Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last six months.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Parental support and exclusive breastfeeding at 3 months in West Java, Indonesia: a mixed-methods approach (59 times)
- Ratu Ayu Dewi Sartika, Fadila Wirawan, Wawan Gunawan, Primasti Nuryandari Putri, Nurul Husna Mohd Shukri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):358-367. Published online June 21, 2024
-
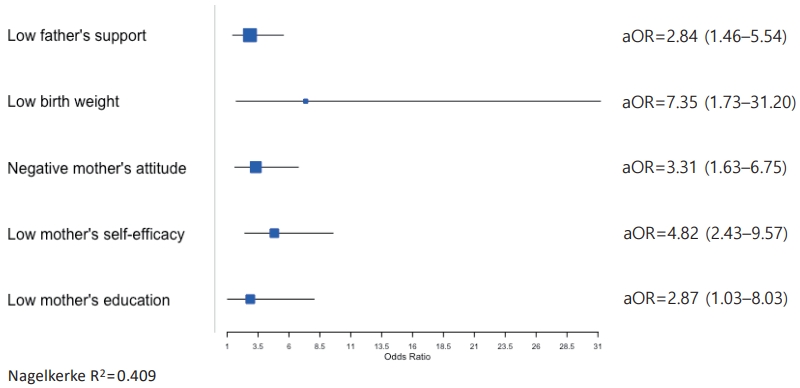
Question: Does paternal support affect exclusive breastfeeding failure?
Finding: Exclusive breastfeeding failure by 3 months was affected by paternal support.
Meaning: Fathers should be included in breastfeeding education and antenatal care.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin levels can predict allergic disease development and atopic march in children (59 times)
- Zak Callaway, Chang-Keun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):398-405. Published online February 3, 2025
-
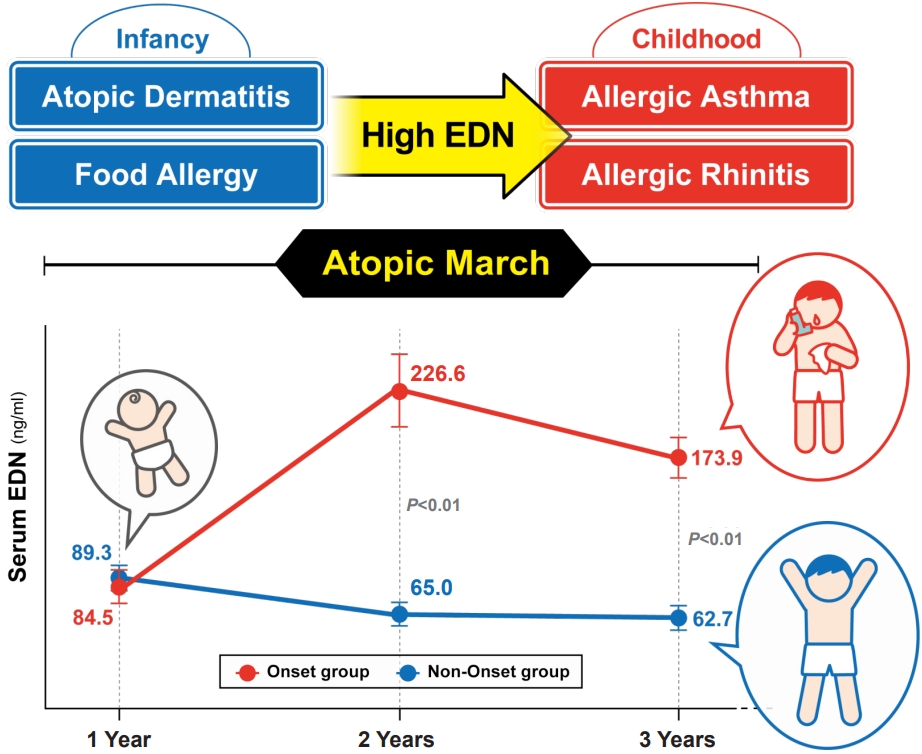
· Allergic march occurs in a subset of children, beginning with atopic dermatitis and progressing to food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and/or asthma. Its early diagnosis is important to slowing its progression.
· Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN), an excellent biomarker of eosinophil activity, is often elevated in allergic diseases.
· EDN levels have been used to predict allergic disease development and diagnose, treat, and monitor allergic diseases.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Lipoprotein(a) prevalence trends in Portuguese children and adolescents: a real-world perspective (58 times)
- Isabel Morais Ribeiro, Susete Vieira, Miguel Saraiva, Mónica Tavares, José Carlos Oliveira, Isabel Mangas Palma, Helena Ferreira Mansilha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):1031-1040. Published online November 24, 2025
-

Early lipid screening, including lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)), in children/adolescents is key to identifying and managing dyslipidemia and reducing the risk of early-onset cardiovascular disease. This study shows that prevalence of elevated Lp(a) in high-risk Portuguese children is alarming, with over 30% at intermediate/high risk and nearly 1% at very high-risk (>430 nmol/L). Since Lp(a) is mostly genetically determined, one-time early screening in atrisk children is crucial for timely monitoring and prevention.
- Clinical Note
- Gastroenterology
- Successful rescue after catastrophic bleeding of carotid artery pseudoaneurysm following button battery ingestion in a toddler (58 times)
- Manjit Kaur, Ujjal Poddar, Basant Kumar, Abdul Muzil Munshi, Rajanikant R. Yadav, Moinak Sen Sarma, Anshu Srivastava
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):1041-1044. Published online October 22, 2025
-
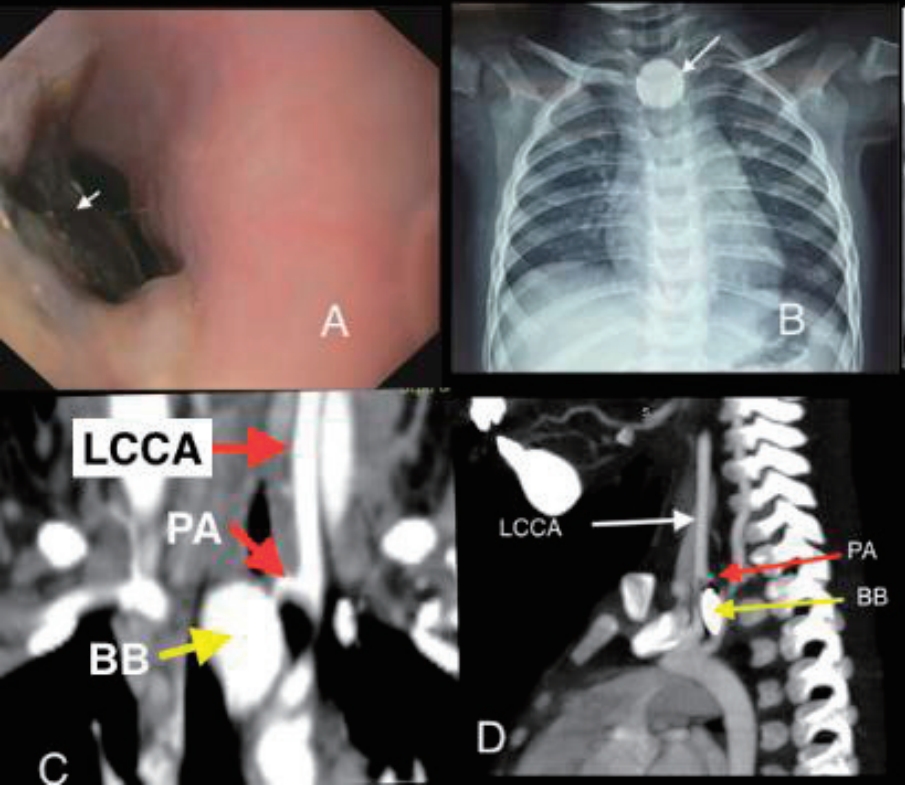
Button battery (BB) ingestion is an increasing hazard. Catastrophic gastrointestinal bleeding due to pseudoaneurysm rupture following BB impaction is often fatal. Here we report the case of an unwitnessed BB ingestion in an 18-month-old boy who presented with repeated massive UGIB due to a left CCA pseudoaneurysm that was successfully managed multidisciplinarily. BB ingestion should be considered in toddlers presenting with hematemesis.
