Most cited
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most cited
Most-cited articles are from the articles published during the last two years (2023 ~ ).
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Global burden of asthma among children and adolescents with projections to 2050: a comprehensive review and forecasted modeling study
- Tae Hyeon Kim, Hyunjee Kim, Jiyeon Oh, Soeun Kim, Michael Miligkos, Dong Keon Yon, Nikolaos G Papadopoulos
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):329-343. Published online April 22, 2025
-

Pediatric asthma can persist to adulthood and must be effectively managed. This review examined the prevalence of asthma among individuals younger than 20 years and revealed a decline from 1990 to 2021, higher rates in males, and a peak in children aged 5–9 years. Despite a projected continued decrease in prevalence by 2050, asthma will remain a significant health concern for children and adolescents.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding dengue vaccine: a baseline study of community members and health providers in Indonesia
- Abdul Wahab, Ida Safitri Laksanawati, Retna Siwi Padmawati, Asal Wahyuni Erlin Mulyadi, Wahyu Triadmajani, Jarir At Thobari
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):228-237. Published online November 13, 2024
-
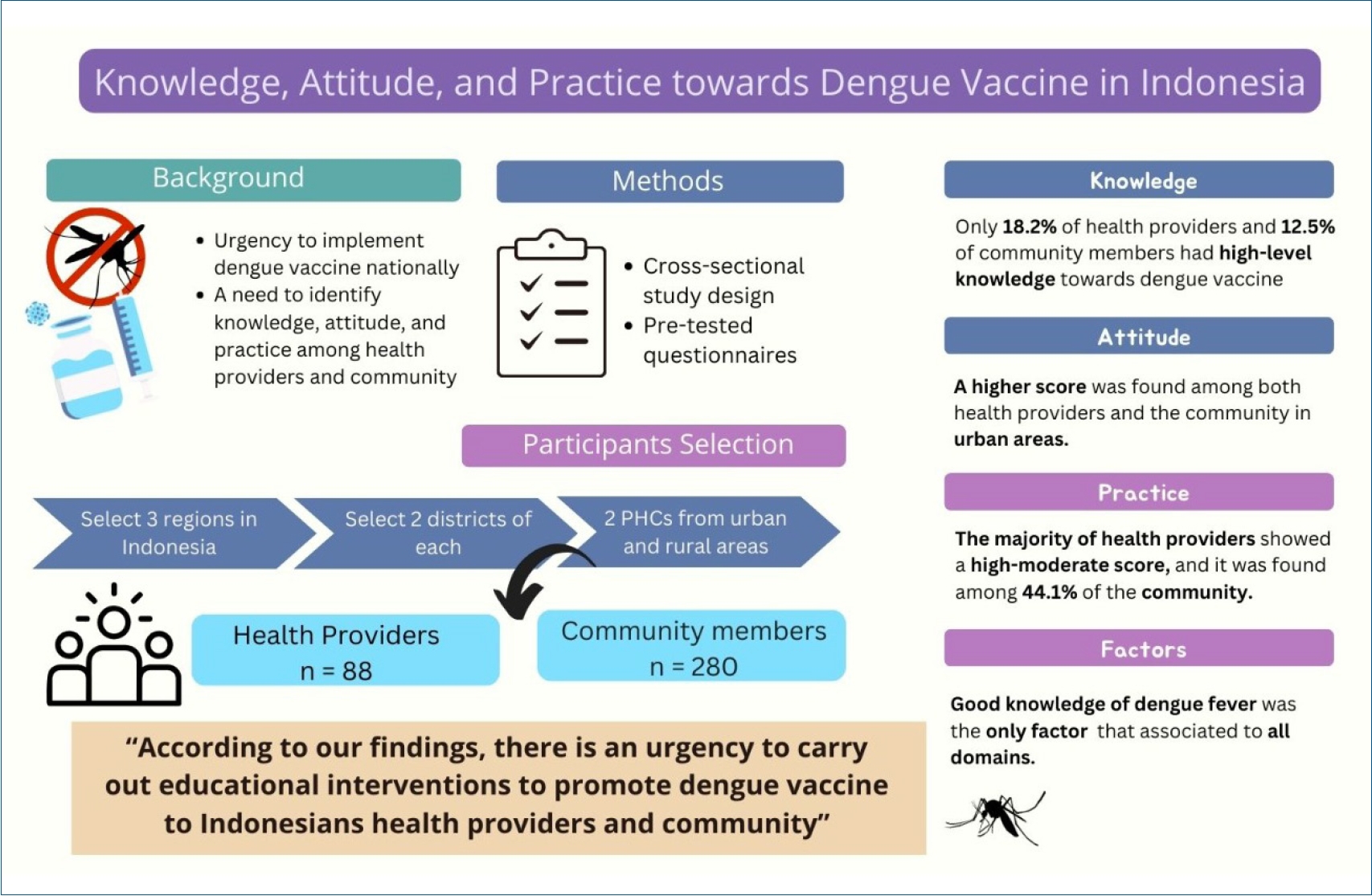
Question: Do community members and health providers show different level of knowledge, attitude, and practice towards dengue vaccine?
