Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Impact of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on growth outcomes in mucopolysaccharidosis: a systematic review
- Farzaneh Abbasi, Asal Khalili Dehkordi, Reihaneh Mohsenipour
-
Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) is a group of genetic disorders characterized by defective lysosomal enzyme activity that can result in growth abnormalities and other complications. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), especially bone marrow transplantation (BMT), aims to restore enzyme function and improve growth parameters in patients with MPS. This systematic review evaluates the impact of HSCT on growth outcomes, including height, weight,... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.01725 [Accepted]
- Original Article
- Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in pediatric patients with type VI mucopolysaccharidosis
- Vedat Uygun, Koray Yalçın, Hayriye Daloğlu, Seda Öztürkmen, Suna Çelen, Suleimen Zhumatayev, Gülsün Karasu, Akif Yeşilipek
-
Background: It is uncertain whether hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), versus standard enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), is effective for type VI mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS VI).
Purpose: New related advances in HSCT prompted an examination of the transplant procedures performed in a recent cohort. Methods: This single-center retrospective study reviewed the medical records of 17 pediatric patients with MPS VI who underwent allogeneic... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.02033 [Accepted]
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Pediatric heart transplantation: how to manage problems affecting long-term outcomes?
- Young Hwue Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(2):49-59. Published online April 8, 2020
-

Since the initial International Society of Heart Lung Transplantation registry was published in 1982, the number of pediatric heart transplantations has increased markedly, reaching a steady state of 500–550 transplantation annually and occupying up to 10% of total heart transplantations. Heart transplantation is considered an established therapeutic option for patients with end-stage heart disease. The long-term outcomes of pediatric heart...
- Gastroenterology
- Increasing incidence of inflammatory bowel disease in children and adolescents: significance of environmental factors
- Sowon Park, Yunkoo Kang, Hong Koh, Seung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):337-344. Published online December 6, 2019
-
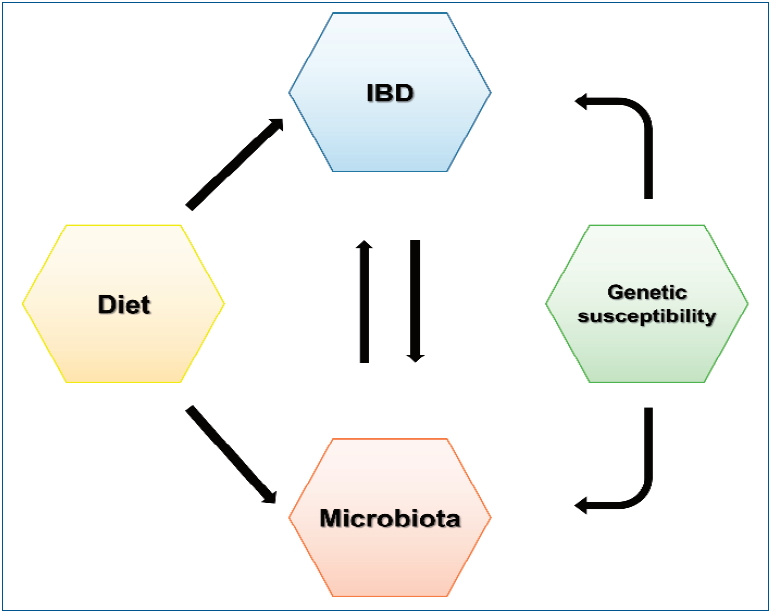
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic relapsing immune-mediated disease of the intestinal tract. Although its prevalence is reportedly lower in Asia than in Western countries, the rapid increase in the incidence of IBD has drawn attention to its etiology, including genetic susceptibility and environmental factors. Specifically, recent studies concerning dietary treatments and intestinal microbiota suggest that these factors may...
