Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Outcome of ultrasonographic imaging in infants with sacral dimple
- Jin Hyuk Choi, Taekwan Lee, Hyeok Hee Kwon, Sun Kyoung You, Joon Won Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(6):194-199. Published online June 25, 2018
-
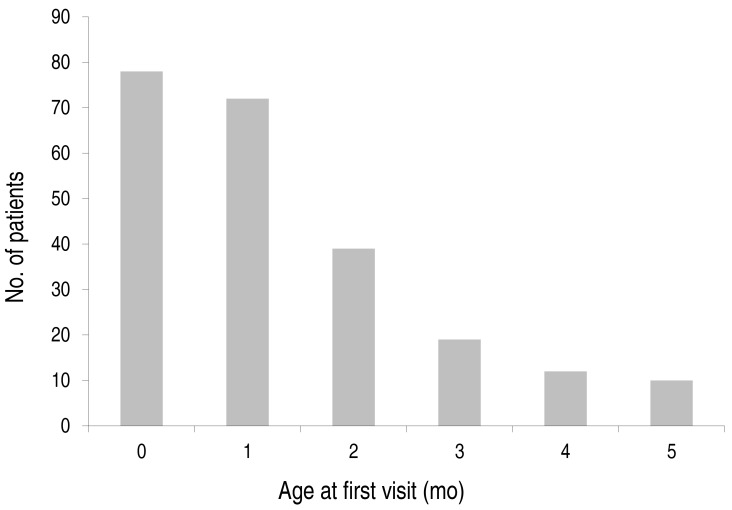
Purpose Sacral dimples are a common cutaneous anomaly in infants. Spine ultrasonography (USG) is an effective and safe screening tool for patients with a sacral dimple. The aim of this study was to determine the clinical manifestations in patients with an isolated sacral dimple and to review the management of spinal cord abnormalities identified with USG.
Methods We reviewed clinical records and collected...
- Long-term prenatal stress increases susceptibility of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid-induced spasms in infant rats
- Hyeok Hee Kwon, Taekwan Lee, Jinpyo Hong, Dong Woon Kim, Joon Won Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(5):150-155. Published online May 28, 2018
-
Purpose Infantile spasms, also known as West syndrome, is an age-specific epileptic seizure. Most patients with this condition also exhibit delayed development. This study aimed to determine the effect of long-term prenatal stress on susceptibility to infantile spasms.
Methods We subjected pregnant rats to acute or chronic immobilization stress. Resulting offspring received N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (15 mg/kg, intraperitoneally) on postnatal day 15, and their...
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Epilepsy syndromes during the first year of life and the usefulness of an epilepsy gene panel
- Eun Hye Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(4):101-107. Published online April 23, 2018
-

Recent advances in genetics have determined that a number of epilepsy syndromes that occur in the first year of life are associated with genetic etiologies. These syndromes range from benign familial epilepsy syndromes to early-onset epileptic encephalopathies that lead to poor prognoses and severe psychomotor retardation. An early genetic diagnosis can save time and overall cost by reducing the amount...
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Augmentation of respiratory muscle activities in preterm infants with feeding desaturation
- Dong Rak Kwon, Gi Young Park, Ji Eun Jeong, Woo Taek Kim, Eun Joo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(3):78-83. Published online March 19, 2018
-
Purpose Frequent desaturation due to immature incoordination of suck-swallow-breathing in preterm infants can influence multiple organs such as the heart, lungs, and brain, which can then affect growth and development. Most notably in preterm infants, feeding desaturation may even affect pulmonary function during gavage feeding. Because respiratory muscle activities may reflect the work required during respiration, we evaluated the differences in...