Finding: These 2 groups only differed in practice component, while the knowledge and attitude constituents were relatively low for both.
Meaning: There is an urgent need to deliver educational interventions to raise awareness of community members and health providers regarding dengue vaccination.
- Endocrinology
- Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone score changes in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency
- Pattara Wiromrat, Yutapong Raruenrom, Phanpaphorn Namphaisan, Nantaporn Wongsurawat, Ouyporn Panamonta, Chatlert Pongchaiyakul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):238-246. Published online November 13, 2024
-
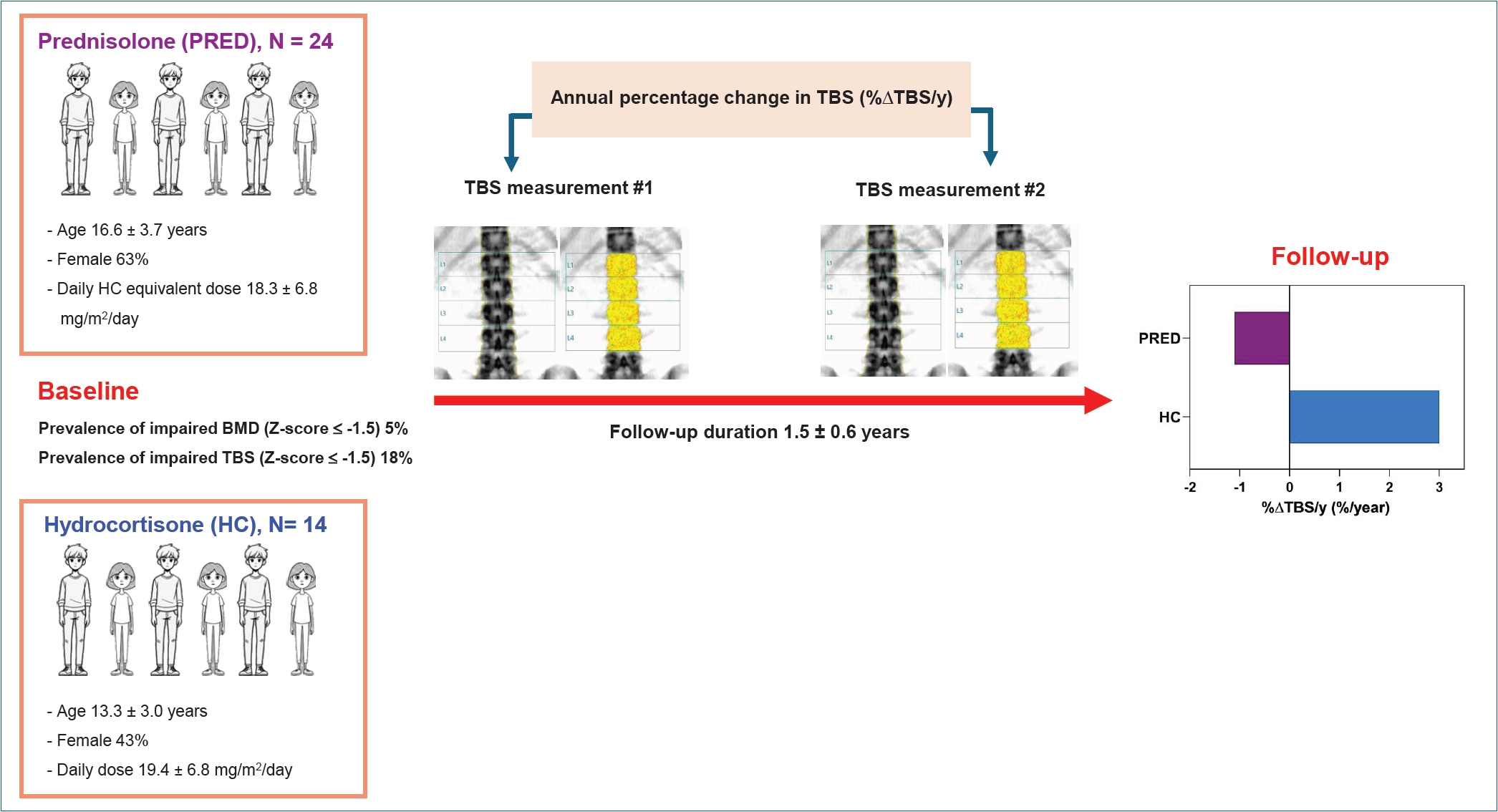
Question: What is the prevalence of an impaired trabecular bone score (TBS), a measure of bone microarchitecture, in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency (21OHD)? Do prednisolone and hydrocortisone affect TBS differently in this patient population?
Finding: Impaired TBS was observed in 18% of participants. Prednisolone use negatively impacted TBS change.
Meaning: Impaired TBS is prevalent among adolescents with 21OHD. Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone microarchitecture development.
