Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Attention-deficit/hyperactive-impulsive disorder symptoms among grade 1 students with reading disorder in Thailand
- Patcharapun Sarisuta, Issarapa Chunsuwan, Tippawan Hansakunachai, Paskorn Sritipsukho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):485-492. Published online October 24, 2023
-
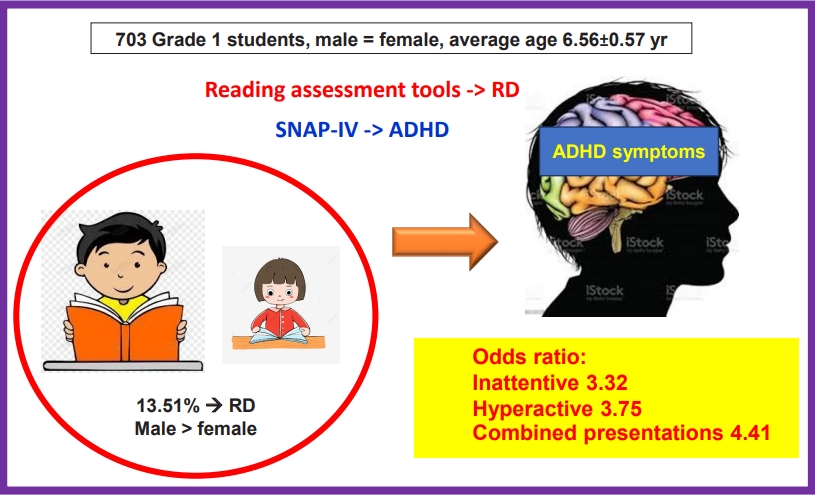
Question: Would students with reading disorder have a significantly higher prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactiveimpulsive disorder (ADHD) symptoms than neurotypical students?
Finding: Students at risk of reading disorder exhibited significant ADHD symptoms compared with those not at risk of reading disorder according to all presentations of teacher assessments versus only for predominantly inattentive presentations of the parental assessments.
Meaning: Students with reading disorder have a significantly higher prevalence of ADHD symptoms than neurotypical students. Sex, parental education level, average family income, and children’s school affiliation significantly influenced reading disorder prevalence.
- Impact of short and intensive art-based intervention on symptomatology and social interactions among children with autism spectrum disorder
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Bayar Mohammed Omar Abdulla, Pranee Liamputtong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):447-454. Published online September 14, 2023
-

Question: Does a short and intensive art-based intervention affect symptoms and social interactions among children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Finding: The short and intensive art-based intervention did not affect symptoms in children with ASD level 2 or 3, including social awareness, social cognition, social communication, social motivation, and autistic mannerisms.
Meaning: The short and intensive art-based intervention did not improve the symptoms of patients with ASD.
- Review Article
- Other
- Children’s health affected by parent’s behavioral characteristics: a review
- Sung Eun Kim, Jongin Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):232-239. Published online August 21, 2023
-

· Parents’ occupational hazards, long working hours, and smoking behaviors should be modified adequately to minimize adverse health effects on their children.
· As of 2023, several diseases from fetal exposure to occupational hazards can be compensated with Industrial Accident Compensation Insurance in South Korea.
· A directed acyclic graph is recommended for medical research to control the effects of parents’ behaviors on children’s health.
- Gastroenterology
- Prevalence, risk factors, and treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in children
- Yu Kyung Cho, Jin Lee, Chang Nyol Paik
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):377-383. Published online August 21, 2023
-
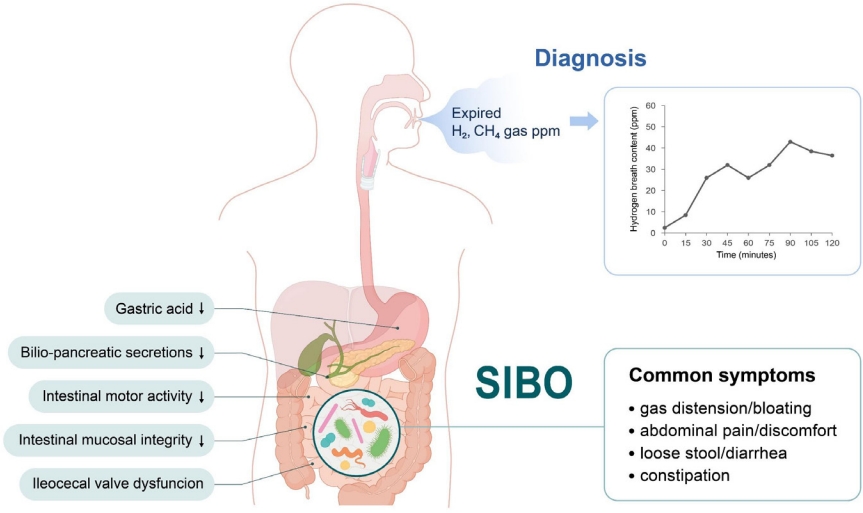
· Pediatric small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) manifestations range from nonspecific abdominal symptoms to malabsorption or malnutrition.
· SIBO is prevalent in children and adolescents with functional abdominal pain disorders.
· Predisposing factors include disturbed intestinal motility, altered anatomy, and/or abnormal body defense systems against intestinal bacteria.
· Breath tests are safe and noninvasive.
· Treatment principles include managing predisposing conditions, nutritional support, symptom control, and antibiotics.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Neonatal risk factors associated with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: an umbrella review
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Erfan Ayubi, Sajjad Farashi, Saeid Bashirian, Fereshteh Mehri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):441-446. Published online July 14, 2023
-
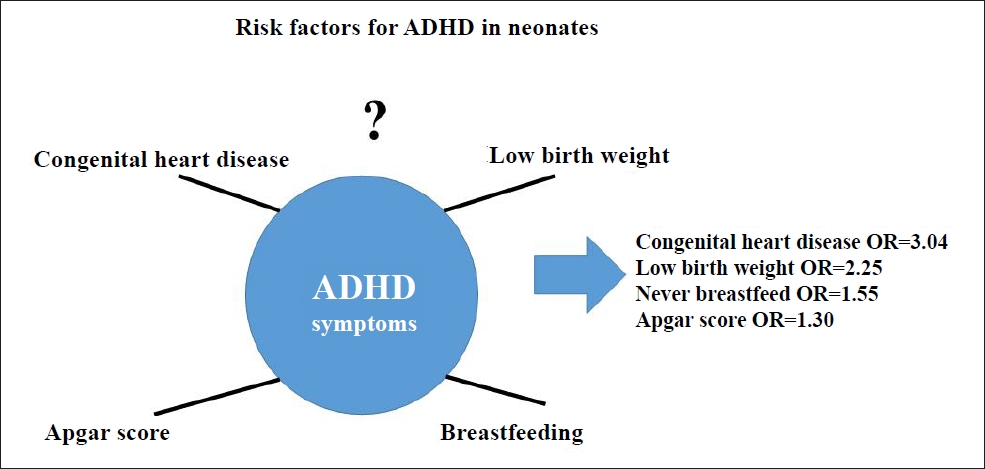
Question: The risk factors for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), such as breastfeeding, congenital heart disease, and low birth weight, in neonates are not well understood.
Finding: This umbrella review obtained significant effect sizes for ADHD for congenital heart disease (odds ratio [OR], 3.04), low birth weight (OR, 2.25), never breastfed (OR, 1.55), and Apgar score (OR, 1.30).
