Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last six months.
- Clinical Note
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- External tracheal compression and mucosal injury in a neonate with cervical teratoma: a rare airway challenge (27 times)
- Rhodora Guillen, Arijit Lodha, Prashanth Murthy
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):73-75. Published online December 4, 2025
-

- Original Article
- Immunology
- Serum bactericidal activity against meningococcus in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (26 times)
- Soyoung Lee, Kyung-Hyo Kim, Ji Hyen Lee, Han Wool Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):362-369. Published online January 13, 2025
-
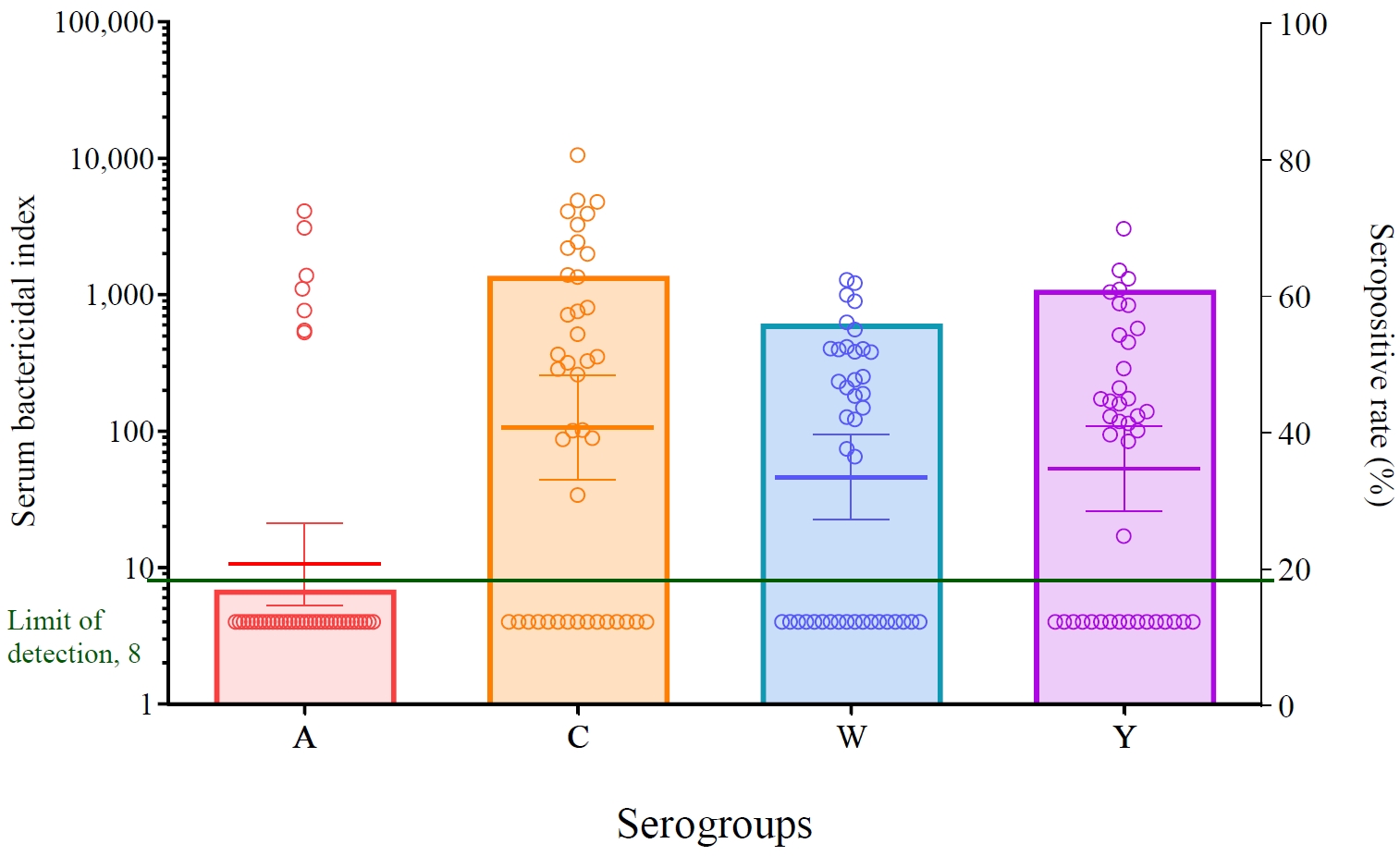
Question: What is the level of immunity against meningococcal infections in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) under the age of 19, and is vaccination against meningococcus necessary for these patients, given their susceptibility to infections due to immunosuppressive treatments and disease characteristics?
Finding: Although some of our study patients exhibited serum bactericidal activity against meningococci, most remained seronegative.
Meaning: These findings suggest that patients with SLE who are at risk of meningococcal infection receive appropriate vaccinations.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Prioritizing maternal sleep: a public health strategy for preventing childhood allergic diseases (26 times)
- Eunchae Lee, Seohyun Hong, Dong Keon Yon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):22-25. Published online December 18, 2025
-

Sleep disorders affect more than half of pregnancies worldwide and can harm maternal health and offspring outcomes. Prioritizing maternal sleep as a public health strategy may help prevent prenatal and pediatric allergic diseases and reduce their burden. Other maternal health strategies may also reduce the burden of offspring allergic diseases, while adequate maternal sleep is associated with other offspring outcomes, underscoring its importance as a key public health strategy.
