Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Long-term follow-up of neurocognitive function in patients with citrin deficiency and cholestasis
- Meng-Ju Melody Tsai, Jung-Chi Chang, Heng-Yu Lu, Susan Shur-Fen Gau, Yin-Hsiu Chien, Wuh-Liang Hwu, Yen-Hsuan Ni, Huey-Ling Chen, Ni-Chung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):257-265. Published online November 28, 2024
-
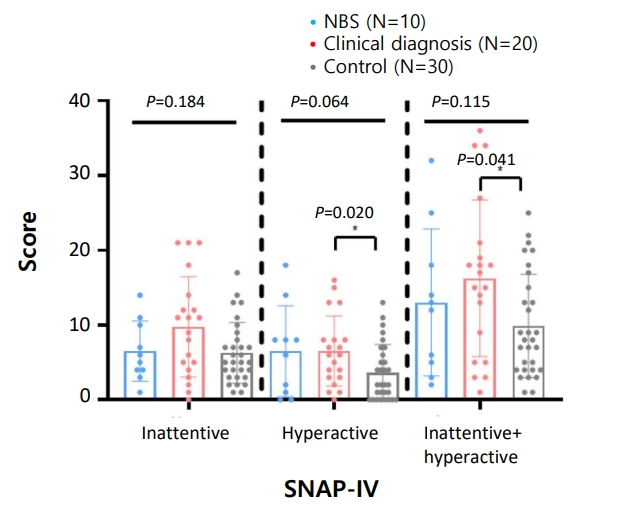
Question: Do transient metabolic disturbances in early childhood due to citrin deficiency have lasting effects on neurocognitive function?
Finding: Children with citrin deficiency have a higher prevalence of ADHD compared to the general population, with elevated ammonia levels in infancy associated with increased hyperactivity-impulsivity risk.
Meaning: Metabolic disturbances in early childhood due to citrin deficiency may contribute to long-term neurocognitive impacts, particularly ADHD, while IQ and life outcomes generally remain normal.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Hidden link between endocrine-disrupting chemicals and pediatric obesity
- Min Won Shin, Shin-Hye Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):199-222. Published online November 28, 2024
-
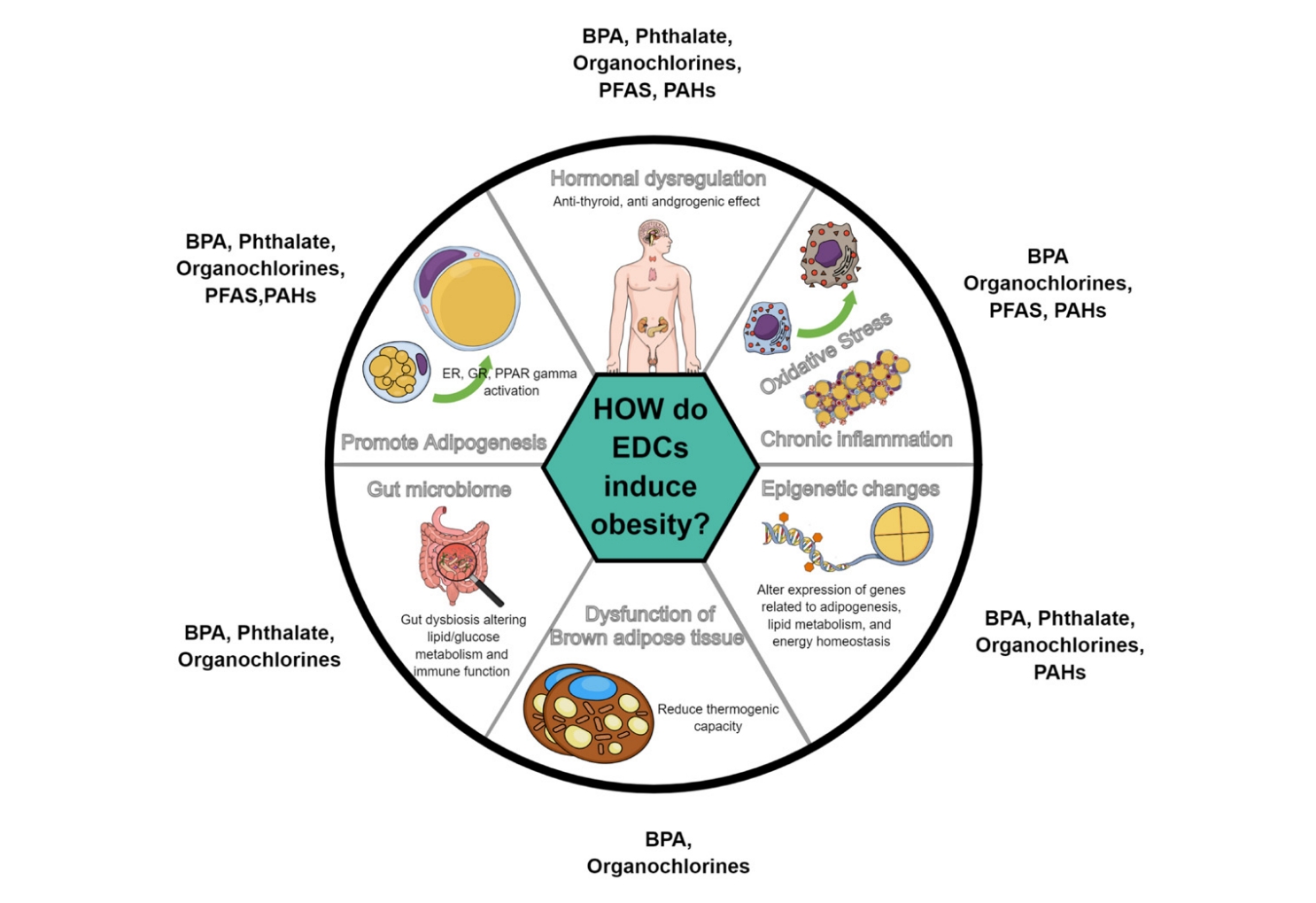
Studies indicate potential connections between exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and childhood obesity. Variations in the impact of EDCs in epidemiological studies may result from differences in exposure concentrations and timing, measurement methods, and interactive effects of multiple EDCs. Longitudinal studies on exposure to multiple EDCs are crucial to elucidating their contribution to pediatric obesity and minimize the adverse health consequences of EDC exposure.
- Letter to the Editor
- Other
- Adolescent hypertension and carotid intima-media thickness: significance of submillimetric differences
- Christian Saleh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):104-105. Published online November 28, 2024
-
- Original Article
- Infection
- Clinical, biochemical, and genetic study of TACE/TNF-α/ACE signaling pathway in pediatric COVID-19 infection
- Ahmed El-Abd Ahmed, Sawsan M.A. Abuhamdah, Mohammed H. Hassan, Nagwan I. Rashwan, Eman A. Abd-Elmawgood, Haggagy Mansour, Hoda S. Sherkawy, Shymaa G. Rizk
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):704-717. Published online November 27, 2024
-
Question: Is the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathway (TNF-α-converting enzyme [TACE]/TNF-α/angiotensin converting enzyme [ACE]) involved in pediatric coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection?
Finding: Significantly increased circulating TACE/TNF-α and decreased ACE2 levels were noted. TNF-α-308G/A plays a significant role in susceptibility to COVID-19 infection among children. The ACE (I/D) (rs4646994) and ACE2 (rs2285666) single nucleotide polymorphisms lack significant associations with pediatric COVID-19 infection.
Meaning: The TNF signaling pathway participates in pediatric COVID-19 infection.
