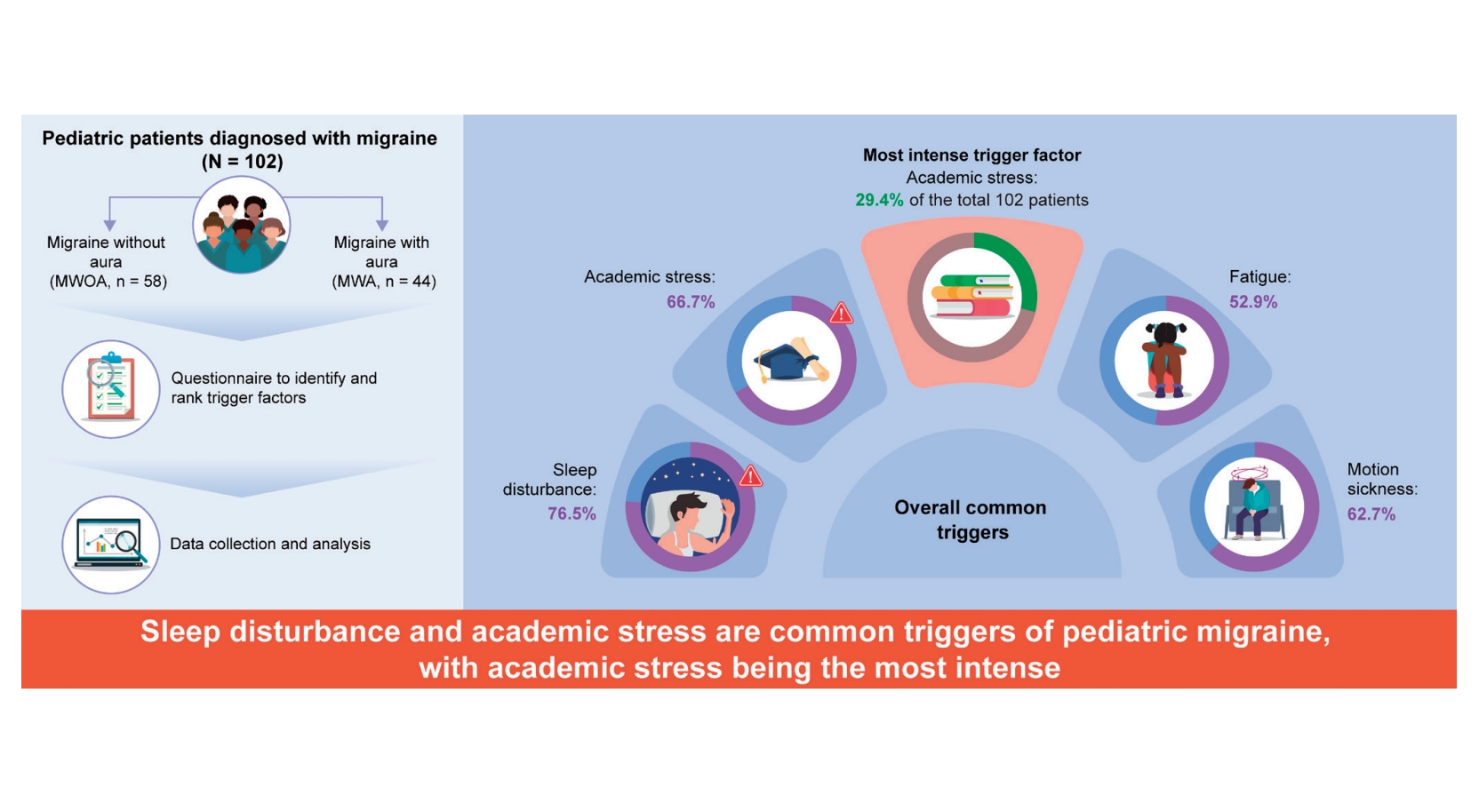
Question: What are the primary triggers for pediatric migraines, and how do they impact clinical management?
