Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Characterization of gut microbiota in very low birth weight infants with versus without bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Anucha Thatrimontrichai, Manapat Praditaukrit, Gunlawadee Maneenil, Supaporn Dissaneevate, Kamonnut Singkhamanan, Komwit Surachat
-
Background: Gut–lung crosstalk is a pathway involving interactions between the gastrointestinal, respiratory, and immune systems. The immune responses of the gut and lungs are intricately linked, and previous studies demonstrated that the gut microbiota can influence systemic immune responses in the respiratory system as well as bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD).
Purpose: To analyze the composition of the gut microbiota in very low... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.01718 [Accepted]
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Recent advances in understanding pathophysiology of non-nutritional stunting in very preterm infants
- Eduardo Cuestas, Alina Rizzotti
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):287-297. Published online December 23, 2024
-

· Previous reviews of extrauterine growth restriction focused mainly on weight growth restriction caused by nutritional factors or pathological conditions.
· This review summarizes recent developments in the pathophysiology of nonnutritional length growth restriction in very preterm infants with focus on the impact of sustained neonatal inflammation on their short- and long-term outcomes.
· Further research is needed to investigate optimal strategies to improve length growth restriction in very preterm infants.
- Need for national guidance regarding proactive care of infants born at 22–23 weeks' gestation
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):53-61. Published online November 13, 2024
-

With advancements in neonatal intensive care, the limit of viability has shifted to 22–23 weeks' gestation, whose survival rates vary across countries and institutions. These rates are not static and can be improved through the proactive and centralized care guided by national protocols, including maternal transfer to high-activity regions with better neonatal intensive care practices before delivery.
- Strategies to support language development in neonatal intensive care unit: a narrative review
- Ju Sun Heo, Ee-Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):651-663. Published online November 6, 2024
-
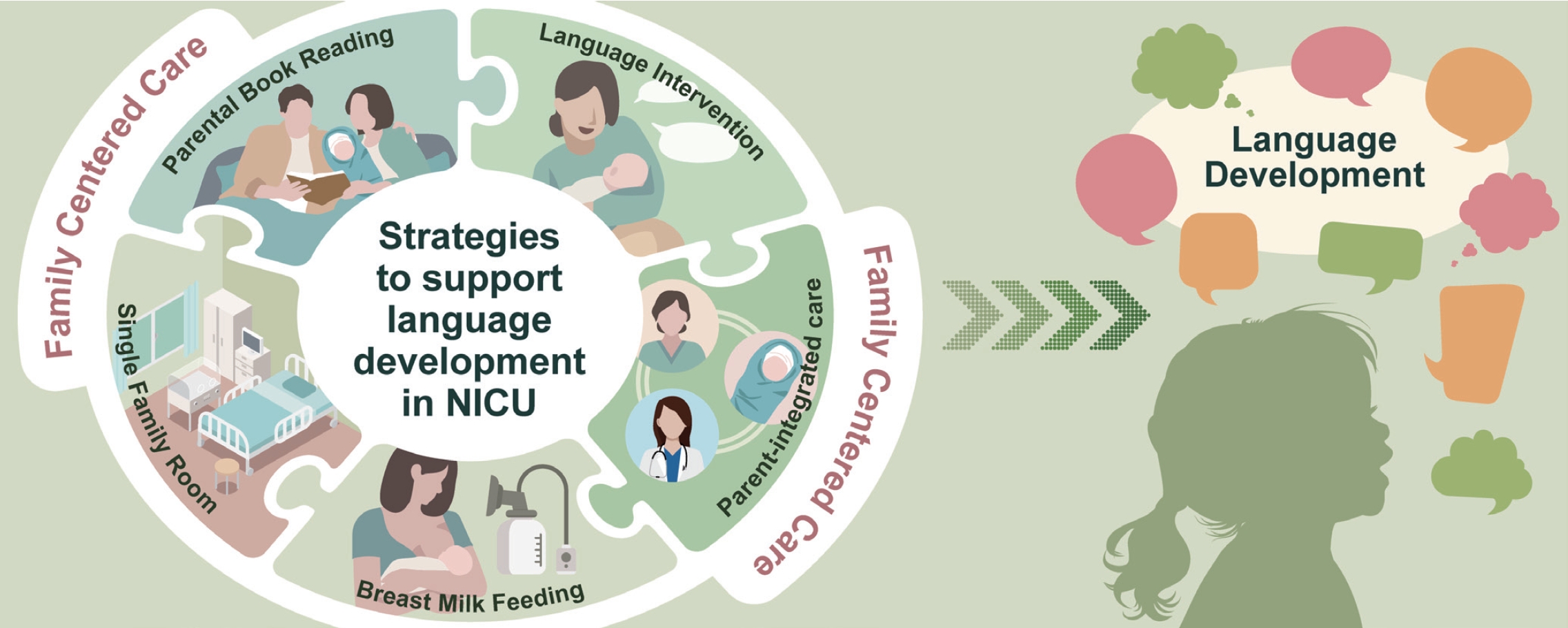
· Preterm infants often experience speech and language development delays during early childhood, impacting children's ultimate outcomes.