- Clinical Note
- Oncology
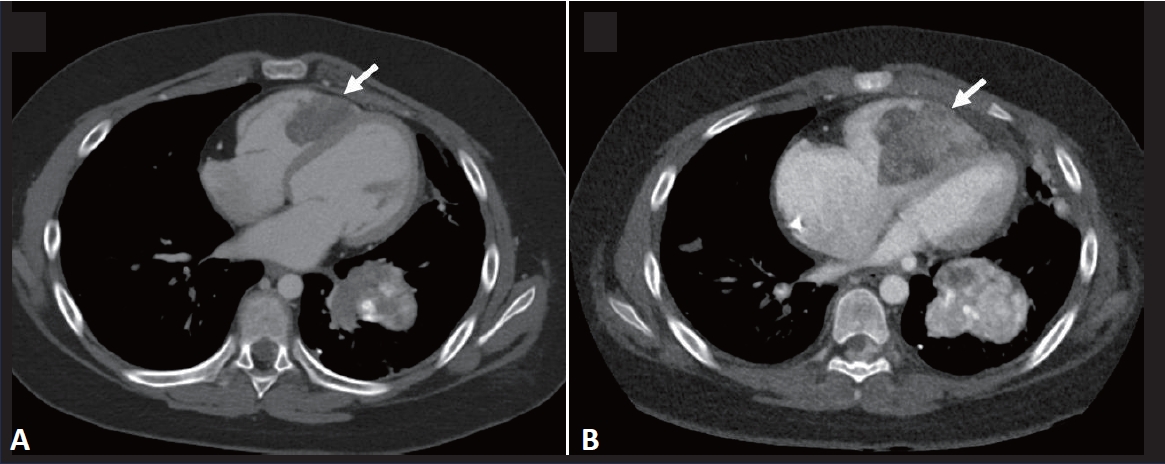
- Right ventricular mass in a 10-year-old girl with osteosarcoma: an unusual case of asymptomatic cardiac metastasis
- Jun Ah Lee, Hyun-Ju Lim, Jong Woong Park, Sang-Hoon Shin, Mi Hyang Kwak
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):725-727. Published online November 26, 2024
-
- Editorial
- Other
- Further research on impact of microplastics on children's health is essential to protecting future generations
- Jongin Lee, Dong-Wook Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):359-361. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· The ecological impacts of microplastics have been documented. It was recently recognized that they can directly or indirectly cause diseases in humans.
· There are few established methods for assessing human exposure to microplastics.
· Standardization of exposure assessments and large-scale epidemiological studies are required to explore the human effects of microplastics.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Impact of obesity on pulmonary function of preschool children: an impulse oscillometry study
- Anuvat Klubdaeng, Kanokporn Udomittipong, Apinya Palamit, Pawinee Charoensittisup, Khunphon Mahoran
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):319-325. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: Does obesity in preschool children affect lung function, and which obesity indices can predict such alterations?
Finding: Preschool children with obesity exhibit impaired lung function characterized by elevated total and peripheral airway resistance. Waist-to-height ratio was the strongest predictor of such changes.
Meaning: Early obesity prevention and treatment are needed. Monitoring waist-to-height ratio, body weight, and body mass index may help identify children at risk of altered lung function.
- Neurology
- Occurrence of stroke in children and young adults in Indonesia: a multicenter private hospital study
- Jeanne Leman, Veli Sungono, Yosua Timotius Haryono, Muhammad Adam Mudzakir, Dewi Lestari Rahmawati, Callistus Bruce Henfry Sulay, Gilbert Sterling Octavius
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):303-310. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: What is the occurrence of pediatric stroke in Indonesia?
Finding: This multicenter study identified 1,074 stroke cases, predominantly hemorrhagic (83.4%), with males and older children at higher risk. Accidents were the primary cause (73.2%).
Meaning: Pediatric stroke in Indonesia shows critical epidemiological trends, highlighting the need for targeted prevention efforts, particularly for high-risk groups like males and accident victims.
- Editorial
- General Pediatrics
- Global breastfeeding efforts: a long way to go
- Hye-Jung Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):300-302. Published online November 13, 2024
-

· Despite much effort, breastfeeding practices remain unsatisfactory worldwide.
· Effective breastfeeding-promoting interventions are needed that are appropriate for age, culture, and social environment.
· Interventions can promote breastfeeding, especially in younger populations such as adolescent mothers.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Outcome of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease in Asian children: a multinational 1-year follow-up study
- Pornthep Tanpowpong, Suporn Treepongkaruna, James Guoxian Huang, Kee Seang Chew, Karen Sophia Calixto Mercado, Almida Reodica, Shaman Rajindrajith, Wathsala Hathagoda, Yoko Kin Yoke Wong, Way Seah Lee, Marion Margaret Aw
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):247-256. Published online November 13, 2024
-
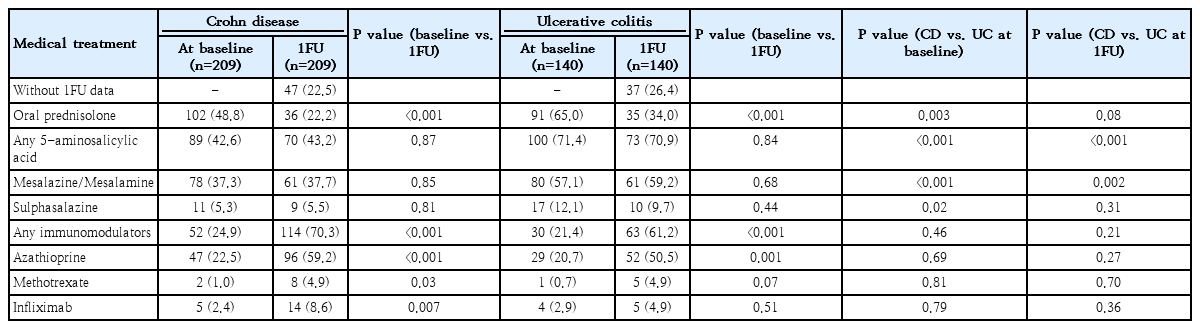
Question: Short-term (1-year) follow-up data in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), especially in Southeast Asian countries, are limited.
Finding/Meaning: Abdominal pain and pallor rates remained high at 1 year after IBD diagnosis. Three independent factors of 1-year clinical remission for Crohn disease were oral prednisolone, antibiotic, and immunomodulator use at 1-year follow-up. A history of weight loss at diagnosis was the only independent risk factor of IBD flare.
