Original article
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Original article
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Establishing an induced pluripotent stem cell bank using urine cells from pediatric patients with neurogenetic diseases
- Hien Bao Dieu Thai, WonWoo Jung, Sol Choi, Woo Joong Kim, JangSup Moon, ByungChan Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):569-577. Published online April 1, 2025
-
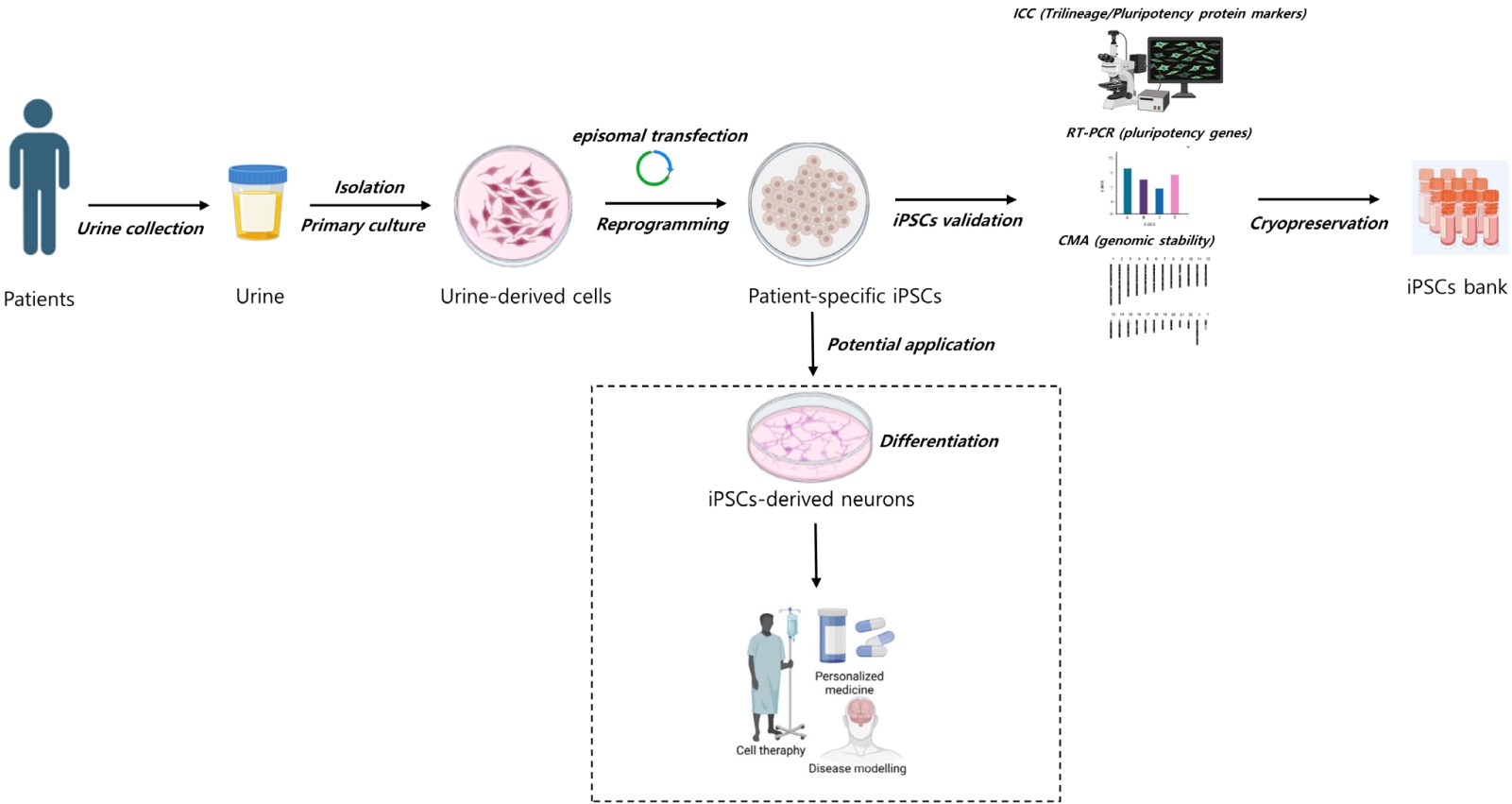
Question: What can be used to create a reliable supply of somatic cells for induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) generation and standardize procedures for building an iPSC bank for researching pediatric neurogenetic disorders?
