Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Infection
- Evolving treatment strategies for invasive Streptococcus pyogenes in children in the postpandemic era
- Laura Buricchi, Giuseppe Indolfi, Marco Renni, Elisabetta Venturini, Luisa Galli, Elena Chiappini
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):921-931. Published online August 11, 2025
-

Question: What are the roles of linezolid, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), and corticosteroids in pediatric invasive group A streptococcal infection (iGAS)? Can any improve outcomes beyond beta-lactams and clindamycin?
Finding: Two of 46 patients with iGAS died. Nearly all received beta-lactams plus clindamycin. Linezolid was effective in refractory cases. IVIG and corticosteroids had variable efficacies.
Meaning: Linezolid may be valuable in refractory cases. IVIG may be considered in severe presentations. The role of corticosteroids remains less clearly defined.
- Construction and validation of predictive models for intravenous immunoglobulin–resistant Kawasaki disease using an interpretable machine learning approach
- Linfan Deng, Jian Zhao, Ting Wang, Bin Liu, Jun Jiang, Peng Jia, Dong Liu, Gang Li
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):405-414. Published online July 23, 2024
-

Question: Is there a reliable model to predict intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)-resistant Kawasaki disease (KD)?
Finding: We constructed 5 machine learning models to predict IVIG-resistant KD. Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) model was superior to logistic, support vector machine, light gradient boosting machine and multiple layers perception models. The SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) value interpreted the contribution of each feature in XGBoost model.
Meaning: XGBoost model showed the excellent performance to predict IVIG-resistant KD with explainable and visualizable machine learning algorithm.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Two- versus one-bag fluid delivery in pediatric and adolescent diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Maya L. Nasser, Joseph Nasr, Reem B. Zalloum, Nathanael Q.E. Yap, Natalie E. Bourdakos, Shahid Miangul, Tara A. Betts, Hayato Nakanishi, Christian A. Than, Serge Jabbour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):486-497. Published online June 27, 2024
-

· The safety and efficacy of the two-bag versus one-bag system for treating patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) < 21 years remains unestablished.
· Our meta-analysis demonstrated similar safety outcomes but sooner DKA resolution and shorter mean response time for intravenous fluid changes for the two-bag system.
· This preliminary evidence suggests that the two-bag system has some advantages in efficacy, but further studies are needed to evaluate their extent.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Virtual reality for pain reduction during intravenous injection in pediatrics: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Amir Mohammad Salehi, Masoud Rafiee, Mozhdeh Bashirian
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):533-537. Published online June 14, 2023
-
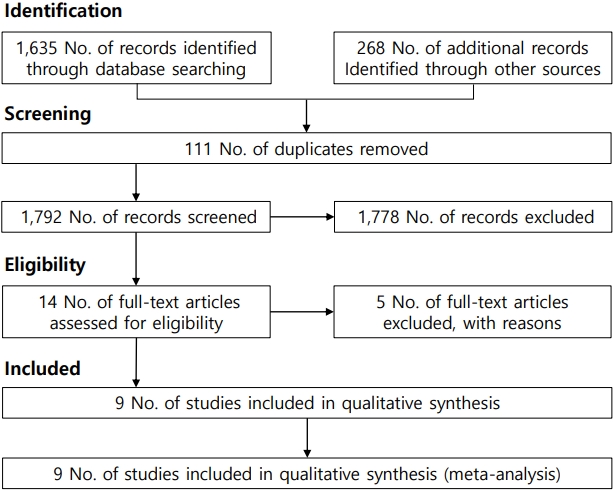
Question: This is the first meta-analysis to examine published evidence of the effectiveness of virtual reality at reducing pain during pediatric intravenous injections.
Finding: Our results suggest that virtual reality effectively reduces pain associated with intravenous injections in pediatric patients.
Meaning: These findings suggest the importance of virtual reality in decreasing the pain of intravenous injections among children.