- Endocrinology
- Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone score changes in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency
- Pattara Wiromrat, Yutapong Raruenrom, Phanpaphorn Namphaisan, Nantaporn Wongsurawat, Ouyporn Panamonta, Chatlert Pongchaiyakul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):238-246. Published online November 13, 2024
-
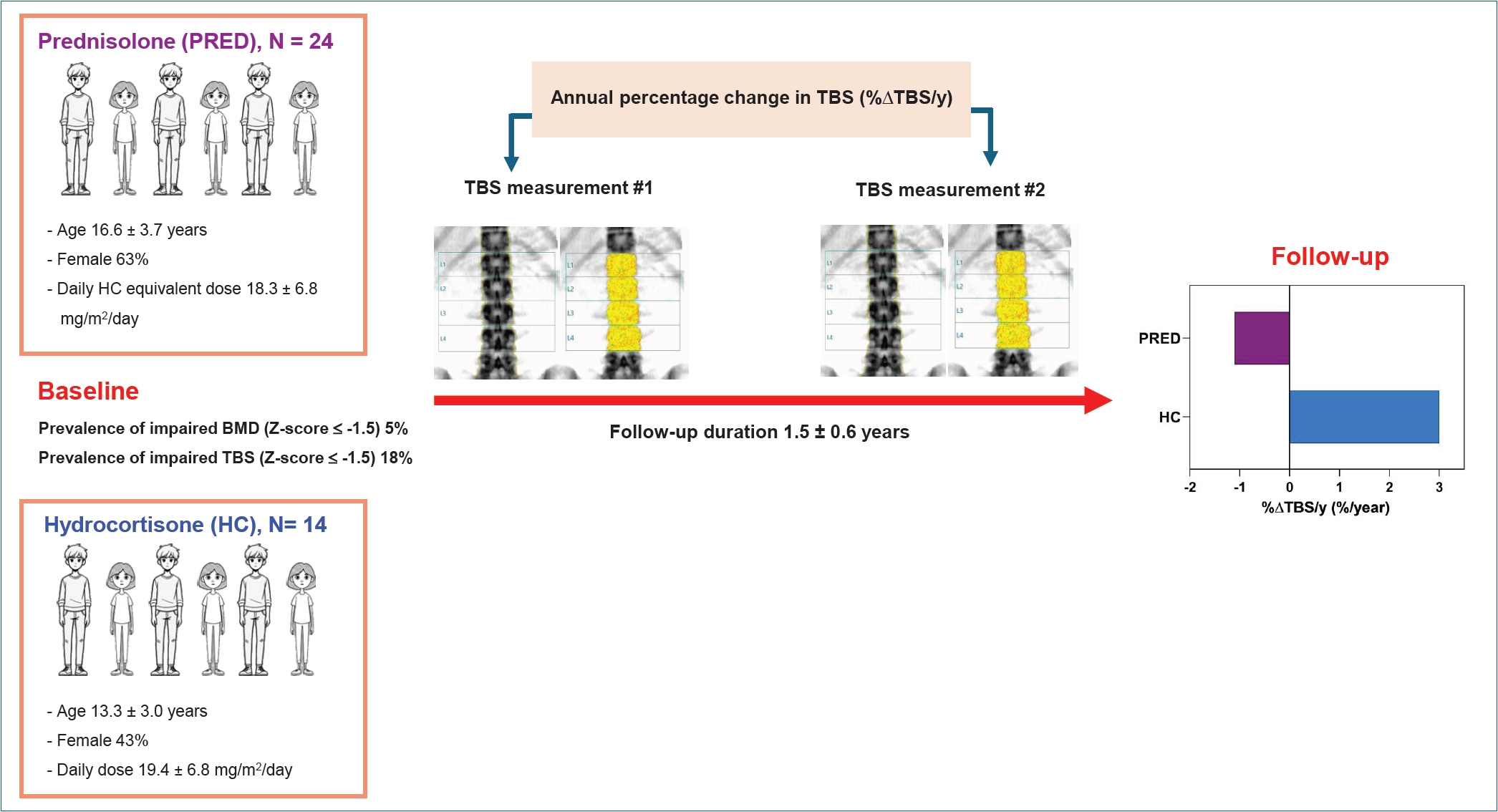
Question: What is the prevalence of an impaired trabecular bone score (TBS), a measure of bone microarchitecture, in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency (21OHD)? Do prednisolone and hydrocortisone affect TBS differently in this patient population?
Finding: Impaired TBS was observed in 18% of participants. Prednisolone use negatively impacted TBS change.
Meaning: Impaired TBS is prevalent among adolescents with 21OHD. Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone microarchitecture development.
- General Pediatrics
- Knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding dengue vaccine: a baseline study of community members and health providers in Indonesia
- Abdul Wahab, Ida Safitri Laksanawati, Retna Siwi Padmawati, Asal Wahyuni Erlin Mulyadi, Wahyu Triadmajani, Jarir At Thobari
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):228-237. Published online November 13, 2024
-
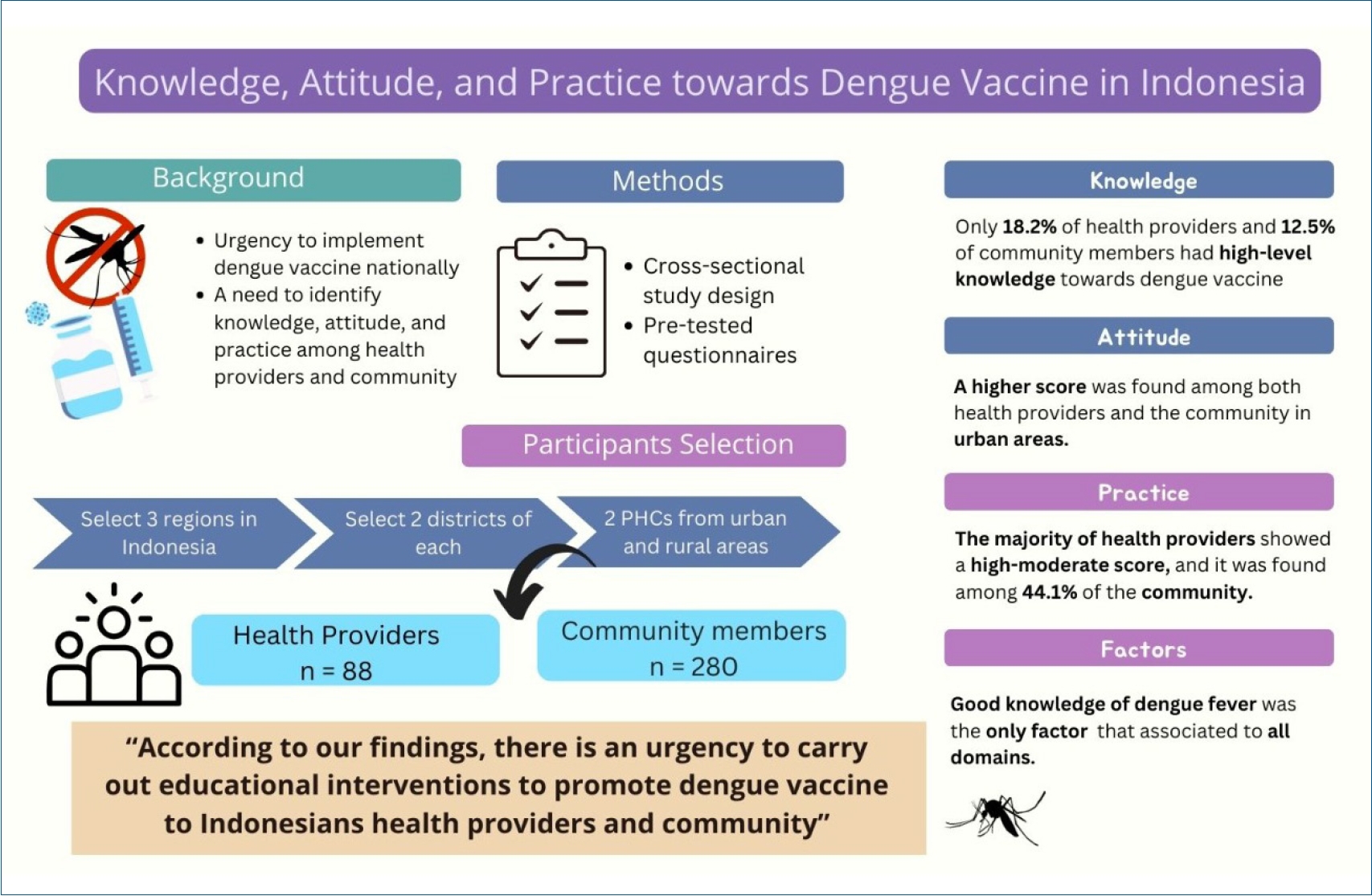
Question: Do community members and health providers show different level of knowledge, attitude, and practice towards dengue vaccine?