Finding: Common triggers for pediatric migraines include sleep disturbances, academic stress, and motion sickness, with academic stress identified as the most intense.
Meaning: Recognizing and addressing specific triggers like sleep disturbance and academic stress is crucial to effectively managing pediatric migraines with emphasis on personalized care to improve outcomes.
- Review Article
- Other
- Global trends in importance of 24-hour movement behaviors to pediatric health: implications for South Korea
- Eun-Young Lee, Reyana Jayawardena, Seiyeong Park, Justin Y Jeon, Yeon-Soo Kim, Mark S. Tremblay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):16-29. Published online November 11, 2024
-

· The 24-hour movement behavior paradigm provides an important framework for future pediatric health promotion efforts.
· Policy priorities should include advancing surveillance and monitoring assessments related to 24-hour movement behaviors, evaluating their implementation in school and government policies, and building preparedness for future pandemics and natural disasters, including climate change, by promoting healthy 24-hour movement behaviors.
· Future research should advocate for the promotion of 24- hour movement behaviors.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Nonpharmacological interventions for managing postoperative pain and anxiety in children: a randomized controlled trial
- Edlin Glane Mathias, Mamatha Shivananda Pai, Vijay Kumar, Dinesh Narayanakurup, Malavika Kulkarni, Vasudeva Guddattu, Ann-Cathrine Bramhagen, Baby S Nayak, Anice George
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):677-685. Published online October 31, 2024
-
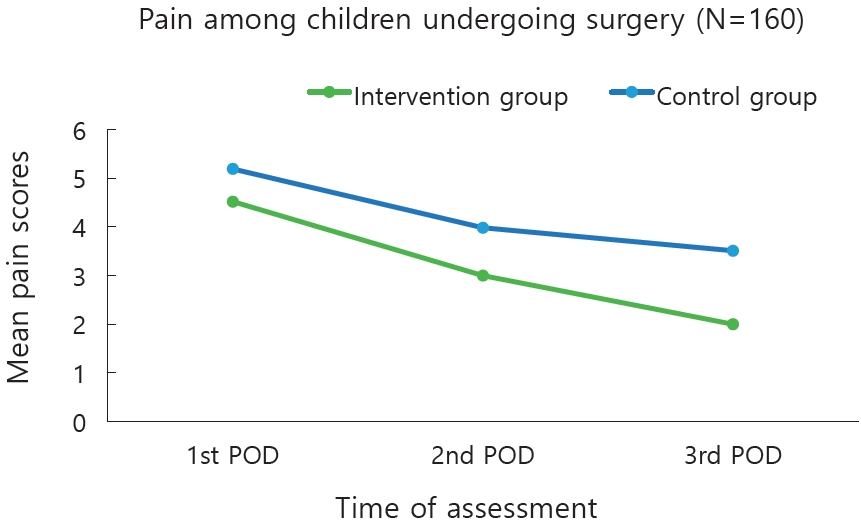
Question: What is the effect of nonpharmacological interventions on postoperative pain and anxiety among children.
Finding: Nurse-provided distraction interventions reduce pain and anxiety among pediatric surgical patients.
Meaning: The findings suggest that nonpharmacological interventions provided postoperatively to children reduce their pain and anxiety levels.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Protecting our future: environmental hazards and children’s health in the face of environmental threats: a comprehensive overview
- Jungha Lee, Hyo-Bin Kim, Hun-Jong Jung, Myunghee Chung, So Eun Park, Kon-Hee Lee, Won Seop Kim, Jin-Hwa Moon, Jung Won Lee, Jae Won Shim, Sang Soo Lee, Yunkoo Kang, Young Yoo; The Environmental Health Committee of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):589-598. Published online October 31, 2024
-

· Exposure to air pollutants cause allergic and respiratory diseases as well as chronic kidney disease.
· Adequate physical activity and proper nutrition are essential for children to maintain good health.
