Review article
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Review article
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm infants
- In Gyu Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):281-287. Published online December 30, 2022
-
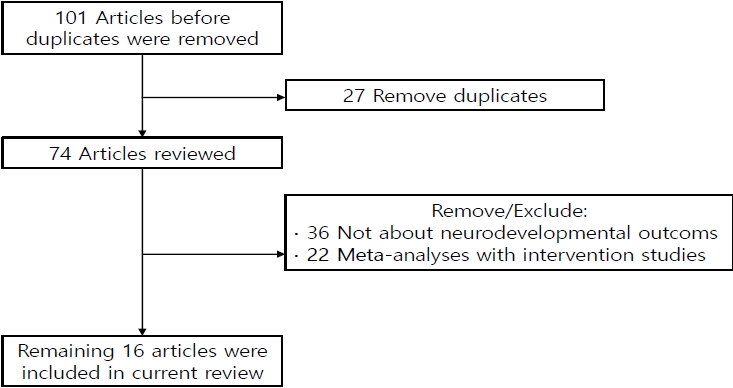
· Among survivors, 60.9% of infants born at 22 weeks’ gestation had moderate to severe impairments, whereas 50.3% born at 23 weeks’ and 42.2% at 24 weeks’ gestation had moderate to severe impairments.
· Moderate and late preterm infants reportedly have less severe disease than very preterm infants, but they still experience adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes.
· The careful follow-up and early detection of developmental problems in these patients are required.
- Neurology
- Gut microbiota affects brain development and behavior
- Gun-Ha Kim, Jung-Ok Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):274-280. Published online November 8, 2022
-

· The gut microbiota can alter a host’s brain development and behavior.
· Gut bacteria communicate with the brain via the microbiota-gut-brain axis.
· Fecal microbial transplantation is a promising treatment strategy for autism spectrum disorder.
- Allergy
- Recent topics on gastrointestinal allergic disorders
- Yoshiyuki Yamada
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):240-249. Published online January 9, 2023
-

Gastrointestinal (GI) allergies are divided into immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated, non-IgE-mediated, and mixed types. In addition to non-IgE-mediated, overlapping eosinophilic GI disorders (EGIDs) have increased in Japan. EGIDs, a mixed-type allergy category, include eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) and non-EoE EGIDs. The number of EoE cases has increased in Western countries, followed by Asian countries. Recent GI allergies may also be associated with type 2 inflammation.
- Gastroenterology
- Update on eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease beyond eosinophilic esophagitis in children
- Hye Ran Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):233-239. Published online January 3, 2023
-

· Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease (EGID) is uncommon, with a prevalence of 1–30/100,000 in the general population; however, it is increasing worldwide.
· The diagnosis of EGID is based on histopathological findings of endoscopic mucosal biopsy in which tissue eosinophils are counted in each gastrointestinal tract segment of patients with chronic or recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms.
· Individualized treatment strategies, including adequate dietary and pharmacological therapy, may help improve outcomes of children with EGID.
- Role of social media use in onset of functional gastrointestinal disorders in children
- Mauro Cinquetti, Vanessa Dargenio, Michele Fingerle, Carolina Marchiotto, Marco Biasin, Massimo Pettoello Mantovani, Flavia Indrio
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):226-232. Published online December 21, 2022
-
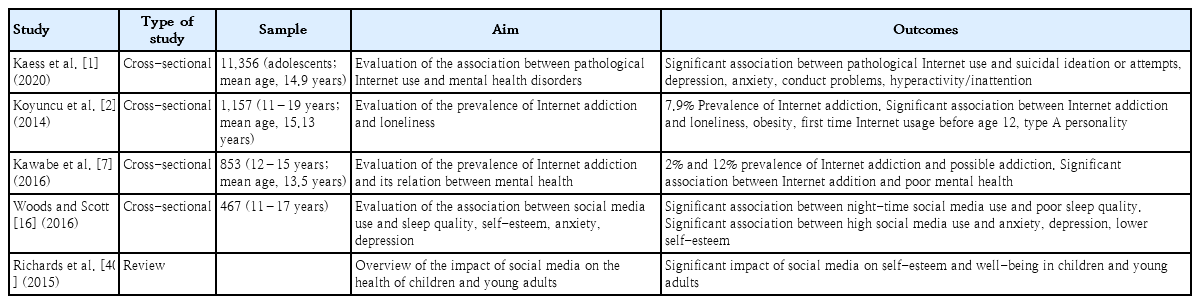
· Social media use can cause adverse health outcomes, including gastrointestinal disorders, in children and adolescents.
· Recent findings have shown a high prevalence of social media use and decreased well-being in patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders.
· The biopsychosocial nature of functional gastrointestinal disorders and the clear influence of social media on the psychosocial lives of children suggests the likely involvement of social media in their development.