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Lifelong impact of elevated blood pressure from childhood to adulthood (58 times)
- Junhyun Kwon, Eunji Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):278-286. Published online November 28, 2024
-

· Childhood blood pressure (BP) is significantly associated with adult hypertension and cardiovascular disease.
· Despite ongoing debate regarding the need for regular BP screening and early pharmacotherapy in children, the benefits of optimizing BP throughout childhood are clear.
· Childhood presents a critical window for normalizing BP through lifestyle modifications such as reducing sodium intake and increasing physical activity to promote lifelong cardiovascular health and prevent longterm complications.
- Editorial
- Other
- Beyond the eye: a multidisciplinary perspective on managing pediatric myopia (58 times)
- Eoi Jong Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):566-568. Published online July 18, 2025
-
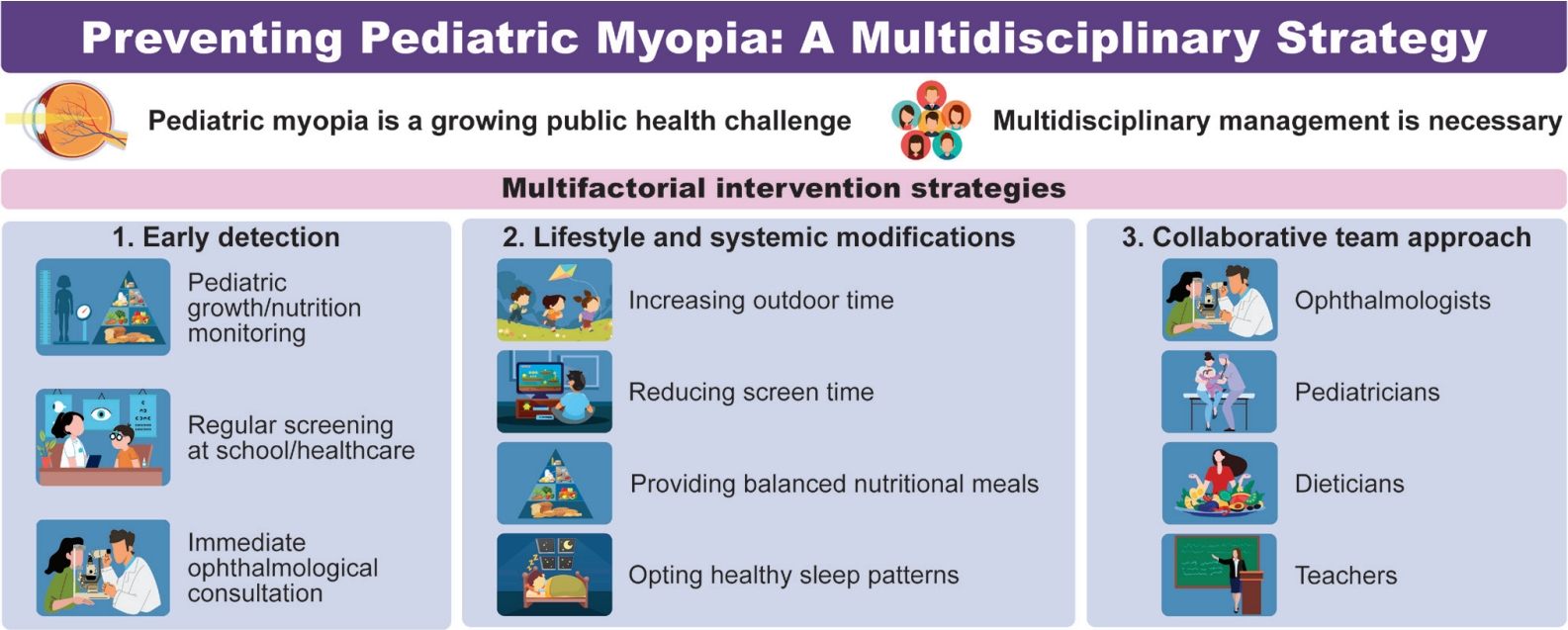
Myopia is a growing global public health concern because of its association with irreversible vision loss such as myopic traction maculopathy, rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, and glaucoma. The effective prevention of myopia in childhood requires a multidisciplinary approach that integrates ophthalmologic care with lifestyle, nutrition, and sleep interventions. Early detection through regular visual screening in schools and primary care settings and timely ophthalmology referrals are critical to preventing high myopia.
- Review Article
- Nutrition
- Exploring nutritional screening tools for hospitalized children: a narrative review (58 times)
- Pankaj Soni, Amit Agrawal, Gaurav Jadon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):963-970. Published online October 22, 2025
-
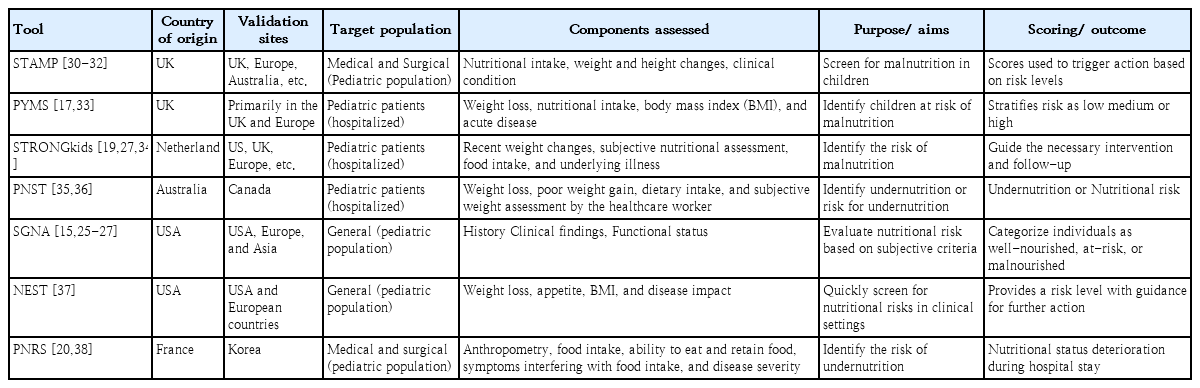
Malnutrition is frequently identified in hospitalized children, and the use of nutritional screening tools is crucial for assessing their nutritional status during their hospital admission and stay. Common tools include the Pediatric Yorkhill Malnutrition Score, Screening Tool for Assessment of Malnutrition in Pediatrics, and Screening Tool for Risk of Nutritional Status and Growth. However, these tools have varying sensitivities and specificities, and none is recommended for all hospitalized children.
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Occurrence of stroke in children and young adults in Indonesia: a multicenter private hospital study (56 times)
- Jeanne Leman, Veli Sungono, Yosua Timotius Haryono, Muhammad Adam Mudzakir, Dewi Lestari Rahmawati, Callistus Bruce Henfry Sulay, Gilbert Sterling Octavius
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):303-310. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: What is the occurrence of pediatric stroke in Indonesia?
Finding: This multicenter study identified 1,074 stroke cases, predominantly hemorrhagic (83.4%), with males and older children at higher risk. Accidents were the primary cause (73.2%).
Meaning: Pediatric stroke in Indonesia shows critical epidemiological trends, highlighting the need for targeted prevention efforts, particularly for high-risk groups like males and accident victims.
- Pulmonology
- Association of macrophage migration-inhibitory factor gene and growth differentiation factor 15 gene polymorphisms and their circulating levels with respiratory distress syndrome among preterm neonates (56 times)
- Ali Helmi Bakri, Mohammed H. Hassan, Khaled Abdalla Abd-Elbaseer, Mahmoud Abo-Alhassan Sayed, Ahmed Alamir Mahmoud Abdallah, Eman Ahmed Abd-Elmawgood
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):680-689. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: Do macrophage migration-inhibitory factor (MIF) and growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) levels and their gene polymorphisms affect RDS among preterm babies?