- Oncology
- Excellent treatment outcomes in children younger than 18 months with stage 4
MYCN nonamplified neuroblastoma - Chiwoo Kim, Young Bae Choi, Ji Won Lee, Keon Hee Yoo, Ki Woong Sung, Hong Hoe Koo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(2):53-58. Published online February 28, 2018
-
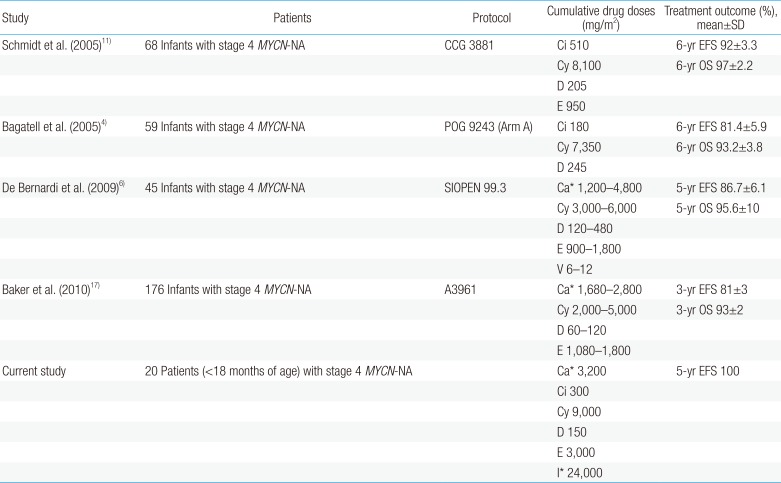
Purpose Although the prognosis is generally good in patients with intermediate-risk neuroblastoma, no consensus has been reached on the ideal treatment regimen. This study analyzed treatment outcomes and toxicities in patients younger than 18 months with stage 4
MYCN nonamplified neuroblastoma.Methods We retrospectively analyzed 20 patients younger than 18 months newly diagnosed with stage 4
MYCN nonamplified neuroblastoma between January 2009 and...
- Case Report
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Case of mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung associated with congenital pulmonary airway malformation in a neonate
- Juneyoug Koh, Euiseok Jung, Se Jin Jang, Dong Kwan Kim, Byong Sop Lee, Ki-Soo Kim, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(1):30-34. Published online January 22, 2018
-
Congenital pulmonary airway malformation (CPAM), previously known as congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation, is a rare developmental lung abnormality associated with rhabdomyosarcoma, pleuropulmonary blastoma, and mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung. We report an unusual case of a 10-day-old male newborn with a left lower lobe pulmonary cyst who underwent lobectomy, which revealed type II CPAM complicated by multifocal mucinous adenocarcinoma. KRAS...
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Usefulness of the Korean Developmental Screening Test for infants and children for the evaluation of developmental delay in Korean infants and children: a single-center study
- Chung-Hyuk Yim, Gun-Ha Kim, Baik-Lin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(10):312-319. Published online October 20, 2017
-

Purpose To evaluate the usefulness of the Korean Developmental Screening Test (K-DST) for infants and children for developmental delay assessment.
Methods This study was based on retrospective studies of the results of the K-DST, Preschool Receptive-Expressive Language Scale (PRES), Sequenced Language Scale for Infants (SELSI), Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS), Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT), electroencephalography, magnetic resonance imaging, and extensive...
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Fetal and preterm infant microbiomes: a new perspective of necrotizing enterocolitis
- Yong-Sung Choi, In Gyu Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(10):307-311. Published online October 20, 2017
-
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating condition of hospitalized preterm infants. Numerous studies have attempted to identify the cause of NEC by examining the immunological features associated with pathogenic microorganisms. No single organism has proven responsible for the disease; however, immunological studies are now focused on the microbiome. Recent research has investigated the numerous bacterial species residing in the body...
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Comparison of cytokine expression profiles in infants with a rhinovirus induced lower respiratory tract infection with or without wheezing: a comparison with respiratory syncytial virus
- Da Eun Roh, Sook-Hyun Park, Hee Joung Choi, Yeo Hyang Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(9):296-301. Published online September 21, 2017
-
Purpose The aim of this study was to evaluate whether infants with rhinovirus (RV) infection-induced wheezing and those with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection-induced wheezing have different cytokine profiles in the acute stage.
