Review article
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Review article
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Sacral dimple: clinical perspectives of lesions hidden beneath the skin
- Jin Eun, Kwan Sung Lee, Seung Ho Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(2):103-113. Published online November 26, 2025
-
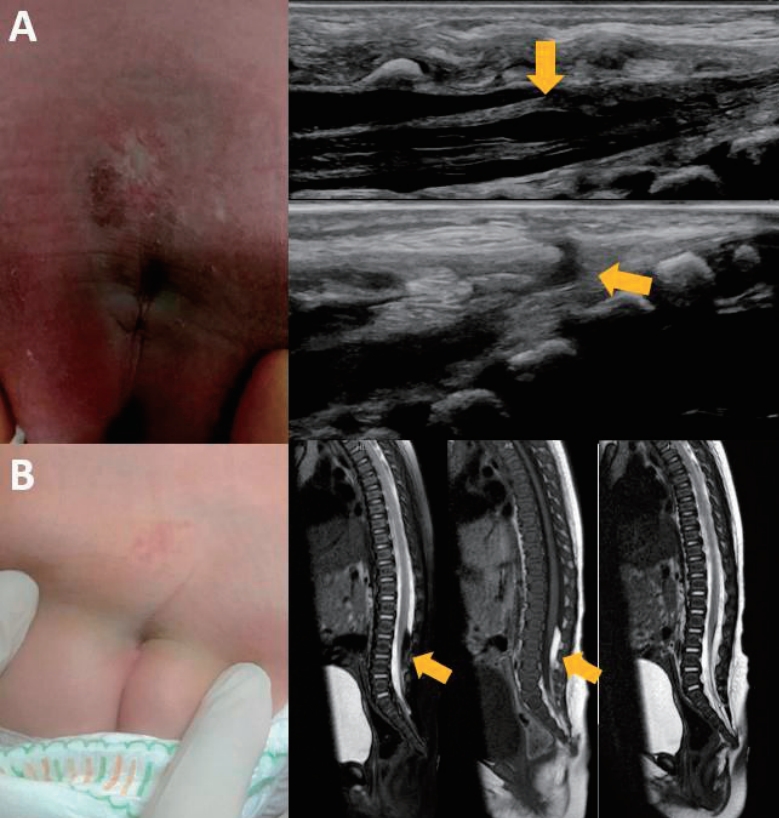
· Most sacral dimples are benign, but atypical features may indicate occult spinal dysraphism.
· Simple dimples meeting strict criteria require no imaging, whereas atypical dimples require targeted ultrasonography or magnetic resonance imaging.
· The early diagnosis and surgical management of highrisk cases prevents irreversible neurological, orthopedic, and urological deficits.
- General Pediatrics
- Systematic review of influence of ethnicity on efficacy and safety of pharmacotherapy for childhood and adolescent obesity
- Surendra Gupta, Purushottam Lal, Abhishek Gupta, Brajesh Raj Chaudhary
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(2):84-102. Published online January 26, 2026
-
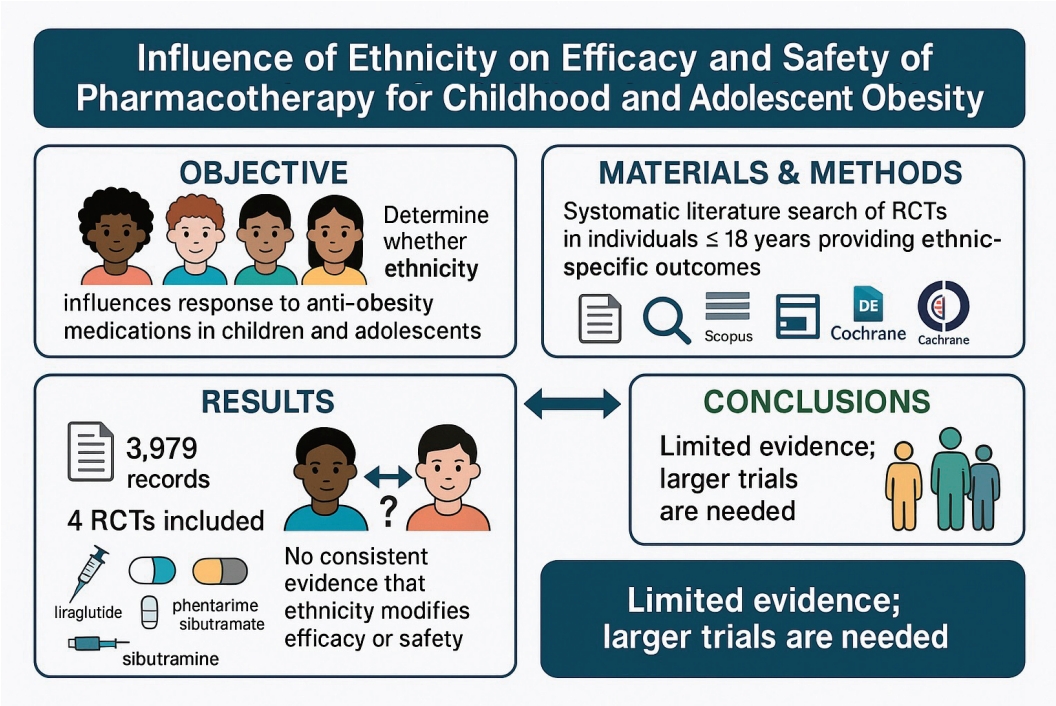
Ethnic variations may influence the response of children and adolescents to obesity pharmacotherapy. Current evidence does not show consistent differences in efficacy or safety among ethnic groups; however, available data are limited. Larger, ethnically diverse trials are needed to develop personalized obesity treatment strategies.
- Gastroenterology
- Ingestion of foreign bodies and caustic substances in children: a narrative review on clinical evaluation and management update
- Maria Rogalidou
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):11-21. Published online December 10, 2025
-

Foreign body and caustic substance ingestion in children aged 1–5 years can feature to severe and, sometimes life-threatening complications. High-risk items include batteries, magnets, and corrosive chemicals. Severity depends on object type, location, and ingestion timing. Prompt diagnosis and early endoscopic intervention are crucial. Individualized management, high clinical suspicion, and parental education are essential to improving outcomes and preventing immediate and long-term complications affecting a child’s quality of life.
- Endocrinology
- Pubertal induction in prepubertal males with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: testosterone or gonadotropins?
- Paolo Cavarzere, Riccardo Battiston, Valentina Lupieri, Valentina Mancioppi, Claudio Maffeis
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):1-10. Published online December 18, 2025
-

The pubertal induction process in males still poses a challenge for pediatric endocrinologists. The existing literature is limited, and it is not yet possible to make definitive recommendations. We described the various treatment for this condition and tried to analyze the unresolved questions to address the question posed in the title of our manuscript.