· Promoting breastfeeding, increasing parent-infant interactions in a single-family room, promoting a nurturing language environment by parental book reading and language interventions, and parent-integrated interventions in the neonatal intensive care unit could potentially enhance children's language development.
· Integrating these strategies through family-centered care is essential.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Kisspeptin and DLK1 levels for monitoring treatment of girls with central precocious puberty
- Witchuwan Onsoi, Nattakarn Numsriskulrat, Suphab Aroonparkmongkol, Vichit Supornsilchai, Khomsak Srilanchakon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):296-302. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Questions: Can the serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 be potential biomarkers for monitoring the treatments for central precocious puberty (CPP)?
Findings: There were no significant differences in the baseline serum kisspeptin and DLK1 levels in CPP girls compared to girls with premature thelarche (PT). After 6 months of GnRH analogue treatment in CPP girls, median serum kisspeptin levels decreased, while median serum DLK1 levels increased compared to baseline.
Meanings: Serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 may serve as novel biomarkers for monitoring the efficacy of treatments for CPP.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Spontaneous movements as prognostic tool of neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants: a narrative review
- Hyun Iee Shin, Myung Woo Park, Woo Hyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):458-464. Published online May 16, 2023
-
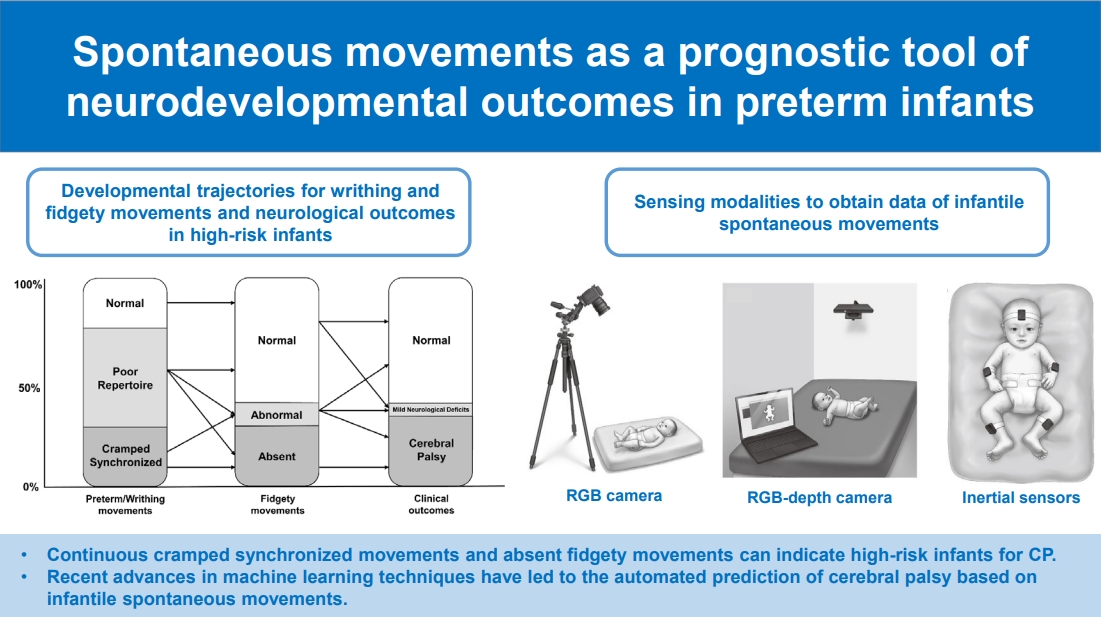
· Spontaneous movements can be useful to evaluate neuronal integrity in preterm infants.