· We must educate people about the harmful effects of noise, blue light, heavy metals and smoke.
· Government and society must actively decrease environ-mental hazards.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Efficacies of different treatment strategies for infants hospitalized with acute bronchiolitis
- Hyeri Jeong, Dawon Park, Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Jeewon Shin, Hey-Sung Baek, Hyunsoo Hwang, Youn Ho Shin, Hye Mi Jee, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):608-618. Published online October 28, 2024
-

· This study analyzed 45 randomized controlled trials (5,061 participants, 13 interventions) of the comparative efficacies of treatments for acute bronchiolitis in infants.
· Inhalation therapy with epinephrine and hypertonic saline significantly reduced the length of hospital stay compared with normal saline.
· Hypertonic saline had the greatest ability to improve the clinical severity score of bronchiolitis in infants younger than 2 years of age.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effect of pesticide exposure on stunting incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Yaltafit Abror Jeem, Muhammad Fathi Banna Al Faruqi, Mahdea Kasyiva, Vita Widyasari, Kuswati Kuswati, Nur Aini Djunet, Muflihah Rizkawati, Ety Sari Handayani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):510-518. Published online September 24, 2024
-

This review aimed to determine whether pesticide exposure is associated with stunting in children. The 13 included studies agree that pesticide exposure is not correlated with stunting incidence regardless of substance type (organophosphate and pyrethroid). Heterogeneity appeared with age covariate as potential confounding. The evidence of this study is challeng-ing, as the adverse effects of pesticides grossly occurred. The protection of children is warranted for preventing future neurodevelopment issues.
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Comparative analysis of adolescent hypertension definitions for predicting early adulthood carotid artery intima-media thickness: Tehran lipid and glucose study
- Maryam Barzin, Shirin Yaghoobpoor, Maryam Mahdavi, Behnaz Abiri, Majid Valizadeh, Fereidoun Azizi, Pooneh Dehghan, Farhad Hosseinpanah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):694-703. Published online September 12, 2024
-
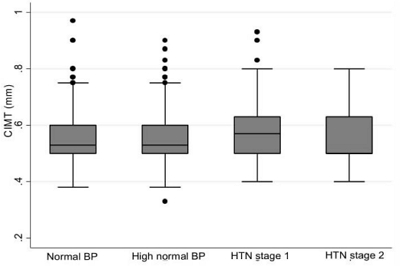
Question: What is the prevalence of HTN among adolescents enrolled in the TLGS according to 3 different accepted definitions (4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG). Also, what is the ability of each of these definitions in predicting early adulthood CIMT, as a surrogate for cardiovascular disease events?
Finding: The highest and lowest prevalence of stage 1 HTN was observed with the AAP-CPG (17.7%) and ESH (8.8%), respectively. Similarly, the highest and lowest prevalence of stage 2 HTN was noted with the AAP-CPG (1.5%) and ESH (0.8%), respectively. The highest to lowest predictive abilities belonged to the 4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG, respectively.
Meaning: Among the various definitions of pediatric HTN, the 4th report offered the best ability to predict a high CIMT during early adulthood, followed by the ESH and AAP-CPG.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Screen time among preschoolers: exploring individual, familial, and environmental factors
- Sangha Lee, Donghee Kim, Yunmi Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):641-650. Published online September 12, 2024
-
This systematic review examined the correlation between screen time and various factors in preschoolers. Findings suggest that media parenting, including setting appropriate media limits, is crucial in protecting against excessive screen exposure. However, limited research has been done on the impact of family and personal factors, particularly with the increasing use of portable devices among young children.
