Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents: prevalence and associated factors
- Jee-Seon Shim, Jeong Mi Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):531-539. Published online September 24, 2024
-

Question: How prevalent is energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents and what are the associated factors?
Findings: The prevalence of energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents increased from 3.2% in 2014 to 12.2% in 2019. Energy drink consumption varies according to sociode-mographic and individual factors.
Meaning: Policies and educational strategies are needed to reduce energy drink consumption in adolescents.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effect of pesticide exposure on stunting incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Yaltafit Abror Jeem, Muhammad Fathi Banna Al Faruqi, Mahdea Kasyiva, Vita Widyasari, Kuswati Kuswati, Nur Aini Djunet, Muflihah Rizkawati, Ety Sari Handayani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):510-518. Published online September 24, 2024
-

This review aimed to determine whether pesticide exposure is associated with stunting in children. The 13 included studies agree that pesticide exposure is not correlated with stunting incidence regardless of substance type (organophosphate and pyrethroid). Heterogeneity appeared with age covariate as potential confounding. The evidence of this study is challeng-ing, as the adverse effects of pesticides grossly occurred. The protection of children is warranted for preventing future neurodevelopment issues.
- Screen time among preschoolers: exploring individual, familial, and environmental factors
- Sangha Lee, Donghee Kim, Yunmi Shin
-
Background: Screen-based activity refers to the use of screened devices, which are changing from stationary devices such as televisions and desktop computers to newer portable devices such as smartphones and electronic tablets. The exposure of younger children to all types of screened devices has increased.
Purpose: This review aimed to provide an overview of previous studies and identify the correlations... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2023.01746 [Accepted]
- Double-negative T cells in pediatric rheumatic diseases
- Dimitri Poddighe, Tilektes Maulenkul, Kuanysh Dossybayeva, Gulsamal Zhubanova, Zaure Mukusheva, Lyudmila Akhmaltdinova
-
Double-negative (CD4-CD8-) T (DNT) cells have been implicated in Autoimmune Lymphoproliferative Syndrome (ALPS), where their expansion inside the circulating pool of T cells represents a diagnostic criterion. Recent experimental evidence has supported the immunomodulatory roles of DNT cells, and studies in adult patients have suggested that they may be altered in some immune-mediated conditions. This study aimed to retrieve available... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2023.01760 [Accepted]
- Original Article
- Comparative analysis of adolescent hypertension definitions for predicting early-adulthood carotid artery intima-media thickness: Tehran lipid and glucose study
- Maryam Barzin, Shirin Yaghoobpoor, Maryam Mahdavi, Behnaz Abiri, Majid Valizadeh, Fereidoun Azizi, Pooneh Dehghan, Farhad Hosseinpanah
-
Background: Definitions of childhood and adolescent hypertension (HTN) do not precisely elucidate the relationship between HTN and cardiovascular outcomes. Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT), as a substitute for cardiovascular outcomes, enables the early identification of cardiovascular events throughout early adulthood.
Purpose: This study aimed to compare the ability of childhood HTN definitions to predict a high CIMT in early adulthood. Methods:... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.00248 [Accepted]
- Role of proper postnatal care in continued exclusive breastfeeding among young Indonesian mothers
- Wahyu Triadmajani, Shinta Prawitasari, Abdul Wahab
-
Background: Exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) provides numerous health benefits to children. However, the EBF rate is unsatisfactory among young mothers because they often experience difficulties. Thus, interventions during the postnatal period are imperative to encouraging EBF practices in these populations. Postnatal care (PNC) should be delivered appropriately to ensure a positive postnatal experience; however, there has been little discussion of evidence... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.00815 [Accepted]
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Interleukin (IL)-1B and IL-1 receptor antagonist gene polymorphisms in children with primary immune thrombocytopenia
- Seham Mohamed Ragab, Wafaa Moustafa Abo ElFotoh, Mahmoud Ahmed El-Hawy, Eman Abdelfatah Badr, Saara Khairat Ali Mostafa, Mai El-Sayad Abd El-Hamid
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):465-473. Published online July 24, 2024
-

· Polymorphisms in interleukin (IL)-1B and IL-1 receptor (IL-1R) antagonists may significantly affect the pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP).
· IL-1B and IL-1R antagonist gene polymorphisms are correlated with severity and susceptibility to primary ITP in children.
- Infection
- Construction and validation of predictive models for intravenous immunoglobulin–resistant Kawasaki disease using an interpretable machine learning approach
- Linfan Deng, Jian Zhao, Ting Wang, Bin Liu, Jun Jiang, Peng Jia, Dong Liu, Gang Li
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):405-414. Published online July 23, 2024
-

Question: Is there a reliable model to predict intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)-resistant Kawasaki disease (KD)?
Finding: We constructed 5 machine learning models to predict IVIG-resistant KD. Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) model was superior to logistic, support vector machine, light gradient boosting machine and multiple layers perception models. The SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) value interpreted the contribution of each feature in XGBoost model.
