General Pediatrics
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- TOPICS
- General Pediatrics
- Topics
-
- Adolescence Medicine (4)
- Allergy (64)
- Cardiology (81)
- Critical Care Medicine (16)
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine (24)
- Emergency Medicine (5)
- Endocrinology (65)
- Gastroenterology (77)
- General Pediatrics (62)
- Genetics and Metabolism (27)
- Hematology (20)
- Immunology (16)
- Infection (82)
- Neonatology (Perinatology) (127)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary) (55)
- Neurology (98)
- Nutrition (33)
- Oncology (19)
- Neurobehavior (12)
- Pulmonology (35)
- Rheumatology (4)
- Other (44)
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Global and regional burden of neonatal disorders (preterm birth, encephalopathy, jaundice, and sepsis), 1990–2021 and projections to 2050
- Yuseon Kang, Jeongseon Oh, Dongjin Yeo, Jaeyu Park, Sooji Lee, Na Yun Kim, Jungmin Park, Seung Ha Hwang, Tae Hyeong Kim, Dong Keon Yon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(2):171-181. Published online October 30, 2025
-
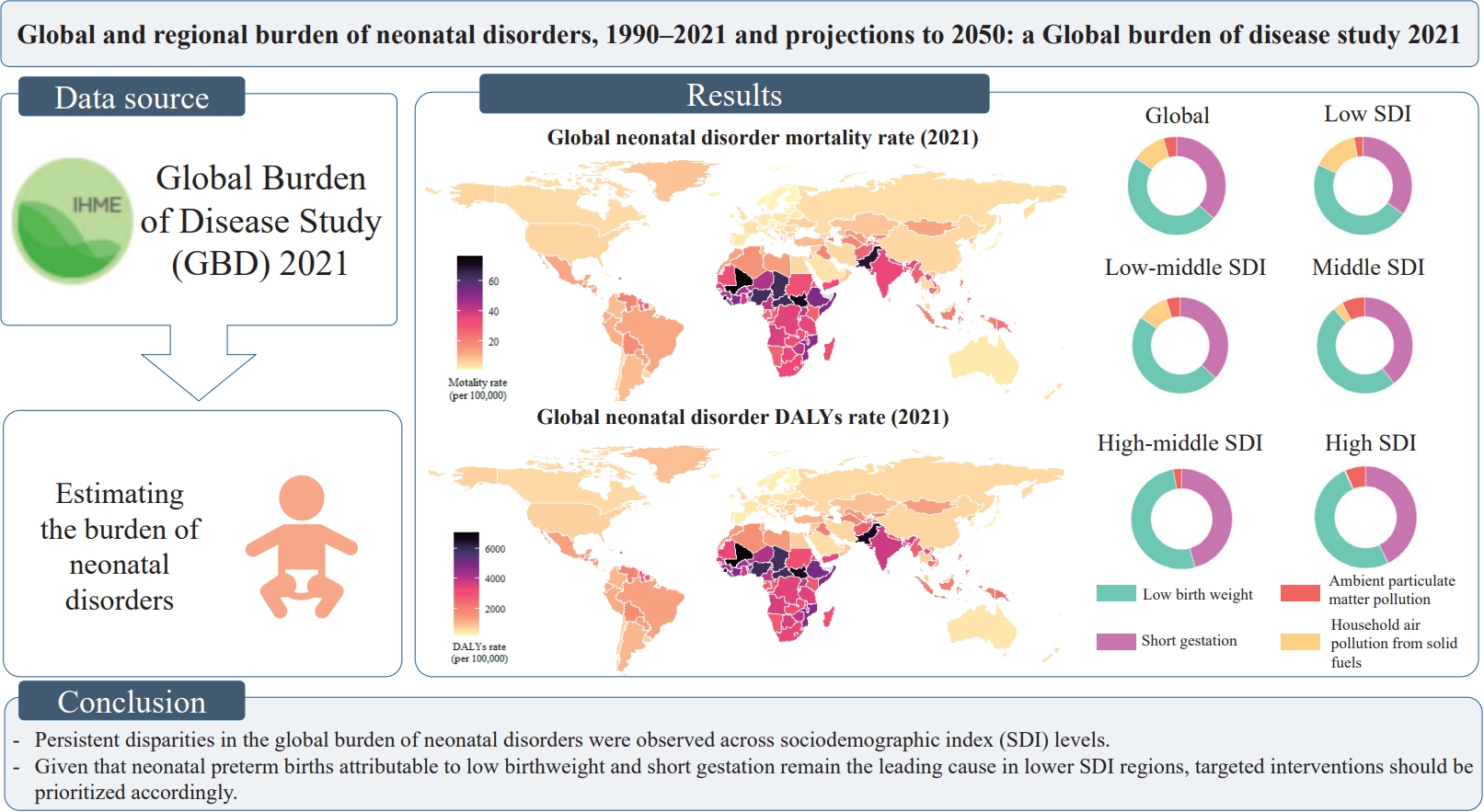
This study provides the first comprehensive estimated global burden of neonatal disorders attributable to risk factors in 1990–2021 stratified by sex, cause, sociodemographic index (SDI), and region. We identified persistent disparities across SDI levels, with low birthweight and short gestation contributing most to the age-standardized disability-adjusted life year rate of neonatal disorders. These findings highlight the urgent need for targeted context-specific interventions to reduce infant mortality and improve neonatal health equity.