- Neurology
- Electroencephalography source localization
- Tae-Hoon Eom
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):201-209. Published online December 29, 2022
-
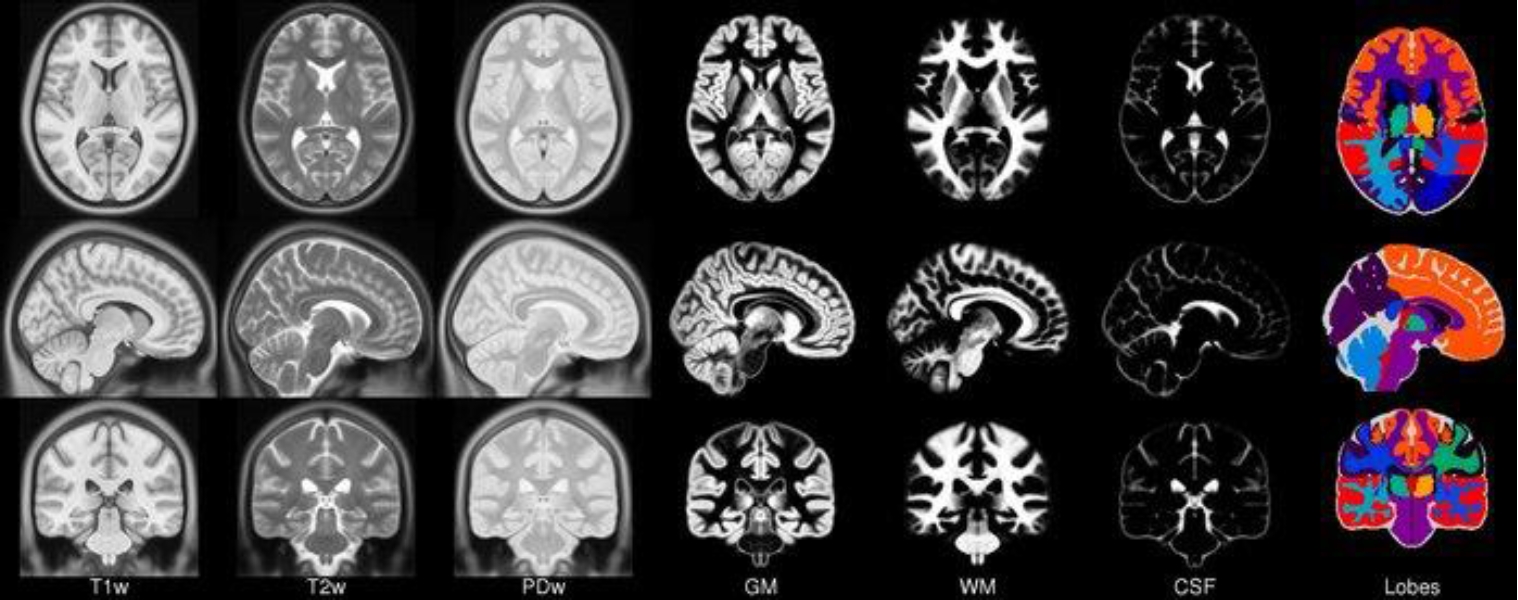
· Electroencephalography (EEG) directly images the electrical activity of neurons at a higher temporal resolution than other neuroimaging techniques.
· EEG is still widely used in brain function research due to its advantages.
· Forward and inverse problems of EEG analyses require solutions.
· Methods such as the dipole and distributed source models have been introduced.
· Applications of EEG are expanding with the integration of other technologies and large-scale data.
- Cardiology
- Arrhythmia and COVID-19 in children
- Mi Kyoung Song, Bryan Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):190-200. Published online April 18, 2023
-
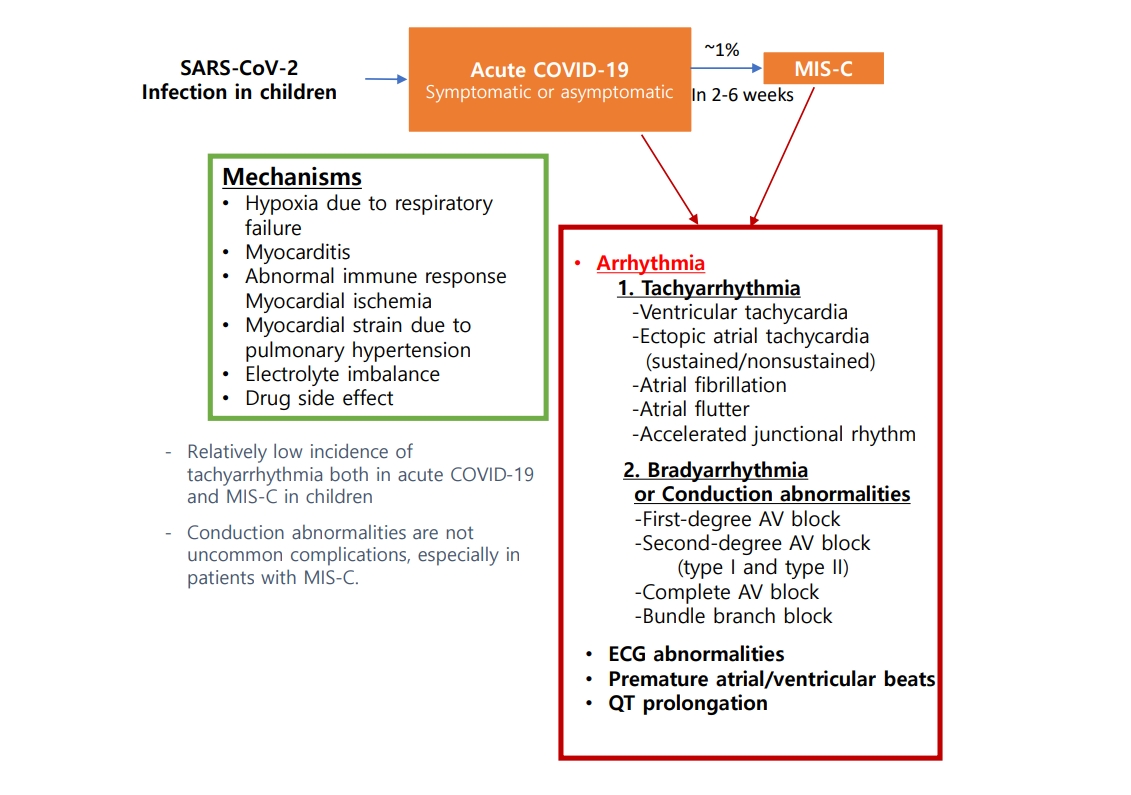
· Pediatric patients have a relatively low incidence of tachyarrhythmia both in acute coronavirus disease 2019 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), but it was associated with an increased risk of poor outcomes.
· Conduction abnormalities were not uncommon, especially in those with MIS-C. Most patients recovered to normal sinus rhythm; however, some progressed to advanced atrioventricular block and rarely required permanent pacemaker implantation.
- Infection
- COVID-19 in immunocompromised children and adolescents
- Byung Ok Kwak, Byung Wook Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):182-189. Published online April 18, 2023
-

Most immunocompromised children and adolescents are not at increased risk of developing severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). COVID-19 outcomes for low- or medium-risk immunocompromised children are favorable, while more serious illness reportedly occurs in high-risk immunocompromised children by underlying disease, its treatments, and other factors. Therefore, the early detection and timely management of severe COVID-19 and treatment of underlying disease are important. Hospitalization and COVID-19 vaccination should be carefully considered.
