Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Systematic review of influence of ethnicity on efficacy and safety of pharmacotherapy for childhood and adolescent obesity
- Surendra Gupta, Purushottam Lal, Abhishek Gupta, Brajesh Raj Chaudhary
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(2):84-102. Published online January 26, 2026
-
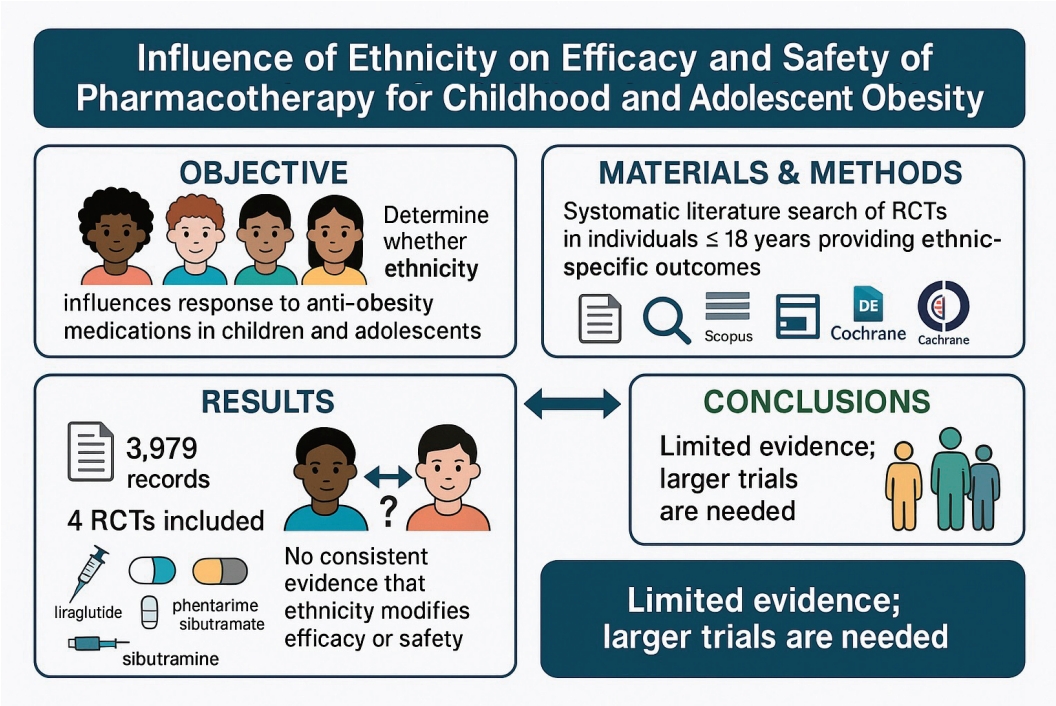
Ethnic variations may influence the response of children and adolescents to obesity pharmacotherapy. Current evidence does not show consistent differences in efficacy or safety among ethnic groups; however, available data are limited. Larger, ethnically diverse trials are needed to develop personalized obesity treatment strategies.
- Original Article
- Improvements in obesity-related measures among Asian patients with severe obesity following a structured lifestyle intervention
- Pei-Shan Chen, Shu-Mei Tsai, Chih-Hsuan Chang, Hui-Ru Yang, Yen-Ju Huang, Hsiang-Yin Liu, Kai-Chi Chang, Huey-Ling Chen
-
Background: The rising prevalence of severe obesity among children and adolescents poses a major public health challenge.
Purpose: In this study, we examined the differences in body composition and physical fitness between obese and severely obese Asian youth and evaluated their responses to a customized lifestyle intervention. Methods: A total of 136 overweight and obese participants (mean age, 11.5±3.0 years) were enrolled... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.01774 [Accepted]
- General Pediatrics
- Associations of routine breakfast and napping habits with early adiposity rebound by age 3 years: a population-based cohort study in Japan
- Toshifumi Yodoshi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(2):163-170. Published online October 22, 2025
-
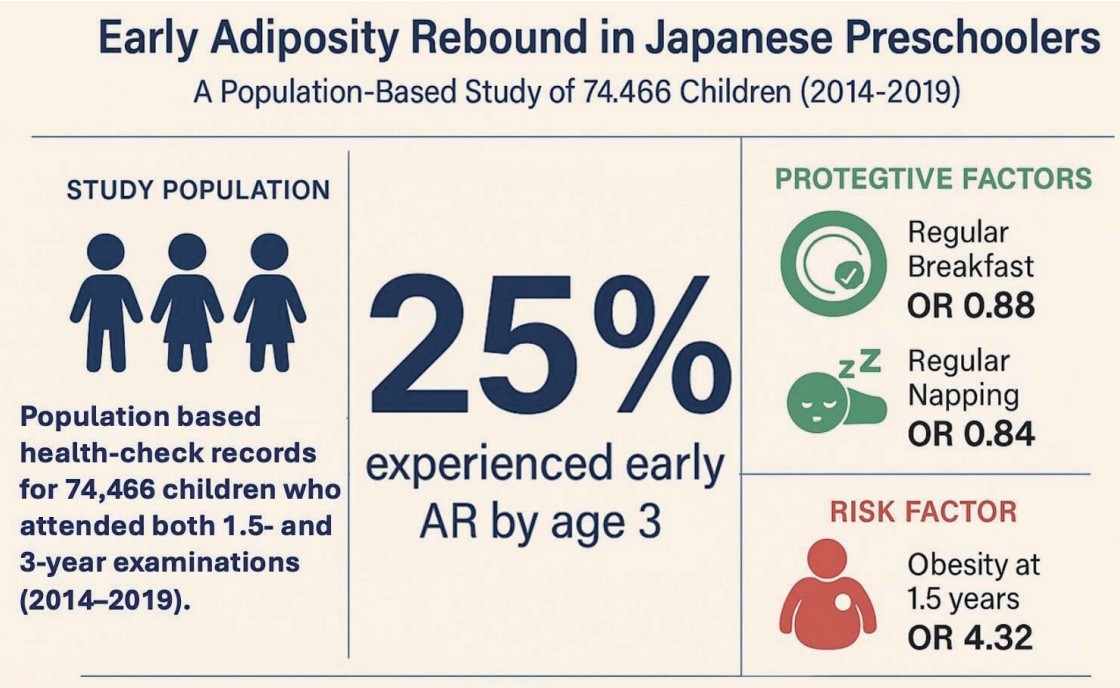
In a population‑based cohort of 74,466 children, 25% experienced early adiposity rebound (AR) by age 3. Daily breakfast and routine napping at 1.5 years were independently associated with lower odds of AR, while obesity at 1.5 years was a strong predictor. These modifiable routines could help delay AR and enable early identification during routine child health checks.