- Associations of routine breakfast and napping habits with early adiposity rebound by age 3 years: a population-based cohort study in Japan
- Toshifumi Yodoshi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(2):163-170. Published online October 22, 2025
-
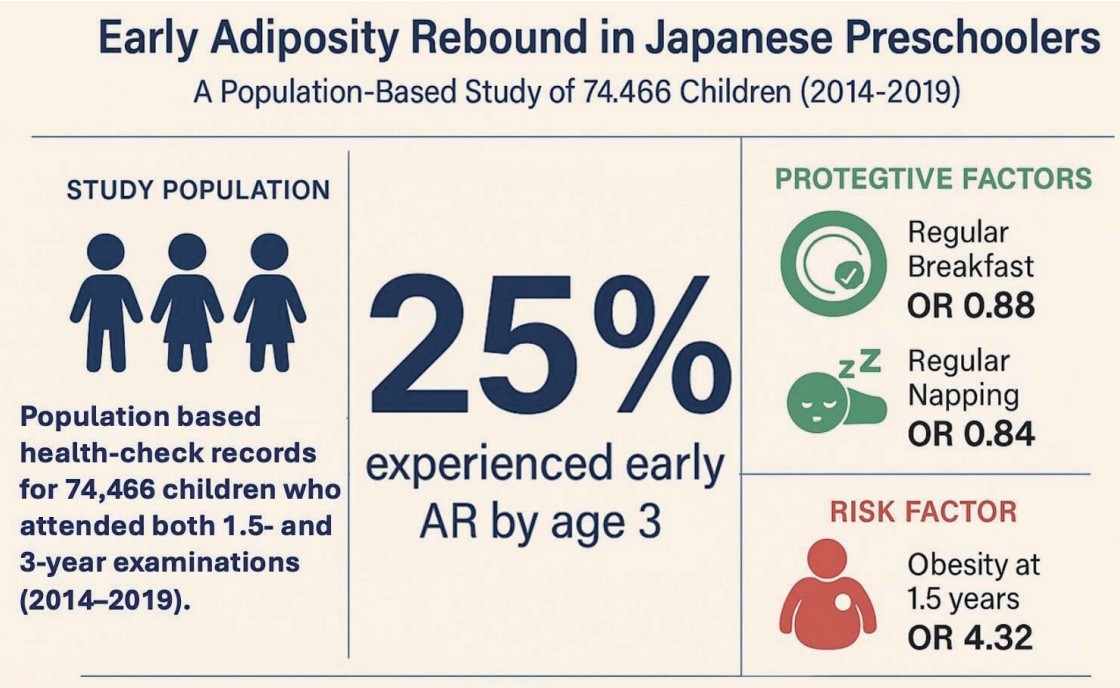
In a population‑based cohort of 74,466 children, 25% experienced early adiposity rebound (AR) by age 3. Daily breakfast and routine napping at 1.5 years were independently associated with lower odds of AR, while obesity at 1.5 years was a strong predictor. These modifiable routines could help delay AR and enable early identification during routine child health checks.
- Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BLa80 for preventing allergic, respiratory, and gastrointestinal diseases in young children in China: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial
- Ke Chen, Xi Zhang, Kaihong Zeng, Jiayi Zhong, Shanshan Jin, Yang Nie, Ping Yang, Nianyang He, Haixia Chen, Yanmei Cao, Yunrong Fu, Ziji Fang, Wei Jiang, Changqi Lium
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(2):150-162. Published online October 30, 2025
-
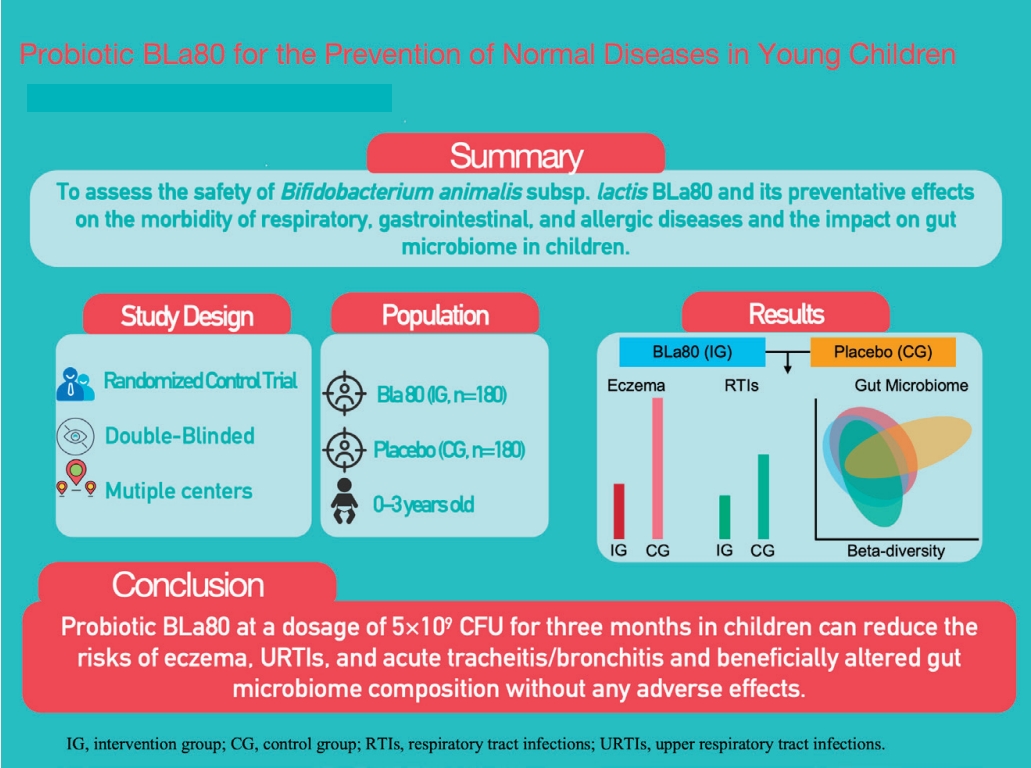
Question: Can probiotic BLa80 bring long-term benefits to the health of young children?
Finding: This trial demonstrated that the daily administration of s BLa80 at 5×109 colony-forming units for 3 months in children can reduce the risk of eczema, upper respiratory tract infections, and acute tracheitis/bronchitis as well as beneficially improve the gut microbiome without any adverse effect.