- Allergy
- New approaches to immunotherapy in house dust mite allergy
- In Sik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):161-168. Published online October 25, 2022
-
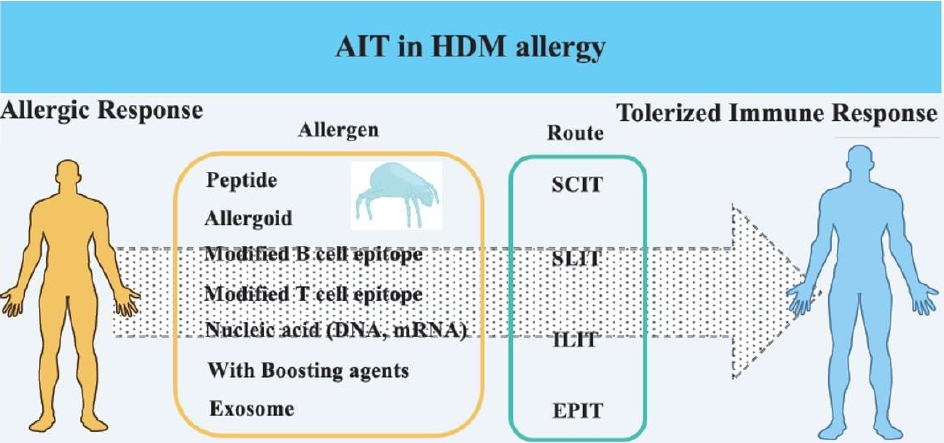
Allergen immunotherapy (AIT) has developed over the last few decades and has emerged as a promising treatment. House dust mite (HDM) is a target allergen in AIT, and various modified HDM allergens have been improved for their efficacy. Moreover, clinical trials have proved their significantly therapeutic effects in allergy. This article review focuses on HDM allergens developed for AIT efficacy,...
- Gastroenterology
- High-resolution esophageal manometry in children
- Yogesh Waikar
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):155-160. Published online October 17, 2022
-

High-resolution esophageal manometry can be safely performed in children where recurrent vomiting and persistent dysphagia is the working diagnosis after excluding nonluminal and structural obstructive pathologies using pediatric upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Normal manometry values are available. Clinical picture, biochemical tests, radiological interpretation, and endoscopic findings with manometry completes the analysis of patients with recurrent vomiting and dysphagia.
- Nutrition
- Association of gut microbiota with obesity in children and adolescents
- Ky Young Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):148-154. Published online November 16, 2022
-

The gut microbiota is an emerging factor in the development of pediatric obesity, which is affected by renowned risk factors such as diet, lifestyle, and socioeconomic status. This review aimed to describe the association between the gut microbiota and childhood obesity.
- Gastroenterology
- Liver fibrosis in children: a comprehensive review of mechanisms, diagnosis, and therapy
- Elif Ozdogan, Cigdem Arikan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):110-124. Published online December 19, 2022
-
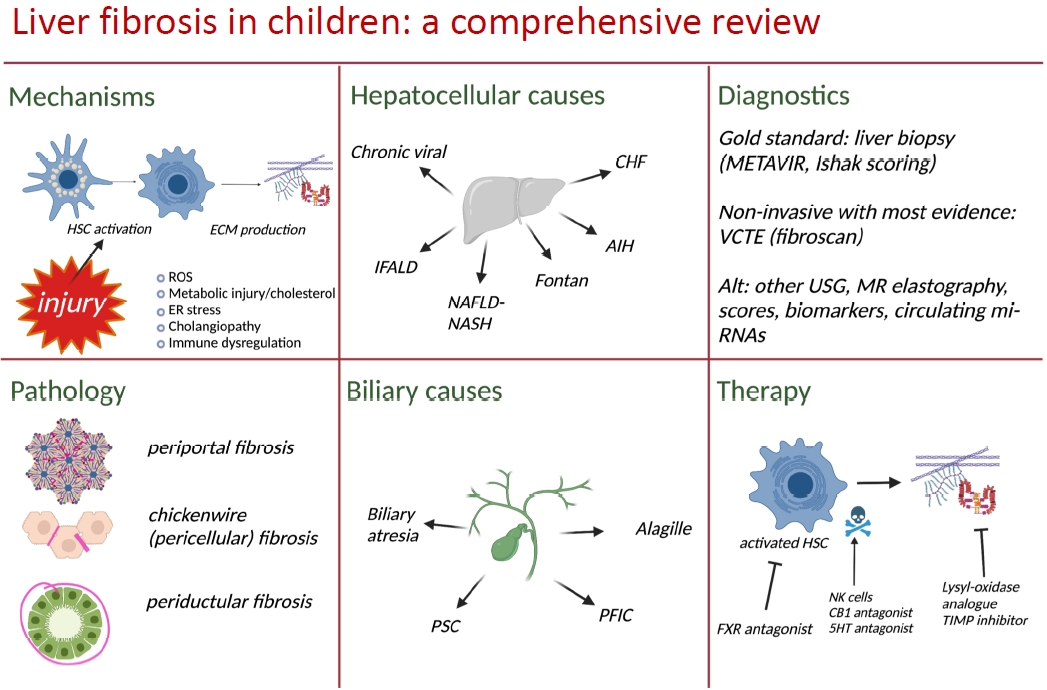
· Chronic liver diseases in children are heterogenous but converge in the common pathway of fibrosis.
· Much of the literature on mechanisms of fibrogenesis focus on adults but pediatric physiology has documented differences.
· Understanding of these distinctions are necessary to define, treat, and prevent fibrosis.