- Gastroenterology
- Outcome of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease in Asian children: a multinational 1-year follow-up study
- Pornthep Tanpowpong, Suporn Treepongkaruna, James Guoxian Huang, Kee Seang Chew, Karen Sophia Calixto Mercado, Almida Reodica, Shaman Rajindrajith, Wathsala Hathagoda, Yoko Kin Yoke Wong, Way Seah Lee, Marion Margaret Aw
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):247-256. Published online November 13, 2024
-
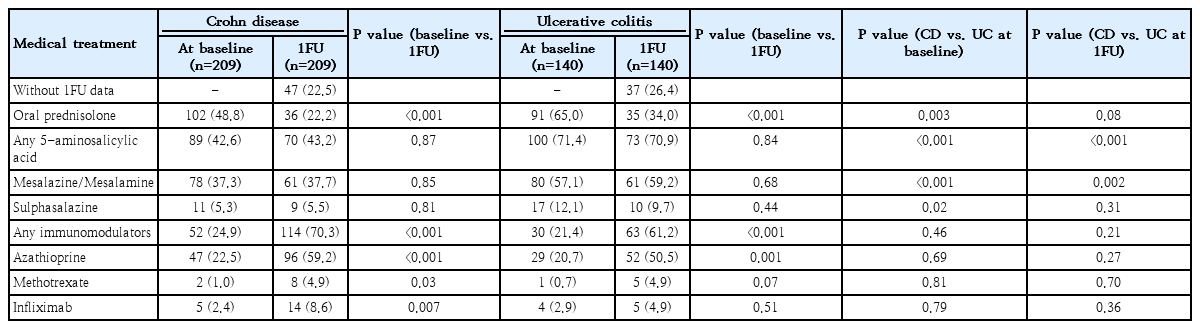
Question: Short-term (1-year) follow-up data in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), especially in Southeast Asian countries, are limited.
Finding/Meaning: Abdominal pain and pallor rates remained high at 1 year after IBD diagnosis. Three independent factors of 1-year clinical remission for Crohn disease were oral prednisolone, antibiotic, and immunomodulator use at 1-year follow-up. A history of weight loss at diagnosis was the only independent risk factor of IBD flare.
- Editorial
- Hematology
- Absolute versus functional iron deficiency
- Hye Lim Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):138-140. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· Iron deficiency (ID), the most common cause of anemia, can be classified into absolute and functional types. Absolute ID is a state of low total body iron, while functional ID is a state of imbalance between iron demand and iron availability due to inflammation and/or infection.
· ID is diagnosed by serum ferritin and transferrin saturation levels.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- A review of vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D receptor polymorphisms in endocrine-related disorders
- Nur Faten Hafizah Rosli, Noor Shafina Mohd Nor, Rose Adzrianee Adnan, Siti Hamimah Sheikh Abdul Kadir
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):30-52. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency is high among children and adolescents and mainly attributed to changes in environmental factors.
· Vitamin D hormone-like properties are associated with many endocrine-related disorders.
· The effect of vitamin D is modulated by the vitamin D receptor, polymorphisms of which are reportedly associated with an increased risk of disease development in children and adolescents.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Need for national guidance regarding proactive care of infants born at 22–23 weeks' gestation
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):53-61. Published online November 13, 2024
-

With advancements in neonatal intensive care, the limit of viability has shifted to 22–23 weeks' gestation, whose survival rates vary across countries and institutions. These rates are not static and can be improved through the proactive and centralized care guided by national protocols, including maternal transfer to high-activity regions with better neonatal intensive care practices before delivery.
- Infection
- Incidence, causative organisms, and risk factors of bloodstream infections in pediatric liver transplant patients: a systematic review
- Mohamad Shieb, Rand Hasanain, Zara Arshad, Faisal A. Nawaz, Rahul Kashyap, Eric J. Stern
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):427-434. Published online April 5, 2024
-

The overall incidence of bloodstream infections was 23.5%. Gram-negative organisms occur at a much higher rate in pediatric liver transplant recipients then that the general pediatric population. However, when comparing pediatric and adult liver transplant recipients Gram-positive organisms occur with a much higher rate in the pediatric population highlighting the importance of early and broad spectrum antimicrobial coverage when bloodstream infections are suspected.
- Allergy
- Comparison and review of international guidelines for treating asthma in children
- Eui Jeong Roh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):447-455. Published online August 20, 2024
-

Asthma is the most common chronic disease among children. Although asthma in children may spontaneously improve, it continues into adulthood in many cases. Therefore, appropriate disease management and medication are essential. Consistent and objective guidelines are needed to manage pediatric asthma and related adverse reactions.
- Recent advances in food allergen immunotherapy
- You Hoon Jeon, Edwin H. Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):386-394. Published online December 7, 2023
-

· To enhance the safety of food allergen immunotherapy, alternative approaches such as sublingual immunotherapy, epicutaneous immunotherapy, low-dose oral immunotherapy (OIT), and omalizumab with OIT are being explored.
· Factors such as causative allergen type, natural outgrowth, symptom severity, and patient age should be considered.
· Individualized food allergen immunotherapy plans should be established to determine the most beneficial treatment for each patient.
- Editorial
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Advancing orphan drug development for rare diseases
- Jung Min Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):356-357. Published online November 17, 2023
-
· Rare diseases present unique challenges and unmet needs for which the development of orphan drugs tailored to them offers hope.