· In General Movements Assessment, continuous cramped synchronized movements and absent fidgety movements can indicate high-risk infants for cerebral palsy.
· Recent advances in machine learning techniques have led to the automated prediction of cerebral palsy based on infantile spontaneous movements.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm infants
- In Gyu Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):281-287. Published online December 30, 2022
-
· Among survivors, 60.9% of infants born at 22 weeks’ gestation had moderate to severe impairments, whereas 50.3% born at 23 weeks’ and 42.2% at 24 weeks’ gestation had moderate to severe impairments.
· Moderate and late preterm infants reportedly have less severe disease than very preterm infants, but they still experience adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes.
· The careful follow-up and early detection of developmental problems in these patients are required.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Neonatal hypertension: concerns within and beyond the neonatal intensive care unit
- Kathleen Altemose, Janis M. Dionne
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):367-376. Published online May 30, 2022
-
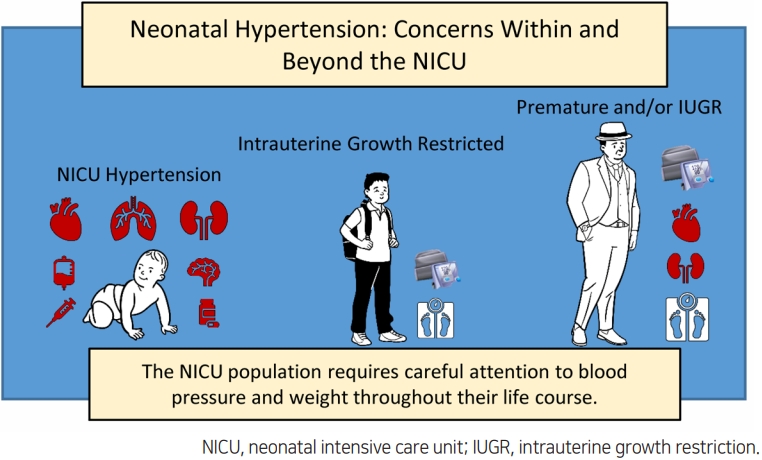
Some neonates, especially those who are premature, may experience hypertension while in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). The most common causes are prematurity-related and the hypertension usually resolves over the first 1–2 years of life. Unfortunately, the increasing population of NICU graduates is at risk for later cardiovascular and kidney disease in childhood and adulthood. This population requires careful attention to blood pressure and weight throughout their life course.
- Original Article
- Other
- Risk factors and screening timing for developmental dysplasia of the hip in preterm infants
- Ga Won Jeon, Hye Jung Choo, Yong Uk Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):262-268. Published online November 5, 2021
-

Question: When is the best screening timing and what is the risk factor for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) in preterm infants?
Finding: Ultrasonography performed earlier than 38 weeks of postmenstrual age caused unnecessary subsequent ultrasonography. DDH did not occur predominantly on the left side or in breech infants.
