Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Infection
- Construction and validation of predictive models for intravenous immunoglobulin–resistant Kawasaki disease using an interpretable machine learning approach
- Linfan Deng, Jian Zhao, Ting Wang, Bin Liu, Jun Jiang, Peng Jia, Dong Liu, Gang Li
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):405-414. Published online July 23, 2024
-

Question: Is there a reliable model to predict intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)-resistant Kawasaki disease (KD)?
Finding: We constructed 5 machine learning models to predict IVIG-resistant KD. Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) model was superior to logistic, support vector machine, light gradient boosting machine and multiple layers perception models. The SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) value interpreted the contribution of each feature in XGBoost model.
Meaning: XGBoost model showed the excellent performance to predict IVIG-resistant KD with explainable and visualizable machine learning algorithm.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Natural course of IgE-mediated food allergy in children
- Kyunguk Jeong, Sooyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):504-511. Published online June 14, 2023
-
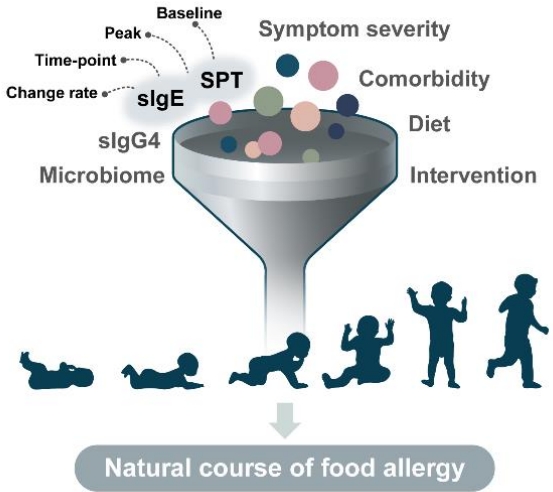
· Dendritic, regulatory T, and regulatory B cells significantly contribute to the natural course of food allergy.
· Cow’s milk and hen’s egg allergies tend to resolve in earlier childhood but recent studies show that 50% of patients still persist into school age.
· The potential factors affecting the natural course of food allergy are age at diagnosis, symptom severity, sensitization status and its change rate, and external factors such as diet and interventions.
· There is a considerable possibility of food allergy outgrow if specific IgE levels are 2–5 kUA/L or less, but other factors such as age and recent symptoms should be considered together.
· With a clear understanding of the natural course of food allergy, pediatricians can provide appropriate assessment and interventions to our patients, and consequently can help patients overcome their food allergy and improve the social safety net.
- Immunology
- Immunopathogenesis of COVID-19 and early immunomodulators
- Kyung-Yil Lee, Jung-Woo Rhim, Jin-Han Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):239-250. Published online June 18, 2020
-

The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading globally. Although its etiologic agent is discovered as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), there are many unsolved issues in COVID-19 and other infectious diseases. The causes of different clinical phenotypes and incubation periods among individuals, species specificity, and cytokine storm with lymphopenia as well as the mechanism of damage to organ...
- Predictors and management of intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease
- Min Seob Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(4):119-123. Published online March 15, 2019
-

Kawasaki disease (KD) is a systemic vasculitis that mainly affects younger children. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) resistant cases are at increasing risk for coronary artery complications. The strategy on prediction of potential nonresponders and treatment of IVIG-resistant patients is now controversial. In this review the definition and predictors of IVIG-resistant KD and current evidence to guide management are discussed.
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Association of Toll-like receptor 2-positive monocytes with coronary artery lesions and treatment nonresponse in Kawasaki disease
- Soo Jung Kang, Nam Su Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(7):208-215. Published online July 31, 2017
-
Purpose Activation of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) present on circulating monocytes in patients with Kawasaki disease (KD) can lead to the production of proinflammatory cytokines and interleukin-10 (IL-10). We aimed to determine the association of the frequency of circulating TLR2+/CD14+ monocytes (FTLR2%) with the outcomes of KD, as well as to compare FTLR2% to the usefulness of sIL-10.