· Despite the hurdles posed by limited patient populations, orphan drug designations from regulatory agencies provide incentives, such as extended market exclusivity and tax credits, that ignite transformative advances.
· Scientific progress in genomics, personalized medicine, and analytics empowers precise interventions by decoding genetic anomalies and encouraging effective treatments.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effectiveness of online responsive teaching in young children with developmental disabilities: a pilot study
- Jung Sook Yeom, Jeongmee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):303-311. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Question: Does online responsive teaching (RT) impact children's and parents’ emotions and behaviors, and do parents find it satisfactory?
Finding: Online RT significantly improved children's pivotal and problem behaviors, decreased parenting stress, and enhanced parental interactive styles with high satisfaction.
Meaning: This pilot study's findings suggest that online RT can enhance child outcomes, offering accessible interventions amid challenges such as limited access and pandemics.
- Letter to the Editor
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Pentraxin 3 as a marker of early-onset neonatal sepsis
- Safaa ELMeneza, Iman El-Bagoury, Hind Rayes, Amira Hassan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):312-314. Published online May 23, 2024
-

- Review Article
- Other
- Children’s health affected by parent’s behavioral characteristics: a review
- Sung Eun Kim, Jongin Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):232-239. Published online August 21, 2023
-

· Parents’ occupational hazards, long working hours, and smoking behaviors should be modified adequately to minimize adverse health effects on their children.
· As of 2023, several diseases from fetal exposure to occupational hazards can be compensated with Industrial Accident Compensation Insurance in South Korea.
· A directed acyclic graph is recommended for medical research to control the effects of parents’ behaviors on children’s health.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Oral administration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates intestinal injury in necrotizing enterocolitis
- Yeong Seok Lee, Yong Hoon Jun, Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):152-160. Published online February 19, 2024
-
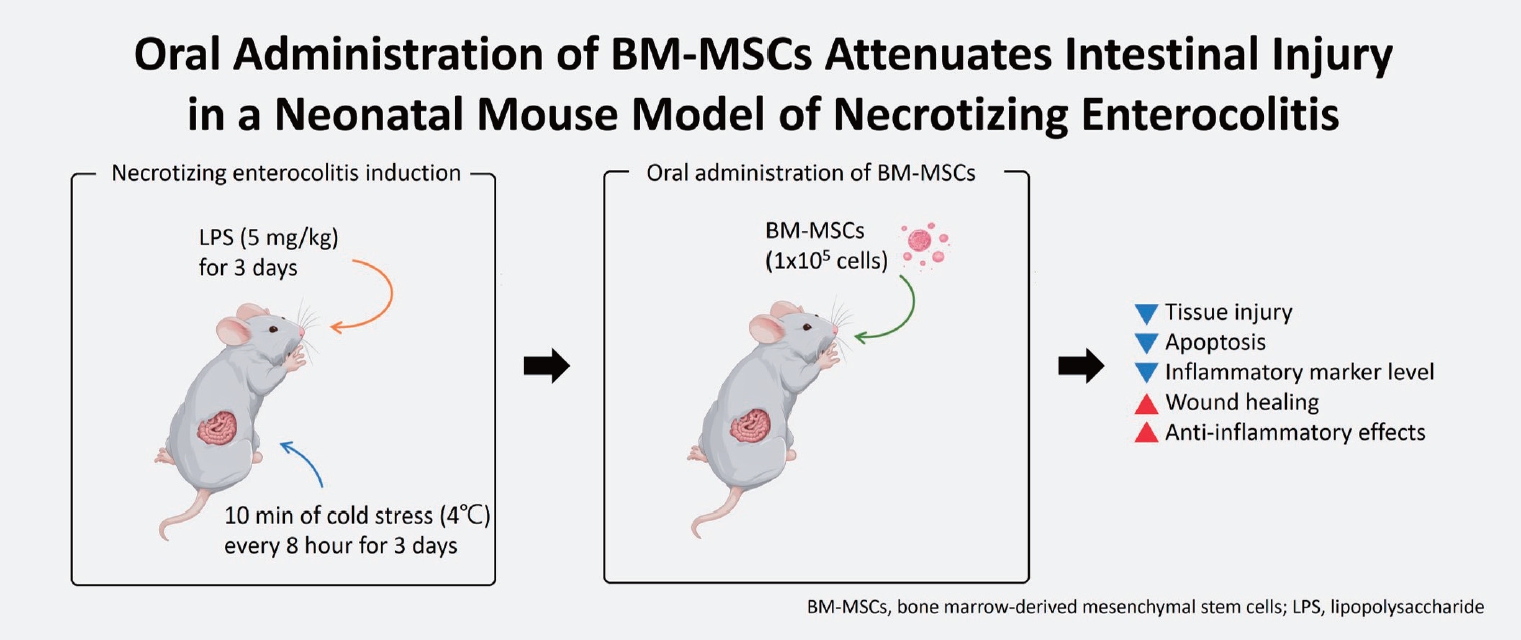
Question: What is the optimal dose of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) for treating necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), and is orally administered BM-MSC effective?
Findings: High (1×106 cells) or multiple BM-MSC doses showed similar effects as low (1×105 cells) doses of intraperitoneally administered BM-MSCs. Furthermore, orally administered BM-MSCs were as effective as intraperitoneally administered BM-MSCs.