Meaning: The screening timing, etiology, and risk factors for DDH in preterm infants are somewhat different from those in term infants.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Pathophysiology, classification, and complications of common asymptomatic thrombocytosis in newborn infants
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):182-187. Published online October 18, 2021
-
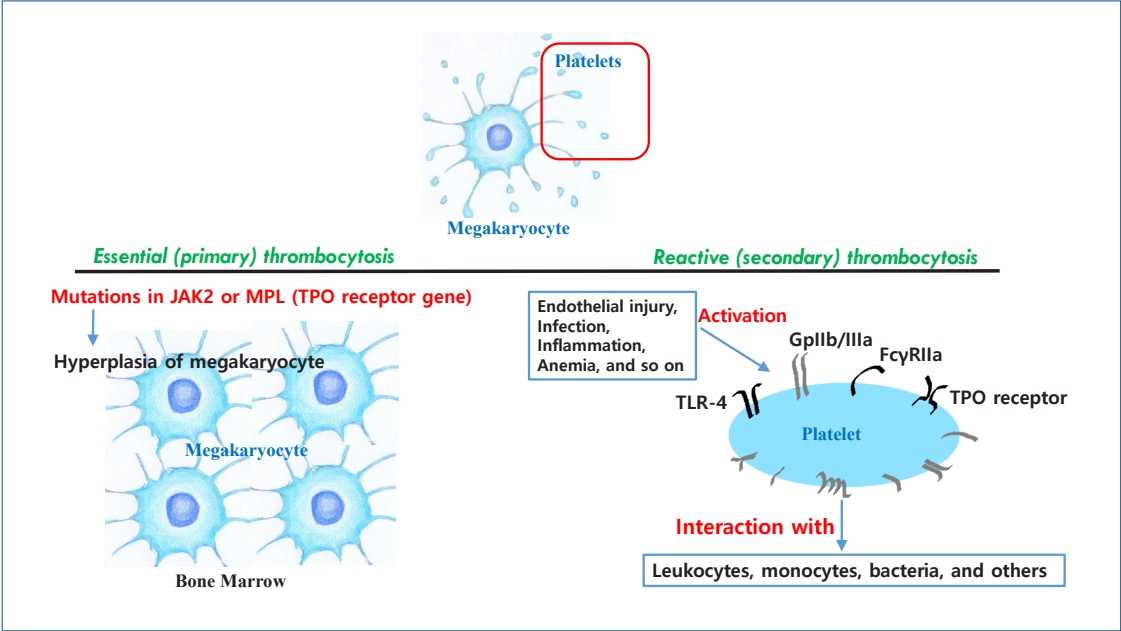
· Thrombocytosis, common in newborns and infants (<2 years) (3%–13%), is caused by elevated thrombopoietin (TPO) concentrations.
· Serum TPO levels are significantly higher immediately to 1 month postnatal and decrease with age.
· Platelet counts are positively correlated with gestational age at birth and postnatal age.
· Thrombocytosis is more common in preterm than in term infants.
· Thrombocytosis in newborns is reactive and resolves spontaneously without complications.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- New modified version of the Risk Adjustment for Congenital Heart Surgery category and mortality in premature infants with critical congenital heart disease
- Young Mi Yoon, Seong Phil Bae, Yoon-Joo Kim, Jae Gun Kwak, Woong-Han Kim, Mi Kyoung Song, Seung Han Shin, Ee-Kyung Kim, Han-Suk Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):395-401. Published online July 15, 2020
-
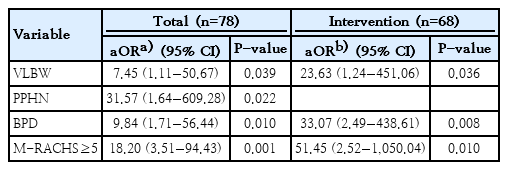
Questions: This study aimed to describe the survival of premature infants with critical congenital heart disease (CHD) and to identify the risk factors including the new modified version of the Risk Adjustment for Congenital Heart Surgery (M-RACHS) associated with mortality.
Finding: For premature infants with critical CHD, survival rate was 76.9% and very low birth weight (VLBW), persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN), bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), and M-RACHS 5 or more were associated with in-hospital mortality.
Meaning: VLBW, PPHN and BPD, as well as M-RACHS≥5, were risk factors for mortality among premature infants with critical CHD.
- Effect of red blood cell transfusion on short-term outcomes in very low birth weight infants
- Eui Young Lee, Sung Shin Kim, Ga Young Park, Sun Hyang Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(2):56-62. Published online February 6, 2020
-
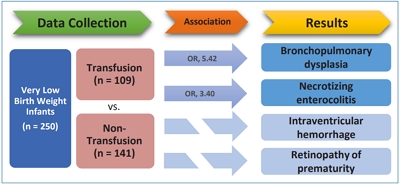
Question: Does RBC transfusion affect the short-term outcomes of VLBW infants?