Meaning: XGBoost model showed the excellent performance to predict IVIG-resistant KD with explainable and visualizable machine learning algorithm.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Neonatal risk factors associated with autism spectrum disorders: an umbrella review
- Amir Mohammad Salehi, Erfan Ayubi, Salman Khazaei, Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Zohreh Salimi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):459-464. Published online July 19, 2024
-

Question: What are the neonatal risk factors for autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Findings: Significant effect sizes were observed for congenital heart disease (odds ratio [OR], 1.35), macrosomia (OR, 1.11), low birth weight (OR, 1.63), very low birth weight (OR, 2.25), small for gestational age (OR, 1.17), jaundice (OR, 1.74), male sex (OR, 1.47), and Apgar score (OR, 1.40).
Meaning: These factors were identified as risk factors for ASD.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Demographic transition in South Korea: implications of falling birth rates
- Chae Young Kim, Sung-Hoon Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):498-509. Published online June 27, 2024
-

· Since 1960, South Korea's TFR decreased from 6.33 to 0.78 in 2022, below the 2.1 replacement level since 1983, with women's average age at first marriage rising to 31.3 in 2022.
· Policies needed: financial incentives, longer parental leave, better childcare.
· The U.S. (15.3% immigrants) and Germany (18.8%) use immigration to maintain demographic stability, a strategy South Korea is considering.
- Endocrinology
- Two- versus one-bag fluid delivery in pediatric and adolescent diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Maya L. Nasser, Joseph Nasr, Reem B. Zalloum, Nathanael Q.E. Yap, Natalie E. Bourdakos, Shahid Miangul, Tara A. Betts, Hayato Nakanishi, Christian A. Than, Serge Jabbour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):486-497. Published online June 27, 2024
-

· The safety and efficacy of the two-bag versus one-bag system for treating patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) < 21 years remains unestablished.
· Our meta-analysis demonstrated similar safety outcomes but sooner DKA resolution and shorter mean response time for intravenous fluid changes for the two-bag system.
· This preliminary evidence suggests that the two-bag system has some advantages in efficacy, but further studies are needed to evaluate their extent.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Parental support and exclusive breastfeeding at 3 months in West Java, Indonesia: a mixed-methods approach
- Ratu Ayu Dewi Sartika, Fadila Wirawan, Wawan Gunawan, Primasti Nuryandari Putri, Nurul Husna Mohd Shukri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):358-367. Published online June 21, 2024
-
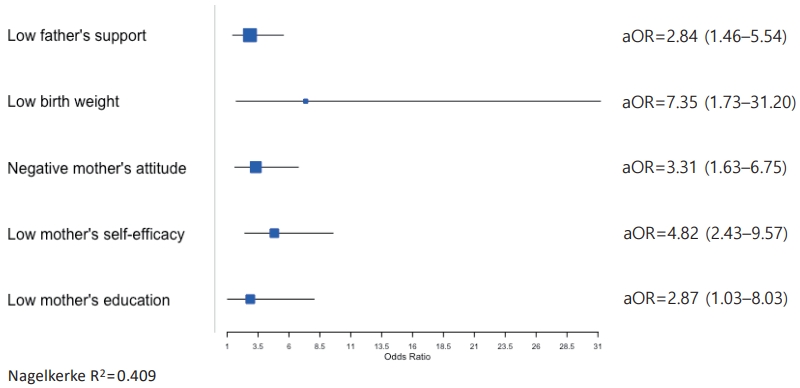
Question: Does paternal support affect exclusive breastfeeding failure?
Finding: Exclusive breastfeeding failure by 3 months was affected by paternal support.
Meaning: Fathers should be included in breastfeeding education and antenatal care.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Comprehensive evaluation of the child with global developmental delays or intellectual disability
- Abdullah Nasser Aldosari, T. Saeed Aldosari
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):435-446. Published online May 29, 2024
-

· A detailed history and comprehensive physical examination remain the cornerstones for establishing a diagnosis of global developmental delay/intellectual disability (GDD/ID).
· Comprehensive surveillance and screening programs play a significant role in the early detection of GDD.
· Whole-exome sequencing is highly recommended as first- or second-line testing for individuals with idiopathic GDD/ID.
· Early intervention by a well-versed multidisciplinary team can significantly improve the outcomes and prognosis of GDD/ID.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effectiveness of online responsive teaching in young children with developmental disabilities: a pilot study
- Jung Sook Yeom, Jeongmee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):303-311. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Question: Does online responsive teaching (RT) impact children's and parents’ emotions and behaviors, and do parents find it satisfactory?
Finding: Online RT significantly improved children's pivotal and problem behaviors, decreased parenting stress, and enhanced parental interactive styles with high satisfaction.
Meaning: This pilot study's findings suggest that online RT can enhance child outcomes, offering accessible interventions amid challenges such as limited access and pandemics.
- Endocrinology
- Kisspeptin and DLK1 levels for monitoring treatment of girls with central precocious puberty
- Witchuwan Onsoi, Nattakarn Numsriskulrat, Suphab Aroonparkmongkol, Vichit Supornsilchai, Khomsak Srilanchakon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):296-302. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Questions: Can the serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 be potential biomarkers for monitoring the treatments for central precocious puberty (CPP)?