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Pediatric kidney transplantation is different from adult kidney transplantation
- Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(7):205-209. Published online July 15, 2018
-
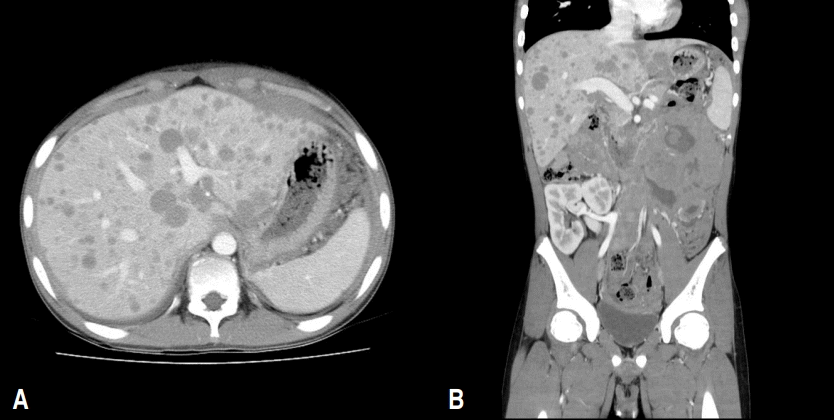
Kidney transplantation (KT) is the gold standard for renal replacement therapy in pediatric patients with end-stage renal disease. Recently, it has been observed that the outcome of pediatric KT is nearly identical to that in adults owing to the development and application of a variety of immunosuppressants and newer surgical techniques. However, owing to several differences in characteristics between children... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/kjp.2018.61.7.205 Correction in: Clin Exp Pediatr 2018;61(8):264
- Original Article
- Oncology
- Posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder after pediatric solid organ transplantation: experiences of 20 years in a single center
- Hyung Joo Jeong, Yo Han Ahn, Eujin Park, Youngrok Choi, Nam-Joon Yi, Jae Sung Ko, Sang Il Min, Jong Won Ha, Il-Soo Ha, Hae Il Cheong, Hee Gyung Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):86-93. Published online March 27, 2017
-
Purpose To evaluate the clinical spectrum of posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) after solid organ transplantation (SOT) in children.
Methods We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 18 patients with PTLD who underwent liver (LT) or kidney transplantation (KT) between January 1995 and December 2014 in Seoul National University Children's Hospital.
Results Eighteen patients (3.9% of pediatric SOTs; LT:KT, 11:7; male to female, 9:9) were diagnosed...
- Case Report
- Oncology
- Targeted busulfan and fludarabine-based conditioning for bone marrow transplantation in chronic granulomatous disease
- Hee Young Ju, Hyoung Jin Kang, Che Ry Hong, Ji Won Lee, Hyery Kim, Sang Hoon Song, Kyung-Sang Yu, In-Jin Jang, June Dong Park, Kyung Duk Park, Hee Young Shin, Joong-Gon Kim, Hyo Seop Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S57-S59. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is a primary immunodeficiency disease caused by impaired phagocytic function. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is a definitive cure for CGD; however, the use of HSCT is limited because of associated problems, including transplantation-related mortality and engraftment failure. We report a case of a patient with CGD who underwent successful HSCT following a targeted busulfan and...
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Deficiency of antidiuretic hormone: a rare cause of massive polyuria after kidney transplantation
- Kyung Mi Jang, Young Soo Sohn, Young Ju Hwang, Bong Seok Choi, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(4):202-204. Published online April 30, 2016
-
A 15-year-old boy, who was diagnosed with Alport syndrome and end-stage renal disease, received a renal transplant from a living-related donor. On postoperative day 1, his daily urine output was 10,000 mL despite normal graft function. His laboratory findings including urine, serum osmolality, and antidiuretic hormone levels showed signs similar to central diabetes insipidus, so he was administered desmopressin acetate...
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in children after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: a case control study using speckle tracking echocardiography
- Beom Joon Kim, Kyung Pil Moon, Ji-Hong Yoon, Eun-Jung Lee, Jae Young Lee, Seong Koo Kim, Jae Wook Lee, Nack Gyun Chung, Bin Cho, Hack Ki Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(4):190-195. Published online April 30, 2016
-
Purpose Severe aplastic anemia (SAA), a fatal disease, requires multiple transfusion, immunosuppressive therapy, and finally, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) as the definitive treatment. We hypothesized that iron overloading associated with multiple transfusions and HSCTrelated complications may adversely affect cardiac function. Left ventricular (LV) function was assessed in children after HSCT for SAA.
Methods Forty-six consecutive patients with a median age of 9.8...