Finding: Significantly higher serum MIF and GDF-15 levels were observed in patients with severe respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). The mutant G- and C-alleles of GDF-15 rs4808793 C>G single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and MIF rs755622 G>C SNP were present at significantly higher frequencies in preterm neonates with RDS.
Meaning: MIF and GDF-15 play a significant role in neonatal RDS and its severity.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Short-term outcomes of oropharyngeal administration of colostrum in preterm neonates: a double-blind placebocontrolled randomized trial (56 times)
- Ameneh Lamsehchi, Maryam Shokouhi Solgi, Mohammad Kazem Sabzehei, Behnaz Basiri, Elahe Talebi Ghane, Kiana Kimiaei Asadi, Sina Azadnajafabad
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):73-79. Published online October 31, 2024
-

Question: What are the short-term outcomes of oropharyngeal administration of colostrum (OAC) in preterm neonates?
Finding: This study demonstrated the significantly lower rates of necrotizing enterocolitis, clinically suspected sepsis, shorter hospital stay, period to full enteral feeding, and antibiotic therapy period in the OAC group.
Meaning: This trial may further expand the clinical application of OAC in premature infants to reduce their length of hospital stay and complications.
- Perspective
- General Pediatrics
- Parenting principles to combat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and form resilient young minds (55 times)
- Jandy Le, Sandhya J. Kadam
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):838-841. Published online September 22, 2025
-
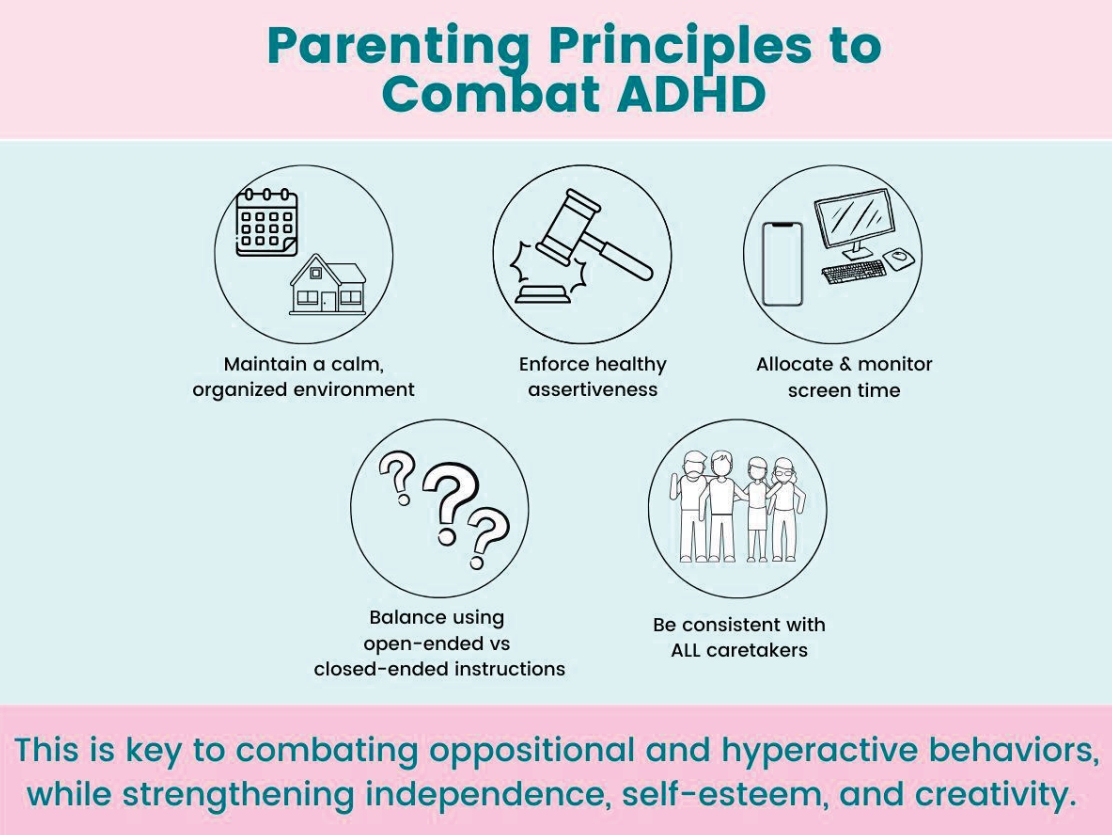
The prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, conduct disorder, and other related behavioral problems is increasing among children, likely due to less interaction with their parents and the real world and more time spent on screens, on social media, and in the virtual world. This article highlights several simple, basic parenting principles to facilitate the growth of healthy, resilient minds and combat the symptoms of opposition, hyperactivity, and distractibility.
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Evaluation of Bak and Bcl-Xl gene expression among pediatric patients with acute primary immune thrombocytopenia (55 times)
- Amira Zaki Badawy, Samia Hassan Kandel, Iman Aly Ahmedy, Mahmoud Ahmed Elhawy, Sally Mohamed El-Hefnawy, Dina Fouad Sief El-Nasr Zidan, Hanan Hassan El-sheity
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):901-908. Published online August 6, 2025
-

The B-cell lymphoma protein 2 family proteins Bak and Bcl- Xl, important markers of apoptosis, may contribute to primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). Thus, their expression may serve as biomarkers for the diagnosis and monitoring of pediatric ITP. Targeting these pathways may improve platelet survival, particularly in treatment-resistant cases. Personalized treatments based on apoptotic profiles can optimize therapy and reduce the unnecessary use of immunosuppressive drugs.
- Review Article
- Adolescence Medicine
- Diet-related behaviors affecting health and substance use among children and adolescents (54 times)
- Ji-Hyun Seo, Sochung Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):664-671. Published online October 31, 2024
-
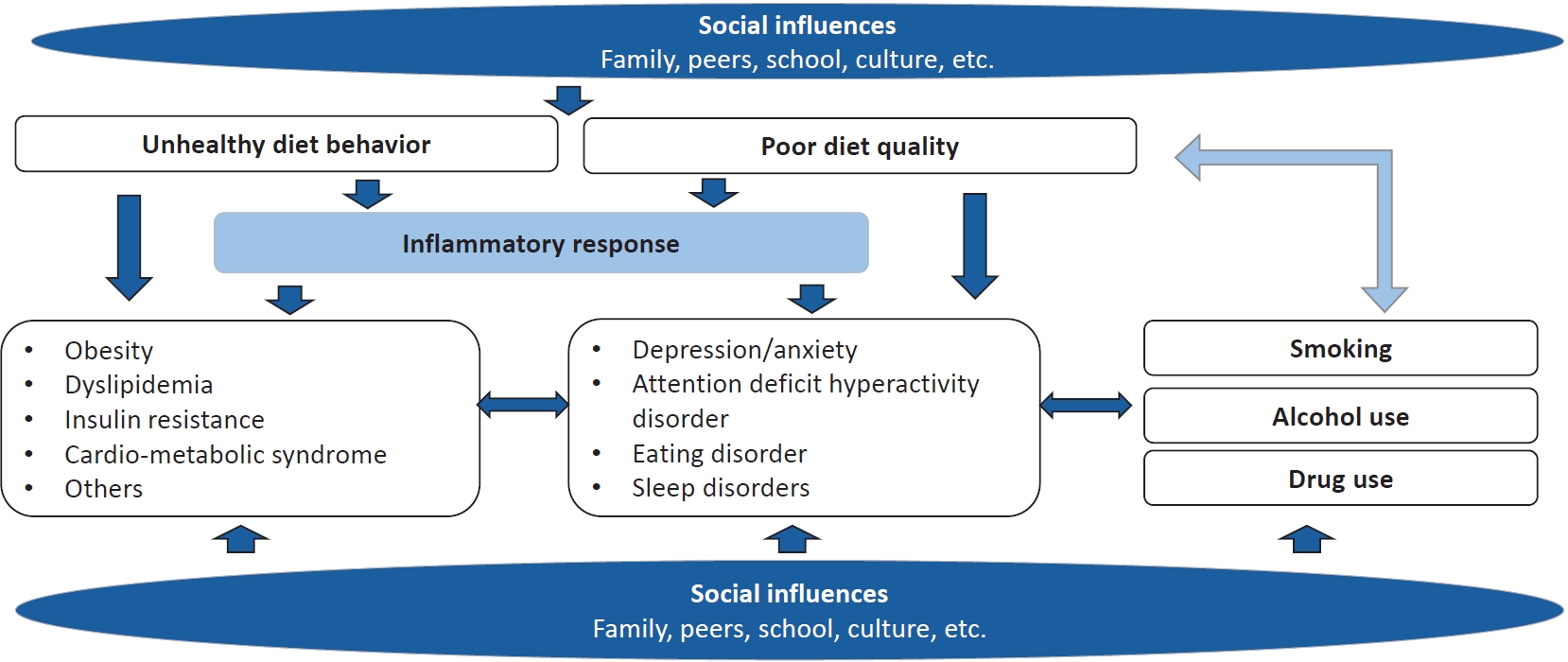
· Diet behaviors in children and adolescents are influenced by environmental and sociocultural factors.