- Nutrition
- Exploring nutritional screening tools for hospitalized children: a narrative review
- Pankaj Soni, Amit Agrawal, Gaurav Jadon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):963-970. Published online October 22, 2025
-
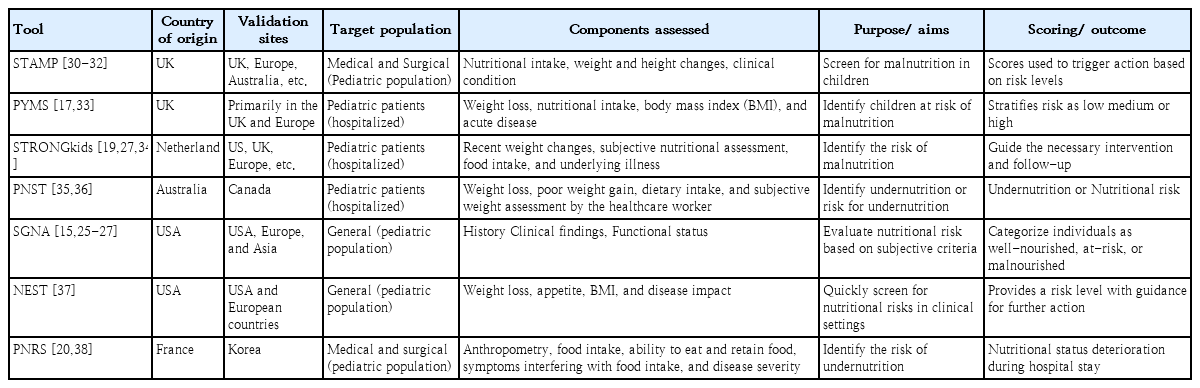
Malnutrition is frequently identified in hospitalized children, and the use of nutritional screening tools is crucial for assessing their nutritional status during their hospital admission and stay. Common tools include the Pediatric Yorkhill Malnutrition Score, Screening Tool for Assessment of Malnutrition in Pediatrics, and Screening Tool for Risk of Nutritional Status and Growth. However, these tools have varying sensitivities and specificities, and none is recommended for all hospitalized children.
- Oncology
- Breaking the barrier: a guidelines-based review of antiangiogenesis drug resistance in pediatric cancer therapy
- Nader Shakibazad, Mahdi Shahriari, Mani Ramzi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):952-962. Published online November 24, 2025
-
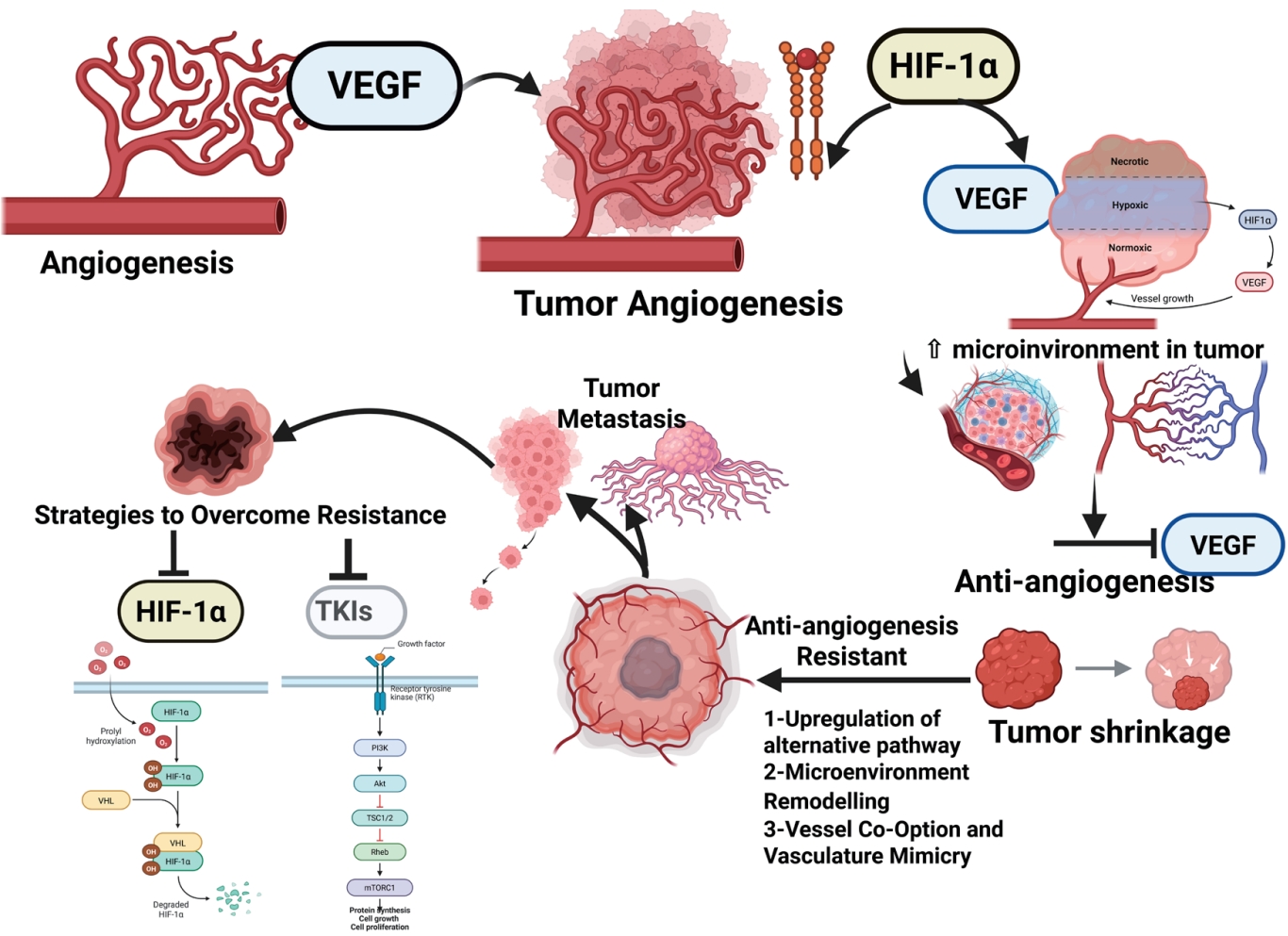
Antiangiogenic therapy resistance in pediatric cancers involves alternative angiogenic pathways, microenvironmental support, hypoxia-driven signaling, metabolic reprogramming, and structural adaptations such as vascular co-option. Metabolic adaptation highlights tumor plasticity. Effective treatments combine immunotherapy with biomarkers. To address vascular endothelial growth factor limitations, emerging targets include hypoxia-inducible factor-2α, endoglin, CXCR4, angiopoietin/Tie2, and bispecific antibodies. In resource-constrained settings, the guidelines recommend low-dose chemotherapy plus oral multiantiangiogenic agents to ensure improved accessibility and treatment outcomes.