Methods Of the infants with lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI) between September 2011 and May 2012, 88 were confirmed using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and hospitalized. Systemic interferon-gamma (IFN-γ),...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effects of cord blood vitamin D levels on the risk of neonatal sepsis in premature infants
- Birgul Say, Nurdan Uras, Suzan Sahin, Halil Degirmencioglu, Serife Suna Oguz, Fuat Emre Canpolat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(8):248-253. Published online August 14, 2017
-
Purpose Vitamin D plays a key role in immune function. Vitamin D deficiency may play a role in the pathogenesis of infections, and low levels of circulating vitamin D are strongly associated with infectious diseases. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the effects of low vitamin D levels in cord blood on neonatal sepsis in preterm infants.
Methods One hundred seventeen premature...
- Individualized ibuprofen treatment using serial B-type natriuretic peptide measurement for symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus in very preterm infants
- Jeonghee Shin, Eun Hee Lee, Jee Hyun Lee, Byung Min Choi, Young Sook Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(6):175-180. Published online June 22, 2017
-
Purpose Plasma level of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), an emerging, sensitive, and specific biomarker of hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), rapidly decreases in infants receiving cyclooxygenase inhibitors for ductal closure. We investigated the usefulness of serial BNP measurement as a guide for individual identification of early constrictive responses to ibuprofen in preterm infants with symptomatic PDA (sPDA).
Methods Before March 2010, the...
- Healthcare access challenges facing six African refugee mothers in South Korea: a qualitative multiple-case study
- Min Sun Kim, In Gyu Song, Ah Reum An, Kyae Hyung Kim, Ji Hoon Sohn, Sei Won Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(5):138-144. Published online May 31, 2017
-
Purpose Following legal reform in 2013, the annual number of asylum seekers entering South Korea has increased from 1,143 in 2012 to 5,711 in 2015. We interviewed six African refugee mothers of young children regarding their health needs and barriers to access maternal child health services.
Methods We recruited mothers who had visited a clinic for immigrants between July 2013 and August 2015....
- Nutrition
- Maternal food restrictions during breastfeeding
- Goun Jeong, Sung Won Park, Yeon Kyung Lee, Sun Young Ko, Son Moon Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):70-76. Published online March 27, 2017
-
Purpose This study investigated self-food restriction during breastfeeding, reviewed the literature showing the effect of maternal diet on the health of breast-fed infants, and explored the validity of dietary restrictions.
Methods Questionnaire data were collected from breastfeeding Korean mothers who visited the pediatric clinic of Cheil General Hospital & Women's Healthcare Center from July 2015 through August 2015. The survey included items assessing...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Postdischarge growth assessment in very low birth weight infants
- Joon-Sik Park, Jungho Han, Jeong Eun Shin, Soon Min Lee, Ho Seon Eun, Min-Soo Park, Kook-In Park, Ran Namgung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):64-69. Published online March 27, 2017
-
Purpose The goal of nutritional support for very-low-birth-weight (VLBW) infants from birth to term is to match the
in utero growth rates; however, this is rarely achieved.Methods We evaluated postdischarge growth patterns and growth failure in 81 Korean VLBW infants through a retrospective study. Weight and height were measured and calculated based on age percentile distribution every 3 months until age 24...
- The influencing factors on procalcitonin values in newborns with noninfectious conditions during the first week of life
- Jueseong Lee, Yong Hyeon Bang, Eun Hee Lee, Byung Min Choi, Young Sook Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(1):10-16. Published online January 16, 2017
-

Purpose Although procalcitonin (PCT) level is useful for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis, PCT reliability is inconsistent because of the varied conditions encountered in neonatal intensive care units. This study aimed to investigate PCT levels and factors influencing increased PCT levelin newborns without bacterial infection during the first week of life.
Methods In newborns hospitalized between March 2013 and October 2015, PCT levels...
- Neurology
- Single-center experience of the Korean-Developmental Screening Test for infants and children
- Chae-Ri Suh, Su Ye Sohn, Gun-Ha Kim, Seong-Kwan Jung, Baik-Lin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(12):483-489. Published online December 31, 2016
-
Purpose We investigated the number of test takers of the Korean-Developmental Screening Test (K-DST) in a single children's hospital within a year, according to age, referral rate, and follow-up percentage.
Methods For this study, 4,062 children who visited and received K-DST at Woorisoa Children's Hospital between January and December 2015 were enrolled. Seven test sets were used according to the Korean National Health...