Findings: Noninvasively acquired urine cells are a desirable cell source for iPSC reprogramming.
Meaning: An iPSC bank can be created from diverse patient cell sources and offer a useful resource for translating research results into clinical therapy for pediatric neurogenetic disorders.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Evaluation of total serum bilirubin thresholds for discontinuing phototherapy in jaundiced neonates: a randomized study
- Ajay Kumar, Nidhi Jain
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):539-545. Published online February 26, 2025
-

Question: What are the outcomes of jaundiced neonates when phototherapy is discontinued at 2 different total serum bilirubin (TSB) thresholds?
Findings: The study involved 80 neonates, comparing a recommended TSB threshold and a lower threshold for phototherapy discontinuation. Results showed a 14.3% reinstitution rate of treatment, with no adverse outcomes.
Meaning: Careful posttreatment monitoring is essential when discontinuing phototherapy, and future research should consider updated guidelines like those from the American Academy of Pediatrics.
- Incidence of neural tube defects in tertiary care university hospital in Bangladesh
- Ismat Jahan, Arif Hossain, Shah Nizam Uddin Shaon, Sadeka Choudhury Moni, Mohammad Kamrul Hassan Shabuj, Sanjoy Kumer Dey, Mohammad Abdul Mannan, Mohammod Shahidullah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):530-538. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: What is the burden of neural tube defects (NTDs) in a tertiary care neonatal intensive care unit in Bangladesh?
Finding: The overall incidence of NTD was 6.4 (range, 4.59–11.2) per 1,000 live births, and the meningomyelocele complex was the most frequent location.
Meaning: The high incidence of NTD found in a leading tertiary care multidisciplinary referral hospital in Bangladesh may not reflect that of the wider population.
- Hematology
- Treatment and clinical outcomes of pediatric autoimmune hemolytic anemia: real-world single-center data from Korea
- Young Dai Kwon, Eun Sun Jung, Yeon Jung Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):522-529. Published online April 16, 2025
-

Question: Can pediatric autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) be effectively managed using first-line steroids?
Finding: In this single-center study, pediatric patients with AIHA achieved normal hemoglobin levels within 16.5 days (range, 9.0–22.0 days) of first-line steroid treatment and maintained effective responses for 2 months.
Meaning: These outcomes highlight the efficacy of steroid treatment in pediatric versus adult AIHA and underscore the need for multicenter trials to establish standardized treatment guidelines.
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Role of microRNA-498 and microRNA-410 in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Eman Salah Eldeen Arafat, Hasnaa Hesham Abotaleb, Dina Abdel Razek Midan, Abdel Hamid Abdo Ismail, Zeinab Sabri Abouzouna
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):512-521. Published online February 26, 2025
-

Question: Is it role of microRNA-410 (miRNA-410) and microRNA-498 (miRNA-498) in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)?
Findings: miRNA-498 and miRNA-410 can be auxiliary diagnostic and prognostic tools for neonatal HIE.
Meaning: we can use miRNA-498 and miRNA-410 as markers and indicator for HIE.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Characterization of gut microbiota in very low birth weight infants with versus without bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Anucha Thatrimontrichai, Manapat Praditaukrit, Gunlawadee Maneenil, Supaporn Dissaneevate, Kamonnut Singkhamanan, Komwit Surachat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):503-511. Published online February 26, 2025
-

Question: Does the gut microbiota differ between very low birth weight (VLBW) infants with versus without bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)?
Finding: Common respiratory pathogens were notably elevated in the BPD group, whereas anaerobic and butyrate-producing taxa, key components of postbiotics, were dominant in the non-BPD group.
Meaning: In gut-lung communication, the interplay between the intestinal and respiratory systems may implicate pro- and postbiotics in VLBW infants with BPD.