· Current management of liver fibrosis relies heavily on liver biopsy. Multiple tools have shown high diagnostic performance in pediatric and adult populations. Large, multicenter studies are needed for validation.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Ferritin in pediatric critical illness: a scoping review
- Ivy Cerelia Valerie, Anak Agung Sagung Mirah Prabandari, Dyah Kanya Wati
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):98-109. Published online September 16, 2022
-
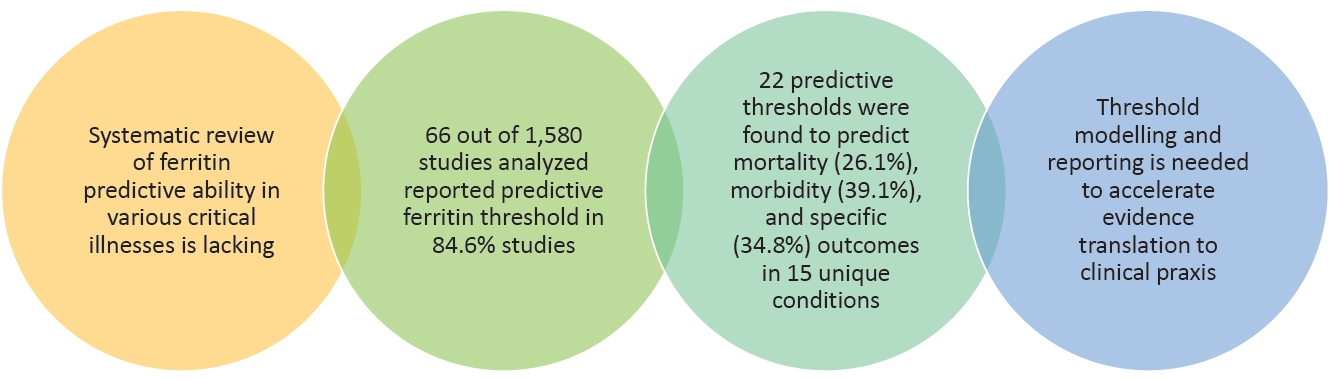
The number of studies on ferritin predictive ability in pediatric critical illness has grown exponentially over the past 2 decades. However, among the 66 of 1,580 studies analyzed here, summary statistics for overall and condition-specific studies were only reported in 45.4% and 71.2%, respectively. In contrast, ferritin as a categorical variable with a preset threshold was a significant predictor in 84.6% of studies.
- Neurology
- Pediatric syncope: pearls and pitfalls in history taking
- Jung Sook Yeom, Hyang-Ok Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):88-97. Published online February 15, 2023
-
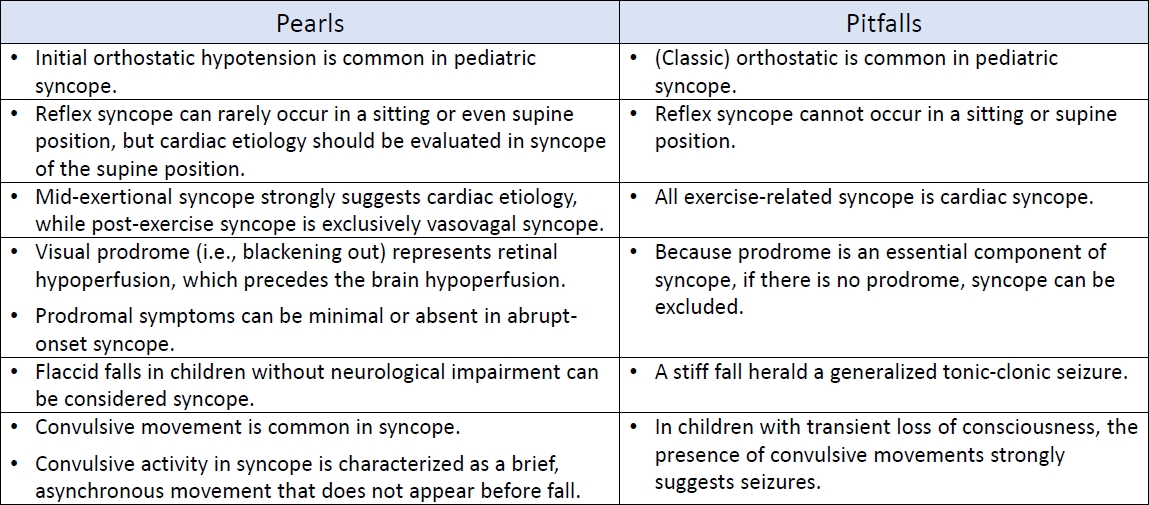
An accurate diagnosis depends on correct history taking and its interpretation. An in-depth understanding of the symptoms of syncope in connection with its pathophysiology can lead to avoiding critical pitfalls in the diagnostic process of history taking.
- Nutrition
- Total energy expenditure measured by doubly labeled water method in children and adolescents: a systematic review
- Nahyun Kim, Jonghoon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):54-65. Published online October 17, 2022
-
This systematic review summarizes convincing evidence that total energy expenditure (TEE) measured using the doubly labeled water technique increased with age from 1 to 18 years, while fat-free mass (FFM) increased with growth. TEE and in normal-weight participants, while physical activity level did not differ from that of normal-weight participants.
- Infection
- Pathogenetic and etiologic considerations of febrile seizures
- Ji Yoon Han, Seung Beom Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):46-53. Published online January 13, 2023
-

· Inflammatory responses accompanying fever increase neuronal excitability in the central nervous system, which in turn provokes seizures.
· Fever in children with febrile seizures is usually caused by common respiratory viruses, the distributions of which match those of seasonal community-acquired respiratory tract infections.
· Several genetic variations in ion channels seem associated with neuronal hyperexcitability in children with febrile seizures.