Findings: There were no significant differences in the baseline serum kisspeptin and DLK1 levels in CPP girls compared to girls with premature thelarche (PT). After 6 months of GnRH analogue treatment in CPP girls, median serum kisspeptin levels decreased, while median serum DLK1 levels increased compared to baseline.
Meanings: Serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 may serve as novel biomarkers for monitoring the efficacy of treatments for CPP.
- Review Article
- Hematology
- Iron deficiency in children with a focus on inflammatory conditions
- Na Hee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):283-293. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· Iron deficiency has important effects on neurodevelopment and the immune system in children.
· Hepcidine plays an important role in iron homeostasis.
· Diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency in chronic inflammatory disease are important for patients' quality of life and disease course.
- Other
- Use of virtual reality in children in a broad range of medical settings: a systematic narrative review of recent meta-analyses
- Emily Antonovics, Grammatina Boitsios, Thomas Saliba
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):274-282. Published online May 21, 2024
-
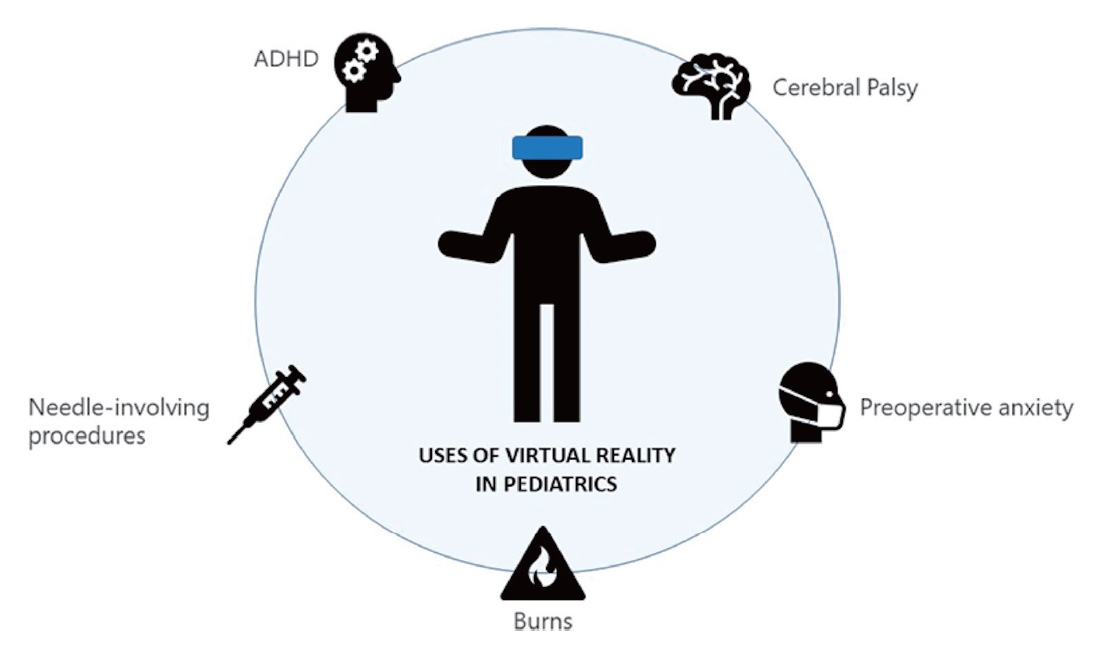
· Virtual reality (VR) is becoming increasingly common for entertainment and in medical settings.
· VR is useful for treating children with cerebral palsy.
· VR can help with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms.
· VR can decrease pain perception in children undergoing burn wound care.
· VR can reduce preoperative anxiety.
· VR can reduce fear and pain during needle-involving procedures.
- Allergy
- Action-plan and as-needed therapy in allergic rhinitis
- Hyeon-Jong Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):267-273. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· The guidelines may not work in the real world.
· An action-plan reflecting patient’s severity and variable of symptoms, values and preferences as well as the benefits and harms of treatment, may be a useful alternative.
· The action plan and as-needed therapy must include the following elements: when, what, how, and why.
· Action plan and as-needed therapy can help patients manage their symptoms more effectively.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Oligohydramnios affects pulmonary functional/structural abnormalities in school-aged children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Jeong Eun Shin, Soon Min Lee, Mi-Jung Lee, Jungho Han, Joohee Lim, Haerin Jang, Ho Seon Eun, Min Soo Park, Soo Yeon Kim, Myung Hyun Sohn, Ji Ye Jung, Kyung Won Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):257-266. Published online April 16, 2024
-

Question: Is bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) associated with functional/structural abnormalities later in life?
Finding: School-aged children with severe BPD had abnormalities on pulmonary function tests and lung computed tomography despite no subjective respiratory symptoms; however, only prenatal oligohydramnios and prolonged ventilator use were associated with abnormal lung function.