Meaning: Bla80 can bring definite health benefits to young children.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Systematic review of influence of ethnicity on efficacy and safety of pharmacotherapy for childhood and adolescent obesity
- Surendra Gupta, Purushottam Lal, Abhishek Gupta, Brajesh Raj Chaudhary
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(2):84-102. Published online January 26, 2026
-
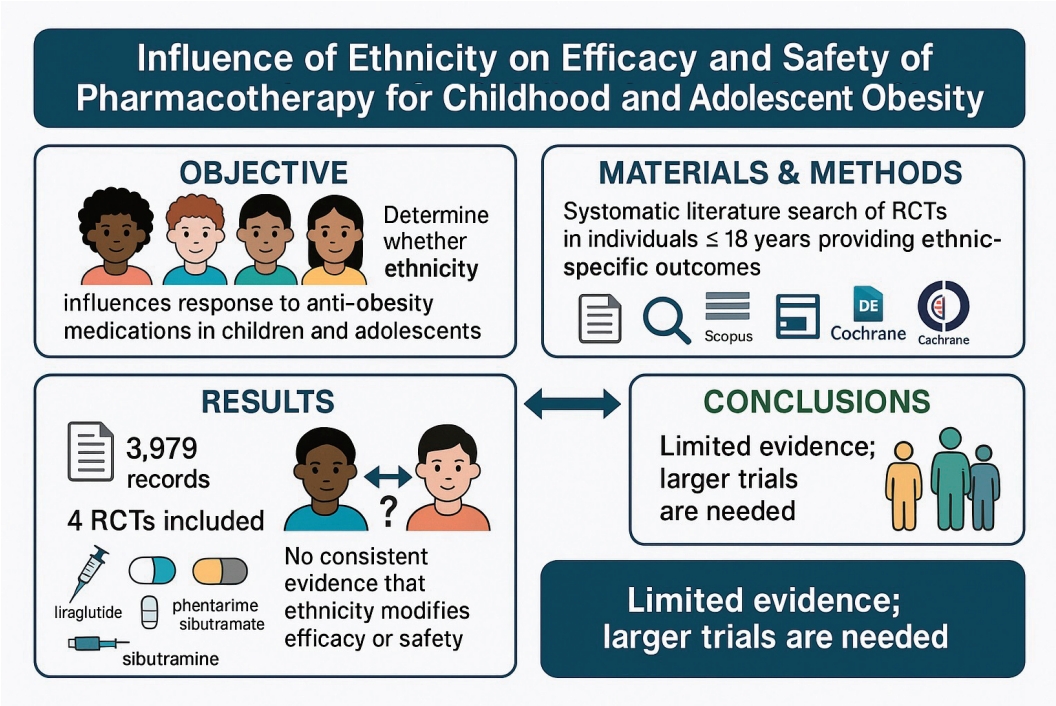
Ethnic variations may influence the response of children and adolescents to obesity pharmacotherapy. Current evidence does not show consistent differences in efficacy or safety among ethnic groups; however, available data are limited. Larger, ethnically diverse trials are needed to develop personalized obesity treatment strategies.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Lipoprotein(a) prevalence trends in Portuguese children and adolescents: a real-world perspective
- Isabel Morais Ribeiro, Susete Vieira, Miguel Saraiva, Mónica Tavares, José Carlos Oliveira, Isabel Mangas Palma, Helena Ferreira Mansilha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):1031-1040. Published online November 24, 2025
-

Early lipid screening, including lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)), in children/adolescents is key to identifying and managing dyslipidemia and reducing the risk of early-onset cardiovascular disease. This study shows that prevalence of elevated Lp(a) in high-risk Portuguese children is alarming, with over 30% at intermediate/high risk and nearly 1% at very high-risk (>430 nmol/L). Since Lp(a) is mostly genetically determined, one-time early screening in atrisk children is crucial for timely monitoring and prevention.
- Effectiveness of Kinder Lebensqualität Fragebogen (KINDL) and Children’s Somatic Symptom Inventory-24 (CSSI-24) for measuring postacute sequelae of COVID-19 in children: a diagnostic validation study
- Lawrence Shih-Hsin Wu, Pei-Chi Chen, Xiao-Ling Liu, Shu-Tsen Liu, Chi-Hung Wei, Yu-Lung Hsu, Kai-Sheng Hsieh, Huan-Cheng Lai, Chien-Heng Lin, Chieh-Ho Chen, An-Chyi Chen, I-Ching Chou, Wen-Jue Soong, Hui-Ju Tsai, Chung-Ying Lin, Jiu-Yao Wang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):944-951. Published online September 12, 2025
-

Question: Although children with postacute sequelae of coronavirus disease 2019 (PASC) may experience persistent symptoms that affect their quality of life (QoL), a screening tool for identifying high-risk children is lacking.
Finding: Kinder Lebensqualität fragebogen (KINDL) and Children's Somatic Symptom Inventory-24 (CSSI-24) were significantly correlated. An optimal KINDL cutoff score (74.75) detected those at high risk of a reduced QoL.
Meaning: Integrating KINDL and CSSI-24 into routine pediatric outpatient care may enable timely identification and interventions for children at risk of PASC-related impairments.
- Comparative analysis of goal attainment for helmet therapy versus conservative management for positional plagiocephaly in infants
- Bjoern Vogt, Ariane Deutschle, Georg Gosheger, Adrien Frommer, Andrea Laufer, Henning Tretow, Robert Roedl, Gregor Toporowski
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):892-900. Published online October 2, 2025
-

Question: Is helmet therapy more effective than conservative management in treating positional plagiocephaly?
Finding: Both approaches reduced cranial asymmetry with comparable correction speed. Helmet therapy showed a trend toward greater severity reduction.
Meaning: Early treatment initiation was the strongest predictor of improvement. Helmet therapy may offer additional benefit in more severe cases.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Bridging the gap: autism spectrum disorder in children in the United States and worldwide: a narrative review
- Sandhya J. Kadam, Malika Goel
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):852-857. Published online October 2, 2025
-

The prevalence of autism is increasing worldwide. The United States has the highest numbers, likely due to the availability of better treatment options. However, global disparities exist, especially in low-resource settings in which stigma, underdiagnosis, and limited services hinder care. A coordinated international approach emphasizing early screening, inclusive policies, and culturally sensitive support systems can bridge this gap and improve the outcomes for children with autism and their families worldwide.