Meaning: Orally administered low-dose BM-MSCs are a potential treatment for NEC.
- Letter to the Editor
- Pulmonology
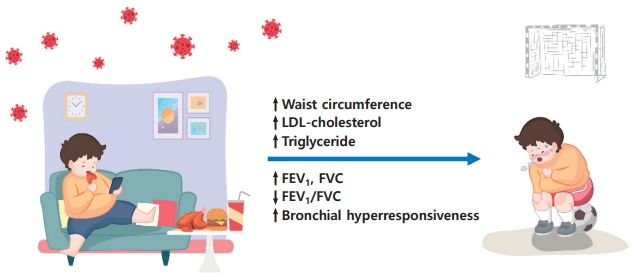
- Metabolic syndrome and pulmonary dysfunction in asthmatic children during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Jue Seong Lee, Sang Hyun Park, Yoon Lee, Seunghyun Kim, Wonsuck Yoon, Young Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):168-170. Published online February 19, 2024
-
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children: focus on systemic Th2 cytokine receptor antagonists and Janus kinase inhibitors
- Jeong Hee Kim, Mona Salem Samra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):64-79. Published online June 14, 2023
-
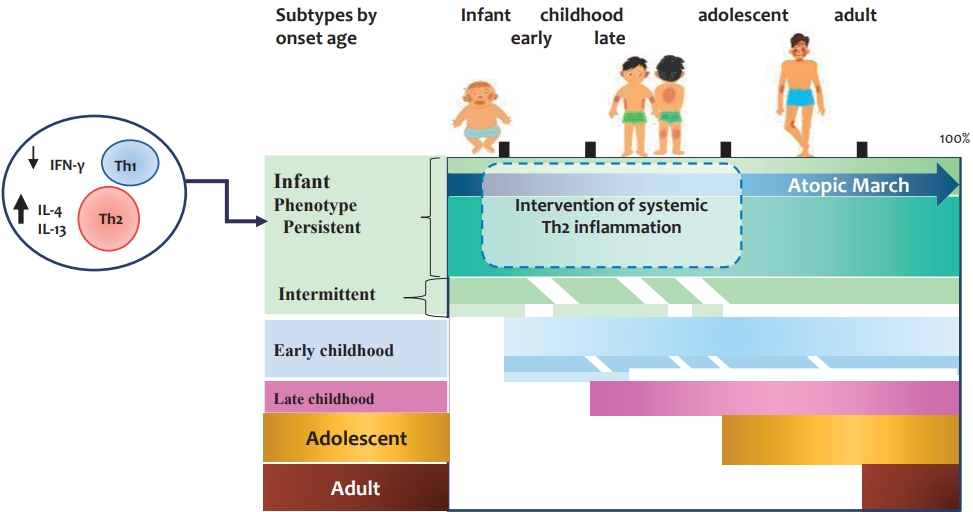
· Atopic dermatitis (AD) is characterized by a strong T helper (Th)2 response, although the extents of Th22, Th17/ interleukin (IL)-23, and Th1 responses vary among disease subtypes.
· Children with moderate to severe AD may require early systemic therapy to reduce the systemic inflammation caused by increased Th2 cytokine levels.
· Dupilumab, which blocks IL-4/IL-13 receptor, has equivalent efficacy for extrinsic and intrinsic AD and a favorable safety profile in infants and children aged 6 months and older.
- Rheumatology
- Double-negative T cells in pediatric rheumatic diseases
- Dimitri Poddighe, Tilektes Maulenkul, Kuanysh Dossybayeva, Gulsamal Zhubanova, Zaure Mukusheva, Lyudmila Akhmaltdinova
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):632-640. Published online September 12, 2024
-
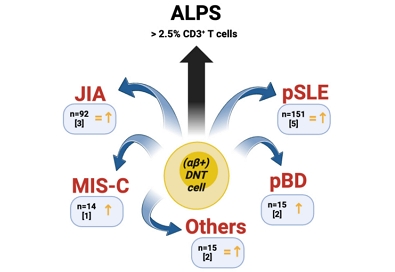
Double-negative T (DNT) cells appear to be increased in several pediatric rheumatic diseases and this finding may be correlated with disease activity to some extent. However, due to significant heterogeneity in several methodological aspects, further investigations in rheumatic children are needed to assess the potential relevance of DNT cells as biomarkers and clarify their immunopathological role.
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Comparative analysis of adolescent hypertension definitions for predicting early adulthood carotid artery intima-media thickness: Tehran lipid and glucose study
- Maryam Barzin, Shirin Yaghoobpoor, Maryam Mahdavi, Behnaz Abiri, Majid Valizadeh, Fereidoun Azizi, Pooneh Dehghan, Farhad Hosseinpanah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):694-703. Published online September 12, 2024
-
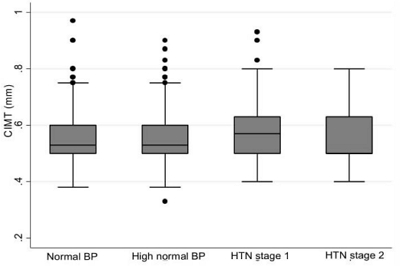
Question: What is the prevalence of HTN among adolescents enrolled in the TLGS according to 3 different accepted definitions (4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG). Also, what is the ability of each of these definitions in predicting early adulthood CIMT, as a surrogate for cardiovascular disease events?