- Gastroenterology
- Current diagnosis and image-guided reduction for intussusception in children
- Jisun Hwang, Hee Mang Yoon, Pyeong Hwa Kim, Ah Young Jung, Jin Seong Lee, Young Ah Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):12-21. Published online July 4, 2022
-
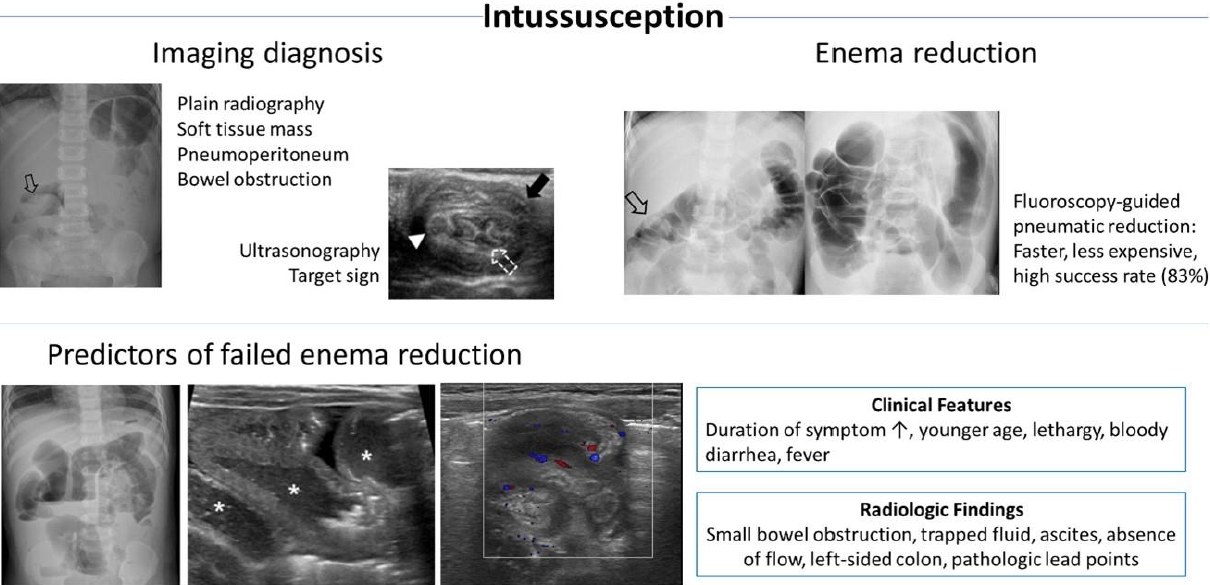
· Intussusception, the most common cause of small bowel obstruction in young children, has an overall incidence in Korea of 28.3 cases per 100,000 person-years.
· Its cause is idiopathic inmost cases, although viral or bacterial gastroenteritis has beenpostulated as a cause. Approximately 4% of children have pathological lead points for intussusception, and Meckel’s diverticulum is the most common cause.
· Intussusception in preterm infants is extremely rare. Older children (>5 years of age) are at increased risk of pathological lead points.
- Cardiology
- Research trends on causes of Kawasaki disease in the COVID-19 era: focus on viral infections
- Young Hwan Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):1-11. Published online June 22, 2022
-
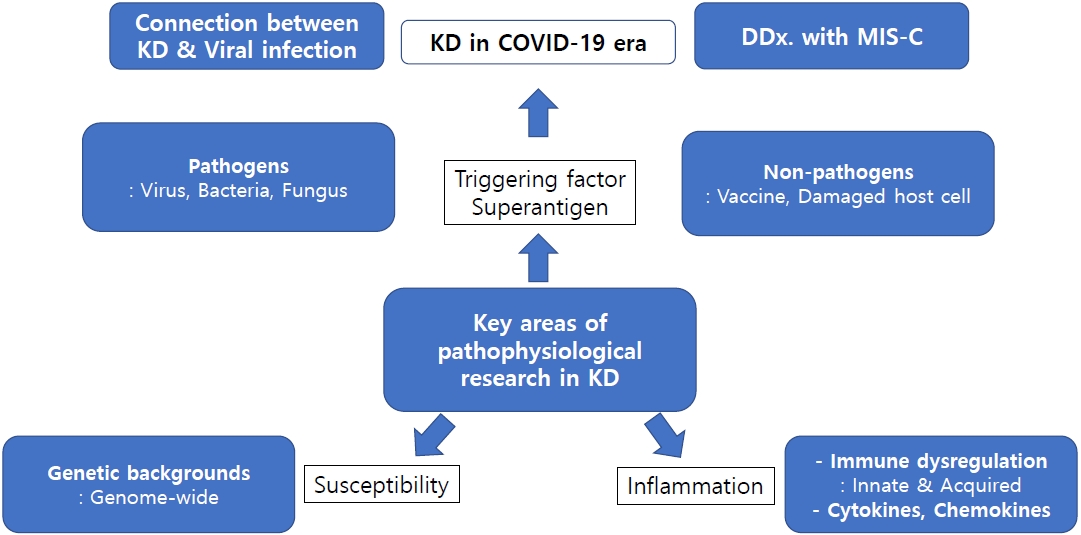
· The etiology of Kawasaki disease (KD) is unclear, but its clinical, epidemiological, and pathophysiological characteristics are strongly associated with infectious diseases.
· In the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic era, viruses are attracting the most attention. Sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection causes various hyperinflammation in children that require differentiation from KD.
· Immune responses in patients with KD may be induced by host cell damage. To effectively prevent and treat KD, the genetic background and immune responses of KD patients and triggering pathogens require identification.
- Allergy
- Diagnosis and management of asthma in infants and preschoolers
- Hai Lee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):574-584. Published online April 19, 2022
-
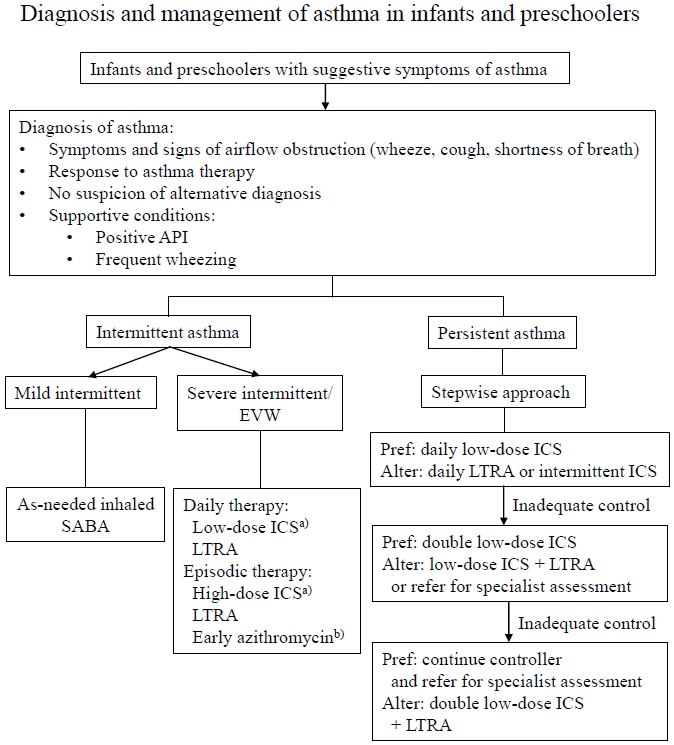
· Asthma in infants and preschoolers involves heterogeneous phenotypes.