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Effect of face mask on pulmonary artery pressure during echocardiography in children and adolescents (25 times)
- Alireza Ahmadi, Mohammad Reza Sabri, Zohreh Sadat Navabi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):161-167. Published online January 23, 2024
-
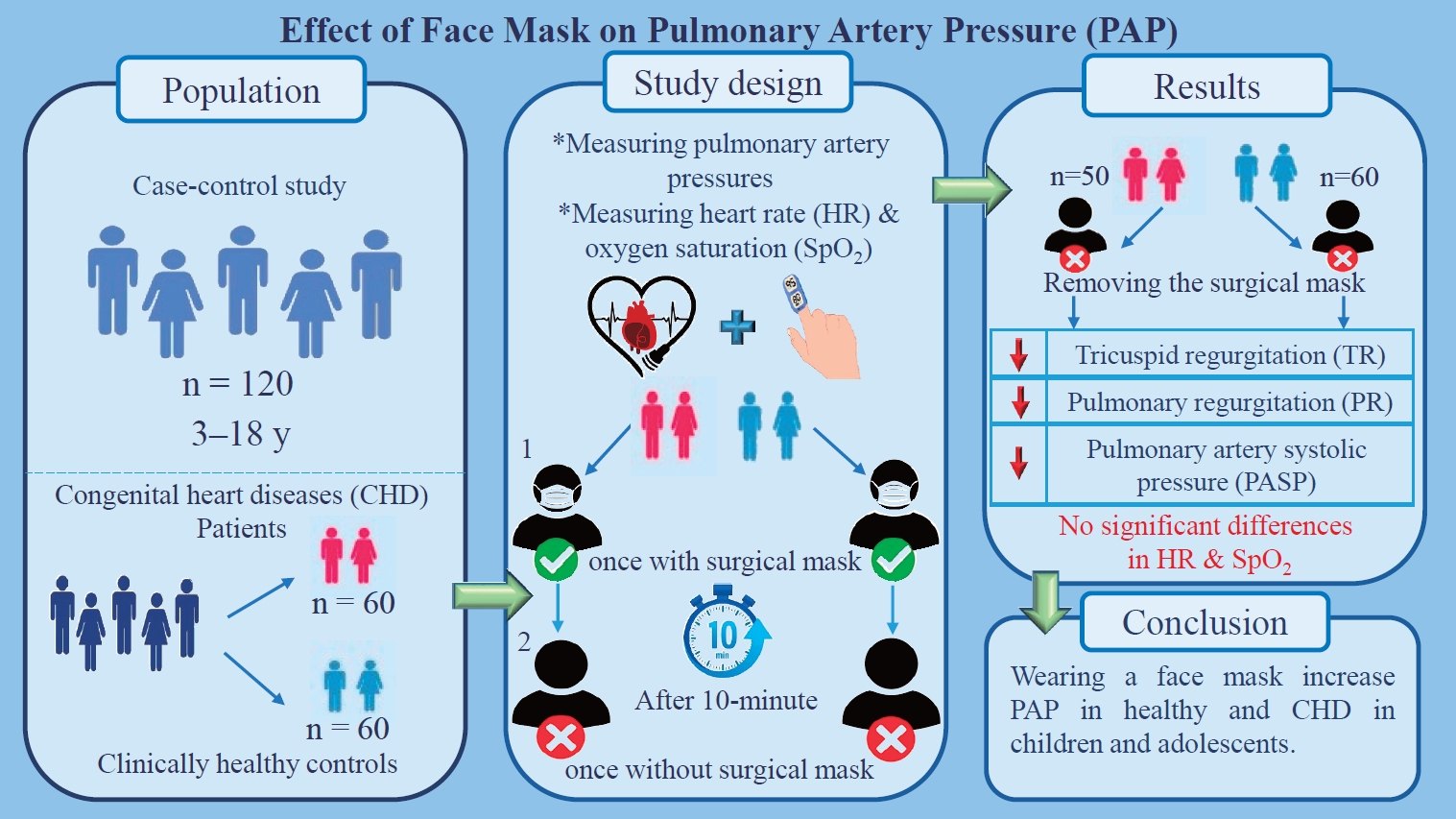
Question: Can face masks alter pulmonary pressure in children and adolescents with and without congenital heart disease?
Findings: Mask removal during echocardiography (ECHO) reduced pulmonary pressure.
Meaning: These findings suggest that face masks should be removed during ECHO in children and adolescents.