Finding: The highest and lowest prevalence of stage 1 HTN was observed with the AAP-CPG (17.7%) and ESH (8.8%), respectively. Similarly, the highest and lowest prevalence of stage 2 HTN was noted with the AAP-CPG (1.5%) and ESH (0.8%), respectively. The highest to lowest predictive abilities belonged to the 4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG, respectively.
Meaning: Among the various definitions of pediatric HTN, the 4th report offered the best ability to predict a high CIMT during early adulthood, followed by the ESH and AAP-CPG.
- General Pediatrics
- Role of proper postnatal care in continued exclusive breastfeeding among young Indonesian mothers
- Wahyu Triadmajani, Shinta Prawitasari, Abdul Wahab
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):686-693. Published online September 12, 2024
-
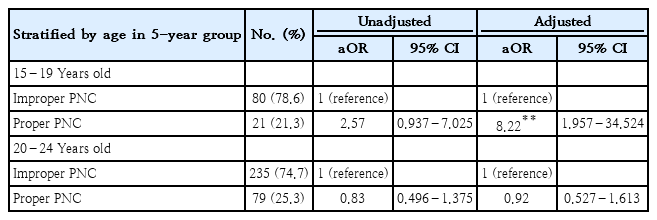
Question: Is proper postnatal care (PNC) associated with exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) practice among young Indonesian mothers?
Finding: Proper PNC elevates the likelihood of EBF among Indonesian adolescent mothers aged 15–19 years.
Meaning: Breastfeeding services should be provided during the early postnatal period to support EBF practice among adolescent mothers. High-quality PNC is a tailored intervention for vulnerable populations.
- Review Article
- Adolescence Medicine
- Diet-related behaviors affecting health and substance use among children and adolescents
- Ji-Hyun Seo, Sochung Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):664-671. Published online October 31, 2024
-
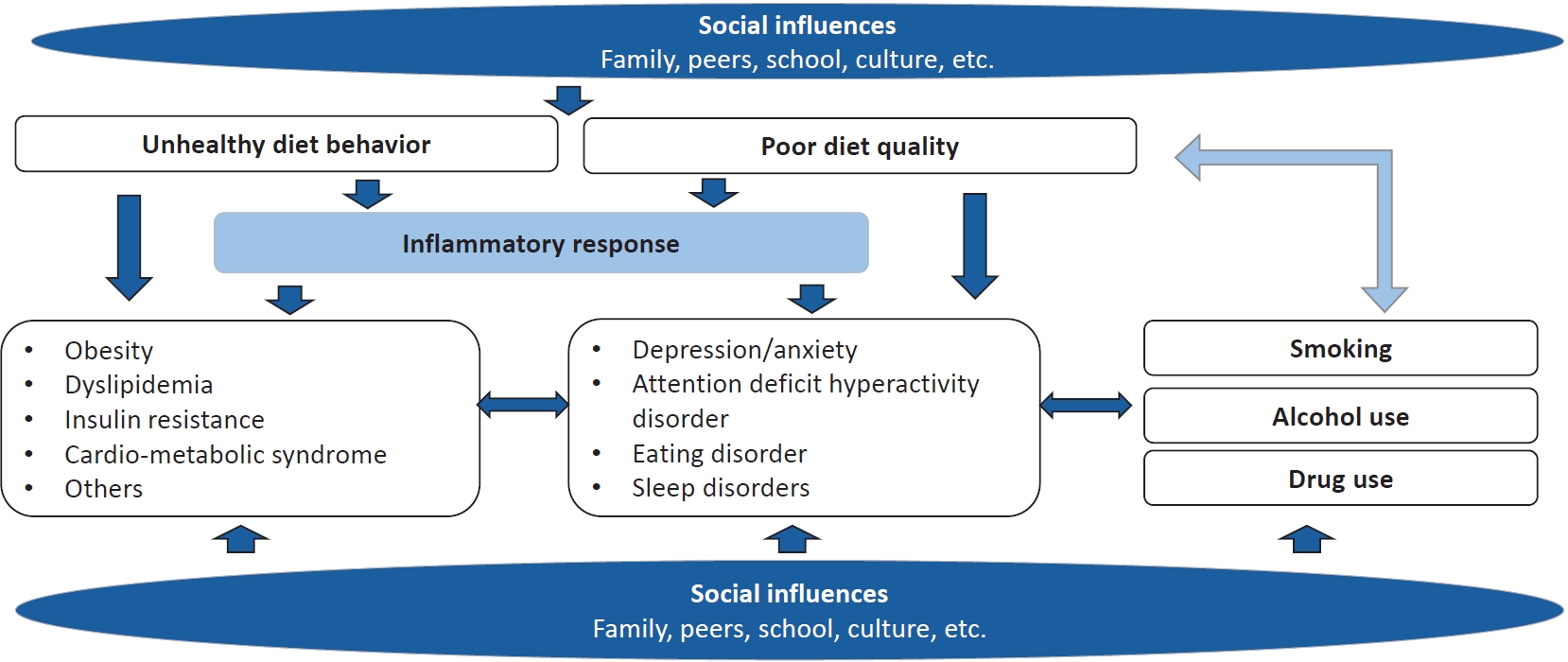
· Diet behaviors in children and adolescents are influenced by environmental and sociocultural factors.