· Unhealthy diet behaviors and poor diet quality are the main contributing factors to noncommunicable diseases and mental health problems during childhood and adolescence.
· Smoking and alcohol drinking in children and adolescents may be associated with unhealthy diet behavior or poor diet quality.
- Immunology
- NLRP3 inflammasome: a key player in neonatal brain injury (54 times)
- Cagla Kiser, Ilkcan Ercan, Defne Engur, Sermin Genc
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):475-485. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is the major cause of neonatal brain injury. NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome activation leads to neuroinflammation, which significantly affects newborn mortality. The establishment of preventive and therapeutic strategies against brain damage requires a thorough understanding of the mechanisms underlying neuroinflammation and inflammasome activation in the neonatal brain.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Carbapenem resistance in gram-negative pathogens in an Iranian hospital: high prevalence of OXA-type carbapenemase genes (54 times)
- Setareh Mamishi, Reihaneh Hosseinpour Sadeghi, Sadaf Sajedi Moghaddam, Babak Pourakbari, Shiva Poormohammadi, Maryam Sotoudeh Anvari, Shima Mahmoudi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):65-72. Published online October 31, 2024
-

Question: What is the prevalence of carbapenem resistance in gram-negative bacteria and associated carbapenemase genes?
Findings: This study identified a notable prevalence of carbapenem-resistant gram-negative isolates, with Escherichia coli being the predominant contributor, follow ed by Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, while bla OXA48 was the most prevalent carbapenemase gene.
Meaning: These findings highlight the urgent need for proactive measures including the rapid detection of carbapenemase- producing isolates and effective infection control.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Effect of postoperative enteral protein supplementation on nitrogen balance in critically ill children (54 times)
- Irene Yuniar, Kadek Apik Lestari, Antonius Hocky Pudjiadi, Fatima Safira Alatas, Yoga Devaera
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):790-800. Published online May 30, 2025
-
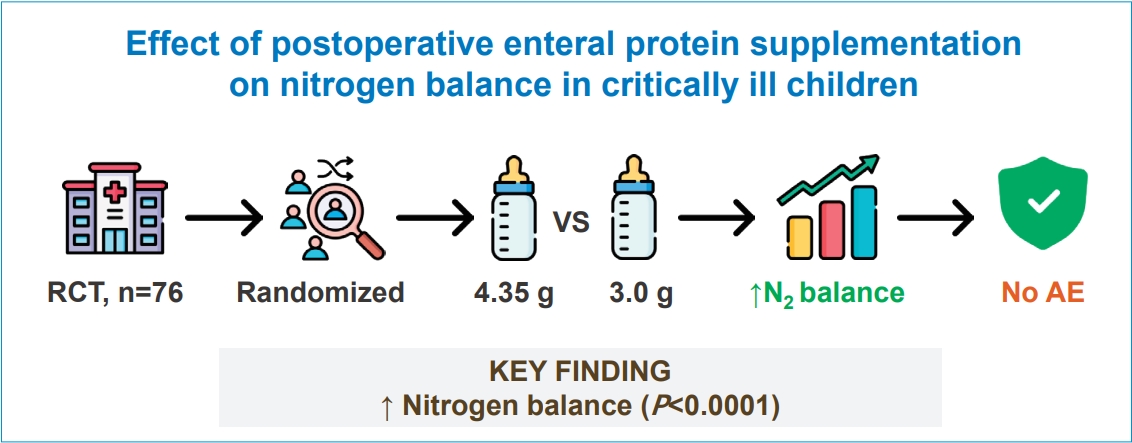
Question: Does high-protein enteral nutrition better increase the average nitrogen balance (NB) and decrease the intestinal fatty acid-binding protein (I-FABP) level of critically ill postoperative children than standard-protein enteral nutrition?
Finding: The study demonstrated a significant increase in average NB but no significant decrease in I-FABP levels in the high- versus low-protein group.
Meaning: These findings suggest that high-protein enteral nutrition can improve NB in critically ill postoperative children, thereby supporting their recovery.
- Other
- Impact of thyroid hormones and serum endothelin levels on pediatric asthma control: a case-control study of an Indian population (53 times)
- Murugaiyan Sathishbabu, Sathiya Ramasamy, Niranjjan Ramachandran, Soundararajan Palanisamy, Arulvijayavani Subramaniam
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):831-837. Published online September 22, 2025
-
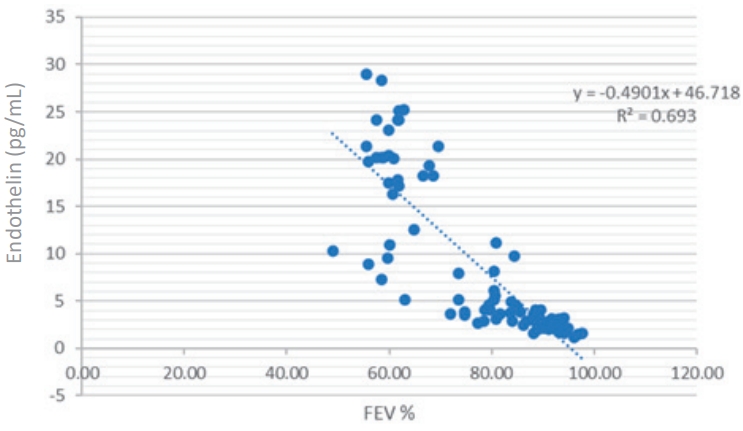
Question: What are the roles of thyroid hormones and endothelin in South Indian children with asthma?
Finding: Thyroid hormone and endothelin levels were significantly elevated in South Indian children with asthma; poorly controlled cases exhibited the highest levels. Elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone and endothelin levels were correlated with asthma severity.
Meaning: Serum endothelin is a potential surrogate marker for asthma severity that could aid the assessment and management of childhood asthma.