- Adolescence Medicine
- Relationship between inflammatory biomarkers and insulin resistance in excess-weight Latin children (25 times)
- Mariano Nicolás Aleman, María Constanza Luciardi, Emilce Romina Albornoz, María Cristina Bazán, Adela Victoria Abregú
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):37-45. Published online December 21, 2023
-
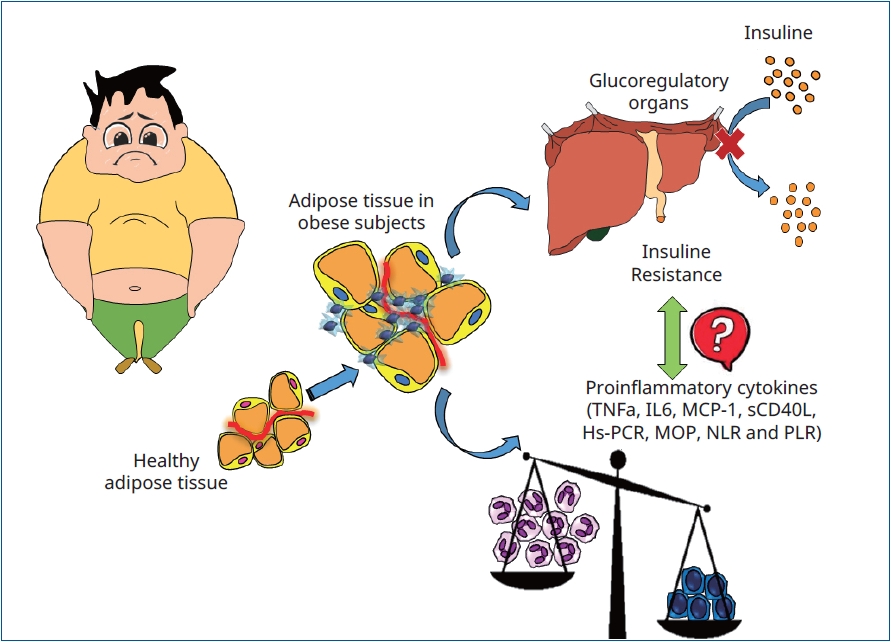
Question: What is the prevalence of insulin resistance (IR) in excess-weight Latin children, and can proinflammatory biomarkers predict it?
Finding: IR prevalence was elevated and tumor necrosis factor- α, interleukin-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein- 1, soluble CD40 ligand, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels were increased in excess-weight Latin children. However, none predicted IR status.
Meaning: These inflammatory biomarkers were unable to predict IR status. Therefore, further investigations are necessary.
- Correspondence
- Infection
- A commentary on "COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus" (25 times)
- Hinpetch Daungsupawong, Viroj Wiwanitkit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):624-625. Published online April 16, 2025
-
- Review Article
- Other
- MicroRNAs as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric diseases (24 times)
- Hwal Rim Jeong, Il Tae Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):119-125. Published online May 24, 2023
-

MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression post transcriptionally, and MiRNA expression levels vary with developmental stages. MiRNAs play an important role in several biological processes in children, including growth, neuro-development, inflammation, and tumor formation. Research on miRNAs may uncover the molecular mechanisms underlying various pediatric diseases, leading to the development of novel biomarkers that aid in the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of these diseases.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effect of vitamin E supplementation on bilirubin levels in infants with hyperbilirubinemia: a double-blind randomized clinical trial (24 times)
- Mojtaba Cheraghi, Maziar Nikouei, Majid Mansouri, Siros Hemmatpour, Yousef Moradi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):249-256. Published online March 26, 2024
-
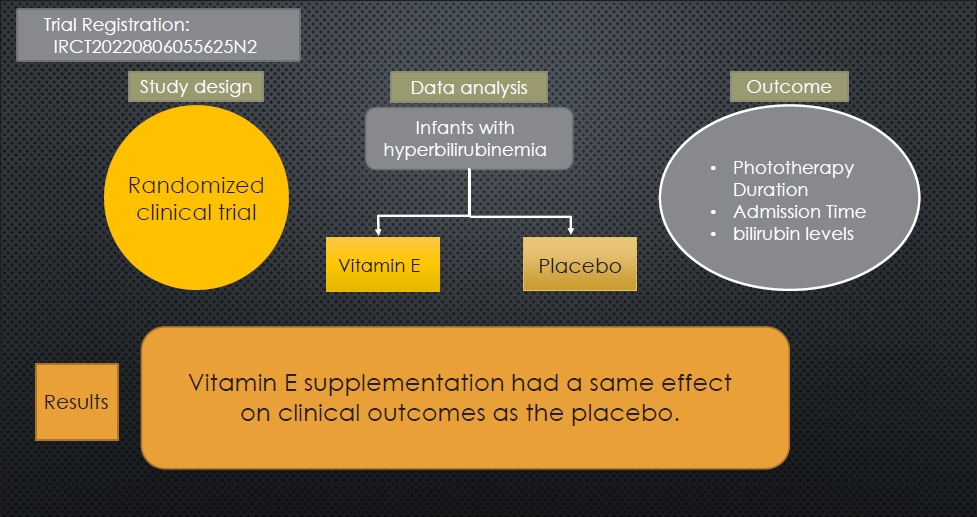
Question: Is vitamin E a viable therapeutic option for managing neonatal hyperbilirubinemia?
Finding: This randomized clinical trial examined the effects of oral vitamin E supplementation on bilirubin reduction (primary outcome), phototherapy duration, and length of hospital stay (secondary outcome) in 138 infants.
Meaning: Infants administered vitamin E versus placebo demonstrated similar reductions in bilirubin levels and length of hospital stay.
