Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Association between vitamin D polymorphisms and binding protein and COVID-19 risk and severity in children
- Victoria Giatraki, Helen Dimitriou, Georgia Martimianaki, Christos Tsatsanis, Emmanouil Galanakis, Chrysoula Perdikogianni
-
Background: The effects of genetic background on the biological effects of vitamin D on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in children remain unclear.
Purpose: This study aimed to explore the association between vitamin D-related genetic background and 25- hydroxyvitamin D status and COVID-19 occurrence and severity in children. Here we explored key genetic variants within the vitamin D pathway in pediatric COVID-19 patients in relation to circulating vitamin D... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.00577 [Accepted]
- Basic Research
- Linezolid mitigates tissue injury in experimental model of pediatric testicular torsion: TLR-4/MAPK/NF-κB involvement
- Moein Ghasemi, Abolfazl Basiri, Houman Kazemzadeh, Mohammad Amin Manavi, Seyed Mohammad Tavangar, Ahmad Reza Dehpour, Hamed Shafaroodi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):700-711. Published online August 26, 2025
-

Question: What pharmacological strategies can limit ischemia-reperfusion injury in pediatric patients with testicular torsion?
Finding: In a rat model of testicular torsion, linezolid reduced oxidative stress, inflammation, and tissue injury via the Toll-like receptor 4/mitogen-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor kappa beta pathway.
Meaning: Linezolid may offer a pharmacological approach to attenuate testicular damage in pediatric patients with testicular torsion, warranting further clinical investigation.
- Hematology
- Evaluation of Bak and Bcl-Xl gene expression among pediatric patients with acute primary immune thrombocytopenia
- Amira Zaki Badawy, Samia Hassan Kandel, Iman Aly Ahmedy, Mahmoud Ahmed Elhawy, Sally Mohamed El-Hefnawy, Dina Fouad Sief El-Nasr Zidan, Hanan Hassan El-sheity
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):901-908. Published online August 6, 2025
-

The B-cell lymphoma protein 2 family proteins Bak and Bcl- Xl, important markers of apoptosis, may contribute to primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). Thus, their expression may serve as biomarkers for the diagnosis and monitoring of pediatric ITP. Targeting these pathways may improve platelet survival, particularly in treatment-resistant cases. Personalized treatments based on apoptotic profiles can optimize therapy and reduce the unnecessary use of immunosuppressive drugs.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Effect of postoperative enteral protein supplementation on nitrogen balance in critically ill children
- Irene Yuniar, Kadek Apik Lestari, Antonius Hocky Pudjiadi, Fatima Safira Alatas, Yoga Devaera
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):790-800. Published online May 30, 2025
-
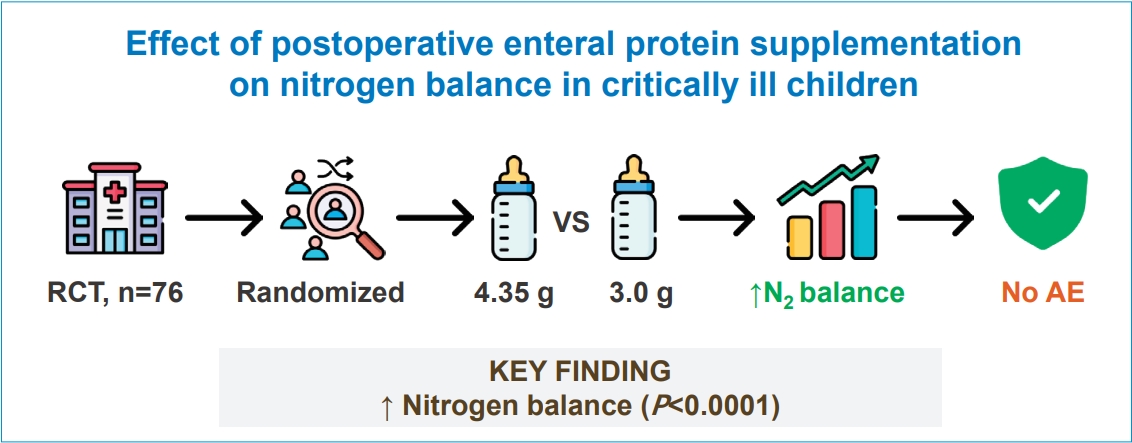
Question: Does high-protein enteral nutrition better increase the average nitrogen balance (NB) and decrease the intestinal fatty acid-binding protein (I-FABP) level of critically ill postoperative children than standard-protein enteral nutrition?