- Gastroenterology
- Neonatal ichthyosis-sclerosing cholangitis syndrome caused by a novel CLDN1 mutation: a case report and literature review
- Upasana Ghosh, Ankit Agrawal, Varunvenkat M. Srinivasan, Rani Manisha, Umesh Shukla, Vikas Jain, Mayank Nilay, Harish Kumar
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):858-867. Published online October 2, 2025
-

· Neonatal ichthyosis-sclerosing cholangitis (NISCH) syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by cholestasis and manifestations such as generalized ichthyosis, alopecia, and dental anomalies.
· The clinical features of NISCH syndrome are distinct and necessitate an early genetic diagnosis.
· The disease phenotype can vary significantly, ranging from no liver involvement and transient neonatal cholestasis to end-stage liver disease.
· Management requires a multidisciplinary approach with long-term follow-up.
- General Pediatrics
- Bridging the gap: autism spectrum disorder in children in the United States and worldwide: a narrative review
- Sandhya J. Kadam, Malika Goel
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):852-857. Published online October 2, 2025
-

The prevalence of autism is increasing worldwide. The United States has the highest numbers, likely due to the availability of better treatment options. However, global disparities exist, especially in low-resource settings in which stigma, underdiagnosis, and limited services hinder care. A coordinated international approach emphasizing early screening, inclusive policies, and culturally sensitive support systems can bridge this gap and improve the outcomes for children with autism and their families worldwide.
- Endocrinology
- Continuous glucose monitoring in Korean pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes: current landscape and clinical implications
- Hwa Young Kim, Jaehyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):842-851. Published online October 2, 2025
-

Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has transformed pediatric type 1 diabetes care by facilitating tighter glycemic control, reducing hypoglycemia, and improving quality of life.
Recent advances in CGM technology and the expansion of insurance coverage in Korea have led to its broader adoption.
Emerging metrics such as time in tight range offer refined tools for individualized glycemic assessment, highlighting CGM’s evolving role in personalized pediatric diabetes management.
- General Pediatrics
- Impact of screen exposure during pediatric ages including multifaceted aggravating factors: a literature review
- Daniel González-Pérez, David Sebastián Huertas-Moreno, Manuela Granados-Pinilla, Sofía Hernandez-Rojas, Laura González-Rincon, Geraldine Hurtado-Garcia, Simón Grisales-Calle, María José González-Mariño, Luz Dary Gutierrez-Castañeda, Jhon Camacho-Cruz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):751-760. Published online September 24, 2025
-
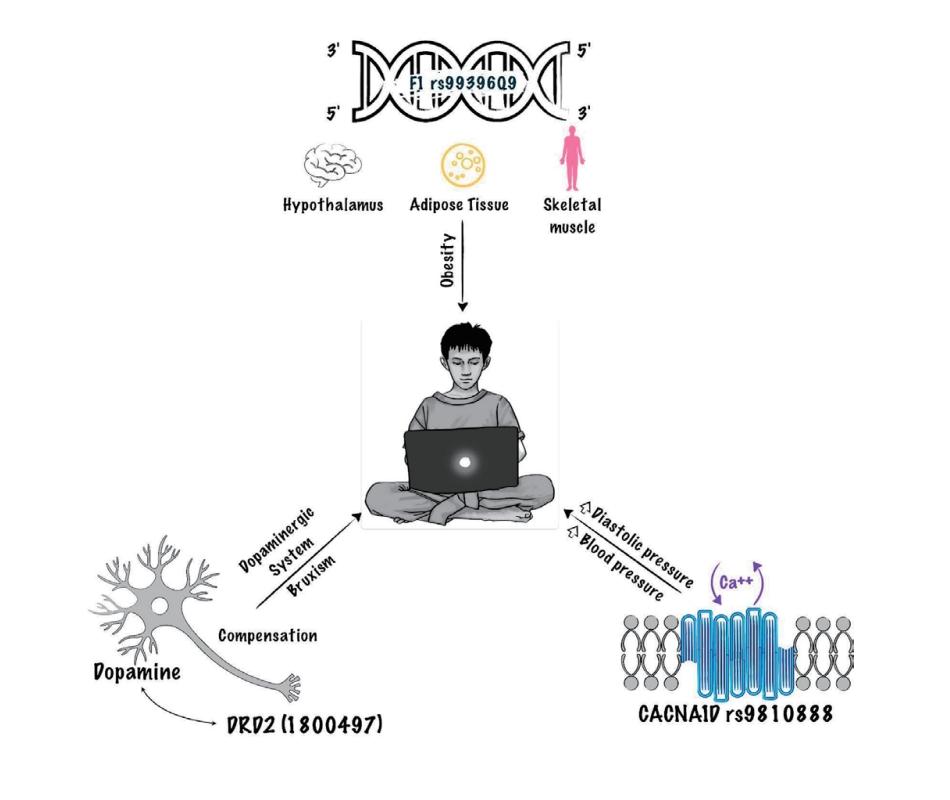
Excessive screen time in children is linked to obesity, overweight, sedentary behavior, depression and mood disorders, myopia, behavioral changes, sleep disturbances, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, among others. Polymorphisms in genes like FTO, CACNA1D, and DRD2 could further increase these risks. Implementing strategies such as limiting screen use, creating screen-free zones, and monitoring content is essential to mitigate adverse physical and mental health effects in the pediatric population.