- Rheumatology
- Double-negative T cells in pediatric rheumatic diseases
- Dimitri Poddighe, Tilektes Maulenkul, Kuanysh Dossybayeva, Gulsamal Zhubanova, Zaure Mukusheva, Lyudmila Akhmaltdinova
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):632-640. Published online September 12, 2024
-
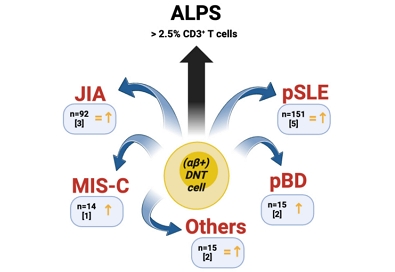
Double-negative T (DNT) cells appear to be increased in several pediatric rheumatic diseases and this finding may be correlated with disease activity to some extent. However, due to significant heterogeneity in several methodological aspects, further investigations in rheumatic children are needed to assess the potential relevance of DNT cells as biomarkers and clarify their immunopathological role.
- Allergy
- Comparison and review of international guidelines for treating asthma in children
- Eui Jeong Roh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):447-455. Published online August 20, 2024
-

Asthma is the most common chronic disease among children. Although asthma in children may spontaneously improve, it continues into adulthood in many cases. Therefore, appropriate disease management and medication are essential. Consistent and objective guidelines are needed to manage pediatric asthma and related adverse reactions.
- Original Article
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Interleukin (IL)-1B and IL-1 receptor antagonist gene polymorphisms in children with primary immune thrombocytopenia
- Seham Mohamed Ragab, Wafaa Moustafa Abo ElFotoh, Mahmoud Ahmed El-Hawy, Eman Abdelfatah Badr, Saara Khairat Ali Mostafa, Mai El-Sayad Abd El-Hamid
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):465-473. Published online July 24, 2024
-

· Polymorphisms in interleukin (IL)-1B and IL-1 receptor (IL-1R) antagonists may significantly affect the pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP).
· IL-1B and IL-1R antagonist gene polymorphisms are correlated with severity and susceptibility to primary ITP in children.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Comprehensive evaluation of the child with global developmental delays or intellectual disability
- Abdullah Nasser Aldosari, T. Saeed Aldosari
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):435-446. Published online May 29, 2024
-

· A detailed history and comprehensive physical examination remain the cornerstones for establishing a diagnosis of global developmental delay/intellectual disability (GDD/ID).
· Comprehensive surveillance and screening programs play a significant role in the early detection of GDD.
· Whole-exome sequencing is highly recommended as first- or second-line testing for individuals with idiopathic GDD/ID.
· Early intervention by a well-versed multidisciplinary team can significantly improve the outcomes and prognosis of GDD/ID.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effectiveness of online responsive teaching in young children with developmental disabilities: a pilot study
- Jung Sook Yeom, Jeongmee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):303-311. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Question: Does online responsive teaching (RT) impact children's and parents’ emotions and behaviors, and do parents find it satisfactory?
Finding: Online RT significantly improved children's pivotal and problem behaviors, decreased parenting stress, and enhanced parental interactive styles with high satisfaction.
Meaning: This pilot study's findings suggest that online RT can enhance child outcomes, offering accessible interventions amid challenges such as limited access and pandemics.
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- Evidence-based management guidelines for noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis in children and adolescents
- Eun Lee, Kyunghoon Kim, You Hoon Jeon, In Suk Sol, Jong Deok Kim, Taek Ki Min, Yoon Ha Hwang, Hyun-Ju Cho, Dong In Suh, Hwan Soo Kim, Yoon Hee Kim, Sung-Il Woo, Yong Ju Lee, Sungsu Jung, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Gwang Cheon Jang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):418-426. Published online January 23, 2024
-

· We suggest offering long-term macrolides to children with noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis with frequent exacerbations (conditional recommendation, moderate quality of evidence).
· We do not recommend the routine use of mucolytic agents, inhaled corticosteroids, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent exacerbation of bronchiectasis in children (inconclusive, very low quality of evidence).
· We recommend the use of nebulized hypertonic saline to prevent exacerbations and improve the lung function of children with noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis (weak recommendation, moderate quality of evidence).