- Infection
- Serum copper and ceruloplasmin levels as biomarkers reflecting liver fibrosis in children with autoimmune hepatitis (53 times)
- Salma Abdel Megeed Nagi, Mai Ibrahim Elashmawy, Amany E. Elashkar, Mohamed Zaeim Hafez, Ashraf A.E. Emara, Osama Mohammad Abdelhay, Albayoumi A.B. Fouda, Mohamed AbdelAziz Doma, Ahmad Mohamed Awad, Ahmed Mohammed Saba, Hesham Abdelrahman Ahmed, Ahmed Mohamed Gad Allah, Fatma Mahmoud Abdelraheem, Mohamed A. Gad, Mohamad A. Soliman, Tamer I. Abdalrhman, Khaled Hassaan Awad, Ismael A.K.M. El-lebedy, Mostafa M. Abdelnaser, Mohammed Z. Abdel Kareem, Marwa Fekry Hassan, Shymaa Sobhy Menshawy Khalifa
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):909-920. Published online August 6, 2025
-

· A total of 159 children with autoimmune hepatitis (AIH; 60.3% female, 13.2% type 2 AIH) were identified. According to a global study, the estimated annual incidence of AIH in Egypt is 1.28 cases per 100,000 inhabitant-years.
· No studies to date have examined the serum levels of copper or ceruloplasmin in children with AIH. Therefore, here we investigated whether serum copper and ceruloplasmin levels are useful for identifying liver fibrosis in children with AIH.
· Serum copper and ceruloplasmin levels may provide important information for the identification of advanced liver fibrosis in children with AIH.
- Allergy
- Maternal sleep disorders during pregnancy and subsequent risk of allergic diseases in Japanese children: the TMM BirThree Cohort Study (53 times)
- Ami Uematsu, Masatsugu Orui, Mami Ishikuro, Keiko Murakami, Aoi Noda, Genki Shinoda, Taku Obara, Shinichi Kuriyama
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):36-45. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Question: Associations have been made between maternal sleep disorders during pregnancy and allergic diseases including bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis, food allergy, and allergic conjunctivitis/rhinitis/hay fever in their children.
Finding: In the crude model, sleep disorders during pregnancy were associated with all examined allergic diseases in children. After adjustment, significant associations remained for atopic dermatitis and allergic conjunctivitis/rhinitis/hay fever.
Meaning: The study highlights associations between maternal sleep and child allergic diseases.
- Neurology
- Establishing an induced pluripotent stem cell bank using urine cells from pediatric patients with neurogenetic diseases (52 times)
- Hien Bao Dieu Thai, WonWoo Jung, Sol Choi, Woo Joong Kim, JangSup Moon, ByungChan Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):569-577. Published online April 1, 2025
-
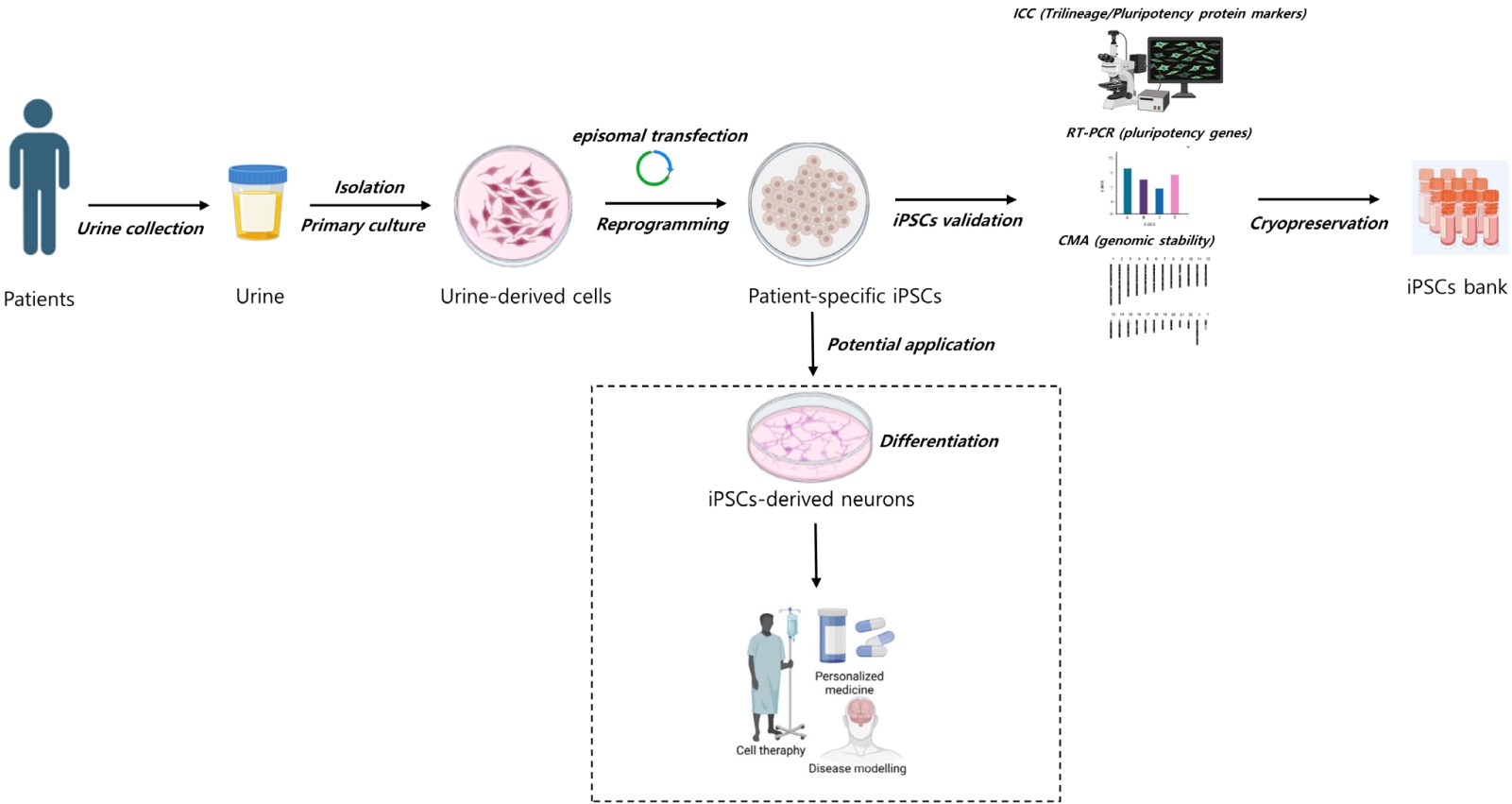
Question: What can be used to create a reliable supply of somatic cells for induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) generation and standardize procedures for building an iPSC bank for researching pediatric neurogenetic disorders?
Findings: Noninvasively acquired urine cells are a desirable cell source for iPSC reprogramming.
Meaning: An iPSC bank can be created from diverse patient cell sources and offer a useful resource for translating research results into clinical therapy for pediatric neurogenetic disorders.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Two- versus one-bag fluid delivery in pediatric and adolescent diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis (50 times)
- Maya L. Nasser, Joseph Nasr, Reem B. Zalloum, Nathanael Q.E. Yap, Natalie E. Bourdakos, Shahid Miangul, Tara A. Betts, Hayato Nakanishi, Christian A. Than, Serge Jabbour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):486-497. Published online June 27, 2024
-

· The safety and efficacy of the two-bag versus one-bag system for treating patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) < 21 years remains unestablished.
· Our meta-analysis demonstrated similar safety outcomes but sooner DKA resolution and shorter mean response time for intravenous fluid changes for the two-bag system.
· This preliminary evidence suggests that the two-bag system has some advantages in efficacy, but further studies are needed to evaluate their extent.