- Infection
- Recommendation for use of a long-acting monoclonal antibody to prevent respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants and young children
- Soo-Han Choi, Dong Hyun Kim, Jong Gyun Ahn, Ki Wook Yun, Byung-Wook Eun, Jin Lee, Jina Lee, Taek-Jin Lee, Hyunju Lee, Dae Sun Jo, Eun Young Cho, Hye-Kyung Cho, Young June Choe, Ui Yoon Choi, Yun-Kyung Kim; The Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):742-750. Published online September 3, 2025
-
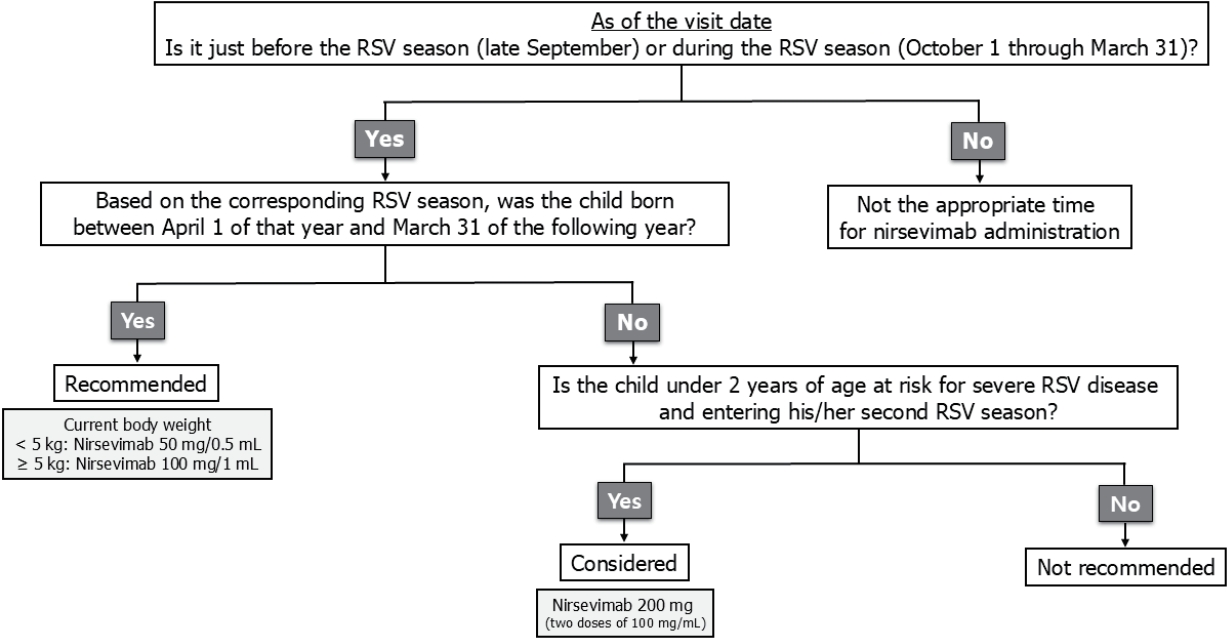
To prevent respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)-associated lower respiratory tract infections, a single dose of nirsevimab, a long-acting monoclonal antibody, is recommended for all neonates born during the RSV season (October to March) and all infants younger than 6 months old at the start of the RSV season. Nirsevimab should be administered shortly after birth to neonates and just before or early in the season to infants entering their first RSV season.
- Other
- Artificial intelligence in pediatric healthcare: current applications, potential, and implementation considerations
- Taejin Park, In-Hee Lee, Seung Wook Lee, Sek Won Kong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):641-651. Published online June 25, 2025
-

Artificial intelligence (AI) offers potential benefits in pediatric care, but its real-world adoption requires clinician literacy, ethical and legal safeguards, and cautious implementation. Large language models are emerging across healthcare, but their use in pediatric clinical practice remains premature. Thus, the cautious and accountable implementation of AI is crucial to preventing unintended harm and realizing its potential.
- Cost-effectiveness of newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency: a systematic review
- Rezwanul Rana, Syed Afroz Keramat, Moin Ahmed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):628-640. Published online April 16, 2025
-

Universal newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) demonstrates robust cost-effectiveness across diverse high-income healthcare systems, both from healthcare and societal standpoints. Early detection yields substantial savings. While uncertainties persist, impacting precise cost-effectiveness, the overall finding is positive. Future research must prioritize enhanced data collection and statistical rigor to refine our understanding of SCID's economic impact within the Australian context.
- Myopia: a review of current concepts, association with nonophthalmological conditions, and treatment strategy in children and adolescents
- Yeon Woong Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):554-565. Published online April 1, 2025
-
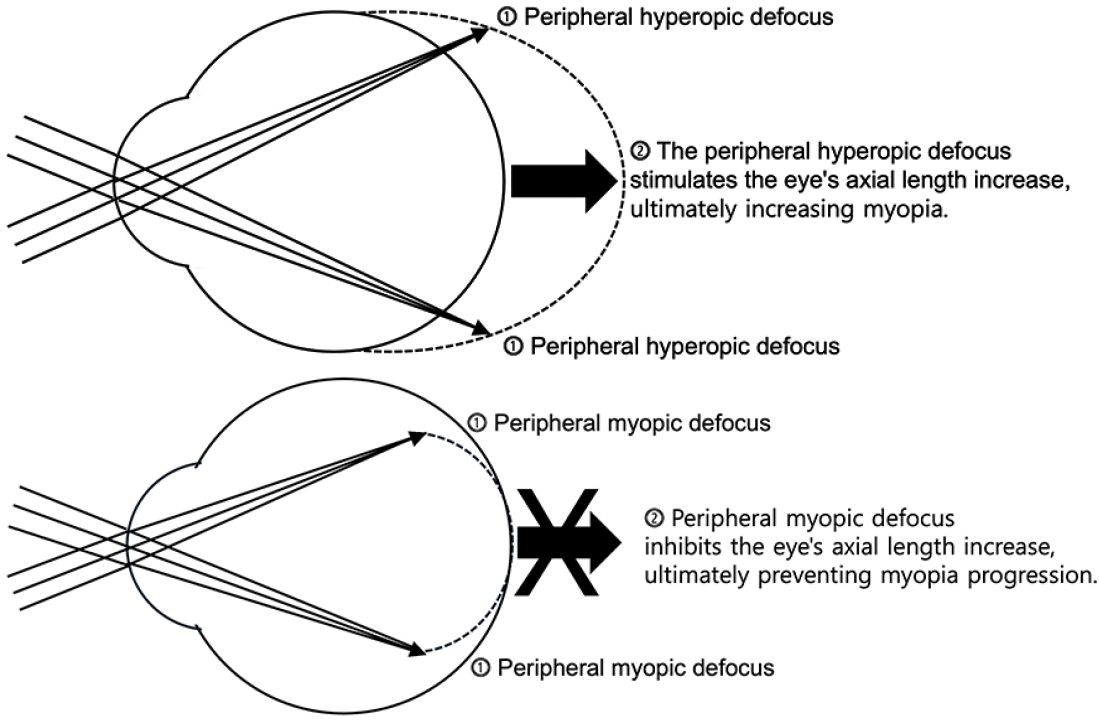
Myopia is a major ophthalmological disorder with increasing prevalence worldwide, particularly in East Asia. Evidence indicates that its development involves complex interactions between genetic and environmental factors. Body stature, sleep patterns, and nutritional status significantly influence the progression of myopia during childhood and adolescence. Its treatment and prevention strategies include optical correction, atropine therapy, increased outdoor activity, decreased near work, and regular retinal monitoring.