- Nutrition
- Differential effects of dietary and physical activity interventions on adiposity of children with obesity
- Anekchoke Tangtongsoong, Chonnikant Visuthranukul, Yuda Chongpison, Sirinuch Chomtho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):370-378. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: How do dietary intake and physical activity affect body mass index (BMI) z scores and adiposity among children with obesity?
Finding: Higher dietary protein and fiber intakes were significantly associated with a decrease in BMI z scores and adiposity among children with obesity.
Meaning: Optimizing dietary interventions by focusing on protein and fiber intakes could be an effective strategy for managing childhood obesity.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Hidden link between endocrine-disrupting chemicals and pediatric obesity
- Min Won Shin, Shin-Hye Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):199-222. Published online November 28, 2024
-
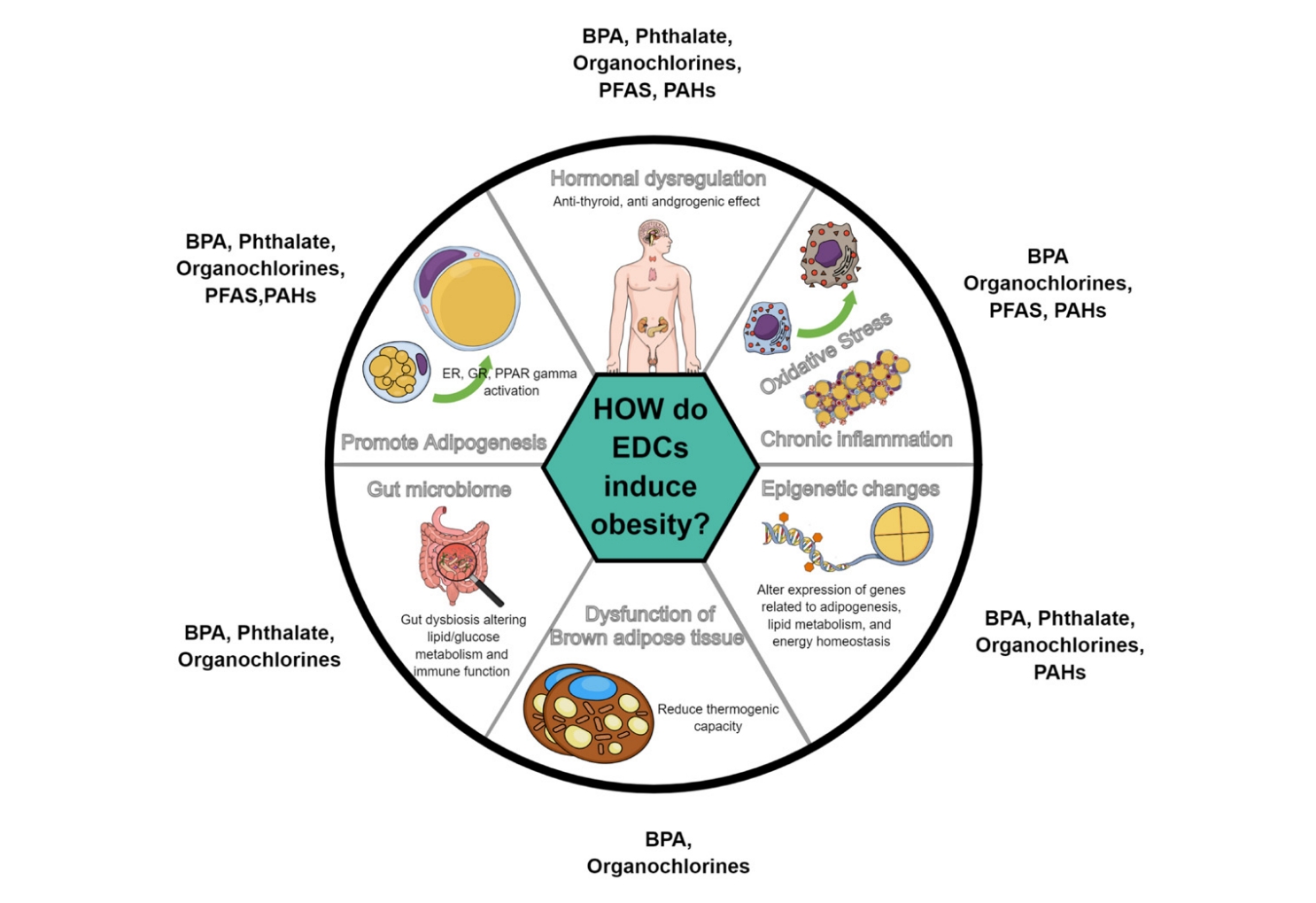
Studies indicate potential connections between exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and childhood obesity. Variations in the impact of EDCs in epidemiological studies may result from differences in exposure concentrations and timing, measurement methods, and interactive effects of multiple EDCs. Longitudinal studies on exposure to multiple EDCs are crucial to elucidating their contribution to pediatric obesity and minimize the adverse health consequences of EDC exposure.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Impact of obesity on pulmonary function of preschool children: an impulse oscillometry study
- Anuvat Klubdaeng, Kanokporn Udomittipong, Apinya Palamit, Pawinee Charoensittisup, Khunphon Mahoran
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):319-325. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: Does obesity in preschool children affect lung function, and which obesity indices can predict such alterations?
Finding: Preschool children with obesity exhibit impaired lung function characterized by elevated total and peripheral airway resistance. Waist-to-height ratio was the strongest predictor of such changes.