Meaning: Congenital heart disease, low birth weight, lack of breastfeeding, and Apgar scores were significant factors for ADHD.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Updates in neonatal resuscitation: routine use of laryngeal masks as an alternative to face masks
- Eun Song Song, Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):240-246. Published online July 11, 2023
-

In neonatal resuscitation:
· Laryngeal masks are recommended when endotracheal intubation or positive-pressure ventilation fails.
· Laryngeal masks are useful even during chest compressions.
· Laryngeal masks aid neonates >34 weeks’ gestation and/or with a birth weight >2 kg.
· Main usage barriers include limited experience (81%), preference for endotracheal tubes (57%), and lack of awareness (56%).
· Second-generation laryngeal masks have a built-in esophageal drainage tube that prevents regurgitation into the glottis, and an orogastric tube can be inserted within the esophageal drainage tube to protect against gastric inflation.
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Development of orphan drugs for rare diseases
- Han-Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):315-327. Published online June 28, 2023
-
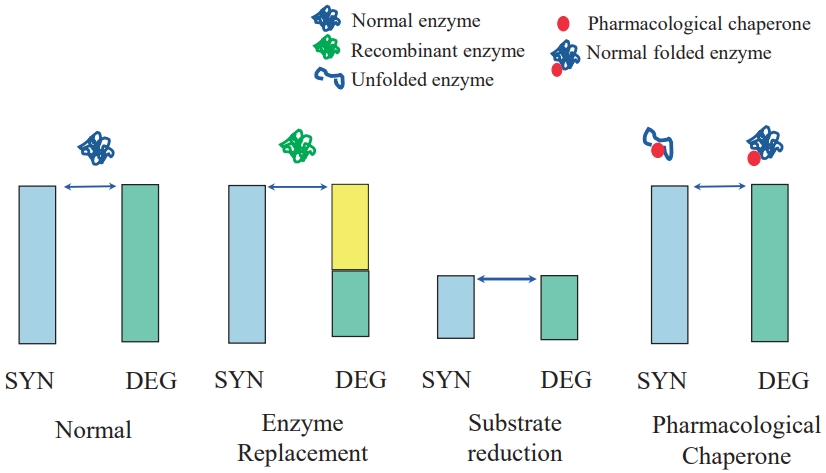
· Orphan disease is a rare disease, primarily affecting newborn and children. Vast majority of orphan diseases has genetic background.
· Orphan disease is individually rare. But as a whole, it is not rare, becoming a great socioeconomic burden.
· The diagnosis of rare genetic disease has been problematic, but recent progress of genome analysis technologies makes it faster and more precise.
· There are many unmet needs as to the curative treatment. However, the number of treatable rare diseases is growingly increasing owing to the development of biotechnology.
· Most orphan drugs are extremely expensive because of numer ous hurdles during the process of drug development as well as small number of patients.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Kidney complications associated with COVID-19 infection and vaccination in children and adolescents: a brief review
- Hee Sun Baek, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):424-431. Published online June 28, 2023
-
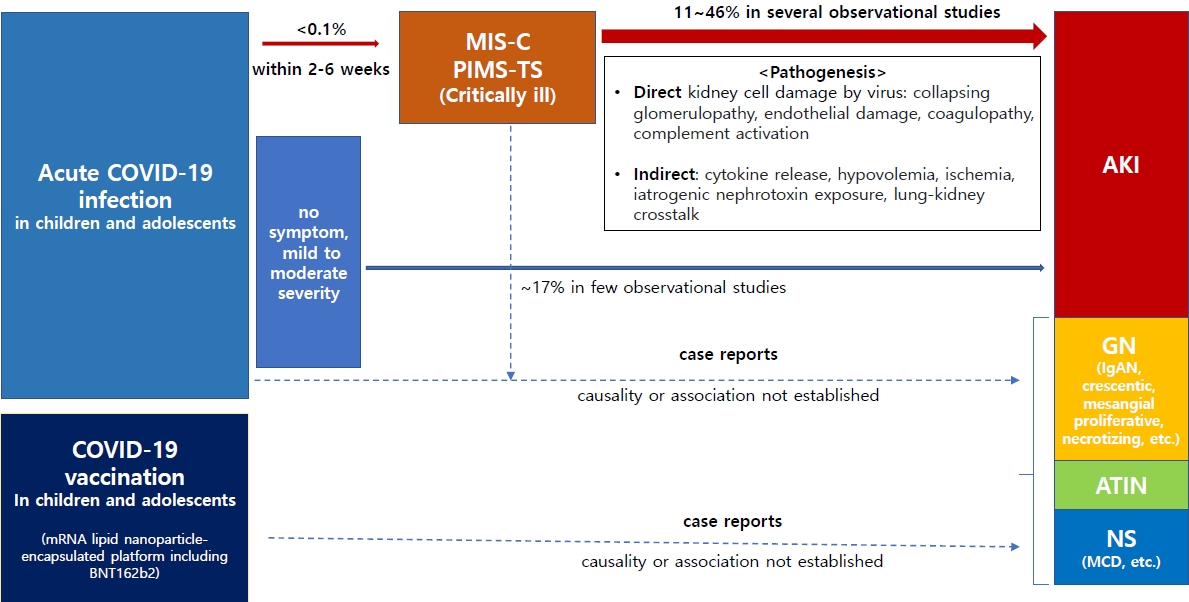
Several observational studies have shown that acute kidney injury affects up to 46% of children and adolescents who develop severe postinflammatory responses, such as multisystem inflammatory syndrome in childhood, due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Although causality has not been established, some cases of glomerulopathy or nephrotic syndrome occurring after COVID-19 infection or vaccination have been reported. Therefore, kidney complications associated with these conditions in children and adolescents warrant attention.