Finding: The study demonstrated a significant increase in average NB but no significant decrease in I-FABP levels in the high- versus low-protein group.
Meaning: These findings suggest that high-protein enteral nutrition can improve NB in critically ill postoperative children, thereby supporting their recovery.
- Gastroenterology
- Adenosine deaminase and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist genetic polymorphisms among obese children with versus without metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease
- Hala M. Sakhr, Mohammed H. Hassan, Azza Mohamed Taha, Ali Helmi Bakri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):808-818. Published online May 29, 2025
-
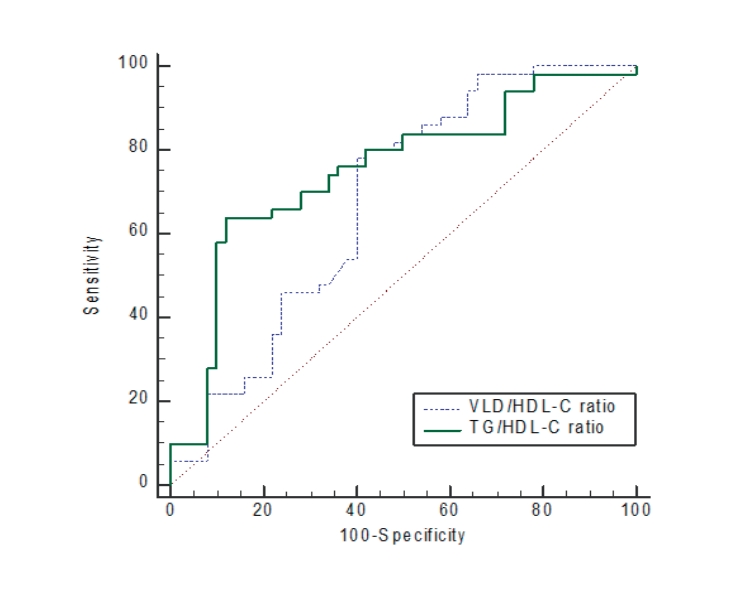
Question: Is there an association between adenosine deaminase (ADA) G22A and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RN) genetic polymorphisms and pediatric metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)?
Finding: The GG genotype and G allele of ADA G22A were significantly associated with obesity but not pediatric MAFLD, while the *1/*2 genotype of the IL-1RN gene was significantly associated with obesity and pediatric MAFLD.
Meaning: The IL-1RN gene may contribute to pediatric MAFLD.
- Nutrition
- Differential effects of dietary and physical activity interventions on adiposity of children with obesity
- Anekchoke Tangtongsoong, Chonnikant Visuthranukul, Yuda Chongpison, Sirinuch Chomtho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):370-378. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: How do dietary intake and physical activity affect body mass index (BMI) z scores and adiposity among children with obesity?
Finding: Higher dietary protein and fiber intakes were significantly associated with a decrease in BMI z scores and adiposity among children with obesity.
Meaning: Optimizing dietary interventions by focusing on protein and fiber intakes could be an effective strategy for managing childhood obesity.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Differential roles of interleukin-6 and adrenomedullin in early diagnosis and mortality predictions in late-onset neonatal sepsis
- Emilly Henrique dos Santos, Gabriel Acca Barreira, Mariana Okay Saippa, Maria Carolina Pires Cruz, Karen Alessandra Rodrigues, Ronaldo Arkader, Thelma Suely Okay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):463-471. Published online December 23, 2024
-

Question: Can adrenomedullin (ADM) or interleukin-6 (IL-6) detect late-onset neonatal sepsis (LOS) at admission (area under the curve [AUC]>0.90) as an early diagnostic marker?
Finding: Only IL-6 consistently distinguished survivors from nonsurvivors (AUC>0.90) on admission and antibiotic treatment days 3 and 7. C-reactive protein level identified infections from day 3 but failed to predict outcomes (AUC<0.70).