Meaning: Early obesity prevention and treatment are needed. Monitoring waist-to-height ratio, body weight, and body mass index may help identify children at risk of altered lung function.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Prevalence of childhood overweight and obesity in Malaysia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ker Yang Chua, Ker Yung Chua, Karuthan Chinna, Chooi Ling Lim, Maheeka Seneviwickrama
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):115-126. Published online November 13, 2024
-
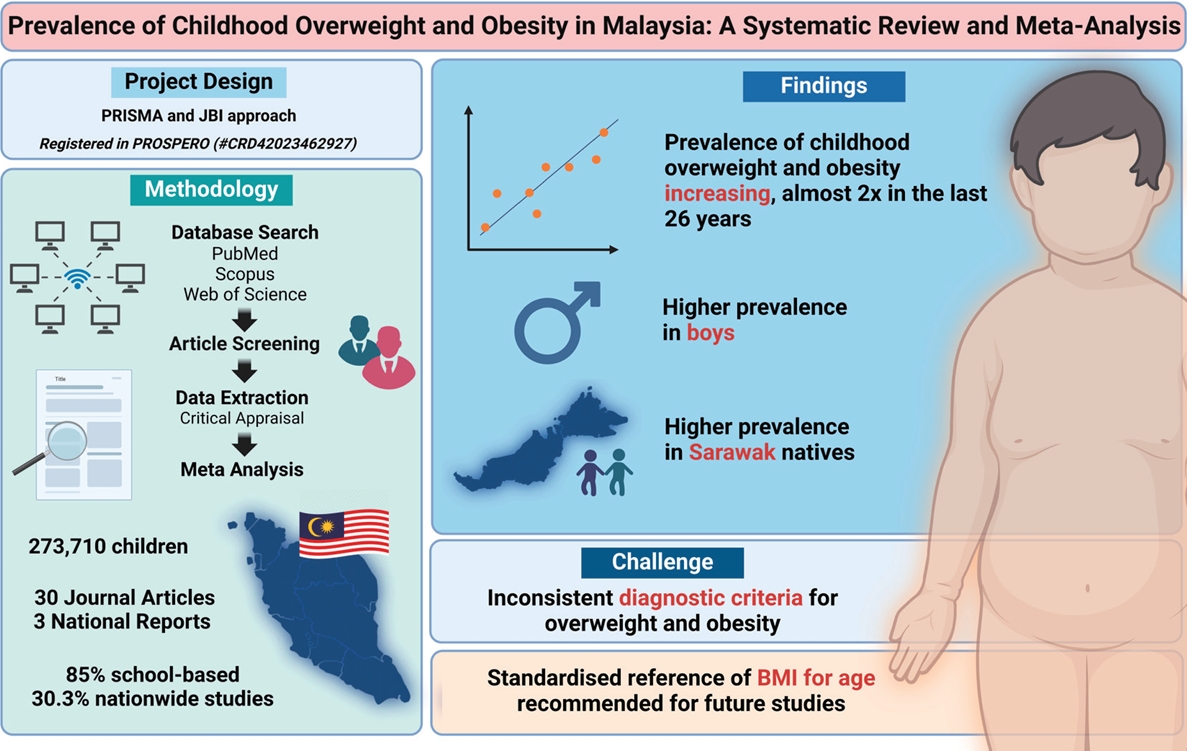
The incidence of childhood obesity is increasing worldwide. National surveys in Malaysia have shown similar trends. This review aimed to increase our understanding of the prevalence and associated factors of childhood overweight, obesity, and excess weight in Malaysia. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted of studies reporting the prevalence of overweight and obesity in Malaysian children aged <18 years....
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Polysomnographic features of children with obesity: body mass index predict severe obstructive sleep apnea in obese children?
- Rungrat Sukharom, Prakarn Tovichien, Kanokporn Udomittipong, Pinyapach Tiamduangtawan, Wattanachai Chotinaiwattarakul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):80-90. Published online November 6, 2024
-

Question: How Common is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in obese children? OSA is common in obese children, even without habitual snoring.
Finding: Among the subjects, 60.6% had positional OSA, 40.2% had rapid eye movement-related OSA, 59.8% had desaturation, 20.5% had sleep-related hypoventilation, and 5.0% had obesity hypoventilation syndrome. Body mass index (BMI) and neck and waist circumferences were significantly associated with severe OSA.
Meaning: We recommend screening obese children (BMI > 29.2 kg/m2) for OSA.
- Adolescence Medicine
- Relationship between inflammatory biomarkers and insulin resistance in excess-weight Latin children
- Mariano Nicolás Aleman, María Constanza Luciardi, Emilce Romina Albornoz, María Cristina Bazán, Adela Victoria Abregú
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):37-45. Published online December 21, 2023
-
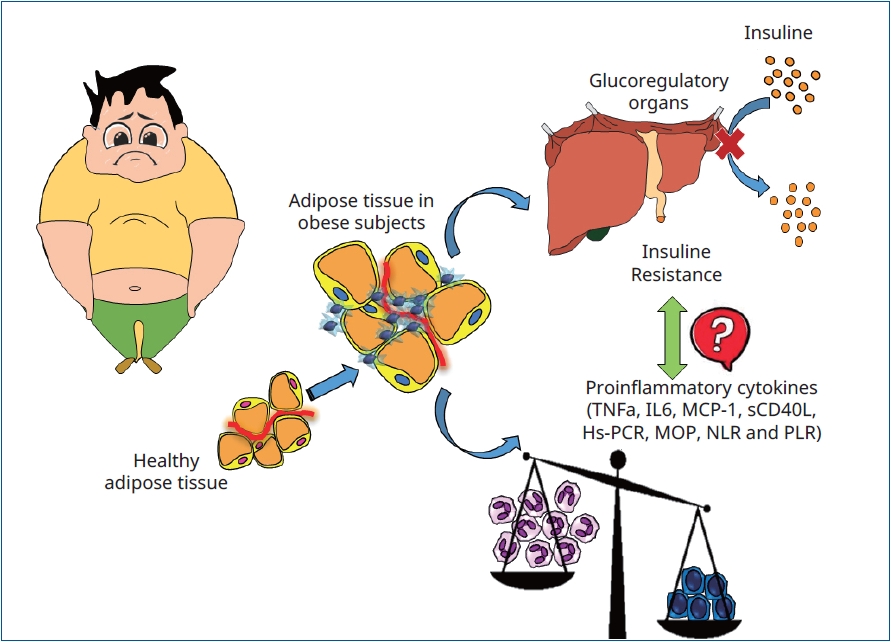
Question: What is the prevalence of insulin resistance (IR) in excess-weight Latin children, and can proinflammatory biomarkers predict it?