· Asthma diagnosis is based on symptom patterns, therapeutic responses, and the presence of risk factors with careful consideration of differential diagnosis.
· Daily inhaled corticosteroid therapy remains the most effective strategy for managing persistent asthma symptoms irrespective of phenotype.
· Future research, including genetic and molecular studies, is needed to develop a clear definition of asthma and personalized therapeutic approaches.
- Pulmonology
- Epidemiology and surveillance implications of community-acquired pneumonia in children
- Eui Jeong Roh, Jung Yeon Shim, Eun Hee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):563-573. Published online October 17, 2022
-
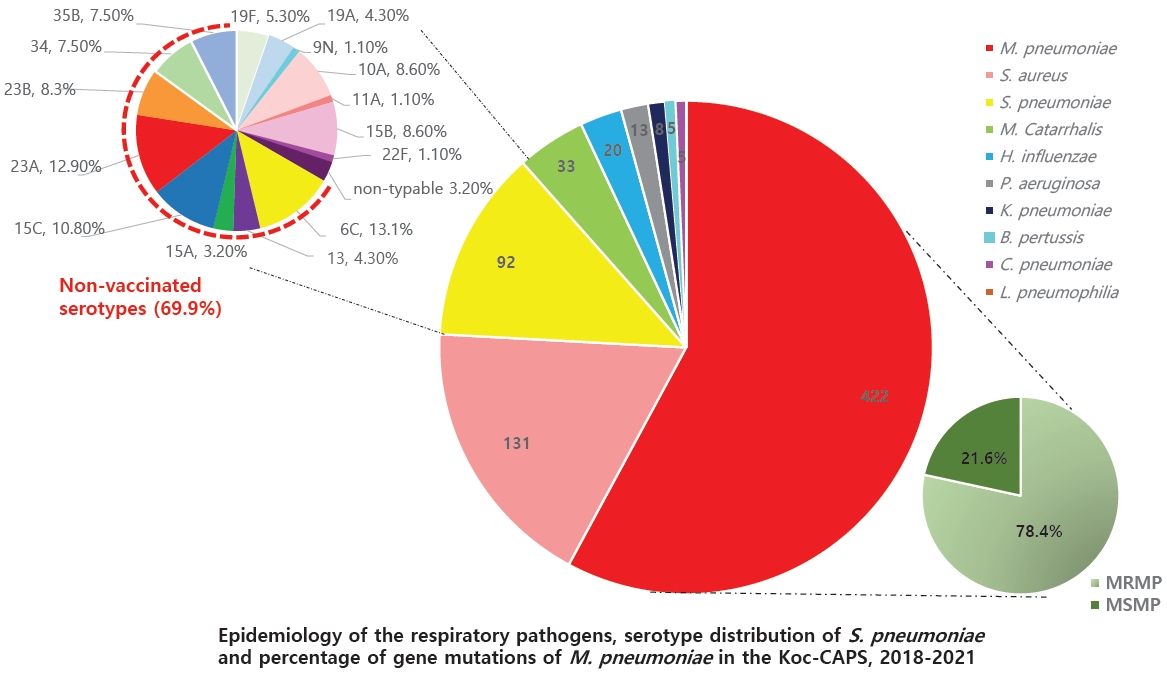
The identification of the causative pathogens of community-acquired pneumonia and appropriate treatment and prevention can reduce mortality and the socioeconomic burden by reducing the medical expenses. The world has been in the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic since 2020, and there is always a risk of continuous emergence and epidemic of new respiratory infectious diseases. Therefore, it is important to sustain a monitoring system for respiratory infectious diseases including pneumonia.
- Infection
- Global varicella vaccination programs
- Young Hwa Lee, Young June Choe, Jia Lee, Eunseong Kim, Jae Young Lee, Kwan Hong, Yoonsun Yoon, Yun-Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):555-562. Published online November 2, 2022
-
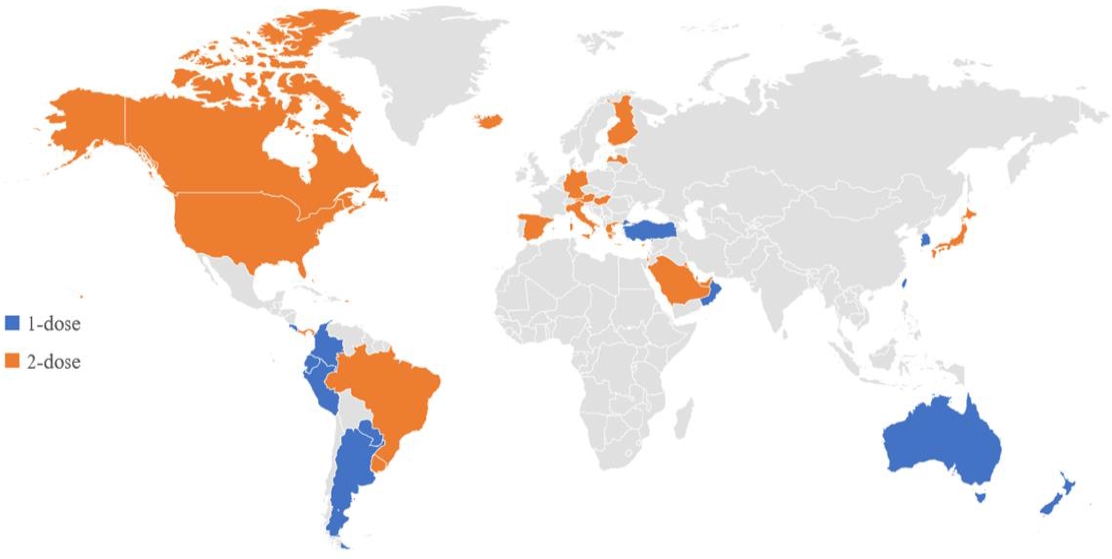
It is important to evaluate its effectiveness at the national level and to determine the varicella vaccine schedule based on the evidence generated through the studies.