Finding: The results showed that RBC transfusion was significantly related to the incidence of BPD (OR, 5.42; P<0.001) and NEC (OR, 3.40; P=0.009).
Meaning: Careful consideration of the patient’s clinical condition and appropriate guidelines is required before administering RBC transfusions.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Short- and long-term outcomes of very low birth weight infants in Korea: Korean Neonatal Network update in 2019
- Jang Hoon Lee, YoungAh Youn, Yun Sil Chang; Korean Neonatal Network
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):284-290. Published online February 5, 2020
-

The Korean Neonatal Network (KNN) has collected population-based data for very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs) born in Korea since 2013. The survival rate of all VLBWIs was 86% in Korea. The overall prevalence of cerebral palsy was 6.2%–6.6%. Bilateral blindness and hearing loss were reported in 0.2%–0.3%, 0.8%–1.9%, respectively. The KNN has published annual reports and papers for facilitating the improvement of VLBWIs outcome in Korea.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Clinical impact of admission hypothermia in very low birth weight infants: results from Korean Neonatal Network
- Na Hyun Lee, Soo Kyung Nam, Juyoung Lee, Yong Hoon Jun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):386-394. Published online May 22, 2019
-
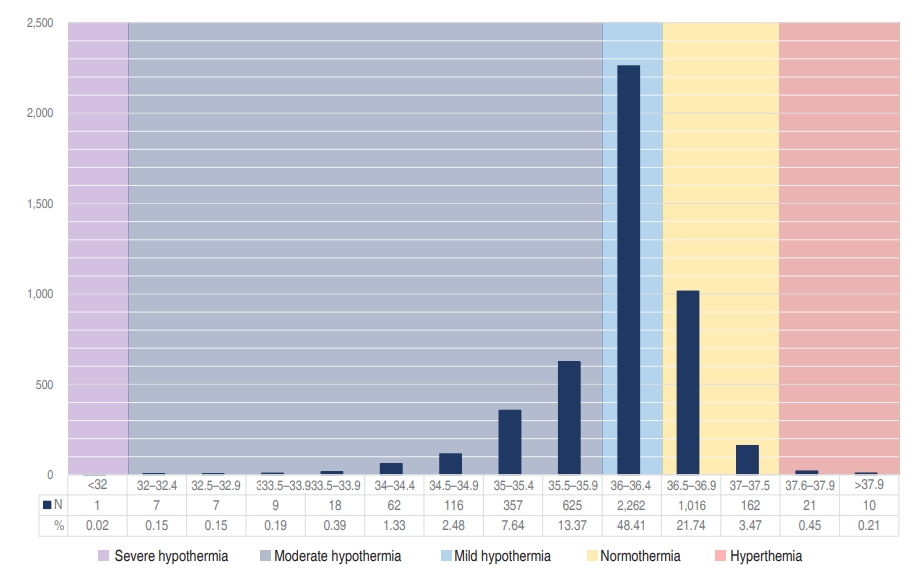
Background: Preterm infants have difficulty maintaining body temperature after birth. However, clinical guidelines advocate that neonatal body temperature should be maintained at 36.5°C–37.5°C.
Purpose: We aimed to investigate the incidence of admission hypothermia in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants and to determine the association of admission temperature with in-hospital mortality and morbidities. Methods: A cohort study using prospectively collected data involving...
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: how can we improve its outcomes?
- Tae-Jung Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):367-373. Published online May 17, 2019
-
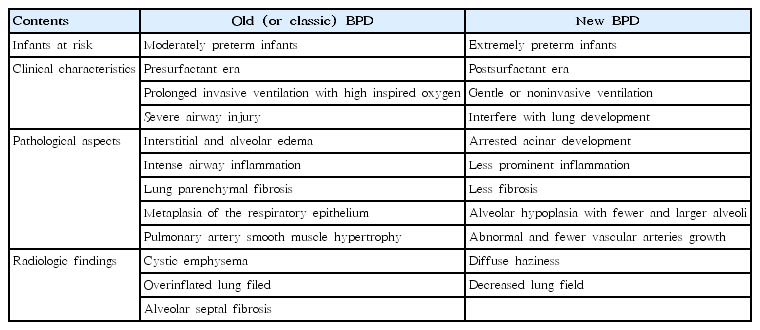
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is a chronic lung disease of preterm infants with multiple factors affected from prenatal to postnatal periods. Despite significant advances in neonatal care over almost 50 years, BPD rates have not decreased; in fact, they may have even increased. Since more preterm infants, even at periviable gestational age, survive today, different stages of lung development affect the...