Finding: IR prevalence was elevated and tumor necrosis factor- α, interleukin-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein- 1, soluble CD40 ligand, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels were increased in excess-weight Latin children. However, none predicted IR status.
Meaning: These inflammatory biomarkers were unable to predict IR status. Therefore, further investigations are necessary.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Metabolic complications of obesity in children and adolescents
- Hyunjin Park, Jung Eun Choi, Seunghee Jun, Hyelim Lee, Hae Soon Kim, Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):347-355. Published online November 16, 2023
-
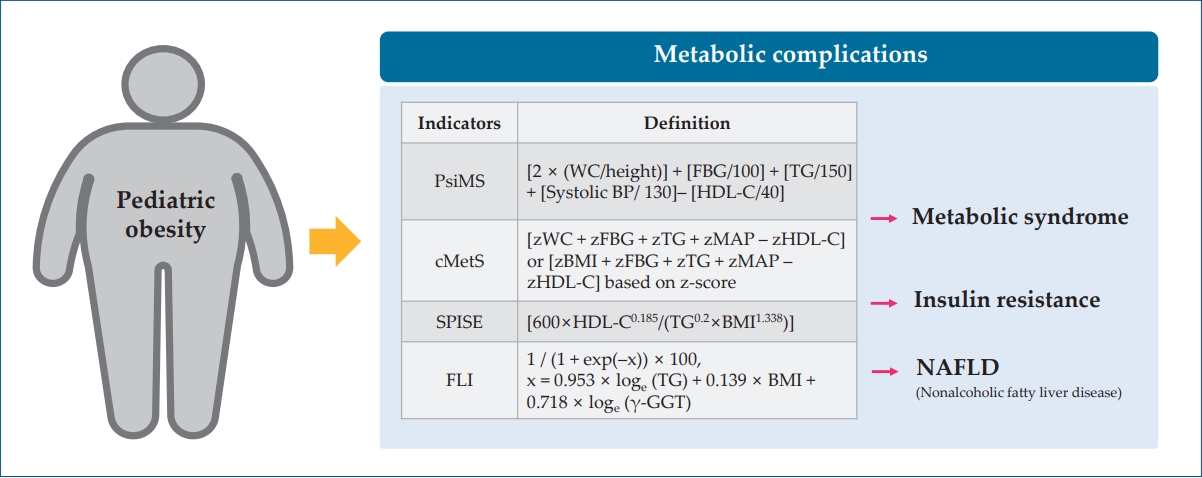
· Pediatric obesity increases the risk of metabolic complications (insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease) and long-term cardiovascular diseases.
· A new obesity definition and various indicators (continuous metabolic syndrome score, pediatric simple metabolic syndrome score, fatty liver index) have been proposed to evaluate children’s susceptibility to metabolic disorders.
· Laboratory and body composition tests in pediatric screenings can identify groups at high risk of metabolic complications of obesity.
- Nutrition
- Macronutrients modified dietary intervention in the management of overweight/obese children and adolescents: a systematic review
- Jihyun Park, Oh Yoen Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):191-200. Published online July 11, 2023
-
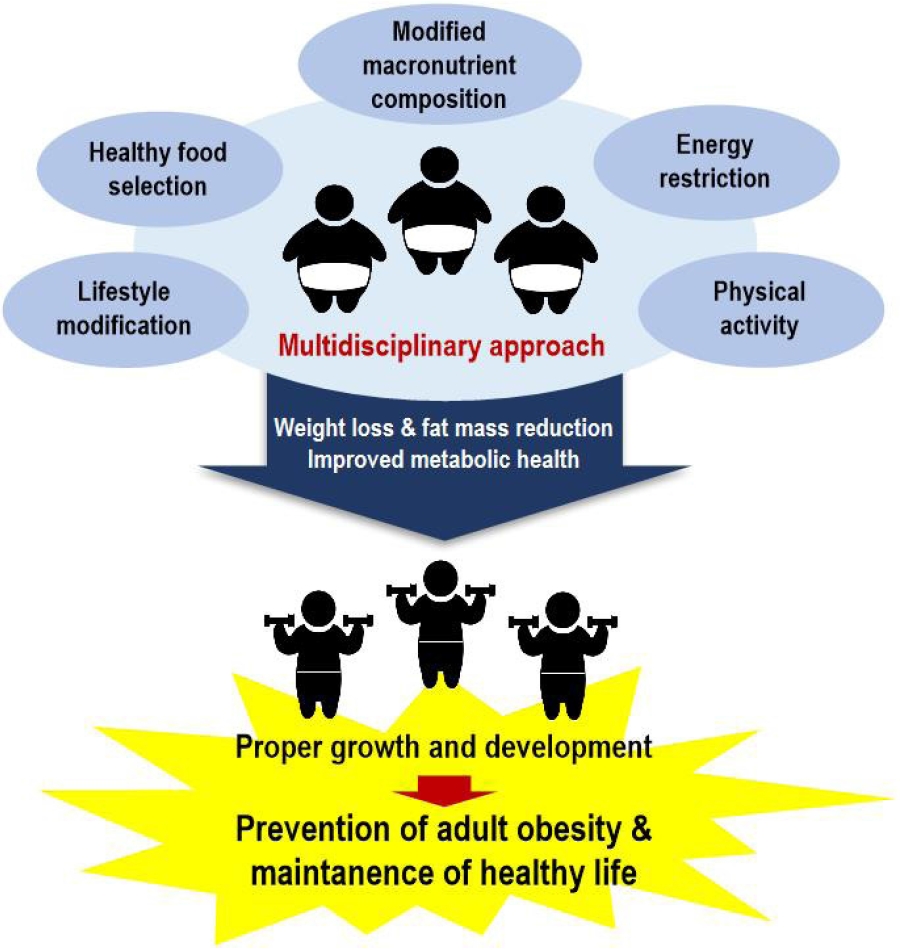
· Dietary macronutrient modifications affect the body composition of and metabolic markers in children and adolescents.