- Pulmonology
- Clinical course of children with postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans with versus without comorbid bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Lamia Medghoul, Julien Grosjean, Christophe Marguet, Hortense Petat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):497-502. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: Postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans (PIBO) is a chronic respiratory disease that typically develops in children after a severe respiratory infection. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is often comorbid in patients with PIBO.
Finding: Corticosteroid pulse therapy effectively manages PIBO with or without comorbid BPD, significantly reducing exacerbations and decreasing the daily requirement for inhaled corticosteroids.
Meaning: Therapeutic effects of corticosteroid pulses are rapid and sustained over time, in both groups.
- Nonlinear association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and asthma in children and adolescents in the United States: a cross-sectional study
- Chuhan Cheng, Liyan Zhang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):489-496. Published online March 11, 2025
-

Question: Is there a nonlinear relationship between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and asthma in children and adolescents?
Finding: NLR showed a nonlinear association with asthma, with an NLR threshold of 2.23 identifying individuals at higher risk.
Meaning: An NLR<2.23 may serve as a potential biomarker for asthma risk assessment and management in pediatric populations, thereby offering a simple tool for the early identification of at-risk individuals.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Differential roles of interleukin-6 and adrenomedullin in early diagnosis and mortality predictions in late-onset neonatal sepsis
- Emilly Henrique dos Santos, Gabriel Acca Barreira, Mariana Okay Saippa, Maria Carolina Pires Cruz, Karen Alessandra Rodrigues, Ronaldo Arkader, Thelma Suely Okay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):463-471. Published online December 23, 2024
-

Question: Can adrenomedullin (ADM) or interleukin-6 (IL-6) detect late-onset neonatal sepsis (LOS) at admission (area under the curve [AUC]>0.90) as an early diagnostic marker?
Finding: Only IL-6 consistently distinguished survivors from nonsurvivors (AUC>0.90) on admission and antibiotic treatment days 3 and 7. C-reactive protein level identified infections from day 3 but failed to predict outcomes (AUC<0.70).
Meaning: IL-6 level can improve LOS diagnosis and prognosis.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus
- Karnchanit Sausukpaiboon, Nuanpan Penboon, Pornpimol Rianthavorn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):454-462. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: What is the acceptance rate for coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
Finding: One-third of parents were hesitant to vaccinate their child. Parental willingness to vaccinate themselves, older patient age, and belief in the vaccine's potency were associated with vaccine acceptance.
Meaning: These findings highlight the need for targeted interventions to improve vaccine acceptance among parents of children with SLE.
- Oncology
- Prognostic role of mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin in predicting infection in pediatric cancer with febrile neutropenia
- Seham M. Ragab, Sara Mahmoud El-Deeb, Ahmed Saeed, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):445-453. Published online January 13, 2025
-

· Infection remains a leading cause of death in febrile neutropenia (FN).
· Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-ProADM) levels are higher among patients with FN and a bacterial infection.
· A longer FN duration and hospital stay length as well as elevated C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and MR-ProADM levels are significant risk factors for mortality.
- Hematology
- Impact of Xmn1 polymorphism on hydroxyurea therapy in children with HbE-β non-transfusion dependent thalassemia: a cohort study
- Saheli Roy, Paramita Bhattacharya, Atanu Kumar Dutta, Mrinal Kanti Das
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):437-444. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: Does the T allele of Xmn1 polymorphism favorably influence hydroxyurea efficacy in children of Eastern descent with fetal hemoglobin (HbE)-β nontransfusion dependent thalassemia (NTDT)?
Finding: Decrease in transfusion requirement and increase in height following hydroxyurea therapy was noted in both groups, however, change in CT was more critical than that in CC genotype.
Meaning: T allele of Xmn1 polymorphism favorably influences hydroxyurea efficacy in children with HbE-β NTDT.
- General Pediatrics
- The role of serum zinc and selenium levels in etiology of febrile seizures
- Yavuz Ataş, Hatice Gamze Poyrazoğlu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):388-394. Published online January 13, 2025
-

Zinc may play a key role in preventing febrile seizures by increasing the seizure threshold and reducing oxidative stress. Incorporating zinc supplements into treatment could help protect children from the adverse effects of febrile seizures and improve their overall outcomes.