- Review Article
- Immunology
- Immunopathogenesis of COVID-19 and early immunomodulators
- Kyung-Yil Lee, Jung-Woo Rhim, Jin-Han Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):239-250. Published online June 18, 2020
-

The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading globally. Although its etiologic agent is discovered as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), there are many unsolved issues in COVID-19 and other infectious diseases. The causes of different clinical phenotypes and incubation periods among individuals, species specificity, and cytokine storm with lymphopenia as well as the mechanism of damage to organ...
- Predictors and management of intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease
- Min Seob Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(4):119-123. Published online March 15, 2019
-

Kawasaki disease (KD) is a systemic vasculitis that mainly affects younger children. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) resistant cases are at increasing risk for coronary artery complications. The strategy on prediction of potential nonresponders and treatment of IVIG-resistant patients is now controversial. In this review the definition and predictors of IVIG-resistant KD and current evidence to guide management are discussed.
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Prediction of nonresponsiveness to medium-dose intravenous immunoglobulin (1 g/kg) treatment: an effective and safe schedule of acute treatment for Kawasaki disease
- Kyung Pil Moon, Beom Joon Kim, Kyu Jin Lee, Jin Hee Oh, Ji Whan Han, Kyung Yil Lee, Soon Ju Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(4):178-182. Published online April 30, 2016
-
Purpose Medium-dose (1 g/kg) intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is effective in the majority of patients with Kawasaki disease (KD) but some patients who do not respond to medium-dose IVIG are at high risk for the development of coronary artery lesions (CALs). The purpose of this study was to identify the clinical predictors associated with unresponsiveness to medium-dose IVIG and the development of...
- Meta-analysis of factors predicting resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease
- Jin-Young Baek, Min Seob Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(2):80-90. Published online February 29, 2016
-
Purpose Studies have been conducted to identify predictive factors of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) for Kawasaki disease (KD). However, the results are conflicting. This study aimed to identify laboratory factors predictive of resistance to high-dose IVIG for KD by performing meta-analysis of available studies using statistical techniques.
Methods All relevant scientific publications from 2006 to 2014 were identified through PubMed searches. For...
- Intravenous fluid prescription practices among pediatric residents in Korea
- Jiwon M. Lee, Younghwa Jung, Se Eun Lee, Jun Ho Lee, Kee Hyuck Kim, Ja Wook Koo, Young Seo Park, Hae Il Cheong, Il-Soo Ha, Yong Choi, Hee Gyung Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(7):282-285. Published online July 19, 2013
-
Purpose Recent studies have established the association between hypotonic fluids administration and hospital-acquired hyponatremia in children. The present paper investigated the pattern of current practice in intravenous fluid prescription among Korean pediatric residents, to underscore the need for updated education.
Methods A survey-based analysis was carried out. Pediatric residents at six university hospitals in Korea completed a survey consisting of four questions. Each...
- Predictors of nonresponse to intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in Kawasaki disease
- Hyo Min Park, Dong Won Lee, Myung Chul Hyun, Sang Bum Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(2):75-79. Published online February 25, 2013
-
Purpose It has been reported that 10% to 20% of children with Kawasaki disease (KD) will not respond to intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment. In this study, we aimed to identify useful predictors of therapeutic failure in children with KD.
Methods We examined 309 children diagnosed with KD at the Kyungpook National University Hospital and the Inje University Busan Paik Hospital between January 2005...