- Allergy
- Management of patients with allergic diseases in the era of COVID-19
- Eun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):529-535. Published online September 23, 2022
-
In the early days of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, allergic diseases, especially asthma, were considered to be risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, hospitalization, and death. These concerns stemmed from the idea that individuals with allergic diseases are generally more susceptible to respiratory virus infections, which are major causes of exacerbation of allergic diseases. However, epidemiologic data with...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal seizures: stepping outside the comfort zone
- Menna Hashish, Mohamed Reda Bassiouny
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):521-528. Published online April 4, 2022
-
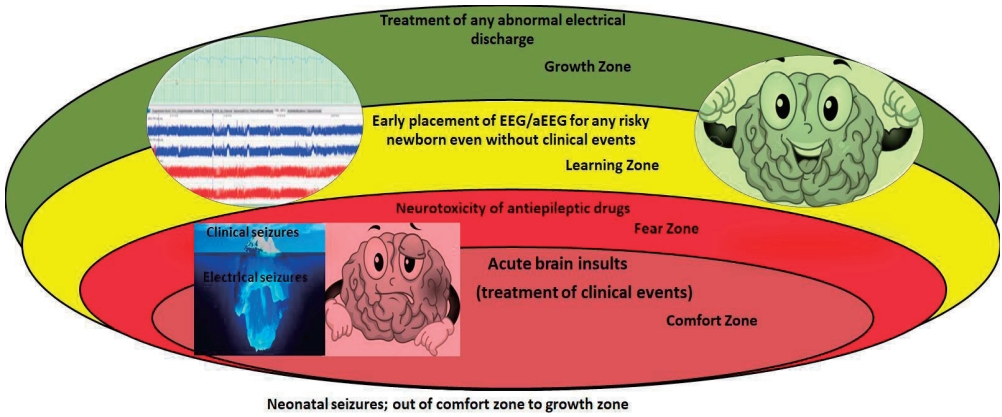
· Use conventional and amplitude-integrated electroencephalography to confirm clinical seizures and screen high-risk newborns.
· Select an explicit clear elective event to be treated with less toxic and more effective antiepileptics.
- General Pediatrics
- Motor performance of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: focus on the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency
- Khushboo Prashant Adhvaryu, Suruliraj Karthikbabu, Pratiksha Tilak Rao
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):512-520. Published online February 17, 2022
-
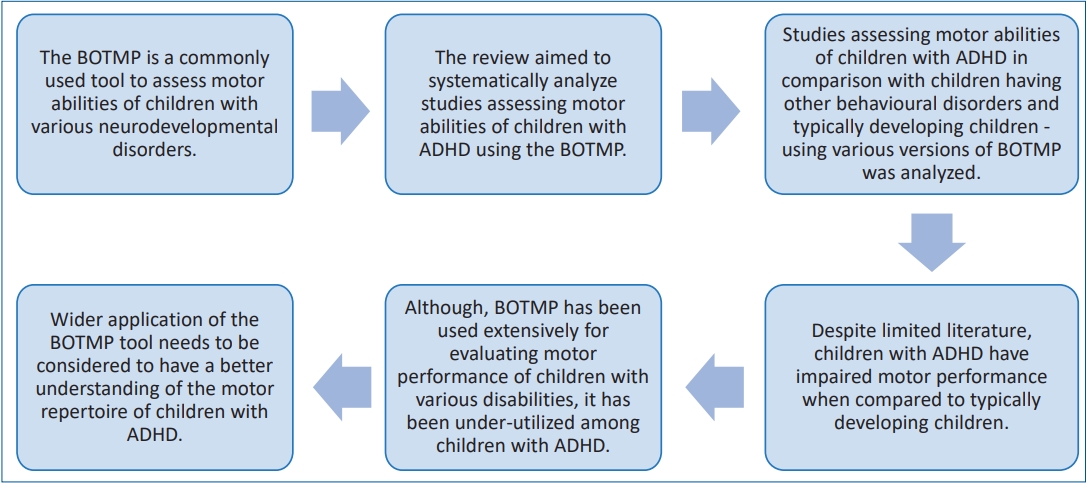
· Children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) tend to have impaired motor performance that may affect their growth and development.
· Although widely used among children with developmental disorders, the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency (BOTMP) is used sparsely among children with ADHD.
· Assessment by the BOTMP increases our understanding of the motor repertoire of children with ADHD.
· Wider usage of the BOTMP will enable more comprehensive planning of rehabilitation goals to enhance the motor abilities of children with ADHD.
- Neurology
- Rotavirus infection-associated central nervous system complications: clinicoradiological features and potential mechanisms
- Kyung Yeon Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):483-493. Published online February 7, 2022
-

∙ Rotavirus infection-associated central nervous system (CNS) complications are fairly common in children.
∙ Common clinicoradiological features include benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis, acute encephalopathies/encephalitis, cerebellitis, and neonatal rotavirus-associated leukoencephalopathy.
∙ Possible mechanisms for CNS complications include direct viral invasion into the brain via several potential routes such as the blood-brain barrier and vagus nerve, and entry of various brain-damaging mediators and activated immune cells into the brain.
- Oncology
- Application of 3-dimensional printing implants for bone tumors
- Jong Woong Park, Hyun Guy Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):476-482. Published online December 23, 2021
-

∙ The application of 3-dimensional (3D) printing in orthopedic oncology is summarized into bone and tumor modeling, patient-specific instruments (PSIs), custom-made implants, and tissue engineering.
∙ The 3D-printed customized implant is the most central application, while modeling and PSI often play adjunct roles.
∙ Short-term surgical outcomes of custom-made 3D-printed implants are promising.