- Perspective
- General Pediatrics
- Parenting principles to combat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and form resilient young minds
- Jandy Le, Sandhya J. Kadam
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):838-841. Published online September 22, 2025
-
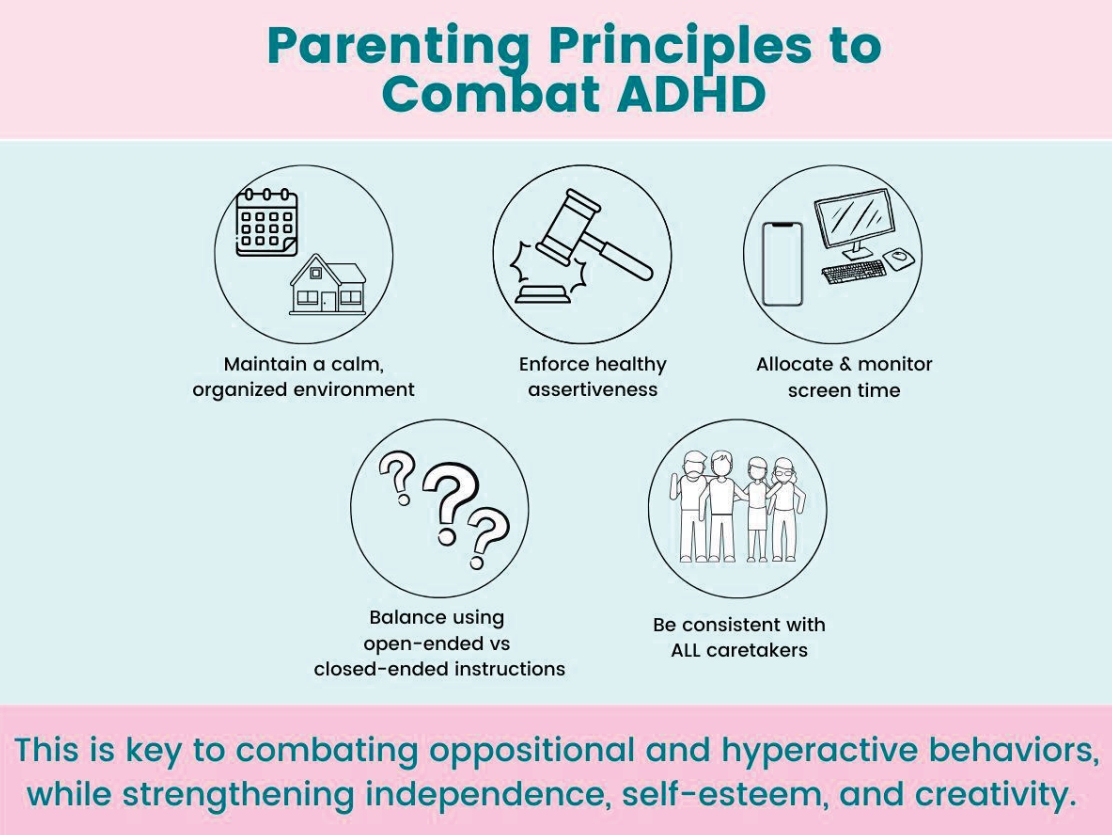
The prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, conduct disorder, and other related behavioral problems is increasing among children, likely due to less interaction with their parents and the real world and more time spent on screens, on social media, and in the virtual world. This article highlights several simple, basic parenting principles to facilitate the growth of healthy, resilient minds and combat the symptoms of opposition, hyperactivity, and distractibility.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Trends and determinants in breastfeeding among Korean infants (2007–2021): a nationwide study using the National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children
- Minwoong Kang, Eui Kyung Choi, Jeung Min Lee, Hye-Jung Shin, Woo Ryoung Lee, Son Moon Shin; Korean Society of Breastfeeding Medicine
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):772-780. Published online July 4, 2025
-
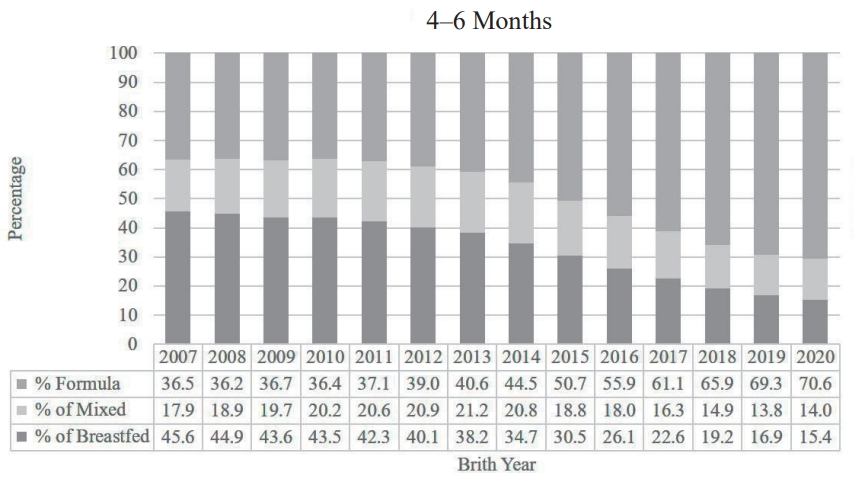
Question: What are the recent trends and determinants of breastfeeding in South Korea?
Finding: Breastfeeding rates in South Korea declined significantly from 2007 to 2021, with lower rates observed in preterm, low-birthweight, and multiple-birth infants as well as rural or lower-income households.
Meaning: Targeted interventions, including prenatal education, postnatal support, and community-based programs, are required to address disparities and improve breastfeeding rates.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Impact of screen exposure during pediatric ages including multifaceted aggravating factors: a literature review
- Daniel González-Pérez, David Sebastián Huertas-Moreno, Manuela Granados-Pinilla, Sofía Hernandez-Rojas, Laura González-Rincon, Geraldine Hurtado-Garcia, Simón Grisales-Calle, María José González-Mariño, Luz Dary Gutierrez-Castañeda, Jhon Camacho-Cruz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):751-760. Published online September 24, 2025
-
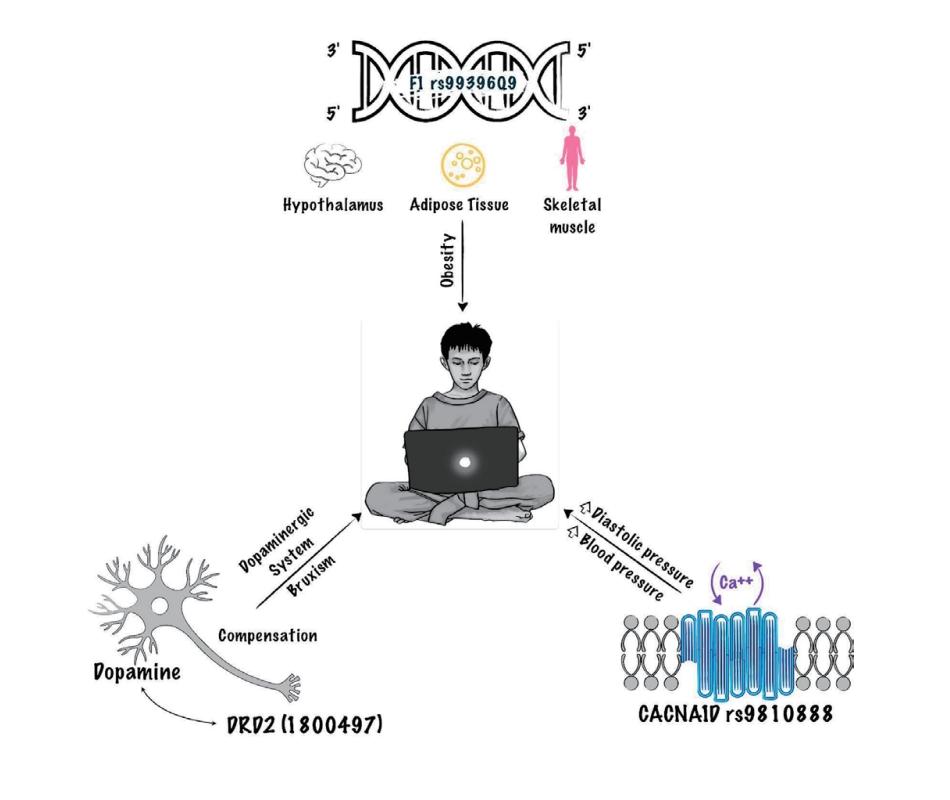
Excessive screen time in children is linked to obesity, overweight, sedentary behavior, depression and mood disorders, myopia, behavioral changes, sleep disturbances, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, among others. Polymorphisms in genes like FTO, CACNA1D, and DRD2 could further increase these risks. Implementing strategies such as limiting screen use, creating screen-free zones, and monitoring content is essential to mitigate adverse physical and mental health effects in the pediatric population.