Finding: These 2 groups only differed in practice component, while the knowledge and attitude constituents were relatively low for both.
Meaning: There is an urgent need to deliver educational interventions to raise awareness of community members and health providers regarding dengue vaccination.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Practical concepts and strategies for early diagnosis and management of eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders in East-Asian children
- Byung-Ho Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):185-198. Published online November 13, 2024
-
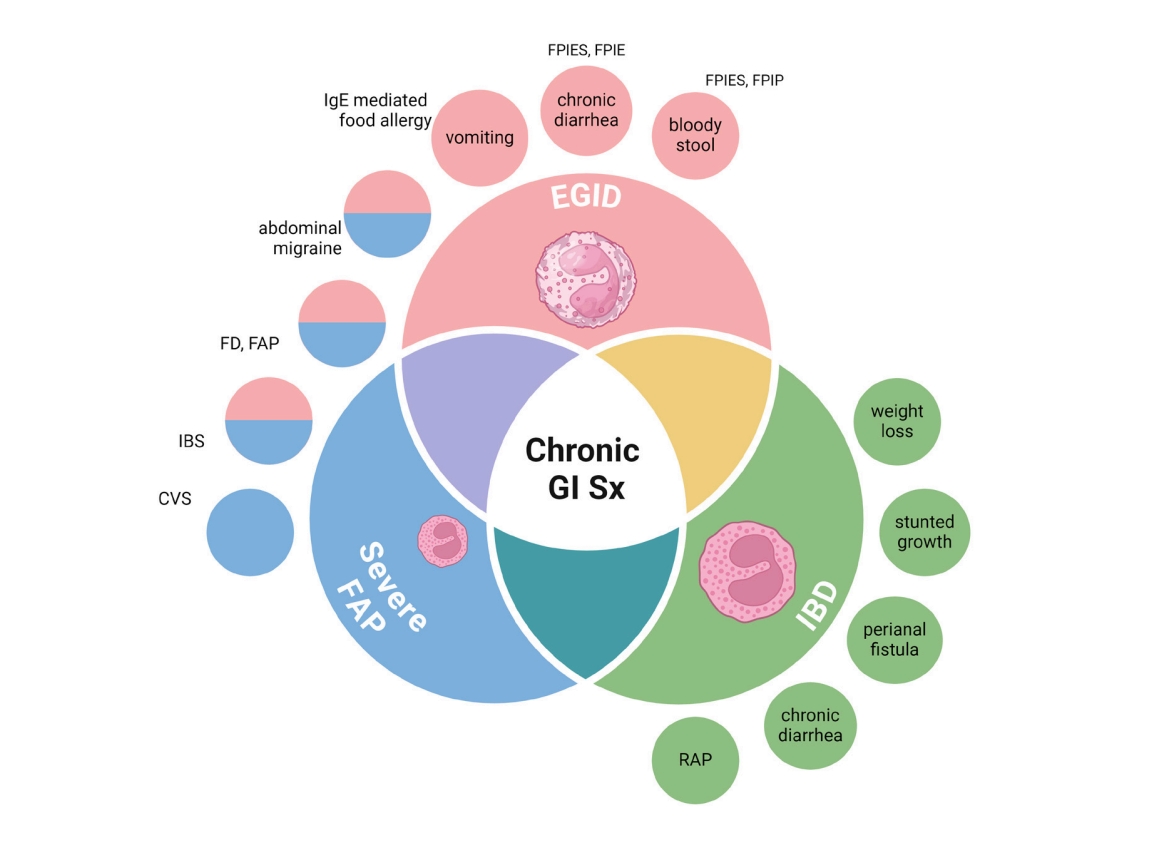
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs) often coexist with functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) and other IgE or non-IgE mediated GI diseases. Diagnosing EGIDs requires a high index of suspicion and a comprehensive approach to differentiate them from conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. Tests such as fecal calprotectin and biopsies aid in severe cases. Maintaining a food diary helps identify triggers for long-term elimination. Awareness and education are key to effective management.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effect of high-frequency oscillatory ventilation with intermittent sigh breaths on carbon dioxide levels in neonates
- Kulthida Baingam, Anucha Thatrimontrichai, Manapat Praditaukrit, Gunlawadee Maneenil, Supaporn Dissaneevate
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):178-184. Published online November 13, 2024
-
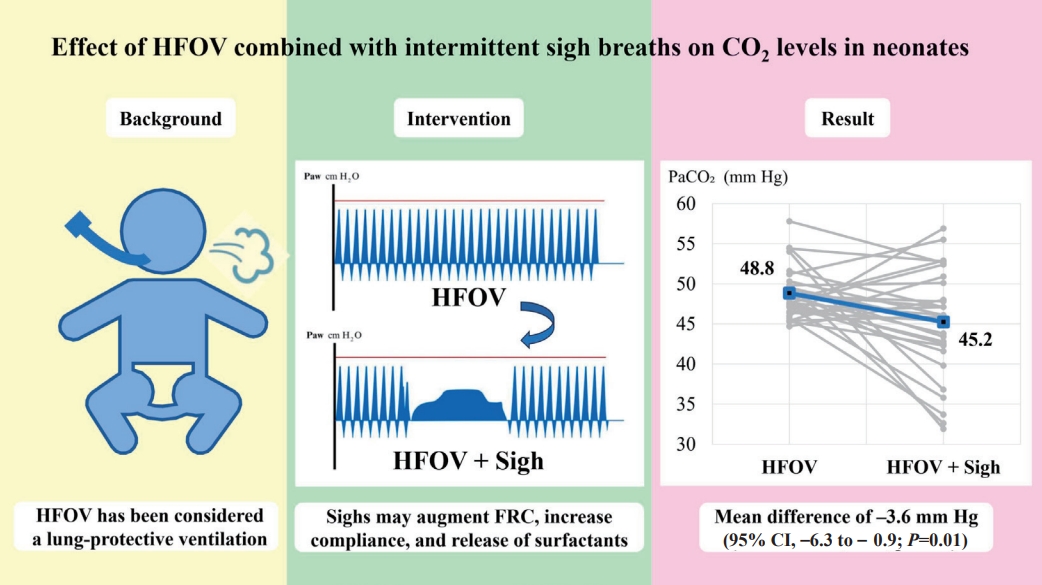
Question: Can sigh breaths (Sighs) application during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV) decrease partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) levels?
Finding: The mean PaCO2 level after Sighs during HFOV was significantly decreased compared to that after HFOV alone (mean difference, -3.6 mmHg).