Methods The FTLR2% in patients...
- Predictive factors of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin and coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease
- Hye Young Lee, Min Seob Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(12):477-482. Published online December 31, 2016
-
Purpose We conducted a study to determine which factors may be useful as predictive markers in identifying Kawasaki disease (KD) patients with a high risk of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and developing coronary artery lesions (CAL).
Methods We enrolled 287 patients in acute phase of KD at a single center. The demographic, clinical and laboratory data were collected retrospectively.
Results There were 34 patients...
- Prediction of unresponsiveness to second intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease refractory to initial treatment
- Euri Seo, Jeong Jin Yu, Hyun Ok Jun, Eun Jung Shin, Jae Suk Baek, Young-Hwue Kim, Jae-Kon Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(10):408-413. Published online October 17, 2016
-
Purpose This study investigated predictors of unresponsiveness to second-line intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment for Kawasaki disease (KD).
Methods This was a single-center analysis of the medical records of 588 patients with KD who had been admitted to Asan Medical Center between 2006 and 2014. Related clinical and laboratory data were analyzed by univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses.
Results Eighty (13.6%) of the 588 patients...
- Prediction of nonresponsiveness to medium-dose intravenous immunoglobulin (1 g/kg) treatment: an effective and safe schedule of acute treatment for Kawasaki disease
- Kyung Pil Moon, Beom Joon Kim, Kyu Jin Lee, Jin Hee Oh, Ji Whan Han, Kyung Yil Lee, Soon Ju Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(4):178-182. Published online April 30, 2016
-
Purpose Medium-dose (1 g/kg) intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is effective in the majority of patients with Kawasaki disease (KD) but some patients who do not respond to medium-dose IVIG are at high risk for the development of coronary artery lesions (CALs). The purpose of this study was to identify the clinical predictors associated with unresponsiveness to medium-dose IVIG and the development of...
- Meta-analysis of factors predicting resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease
- Jin-Young Baek, Min Seob Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(2):80-90. Published online February 29, 2016
-
Purpose Studies have been conducted to identify predictive factors of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) for Kawasaki disease (KD). However, the results are conflicting. This study aimed to identify laboratory factors predictive of resistance to high-dose IVIG for KD by performing meta-analysis of available studies using statistical techniques.
Methods All relevant scientific publications from 2006 to 2014 were identified through PubMed searches. For...
- Comparison between Kawasaki disease with lymph-node-first presentation and Kawasaki disease without cervical lymphadenopathy
- Jung Ok Kim, Yeo Hyang Kim, Myung Chul Hyun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(2):54-58. Published online February 29, 2016
-
Purpose We evaluated the characteristics of patients with Kawasaki disease (KD) who presented with only fever and cervical lymphadenopathy on admission, and compared them with the characteristics of those who presented with typical features but no cervical lymphadenopathy.
Methods We enrolled 98 patients diagnosed with KD. Thirteen patients had only fever and cervical lymphadenopathy on the day of admission (group 1), 31 had...
- Vitamin D serum levels in children with allergic and vasomotor rhinitis
- Seung Jin Lee, Bong Hwa Kang, Bong Seok Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(9):325-329. Published online September 21, 2015
-
Purpose In addition to regulating calcium and phosphorus homeostasis and bone metabolism, vitamin D is known as an immune modulator. Recently, there has been increased worldwide interest in the association between low levels of vitamin D and allergic diseases. The purpose of this study was to assess the relationship between serum vitamin D levels and allergic/vasomotor rhinitis (AR/VR) in children.
Methods This study...