Meaning: IL-6 level can improve LOS diagnosis and prognosis.
- Review Article
- Nutrition
- Protein substitutions as new-generation pharmanutrition approach to managing phenylketonuria
- Fatma Nur Keskin, Teslime Özge Şahin, Raffaele Capasso, Duygu Ağagündüz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):320-331. Published online November 1, 2022
-
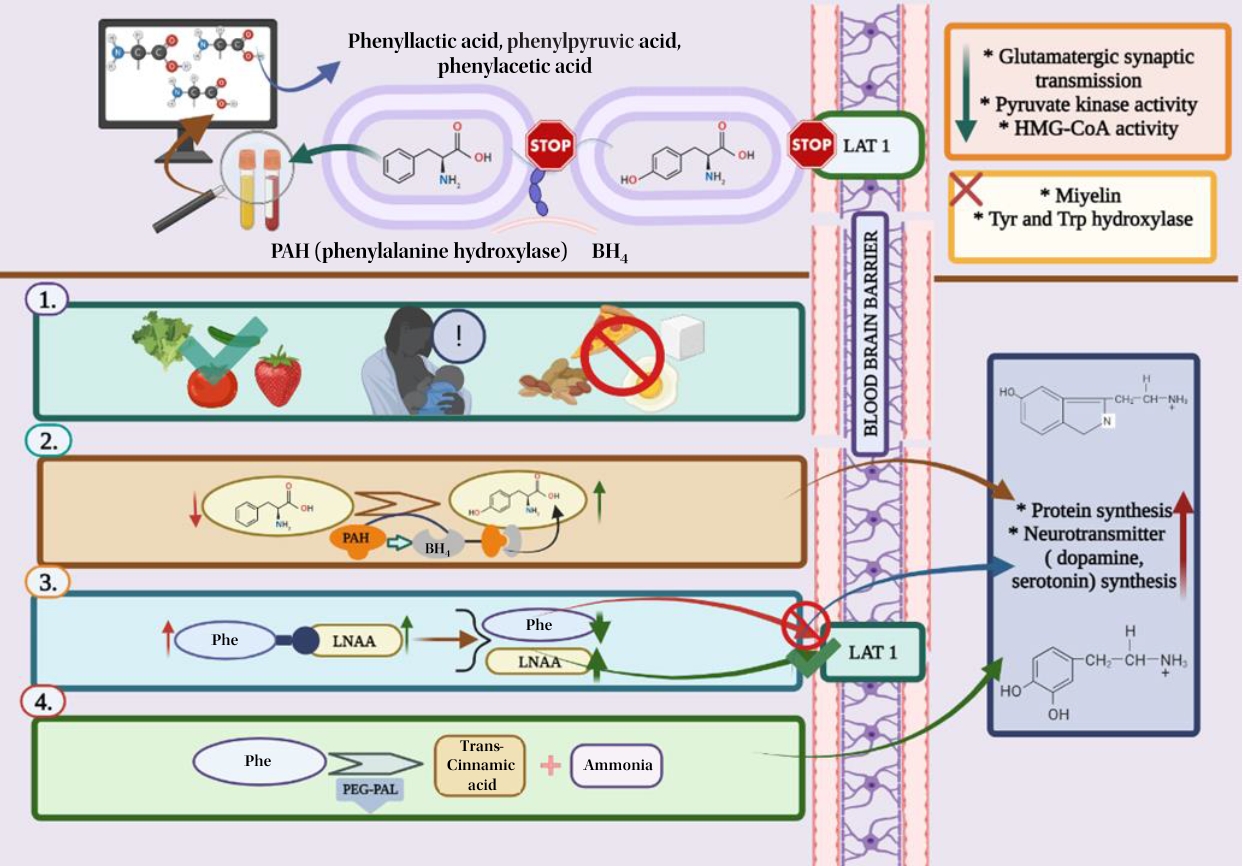
Phenylketonuria, an autosomal recessive disease that results from the inability to metabolize phenylalanine, is currently treated with medical nutrition therapy. New treatment approaches such as tetrahydrobiopterin, glycomacropeptide, large neutral amino acids, pegvaliase, and gene therapy significantly impact disease management and dietary enrichment. This article also reviews animal and human studies that have evaluated the efficacy and safety of these new protein substitutes.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Obesity and chronic kidney disease: prevalence, mechanism, and management
- Hyung Eun Yim, Kee Hwan Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):511-518. Published online April 6, 2021
-
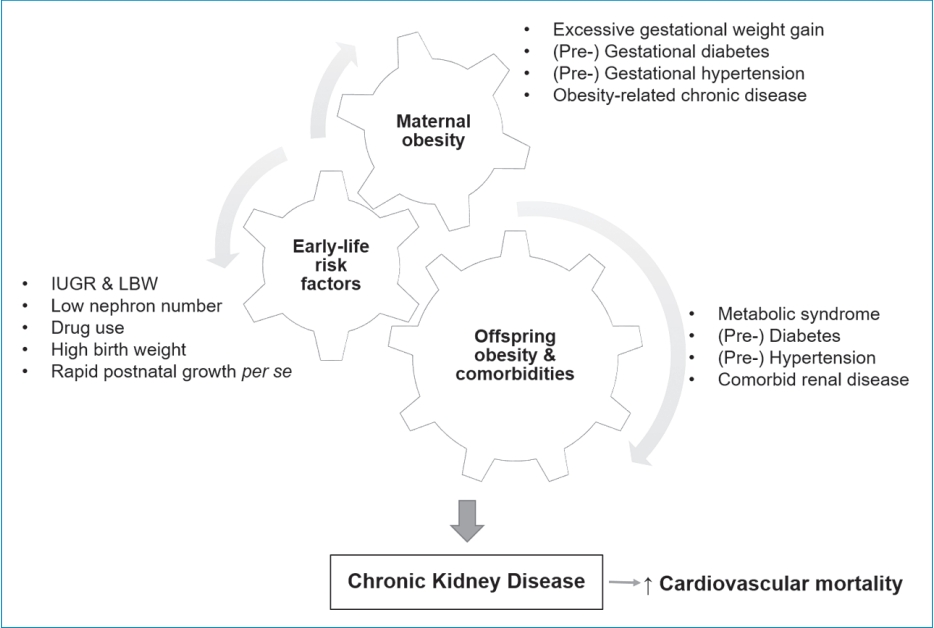
· Obesity is strongly associated with the development and progression of chronic kidney disease.
· Altered renal hemodynamics, metabolic effects, and lipid nephrotoxicity may play a key role in the development of obesity-related kidney disease.
· Children born to obese mothers are at increased risk of developing obesity and chronic kidney disease later in life.
· A multilevel approach is needed to prevent obesity and related chronic diseases.
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Understanding the genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus using Bayesian statistics and gene network analysis
- Seoung Wan Nam, Kwang Seob Lee, Jae Won Yang, Younhee Ko, Michael Eisenhut, Keum Hwa Lee, Jae Il Shin, Andreas Kronbichler
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(5):208-222. Published online July 15, 2020
-

Bayesian false-discovery probability and false-positive report probability are the 2 major Bayesian methods used to evaluate noteworthiness of a genetic variant.
Application of stricter P value is needed to confirm statistical significance in meta-analyses.
Gene network analysis of noteworthy genetic variants shows a blueprint of the genetic background in complex diseases.
- Immunology
- Immunopathogenesis of COVID-19 and early immunomodulators
- Kyung-Yil Lee, Jung-Woo Rhim, Jin-Han Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):239-250. Published online June 18, 2020
-

The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading globally. Although its etiologic agent is discovered as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), there are many unsolved issues in COVID-19 and other infectious diseases. The causes of different clinical phenotypes and incubation periods among individuals, species specificity, and cytokine storm with lymphopenia as well as the mechanism of damage to organ...