Meaning: HFOV plus Sighs functionality can reduce PaCO2 levels. However, further studies are required to conclusively determine the effects of Sighs.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Characteristics of temper tantrums in 1–6-year-old children and impact on caregivers
- Warangkana Prutipaisan, Issarapa Chunsuwan, Tippawan Hansakunachai, Paskorn Sritipsukho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):170-177. Published online November 13, 2024
-
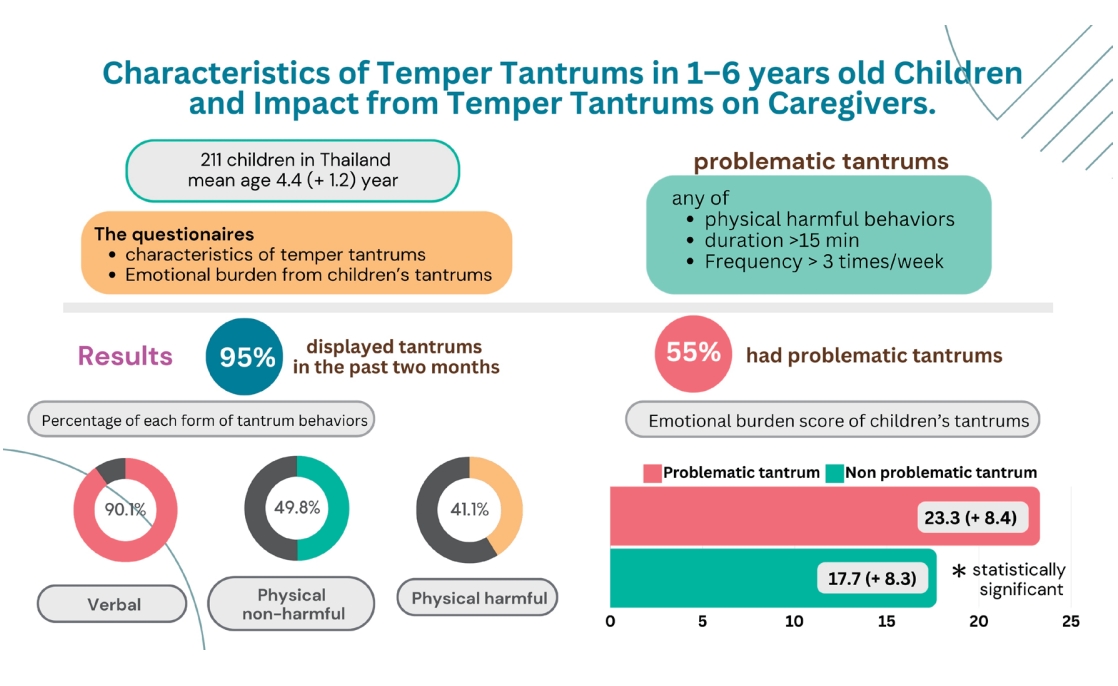
Question: What are common tantrum behaviors in preschool children, and how frequently are problematic behaviors observed? Do problematic tantrums have a different emotional impact on caregivers compared to typical tantrums?
Finding: Temper tantrums are common in preschool children, and verbal tantrums are the most common type.
Meaning: Problematic tantrums, defined as tantrums exhibiting aggressive physical behavior, long duration (>15 minutes), or frequent occurrence (>3 days/wk), significantly affected caregivers’ emotions.
- Editorial
- Hematology
- Absolute versus functional iron deficiency
- Hye Lim Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):138-140. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· Iron deficiency (ID), the most common cause of anemia, can be classified into absolute and functional types. Absolute ID is a state of low total body iron, while functional ID is a state of imbalance between iron demand and iron availability due to inflammation and/or infection.
· ID is diagnosed by serum ferritin and transferrin saturation levels.
- Allergy
- Effect of metabolic syndrome on pulmonary dysfunction in children with asthma
- Hyo-Bin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):136-137. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· The prevalence of metabolic syndrome increased in Korean children during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic owing to reduced physical activity resulting from social distancing.
· Metabolic syndrome impacts pulmonary dysfunction in childhood asthma.
· Further studies are needed to understand the mechanism linking asthma and metabolic syndrome and develop interventions.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Value of transabdominal ultrasonography for diagnosing functional constipation in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Duc Long Tran, Phu Nguyen Trong Tran, Paweena Susantitaphong, Phichayut Phinyo, Palittiya Sintusek
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):127-135. Published online November 13, 2024
-
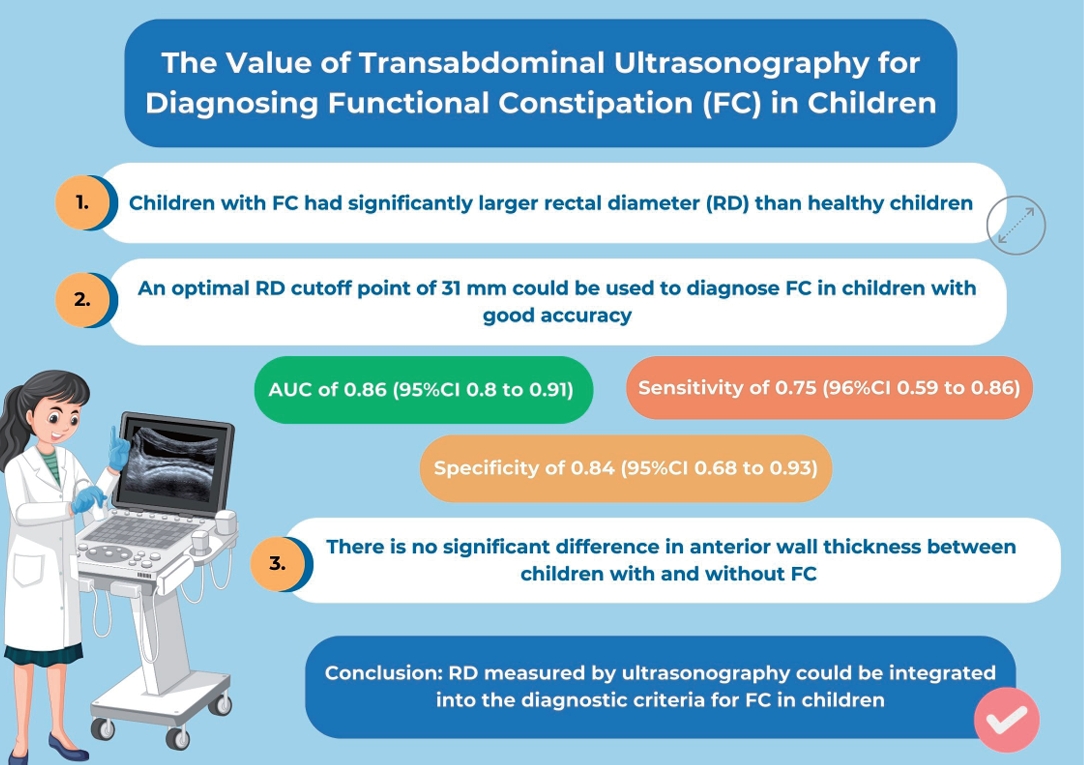
Transabdominal ultrasonography is increasingly used as a novel modality for detecting pediatric functional constipation (FC). This systematic review and metaanalysis aimed to assess the diagnostic parameters of FC including rectal diameter (RD) and anterior rectal wall thickness. A systematic search was conducted of the Ovid MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, and PubMed databases through September 29, 2023, to identify studies comparing RD...