- Clinical Note
- Genetics and Metabolism
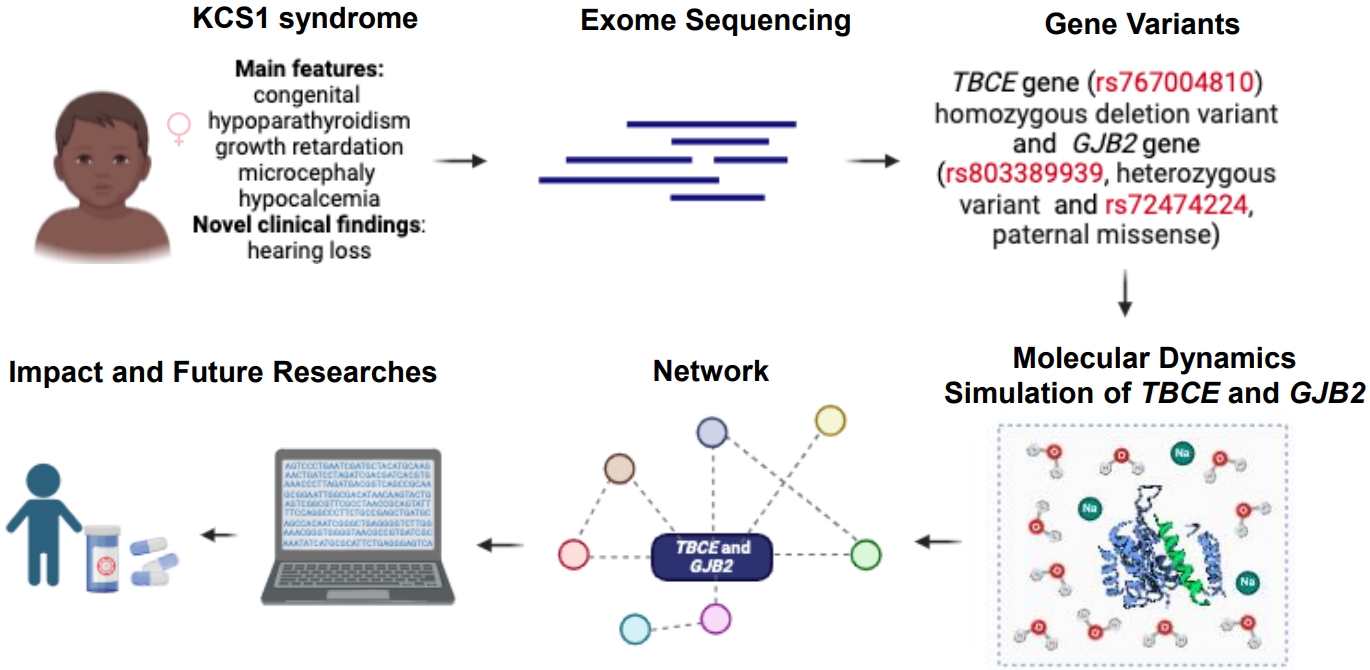
- Expanding genotype-phenotype correlation of Kenny-Caffey syndrome type 1 (50 times)
- Manuela Lo Bianco, Federica Sipala, Xena Giada Pappalardo, Gaia Fusto, Roberta Rizzo, Federico Favata, Carla Cimino, Silvia Marino, Martino Ruggieri, Agnese Suppiej, Simone Ronsisvalle, Raffaele Falsaperla
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):616-619. Published online May 12, 2025
-
- Original Article
- Other
- Role of neutrophil elastase in predicting infection among children with chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia (50 times)
- Mahmoud A. El-Hawy, Doaa M. Elian, Mai El-Sayad Abd El-Hamid, Esraa T. Allam, Mariam S. Kandeel, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):801-807. Published online June 10, 2025
-
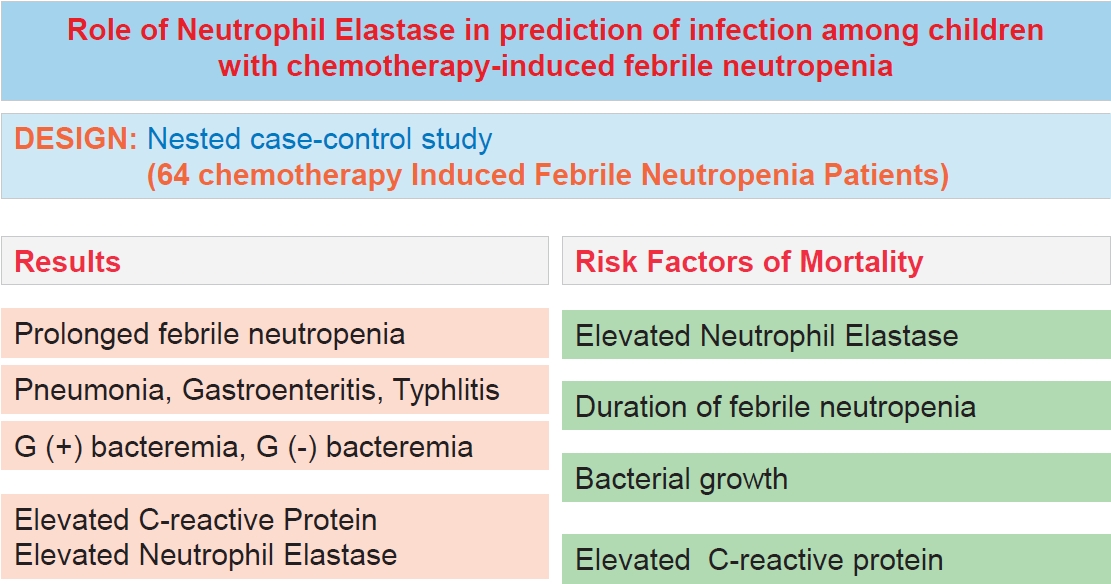
Question: Can neutrophil elastase (NE) levels predict infection— the primary cause of mortality—among children with hematological malignancies and febrile neutropenia (FN)?
Finding: Elevated levels of NE were found in children with chemotherapy-induced FN and a bacterial infection.
Meaning: Increased NE levels and prolonged FN are important factors associated with mortality risk.
- Nutrition
- Energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents: prevalence and associated factors (49 times)
- Jee-Seon Shim, Jeong Mi Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):531-539. Published online September 24, 2024
-

Question: How prevalent is energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents and what are the associated factors?
Findings: The prevalence of energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents increased from 3.2% in 2014 to 12.2% in 2019. Energy drink consumption varies according to sociode-mographic and individual factors.
Meaning: Policies and educational strategies are needed to reduce energy drink consumption in adolescents.