- Practice for preterm patent ductus arteriosus; focusing on the hemodynamic significance and the impact on the neonatal outcomes
- Jin A Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(7):245-251. Published online April 8, 2019
-
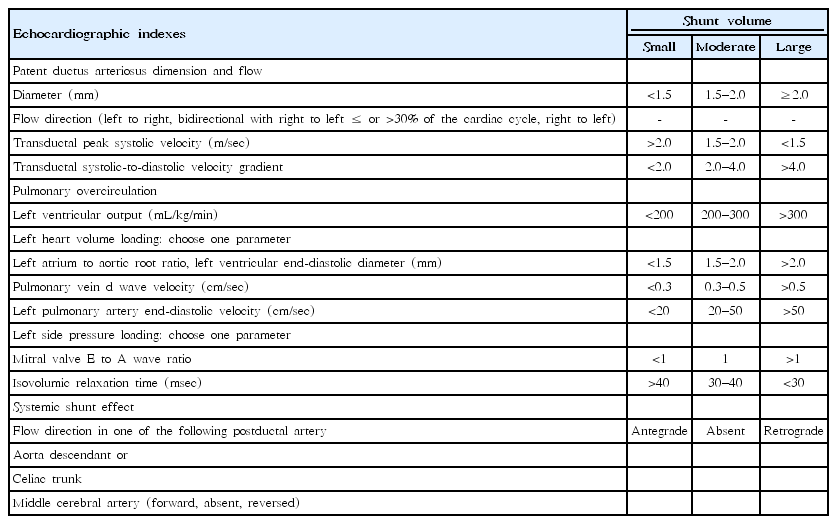
Hemodynamically significant preterm patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) affects mortality; comorbidities such as necrotizing enterocolitis, intraventricular hemorrhage, and bronchopulmonary dysplasia; and adverse long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants, particularly in very low birth weight infants. However, recent studies have indicated that there is no consensus on the causal relationship between PDA and neonatal outcomes, the benefit of PDA treatment, the factors...
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Evaluation of prolonged pain in preterm infants with pneumothorax using heart rate variability analysis and EDIN (Échelle Douleur Inconfort Nouveau-Né, neonatal pain and discomfort scale) scores
- Mehmet Buyuktiryaki, Nurdan Uras, Nilufer Okur, Mehmet Yekta Oncel, Gulsum Kadioglu Simsek, Sehribanu Ozluer Isik, Serife Suna Oguz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(10):322-326. Published online September 16, 2018
-
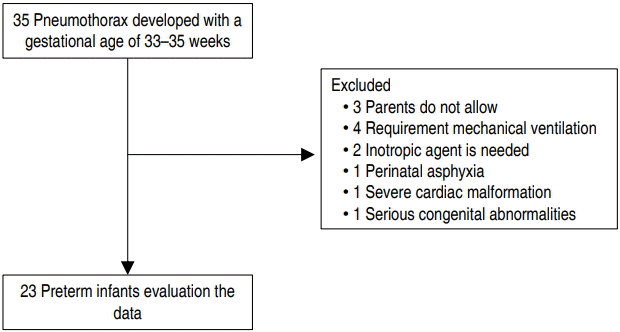
Purpose: The EDIN scale (Échelle Douleur Inconfort Nouveau-Né, neonatal pain and discomfort scale) and heart rate variability has been used for the evaluation of prolonged pain. The aim of our study was to assess the value of the newborn infant parasympathetic evaluation (NIPE) index and EDIN scale for the evaluation of prolonged pain in preterm infants with chest tube placement...