Meaning: Long-term monitoring of preterm infants’ lung health is essential, especially for those with prenatal oligohydramnios or prolonged ventilator use.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Incidence, causative organisms, and risk factors of bloodstream infections in pediatric liver transplant patients: a systematic review
- Mohamad Shieb, Rand Hasanain, Zara Arshad, Faisal A. Nawaz, Rahul Kashyap, Eric J. Stern
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):427-434. Published online April 5, 2024
-

The overall incidence of bloodstream infections was 23.5%. Gram-negative organisms occur at a much higher rate in pediatric liver transplant recipients then that the general pediatric population. However, when comparing pediatric and adult liver transplant recipients Gram-positive organisms occur with a much higher rate in the pediatric population highlighting the importance of early and broad spectrum antimicrobial coverage when bloodstream infections are suspected.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effect of vitamin E supplementation on bilirubin levels in infants with hyperbilirubinemia: a double-blind randomized clinical trial
- Mojtaba Cheraghi, Maziar Nikouei, Majid Mansouri, Siros Hemmatpour, Yousef Moradi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):249-256. Published online March 26, 2024
-
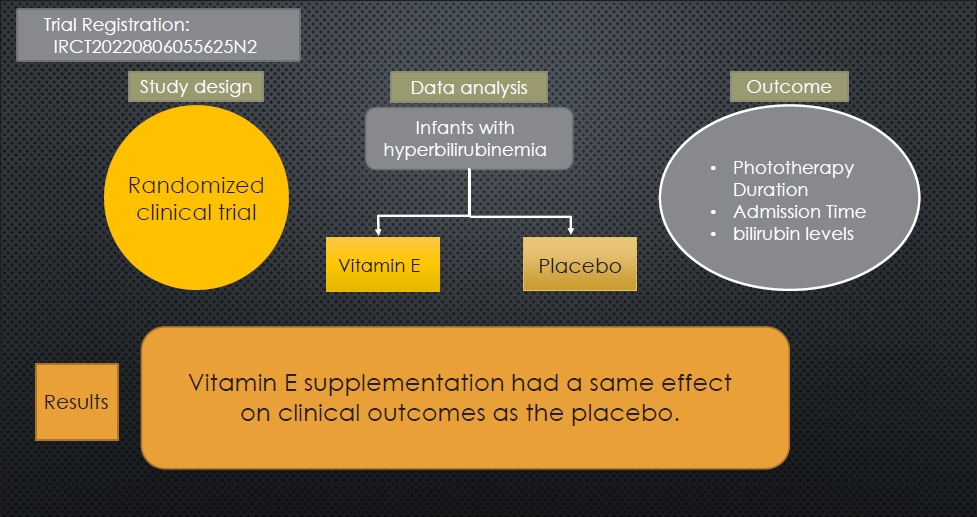
Question: Is vitamin E a viable therapeutic option for managing neonatal hyperbilirubinemia?
Finding: This randomized clinical trial examined the effects of oral vitamin E supplementation on bilirubin reduction (primary outcome), phototherapy duration, and length of hospital stay (secondary outcome) in 138 infants.
Meaning: Infants administered vitamin E versus placebo demonstrated similar reductions in bilirubin levels and length of hospital stay.
- Nutrition
- Effect of probiotics plus zinc supplementation on clinical outcomes of infants and children with acute infectious diarrhea: a randomized controlled trial
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Saad Jbraeil Sulaiman, Zaid Waad Ahmed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):203-212. Published online February 19, 2024
-

Question: Does zinc supplementation along with probiotics affect disease severity or clinical outcomes of children with acute diarrhea?
Findings: This study indicated that zinc supplementation and probiotics had no effect on clinical improvement or disease severity among pediatric patients with acute diarrhea.