- House dust mite-specific immunoglobulin E and longitudinal exhaled nitric oxide measurements in children with atopic asthma
- Youn Kyung Lee, Sohyoung Yang, Joohyun Park, Heon Kim, Youn-Soo Hahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(3):89-95. Published online March 20, 2015
-
Purpose House dust mite (HDM) has been suggested to be the most important aeroallergen responsible for atopic asthma in Korea. We aimed to investigate that specific IgE antibodies to HDM and other common indoor aeroallergens contribute differently to total serum IgE and show different relationships with longitudinal fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) measurements in Korean atopic asthmatic patients.
Methods A total of 193...
- Outbreaks of mumps: an observational study over two decades in a single hospital in Korea
- Ji-Ung Ryu, Eun-Kyung Kim, You-Sook Youn, Jung-Woo Rhim, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(9):396-402. Published online September 30, 2014
-
Purpose The introduction of the mumps vaccine has dramatically reduced the number of mumps cases, but outbreaks have recently occurred among highly vaccinated populations in developed countries. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of patients with mumps admitted between 1989 and 2012 in a single hospital in Korea are described in the present study.
Methods We retrospectively evaluated inpatients with mumps between 1989 and 2012...
- Case Report
- Use of intravenous immunoglobulin in a disseminated varicella infection in an immunocompromised child
- Jae Hong Kim, Dae Hyun Kwon, E Young Bae, Seung Beom Han, Jae Wook Lee, Nack Gyun Chung, Dae Chul Jeong, Bin Cho, Jin Han Kang, Hack Ki Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(8):370-373. Published online August 25, 2014
-
Varicella-zoster virus infection can lead to severe illness in immunocompromised patients. Further the mortality rate of disseminated varicella infection is extremely high particularly in immunocompromised children. We report a case of disseminated varicella infection in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who was receiving chemotherapy, but was initially admitted with only for acute abdominal pain. The patient rapidly developed severe...
- Pulmonary hemorrhage in pediatric lupus anticoagulant hypoprothrombinemia syndrome
- Ji Soo Kim, Min Jae Kim, E Young Bae, Dae Chul Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(4):202-205. Published online April 30, 2014
-
Lupus anticoagulant-hypoprothrombinemia syndrome (LAHPS), a very rare disease that is caused by the presence of antifactor II antibodies, is usually counterbalanced by the prothrombotic effect of lupus anticoagulant (LAC). Patients with LAHPS are treated using fresh frozen plasma, steroids, immunosuppressive agents, and immunoglobulins for managing the disease and controlling hemorrhages. Notably, steroids are the important treatment for treating hypoprothrombinemia and...
- Original Article
- Predictors of nonresponse to intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in Kawasaki disease
- Hyo Min Park, Dong Won Lee, Myung Chul Hyun, Sang Bum Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(2):75-79. Published online February 25, 2013
-
Purpose It has been reported that 10% to 20% of children with Kawasaki disease (KD) will not respond to intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment. In this study, we aimed to identify useful predictors of therapeutic failure in children with KD.
Methods We examined 309 children diagnosed with KD at the Kyungpook National University Hospital and the Inje University Busan Paik Hospital between January 2005...