- Other
- Balance assessment with decreased base of support for children with disabilities (49 times)
- Guilherme M. Cesar, Madison Giebler, Thad W. Buster, Judith M. Burnfield
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):718-724. Published online November 11, 2024
-
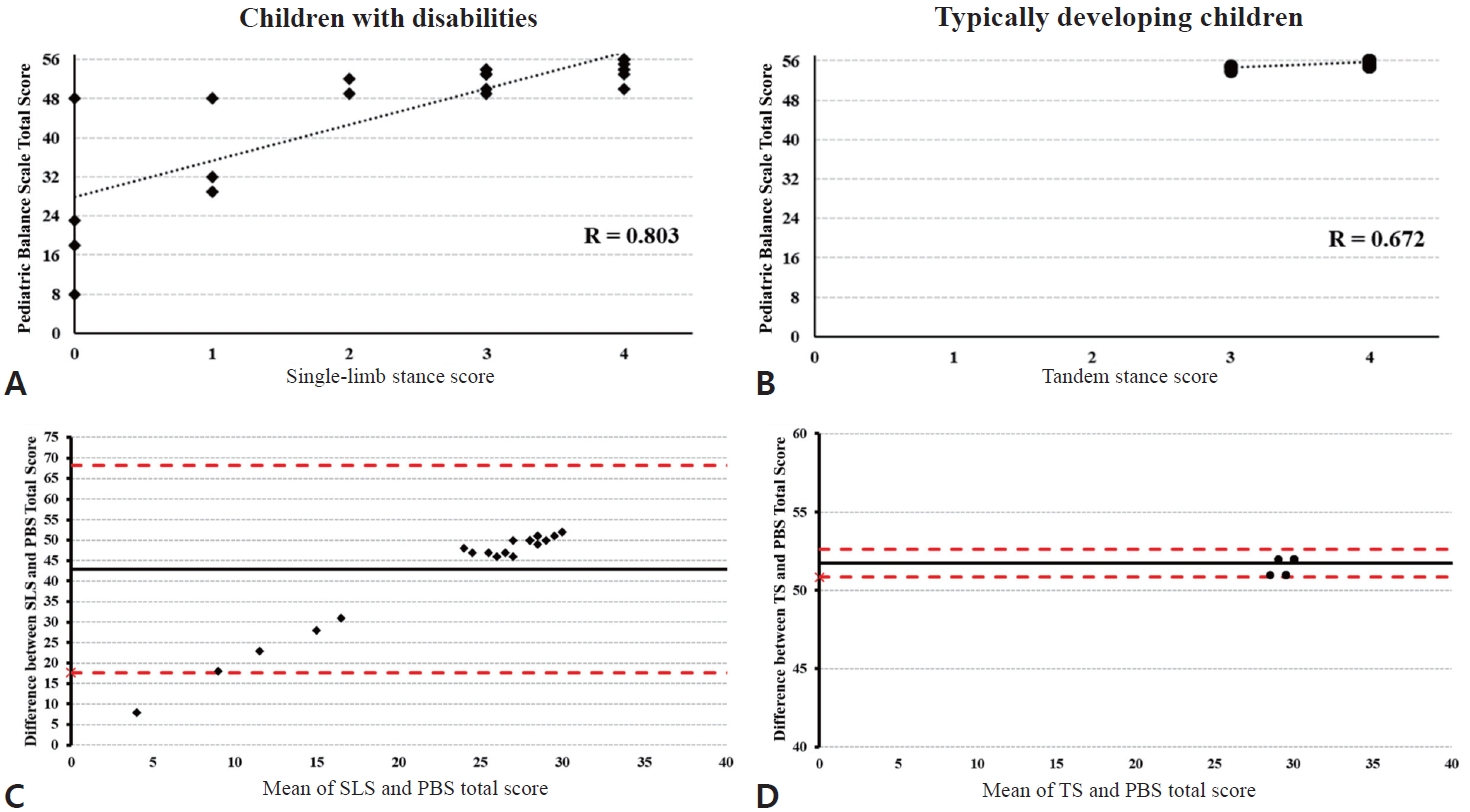
Question: Can a balance task with narrowed base of support indicate overall functional balance control in children with disabilities?
Finding: While single-limb standing could explain overall balance control for children with disabilities, it was unrelated with balance control for typically developing children.
Meaning: One balance task with narrowed base of support can be used as practical assessment of balance abilities for children with disabilities when allocated session time is of concern.
- Review Article
- Hematology
- Promising role of voxelotor in managing sickle cell disease in children: a narrative review (49 times)
- Amit Agrawal, Gaurav Jadon, Japna Singh, Dalwinder Janjua
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):106-114. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Voxelotor has promising ability to increase hemoglobin levels and reduce hemolysis markers in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD). Several preclinical and phase II/III trials have demonstrated its efficacy, dose-dependent responses, and tolerability in children. Ongoing trials are assessing its safety and effectiveness in various populations, including children younger than 12 years. These findings suggest its potential as a disease-modifying drug, warranting further exploration of its role in SCD management.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Somatic symptom severity during acute illnesses among children with functional gastrointestinal disorders (49 times)
- Rattanachart Sirinil, Anundorn Wongteerasut
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):587-593. Published online March 11, 2025
-
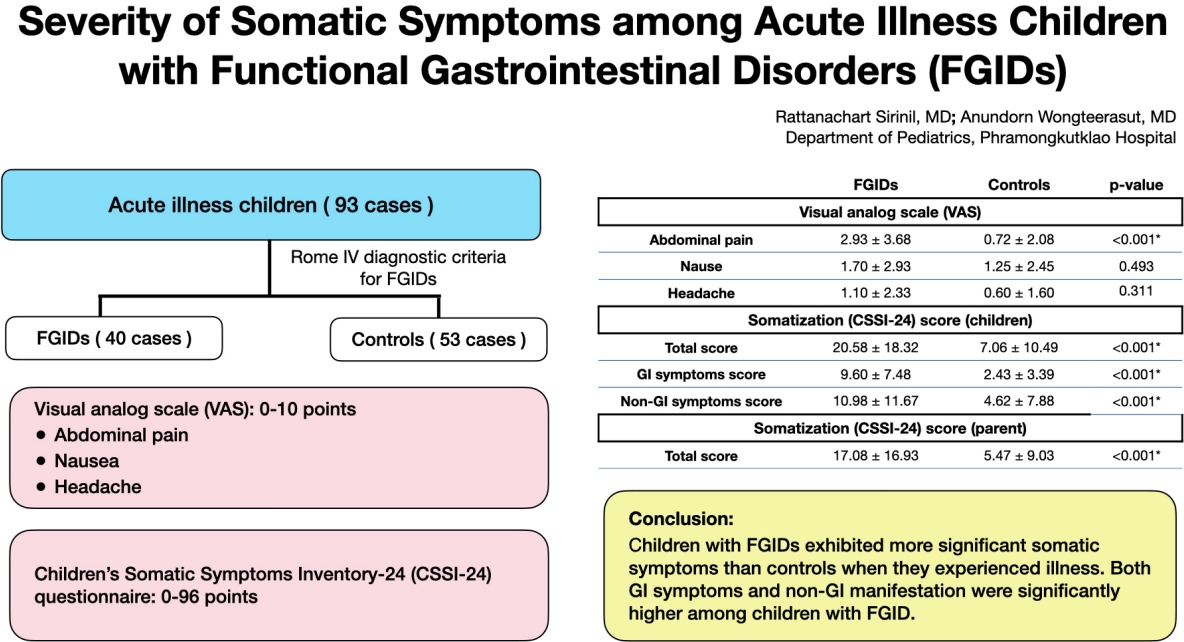
Functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) are associated with various somatic symptoms measured using a visual analogue scale and the Children’s Somatic Symptoms Inventory-24 questionnaire. Children with FGIDs exhibited more significant somatic symptoms than controls during acute illnesses. Gastrointestinal (GI) and non-GI manifestations are significantly more common in children with FGIDs.
- Basic Research
- Linezolid mitigates tissue injury in experimental model of pediatric testicular torsion: TLR-4/MAPK/NF-κB involvement (49 times)
- Moein Ghasemi, Abolfazl Basiri, Houman Kazemzadeh, Mohammad Amin Manavi, Seyed Mohammad Tavangar, Ahmad Reza Dehpour, Hamed Shafaroodi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):700-711. Published online August 26, 2025
-

Question: What pharmacological strategies can limit ischemia-reperfusion injury in pediatric patients with testicular torsion?
Finding: In a rat model of testicular torsion, linezolid reduced oxidative stress, inflammation, and tissue injury via the Toll-like receptor 4/mitogen-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor kappa beta pathway.
Meaning: Linezolid may offer a pharmacological approach to attenuate testicular damage in pediatric patients with testicular torsion, warranting further clinical investigation.