- Letter to the Editor
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Pentraxin 3 as a marker of early-onset neonatal sepsis (24 times)
- Safaa ELMeneza, Iman El-Bagoury, Hind Rayes, Amira Hassan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):312-314. Published online May 23, 2024
-

- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Oral administration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates intestinal injury in necrotizing enterocolitis (23 times)
- Yeong Seok Lee, Yong Hoon Jun, Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):152-160. Published online February 19, 2024
-
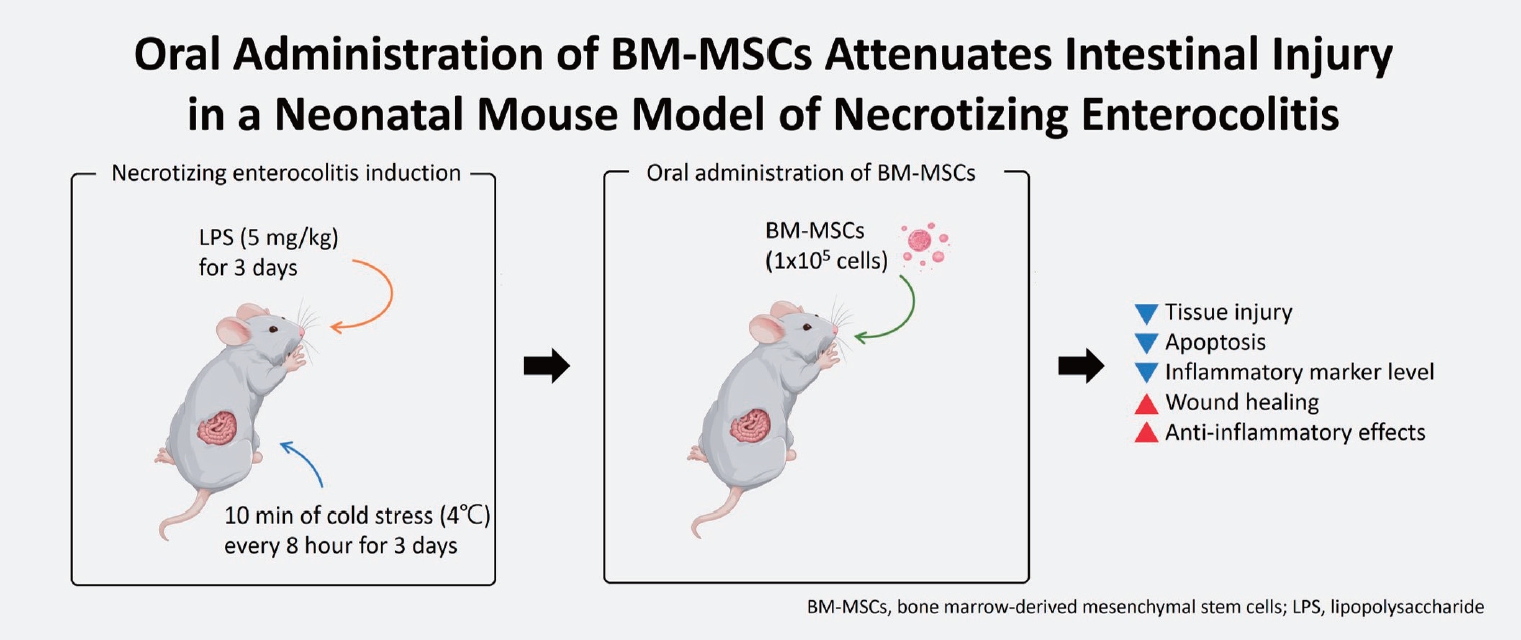
Question: What is the optimal dose of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) for treating necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), and is orally administered BM-MSC effective?
Findings: High (1×106 cells) or multiple BM-MSC doses showed similar effects as low (1×105 cells) doses of intraperitoneally administered BM-MSCs. Furthermore, orally administered BM-MSCs were as effective as intraperitoneally administered BM-MSCs.
Meaning: Orally administered low-dose BM-MSCs are a potential treatment for NEC.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effectiveness of online responsive teaching in young children with developmental disabilities: a pilot study (23 times)
- Jung Sook Yeom, Jeongmee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):303-311. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Question: Does online responsive teaching (RT) impact children's and parents’ emotions and behaviors, and do parents find it satisfactory?
Finding: Online RT significantly improved children's pivotal and problem behaviors, decreased parenting stress, and enhanced parental interactive styles with high satisfaction.
Meaning: This pilot study's findings suggest that online RT can enhance child outcomes, offering accessible interventions amid challenges such as limited access and pandemics.
- Neonatal risk factors associated with autism spectrum disorders: an umbrella review (23 times)
- Amir Mohammad Salehi, Erfan Ayubi, Salman Khazaei, Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Zohreh Salimi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):459-464. Published online July 19, 2024
-

Question: What are the neonatal risk factors for autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Findings: Significant effect sizes were observed for congenital heart disease (odds ratio [OR], 1.35), macrosomia (OR, 1.11), low birth weight (OR, 1.63), very low birth weight (OR, 2.25), small for gestational age (OR, 1.17), jaundice (OR, 1.74), male sex (OR, 1.47), and Apgar score (OR, 1.40).
Meaning: These factors were identified as risk factors for ASD.
- Clinical Note
- Immunology
- Comparative analysis of rare periodic fever syndromes including the first Korean case of hyperimmunoglobulinemia D and periodic fever syndrome (23 times)
- Yoonsun Yoon, Hyun Seo Kim, Jung Ok Shim, JungHwa Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):550-552. Published online September 24, 2024
-

- Editorial
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Advancing orphan drug development for rare diseases (22 times)
- Jung Min Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):356-357. Published online November 17, 2023
-
· Rare diseases present unique challenges and unmet needs for which the development of orphan drugs tailored to them offers hope.