- The characteristic laboratory findings of non-responsiveness to intravenous immunoglobulin in children with Kawasaki disease
- Han Gil Cho, Young Kuk Cho, Jae Sook Ma
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(2):228-234. Published online February 15, 2010
-
Purpose : Although intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment is an effective first-line treatment for Kawasaki disease, 10-20% of the patients develop persistent fever or coronary artery complications. Medical records of Kawasaki disease patients were reviewed to assess the characteristic laboratory findings of IVIG nonresponsiveness. Methods : We reviewed the clinical records of 118 children with Kawasaki disease who were treated at... -
- Case Report
- Change of neutrophil count after treatment of intravenous immunoglobulin in children with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Jun Young Park, Ji Ae Park, Seong Shik Park, Young Tak Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(2):204-208. Published online February 15, 2008
-
Purpose : The aim of this study was to investigate the incidence and course of neutropenia following intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapy in children with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP). Methods : From January 2001 to June 2006, fifty-four patients with ITP were enrolled in this study. Forty-two of 54 patients were treated with IVIG, while the other 12 were treated with... -
- Original Article
- Change of absolute neutrophil count after intravenous immunoglobulin administration for the children with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Hyun Jung Shin, In Kug Bang, Byung Kyu Choe, Jin-Bok Hwang, Jun Sik Kim, Heung Sik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(10):982-986. Published online October 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is effective for the treatment of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) in children. Recently, several reports have been published that show its impact on the absolute neutrophil count. The present study was performed to confirm these findings. Methods : Data on 26 ITP patients were analyzed. Patients with febrile illness or increased C-reactive protein levels... -
- The effects of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin on plasma protein and lipid levels in the patients with Kawasaki disease
- Keun Young Lee, Dong-Un Kim, Hyun Seung Lee, Pil Sang Jang, Young-Hoon Kim, Jin Tack Kim, Hyun Hee Kim, Kyung-Yil Lee, Joon-Sung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(12):1348-1353. Published online December 15, 2006
-
Purpose : The reticuloendothelial system is composed of sinusoidal capillaries, through which even large protein molecules are freely movable between plasma and interstitial space, including the lymphatic system. Therefore, high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) would cause a redistribution of proteins between two compartments. To investigate this hypothesis, we measured plasma protein and lipid levels in patients with Kawasaki disease before and... -
- Analysis of cow's milk specific IgE positive patients in newborns
- Gil Sang Lee, Nam Kyung Baek, Won Duck Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(10):1061-1066. Published online October 15, 2006
-
Purpose : The purpose of this study was to research whether measurement of cow's milk specific IgE on the newborn would be helpful in the diagnosis of cow's milk allergy. We tried to find out the relation between cow's milk specific IgE and other allergy diseases by following up cases. Methods : We reviewed clinical features of 87 episodes in infants... -
- Case Report
- Steroid and enalapril therapy - possible cause of toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Dong Wook Kim, Da Eun Jung, Ja Wook Koo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(3):332-336. Published online March 15, 2006
-
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) is a rare, acute and life-threatening cutaneous drug reaction. TEN is characterized by the sudden onset of extensive necrosis in the epidermis and frequent mucous membrane involvement. The pathogenesis has not yet been elucidated. In addition, no particular treatment for TEN has been established. We report a case of TEN in a 14-year-old-boy, which might have... -
- Original Article
- The alteration of the positive rate of cytomegalovirus IgG antibody among preschool period children
- Se-Young Seo, Sang-Jun Park, Ja-Young Hwang, Seong-Hoon Hahn, So-Young Kim, Hyun-Hee Kim, Wonbae Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(1):51-55. Published online January 15, 2006
-
Purpose : In order to evaluate the time of disappearance of cytomegalovirus(CMV) IgG antibodies from mothers, and the alteration of the positive rate of CMV IgG antibodies among preschool period children, we investigated the positive rate of CMV antibodies among preschool children. Methods : We studied 391 children who visited the Department of Pediatrics from March, 2001 to February, 2004. We... -
- Therapeutic Effect of Anti-Rotavirus Chicken Egg Yolk Immunoglobulin(IgY) on Diarrhea by Infection of Rotavirus