- Cardiology
- Heart failure in children and adolescents: an update on diagnostic approaches and management
- Amit Agrawal, Dalwinder Janjua, Abdulrahman Ahmed Alsayed Ali Zeyada, Ahmed Taher Elsheikh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):178-190. Published online June 19, 2023
-
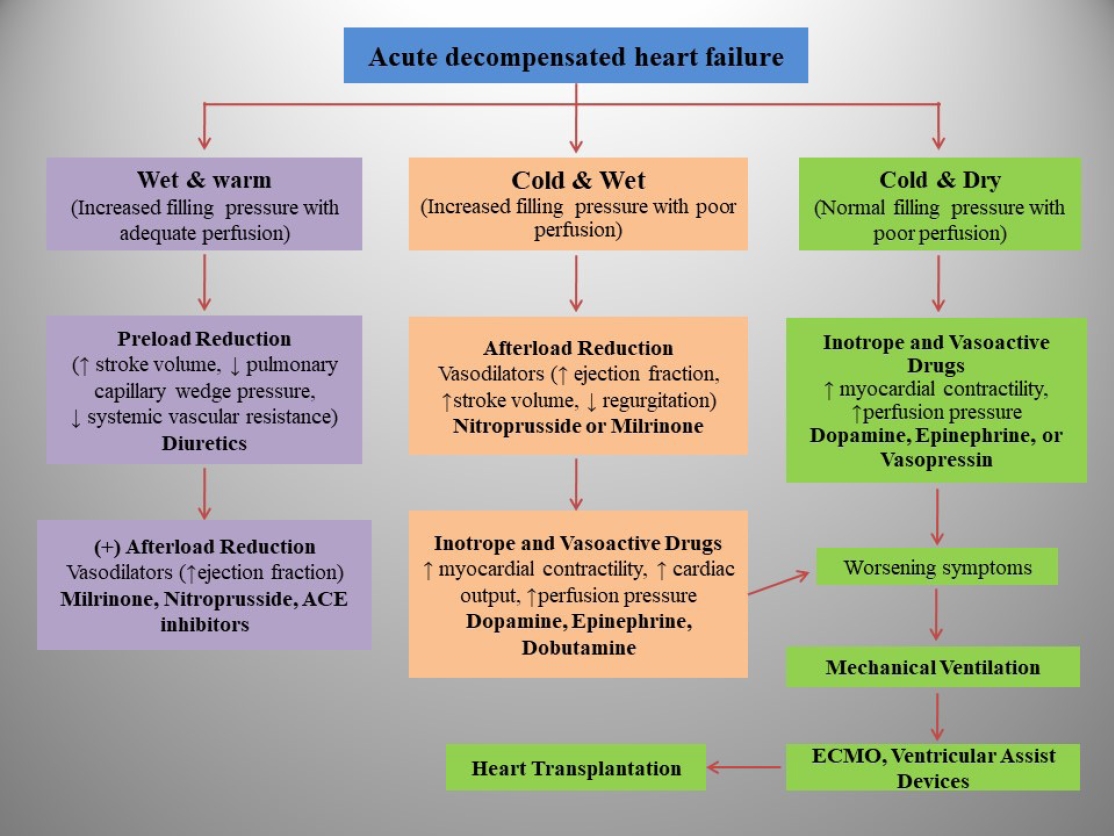
· Pediatric heart failure (PHF) is a clinical syndrome featuring various symptoms (shortness of breath, ankle swelling, fatigue) and signs (pulmonary crackles, peripheral edema).
· Congenital heart diseases are the most common underlying etiology of PHF, whereas myocarditis and primary cardio-myopathies are common in children without structural ab-normalities.
· PHF pathophysiology is complex and multifactorial and varies by etiology and age.
· PHF management includes decongestive therapy, treatment of underlying causes, preventing progression, and managing pulmonary or systemic obstructions.
· Drugs should be chosen based on pharmacodynamics, clinical manifestations, hemodynamic state, and renal function.
- Allergy
- Practical issues of oral immunotherapy for egg or milk allergy
- Sukyung Kim, Kangmo Ahn, Jihyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):140-148. Published online June 19, 2023
-
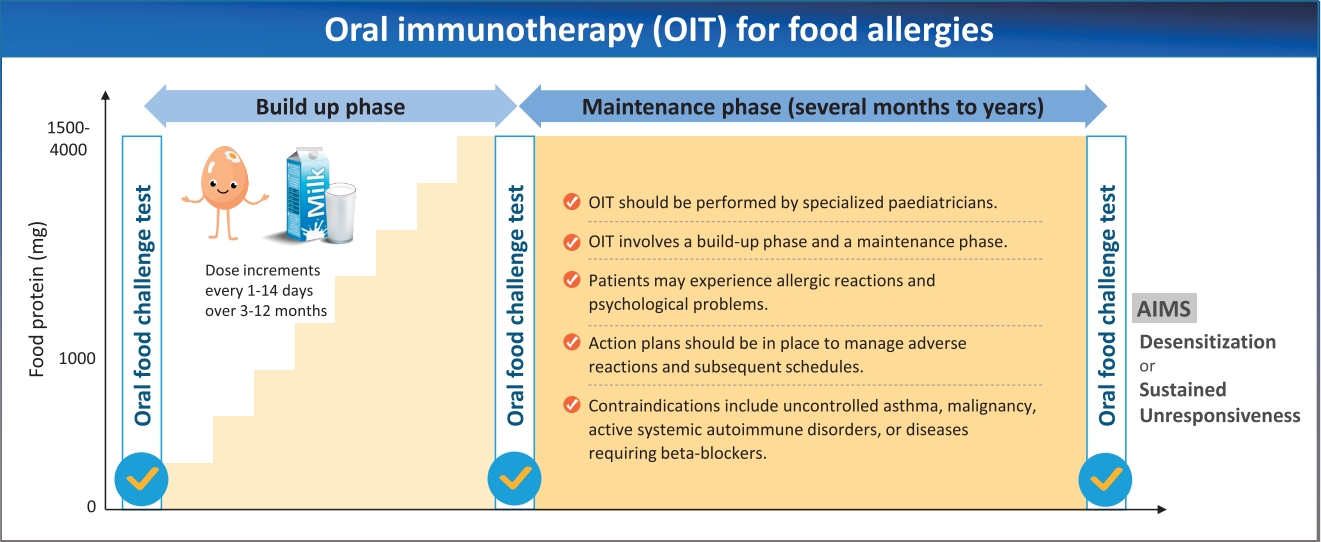
· Oral immunotherapy should be supervised by pediatricians with experience administering oral food challenge tests and managing allergic reactions.
· Food allergen intake is gradually increased and maintained for years.
· Patients may experience allergic reactions and psychological problems.
· Adjunctive therapies (biologics, antihistamines, and leukotriene receptor antagonists) may improve efficacy and safety.
· Contraindications include uncontrolled asthma, malignancy, active autoimmune disorders, and beta-blocker usage.
- Pulmonology
- Long COVID in children and adolescents: prevalence, clinical manifestations, and management strategies
- Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):465-474. Published online June 19, 2023
-
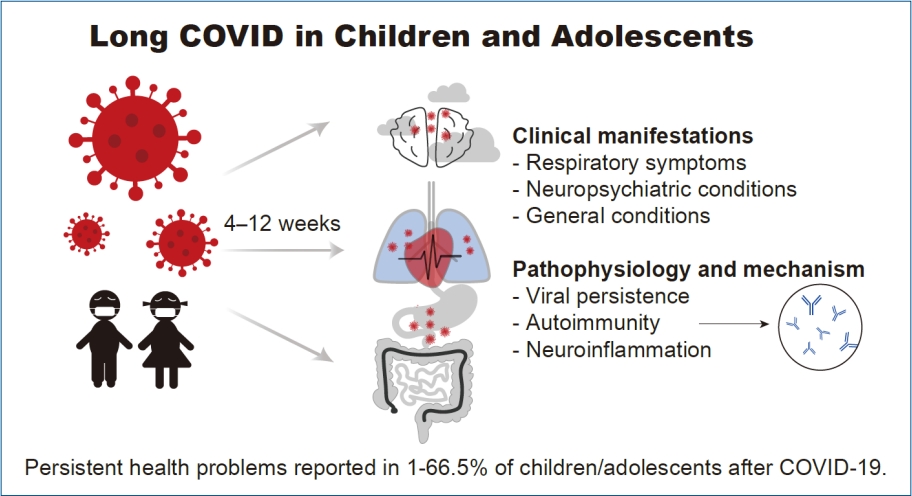
· Current definitions of long coronavirus disease (COVID) in children and adolescents vary in duration, ranging from 4 to 12 weeks or more.
· The clinical spectrum of long COVID in children and adolescents comprises a wide range of symptoms and might be a multisystem disorder.