- Immunology
- NLRP3 inflammasome: a key player in neonatal brain injury
- Cagla Kiser, Ilkcan Ercan, Defne Engur, Sermin Genc
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):475-485. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is the major cause of neonatal brain injury. NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome activation leads to neuroinflammation, which significantly affects newborn mortality. The establishment of preventive and therapeutic strategies against brain damage requires a thorough understanding of the mechanisms underlying neuroinflammation and inflammasome activation in the neonatal brain.
- Other
- Peripheral nerve sheath tumors in the head and neck in patients with APC gene deletion mutations: a case report and scoping review of the literature
- Koral M. Blunt, Monirah Albathi, Miriam Conces, Tendy Chiang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):428-433. Published online January 13, 2025
-
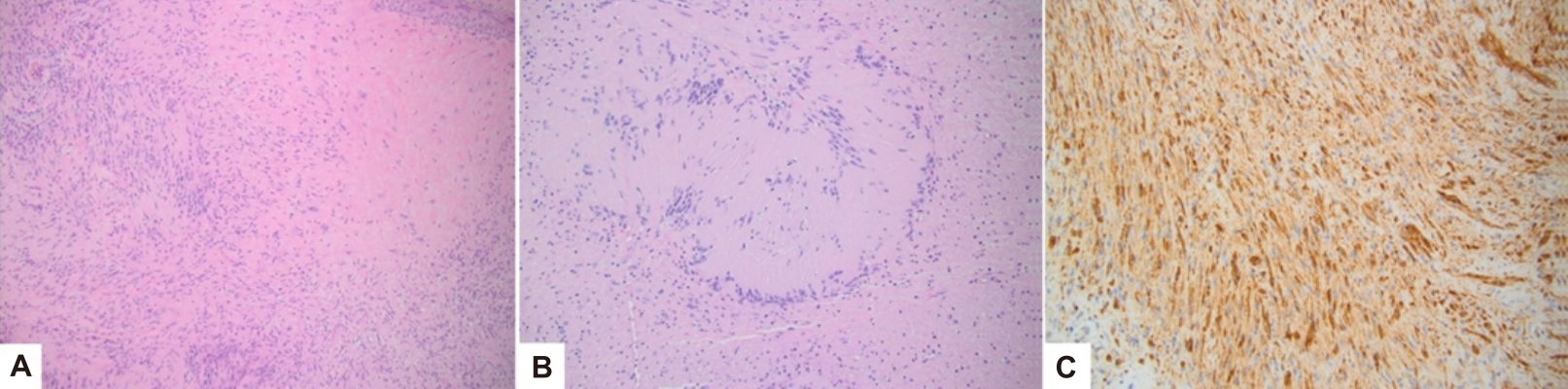
In this report, we describe our experience with a patient with an APC-related genetic syndrome who presented with a rare palatal lesion with characteristics of a schwannoma. We discuss the role of immunohistochemical staining in discerning the differential diagnosis.
- Endocrinology
- Impact of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on growth outcomes in mucopolysaccharidosis: a systematic review
- Farzaneh Abbasi, Asal Khalili Dehkordi, Reihaneh Mohsenipour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):417-427. Published online March 11, 2025
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) enhances the growth outcomes of pediatric patients with mucopolysaccharidosis, with early intervention leading to improved height, weight, and body mass index. However, achieving a standard adult height remains uncommon among these patients, even in cases of early HSCT. Growth hormone therapy provides short-term benefits but does not address long-term height deficits. Pubertal development is generally normal; however, precocious puberty and pubertal arrest may occur.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Protocolized sedation may reduce ventilation and sedation requirements in the pediatric intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ambrus Szemere, Alíz Fazekas, Anna Réka Sebestyén, Rani Ezzeddine, Veronika Upor, Marie Anne Engh, Péter Hegyi, Zsolt Molnár, Klára Horváth
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):406-416. Published online February 19, 2025
-
Protocolized sedation may reduce ventilation requirements, pediatric intensive care unit length of stay, and sedative exposure. However, it may increase the likelihood of unplanned extubation, highlighting the importance of incorporating preventive measures to mitigate this risk.
- Allergy
- Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin levels can predict allergic disease development and atopic march in children
- Zak Callaway, Chang-Keun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):398-405. Published online February 3, 2025
-
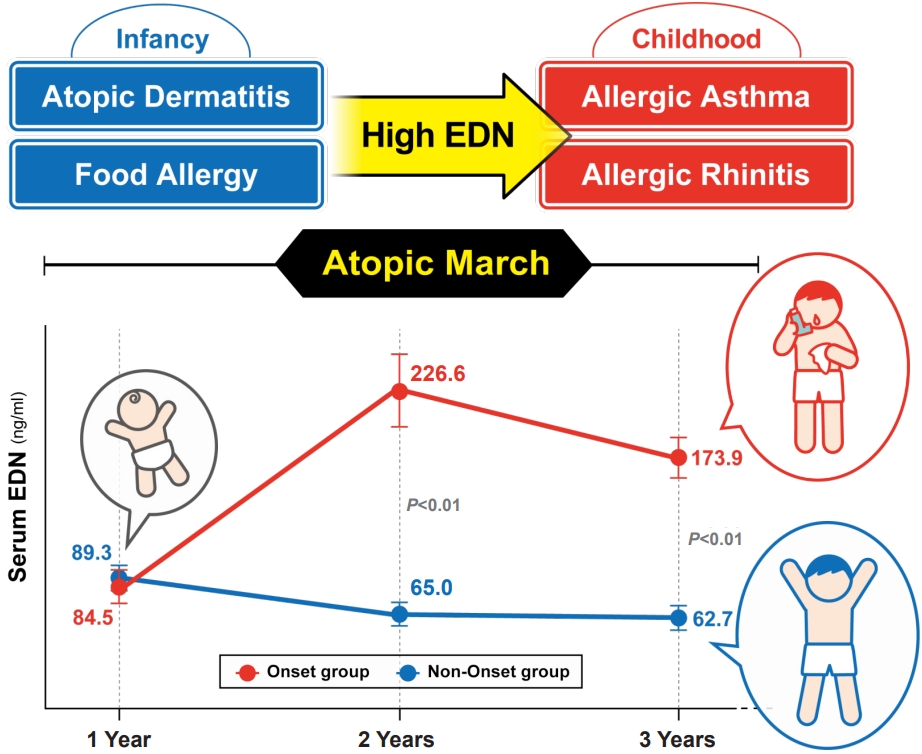
· Allergic march occurs in a subset of children, beginning with atopic dermatitis and progressing to food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and/or asthma. Its early diagnosis is important to slowing its progression.
· Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN), an excellent biomarker of eosinophil activity, is often elevated in allergic diseases.
· EDN levels have been used to predict allergic disease development and diagnose, treat, and monitor allergic diseases.
- Nutrition
- The Korea Infant Physical Growth Examination Survey (KIPGroS): a study protocol
- Jong Woo Hahn, MinSoo Shin, Jin Gyu Lim, Yoon-Joo Kim, Ki Soo Kang, Narae Lee, Seong Hee Jeong, Mun Hui Jeong, Yeoun Joo Lee, Eui Kyung Choi, Jung Ok Shim, Jee Yoon Park, Chan-Wook Park, Joo Young Kim, Su Jin Jeong, Young Hwa Jung, Jaehyun Kim, Chang Won Choi, Ju Whi Kim, Seung Han Shin, Yun Jeong Lee, Young Ah Lee, Choong-Ho Shin, Seung-sik Hwang, Young Eun Kim, Youn Ha Kang, Kyungwon Oh, Sungha Yun, Jae Sung Ko, Jin Soo Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):352-358. Published online February 13, 2025
-
The suitability of World Health Organization (WHO) growth charts for assessing the growth of children under 3 years of age in all countries remains controversial, and their applicability must be evaluated based on country-specific growth data. The Korea Infant Physical Growth Examination Survey evaluated the suitability of WHO growth charts to contribute to the next revision of growth charts in Korea.
- Gastroenterology
- Anxiety disorders presenting as gastrointestinal symptoms in children – a scoping review
- Anjali Kumar, Pramodh Vallabhaneni
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):344-351. Published online January 13, 2025
-

A positive bidirectional relationship between gastrointestinal disorders and anxiety, but with no clear aetiology, was identified. Factors such as somatisation and pain catastrophising resulted in poorer pain-related outcomes in children. Further studies are required to understand this relationship in order to have targeted treatments and ensure better long term outcomes.
- Allergy
- Global burden of asthma among children and adolescents with projections to 2050: a comprehensive review and forecasted modeling study
- Tae Hyeon Kim, Hyunjee Kim, Jiyeon Oh, Soeun Kim, Michael Miligkos, Dong Keon Yon, Nikolaos G Papadopoulos
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):329-343. Published online April 22, 2025
-

Pediatric asthma can persist to adulthood and must be effectively managed. This review examined the prevalence of asthma among individuals younger than 20 years and revealed a decline from 1990 to 2021, higher rates in males, and a peak in children aged 5–9 years. Despite a projected continued decrease in prevalence by 2050, asthma will remain a significant health concern for children and adolescents.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Recent advances in understanding pathophysiology of non-nutritional stunting in very preterm infants
- Eduardo Cuestas, Alina Rizzotti
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):287-297. Published online December 23, 2024
-

· Previous reviews of extrauterine growth restriction focused mainly on weight growth restriction caused by nutritional factors or pathological conditions.