- The characteristic laboratory findings of non-responsiveness to intravenous immunoglobulin in children with Kawasaki disease
- Han Gil Cho, Young Kuk Cho, Jae Sook Ma
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(2):228-234. Published online February 15, 2010
-
Purpose : Although intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment is an effective first-line treatment for Kawasaki disease, 10-20% of the patients develop persistent fever or coronary artery complications. Medical records of Kawasaki disease patients were reviewed to assess the characteristic laboratory findings of IVIG nonresponsiveness. Methods : We reviewed the clinical records of 118 children with Kawasaki disease who were treated at... -
- Case Report
- Change of neutrophil count after treatment of intravenous immunoglobulin in children with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Jun Young Park, Ji Ae Park, Seong Shik Park, Young Tak Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(2):204-208. Published online February 15, 2008
-
Purpose : The aim of this study was to investigate the incidence and course of neutropenia following intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapy in children with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP). Methods : From January 2001 to June 2006, fifty-four patients with ITP were enrolled in this study. Forty-two of 54 patients were treated with IVIG, while the other 12 were treated with... -
- Original Article
- Effect of intravenous deferoxamine in multiply transfused patients
- Sang Min Oh, Joon Won Kang, Sun Young Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(12):1225-1230. Published online December 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Multiple transfusions in patients with chronic anemia can result in excessive iron deposition in tissues and organs. Effective iron chelation therapy in chronically transfused patients can only be achieved when iron chelators remove sufficient amounts of iron equivalent to those accumulated in the body from transfusions, thus leading to maintain body iron load at a non-toxic level. This... -
- Clinical characteristics and progress of Kawasaki disease patients who had early treatment with intravenous immune globulin
- So-Yoon Park, Young Hwan Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(10):1005-1010. Published online October 15, 2007
-
Purpose : To determine the optimal time of high dose intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) treatment, we analysed the clinical characteristics and progress of a group of Kawasaki disease patients who had early treatment with IVIG. Method : A retrospective study was conducted of 188 patients with Kawasaki disease who were admitted to Yeungnam University Medical Center from January 2000 to December... -
- Change of absolute neutrophil count after intravenous immunoglobulin administration for the children with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Hyun Jung Shin, In Kug Bang, Byung Kyu Choe, Jin-Bok Hwang, Jun Sik Kim, Heung Sik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(10):982-986. Published online October 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is effective for the treatment of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) in children. Recently, several reports have been published that show its impact on the absolute neutrophil count. The present study was performed to confirm these findings. Methods : Data on 26 ITP patients were analyzed. Patients with febrile illness or increased C-reactive protein levels... -
- The effects of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin on plasma protein and lipid levels in the patients with Kawasaki disease
- Keun Young Lee, Dong-Un Kim, Hyun Seung Lee, Pil Sang Jang, Young-Hoon Kim, Jin Tack Kim, Hyun Hee Kim, Kyung-Yil Lee, Joon-Sung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(12):1348-1353. Published online December 15, 2006
-
Purpose : The reticuloendothelial system is composed of sinusoidal capillaries, through which even large protein molecules are freely movable between plasma and interstitial space, including the lymphatic system. Therefore, high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) would cause a redistribution of proteins between two compartments. To investigate this hypothesis, we measured plasma protein and lipid levels in patients with Kawasaki disease before and... -
- Case Report
- Steroid and enalapril therapy - possible cause of toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Dong Wook Kim, Da Eun Jung, Ja Wook Koo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(3):332-336. Published online March 15, 2006
-
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) is a rare, acute and life-threatening cutaneous drug reaction. TEN is characterized by the sudden onset of extensive necrosis in the epidermis and frequent mucous membrane involvement. The pathogenesis has not yet been elucidated. In addition, no particular treatment for TEN has been established. We report a case of TEN in a 14-year-old-boy, which might have... -