- Neurology
- Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disorders: clinical spectrum, diagnostic evaluation, and treatment options
- Yun-Jin Lee, Sang Ook Nam, Ara Ko, JuHyun Kong, Shin Yun Byun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(3):103-110. Published online May 14, 2020
-
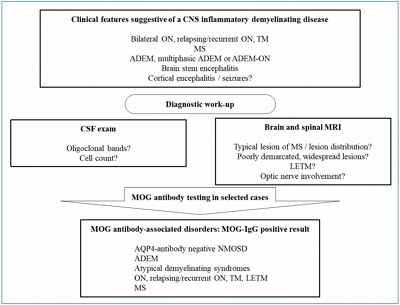
MOG antibody-associated disorder exhibits different pathophysiological and phenotypic findings than both aquaporin-4 antibody-associated neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder and typical MS. MOG-antibody is of particular interest in pediatric patients with clinical or radiological non-MS typical findings. MOG-antibody was included in a diagnostic algorithm for children recommending for the first time a standardized use in clinical practice except in cases of typical MS.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Lipid accumulation product is a predictor of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in childhood obesity
- Bahar Özcabı, Salih Demirhan, Mesut Akyol, Hatice Öztürkmen Akay, Ayla Güven
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(12):450-455. Published online October 28, 2019
-

Background: Lipid accumulation product (LAP) is associated with the presence and severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in adults.
Purpose: Here we evaluated the ability of LAP to predict NAFLD in obese children. Methods: Eighty obese children (38 girls; age 6–18 years) were included. Anthropometric measurements and biochemical values were obtained from the patients’ medical records. LAP was calculated as [waist...
- Review Article
- Nutrition
- A perspective on partially hydrolyzed protein infant formula in nonexclusively breastfed infants
- Yvan Vandenplas, Zakiudin Munasir, Badriul Hegar, Dewi Kumarawati, Ahmad Suryawan, Muzal Kadim, Julistio Tb Djais, Ray Wagiu Basrowi, Deni Krisnamurti
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(5):149-154. Published online January 14, 2019
-
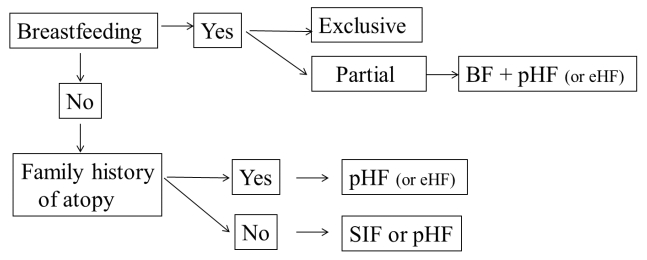
The World Health Organization recommends that infants should be exclusively breastfed for the first 6 months of life to provide optimal nutrition in this critical period of life. After this, infants should receive nutritionally adequate and safe complementary foods while breastfeeding continues for up to 2 years of age or beyond. For nonbreastfed infants, infant formula is an available option...
- Original Article
- Allergy
- Common features of atopic dermatitis with hypoproteinemia
- So Yoon Jo, Chan-Ho Lee, Woo-Jin Jung, Sung-Won Kim, Yoon-Ha Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(11):348-354. Published online September 16, 2018
-
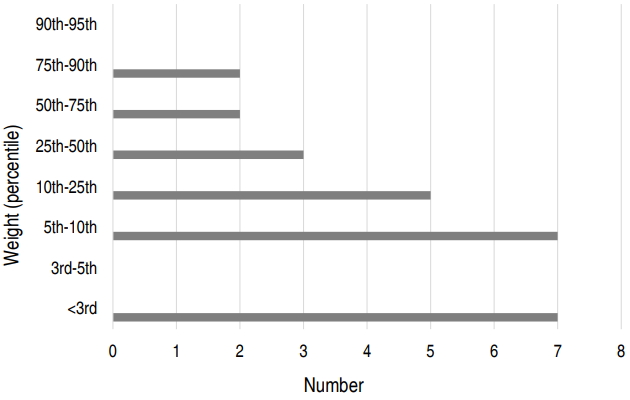
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to identify the causes, symptoms, and complications of hypoproteinemia to prevent hypoproteinemia and provide appropriate treatment to children with atopic dermatitis. Methods: Children diagnosed with atopic dermatitis with hypoproteinemia and/or hypoalbuminemia were retrospectively reviewed. The patients’ medical records, including family history, weight, symptoms, treatment, complications, and laboratory test results for allergies and skin cultures,...