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Enteral nutrition for optimal growth in preterm infants
- Myo-Jing Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(12):466-470. Published online December 31, 2016
-
Early, aggressive nutrition is an important contributing factor of long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes. To ensure optimal growth in premature infants, adequate protein intake and optimal protein/energy ratio should be emphasized rather than the overall energy intake. Minimal enteral nutrition should be initiated as soon as possible in the first days of life, and feeding advancement should be individualized according to the...
- Infection
- Recommended immunization schedule for children and adolescents: Immunization Guideline (8th edition) released by the Korean Pediatric Society in 2015
- Jong-Hyun Kim, Eun Hwa Choi, Su Eun Park, Yae-Jean Kim, Dae Sun Jo, Yun-Kyung Kim, Byung-Wook Eun, Jina Lee, Soo-Young Lee, Hyunju Lee, Ki Hwan Kim, Kyung-Hyo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(12):461-465. Published online December 31, 2016
-
This report includes the recommended immunization schedule table for children and adolescents based on the 8th (2015) and revised 7th (2012) Immunization Guidelines released by the Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society (KPS). Notable revised recommendations include: reorganization of the immunization table with a list of vaccines on the vertical axis and the corresponding age on the...
- Case Report
- Cardiology
- Anomalous right coronary artery from pulmonary artery discovered incidentally in an asymptomatic young infant
- Kyu Seon Kim, Eun Young Jo, Jae Hyeon Yu, Hong Rang Kil
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S80-S83. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Isolated anomalous right coronary artery originating from the pulmonary artery (ARCAPA) is a rare congenital coronary anomaly that is asymptomatic and discovered incidentally in most cases. ARCAPA is generally not considered a fatal defect in infancy or childhood, although cases of sudden death have been reported. Here, we report a 2-month-old female infant who presented with a prolonged fever that...
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Compound heterozygous mutations of
ACADS gene in newborn with short chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: case report and literatures review - Se Jin An, Sook Za Kim, Gu Hwan Kim, Han Wook Yoo, Han Hyuk Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S45-S48. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (SCADD) is a rare autosomal recessive mitochondrial disorder of fatty acid β-oxidation, and is associated with mutations in the acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (
ACADS ) gene. Recent advances in spectrometric screening for inborn errors of metabolism have helped detect several metabolic disorders, including SCADD, without symptoms in the neonate period. This allows immediate initiation of treatment and monitoring, so...
- Neurology
- Glucose transport 1 deficiency presenting as infantile spasms with a mutation identified in exon 9 of
SLC2A1 - Hyun Hee Lee, Yun Jung Hur
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S29-S31. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Glucose transport 1 (GLUT-1) deficiency is a rare syndrome caused by mutations in the glucose transporter 1 gene (
SLC2A1 ) and is characterized by early-onset intractable epilepsy, delayed development, and movement disorder.De novo mutations and several hot spots in N34, G91, R126, R153, and R333 of exons 2, 3, 4, and 8 ofSLC2A1 are associated with this condition. Seizures,...
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Apparent life-threatening event in infancy
- Hee Joung Choi, Yeo Hyang Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(9):347-354. Published online September 21, 2016
-
An apparent life-threatening event (ALTE) is defined as the combination of clinical presentations such as apnea, marked change in skin and muscle tone, gagging, or choking. It is a frightening event, and it predominantly occurs during infancy at a mean age of 1–3 months. The causes of ALTE are categorized into problems that are: gastrointestinal (50%), neurological (30%), respiratory (20%),...
- Neurology
- White matter injury following rotavirus infection in neonates: new aspects to a forgotten entity, 'fifth day fits'?
- Jung Sook Yeom, Chan-Hoo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(7):285-291. Published online July 31, 2016
-
That rotavirus infection can cause neurological symptoms in young children has been well established. However, it is surprising why rotavirus infection has been overlooked as a cause of neonatal seizures for many years, despite significant research interest in neonatal rotavirus infection. Neonates are the age group most vulnerable to seizures, which are typically attributed to a wide range of causes....