· Despite the hurdles posed by limited patient populations, orphan drug designations from regulatory agencies provide incentives, such as extended market exclusivity and tax credits, that ignite transformative advances.
· Scientific progress in genomics, personalized medicine, and analytics empowers precise interventions by decoding genetic anomalies and encouraging effective treatments.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Incidence, causative organisms, and risk factors of bloodstream infections in pediatric liver transplant patients: a systematic review (22 times)
- Mohamad Shieb, Rand Hasanain, Zara Arshad, Faisal A. Nawaz, Rahul Kashyap, Eric J. Stern
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):427-434. Published online April 5, 2024
-

The overall incidence of bloodstream infections was 23.5%. Gram-negative organisms occur at a much higher rate in pediatric liver transplant recipients then that the general pediatric population. However, when comparing pediatric and adult liver transplant recipients Gram-positive organisms occur with a much higher rate in the pediatric population highlighting the importance of early and broad spectrum antimicrobial coverage when bloodstream infections are suspected.
- Other
- Peripheral nerve sheath tumors in the head and neck in patients with APC gene deletion mutations: a case report and scoping review of the literature (22 times)
- Koral M. Blunt, Monirah Albathi, Miriam Conces, Tendy Chiang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):428-433. Published online January 13, 2025
-
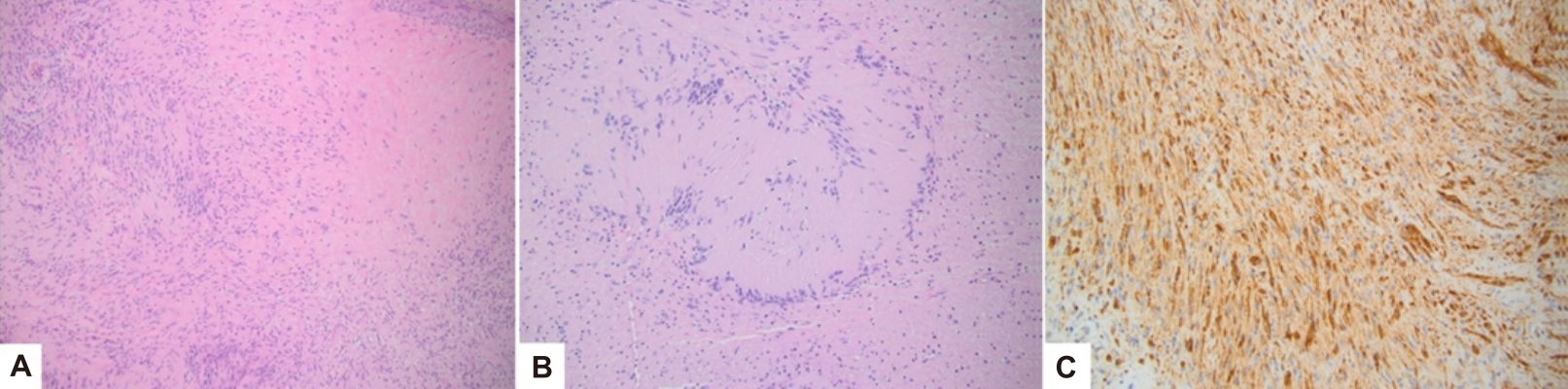
In this report, we describe our experience with a patient with an APC-related genetic syndrome who presented with a rare palatal lesion with characteristics of a schwannoma. We discuss the role of immunohistochemical staining in discerning the differential diagnosis.
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Impact of Xmn1 polymorphism on hydroxyurea therapy in children with HbE-β non-transfusion dependent thalassemia: a cohort study (22 times)
- Saheli Roy, Paramita Bhattacharya, Atanu Kumar Dutta, Mrinal Kanti Das
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):437-444. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: Does the T allele of Xmn1 polymorphism favorably influence hydroxyurea efficacy in children of Eastern descent with fetal hemoglobin (HbE)-β nontransfusion dependent thalassemia (NTDT)?
Finding: Decrease in transfusion requirement and increase in height following hydroxyurea therapy was noted in both groups, however, change in CT was more critical than that in CC genotype.
Meaning: T allele of Xmn1 polymorphism favorably influences hydroxyurea efficacy in children with HbE-β NTDT.
- Pulmonology
- Oligohydramnios affects pulmonary functional/structural abnormalities in school-aged children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (21 times)
- Jeong Eun Shin, Soon Min Lee, Mi-Jung Lee, Jungho Han, Joohee Lim, Haerin Jang, Ho Seon Eun, Min Soo Park, Soo Yeon Kim, Myung Hyun Sohn, Ji Ye Jung, Kyung Won Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):257-266. Published online April 16, 2024
-

Question: Is bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) associated with functional/structural abnormalities later in life?
Finding: School-aged children with severe BPD had abnormalities on pulmonary function tests and lung computed tomography despite no subjective respiratory symptoms; however, only prenatal oligohydramnios and prolonged ventilator use were associated with abnormal lung function.
Meaning: Long-term monitoring of preterm infants’ lung health is essential, especially for those with prenatal oligohydramnios or prolonged ventilator use.