· Unhealthy diet behaviors and poor diet quality are the main contributing factors to noncommunicable diseases and mental health problems during childhood and adolescence.
· Smoking and alcohol drinking in children and adolescents may be associated with unhealthy diet behavior or poor diet quality.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Recent updates on systemic treatment of atopic dermatitis
- Jiyoung Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):580-588. Published online November 1, 2024
-
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a complex disease with multifactorial pathogenesis and variable clinical presentation. Up to one-fifth of patients with AD develop moderate to severe disease that is often refractory to classical therapies and can compromise quality of life. This review summarizes recent clinical evidence on biological agents and small-molecule immunotherapies for the treatment of AD.
- Clinical Note
- Immunology
- Comparative analysis of rare periodic fever syndromes including the first Korean case of hyperimmunoglobulinemia D and periodic fever syndrome
- Yoonsun Yoon, Hyun Seo Kim, Jung Ok Shim, JungHwa Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):550-552. Published online September 24, 2024
-

- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents: prevalence and associated factors
- Jee-Seon Shim, Jeong Mi Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):531-539. Published online September 24, 2024
-

Question: How prevalent is energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents and what are the associated factors?
Findings: The prevalence of energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents increased from 3.2% in 2014 to 12.2% in 2019. Energy drink consumption varies according to sociode-mographic and individual factors.
Meaning: Policies and educational strategies are needed to reduce energy drink consumption in adolescents.
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- Arrhythmias in pediatric patients with COVID-19
- Ji-Eun Ban
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):348-349. Published online June 14, 2023
-
· Childrens with coronavirus disease 2019 less commonly display life-threatening arrhythmias, including premature atrial or ventricular beats, or conduction disturbances such as first-degree atrioventricular blocks.
· Life-threatening arrhythmias (e.g., nonsustained or sustained ventricular tachycardia, atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, complete atrioventricular block) occur in children with sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection suffering from myocarditis or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C).
· Monitoring clinical status and assessing and managing arrhythmias are crucial in MIS-C.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
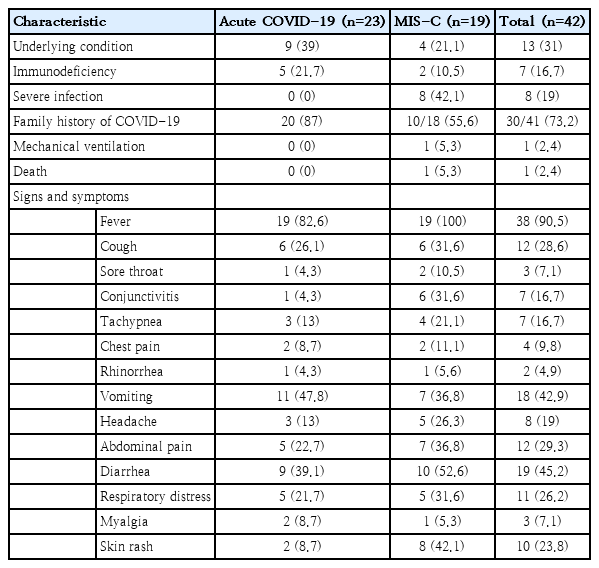
- SARS-CoV-2 fecal shedding pattern in pediatric patients with acute COVID-19 or COVID-19-associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome
- Setareh Mamishi, Fatemeh Jalali, Sepideh Benvari, Babak Pourakbari, Mohammad Reza Abdolsalehi, Reihaneh Hosseinpour Sadeghi, Mohammad Shahbabaie, Amene Navaeian, Shima Mahmoudi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):366-368. Published online June 14, 2023
-
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Trends of vitamin D in asthma in the pediatric population for two decades: a systematic review
- Myongsoon Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):339-347. Published online June 14, 2023
-
· Vitamin D may affect asthma via multiple mechanisms, including lung and optimal immune system functions.
· Many clinical trials have demonstrated the beneficial effects of vitamin D on asthma onset and aggravation. However, definitive clinical trials are lacking, and reports have detailed contradictory effects of vitamin D in children with asthma.