- General Pediatrics
- Prevalence of childhood overweight and obesity in Malaysia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ker Yang Chua, Ker Yung Chua, Karuthan Chinna, Chooi Ling Lim, Maheeka Seneviwickrama
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):115-126. Published online November 13, 2024
-
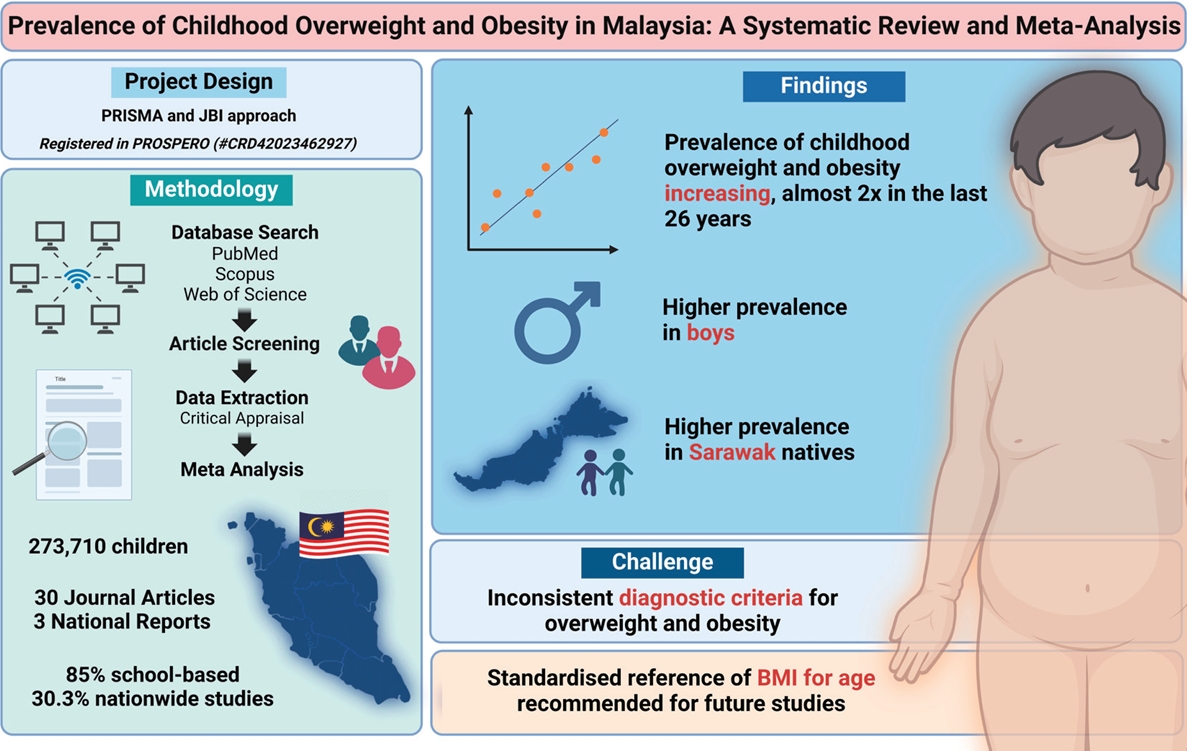
The incidence of childhood obesity is increasing worldwide. National surveys in Malaysia have shown similar trends. This review aimed to increase our understanding of the prevalence and associated factors of childhood overweight, obesity, and excess weight in Malaysia. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted of studies reporting the prevalence of overweight and obesity in Malaysian children aged <18 years....
- Hematology
- Promising role of voxelotor in managing sickle cell disease in children: a narrative review
- Amit Agrawal, Gaurav Jadon, Japna Singh, Dalwinder Janjua
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):106-114. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Voxelotor has promising ability to increase hemoglobin levels and reduce hemolysis markers in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD). Several preclinical and phase II/III trials have demonstrated its efficacy, dose-dependent responses, and tolerability in children. Ongoing trials are assessing its safety and effectiveness in various populations, including children younger than 12 years. These findings suggest its potential as a disease-modifying drug, warranting further exploration of its role in SCD management.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Need for national guidance regarding proactive care of infants born at 22–23 weeks' gestation
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):53-61. Published online November 13, 2024
-

With advancements in neonatal intensive care, the limit of viability has shifted to 22–23 weeks' gestation, whose survival rates vary across countries and institutions. These rates are not static and can be improved through the proactive and centralized care guided by national protocols, including maternal transfer to high-activity regions with better neonatal intensive care practices before delivery.
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Evaluation of pediatric migraine triggers: a single-center study
- Hey-Joon Son, Joo-Ok Jin, Kon-Hee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):163-169. Published online November 11, 2024
-
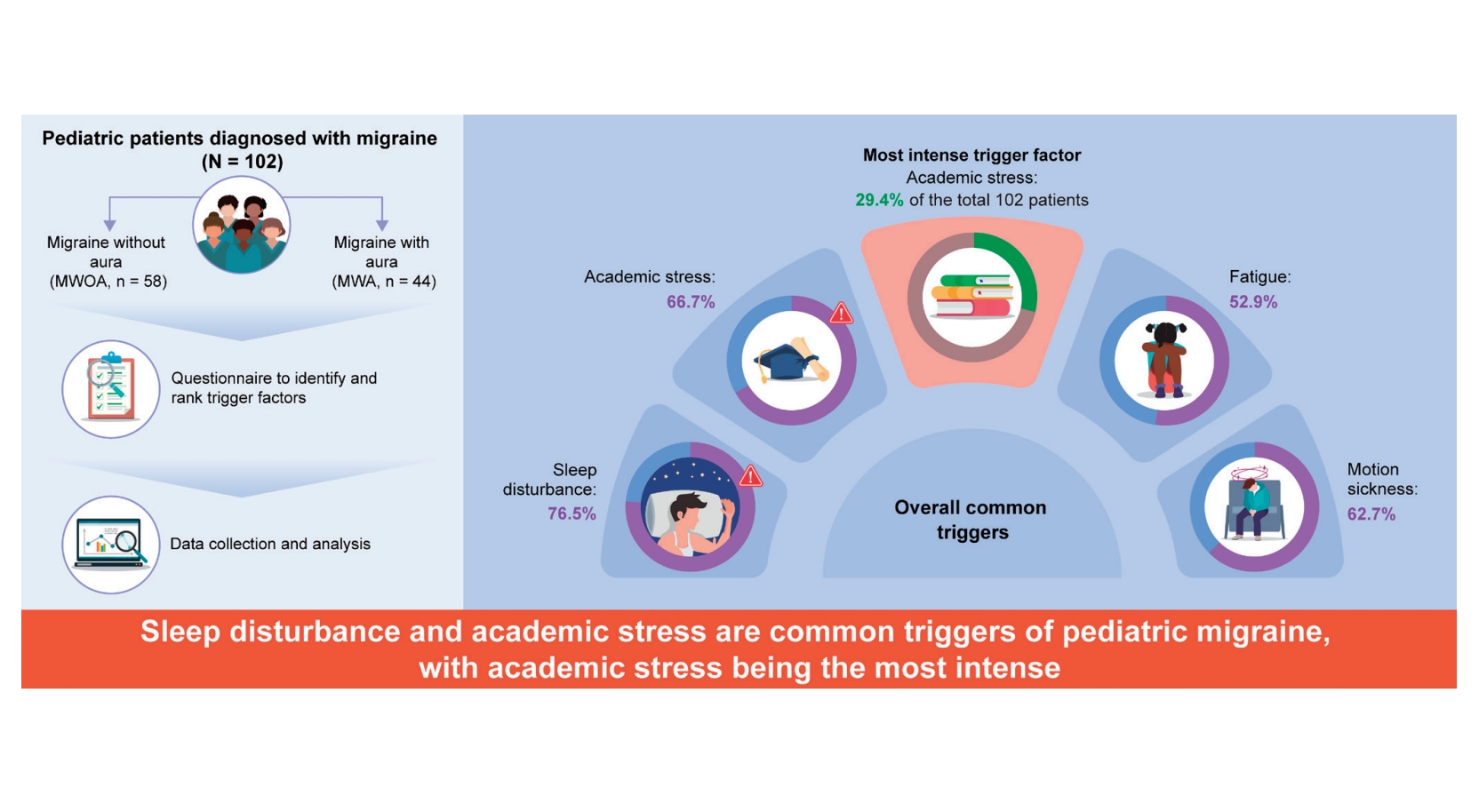
Question: What are the primary triggers for pediatric migraines, and how do they impact clinical management?
Finding: Common triggers for pediatric migraines include sleep disturbances, academic stress, and motion sickness, with academic stress identified as the most intense.