· Hypocaloric diets, regardless of macronutrient composition, are reportedly effective for weight loss in obese children.
· Future interventional studies with meta-analyses that include Korean children and adolescents are needed to provide basic information applicable to this population.
- Allergy
- Trends of vitamin D in asthma in the pediatric population for two decades: a systematic review
- Myongsoon Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):339-347. Published online June 14, 2023
-
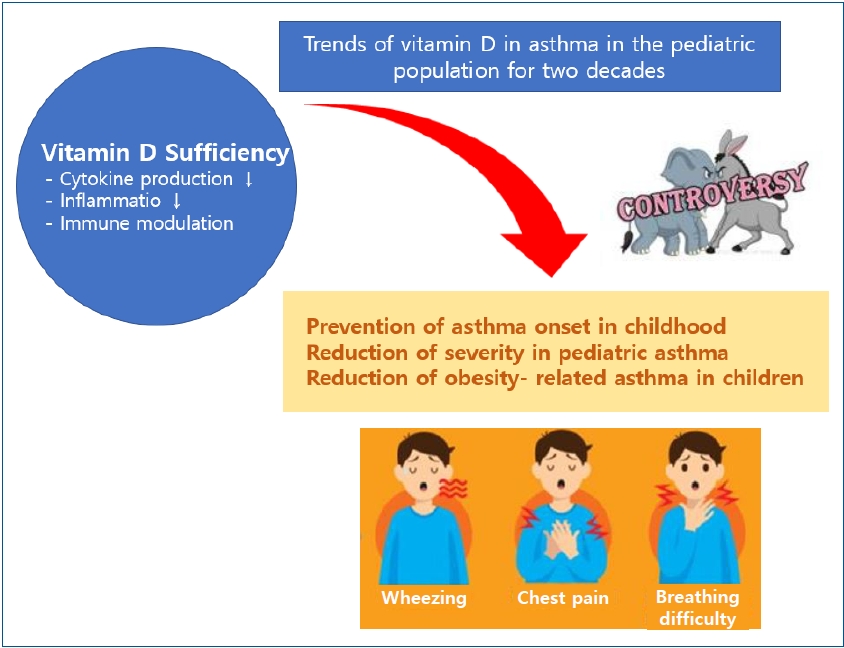
· Vitamin D may affect asthma via multiple mechanisms, including lung and optimal immune system functions.
· Many clinical trials have demonstrated the beneficial effects of vitamin D on asthma onset and aggravation. However, definitive clinical trials are lacking, and reports have detailed contradictory effects of vitamin D in children with asthma.
· Some exciting reports stated that obesity and vitamin D deficiency are associated with increased asthma symptoms in the pediatric population.
- Nutrition
- Association of gut microbiota with obesity in children and adolescents
- Ky Young Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):148-154. Published online November 16, 2022
-

The gut microbiota is an emerging factor in the development of pediatric obesity, which is affected by renowned risk factors such as diet, lifestyle, and socioeconomic status. This review aimed to describe the association between the gut microbiota and childhood obesity.
- Total energy expenditure measured by doubly labeled water method in children and adolescents: a systematic review
- Nahyun Kim, Jonghoon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):54-65. Published online October 17, 2022
-
This systematic review summarizes convincing evidence that total energy expenditure (TEE) measured using the doubly labeled water technique increased with age from 1 to 18 years, while fat-free mass (FFM) increased with growth. TEE and in normal-weight participants, while physical activity level did not differ from that of normal-weight participants.
- Endocrinology
- Pediatric hypertension based on Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines (JSH 2019) with actual school blood pressure screening data in Japan
- Toru Kikuchi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):283-290. Published online November 26, 2021
-
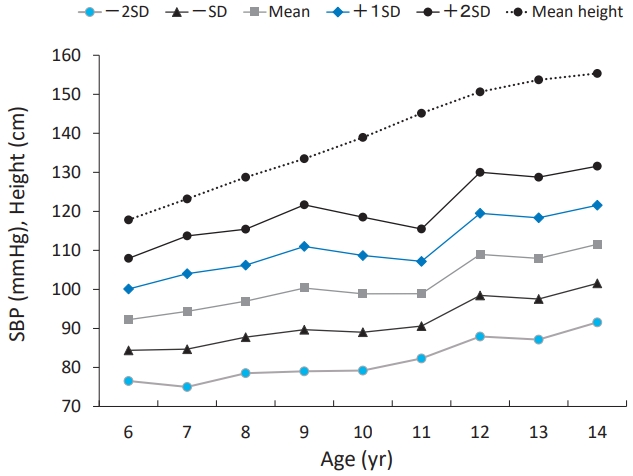
The prevalence of Japanese pediatric hypertension is 0.9% based on proper measurement protocols. Hypertensive children tend to be hypertensive adults. Pediatric essential hypertension is characterized by an absence of symptoms, obesity, a family history of hypertension, and a low birth weight. The most common causes of pediatric secondary hypertension are renal parenchymal and renovascular diseases. Important factors controlling pediatric hypertension include healthy lifestyle modifications and pharmacotherapy.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Effects of probiotics combined with dietary and lifestyle modification on clinical, biochemical, and radiological parameters in obese children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized clinical trial
- Thushara Rodrigo, Samaranayake Dulani, Sumudu Nimali Seneviratne, Arjuna P. De Silva, Jerad Fernando, H. Janaka De Silva, Jayasekera , V. Pujitha Wickramasinghe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):304-311. Published online November 11, 2021
-
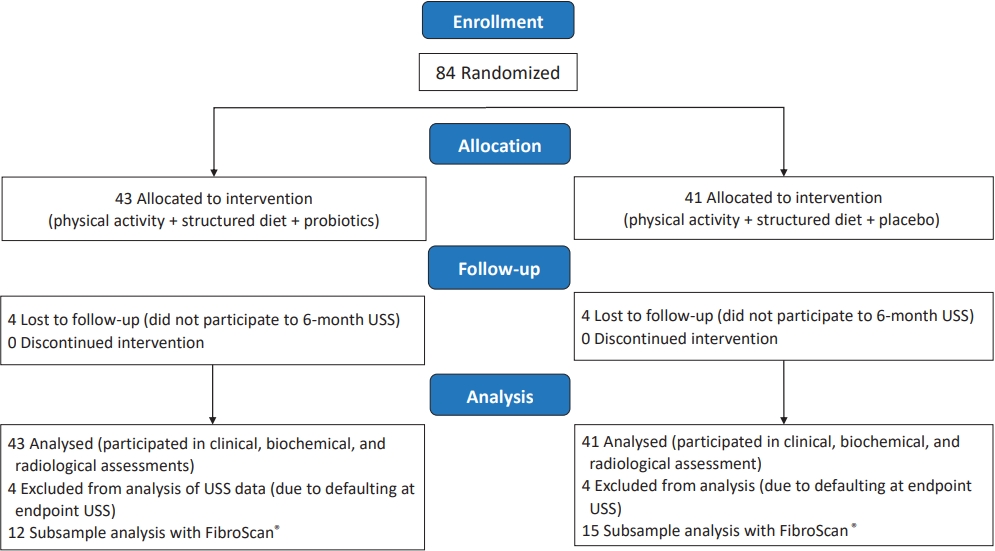
Question: Could probiotics be used as a therapeutic modality in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis?