- Neurology
- Update on benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis
- Yeong Seok Lee, Ga Hee Lee, Young Se Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):469-475. Published online December 27, 2021
-
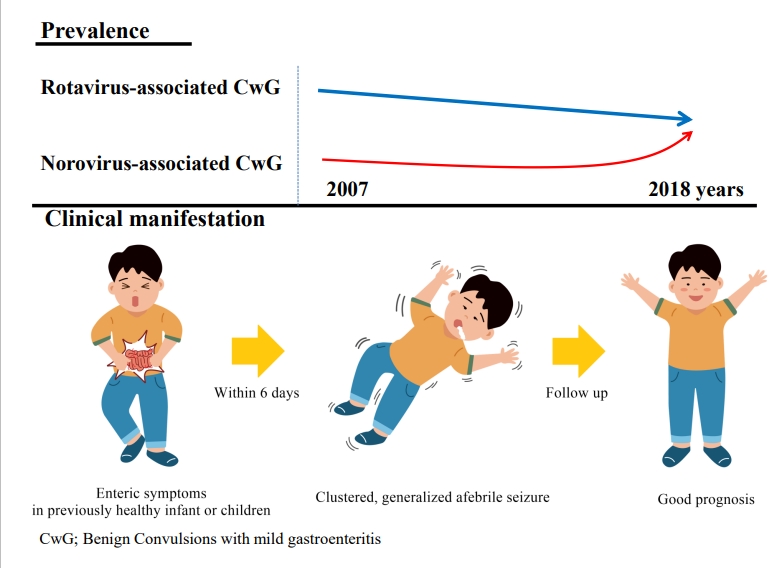
∙ The main pathogen for benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (CwG) was previously rotavirus; however, cases associated with norovirus are increasing.
∙ CwG is characterized by clustered generalized seizures. Electroencephalography and magnetic resonance imaging show transiently abnormal findings in the acute phase that eventually normalize with progression. Its prognosis is good, and long-term treatment is unnecessary.
∙ There are many reports on the pathophysiological mechanism of CwG, which remains unclear.
- Gastroenterology
- Factors influencing development of the infant microbiota: from prenatal period to early infancy
- Sujin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):439-447. Published online December 23, 2021
-
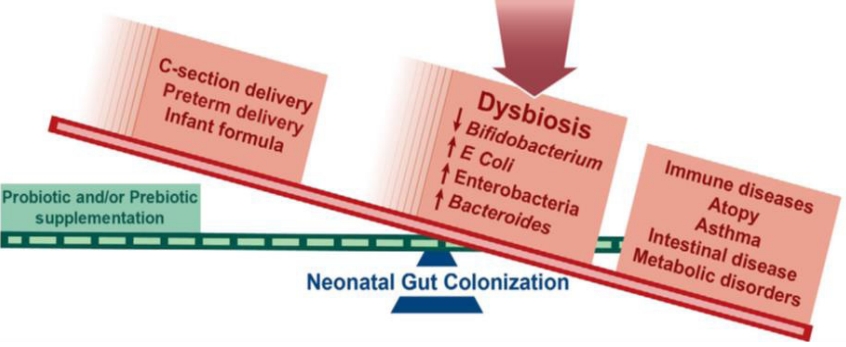
∙ Microbial colonization primarily occurs after birth but there may be some colonization in utero, although this remains highly controversial.
∙ Maternal factors during pregnancy affect the infant microbiota: diet, weight, gestational weight gain, and antibiotic usage.
∙ Microbes are passed from mother-to-infant during and after birth. Delivery mode, breastfeeding, early life antibiotic, and proton pump inhibitor treatment have the largest effects on microbial composition in early life.
∙ The early life gut microbiome plays an important role in the development of the immune system and metabolism.
- Cardiology
- Diagnosis of coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki disease: recent guidelines and z score systems
- Sung Hye Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):430-438. Published online December 17, 2021
-
∙ Kawasaki disease is the leading cause of acquired heart disease among children in the developed countries, and Korea has the second-highest incidence in the world.
∙ Early diagnosis and proper treatment are imperative to prevent coronary complication, and evaluation of coronary artery abnormalities is fundamental.
∙ Recent guidelines have adapted z score system for the diagnosis of coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki disease.
∙ Applying z score in diagnosis of coronary abnormalities has better correlation with clinical outcomes than absolute cutoff values.
∙ Calculated z scores could be different according to the z score formula, which might influence the treatment plan.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Breastfeeding and vitamin D
- Ju Sun Heo, Young Min Ahn, Ai-Rhan Ellen Kim, Son Moon Shin; for the Korean Society of Breastfeeding Medicine
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):418-429. Published online December 14, 2021
-
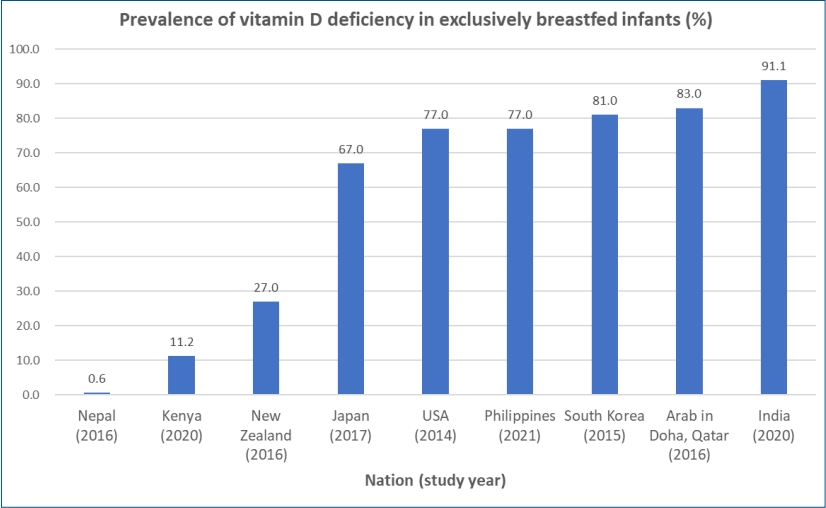
∙ Exclusively breastfed infants are at risk of developing vitamin D deficiency associated with hypocalcemia, rickets, and various health outcomes.
∙ The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in breastfed infants differs vastly between studies and nations at 0.6%–91.1%.
∙ The vitamin D content of breast milk does not meet the requirements of exclusively breastfed infants.
∙ Most international guidelines recommend that breastfed infants be supplemented with 400 IU/day of vitamin D during the first year of life.
∙ Vitamin D intake (milk+supplements) of 800 IU/day can be considered in preterm infants along with biochemical monitoring.
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