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Effect of face mask on pulmonary artery pressure during echocardiography in children and adolescents
- Alireza Ahmadi, Mohammad Reza Sabri, Zohreh Sadat Navabi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):161-167. Published online January 23, 2024
-
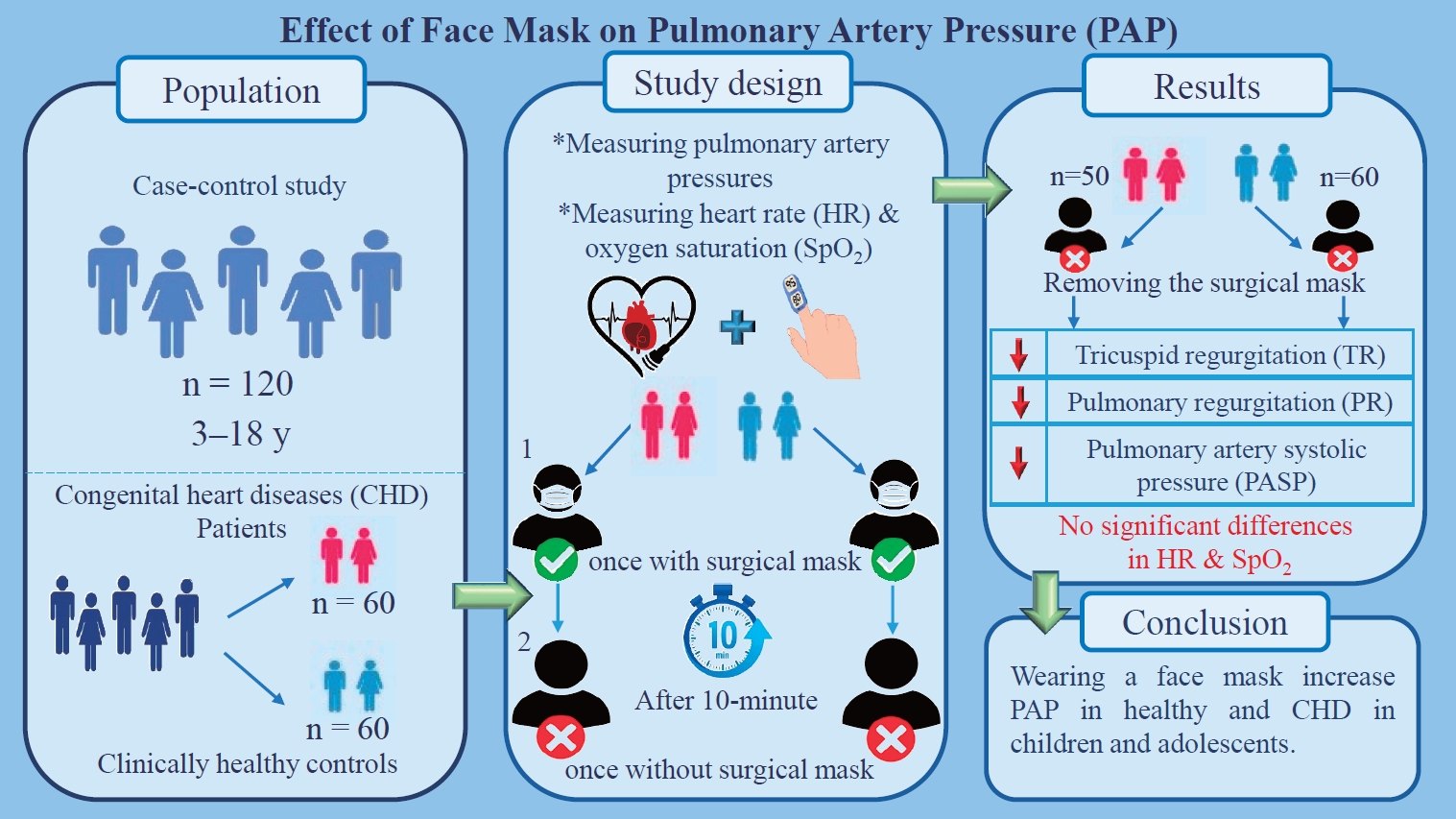
Question: Can face masks alter pulmonary pressure in children and adolescents with and without congenital heart disease?