Finding: There seem no added advantages over lifestyle modifications compared to Probiotics.
Meaning: There does not seem to be an advantage of probiotics over lifestyle modifications in improving obesity-associated metabolic derangement in children.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Endocrine comorbidities of pediatric obesity
- Jieun Lee, Jae Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):619-627. Published online August 26, 2021
-

∙ Pediatric obesity can involve endocrine comorbidities such as prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, polycystic ovary syndrome, and central precocious puberty.
∙ Prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in youth aged 10–19 years had a prevalence of 25.9% and 0.6% in 2013–2014, respectively.
∙ Dyslipidemia in Korean adolescents aged 10–18 years had a prevalence of 7.64% (total cholesterol ≥200 mg/dL), 6.09% (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol ≥130 mg/dL), 8.69% (triglyceride ≥150 mg/dL), and 12.52% (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ≤40 mg/dL) in 2007–2018.
∙ Metabolic syndrome in Korean youth has a prevalence of 1.9%–14.7% in males and 1.7%–12.6% in females with wide variation in definitions.
∙ Appropriate comorbidity screening and management and/or specialist referral are necessary for obese children and adolescents.
- Nutrition
- Changes in health status of North Korean children and emerging health challenges of North Korean refugee children
- Seong-Woo Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):552-558. Published online May 17, 2021
-

· Among North Korean refugee (NKR) children under 5 years, 61% and 9.3% were underweight in 1998 and 2017, respectively.
· The immunization rate of NKR children exceeded 90% since 2006.
· For NKR children, protein-energy malnutrition was the #1 cause of death in 2009 versus #17 in 2019.
· In 2020, stunting affected 5.4% and 0.9% and obesity affected 10.7% and 2.7% of NKR versus South Korean children, respectively.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Obesity and chronic kidney disease: prevalence, mechanism, and management
- Hyung Eun Yim, Kee Hwan Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):511-518. Published online April 6, 2021
-
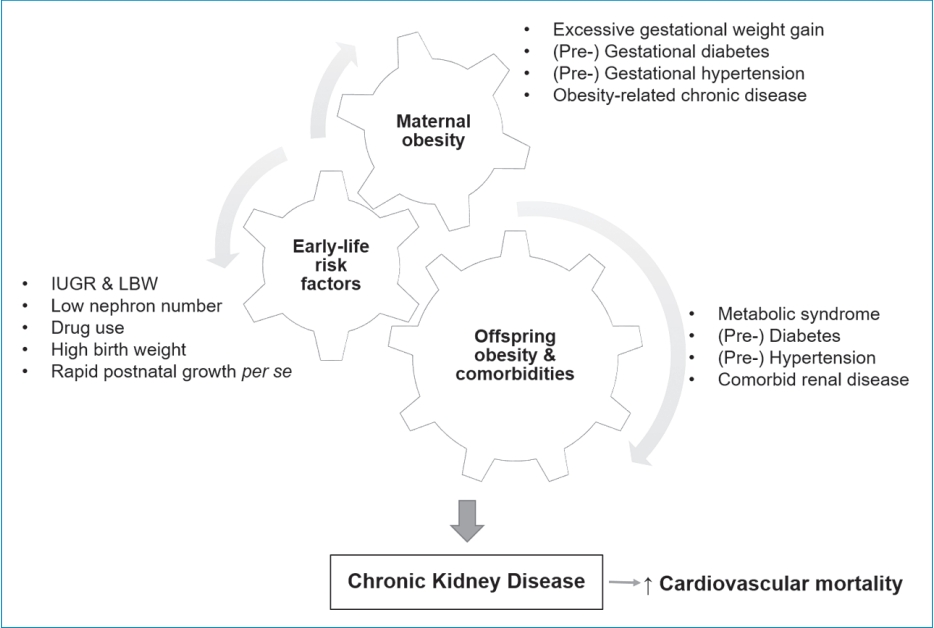
· Obesity is strongly associated with the development and progression of chronic kidney disease.
· Altered renal hemodynamics, metabolic effects, and lipid nephrotoxicity may play a key role in the development of obesity-related kidney disease.
· Children born to obese mothers are at increased risk of developing obesity and chronic kidney disease later in life.
· A multilevel approach is needed to prevent obesity and related chronic diseases.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Global relationship between parent and child obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ju Suk Lee, Mi Hyeon Jin, Hae Jeong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):35-46. Published online March 29, 2021
-

Question: Are parent and child obesity correlated worldwide?