- Editorial
- General Pediatrics
- Artificial intelligence in pediatric healthcare: bridging potential, clinical practice, and ethical considerations
- Yoon Lee, Seohyun Hong, Dong Keon Yon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):652-655. Published online August 28, 2025
-

· Artificial intelligence (AI) holds transformative potential for pediatric healthcare, with applications spanning prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up across diverse subspecialties; however, ethical concerns, scarcity of pediatric- specific data, and limited funding remain significant challenges.
· International consensus on pediatric AI guidelines, expanding child-specific datasets, and incorporating explainable AI are essential to ensure safety and trust.
· Multicenter collaboration and increased investment can address these gaps, enabling equitable, reliable, and pediatric- centered AI solutions.
- Perspective
- General Pediatrics
- Navigating the complex behavioral landscape of children in foster care and adopted families
- Anisha Choi, Sandhya J. Kadam
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):620-623. Published online May 12, 2025
-
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Liposomal SunActive versus conventional iron for treatment of iron-deficiency anemia in children aged 2–12 years: a prospective randomized controlled trial
- Wael A. Bahbah, Yasmin A.H.S. Younis, Hanan Salama Elbelouny, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):608-615. Published online July 18, 2025
-
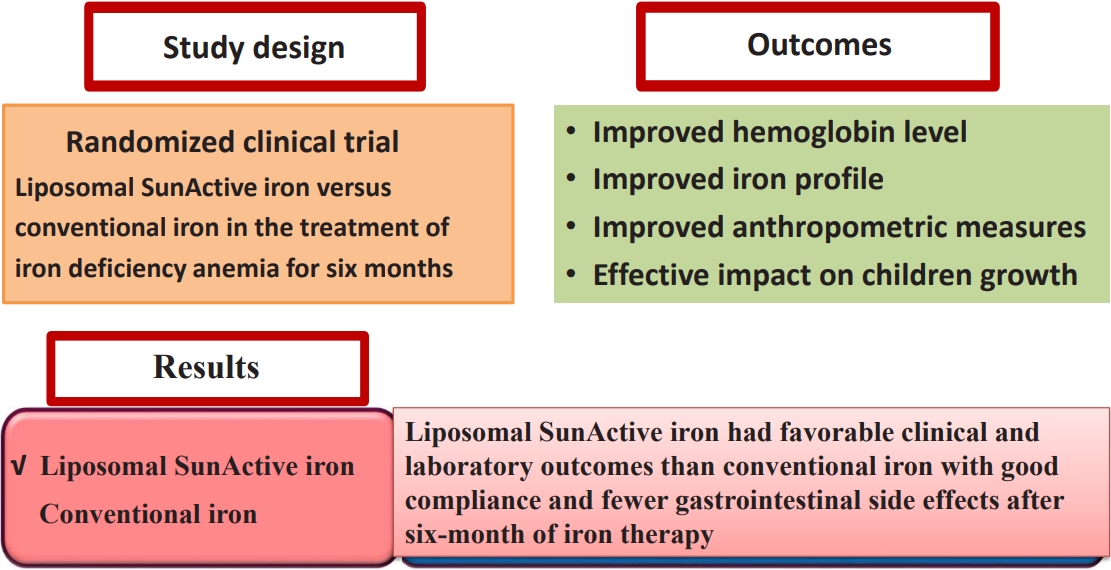
Background: Liposomal iron, a novel oral formulation of ferric pyrophosphate that demonstrates improved gastrointestinal absorption and bioavailability with fewer side effects than conventional iron, represents a significant advancement in the treatment of iron-deficiency anemia (IDA).
Purpose: To conduct an in-depth comparative study of liposomal SunActive and conventional iron supplements (iron polymaltose complex) for treating IDA in children aged 2–12 years Methods: This...
- Letter to the Editor
- General Pediatrics
- Debate around and impact of digital screen time and media parenting on children’s development
- Gowda Parameshwara Prashanth
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):551-553. Published online March 11, 2025
-

- Clinical Note
- General Pediatrics
- Aplasia cutis congenita with unique vascular malformation and cranial hypoplasia: a case in a preterm infant
- Yasufumi Sakata, Natsumi Fujii, Sadahiro Nomura, Yoshihiro Azuma, Hiroki Hamano, Hidenobu Kaneyasu, Seigo Okada, Kazumasa Takahashi, Shunji Hasegawa
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):472-474. Published online March 11, 2025
-
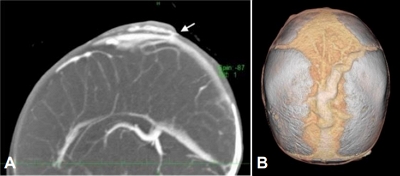
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- The role of serum zinc and selenium levels in etiology of febrile seizures
- Yavuz Ataş, Hatice Gamze Poyrazoğlu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):388-394. Published online January 13, 2025
-

Zinc may play a key role in preventing febrile seizures by increasing the seizure threshold and reducing oxidative stress. Incorporating zinc supplements into treatment could help protect children from the adverse effects of febrile seizures and improve their overall outcomes.
- Editorial
- General Pediatrics
- Global breastfeeding efforts: a long way to go
- Hye-Jung Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):300-302. Published online November 13, 2024
-

· Despite much effort, breastfeeding practices remain unsatisfactory worldwide.
· Effective breastfeeding-promoting interventions are needed that are appropriate for age, culture, and social environment.