- Review Article
- Infection
- COVID-19 among infants: key clinical features and remaining controversies (20 times)
- Nevio Cimolai
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):1-16. Published online November 27, 2023
-
· Clinical studies of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in infants should be supported by rigorous laboratory diagnostic criteria.
· Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spreads to infants similarly to other viral respiratory infections.
· Among infants ≤1 year of age beyond the immediate postpartum period, COVID-19 is relatively mild, but even the low risk of severe disease requires prevention.
· Comorbidities increase infection vulnerability and complications in infants.
· Clinical and laboratory data do not sufficiently distinguish COVID-19 from other respiratory viral infections.
· Coinfection with SARS-CoV-2 is uncommon among infants.
· Unique infection sequelae, including multi-inflammatory syndrome in children and neonates and long COVID require further study and refinement of diagnostic criteria.
· Infection control standards applied to mother-infant dyads should be tempered by standard preventive strategies, maternal input, accommodation potential, and overall safety.
· Maternal vaccination prevents disease in early infancy.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Clinical, biochemical, and genetic study of TACE/TNF-α/ACE signaling pathway in pediatric COVID-19 infection (20 times)
- Ahmed El-Abd Ahmed, Sawsan M.A. Abuhamdah, Mohammed H. Hassan, Nagwan I. Rashwan, Eman A. Abd-Elmawgood, Haggagy Mansour, Hoda S. Sherkawy, Shymaa G. Rizk
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):704-717. Published online November 27, 2024
-
Question: Is the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathway (TNF-α-converting enzyme [TACE]/TNF-α/angiotensin converting enzyme [ACE]) involved in pediatric coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection?
Finding: Significantly increased circulating TACE/TNF-α and decreased ACE2 levels were noted. TNF-α-308G/A plays a significant role in susceptibility to COVID-19 infection among children. The ACE (I/D) (rs4646994) and ACE2 (rs2285666) single nucleotide polymorphisms lack significant associations with pediatric COVID-19 infection.
Meaning: The TNF signaling pathway participates in pediatric COVID-19 infection.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents (20 times)
- Hae Sang Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):90-91. Published online January 24, 2024
-
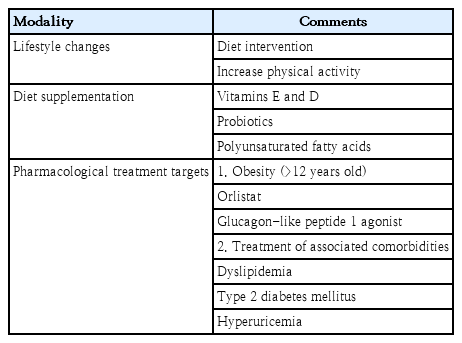
· With the increase in childhood obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become a concern in recent years.
· NAFLD is strongly associated with insulin resistance.
· Lifestyle modifications are the mainstay treatment for NAFLD.
- Letter to the Editor
- Gastroenterology
- Pediatric abdominal ultrasound training program for pediatricians (19 times)
- Soon Chul Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):474-476. Published online August 20, 2024
-

- Original Article
- Allergy
- Regional differences in diagnosis and management of cow's milk allergy (19 times)
- Fabian Hendricx, Emma Robert, Jaime A. Ramirez-Mayans, Karen Rubi Ignorosa Arellano, Erick M. Toro Monjaraz, Yvan Vandenplas
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):601-607. Published online October 28, 2024
-

· Although there is broad consensus on many aspects regarding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of cow's milk allergy, the impact of geographical, cultural, and socioeconomic factors remains unestablished.
· Availability and cost of formula for the management of cow's milk allergy have a major impact on the therapeutic choice.
· Region-specific guidelines for the treatment of cow's milk allergy are required.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus (18 times)
- Karnchanit Sausukpaiboon, Nuanpan Penboon, Pornpimol Rianthavorn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):454-462. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: What is the acceptance rate for coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
Finding: One-third of parents were hesitant to vaccinate their child. Parental willingness to vaccinate themselves, older patient age, and belief in the vaccine's potency were associated with vaccine acceptance.
Meaning: These findings highlight the need for targeted interventions to improve vaccine acceptance among parents of children with SLE.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Lifelong medical challenges and immunogenetics of Turner syndrome (17 times)
- Won Kyoung Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):560-568. Published online July 31, 2024
-
· This summary emphasizes the importance of the early diagnosis of Turner syndrome (TS) and presents a multidisciplinary approach to its prevention and management, high-lighting the need for customized care.
· Advancements in immunogenetic research may improve our understanding of TS and improve its outcomes.