Finding: Overweight and obese status of parents and children were significantly associated worldwide. The association between parent and child obesity was stronger in Asia than in Europe and the Middle East, and in high-income than in middle- and low-income countries.
Meaning: Childhood obesity is highly influenced by parental weight status, indicating that parents could play an important role in its prevention.
- Review Article
- Infection
- The COVID-19 pandemic: an unprecedented tragedy in the battle against childhood obesity
- Maximilian Andreas Storz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):477-482. Published online November 5, 2020
-

Large-scale quarantine and home confinement during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic will impose new and unfamiliar stressors on children, thereby worsening the childhood obesity epidemic. Physical, nutritional, and psychosocial factors that promote obesity in children during this special situation complementarily contribute to an unprecedented obesogenic environment. Involved stakeholders, including governments, schools, and families, must make all efforts to minimize the impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on childhood obesity.
- Adolescence Medicine
- The impacts of exercise on pediatric obesity
- Ronald J. Headid III, Song-Young Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(5):196-207. Published online August 4, 2020
-
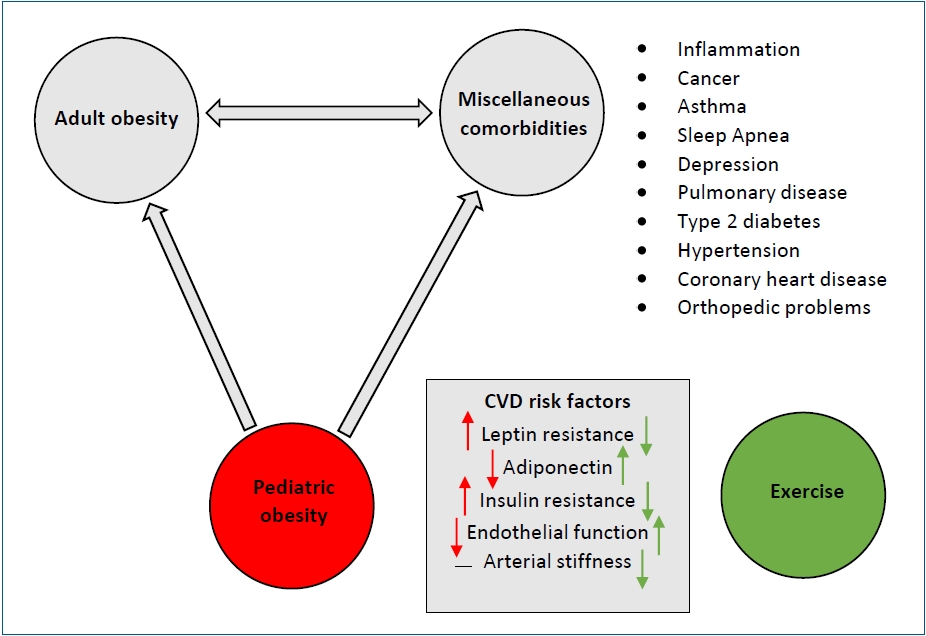
Pediatric obesity contributes to the development of vascular dysfunction and metabolic and cardiovascular diseases which have all been shown to track into adulthood, increasing the risk of early mortality. Early exercise intervention is critical for combating obesity-related comorbidities and the optimal exercise prescription has yet to be well documented. Exercise prescriptions to combat pediatric obesity should incorporate both aerobic and muscle-strengthening exercises with an emphasis on long-term adherence.
- Endocrinology
- Early menarche and its consequence in Korean female: reducing fructose intake could be one solution
- Ji Hyun Kim, Jung Sub Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):12-20. Published online May 14, 2020
-
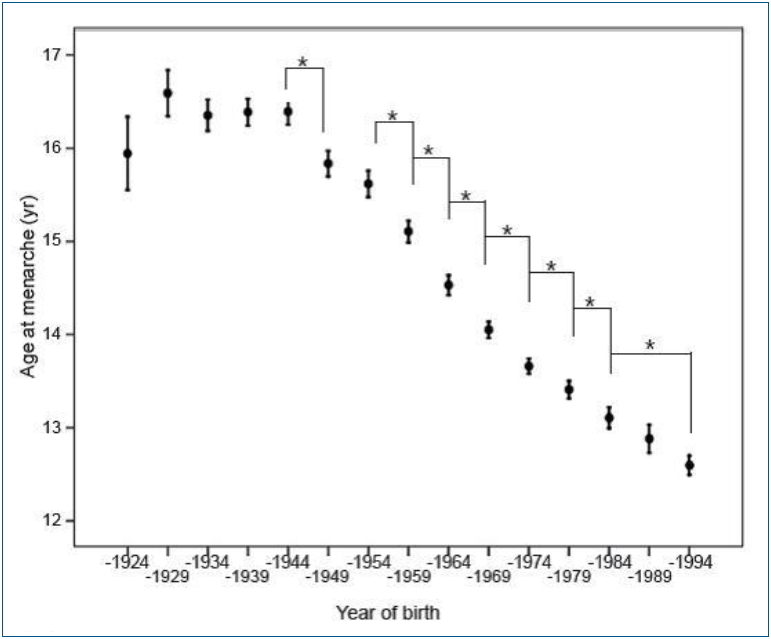
In Korea, the average age of menarche has declined sharply. Early menarche is associated with psychosocial and behavioral problems and cardiometabolic disease. Excess fructose intake has been suggested as one cause of early menarche in recent studies, so reducing fructose intake may be one solution.
- Air pollution and childhood obesity
- Moon Young Seo, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):382-388. Published online March 27, 2020
-
Questions: What are the possible effects of air pollution on the occurrence of childhood obesity and what are the mechanisms?
Finding: Epidemiologic studies suggest that air pollutants might act as obesogens in the pediatric population, and their possible mechanisms include oxidative stress, physical inactivity, and epigenetic modulation.
Meaning: This paper reviews updated information on air pollution, one of the modifiable environmental factors in childhood obesity.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Influence of subclinical hypothyroidism on metabolic parameters in obese children and adolescents
- Ozlem Kara
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(3):110-114. Published online March 6, 2020
-

Question: Does subclinical hypothyroidism in obese children and adolescents affect metabolic parameters?