Findings: Mask removal during echocardiography (ECHO) reduced pulmonary pressure.
Meaning: These findings suggest that face masks should be removed during ECHO in children and adolescents.
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Effects of diethylene glycol contamination of pharmaceutical products on unexplained acute kidney injury in children: a systematic review
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Muhammad Luthfi Adnan, Hilmi Ardian Sudiarto, Satria Bintang Mahathma, Alya Ayu Tazkia, Hana Afifah Firdaus, Alfreda Amelia Khotijah, Miranti Dewi Pramaningtyas, Emi Azmi Choironi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):395-402. Published online January 4, 2024
-

A recent unexplained acute kidney injury (AKI) outbreak due to pharmaceutical product contamination with diethylene glycol (DEG) raises public attention. Our study revealed that DEG-contaminated paracetamol causes unexplained AKI in children. However, paracetamol is not the only contaminated drug. Other drugs, such as cough expectorants, antihistamines, and sedatives, can also be affected. Other chemicals, such as ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, can also contribute to poisonings.
- Original Article
- Adolescence Medicine
- Relationship between inflammatory biomarkers and insulin resistance in excess-weight Latin children
- Mariano Nicolás Aleman, María Constanza Luciardi, Emilce Romina Albornoz, María Cristina Bazán, Adela Victoria Abregú
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):37-45. Published online December 21, 2023
-
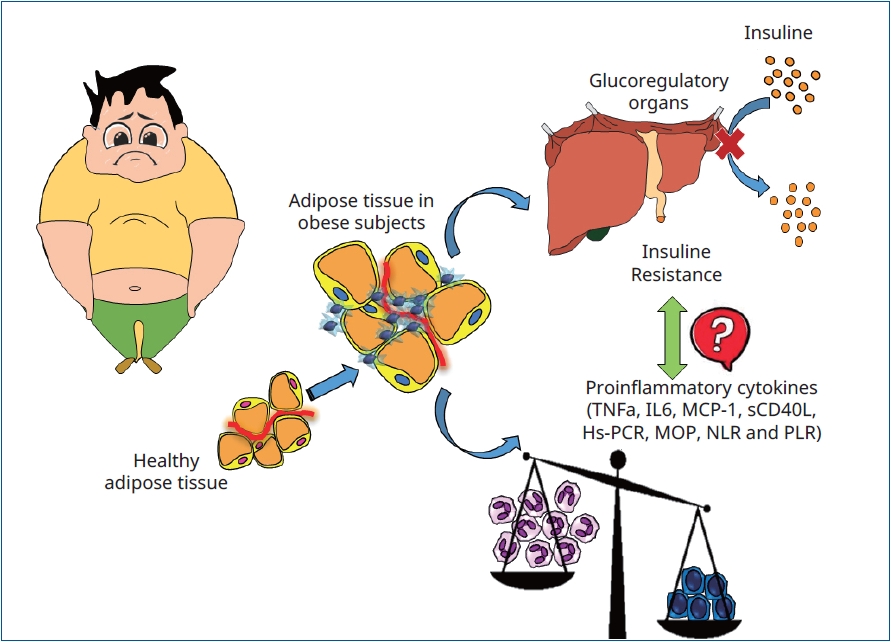
Question: What is the prevalence of insulin resistance (IR) in excess-weight Latin children, and can proinflammatory biomarkers predict it?
Finding: IR prevalence was elevated and tumor necrosis factor- α, interleukin-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein- 1, soluble CD40 ligand, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels were increased in excess-weight Latin children. However, none predicted IR status.
Meaning: These inflammatory biomarkers were unable to predict IR status. Therefore, further investigations are necessary.
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