· Some exciting reports stated that obesity and vitamin D deficiency are associated with increased asthma symptoms in the pediatric population.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
- Chest x-ray findings in children with COVID-19: lesson learned from referral hospitals in Medan, North Sumatera, Indonesia
- Andrew Limavady, Eka Airlangga, Ririe Fachrina Malisie, Ayodhia Pitaloka Pasaribu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):317-319. Published online May 16, 2023
-
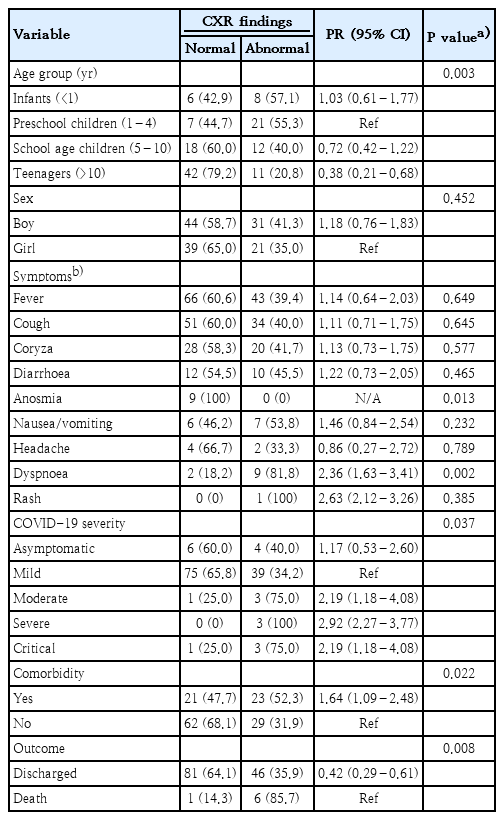
- Original Article
- Infection
- Seroprevalence of maternal peripartum human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the Nigerian literature
- Abdulrasheed Usman, Muhammad Hamis Musa, Bukhari Isah Shuaib, Olayemi Balogun, Mukhtar Adeiza
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):307-316. Published online December 22, 2022
-
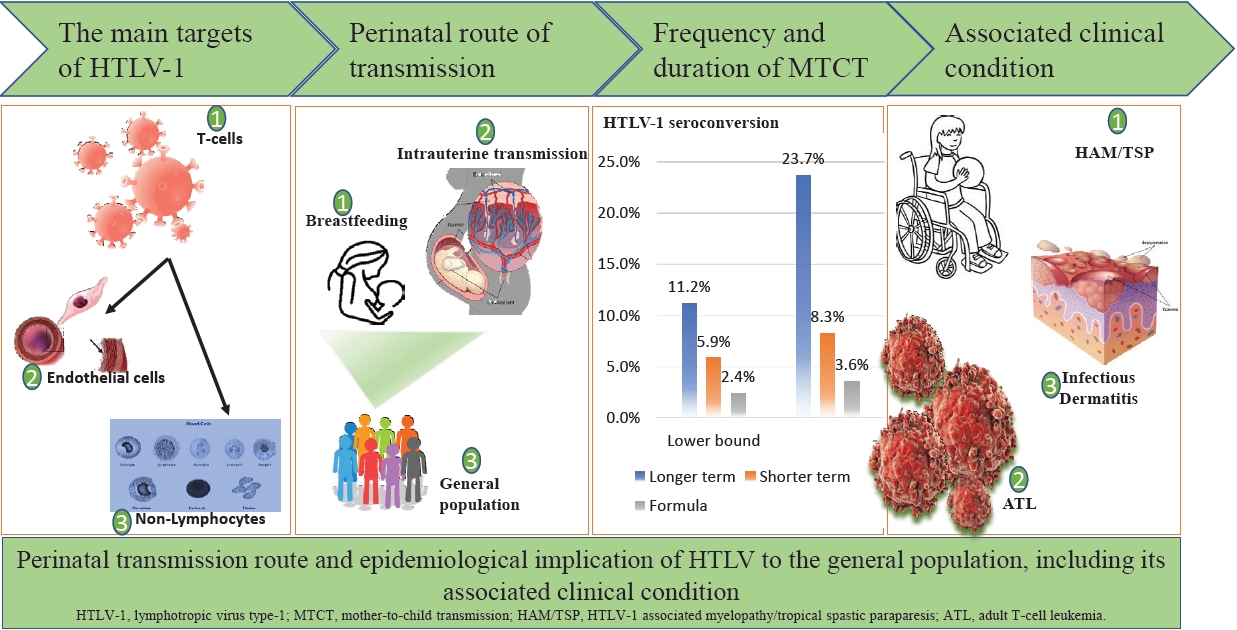
The peripartum period is an important transmission time for human T-cell lymphotropic virus-1 (HTLV-1) infection, mainly via breastfeeding and partly through the placental tissues of carrier mothers. Although most HTLV-1–infected individuals are asymptomatic, fetal and childhood infections often result in several diseases with disappointing treatment outcomes. An estimated HTLV-1 burden in Nigeria among perinatal women must be determined to enable rational planning of a comprehensive health care intervention.
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Gut microbiota’s impact on obesity
- Sujin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):294-295. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· An imbalance of the gut microbiota with a relative increase in Firmicutes versus Bacteroidetes is associated with the pathogenesis of obesity.
· Dysbiosis is associated with microbial genes associated with short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) production and increased colonic SCFA levels. SCFAs have also been shown to regulate appetite and satiety hormones, which can affect food intake and energy balance.
· A dietary high-fat intake is reportedly associated with increased plasma lipopolysaccharide. Altered Toll-like receptor-4 signaling leads to propagating the cascade of further inflammation and promoting insulin resistance.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.