· Persistent health problems with a prevalence of 1%–66.5% were reported in children and adolescents after COVID-19, with a higher incidence of persistent single or multiple symptoms.
- Allergy
- Skin and oral intervention for food allergy prevention based on dual allergen exposure hypothesis
- Kiwako Yamamoto-Hanada, Yukihiro Ohya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):477-485. Published online June 14, 2023
-

To prevent food allergy in infants, based on the dual allergen exposure hypothesis, we recommend a personalized approach consisting of both skin intervention (eczema treatment to achieve early remission and well-controlled skin without eczema to prevent percutaneous immunoglobulin E sensitization) and oral intervention (early allergenic food introduction).
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal family-centered care: evidence and practice models
- Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):171-177. Published online June 14, 2023
-
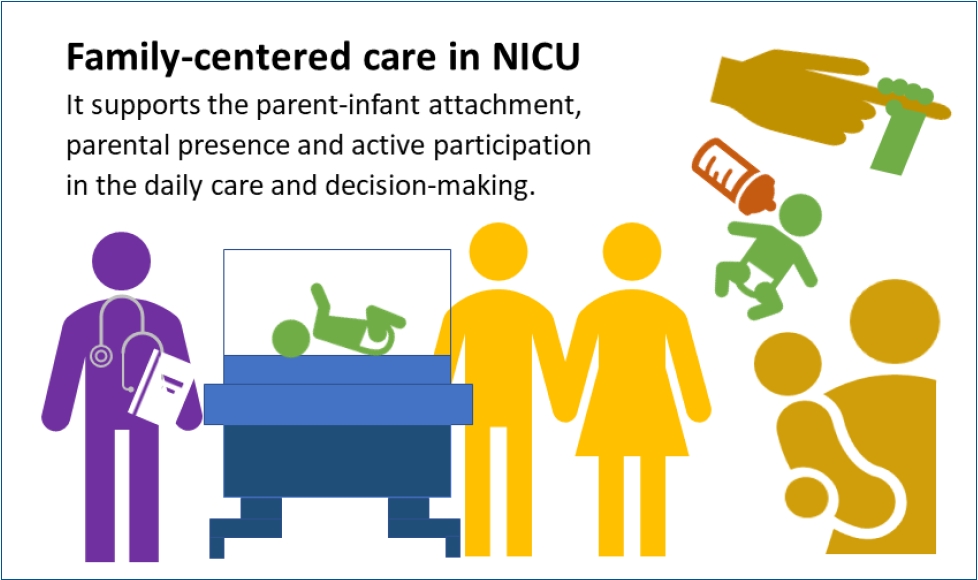
· Concrete evidence exists of early parent-infant attachment supported by family-centered care (FCC) in the neonatal intensive care unit.
· FCC involves the parents’ presence and participation in the infant’s care and decision-making.
· A private and comfortable space should be provided. A single-family room is ideal; however, a quiet space with a recliner can be a good alternative.
· Care culture changes and staff training are required.
- Other
- Acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible babies and children: no valid rationale for controversy
- Lisa Zhao, John P. Jones, Lauren G. Anderson, Zacharoula Konsoula, Cynthia D. Nevison, Kathryn J. Reissner, William Parker
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):126-139. Published online June 14, 2023
-

Despite worldwide acceptance of acetaminophen (paracetamol) in pediatric medicine, careful examination reveals no valid objections to the conclusion that early exposure to acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible babies and children. Nevertheless, debate that early exposure to acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury has centered around the prenatal period, evidence of which is relatively limited compared to that in the postnatal period, which is the time of greatest absolute and relative risk.
- Infection
- Community-acquired pneumonia in children: updated perspectives on its etiology, diagnosis, and treatment
- Ki Wook Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):80-89. Published online June 14, 2023
-
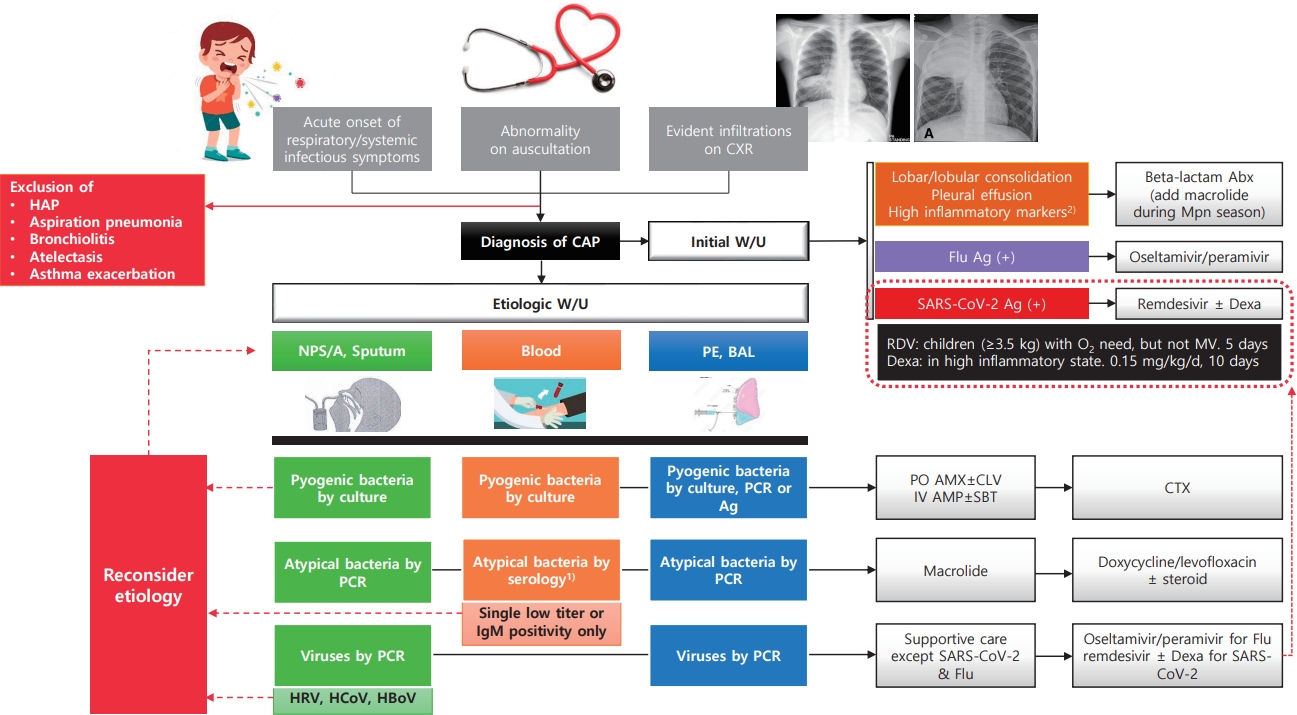
· Most commonly confirmed causes of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in children are Mycoplasma pneumoniae (8%–40%) and respiratory syncytial virus (15%–20%).
· Pyogenic bacteria, most commonly Streptococcus pneumoniae (40%–50%) and Streptococcus pyogenes (10%–25%), are detected in 2%–5% of children hospitalized with CAP.
· CAP should be diagnosed conservatively according to clinical and radiological criteria.
· The etiology should be identified via appropriate test result interpretation.