- Transient intubation for surfactant administration in the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome in extremely premature infants
- Ji Won Koh, Jong-Wan Kim, Young Pyo Chang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(10):315-321. Published online September 16, 2018
-
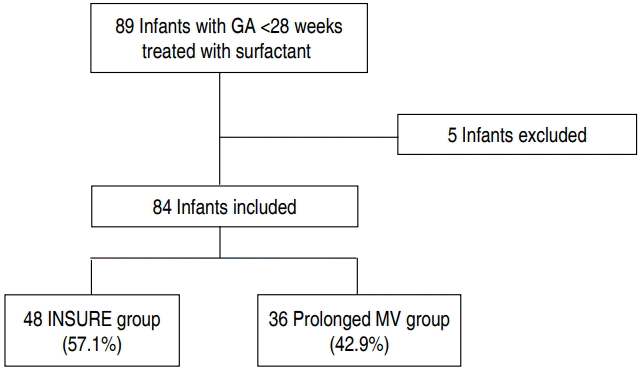
Purpose: To investigate the effectiveness of transient intubation for surfactant administration and extubated to nasal continuous positive pressure (INSURE) for treatment of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and to identify the factors associated with INSURE failure in extremely premature infants. Methods: Eighty-four infants with gestational age less than 28 weeks treated with surfactant administration for RDS for 8 years were included. Perinatal...
- Postdischarge growth assessment in very low birth weight infants
- Joon-Sik Park, Jungho Han, Jeong Eun Shin, Soon Min Lee, Ho Seon Eun, Min-Soo Park, Kook-In Park, Ran Namgung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):64-69. Published online March 27, 2017
-
Purpose The goal of nutritional support for very-low-birth-weight (VLBW) infants from birth to term is to match the
in utero growth rates; however, this is rarely achieved.Methods We evaluated postdischarge growth patterns and growth failure in 81 Korean VLBW infants through a retrospective study. Weight and height were measured and calculated based on age percentile distribution every 3 months until age 24...
- The influencing factors on procalcitonin values in newborns with noninfectious conditions during the first week of life
- Jueseong Lee, Yong Hyeon Bang, Eun Hee Lee, Byung Min Choi, Young Sook Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(1):10-16. Published online January 16, 2017
-

Purpose Although procalcitonin (PCT) level is useful for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis, PCT reliability is inconsistent because of the varied conditions encountered in neonatal intensive care units. This study aimed to investigate PCT levels and factors influencing increased PCT levelin newborns without bacterial infection during the first week of life.
Methods In newborns hospitalized between March 2013 and October 2015, PCT levels...
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Enteral nutrition for optimal growth in preterm infants
- Myo-Jing Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(12):466-470. Published online December 31, 2016
-
Early, aggressive nutrition is an important contributing factor of long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes. To ensure optimal growth in premature infants, adequate protein intake and optimal protein/energy ratio should be emphasized rather than the overall energy intake. Minimal enteral nutrition should be initiated as soon as possible in the first days of life, and feeding advancement should be individualized according to the...
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Correlation of B-type natriuretic peptide levels and echocardiographic parameters in preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus
- Hyun Ah Jeong, Jeonghee Shin, Eunji Kim, Eun Hee Lee, Byung Min Choi, Chang Sung Son, Joo Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(4):183-189. Published online April 30, 2016
-
Purpose This study aimed to evaluate the correlation, according to postnatal age, between plasma B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels and echocardiographic parameters for the assessment of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) in preterm infants with respiratory distress.
Methods We enrolled 42 preterm infants with respiratory distress who underwent serial echocardiographic evaluation with simultaneous plasma BNP measurements until ductal closure. The correlations between BNP levels...
- Severe vitamin D deficiency in preterm infants: maternal and neonatal clinical features
- Sook-Hyun Park, Gi-Min Lee, Jung-Eun Moon, Heng-Mi Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(11):427-433. Published online November 22, 2015
-
Purpose We investigated the vitamin D status of preterm infants to determine the incidence of vitamin D deficiency.
Methods A total of 278 preterm infants delivered at Kyungpook National University Hospital between January 2013 and May 2015 were enrolled. The serum concentrations of calcium, phosphorous, alkaline phosphatase, and 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-OHD) were measured at birth. We collected maternal and neonatal data such as...