- Case Report
- Compartment syndrome due to extravasation of peripheral parenteral nutrition: extravasation injury of parenteral nutrition
- Huee Jin Park, Kyung Hoon Kim, Hyuk Jin Lee, Eui Cheol Jeong, Kee Won Kim, Dong In Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(11):454-458. Published online November 22, 2015
-
Compartment syndrome is a rare but devastating condition that can result in permanent neuromuscular or soft tissue injuries. Extravasation injuries, among the iatrogenic causes of compartment syndrome, occur under a wide variety of circumstances in the inpatient setting. Total parenteral nutrition via a peripheral route is an effective alternative for the management of critically ill children who do not obtain...
- Review Article
- Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children and adolescents with acquired severe aplastic anemia
- Ho Joon Im, Kyung-Nam Koh, Jong Jin Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(6):199-205. Published online June 22, 2015
-
Severe aplastic anemia (SAA) is a life-threatening disorder for which allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is the current available curative treatment. HSCT from matched sibling donors (MSDs) is the preferred therapy for children with acquired SAA. For patients who lack MSDs, immunosuppressive therapy (IST) is widely accepted as a first-line treatment before considering HCT from an unrelated donor (URD)....
- BK virus-associated hemorrhagic cystitis after pediatric stem cell transplantation
- Seung Beom Han, Bin Cho, Jin Han Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(12):514-519. Published online December 31, 2014
-
Hemorrhagic cystitis is a common stem cell transplantation-related complication. The incidence of early-onset hemorrhagic cystitis, which is related to the pretransplant conditioning regimen, has decreased with the concomitant use of mesna and hyperhydration. However, late-onset hemorrhagic cystitis, which is usually caused by the BK virus, continues to develop. Although the BK virus is the most common pathogenic microorganism of poststem...
- Mesenchymal stem cells transplantation for neuroprotection in preterm infants with severe intraventricular hemorrhage
- So Yoon Ahn, Yun Sil Chang, Won Soon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(6):251-256. Published online June 30, 2014
-
Severe intraventricular hemorrhaging (IVH) in premature infants and subsequent posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus (PHH) causes significant mortality and life-long neurological complications, including seizures, cerebral palsy, and developmental retardation. However, there are currently no effective therapies for neonatal IVH. The pathogenesis of PHH has been mainly explained by inflammation within the subarachnoid spaces due to the hemolysis of extravasated blood after IVH. Obliterative...
- Original Article
- Long-term follow-up of Fanconi anemia: clinical manifestation and treatment outcome
- Byung Gyu Yoon, Hee Na Kim, Ui Joung Han, Hae In Jang, Dong Kyun Han, Hee Jo Baek, Tai Ju Hwang, Hoon Kook
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(3):125-134. Published online March 31, 2014
-
Purpose The aim of this study was to characterize Korean patients with Fanconi anemia (FA), which is a rare but very challenging genetic disease.
Methods The medical records of 12 FA patients diagnosed at Chonnam National University Hospital from 1991 to 2012 were retrospectively reviewed.
Results The median age at diagnosis was 6.2 years. All patients showed evidence of marrow failure and one or more...
- Review Article
- Clinical utilization of cord blood over human health: experience of stem cell transplantation and cell therapy using cord blood in Korea
- Young-Ho Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(3):110-116. Published online March 31, 2014
-
Cord blood (CB) has been used as an important and ethical source for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (SCT) as well as cell therapy by manufacturing mesenchymal stem cell, induced pleuripotential stem cell or just isolating mononuclear cell from CB. Recently, the application of cell-based therapy using CB has expanded its clinical utility, particularly, by using autologous CB in children with...
- Original Article
- High-dose chemotherapy and autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in the treatment of children and adolescents with Ewing sarcoma family of tumors
- Juhee Seo, Dong Ho Kim, Jung Sub Lim, Jae-Soo Koh, Ji Young Yoo, Chang-Bae Kong, Won Seok Song, Wan Hyeong Cho, Dae-Geun Jeon, Soo-Yong Lee, Jun Ah Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(9):401-406. Published online September 30, 2013
-
Purpose We performed a pilot study to determine the benefit of high-dose chemotherapy and autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (HDCT/autoPBSCT) for patients with Ewing sarcoma family of tumors.
Methods We retrospectively analyzed the data of patients who received HDCT/autoPBSCT at Korea Cancer Center Hospital. Patients with relapsed, metastatic, or centrally located tumors were eligible for the study.