- Original Article
- The Effectiveness of Intravenous Immunoglobulin for Clinically Suspected Neonatal Sepsis
- Hyun Jung Na, Ji Young Kim, Gyeong Hoon Lee, Jun Hwa Lee, Eun Jin Choi, Jin Kyung Kim, Hai Lee Chung, Woo Taek Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(11):1187-1192. Published online November 15, 2005
-
Purpose : The purpose of this study is to determine the effectiveness of intravenous immunoglobuin (IVIG) administration in fullterm neonates having clinically suspected neonatal sepsis. Methods : Forty full-term neonates admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit with clinically suspected neonatal sepsis, who had at least two positive diagnostic criteria were enrolled. Twenty neonates were enrolled into the IVIG arm and... -
- Inhibition of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-induced Endothelial Cell Differentiation by Intravenous Immunoglobulin and Methylprednisolone
- Hyoun Ah Choi, Kyung Hwa Ha, Jong Seo Yoon, Yoon Lee, Joon Sung Lee, Ji Whan Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(8):886-893. Published online August 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Kawasaki disease is the most common cause of systemic vasculitis in children less than 5 years of age. Recent immunohistochemistry findings suggest that many vascular growth factors play a role in the formation of the coronary artery lesions. Active remodeling of the coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease continues in the form of intimal proliferation and neoangiogenesis for... -
- Statistical Analysis of 1,000 Cases of Kawasaki Disease Patients Diagnosed at a Single Institute
- Dae Hwan Hwang, Kyoung Mi Sin, Kyong Min Choi, Jae Young Choi, Jun Hee Sul, Dong Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(4):416-424. Published online April 15, 2005
-
Purpose : To find the risk factors associated with coronory artery lesions, non-responsiveness to intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) treatment, and recurrences in Kawasaki disease patients. Methods : We retrospectively analyzed 1,000 Kawasaki disease patients who were admitted to Yonsei University Medical Center from September 1990 to December 2003. We compared between responder and non-responder groups to IVIG treatment as well as between relapsed... -
- The Effects of Intravenous Immunoglobulin(IVIG) and Methylprednisolone on the mRNAs Expressions of VEGF, VCAM-1 and IL-1β of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells(HUVEC) Stimulated by IL-1β
- Soh Yeon Kim, Sun Jeong Lim, Ji Whan Han, Kyung Yil Lee, Joon Sung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(12):1325-1333. Published online December 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Kawasaki disease(KD) manifests a systemic vasculitis of unknown etiology in young children. Vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1(VCAM-1) and interleukin-1 beta(IL-1β) may play important roles in the pathogenesis of KD. Intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) and methylprednisolone(MP) are therapeutically effective for KD, however, the precise mechanisms of the two drugs are still unknown. We investigated the therapeutic efficacy of... -
- Aseptic Meningitis Secondary to High-Dose Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy in Kawasaki Disease
- Ae Ra Cho, Jee Yoon Park, Kyung Hyo Kim, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(5):561-566. Published online May 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Kawasaki disease is a multisystemic inflammatory vasculitis and associated with neurologic features such as aseptic meningitis. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) is used to treat Kawasaki disease and generally considered to be safe, but rare cases of aseptic meningitis with unknown etiology have been reported. The aseptic meningitis associated with Kawasaki disease was compared with meningitis as the adverse reaction... -
- Manifestation of Coronary Artery Lesions after Immunoglobulin Re-treatment in Initial Immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki Disease
- Hyo Jung Suk, In Sung Kim, Jo Won Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(4):424-429. Published online April 15, 2004
-
Purpose : To evaluate the predictable factors for why initial intravenous immune globulin(IVIG) therapy failed and the outcome of coronary lesions after additional IVIG retreated in initial IVIG- resistant Kawasaki disease(KD). Methods : Retrospective studies were performed on 284 cases of KD treated with one episode of high-dose IVIG and 63 cases with additional IVIG retreatment at this hospital from January... -
- Prediction of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Non-responders in Patients with Kawasaki Disease
- Gi Bum Lee, Ji-Won Lee, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(1):90-94. Published online January 15, 2004