Meaning: Recognizing and addressing specific triggers like sleep disturbance and academic stress is crucial to effectively managing pediatric migraines with emphasis on personalized care to improve outcomes.
- Infection
- Clinical characteristics and associated factors of pediatric acute necrotizing encephalopathy: a retrospective study
- Huiling Zhang, Yilong Wang, Qianyun Ding, Xuekun Li, Sheng Ye
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):153-162. Published online November 11, 2024
-
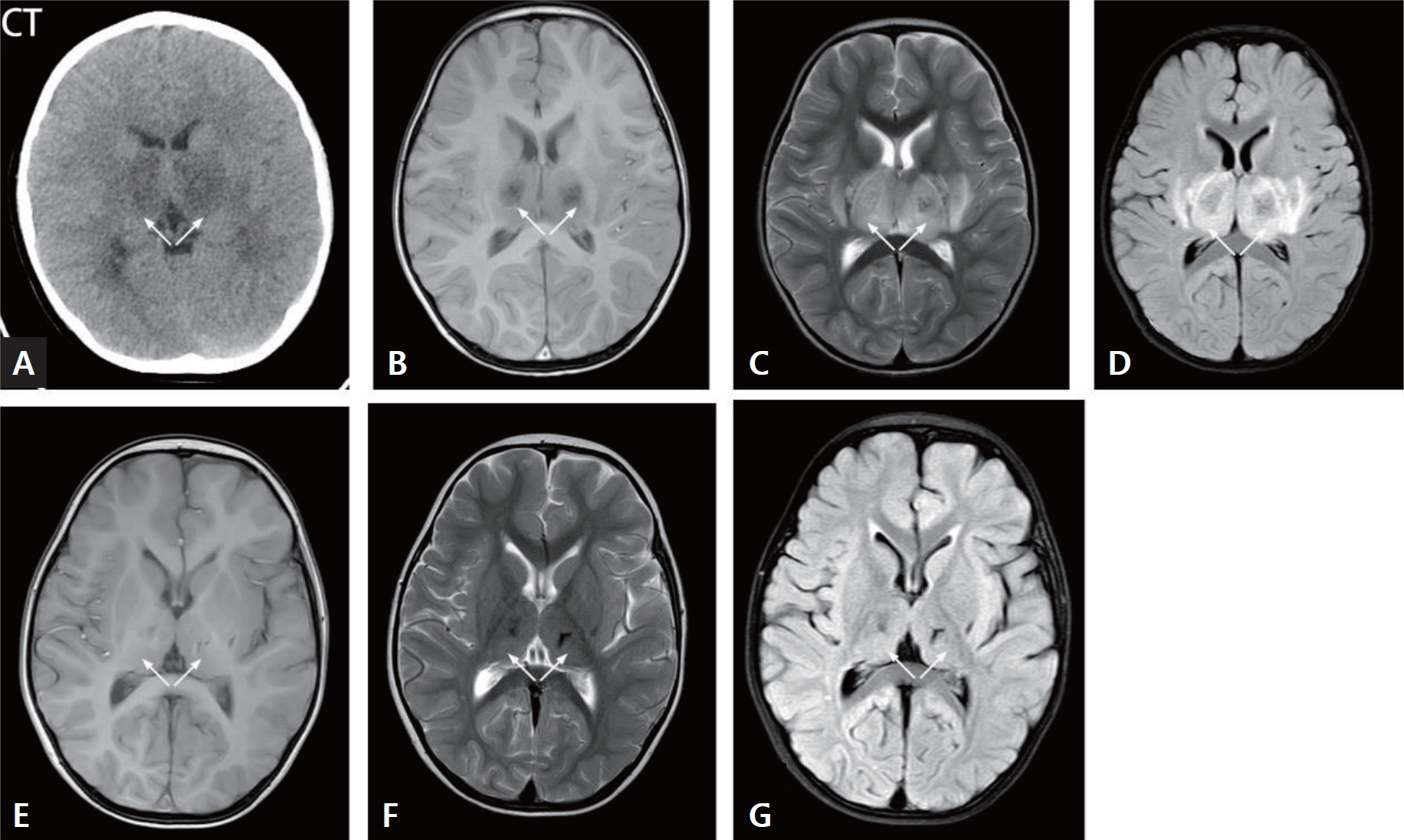
· The mortality rate of acute necrotizing encephalopathy was high.
· Laboratory tests revealed that the fatal group had higher creatinine, lactate, activated partial thromboplastin time, thrombin time, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, creatine kinase, and D-dimer than survivors.
· The fatal group displayed lower Glasgow Coma Scale scores and arterial pH.
- Neurology
- Instability of revised Korean Developmental Screening Test classification in first year of life
- Ji Eun Jeong, You Min Kim, Na Won Lee, Gyeong Nam Kim, Jisuk Bae, Jin Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):97-103. Published online November 11, 2024
-

Question: How stable are the revised Korean Developmental Screening Test score classifications in early infancy?
Finding: A significant number of infants improved into the peer and high-level group (≥-1 standard deviations), especially in the gross motor area.
Meaning: The early detection of developmental delay requires a comprehensive medical history, physical and neurological examinations, and repeated developmental screenings.
- Review Article
- Other
- Global trends in importance of 24-hour movement behaviors to pediatric health: implications for South Korea
- Eun-Young Lee, Reyana Jayawardena, Seiyeong Park, Justin Y Jeon, Yeon-Soo Kim, Mark S. Tremblay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):16-29. Published online November 11, 2024
-

· The 24-hour movement behavior paradigm provides an important framework for future pediatric health promotion efforts.
· Policy priorities should include advancing surveillance and monitoring assessments related to 24-hour movement behaviors, evaluating their implementation in school and government policies, and building preparedness for future pandemics and natural disasters, including climate change, by promoting healthy 24-hour movement behaviors.
· Future research should advocate for the promotion of 24- hour movement behaviors.