Meaning: Children who received probiotics plus zinc recovered faster than those who received probiotics only.
- Cardiology
- Effect of face mask on pulmonary artery pressure during echocardiography in children and adolescents
- Alireza Ahmadi, Mohammad Reza Sabri, Zohreh Sadat Navabi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):161-167. Published online January 23, 2024
-
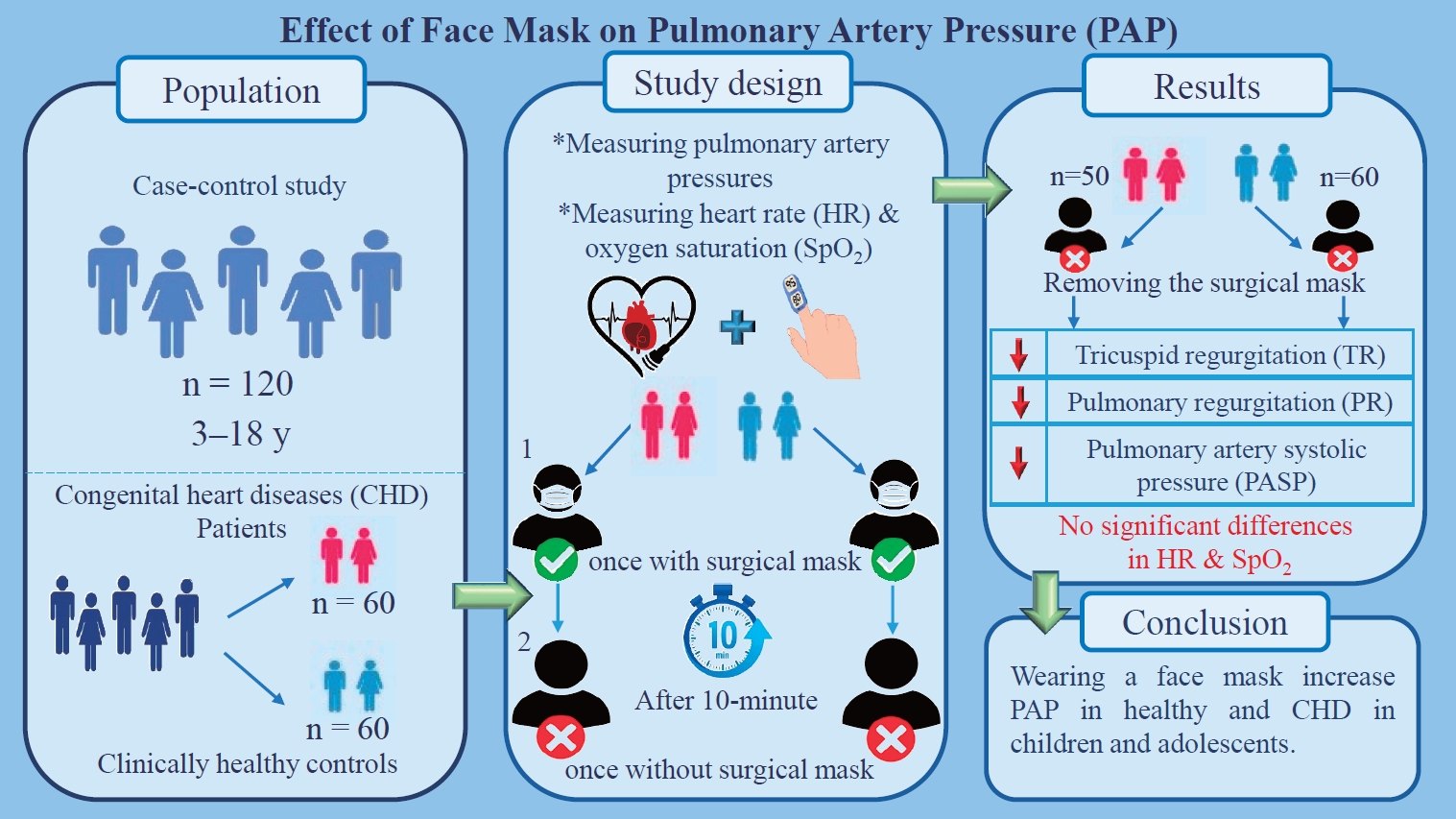
Question: Can face masks alter pulmonary pressure in children and adolescents with and without congenital heart disease?
Findings: Mask removal during echocardiography (ECHO) reduced pulmonary pressure.
Meaning: These findings suggest that face masks should be removed during ECHO in children and adolescents.
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Effects of diethylene glycol contamination of pharmaceutical products on unexplained acute kidney injury in children: a systematic review
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Muhammad Luthfi Adnan, Hilmi Ardian Sudiarto, Satria Bintang Mahathma, Alya Ayu Tazkia, Hana Afifah Firdaus, Alfreda Amelia Khotijah, Miranti Dewi Pramaningtyas, Emi Azmi Choironi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):395-402. Published online January 4, 2024
-

A recent unexplained acute kidney injury (AKI) outbreak due to pharmaceutical product contamination with diethylene glycol (DEG) raises public attention. Our study revealed that DEG-contaminated paracetamol causes unexplained AKI in children. However, paracetamol is not the only contaminated drug. Other drugs, such as cough expectorants, antihistamines, and sedatives, can also be affected. Other chemicals, such as ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, can also contribute to poisonings.
- Allergy
- Recent advances in food allergen immunotherapy
- You Hoon Jeon, Edwin H. Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):386-394. Published online December 7, 2023
-

· To enhance the safety of food allergen immunotherapy, alternative approaches such as sublingual immunotherapy, epicutaneous immunotherapy, low-dose oral immunotherapy (OIT), and omalizumab with OIT are being explored.
· Factors such as causative allergen type, natural outgrowth, symptom severity, and patient age should be considered.
· Individualized food allergen immunotherapy plans should be established to determine the most beneficial treatment for each patient.