- Cardiology
- Clinical implications in laboratory parameter values in acute Kawasaki disease for early diagnosis and proper treatment
- Yu-Mi Seo, Hyun-Mi Kang, Sung-Churl Lee, Jae-Won Yu, Hong-Ryang Kil, Jung-Woo Rhim, Ji-Whan Han, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(5):160-166. Published online May 28, 2018
-
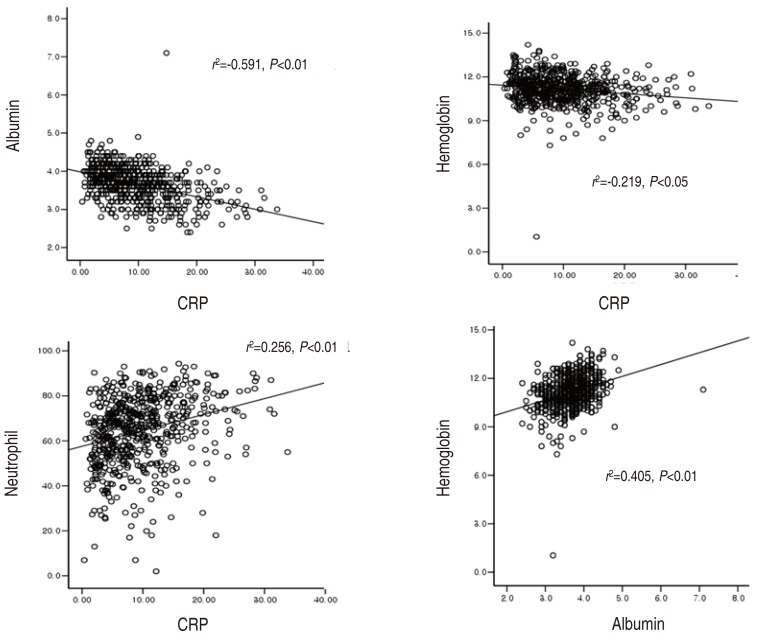
Purpose This study aimed to analyse laboratory values according to fever duration, and evaluate the relationship across these values during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease (KD) to aid in the early diagnosis for early-presenting KD and incomplete KD patients.
Methods Clinical and laboratory data of patients with KD (n=615) were evaluated according to duration of fever at presentation, and were compared between...
- Oncology
- Excellent treatment outcomes in children younger than 18 months with stage 4
MYCN nonamplified neuroblastoma - Chiwoo Kim, Young Bae Choi, Ji Won Lee, Keon Hee Yoo, Ki Woong Sung, Hong Hoe Koo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(2):53-58. Published online February 28, 2018
-
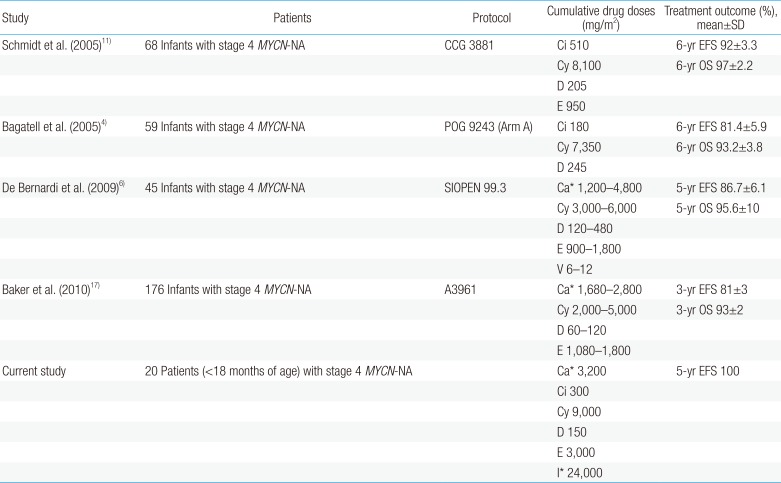
Purpose Although the prognosis is generally good in patients with intermediate-risk neuroblastoma, no consensus has been reached on the ideal treatment regimen. This study analyzed treatment outcomes and toxicities in patients younger than 18 months with stage 4
MYCN nonamplified neuroblastoma.Methods We retrospectively analyzed 20 patients younger than 18 months newly diagnosed with stage 4
MYCN nonamplified neuroblastoma between January 2009 and...