· TS encompasses a wide array of medical challenges, including cardiovascular, endocrine, autoimmune, and mental health issues, as well as a heightened cancer risk.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone score changes in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency (17 times)
- Pattara Wiromrat, Yutapong Raruenrom, Phanpaphorn Namphaisan, Nantaporn Wongsurawat, Ouyporn Panamonta, Chatlert Pongchaiyakul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):238-246. Published online November 13, 2024
-
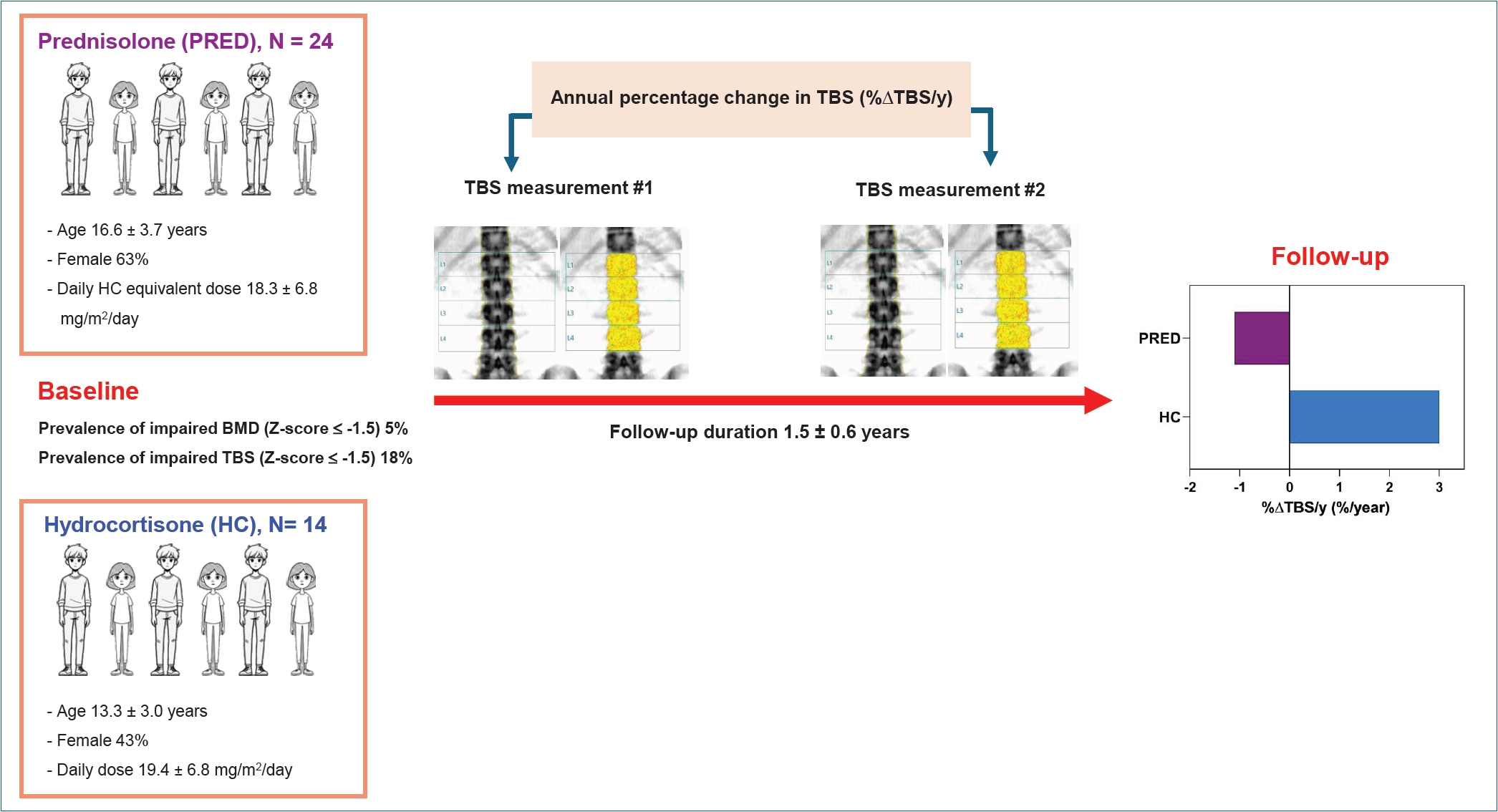
Question: What is the prevalence of an impaired trabecular bone score (TBS), a measure of bone microarchitecture, in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency (21OHD)? Do prednisolone and hydrocortisone affect TBS differently in this patient population?
Finding: Impaired TBS was observed in 18% of participants. Prednisolone use negatively impacted TBS change.