· Interventions can promote breastfeeding, especially in younger populations such as adolescent mothers.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding dengue vaccine: a baseline study of community members and health providers in Indonesia
- Abdul Wahab, Ida Safitri Laksanawati, Retna Siwi Padmawati, Asal Wahyuni Erlin Mulyadi, Wahyu Triadmajani, Jarir At Thobari
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):228-237. Published online November 13, 2024
-
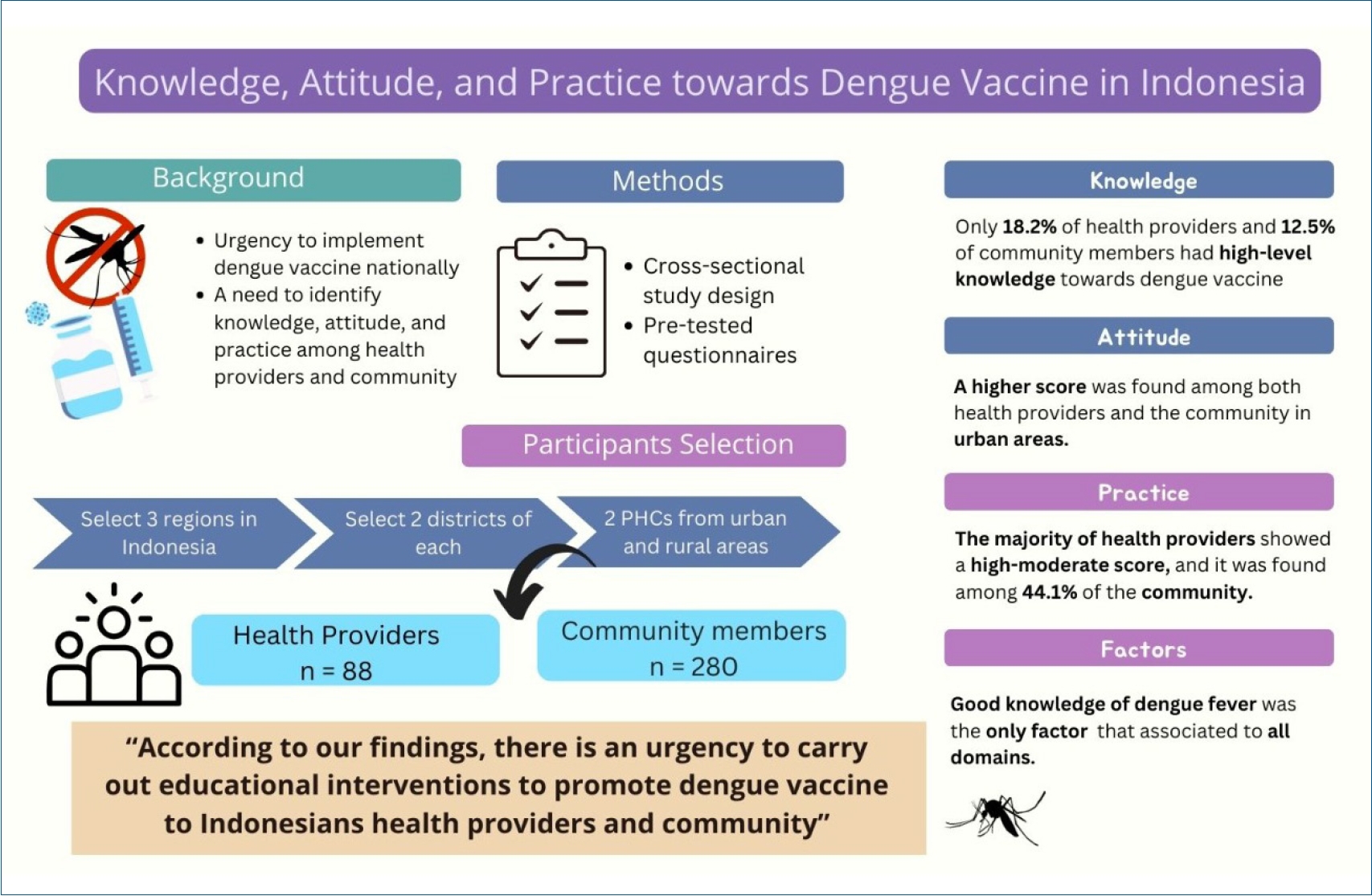
Question: Do community members and health providers show different level of knowledge, attitude, and practice towards dengue vaccine?
Finding: These 2 groups only differed in practice component, while the knowledge and attitude constituents were relatively low for both.
Meaning: There is an urgent need to deliver educational interventions to raise awareness of community members and health providers regarding dengue vaccination.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Prevalence of childhood overweight and obesity in Malaysia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ker Yang Chua, Ker Yung Chua, Karuthan Chinna, Chooi Ling Lim, Maheeka Seneviwickrama
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):115-126. Published online November 13, 2024
-
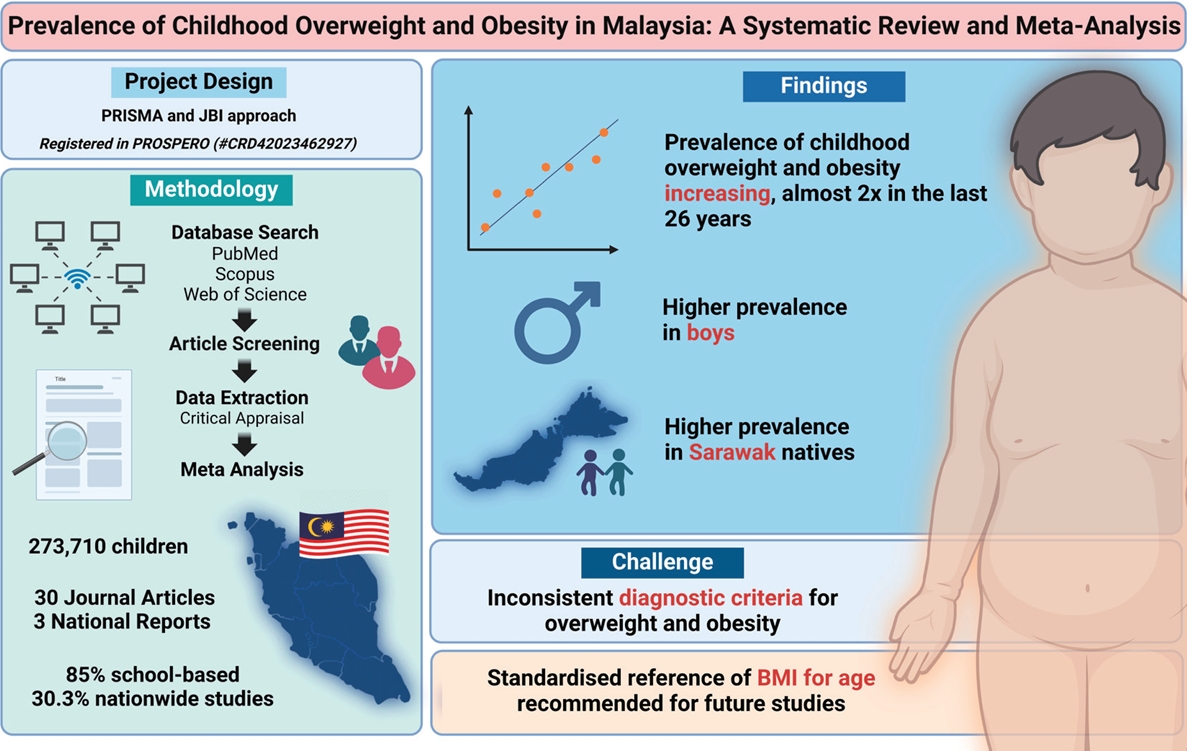
The incidence of childhood obesity is increasing worldwide. National surveys in Malaysia have shown similar trends. This review aimed to increase our understanding of the prevalence and associated factors of childhood overweight, obesity, and excess weight in Malaysia. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted of studies reporting the prevalence of overweight and obesity in Malaysian children aged <18 years....