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Effectiveness of Helmet therapy for infants with moderate to severe positional plagiocephaly
- Jeongho Kim, Jina Kim, Kyu Young Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):46-53. Published online December 5, 2023
-
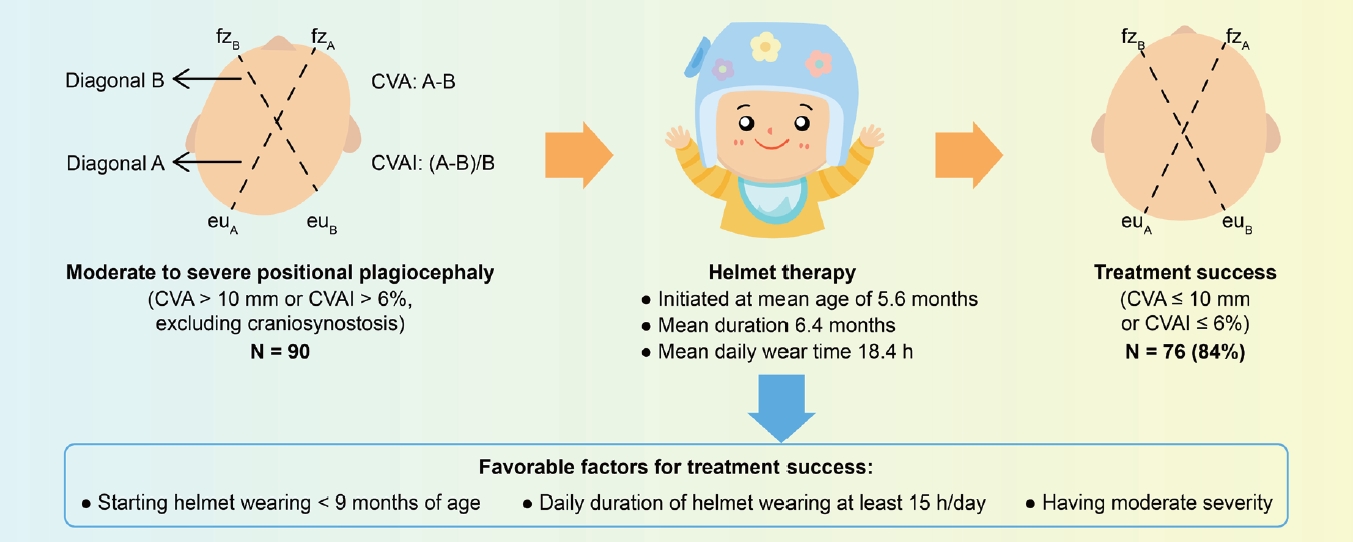
Question: Is helmet therapy effective for positional plagiocephaly? What factors influence helmet therapy efficacy for positional plagiocephaly?
Finding: Helmet therapy is effective for infants with moderate to severe positional plagiocephaly, and its effectiveness is influenced by age at treatment initiation, severity of head asymmetry, and daily duration of helmet wear.
Meaning: Pediatricians should initiate helmet therapy for positional plagiocephaly sooner, ideally before 9 months of age, to maximize treatment efficacy.
- Review Article
- Infection
- COVID-19 among infants: key clinical features and remaining controversies
- Nevio Cimolai
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):1-16. Published online November 27, 2023
-
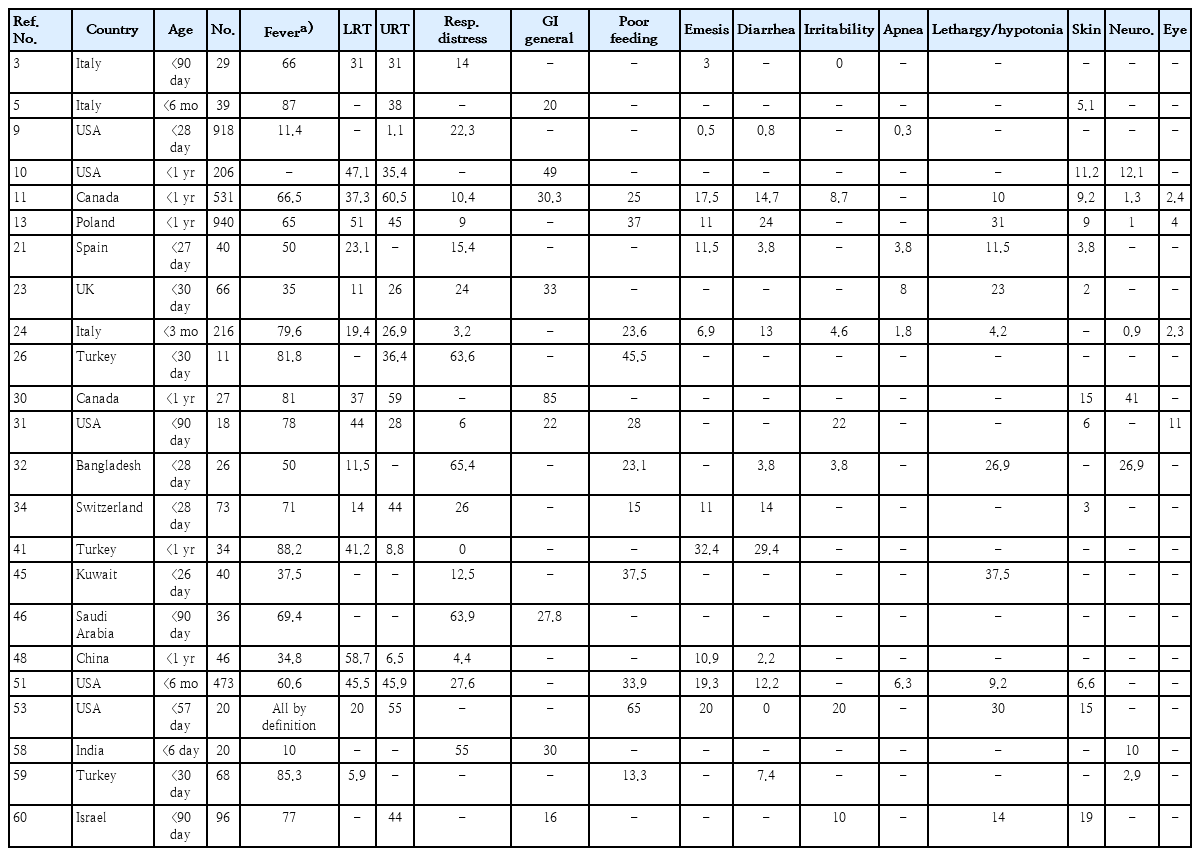
· Clinical studies of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in infants should be supported by rigorous laboratory diagnostic criteria.
· Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spreads to infants similarly to other viral respiratory infections.
· Among infants ≤1 year of age beyond the immediate postpartum period, COVID-19 is relatively mild, but even the low risk of severe disease requires prevention.
· Comorbidities increase infection vulnerability and complications in infants.
· Clinical and laboratory data do not sufficiently distinguish COVID-19 from other respiratory viral infections.
· Coinfection with SARS-CoV-2 is uncommon among infants.
· Unique infection sequelae, including multi-inflammatory syndrome in children and neonates and long COVID require further study and refinement of diagnostic criteria.
· Infection control standards applied to mother-infant dyads should be tempered by standard preventive strategies, maternal input, accommodation potential, and overall safety.
· Maternal vaccination prevents disease in early infancy.
- General Pediatrics
- Metabolic complications of obesity in children and adolescents
- Hyunjin Park, Jung Eun Choi, Seunghee Jun, Hyelim Lee, Hae Soon Kim, Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):347-355. Published online November 16, 2023
-
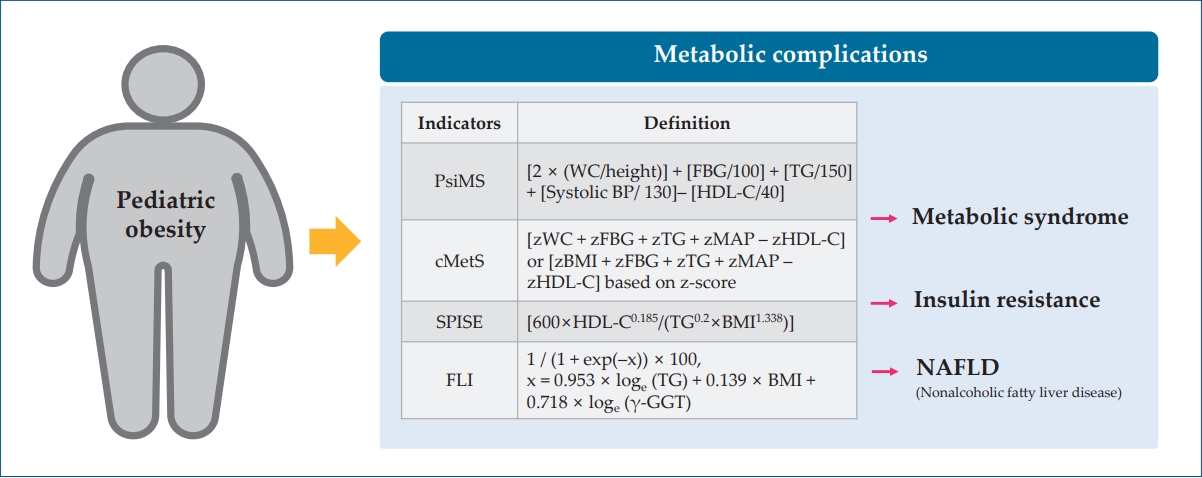
· Pediatric obesity increases the risk of metabolic complications (insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease) and long-term cardiovascular diseases.
· A new obesity definition and various indicators (continuous metabolic syndrome score, pediatric simple metabolic syndrome score, fatty liver index) have been proposed to evaluate children’s susceptibility to metabolic disorders.
· Laboratory and body composition tests in pediatric screenings can identify groups at high risk of metabolic complications of obesity.