- Allergy
- Moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children: focus on systemic Th2 cytokine receptor antagonists and Janus kinase inhibitors
- Jeong Hee Kim, Mona Salem Samra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):64-79. Published online June 14, 2023
-
· Atopic dermatitis (AD) is characterized by a strong T helper (Th)2 response, although the extents of Th22, Th17/ interleukin (IL)-23, and Th1 responses vary among disease subtypes.
· Children with moderate to severe AD may require early systemic therapy to reduce the systemic inflammation caused by increased Th2 cytokine levels.
· Dupilumab, which blocks IL-4/IL-13 receptor, has equivalent efficacy for extrinsic and intrinsic AD and a favorable safety profile in infants and children aged 6 months and older.
- Gastroenterology
- High-resolution anorectal manometry in children
- Yogesh Waikar
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):57-63. Published online June 14, 2023
-
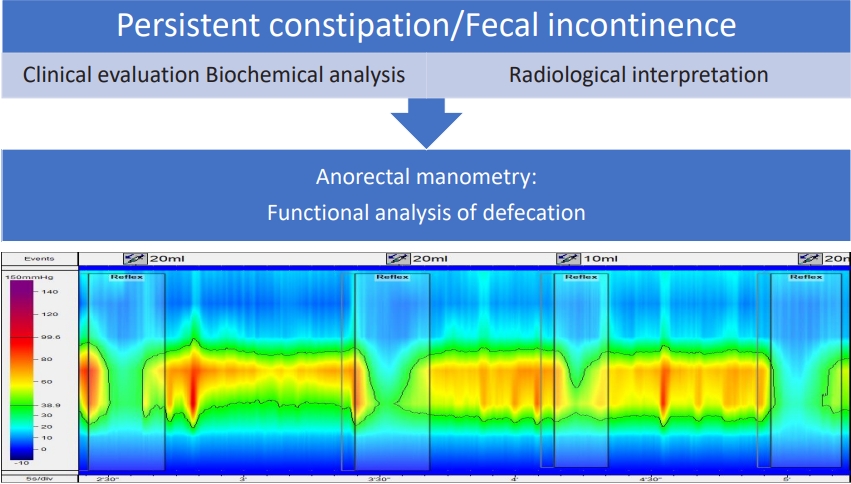
· Anorectal manometry is safe in children.
· Defecation Dyssynergia is one of the commonest cause of chronic constipation.
· Positive Rectoanal inhibiory reflex rules out Hirschsprung's Disease
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Clinical practice guidelines for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: recent updates
- Tae Hoon Eom, Young-Hoon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):26-34. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Primary pediatricians should play a key role in the diagnosis and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
· The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition, has lowered the diagnostic threshold for older teens and adults and a comorbid diagnosis with autism is now allowed.
· The American Academy of Pediatrics had added recommendation-related comorbid conditions in its guideline and the Society of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics recently developed a complex ADHD guideline.
· The European ADHD Guideline Group recently developed a guideline for managing ADHD during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: from diagnosis to management
- Eujin Park, Hee Gyung Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):17-25. Published online June 14, 2023
-
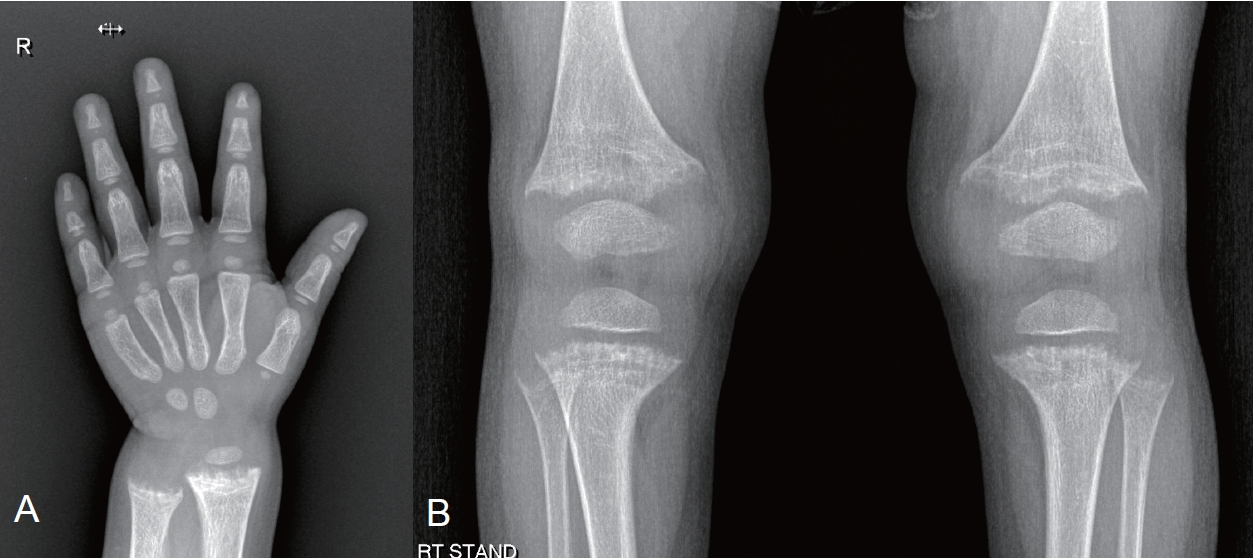
· X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH), the most common cause of hypophosphatemic rickets, affects 1/20,000 people.
· XLH is caused by a loss-of-function mutation of the PHEX gene.
· Its main pathogenesis is elevated fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23) level.
· Burosumab, an FGF23 inhibitor, was developed in the early 2000s.
· Burosumab was approved in Korea in 2020 for XLH patients aged 1+ years with radiographic evidence of bone disease.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Virtual reality for pain reduction during intravenous injection in pediatrics: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Amir Mohammad Salehi, Masoud Rafiee, Mozhdeh Bashirian
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):533-537. Published online June 14, 2023
-
Question: This is the first meta-analysis to examine published evidence of the effectiveness of virtual reality at reducing pain during pediatric intravenous injections.
Finding: Our results suggest that virtual reality effectively reduces pain associated with intravenous injections in pediatric patients.
Meaning: These findings suggest the importance of virtual reality in decreasing the pain of intravenous injections among children.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Natural course of IgE-mediated food allergy in children
- Kyunguk Jeong, Sooyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):504-511. Published online June 14, 2023
-
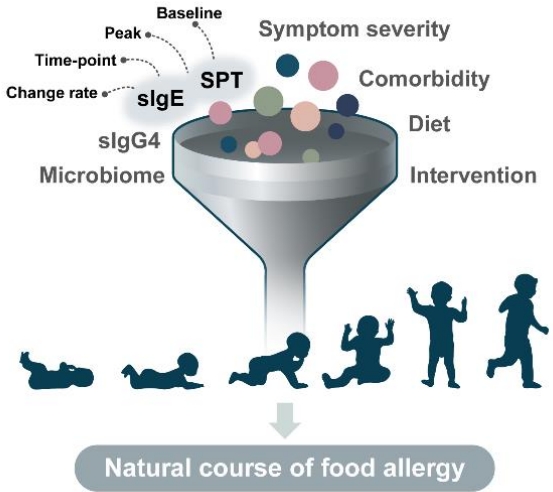
· Dendritic, regulatory T, and regulatory B cells significantly contribute to the natural course of food allergy.
· Cow’s milk and hen’s egg allergies tend to resolve in earlier childhood but recent studies show that 50% of patients still persist into school age.