Meaning: Impaired TBS is prevalent among adolescents with 21OHD. Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone microarchitecture development.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Advancements in food allergen immunotherapy: improving quality of life and reducing risks (16 times)
- Jihyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):672-674. Published online July 31, 2024
-
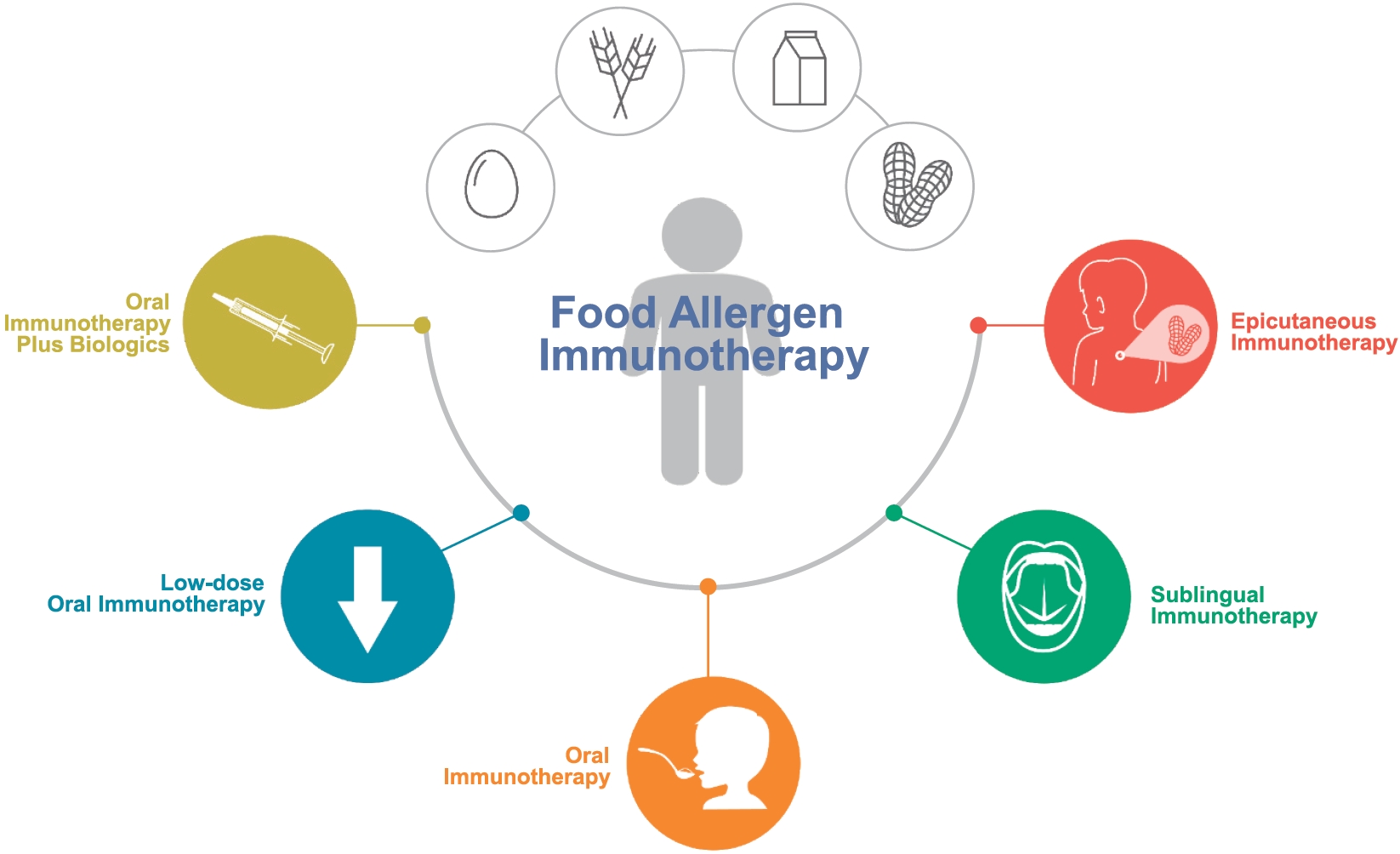
· Pediatric food allergies considerably impair patient and family quality of life, particularly those with persistent allergies to common food allergens.
· Recent research has focused on developing diverse approaches to food allergen immunotherapy, showing promising outcomes of oral, sublingual, and epicutaneous immuno therapies.
· Critical considerations in immunotherapy candidate selection underscore the need for personalized approaches and reliable biomarkers in future studies to improve treatment outcomes.
- Letter to the Editor
- Pulmonology
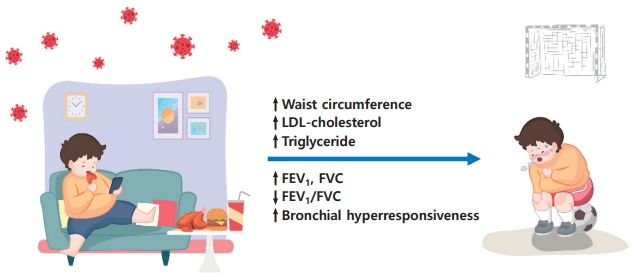
- Metabolic syndrome and pulmonary dysfunction in asthmatic children during the COVID-19 pandemic (15 times)
- Jue Seong Lee, Sang Hyun Park, Yoon Lee, Seunghyun Kim, Wonsuck Yoon, Young Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):168-170. Published online February 19, 2024
-
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Recent advances in food allergen immunotherapy (15 times)
- You Hoon Jeon, Edwin H. Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):386-394. Published online December 7, 2023
-

· To enhance the safety of food allergen immunotherapy, alternative approaches such as sublingual immunotherapy, epicutaneous immunotherapy, low-dose oral immunotherapy (OIT), and omalizumab with OIT are being explored.
· Factors such as causative allergen type, natural outgrowth, symptom severity, and patient age should be considered.
· Individualized food allergen immunotherapy plans should be established to determine the most beneficial treatment for each patient.
- Editorial
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Clinical considerations and practical issues of kidney complications in children after COVID-19 infection or vaccination (14 times)
- Jiwon Jung, Joo Hoon Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):35-36. Published online November 17, 2023
-
· The proper monitoring for and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-induced acute kidney injury, which is common in critically ill children, are recommended.
· Glomerulopathy associated with COVID-19 or its vaccination has been reported, and the overall clinical course is similar to that of non-COVID-19-associated diseases.
· Additional COVID-19 vaccinations are recommended; however, careful and individualized decisions should be made in patients with COVID-19- or vaccination-associated glomerulopathy.
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