-
Purpose : We evaluated the effects of intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) on the levels of laboratory indices examined serially according to the responsiveness to IVIG therapy in children with Kawasaki disease(KD). Methods : Children with KD(n=63) who had been treated with IVIG at a dosage of 2.0 g/kg were classified into two groups : the IVIG-resistant(consistent fever over 48 hours after initiation... -
- Case Report
- Arthritis in the Subacute Stage of Kawasaki Disease after Responding to Intravenous Immunoglobulin Treatment
- Kyung-Yil Lee, Jin-Hee Oh, Dea-Kyun Koh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(11):1124-1127. Published online November 15, 2003
-
We evaluated the clinical and laboratory characteristics of five children with Kawasaki disease who had showed arthritis after responding to intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) treatment. Age distribution was between 13 months and six years of age(mean 3.2?.6 years). There were two males and three females. Arthritis occurred when acute symptoms were subsiding, with the average onset on day 5.8?.8 after final IVIG... -
- A Case of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Nephritis Complicating Encephalopathy Accompanied by Hypertension and Cerebral Vasculitis
- Hee Ra Choi, Eo Jin Kim, Myoung Bum Choi, Jae Young Lim, Chan Hoo Park, Hyang Ok Woo, Hee Sang Youn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(10):1040-1043. Published online October 15, 2003
-
Henoch-Shonlein purpura(HSP) is a systemic small-vessel vasculitis that primarily affects the skin, gastrointestinal tract, joints, and kidneys. The nervous system may be involved, less commonly than other organs. When the central nervous system(CNS) was involved, headache, changes in mental status, seizures, and focal neurologic deficits have been reported. Hypertension, uremic encephalopathy, metabolic abnomalities, electrolyte abnormalities, or cerebral vasculitis were suggested... -
- Original Article
- Safety and Efficacy of Early Treatment with Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Patients with Kawasaki Disease
- Hyun Jin Kim, Hae Won Yom, Hae Soon Kim, Sejung Sohn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(10):1019-1023. Published online October 15, 2003
-
Purpose : To determine the differences in clinical characteristics, blood chemistry and coronary artery complications between patients with Kawasaki disease who received intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) within the fourth day of illness and after the fifth day of illness. Methods : A retrospective chart review was conducted of all children with Kawasaki disease who were admitted to Ewha Mokdong Hospital between January... -
- Alteration of Biochemical Profiles after High-Dose Intravenous Immunoglobulin Administration in Kawasaki Disease
- Ji-Won Lee, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(8):817-820. Published online August 15, 2003
-
Purpose : Intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) has been used as an immunomodulatory treatment for several immune-mediated diseases. The early effect of high-dose IVIG on biochemical profiles including lipids and proteins was evaluated in patients with Kawasaki disease(KD). Methods : Twelve children with KD(nine boys) were treated with IVIG of 2 g/kg over 12 hours. Serial sera were collected from the patients four times... -
- Laboratory Values in Patients with Kawasaki Disease after Intravenous Immunoglobulin : Comparison of Patients with Coronary Artery Lesions to those without Coronary Artery Lesions
- Min-Young Park, Kyung-Yil Lee, Ji-Whan Han, Hyung-Shin Lee, Ja-Hyun Hong, Kyung-Tai Whang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(2):162-166. Published online February 15, 2003
-
Purpose : We evaluated the effects of intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) on level of laboratory parameters examined serially according to the existence of coronary artery lesions in children with Kawasaki disease. Methods : Children with Kawasaki disease(n=63), treated with IVIG at a dose of 2.0 g/kg, were classified as a group with coronary artery lesions(CALs+ group, n=9) or a group without coronary... -
- High-dose Intravenous Immune Globulin Retreatment in Kawasaki Disease
- So Yun Shim, Mi Young Heo, Hae Soon Kim, Sejung Sonh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(10):1273-1277. Published online October 15, 2002
-
Purpose : To determine clinical features, laboratory findings and cardiac abnormalities of highdose immune globulin(IVIG) retreatment in patients with Kawasaki disease, and to report effectiveness of retreatment. Methods : Retrospective study of 174 children diagnosed with Kawasaki disease at Ewha Mokdong hospital from March, 1999 to July, 2001. Results : Twenty(11.5%) of 174 patients were retreated with high-dose IVIG. After this, only two patients(1.1%) did not... -
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