· The potential factors affecting the natural course of food allergy are age at diagnosis, symptom severity, sensitization status and its change rate, and external factors such as diet and interventions.
· There is a considerable possibility of food allergy outgrow if specific IgE levels are 2–5 kUA/L or less, but other factors such as age and recent symptoms should be considered together.
· With a clear understanding of the natural course of food allergy, pediatricians can provide appropriate assessment and interventions to our patients, and consequently can help patients overcome their food allergy and improve the social safety net.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Inferior vena cava to aorta ratio in dehydrated pediatric patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Gilbert Sterling Octavius, Michelle Imanuelly, Johan Wibowo, Nadia Khoirunnisa Heryadi, Melanie Widjaja
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):477-484. Published online June 14, 2023
-
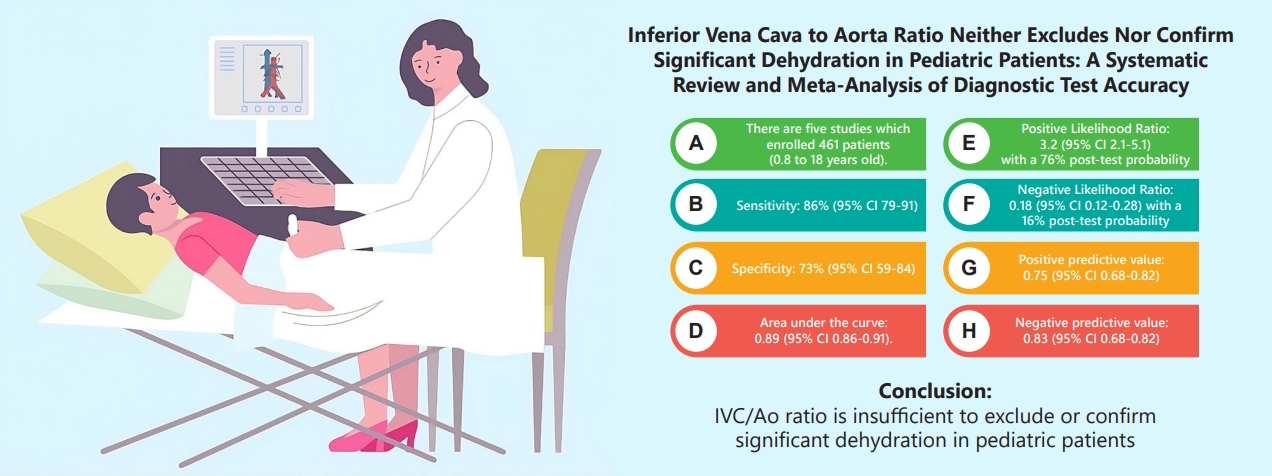
Question: The inferior vena cava to aorta (IVC/Ao) ratio measured via ultrasound has been touted as a promising noninvasive technique to assess clinically significant dehydration in pediatric patients.
Finding: Our meta-analysis found that IVC/Ao ratio had a positive likelihood ratio of 3.2 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.1–5.1) and negative likelihood ratio of 0.18 (95% CI, 0.12–0.28).
Meaning: Hence, IVC/Ao ratio is insufficient to exclude or confirm significant dehydration in pediatric patients.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Timing of parenteral nutrition initiation in critically ill children: a randomized clinical trial
- Nagwan Y. Saleh, Hesham M. Aboelghar, Nehad B. Abdelaty, Mohamed I. Garib, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):403-411. Published online June 14, 2023
-
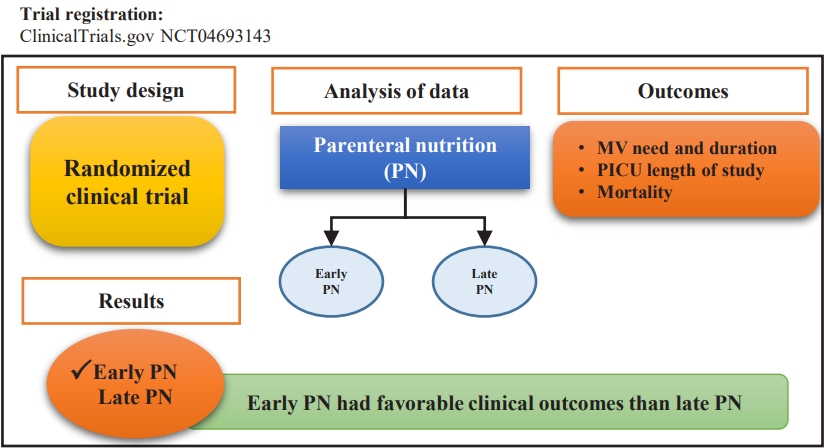
Question: What is the ideal initiation timing of parenteral nutrition for critically ill children?
Finding: This randomized clinical trial of 140 children examined the effects of an early or late start of parenteral nutrition on mechanical ventilation need (primary outcome) and length of stay and mortality (secondary outcomes).
Meaning: Children who received early versus late parenteral nutrition had lower mechanical ventilation need and duration.
- Gastroenterology
- Relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hyperandrogenemia in adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome
- Ozlem Kara, Hanife Aysegul Arsoy, Murat Keskin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):395-402. Published online June 14, 2023
-

Question: Is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) a risk factor for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in adolescents?
Finding: The frequency of NAFLD did not increase in adolescents with PCOS. However, hyperandrogenemia was a risk factor for NAFLD.
Meaning: Adolescents with PCOS and hyperandrogenemia should be closely monitored for hepatic steatosis.
- Allergy
- Association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children: a systematic review and multicenter cohort study using a common data model
- Ji Eun Lim, Hye Min Kim, Ju Hee Kim, Hey Sung Baek, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):357-365. Published online June 14, 2023
-
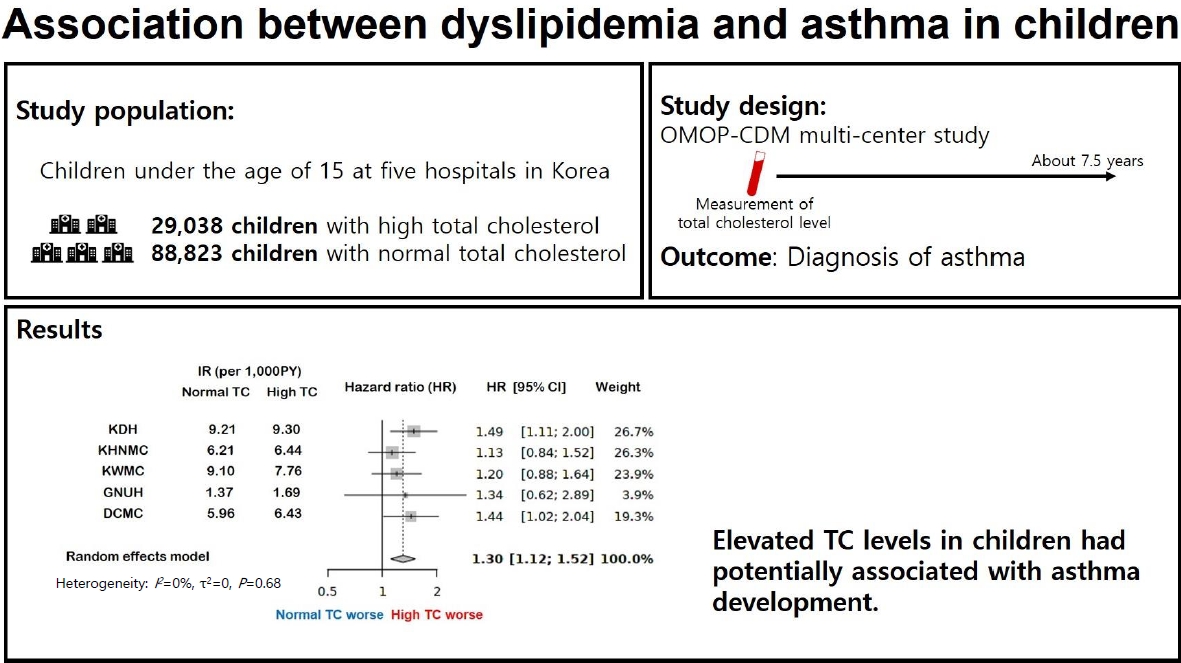
Question: Is dyslipidemia a risk factor for asthma in children?