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Role of proper postnatal care in continued exclusive breastfeeding among young Indonesian mothers
- Wahyu Triadmajani, Shinta Prawitasari, Abdul Wahab
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):686-693. Published online September 12, 2024
-
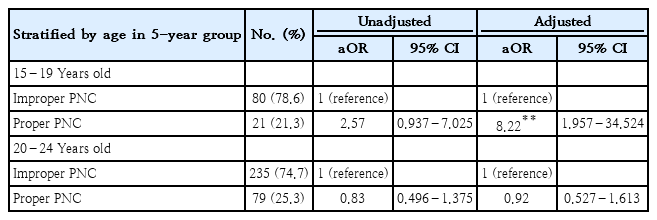
Question: Is proper postnatal care (PNC) associated with exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) practice among young Indonesian mothers?
Finding: Proper PNC elevates the likelihood of EBF among Indonesian adolescent mothers aged 15–19 years.
Meaning: Breastfeeding services should be provided during the early postnatal period to support EBF practice among adolescent mothers. High-quality PNC is a tailored intervention for vulnerable populations.
- Nonpharmacological interventions for managing postoperative pain and anxiety in children: a randomized controlled trial
- Edlin Glane Mathias, Mamatha Shivananda Pai, Vijay Kumar, Dinesh Narayanakurup, Malavika Kulkarni, Vasudeva Guddattu, Ann-Cathrine Bramhagen, Baby S Nayak, Anice George
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):677-685. Published online October 31, 2024
-
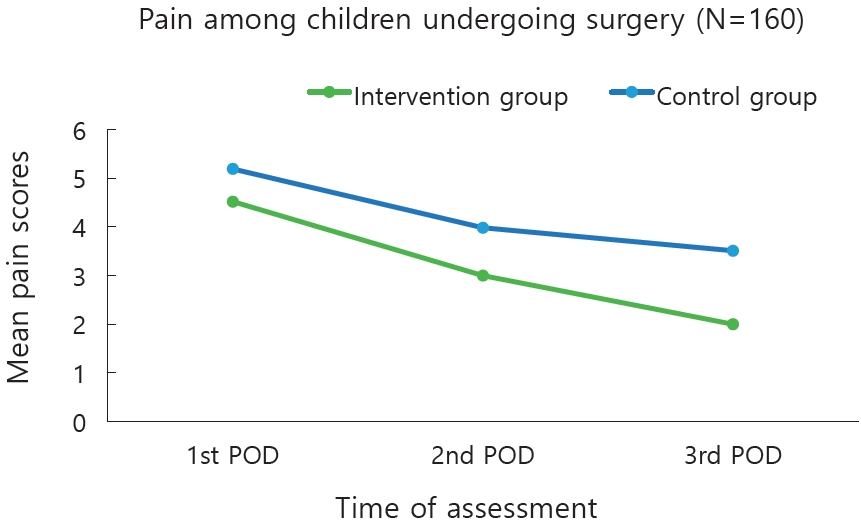
Question: What is the effect of nonpharmacological interventions on postoperative pain and anxiety among children.
Finding: Nurse-provided distraction interventions reduce pain and anxiety among pediatric surgical patients.
Meaning: The findings suggest that nonpharmacological interventions provided postoperatively to children reduce their pain and anxiety levels.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Protecting our future: environmental hazards and children’s health in the face of environmental threats: a comprehensive overview
- Jungha Lee, Hyo-Bin Kim, Hun-Jong Jung, Myunghee Chung, So Eun Park, Kon-Hee Lee, Won Seop Kim, Jin-Hwa Moon, Jung Won Lee, Jae Won Shim, Sang Soo Lee, Yunkoo Kang, Young Yoo; The Environmental Health Committee of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):589-598. Published online October 31, 2024
-

· Exposure to air pollutants cause allergic and respiratory diseases as well as chronic kidney disease.
· Adequate physical activity and proper nutrition are essential for children to maintain good health.
· We must educate people about the harmful effects of noise, blue light, heavy metals and smoke.
· Government and society must actively decrease environ-mental hazards.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Effect of online infant care training and postpartum counseling based on Meleis' transition theory on mothers' readiness for care and breastfeeding: a randomized controlled trial
- Fatma Şule Bilgiç, Gülçin Bozkurt
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):521-530. Published online September 27, 2024
-

Question: Do interventions based on Meleis' transition theory affect mothers' readiness for baby care and breastfeeding?
Findings: We found a statistically significant difference between the intervention and control groups in mothers' readiness for newborn care and breastfeeding (P<0.001).
Meaning: This intervention increased breastfeeding rates while ensuring that mothers were ready to care for their babies and prepared for the role of motherhood.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Metabolic complications of obesity in children and adolescents
- Hyunjin Park, Jung Eun Choi, Seunghee Jun, Hyelim Lee, Hae Soon Kim, Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):347-355. Published online November 16, 2023
-
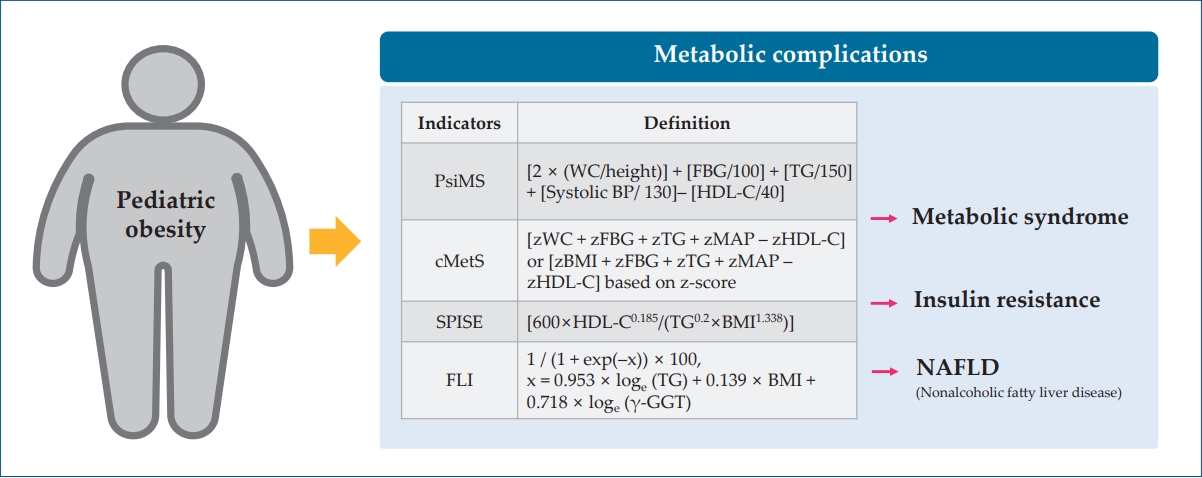
· Pediatric obesity increases the risk of metabolic complications (insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease) and long-term cardiovascular diseases.