- Original Article
- Other
- Balance assessment with decreased base of support for children with disabilities
- Guilherme M. Cesar, Madison Giebler, Thad W. Buster, Judith M. Burnfield
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):718-724. Published online November 11, 2024
-
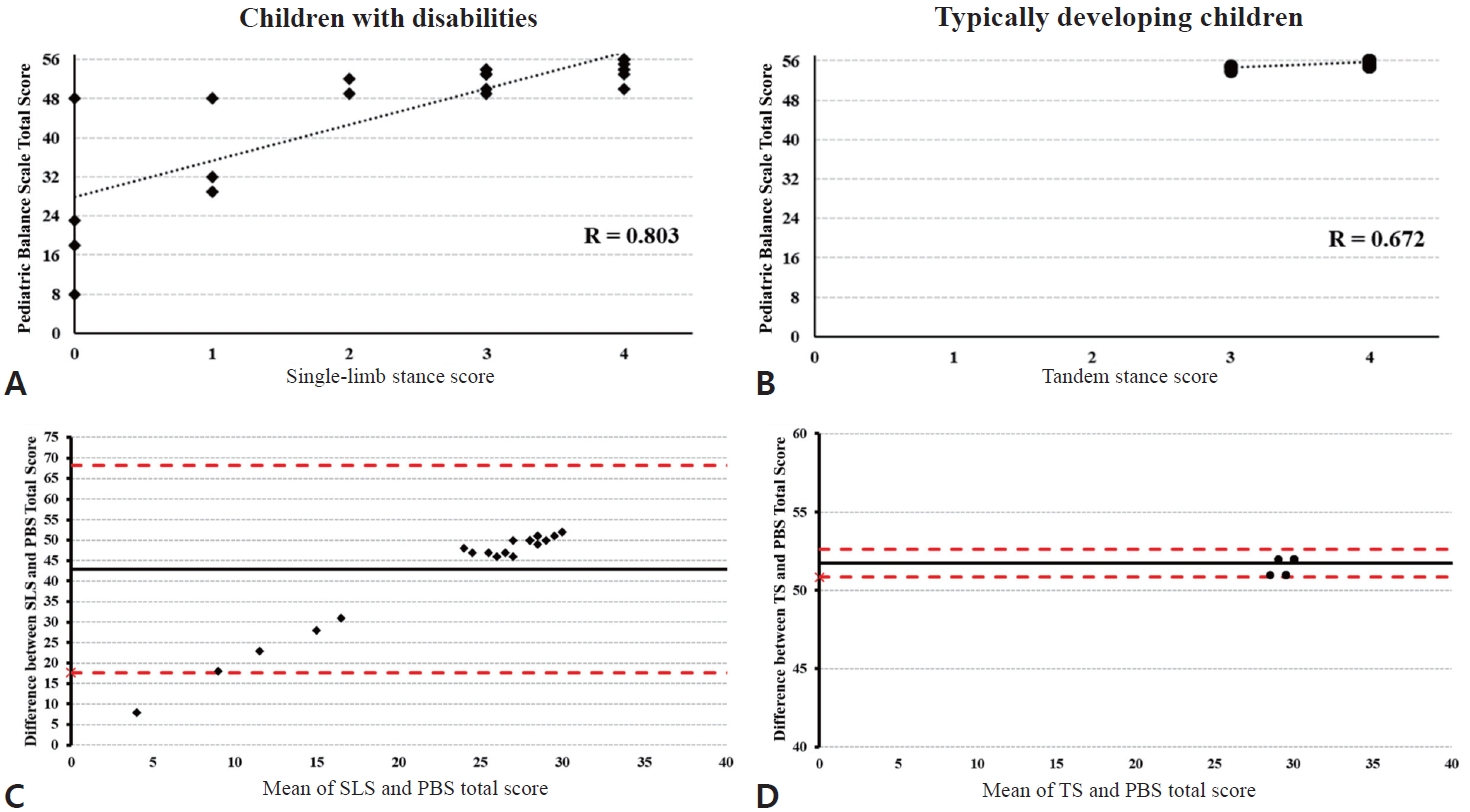
Question: Can a balance task with narrowed base of support indicate overall functional balance control in children with disabilities?
Finding: While single-limb standing could explain overall balance control for children with disabilities, it was unrelated with balance control for typically developing children.
Meaning: One balance task with narrowed base of support can be used as practical assessment of balance abilities for children with disabilities when allocated session time is of concern.
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- The predetermined future: tackling South Korea’s total fertility rate crisis
- Jin Kyu Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):225-227. Published online November 6, 2024
-
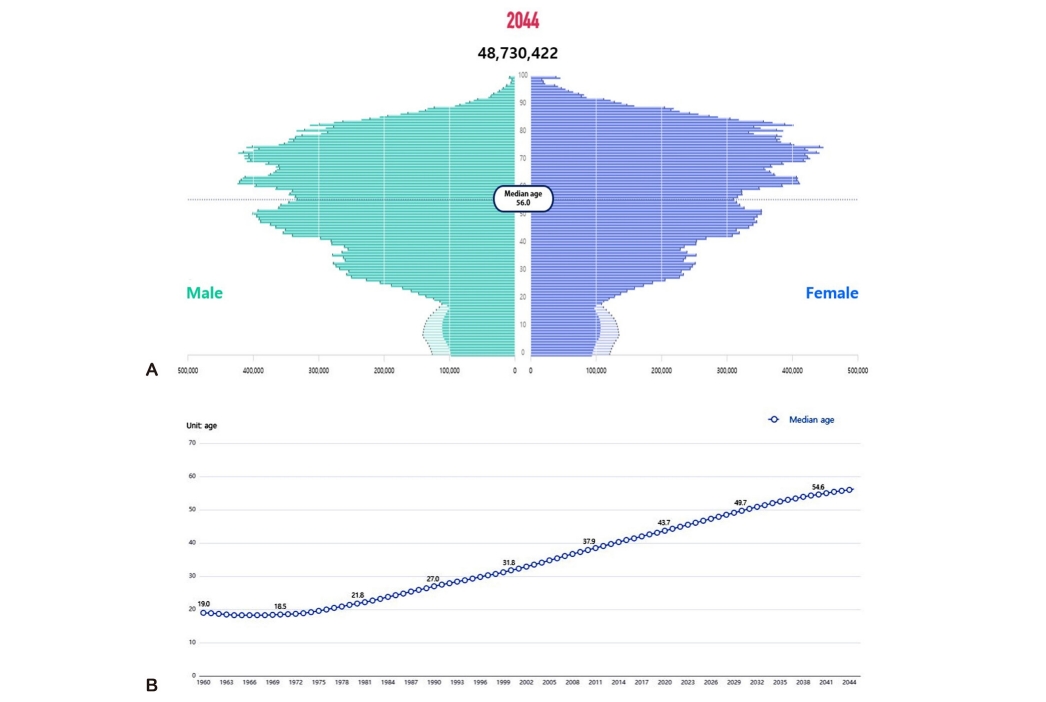
· South Korea faces a severe demographic crisis with the lowest global fertility rate. Despite significant investments, the total fertility rate continues to decline.
· It is necessary to fully mobilize national capabilities and execute comprehensive strategies that focus on both intangible and tangible values.
· Immediate and decisive action is essential to addressing these challenges effectively.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Efficacy of leuprolide acetate versus triptorelin pamoate administered every 3 months for treatment of central precocious puberty
- Thanaporn Thaneetrakool, Suphab Aroonparkmongkol, Nattakarn Numsriskulrat, Vichit Supornsilchai, Suttipong Wacharasindhu, Khomsak Srilanchakon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):91-96. Published online November 6, 2024
-

Question: What are the differences in efficacy between leuprolide acetate and triptorelin pamoate administered every 3 months for the treatment of central precocious puberty (CPP)?
Finding: There were no significant intergroup differences in luteinizing hormone suppression or predicted adult height at the end of treatment in girls with CPP.
Meaning: Leuprolide acetate and triptorelin pamoate have comparable efficacy for treating CPP.
- Pulmonology
- Polysomnographic features of children with obesity: body mass index predict severe obstructive sleep apnea in obese children?
- Rungrat Sukharom, Prakarn Tovichien, Kanokporn Udomittipong, Pinyapach Tiamduangtawan, Wattanachai Chotinaiwattarakul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):80-90. Published online November 6, 2024
-

Question: How Common is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in obese children? OSA is common in obese children, even without habitual snoring.
Finding: Among the subjects, 60.6% had positional OSA, 40.2% had rapid eye movement-related OSA, 59.8% had desaturation, 20.5% had sleep-related hypoventilation, and 5.0% had obesity hypoventilation syndrome. Body mass index (BMI) and neck and waist circumferences were significantly associated with severe OSA.
Meaning: We recommend screening obese children (BMI > 29.2 kg/m2) for OSA.
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- What we should know about pediatric heart failure: children are not small adults
- Ja-Kyoung Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):62-64. Published online November 6, 2024
-
· Pediatric heart failure (PHF) features high morbidity and mortality rates.
· Although adults and children can share a common diagnosis of heart failure, the underlying causes can differ significantly and require distinct therapeutic approaches.
· Treatments designed for adults are often applied to PHF despite the fundamental physiological and developmental differences between them.
· Child-specific data are vital for the development of tailored treatments to meet the unique needs of patients with PHF.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