- Low levels of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 at birth may be associated with subsequent development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants
- Choae Lee, Jaewoo An, Ji Hee Kim, Eun Sun Kim, Soo Hyun Kim, Yeon Kyung Cho, Dong Hyun Cha, Man Yong Han, Kyu Hyung Lee, Youn Ho Sheen
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(11):415-420. Published online November 22, 2015
-
Purpose Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is characterized by inflammation with proteolytic damage to the lung extracellular matrix. The results from previous studies are inconsistent regarding the role of proteinases and antiproteinases in the development of BPD. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-8, MMP-9, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-2, and TIMP-1 levels in the serum of...
- The efficacy and safety of Montelukast sodium in the prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Sang Bum Kim, Jang Hoon Lee, Juyoung Lee, Seung Han Shin, Ho Sun Eun, Soon Min Lee, Jin A Sohn, Han Suk Kim, Byung Min Choi, Min Soo Park, Kook In Park, Ran Namgung, Moon Sung Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(9):347-353. Published online September 21, 2015
-
Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Montelukast sodium in the prevention of bronchopulmonarydysplasia (BPD).
Methods The Interventional study was designed as a multicenter, prospective, and randomized trial, with open labeled and parallel-experimental groups, 66 infants were enrolled and allocated to either the case group (n=30) or the control group (n=36) based on gestational age (GA)....
- Comparison of gastric and other bowel perforations in preterm infants: a review of 20 years' experience in a single institution
- Do Kyung Lee, So Yeon Shim, Su Jin Cho, Eun Ae Park, Sun Wha Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(8):288-293. Published online August 21, 2015
-
Purpose In this study, we aimed to review the clinical presentation of preterm infants with gastrointestinal perforations and compare the clinical features of gastric perforation with other intestinal perforations.
Methods The medical records of preterm neonates with pneumoperitoneum, admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) between January 1994 and December 2013, were retrospectively reviewed.
Results Twenty-one preterm infants underwent exploratory laparotomy to investigate the...
- Thyroid dysfunction in very low birth weight preterm infants
- Ji Hoon Lee, Sung Woo Kim, Ga Won Jeon, Jong Beom Sin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(6):224-229. Published online June 22, 2015
-
Purpose Thyroid dysfunction is common in preterm infants. Congenital hypothyroidism causes neurodevelopmental impairment, which is preventable if properly treated. This study was conducted to describe the characteristics of thyroid dysfunction in very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs), evaluate risk factors of hypothyroidism, and suggest the reassessment of thyroid function with an initially normal thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) as part of a newborn...
- Review Article
- Nutritional strategy of early amino acid administration in very low birth weight infants
- Byong Sop Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(3):77-83. Published online March 20, 2015
-
Relative to a fetus of the same gestational age, very low birth weight (VLBW) infants are more likely to be underfed and to undergo growth restriction during their early hospital stay. The current trend towards "early and aggressive" nutritional strategies in VLBW infants aims to overcome the early nutritional deficiency and thereby boost postnatal catch-up growth, simultaneously improving long-term neurodevelopmental...
- Original Article
- Postnatal weight gain in the first two weeks as a predicting factor of severe retinopathy of prematurity requiring treatment
- Jongmoon Kim, Jang Yong Jin, Sung Shin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(2):52-59. Published online February 28, 2015
-
Purpose This study aimed to investigate the relative weight gain at 2-week intervals up to 6 weeks after birth to predict retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) requiring treatment among very low birth weight infants.
Methods A total of 211 preterm infants with birth weights <1,500 g and gestational age <32 weeks were retrospectively reviewed. The main outcome was the development of ROP requiring treatment....
- Review Article
- Necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns: update in pathophysiology and newly emerging therapeutic strategies
- Young Youn Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(12):505-513. Published online December 31, 2014
-
While the survival of extremely premature infants with respiratory distress syndrome has increased due to advanced respiratory care in recent years, necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) remains the leading cause of neonatal mortality and morbidity. NEC is more prevalent in lower gestational age and lower birth weight groups. It is characterized by various degrees of mucosal or transmural necrosis of the intestine....
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