· This review summarizes recent developments in the pathophysiology of nonnutritional length growth restriction in very preterm infants with focus on the impact of sustained neonatal inflammation on their short- and long-term outcomes.
· Further research is needed to investigate optimal strategies to improve length growth restriction in very preterm infants.
- Cardiology
- Lifelong impact of elevated blood pressure from childhood to adulthood
- Junhyun Kwon, Eunji Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):278-286. Published online November 28, 2024
-

· Childhood blood pressure (BP) is significantly associated with adult hypertension and cardiovascular disease.
· Despite ongoing debate regarding the need for regular BP screening and early pharmacotherapy in children, the benefits of optimizing BP throughout childhood are clear.
· Childhood presents a critical window for normalizing BP through lifestyle modifications such as reducing sodium intake and increasing physical activity to promote lifelong cardiovascular health and prevent longterm complications.
- Neurology
- Cerebral organoid research for pediatric patients with neurological disorders
- Jin Eun, Jung Eun Lee, Seung Ho Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):269-277. Published online November 28, 2024
-

Cerebral organoids obtained from human induced pluripotent stem cells are transforming the study of pediatric neurological diseases by providing more accurate models of human brain development and pathology. These advancements have improved pathology modeling and the potential for novel therapeutic approaches despite existing challenges such as reproducibility and vascularization.
- Endocrinology
- Hidden link between endocrine-disrupting chemicals and pediatric obesity
- Min Won Shin, Shin-Hye Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):199-222. Published online November 28, 2024
-
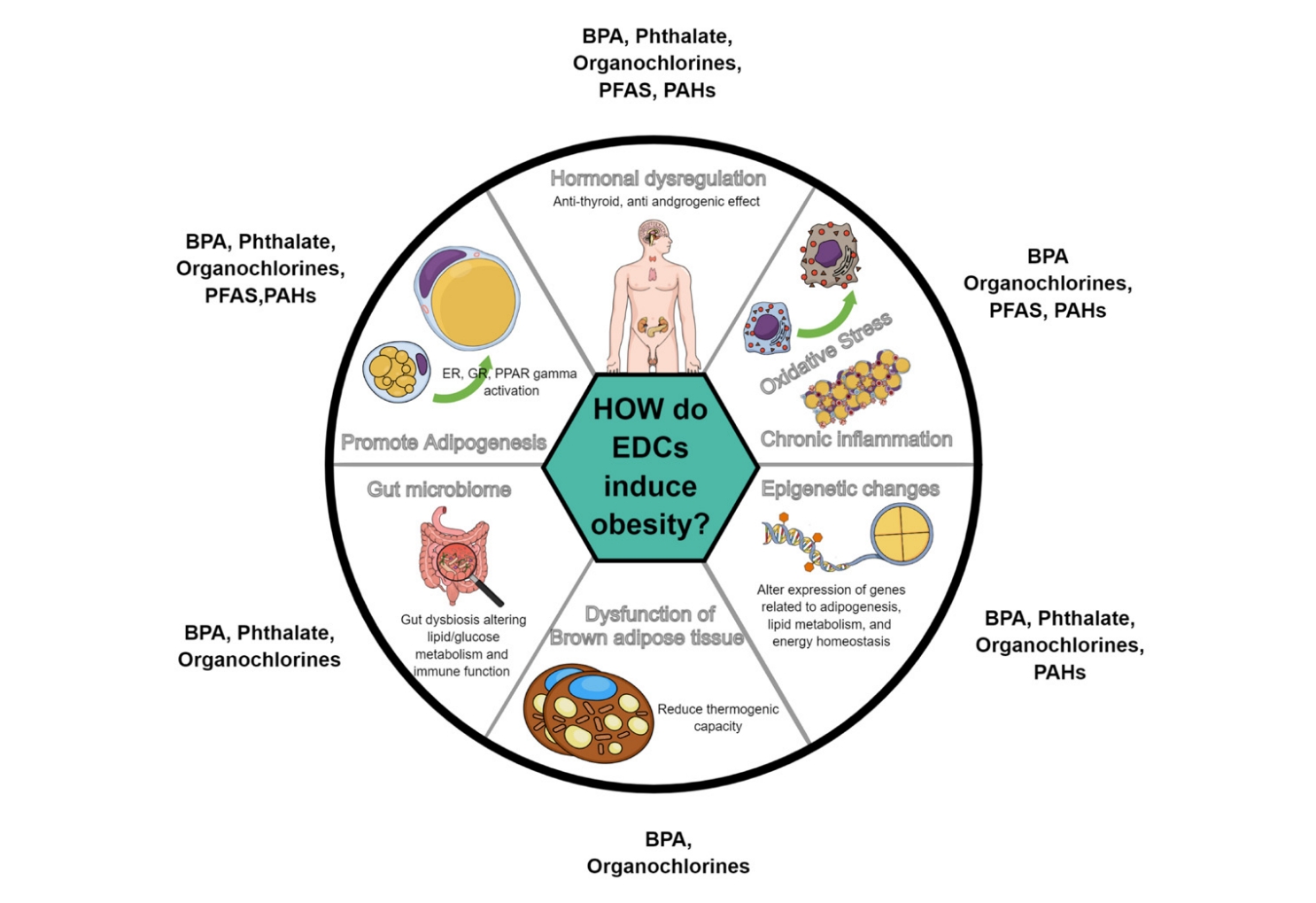
Studies indicate potential connections between exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and childhood obesity. Variations in the impact of EDCs in epidemiological studies may result from differences in exposure concentrations and timing, measurement methods, and interactive effects of multiple EDCs. Longitudinal studies on exposure to multiple EDCs are crucial to elucidating their contribution to pediatric obesity and minimize the adverse health consequences of EDC exposure.
- Gastroenterology
- Practical concepts and strategies for early diagnosis and management of eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders in East-Asian children
- Byung-Ho Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):185-198. Published online November 13, 2024
-
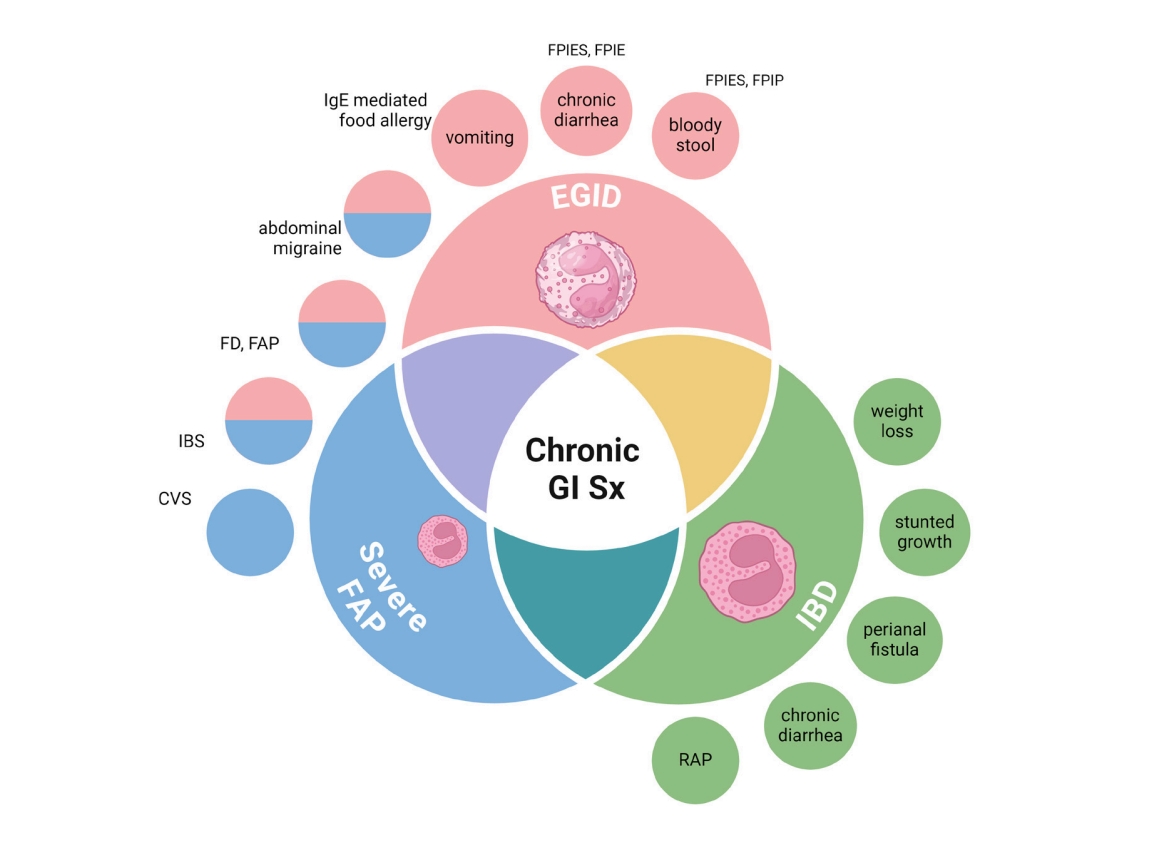
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs) often coexist with functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) and other IgE or non-IgE mediated GI diseases. Diagnosing EGIDs requires a high index of suspicion and a comprehensive approach to differentiate them from conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. Tests such as fecal calprotectin and biopsies aid in severe cases. Maintaining a food diary helps identify triggers for long-term elimination. Awareness and education are key to effective management.