- Infection
- Enteric pathogens implicated in acute infectious diarrhea among young children in resource-limited region with rapidly growing population: a hospital-based cross-sectional study
- Aseel Mahmood Ibrahim Al-Mashahedah, Randa Mohammed Dhahi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):379-387. Published online December 23, 2024
-

Question: What are the most common enteric pathogens in acute diarrhea among children younger than 5 years of age, and which age group is most susceptible?
Finding: Bacteria were the most common causative microorganisms of diarrhea, followed by viruses, parasites, and fungi. The 1–2-year age group was the most commonly affected.
Meaning: There is a need to formulate preventive strategies targeting children exposed to enteric pathogens to limit diarrhea.
- Nutrition
- Differential effects of dietary and physical activity interventions on adiposity of children with obesity
- Anekchoke Tangtongsoong, Chonnikant Visuthranukul, Yuda Chongpison, Sirinuch Chomtho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):370-378. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: How do dietary intake and physical activity affect body mass index (BMI) z scores and adiposity among children with obesity?
Finding: Higher dietary protein and fiber intakes were significantly associated with a decrease in BMI z scores and adiposity among children with obesity.
Meaning: Optimizing dietary interventions by focusing on protein and fiber intakes could be an effective strategy for managing childhood obesity.
- Immunology
- Serum bactericidal activity against meningococcus in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
- Soyoung Lee, Kyung-Hyo Kim, Ji Hyen Lee, Han Wool Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):362-369. Published online January 13, 2025
-
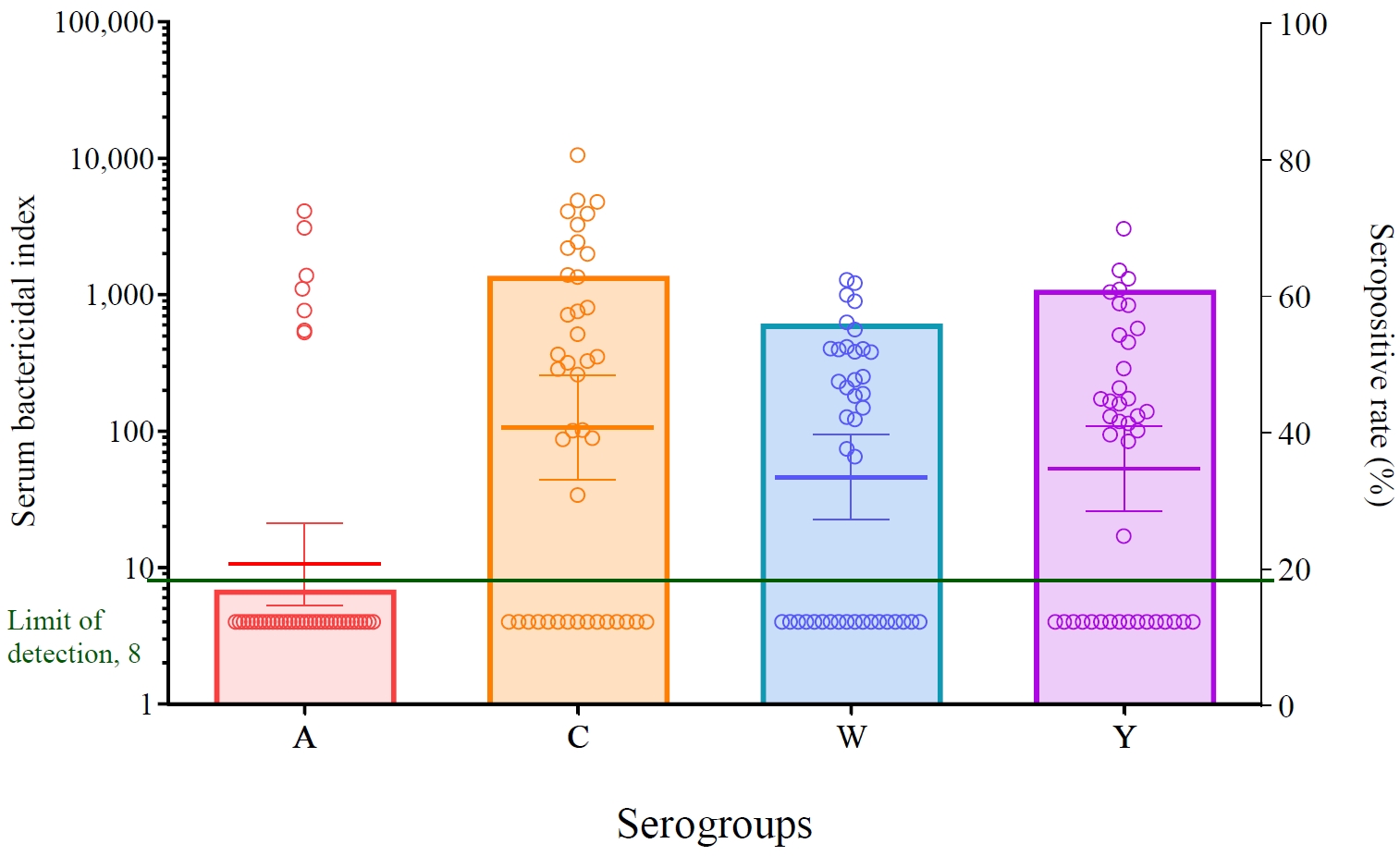
Question: What is the level of immunity against meningococcal infections in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) under the age of 19, and is vaccination against meningococcus necessary for these patients, given their susceptibility to infections due to immunosuppressive treatments and disease characteristics?
Finding: Although some of our study patients exhibited serum bactericidal activity against meningococci, most remained seronegative.
Meaning: These findings suggest that patients with SLE who are at risk of meningococcal infection receive appropriate vaccinations.
- Pulmonology