- Case Report
- Gastroenterology
- A giant choledochal cyst in infancy: a case report
- Nursel Yurttutan, Suleyman Cuneyt Karakus, Naim Koku, Mustafa Demirci, Ramazan Ucak
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(5):239-241. Published online May 31, 2016
-
Choledochal cyst is a dilation that encloses the intrahepatic or both extra- and intrahepatic portions of the biliary ducts. Postnatally, ultrasonography is the initial diagnostic modality of choice, allowing for precise measurements of intra- or extrahepatic duct dilatation and identification of stones and sludge. Symptoms depend on the age at presentation. Common bile duct malformations should be considered as a...
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Efficacy of proton pump inhibitors and H2 blocker in the treatment of symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease in infants
- Hamid Reza Azizollahi, Mandana Rafeey
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(5):226-230. Published online May 31, 2016
-
Purpose Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) occurs in pediatric patients when reflux of gastric contents presents with troublesome symptoms. The present study compared the effects of omeprazole and ranitidine for the treatment of symptomatic GERD in infants of 2-12 months.
Methods This study was a clinical randomized double-blind trial and parallel-group comparison of omeprazole and ranitidine performed at Children Training Hospital in Tabriz, Iran....
- Cardiology
- Correlation of B-type natriuretic peptide levels and echocardiographic parameters in preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus
- Hyun Ah Jeong, Jeonghee Shin, Eunji Kim, Eun Hee Lee, Byung Min Choi, Chang Sung Son, Joo Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(4):183-189. Published online April 30, 2016
-
Purpose This study aimed to evaluate the correlation, according to postnatal age, between plasma B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels and echocardiographic parameters for the assessment of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) in preterm infants with respiratory distress.
Methods We enrolled 42 preterm infants with respiratory distress who underwent serial echocardiographic evaluation with simultaneous plasma BNP measurements until ductal closure. The correlations between BNP levels...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Modification of nutrition strategy for improvement of postnatal growth in very low birth weight infants
- Ah Young Choi, Yong Wook Lee, Mea-young Chang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(4):165-173. Published online April 30, 2016
-
Purpose To identify the effects of modified parenteral nutrition (PN) and enteral nutrition (EN) regimens on the growth of very low birth weight (VLBW) infants.
Methods The study included VLBW infants weighing <1,500 g, admitted to Chungnam National University Hospital between October 2010 and April 2014, who were alive at the time of discharge. Subjects were divided according to 3 periods: period 1...
- Case Report
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Successfully treated infective endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus Aureus in extremely low birth weight infant - Sehwa Jung, Kyung Uk Jeong, Jang Hoon Lee, Jo Won Jung, Moon Sung Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(2):96-99. Published online February 29, 2016
-
Survival rates of preterm infants have improved in the past few decades, and central venous catheters play an important role in the intensive medical treatment of these neonates. Unfortunately, these indwelling catheters increase the risk of intracardiac thrombosis, and they provide a nidus for microorganisms during the course of septicemia. Herein, we report a case of persistent bacteremia due to...
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Infantile Marfan syndrome in a Korean tertiary referral center
- Yeon Jeong Seo, Ko-Eun Lee, Gi Beom Kim, Bo Sang Kwon, Eun Jung Bae, Chung Il Noh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(2):59-64. Published online February 29, 2016
-
Purpose Infantile Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a rare congenital inheritable connective tissue disorder with poor prognosis. This study aimed to evaluate the cardiovascular manifestations and overall prognosis of infantile MFS diagnosed in a tertiary referral center in Korea.
Methods Eight patients diagnosed with infantile MFS between 2004 and 2014 were retrospectively evaluated.
Results Their median age at the time of diagnosis was 2.5 months (range,...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Clinical features of Bednar's aphthae in infants
- Seung-Woo Nam, Seol Hee Ahn, Son-Moon Shin, Goun Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(1):30-34. Published online January 22, 2016
-
Purpose Although Bednar's aphthae are common and regress spontaneously, these lesions may lead to feeding intolerance and are often misdiagnosed, rendering examinations useless. This study sheds new light on the clinical features of Bednar's aphthae.
Methods Sixteen neonates and infants were newly diagnosed with Bednar's aphthae via routine health check-ups in an outpatient clinic. Medical records were retrospectively reviewed, and the following parameters...
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