- Hematology
- Hyperhomocysteinemia in pediatric β-thalassemia: links to vitamin cofactor deficiencies and oxidative stress (49 times)
- Arzu Dadashova, Gunay Aliyeva, Rana Rahimova, Gulnara Azizova, Khayala Mammadova
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):819-830. Published online July 8, 2025
-
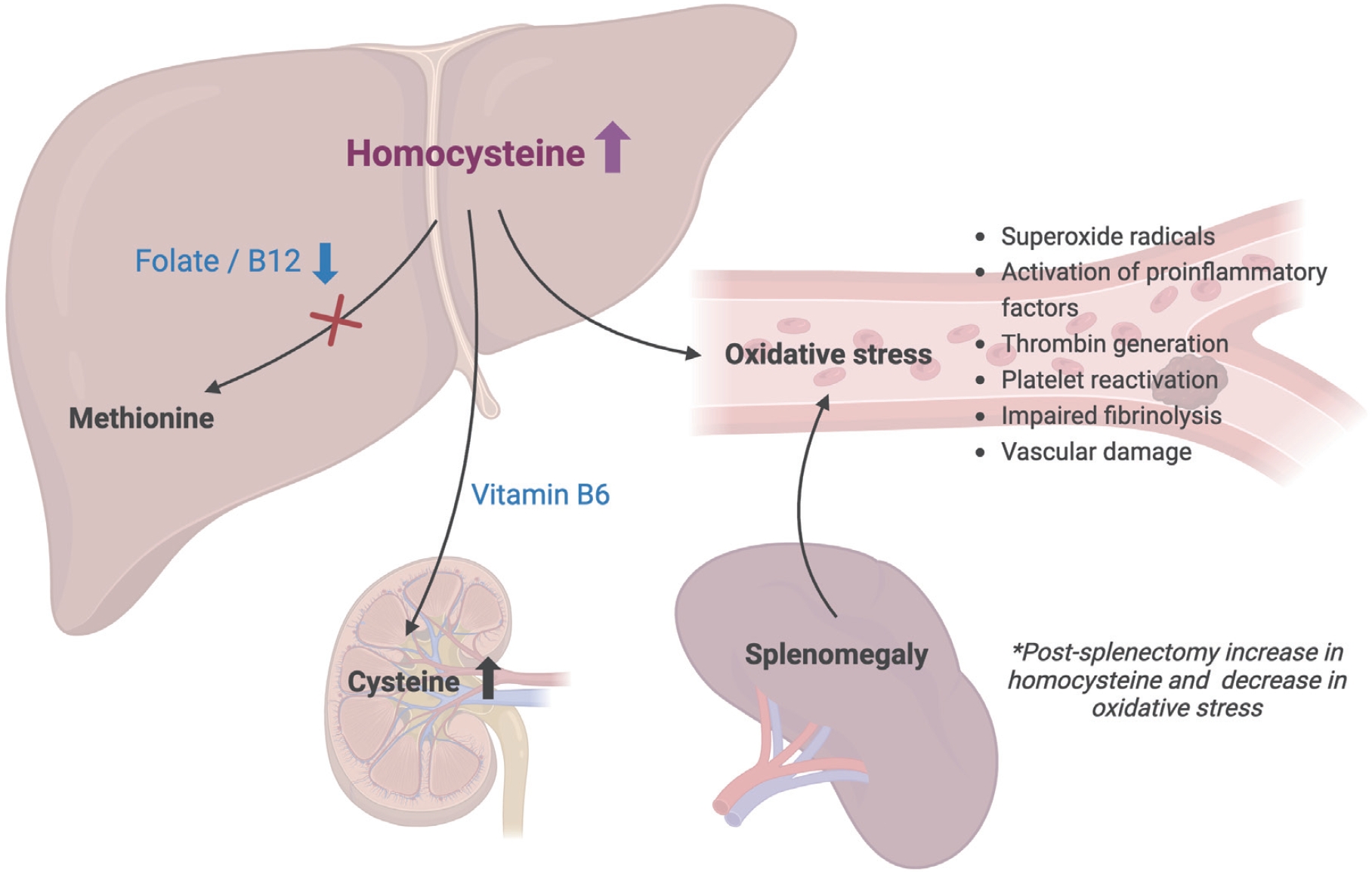
Question: What are the biochemical and clinical correlates of hyperhomocysteinemia in pediatric β-thalassemia, and how does it relate to vitamin status, oxidative stress, and splenectomy?
Finding: Most pediatric β-thalassemia patients exhibited severe hyperhomocysteinemia, which was strongly associated with folate and B12 deficiencies and influenced oxidative stress patterns, particularly in splenectomized individuals.
Meaning: These findings suggest that routine monitoring and correction of B-vitamin deficiencies may mitigate hyperhomocysteinemia-related risks in pediatric thalassemia.
- Infection
- Clinical outcomes and healthcare utilization of hospitalized children with influenza versus COVID-19 (48 times)
- David Chun-Ern Ng, Chuin-Hen Liew, Kah Kee Tan, Joanne Pereira, Muhammad Ihsan Roslan, Xiang Lin Cheng, Hui Yi Lim, Farah Nuruliayana A. Nazri, Asuwani Maran, Wan Fei Wong, Yasothai Chandran, Syaniza Shaharudin, Pon Ling Lau, Naveen Nair Gangadaran, Marlindawati Mohd Ali
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):1007-1014. Published online October 2, 2025
-
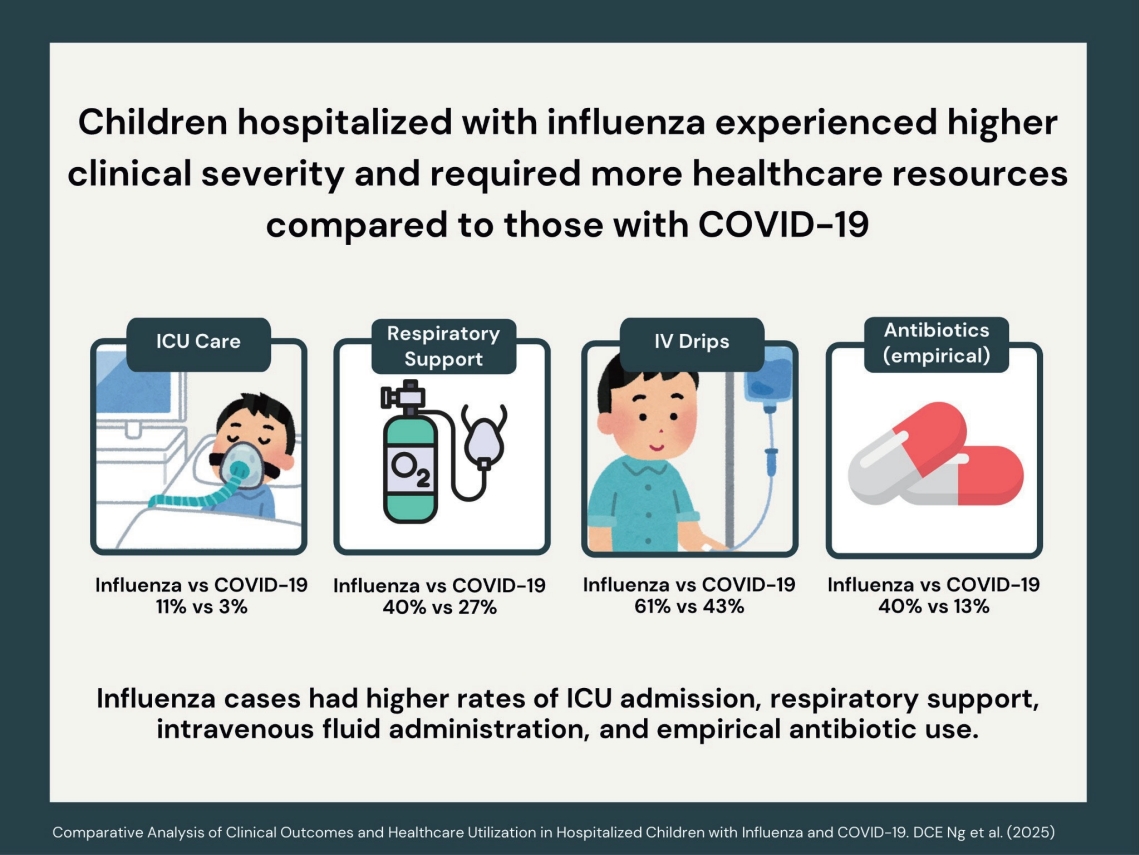
Question: How do clinical presentations, healthcare resource utilization, and outcomes differ between children hospitalized with influenza versus coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)?
Finding: Patients with influenza were older, were more symptomatic, and required greater healthcare resources, including intravenous fluids, empirical antibiotics, respiratory support, and pediatric intensive care unit admission.
Meaning: Influenza involves greater severity and a higher healthcare burden than COVID-19, highlighting the need for preventive strategies such as vaccination and hospital resource planning during seasonal outbreaks.
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