Finding: This was a comprehensive systematic review and retrospective multicenter study of the association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children. In a multicenter cohort analysis using the Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership Common Data Model, elevated total cholesterol levels were associated with increased risk of asthma development.
Meaning: These findings suggest an association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children.
- Neurology
- Need for palliative care from birth to infancy in pediatric patients with neurological diseases
- Raffaele Falsaperla, Silvia Marino, Carla Moscheo, Lucia Giovanna Tardino, Simona Domenica Marino, Concetta Sciuto, Piero Pavone, Giovanna Vitaliti, Federica Sullo, Martino Ruggieri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):350-356. Published online June 14, 2023
-
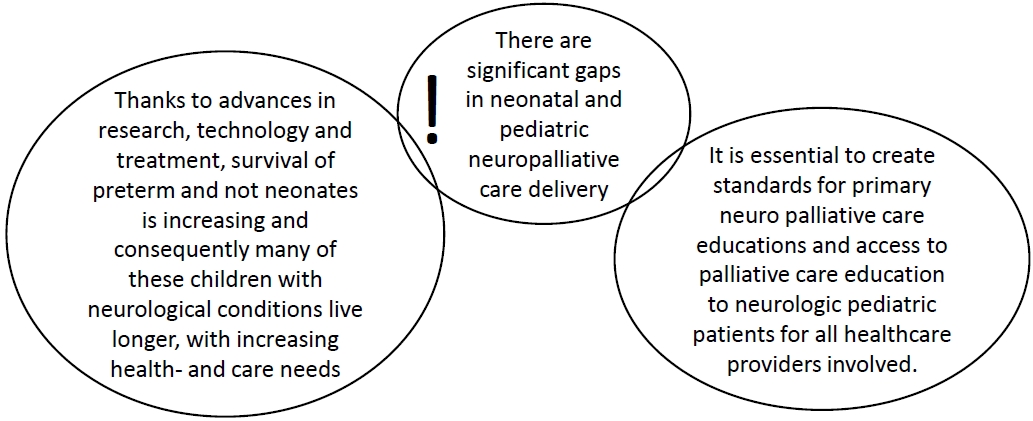
Question: What are the current palliative care protocols, palliative course, and implementable palliative care programs for hospitalized pediatric patients with neurological diseases in Italy?
Finding: We studied 34 newborns with nervous system diseases, all of whom had a poor prognosis.
Meaning: Despite current legislation in Italy, no palliative care network has been implemented. Given the vast number of patients with neurological conditions, standardized palliative care guidelines and protocols are required.
- Gastroenterology
- Assessing indicators and clinical differences between functional and organic childhood constipation: a retrospective study in pediatric gastroenterology clinics
- Hasan M. Isa, Fatema A. Alkharsi, Fatema A. Salman, Maryam S. Ali, Zahra K. Abdulnabibi, Afaf M. Mohamed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):296-306. Published online June 14, 2023
-
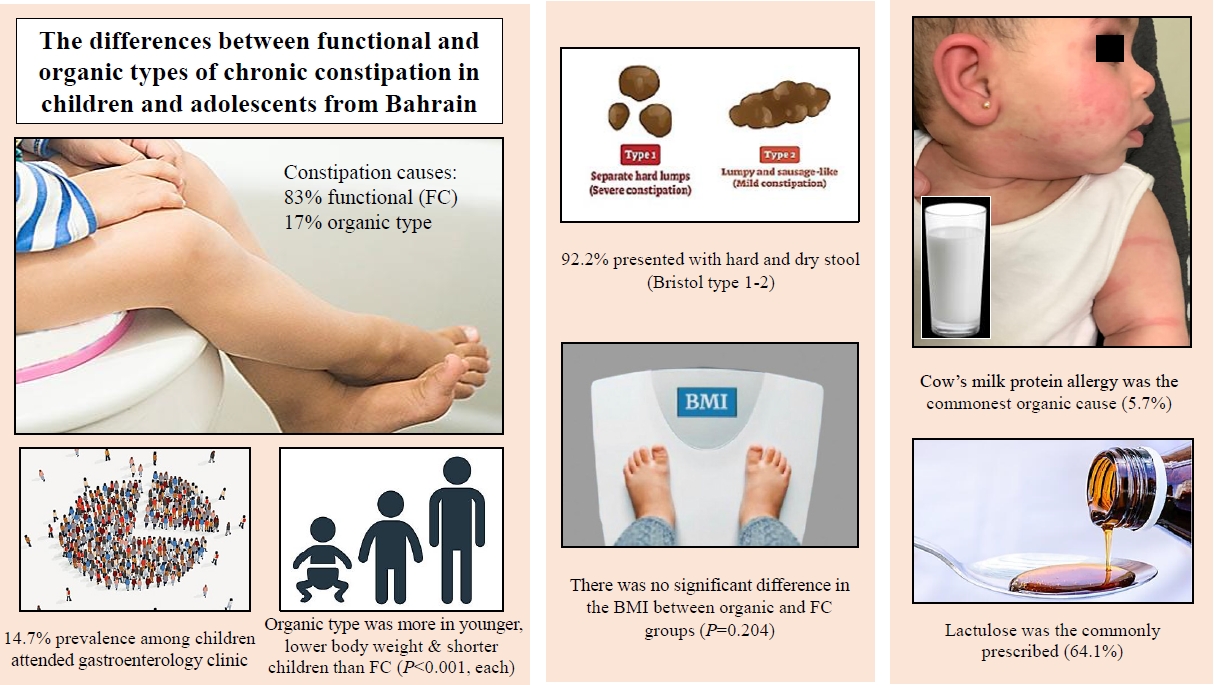
Question: What causes childhood constipation, and what can predict organic constipation?
Finding: Constipation represents 14.7% of gastroenterology visits. Functional constipation is more common among constipation types, while organic constipation is more common in young children and those with a low body weight, stunted growth, mucus in the stool, and associated diseases.