- Impact of obesity on pulmonary function of preschool children: an impulse oscillometry study
- Anuvat Klubdaeng, Kanokporn Udomittipong, Apinya Palamit, Pawinee Charoensittisup, Khunphon Mahoran
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):319-325. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: Does obesity in preschool children affect lung function, and which obesity indices can predict such alterations?
Finding: Preschool children with obesity exhibit impaired lung function characterized by elevated total and peripheral airway resistance. Waist-to-height ratio was the strongest predictor of such changes.
Meaning: Early obesity prevention and treatment are needed. Monitoring waist-to-height ratio, body weight, and body mass index may help identify children at risk of altered lung function.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- C3 glomerulopathy in children: experience at a resource-limited center
- Soumya Reddy, Abhishek Ghante, Mahesha Vankalakunti, Anil Vasudevan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):311-318. Published online November 28, 2024
-

Question: What are the clinicopathological features and outcomes of pediatric C3 glomerulopathy (C3G) in resource-limited settings?
Finding: Children with C3G in resource-limited settings have significant morbidities, and most experience kidney sequelae despite treatment. Electron microscopy was performed in only 50% of our patients, while none received complement assays or genetic testing.
Meaning: Pediatric C3G presentation, management, and kidney outcomes vary. Its thorough evaluation and management are challenging in resource-limited settings.
- Neurology
- Occurrence of stroke in children and young adults in Indonesia: a multicenter private hospital study
- Jeanne Leman, Veli Sungono, Yosua Timotius Haryono, Muhammad Adam Mudzakir, Dewi Lestari Rahmawati, Callistus Bruce Henfry Sulay, Gilbert Sterling Octavius
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):303-310. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: What is the occurrence of pediatric stroke in Indonesia?
Finding: This multicenter study identified 1,074 stroke cases, predominantly hemorrhagic (83.4%), with males and older children at higher risk. Accidents were the primary cause (73.2%).
Meaning: Pediatric stroke in Indonesia shows critical epidemiological trends, highlighting the need for targeted prevention efforts, particularly for high-risk groups like males and accident victims.