- In Seok Lim, Ho Seok Lee, Wonyong Kim, Eung Sang Choi, Dong Hyuk Jung, Hoo Kil Jung, Sung Seob Yun, Ho Nam Chun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(12):1354-1361. Published online December 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Rotavirus is an enteric pathogen that affects millions of children globally each year. But no specific therapy is available for the management of rotavirus diarrhea. Due to the clear need to define improved modality for treatment of rotavirus diarrhea, we evaluated the efficacy of anti- rotavirus IgY in the treatment of infants and children with gastroenteritis. Methods : First,... -
- The Effectiveness of Intravenous Immunoglobulin for Clinically Suspected Neonatal Sepsis
- Hyun Jung Na, Ji Young Kim, Gyeong Hoon Lee, Jun Hwa Lee, Eun Jin Choi, Jin Kyung Kim, Hai Lee Chung, Woo Taek Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(11):1187-1192. Published online November 15, 2005
-
Purpose : The purpose of this study is to determine the effectiveness of intravenous immunoglobuin (IVIG) administration in fullterm neonates having clinically suspected neonatal sepsis. Methods : Forty full-term neonates admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit with clinically suspected neonatal sepsis, who had at least two positive diagnostic criteria were enrolled. Twenty neonates were enrolled into the IVIG arm and... -
- Inhibition of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-induced Endothelial Cell Differentiation by Intravenous Immunoglobulin and Methylprednisolone
- Hyoun Ah Choi, Kyung Hwa Ha, Jong Seo Yoon, Yoon Lee, Joon Sung Lee, Ji Whan Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(8):886-893. Published online August 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Kawasaki disease is the most common cause of systemic vasculitis in children less than 5 years of age. Recent immunohistochemistry findings suggest that many vascular growth factors play a role in the formation of the coronary artery lesions. Active remodeling of the coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease continues in the form of intimal proliferation and neoangiogenesis for... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Systemic Castleman's Disease in a Child and Successful Treatment with Oral Prednisolone
- So Eun Koo, Mee Jeong Lee, Jeong Eun Kim, Joo Ryung Huh, Thad Ghim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(4):443-447. Published online April 15, 2005
-
Castleman's disease is a rare non-neoplastic lymphoproliferative disorder of unknown etiology. It is divided into three histologic subtypes; hyaline-vascular(HV), plasma cell(PC) type and mixed type (HV-PC). It has two clinical expressions. The localized form, which presents as a slow growing mass, has a relatively benign clinical course. The multicentric form is multilocated and holds significant morbidity. The mainstay of treatment... -
- Original Article
- Statistical Analysis of 1,000 Cases of Kawasaki Disease Patients Diagnosed at a Single Institute
- Dae Hwan Hwang, Kyoung Mi Sin, Kyong Min Choi, Jae Young Choi, Jun Hee Sul, Dong Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(4):416-424. Published online April 15, 2005
-
Purpose : To find the risk factors associated with coronory artery lesions, non-responsiveness to intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) treatment, and recurrences in Kawasaki disease patients. Methods : We retrospectively analyzed 1,000 Kawasaki disease patients who were admitted to Yonsei University Medical Center from September 1990 to December 2003. We compared between responder and non-responder groups to IVIG treatment as well as between relapsed... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia Complicated with Guillain-Barr Syndrome and Encephalitis
- Soon Bum Lee, Hee Jung, Yong Seok Lee, Bum Sun Kwon, Jeesuk Yu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(12):1338-1348. Published online December 15, 2004
-
The most common pathogen of respiratory tract infection among school-age children and adolescents is Mycoplasma pneumoniae, which causes clinical manifestations of pneumonia, acute asthmatic attack, pharygitis, and tonsilitis. It can also cause extrapulmonary infections that involves skin, the nervous system, the digestive system, the cardiovascular system, and the hematopoietic system. It is reported that the central nervous system symptoms may... -
- Original Article
- The Effects of Intravenous Immunoglobulin(IVIG) and Methylprednisolone on the mRNAs Expressions of VEGF, VCAM-1 and IL-1β of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells(HUVEC) Stimulated by IL-1β
- Soh Yeon Kim, Sun Jeong Lim, Ji Whan Han, Kyung Yil Lee, Joon Sung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(12):1325-1333. Published online December 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Kawasaki disease(KD) manifests a systemic vasculitis of unknown etiology in young children. Vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1(VCAM-1) and interleukin-1 beta(IL-1β) may play important roles in the pathogenesis of KD. Intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) and methylprednisolone(MP) are therapeutically effective for KD, however, the precise mechanisms of the two drugs are still unknown. We investigated the therapeutic efficacy of... -
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