· A new obesity definition and various indicators (continuous metabolic syndrome score, pediatric simple metabolic syndrome score, fatty liver index) have been proposed to evaluate children’s susceptibility to metabolic disorders.
· Laboratory and body composition tests in pediatric screenings can identify groups at high risk of metabolic complications of obesity.
- Letter to the Editor
- General Pediatrics
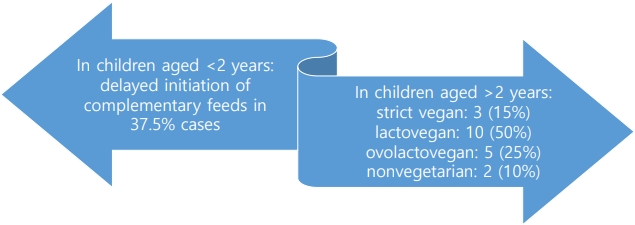
- Vitamin B12 deficiency in anemic children before versus after age 2 years: a form of hidden hunger in India
- Sahil Goel, Ruchika Bhatnagar, Anita Kumari, Brig Prem Lochan Prasad, Lahar Sahai
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):116-118. Published online January 24, 2024
-
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Virtual reality for pain reduction during intravenous injection in pediatrics: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Amir Mohammad Salehi, Masoud Rafiee, Mozhdeh Bashirian
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):533-537. Published online June 14, 2023
-
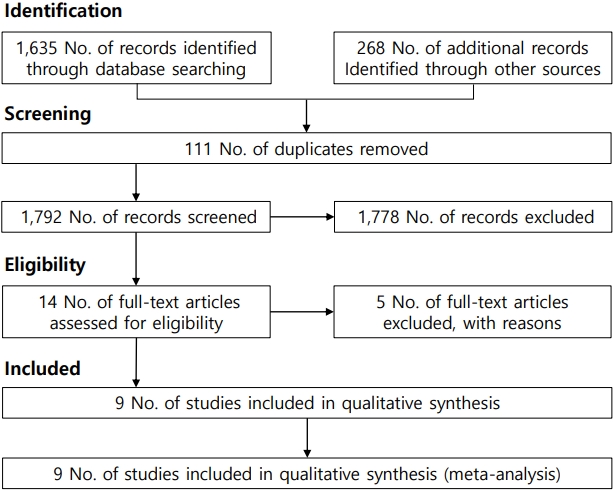
Question: This is the first meta-analysis to examine published evidence of the effectiveness of virtual reality at reducing pain during pediatric intravenous injections.
Finding: Our results suggest that virtual reality effectively reduces pain associated with intravenous injections in pediatric patients.
Meaning: These findings suggest the importance of virtual reality in decreasing the pain of intravenous injections among children.
- Correspondence
- General Pediatrics
- Letter to the editor: Age-, sex-, and height-based blood pressure reference charts, Yazd children 6-18 years, Iran
- Amar Taksande
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):412-413. Published online October 27, 2021
-
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST): development, applications, and implications for future early childhood development interventions
- Dooyoung Kim, Young June Choe, Bilal Aurang Zeb Durrani, EunYoung Kim, Junghye Byeon, Baik-Lin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):288-293. Published online December 22, 2022
-

· This review discusses the development and application of the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST) for ensuring early childhood development.
· Various studies have demonstrated the integral role of the K-DST in facilitating the detection of developmental delays and delivery of timely interventions.
· The tailoring of the K-DST to Korean infants and children suggests that other countries may further translate and adapt it.
- Motor performance of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: focus on the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency
- Khushboo Prashant Adhvaryu, Suruliraj Karthikbabu, Pratiksha Tilak Rao
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):512-520. Published online February 17, 2022
-
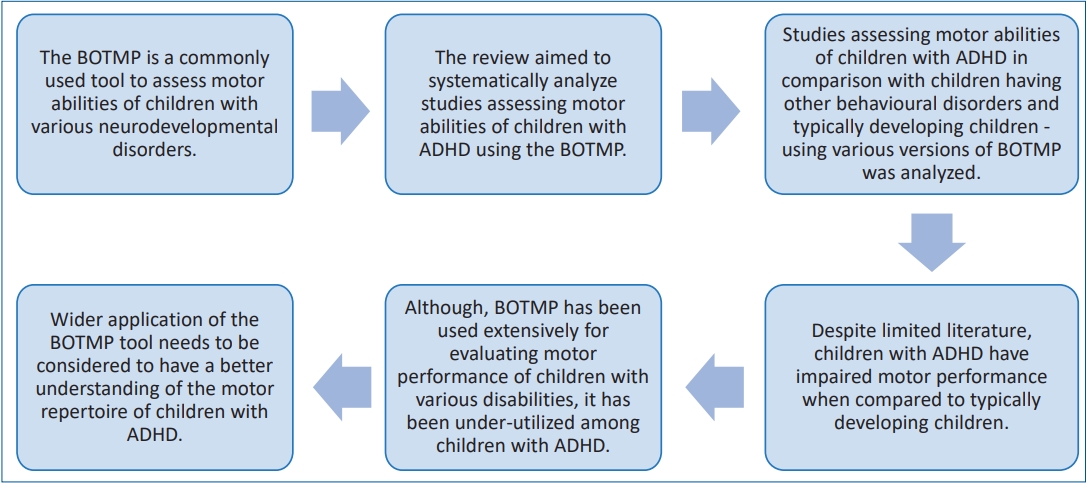
· Children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) tend to have impaired motor performance that may affect their growth and development.
· Although widely used among children with developmental disorders, the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency (BOTMP) is used sparsely among children with ADHD.
· Assessment by the BOTMP increases our understanding of the motor repertoire of children with ADHD.
· Wider usage of the BOTMP will enable more comprehensive planning of rehabilitation goals to enhance the motor abilities of children with ADHD.
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