Finding: Insulin, HOMA-IR, and TG levels were higher and the HDL-C level was lower in patients with SH.
Meaning: A clear association is observed between SH, and insulin resistance and dyslipidemia in obese children. It can be said that the TSH may be evaluated as a metabolic risk factor in obese patients.
- Lipid accumulation product is a predictor of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in childhood obesity
- Bahar Özcabı, Salih Demirhan, Mesut Akyol, Hatice Öztürkmen Akay, Ayla Güven
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(12):450-455. Published online October 28, 2019
-

Background: Lipid accumulation product (LAP) is associated with the presence and severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in adults.
Purpose: Here we evaluated the ability of LAP to predict NAFLD in obese children. Methods: Eighty obese children (38 girls; age 6–18 years) were included. Anthropometric measurements and biochemical values were obtained from the patients’ medical records. LAP was calculated as [waist...
- General Pediatrics
- Prevalence of hyperuricemia and its association with metabolic syndrome and cardiometabolic risk factors in Korean children and adolescents: analysis based on the 2016–2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Jung Hyun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(8):317-323. Published online June 24, 2019
-
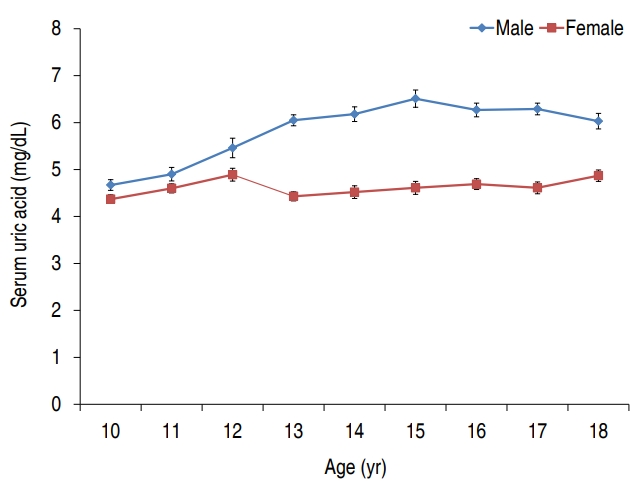
Purpose: Investigating the prevalence of hyperuricemia and its association with metabolic syndrome (MetS) and cardiometabolic risk factors (CMRFs) in Korean children and adolescents. Methods: This cross-sectional survey used data from the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2017); 1,256 males and females aged 10–18 years were included. Hyperuricemia was defined as serum uric acid levels were >6.6 mg/dL at...
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Prevalence of obesity and overweight in Iranian children aged less than 5 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- kamyar mansori, Sorour Khateri, Yousef Moradi, Zaher Khazaei, Hossein Mirzaei, Shiva Mansouri Hanis, Mehran Asadi Aliabadi, Mehdi Ranjbaran, Fatemeh Varse, Serveh Parang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):206-212. Published online April 23, 2019
-
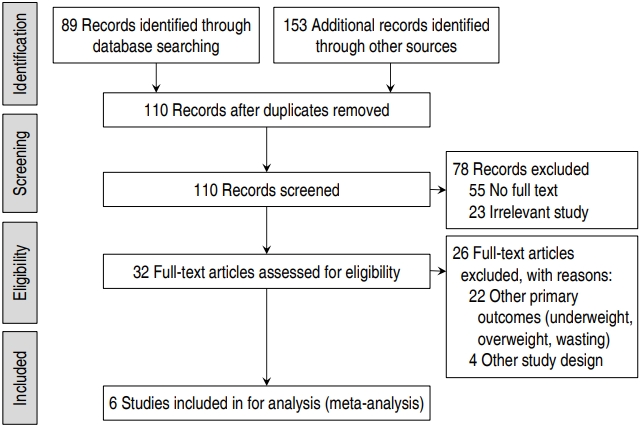
Purpose: The present study aimed to determine the prevalence of childhood obesity and overweight in Iranian children under 5 years of age using a systematic review and meta-analysis. Methods: We searched MEDLINE (PubMed), Web of Science, Google Scholar, Scopus, CINHAL, and the Iranian databases, including Scientific Information Database (www.sid.ir), Iranian Research Institute for Information Science and Technology (Irandoc.ac.ir), Iranmedex (www.iranmedex.com), and...
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Prevalence and associates of obesity and overweight among school-age children in a rural community of Thailand
- Teechaya Nonboonyawat, Wuttipat Pusanasuwannasri, Nattanon Chanrat, Natta Wongthanavimok, Danutanut Tubngern, Piengkwan Panutrakul, Mathirut Mungthin, Thirapa Nivesvivat, Panadda Hatthachote, Ram Rangsin, Phunlerd Piyaraj
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(5):179-186. Published online February 8, 2019
-

Purpose: Information about overweight and obesity among students in rural areas of Thailand is limited. Therefore, we aimed to determine overweight and obesity prevalences and associated factors among school-aged children in a rural community of Thailand. Methods: We selected 9 public schools through cluster sampling in 2 provinces located in central Thailand in 2016. Anthropometric measurements were measured using standard techniques,...
- Guideline
- Nutrition
- Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric obesity: recommendations from the Committee on Pediatric Obesity of the Korean Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition
- Dae Yong Yi, Soon Chul Kim, Ji Hyuk Lee, Eun Hye Lee, Jae Young Kim, Yong Joo Kim, Ki Soo Kang, Jeana Hong, Jung Ok Shim, Yoon Lee, Ben Kang, Yeoun Joo Lee, Mi Jin Kim, Jin Soo Moon, Hong Koh, JeongAe You, Young-Sook Kwak, Hyunjung Lim, Hye Ran Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(1):3-21. Published online December 27, 2018
-

The Committee on Pediatric Obesity of the Korean Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition newly developed the first Korean Guideline on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Obesity in Children and Adolescents to deliver an evidence-based systematic approach to childhood obesity in South Korea. The following areas were systematically reviewed, especially on the basis of all available references published in...
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