- Value of transabdominal ultrasonography for diagnosing functional constipation in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Duc Long Tran, Phu Nguyen Trong Tran, Paweena Susantitaphong, Phichayut Phinyo, Palittiya Sintusek
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):127-135. Published online November 13, 2024
-
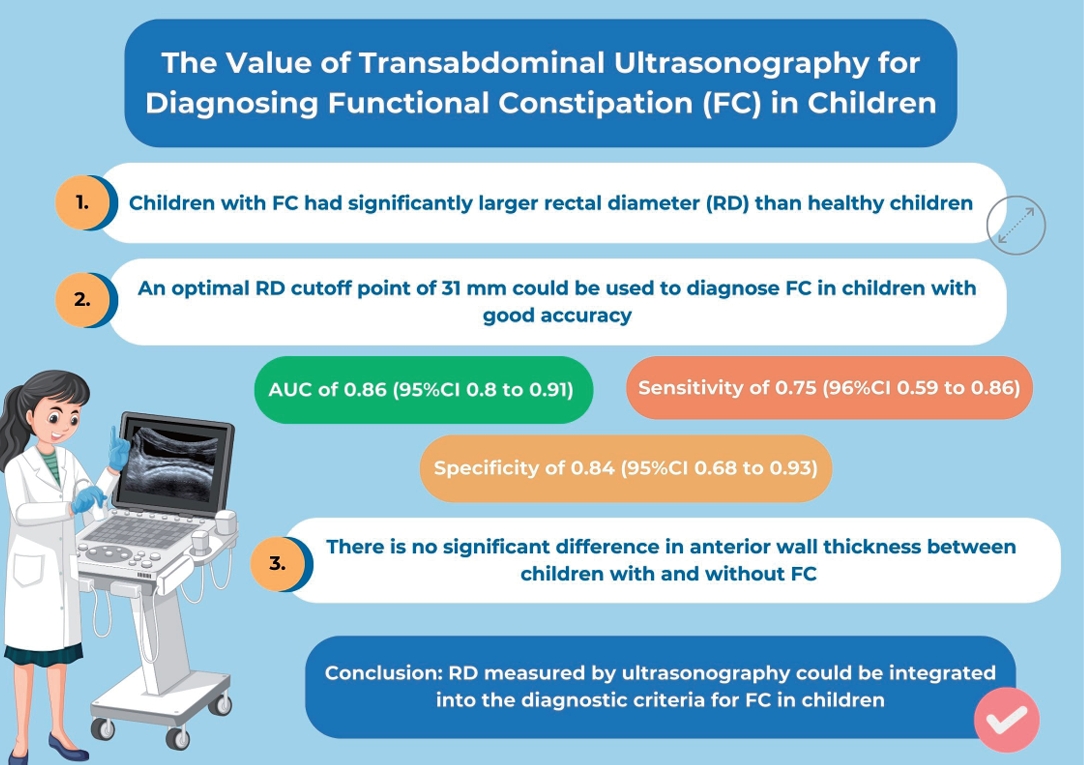
Transabdominal ultrasonography is increasingly used as a novel modality for detecting pediatric functional constipation (FC). This systematic review and metaanalysis aimed to assess the diagnostic parameters of FC including rectal diameter (RD) and anterior rectal wall thickness. A systematic search was conducted of the Ovid MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, and PubMed databases through September 29, 2023, to identify studies comparing RD...
- General Pediatrics
- Prevalence of childhood overweight and obesity in Malaysia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ker Yang Chua, Ker Yung Chua, Karuthan Chinna, Chooi Ling Lim, Maheeka Seneviwickrama
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):115-126. Published online November 13, 2024
-
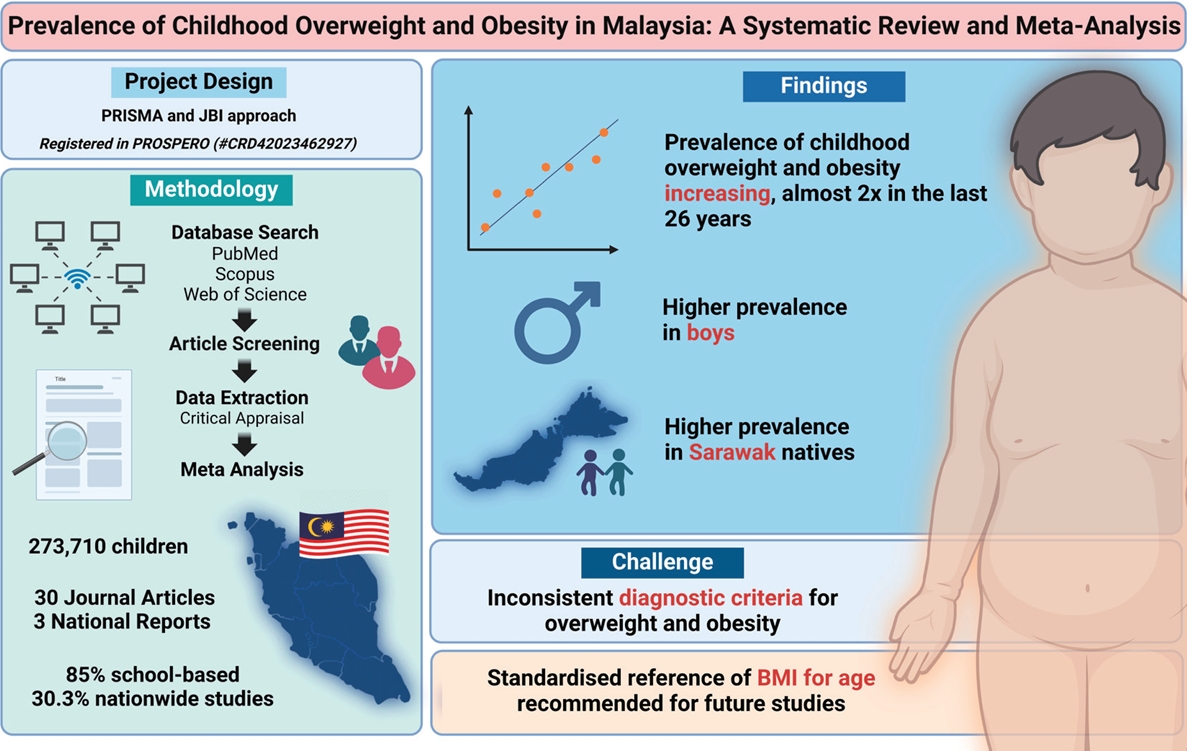
The incidence of childhood obesity is increasing worldwide. National surveys in Malaysia have shown similar trends. This review aimed to increase our understanding of the prevalence and associated factors of childhood overweight, obesity, and excess weight in Malaysia. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted of studies reporting the prevalence of overweight and obesity in Malaysian children aged <18 years....
- Hematology
- Promising role of voxelotor in managing sickle cell disease in children: a narrative review
- Amit Agrawal, Gaurav Jadon, Japna Singh, Dalwinder Janjua
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):106-114. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Voxelotor has promising ability to increase hemoglobin levels and reduce hemolysis markers in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD). Several preclinical and phase II/III trials have demonstrated its efficacy, dose-dependent responses, and tolerability in children. Ongoing trials are assessing its safety and effectiveness in various populations, including children younger than 12 years. These findings suggest its potential as a disease-modifying drug, warranting further exploration of its role in SCD management.
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