- Cardiology
- C-reactive protein and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide discrepancy: a differentiation of adenoviral pharyngoconjunctival fever from Kawasaki disease
- Jung Eun Choi, Hee Won Kang, Young Mi Hong, Sejung Sohn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(1):12-16. Published online January 22, 2018
-
Purpose To differentiate adenoviral pharyngoconjunctival fever (PCF) from acute Kawasaki disease (KD) using laboratory tests before results of virus-real time polymerase chain reaction and ophthalmologic examination are obtained.
Methods Baseline patient characteristics and laboratory measurements were compared between 40 patients with adenovirus infection and 123 patients with KD.
Results The patients with adenovirus infection were generally older than those with KD (median: 3.9 years vs....
- Case Report
- Pulmonology
- A pediatric case of relapsed pulmonary alveolar proteinosis despite successful whole lung lavage
- Seung Young Jin, Hye Ri Yun, Yun Jung Choi, Jun Dong Park, Jin Tae Kim, Chang Hyun Kang, Young Sik Park, Young Hun Choi, Woo Sun Kim, Dong In Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(7):232-236. Published online July 31, 2017
-
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is a rare disease in children characterized by intra-alveolar accumulation of surfactant proteins, which severely reduces gaseous exchange. Whole lung lavage (WLL) is the preferred technique for the treatment of severe PAP. Herein, we present a pediatric case of PAP treated with WLL. An 11-year-old boy was admitted with the chief complaint of a dry cough...
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neuroprotective effects of erythropoietin against hypoxic injury via modulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and apoptosis
- Ji Eun Jeong, Jae Hyun Park, Chun Soo Kim, Sang Lak Lee, Hai Lee Chung, Woo Taek Kim, Eun Joo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(6):181-188. Published online June 22, 2017
-
Purpose Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is a significant cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality. Erythropoietin (EPO) is emerging as a therapeutic candidate for neuroprotection. Therefore, this study was designed to determine the neuroprotective role of recombinant human EPO (rHuEPO) and the possible mechanisms by which mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway including extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2), JNK, and p38 MAPK is modulated in...
- Cardiology
- Predictive factors of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin and coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease
- Hye Young Lee, Min Seob Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(12):477-482. Published online December 31, 2016
-
Purpose We conducted a study to determine which factors may be useful as predictive markers in identifying Kawasaki disease (KD) patients with a high risk of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and developing coronary artery lesions (CAL).
Methods We enrolled 287 patients in acute phase of KD at a single center. The demographic, clinical and laboratory data were collected retrospectively.
Results There were 34 patients...
- Pulmonology
- Clinical predictors of chest radiographic abnormalities in young children hospitalized with bronchiolitis: a single center study
- Ga Ram Kim, Min Sun Na, Kyung Suk Baek, Seung Jin Lee, Kyung Suk Lee, Young Ho Jung, Hye Mi Jee, Tae Hee Kwon, Man Yong Han, Youn Ho Sheen
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(12):471-476. Published online December 31, 2016
-
Purpose Chest radiography is often performed on patients hospitalized with typical clinical manifestations of bronchiolitis. We aimed to determine the proportion of subjects with pathologic chest radiographic findings and the clinical predictors associated with pathologic chest radiographic findings in young children admitted with the typical presentation of bronchiolitis.
Methods We obtained the following data at admission: sex, age, neonatal history, past history of...
- Case Report
- Neurology
- Paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia in a patient with a
PRRT2 mutation and centrotemporal spike discharges on electroencephalogram: case report of a 10-year-old girl - Sun Young Seo, Su Jeong You
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S157-S160. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Coexistence of paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia (PKD) with benign infantile convulsion (BIC) and centrotemporal spikes (CTS) is very rare. A 10-year-old girl presented with a 3-year history of frequent attacks of staggering while laughing and of suddenly collapsing while walking. Interictal electroencephalogram (EEG) revealed bilateral CTS, but no changes in EEG were observed during movement. The patient's medical history showed afebrile...