- Endocrinology
- Association between pre- and postnatal exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals and birth and neurodevelopmental outcomes: an extensive review
- Ozge Yesildemir, Mensure Nur Celik
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):328-346. Published online November 16, 2023
-
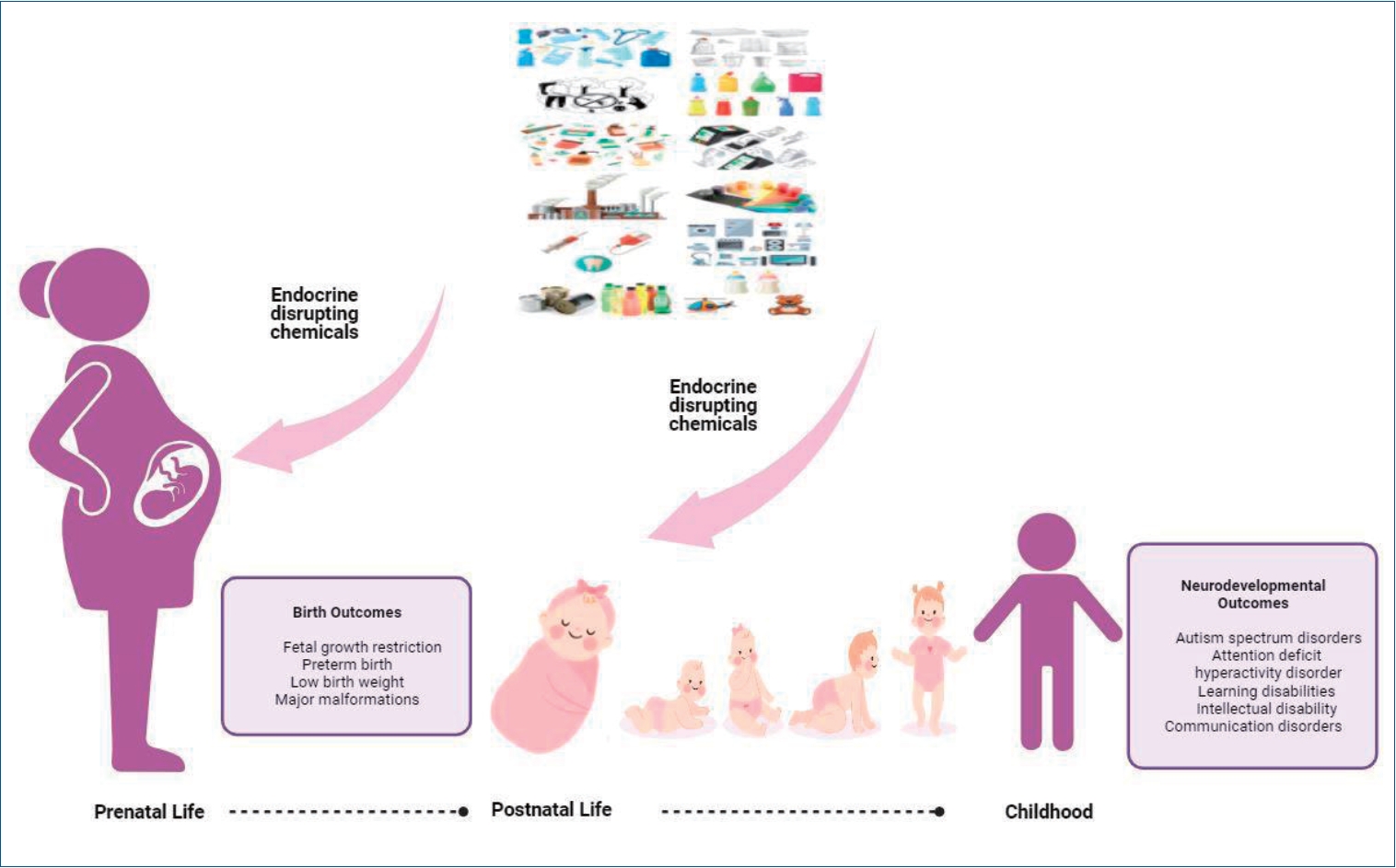
· Sensitivity to endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC) exposure increases during critical developmental periods (in embryos, fetuses, and neonates).
· Pre- and postnatal exposure to EDCs is associated with fetal growth restriction, preterm birth, and low birth weight.
· Exposure to EDCs during fetal and early postnatal life can have lasting and lifelong neurodevelopmental outcomes, including autism spectrum, attention deficit hyperactivity, and other cognitive and behavioral disorders.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Prevalence of anxiety, depression, and stress among parents of neonates admitted to neonatal intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Asha P. Shetty, Kurvatteppa Halemani, Alwin Issac, Latha Thimmappa, Sanjay Dhiraaj, Radha K, Prabhaker Mishra, Vijai Datta Upadhyaya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):104-115. Published online November 14, 2023
-
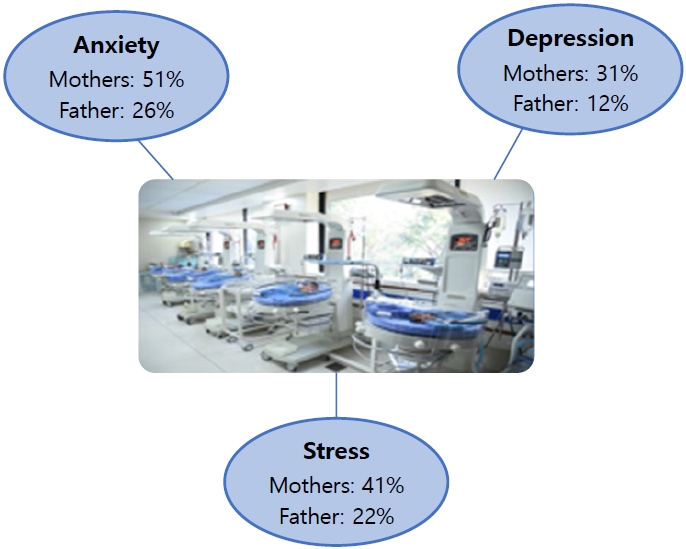
Question: What emotions do parents experience when their newborns are admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)?
Finding: Mothers experienced more anxiety (51%), depression (31%), and stress (41%) symptoms than fathers (26%, 12%, and 22%, respectively).
Meaning: Parents often experience anxiety, stress, and depression following NICU admission. Healthcare workers are responsible for providing regular parental counseling.
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