Meaning: Younger children and those with lower growth or mucus in the stool should be assessed for underlying organic causes of constipation.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccines: February 26, 2021, To June 4, 2022, Republic of Korea
- Yeon-Kyeng Lee, Yunhyung Kwon, Yesul Heo, Eun Kyoung Kim, Seung Yun Kim, Hoon Cho, Seontae Kim, Mijeong Ko, Dosang Lim, Soon-Young Seo, Enhi Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):415-423. Published online June 13, 2023
-
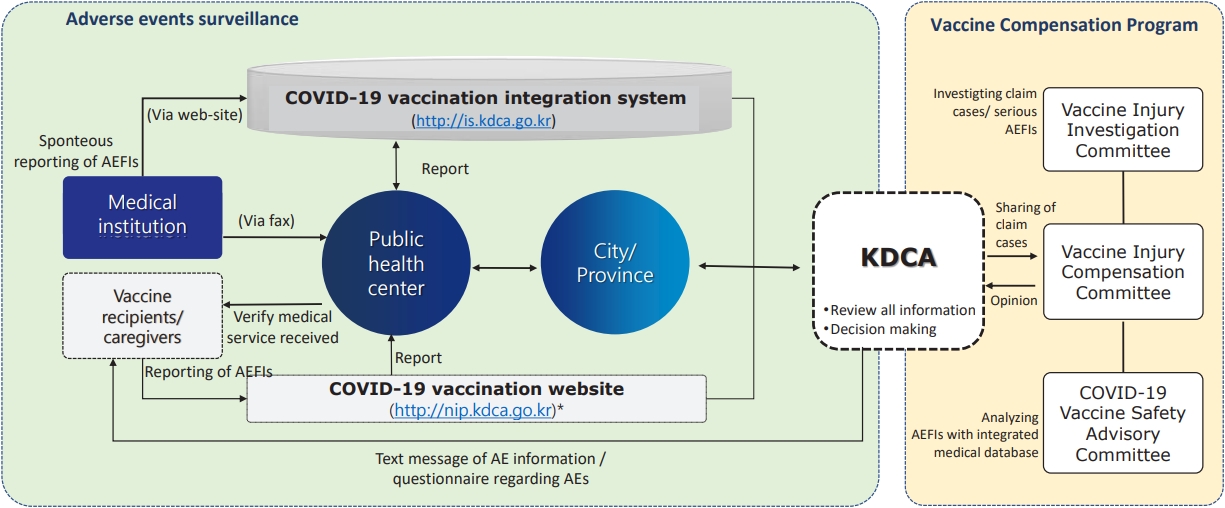
· Enhanced safety monitoring system of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines were implemented to detect signals rapidly as part of the national COVID-19 vaccination program.
· As of June 4, 2023, reported adverse events after COVID-19 vaccination was 0.38% among 125,107,883 doses of COVID- 19 vaccines administered.
· Most reported adverse reactions after COVID-19 vaccinations have shown nonserious and mild intensity.
- Original Article
- Other
- Virtual, augmented, and mixed reality: potential clinical and training applications in pediatrics
- Suyoung Yoo, Meong Hi Son
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):92-103. Published online May 24, 2023
-
· Review of articles that investigated the applications of virtual, augmented, or mixed reality in pediatric clinical settings and in the training of pediatric medical professionals was conducted.
· A total of 89 studies were retrieved, with 36 randomized controlled trials.
· In most studies, intervention using the novel technology was at least as effective or more effective than the traditional method.
· Use of virtual, augmented, and mixed reality has potential in pediatrics.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Parenting stress and interactive engagement behaviors in children with developmental delay
- Jung Sook Yeom, Rock Bum Kim, Jae Young Cho, Ji Sook Park, Eun Sil Park, Ji-Hyun Seo, Jae-Young Lim, Hyang-Ok Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):252-261. Published online May 19, 2023
-
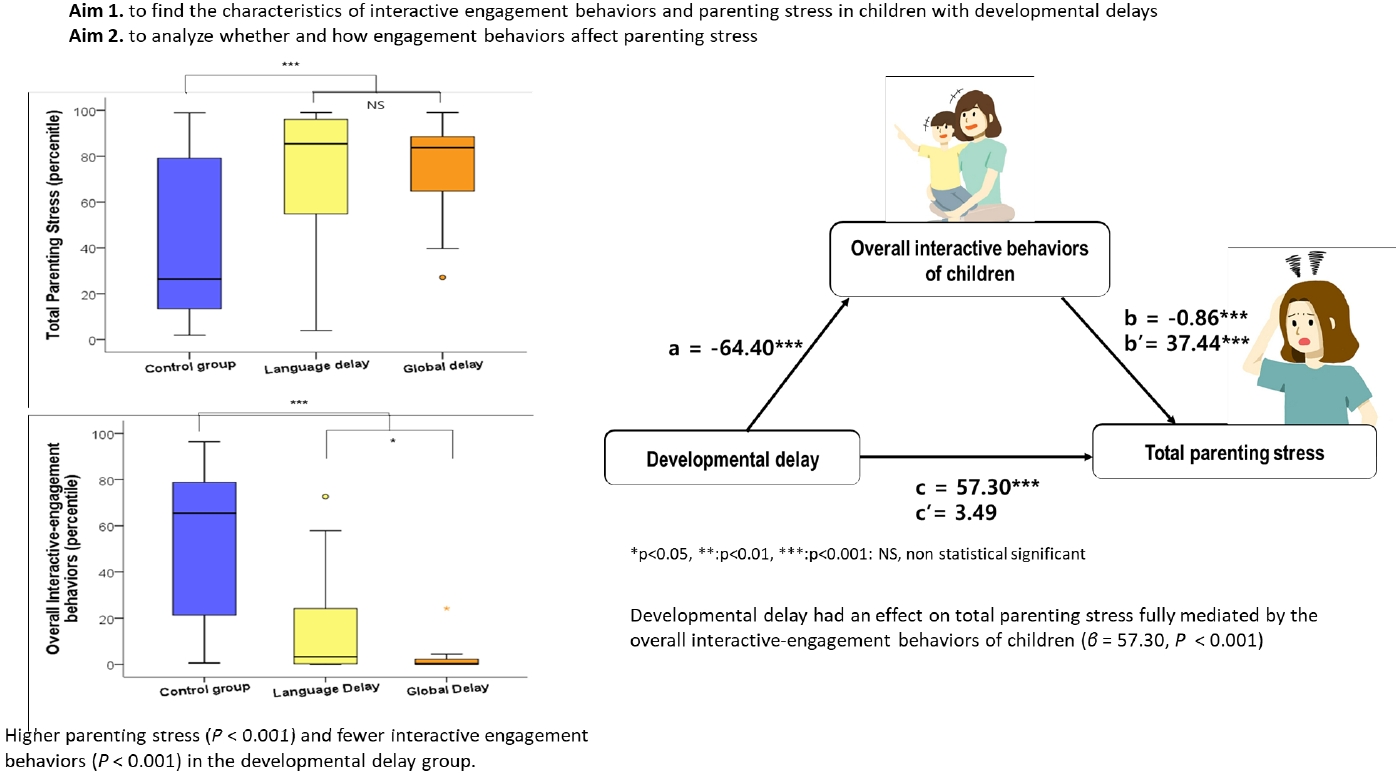
· Question: What level of parenting stress is experienced by parents of children with developmental delays (DDs) without autism spectrum disorder, and what factors contribute to it?
· Findings: Parents of children with DDs experienced high parenting stress that were significantly mediated by their children’s low interactive behaviors.
· Meaning: The interactive behaviors of children with DDs mediate parenting stress.
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