- Glucose transport 1 deficiency presenting as infantile spasms with a mutation identified in exon 9 of
SLC2A1 - Hyun Hee Lee, Yun Jung Hur
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S29-S31. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Glucose transport 1 (GLUT-1) deficiency is a rare syndrome caused by mutations in the glucose transporter 1 gene (
SLC2A1 ) and is characterized by early-onset intractable epilepsy, delayed development, and movement disorder.De novo mutations and several hot spots in N34, G91, R126, R153, and R333 of exons 2, 3, 4, and 8 ofSLC2A1 are associated with this condition. Seizures,...
- Genetics and Metabolism
- A nonsense
PAX6 mutation in a family with congenital aniridia - Kyoung Hee Han, Hye Jin Lee, Il-Soo Ha, Hee Gyung Kang, Hae Il Cheong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S1-S4. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Congenital aniridia is a rare ocular malformation that presents with severe hypoplasia of the iris and various ocular manifestations. Most cases of congenital aniridia are known to be related to mutations in the paired box gene-6 (
PAX6 ), which is an essential gene in eye development. Herein, we report a familial case of autosomal dominant congenital aniridia with four affected members...
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Prediction of unresponsiveness to second intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease refractory to initial treatment
- Euri Seo, Jeong Jin Yu, Hyun Ok Jun, Eun Jung Shin, Jae Suk Baek, Young-Hwue Kim, Jae-Kon Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(10):408-413. Published online October 17, 2016
-
Purpose This study investigated predictors of unresponsiveness to second-line intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment for Kawasaki disease (KD).
Methods This was a single-center analysis of the medical records of 588 patients with KD who had been admitted to Asan Medical Center between 2006 and 2014. Related clinical and laboratory data were analyzed by univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses.
Results Eighty (13.6%) of the 588 patients...
- Case Report
- Neurology
- Two cases of familial cerebral cavernous malformation caused by mutations in the
CCM1 gene - Im-Yong Yang, Mi-Sun Yum, Eun-Hee Kim, Hae-Won Choi, Han-Wook Yoo, Tae-Sung Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(6):280-284. Published online June 30, 2016
-
Cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) is a vascular malformation characterized by abnormally enlarged capillary cavities without any intervening neural tissue. We report 2 cases of familial CCMs diagnosed with the
CCM1 mutation by using a genetic assay. A 5-year-old boy presented with headache, vomiting, and seizure-like movements. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed multiple CCM lesions in the cerebral hemispheres. Subsequent...
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein plasma levels as a biomarker of obesity-related insulin resistance in adolescents
- Ki Eun Kim, Young Sun Cho, Kyung Suk Baek, Lan Li, Kwang-Hyun Baek, Jung Hyun Kim, Ho-Seong Kim, Youn Ho Sheen
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(5):231-238. Published online May 31, 2016
-
Purpose Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) is a 65-kDa acute phase protein, derived from the liver, which is present in high concentrations in plasma. Data regarding the association between circulating plasma LBP levels and obesity-related biomarkers in the pediatric population are scarce. We aimed to determine whether there was a difference in plasma LBP levels between overweight/obese and normal-weight adolescents and to assess...
- Gastroenterology
- Diagnostic value of the Vesikari Scoring System for predicting the viral or bacterial pathogens in pediatric gastroenteritis
- Dong Ho Shim, Dong Yeon Kim, Ky Young Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(3):126-131. Published online March 31, 2016
-
Purpose To evaluate the diagnostic value of the Vesikari Scoring System (VSS) as an early predictor of pathogens in children with acute gastroenteritis (AG).
Methods In this retrospective study, the VSS score, absolute neutrophil count (ANC), and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels were analyzed in 107 hospitalized children with AG, aged 6 months to 17 years. Patients were divided into nonspecific, viral, and bacterial...
- Low levels of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 at birth may be associated with subsequent development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants
- Choae Lee, Jaewoo An, Ji Hee Kim, Eun Sun Kim, Soo Hyun Kim, Yeon Kyung Cho, Dong Hyun Cha, Man Yong Han, Kyu Hyung Lee, Youn Ho Sheen
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(11):415-420. Published online November 22, 2015
-
Purpose Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is characterized by inflammation with proteolytic damage to the lung extracellular matrix. The results from previous studies are inconsistent regarding the role of proteinases and antiproteinases in the development of BPD. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-8, MMP-9, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-2, and TIMP-1 levels in the serum of...
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