Results A total of 9 patients (3...
- Efficacy of imatinib mesylate-based front-line therapy in pediatric chronic myelogenous leukemia
- Hyun Jin Oh, Mun Sung Cho, Jae Wook Lee, Pil-Sang Jang, Nack-Gyun Chung, Bin Cho, Hack-Ki Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(8):343-350. Published online August 27, 2013
-
Purpose Despite the established role of imatinib (IM) in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) in adults, there are few reports on its efficacy in children. In this study, we compared the outcomes of children with CML before and after the advent of IM-based treatment.
Methods The study cohort consisted of 52 patients treated for CML at the Department of Pediatrics, The Catholic University of...
- Risk factors for short term thyroid dysfunction after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children
- You Jin Jung, Yeon Jin Jeon, Won Kyoung Cho, Jae Wook Lee, Nack-Gyun Chung, Min Ho Jung, Bin Cho, Byung-Kyu Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(7):298-303. Published online July 19, 2013
-
Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate short-term thyroid dysfunction and related risk factors in pediatric patients who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) during childhood.
Methods We studied 166 patients (100 boys and 66 girls) who underwent HSCT at the Catholic HSCT Center from January 2004 through December 2009. The mean age at HSCT was 10.0±4.8 years. Thyroid function of...
- Case Report
- Liver transplantation in a child with acute liver failure resulting from drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome
- Seung Min Song, Min Sung Cho, Seak Hee Oh, Kyung Mo Kim, Young Seo Park, Dae Yeon Kim, Sung Gyu Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(5):224-226. Published online May 28, 2013
-
Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome is characterized by a severe idiosyncratic reaction including rash and fever, often with associated hepatitis, arthralgias, lymph node enlargement, or hematologic abnormalities. The mortality rate is approximately 10%, primarily owing to liver failure with massive or multiple disseminated focal necrosis. Here, we report a case of a 14-year-old girl treated with...
- Original Article
- Immune reconstitution after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children: a single institution study of 59 patients
- Hyun O Kim, Hyun Jin Oh, Jae Wook Lee, Pil-Sang Jang, Nack-Gyun Chung, Bin Cho, Hack-Ki Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(1):26-31. Published online January 29, 2013
-
Purpose Lymphocyte subset recovery is an important factor that determines the success of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Temporal differences in the recovery of lymphocyte subsets and the factors influencing this recovery are important variables that affect a patient's post-transplant immune reconstitution, and therefore require investigation.
Methods The time taken to achieve lymphocyte subset recovery and the factors influencing this recovery were investigated...
- Review Article
- Umbilical cord blood transplantation
- Hong Hoe Koo, Hyo Seop Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(7):219-223. Published online July 17, 2012
-
Since the first umbilical cord blood transplantation (CBT) in 1998, cord blood (CB) has now become one of the most commonly used sources of hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation. CBT has advantages of easy procurement, no risk to donor, low risk of transmitting infections, immediate availability and immune tolerance allowing successful transplantation despite human leukocyte antigen disparity. Several studies have...
- Treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma
- Ki Woong Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(4):115-120. Published online April 30, 2012
-
Although high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation (HDCT/autoSCT) have improved the prognosis for patients with high-risk neuroblastoma (NB), event-free survival rates remain in the range of 30 to 40%, which is unsatisfactory. To further improve outcomes, several clinical trials, including tandem HDCT/autoSCT, high-dose 131I-metaiodobenzylguanidine treatment, and immunotherapy with NB specific antibody, have been undertaken and pilot studies have reported...
- Original Article
- Outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in second complete remission: a single institution study
- Eun-Jung Lee, Ji Yoon Han, Jae Wook Lee, Pil-Sang Jang, Nack-Gyun Chung, Dae-Chul Jeong, Bin Cho, Hack-Ki Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(3):100-106. Published online March 16, 2012
-
Purpose The survival rate for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) has improved significantly. However, overall prognosis for the 20 to 25% of patients who relapse is poor, and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) offers the best chance for cure. In this study, we identified significant prognostic variables by analyzing the outcomes of allogeneic HSCT in ALL patients in second complete...
- Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children with acute leukemia: similar outcomes in recipients of umbilical cord blood versus marrow or peripheral blood stem cells from related or unrelated donors
- Eun Sang Yi, Soo Hyun Lee, Meong Hi Son, Ju Youn Kim, Eun Joo Cho, Su Jin Lim, Hee Won Cheuh, Keon Hee Yoo, Ki Woong Sung, Hong Hoe Koo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(3):93-99. Published online March 16, 2012
-
Purpose This study compared outcomes in children with acute leukemia who underwent transplantations with umbilical cord blood (UCB), bone marrow, or peripheral blood stem cells from a human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-matched related donor (MRD) or an unrelated donor (URD).
Methods This retrospective study included consecutive acute leukemia patients who underwent their first allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) at Samsung Medical Center between...
- Review Article
- Treatment of steroid-resistant pediatric nephrotic syndrome
- Hee Gyung Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(8):317-321. Published online August 31, 2011
-
Children who suffer from steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS) require aggressive treatment to achieve remission. When intravenous high-dose methylprednisolone fails, calcineurin inhibitors, such as cyclosporine and tacrolimus, are used as the first line of treatment. A significant number of patients with SRNS progress to end-stage renal disease if remission is not achieved. For these children, renal replacement therapy can also be...
- The treatment of pediatric chronic myelogenous leukemia in the imatinib era
- Jae Wook Lee, Nack Gyun Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(3):111-116. Published online March 31, 2011
-
Childhood chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is a rare hematologic disease, with limited literature on the methods of treatment. Previously, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) was considered the only curative treatment for this disease. Treatment with imatinib, a selective inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase (TKI), has resulted in prolonged molecular response with limited drug toxicity. Imatinib is now implemented...
- Case Report
- A case of tacrolimus-induced encephalopathy after kidney transplantation
- Myoung Uk Kim, Sae Yoon Kim, Su Min Son, Yong Hoon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(1):40-44. Published online January 31, 2011
-
We present a case of tacrolimus-induced encephalopathy after successful kidney transplantation. An 11-year-old girl presented with sudden onset of neurologic symptoms, hypertension, and psychiatric symptoms, with normal kidney function, after kidney transplantation. The symptoms improved after cessation of tacrolimus. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed acute infarction of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) territory in the right frontal lobe. Three days...
- Renal transplantation in a patient with Bartter syndrome and glomerulosclerosis
- Se Eun Lee, Kyoung Hee Han, Yun Hye Jung, Hyun Kyung Lee, Hee Gyung Kang, Kyung Chul Moon, Il Soo Ha, Yong Choi, Hae Il Cheong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(1):36-39. Published online January 31, 2011
-
Bartter syndrome (BS) is a clinically and genetically heterogeneous inherited renal tube disorder characterized by renal salt wasting, hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis and normotensive hyperreninemic hyperaldosteronism. There have been several case reports of BS complicated by focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). Here, we have reported the case of a BS patient who developed FSGS and subsequent end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and provided...
- Original Article
- Comparison of total body irradiation-based or non-total body irradiation-based conditioning regimens for allogeneic stem cell transplantation in pediatric leukemia patients
- Sang Jeong Kim, Dong Kyun Han, Hee Jo Baek, Dong Yeon Kim, Taek Keun Nam, Tai Ju Hwang, Hoon Kook
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(4):538-547. Published online April 15, 2010
-
Purpose : This study aims to compare the outcome of total body irradiation (TBI)- or non-TBI-containing conditioning regimens for leukemia in children. Methods : We retrospectively evaluated 77 children conditioned with TBI (n=40) or non-TBI (n=37) regimens, transplanted at Chonnam National University Hospital between January 1996 and December 2007. The type of transplantation, disease status at the time of transplant, conditioning regimen,... -
- Endocrine dysfunction after bone marrow transplantation during childhood and adolescence
- Hye Young Jin, Jin-Ho Choi, Ho-Joon Im, Jong-Jin Seo, Hyung-Nam Moon, Han-Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(3):420-427. Published online March 15, 2010
-
Purpose : Several complications can occur in patients who received bone marrow transplantation (BMT) during childhood and adolescence. This study aims to investigate endocrine dysfunctions after BMT so that better care can be provided to care for long-term survivors of BMT. Methods : One hundred patients (61 males, 39 females) were included in this study. Clinical parameters such as initial diagnosis,... -
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