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Long-term follow-up of neurocognitive function in patients with citrin deficiency and cholestasis
- Meng-Ju Melody Tsai, Jung-Chi Chang, Heng-Yu Lu, Susan Shur-Fen Gau, Yin-Hsiu Chien, Wuh-Liang Hwu, Yen-Hsuan Ni, Huey-Ling Chen, Ni-Chung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):257-265. Published online November 28, 2024
-
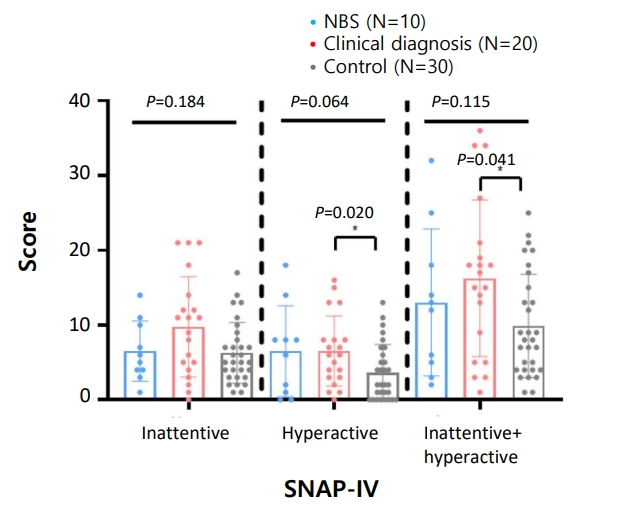
Question: Do transient metabolic disturbances in early childhood due to citrin deficiency have lasting effects on neurocognitive function?
Finding: Children with citrin deficiency have a higher prevalence of ADHD compared to the general population, with elevated ammonia levels in infancy associated with increased hyperactivity-impulsivity risk.
Meaning: Metabolic disturbances in early childhood due to citrin deficiency may contribute to long-term neurocognitive impacts, particularly ADHD, while IQ and life outcomes generally remain normal.
- Gastroenterology
- Outcome of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease in Asian children: a multinational 1-year follow-up study
- Pornthep Tanpowpong, Suporn Treepongkaruna, James Guoxian Huang, Kee Seang Chew, Karen Sophia Calixto Mercado, Almida Reodica, Shaman Rajindrajith, Wathsala Hathagoda, Yoko Kin Yoke Wong, Way Seah Lee, Marion Margaret Aw
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):247-256. Published online November 13, 2024
-
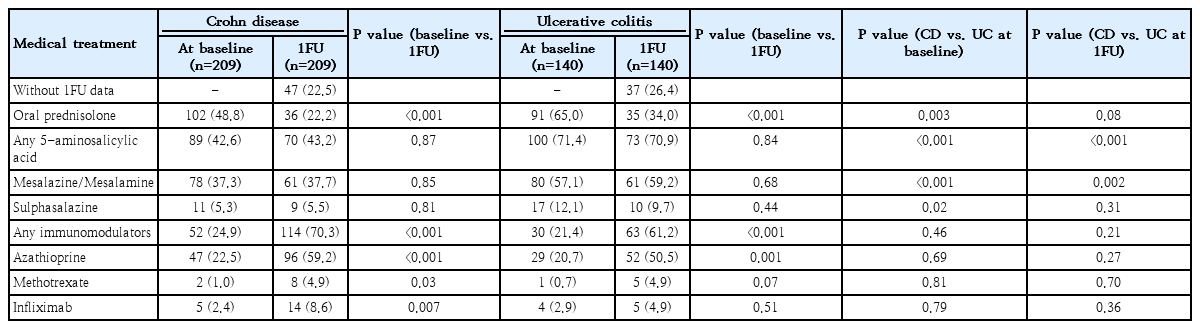
Question: Short-term (1-year) follow-up data in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), especially in Southeast Asian countries, are limited.
Finding/Meaning: Abdominal pain and pallor rates remained high at 1 year after IBD diagnosis. Three independent factors of 1-year clinical remission for Crohn disease were oral prednisolone, antibiotic, and immunomodulator use at 1-year follow-up. A history of weight loss at diagnosis was the only independent risk factor of IBD flare.
- Endocrinology
- Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone score changes in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency
- Pattara Wiromrat, Yutapong Raruenrom, Phanpaphorn Namphaisan, Nantaporn Wongsurawat, Ouyporn Panamonta, Chatlert Pongchaiyakul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):238-246. Published online November 13, 2024
-
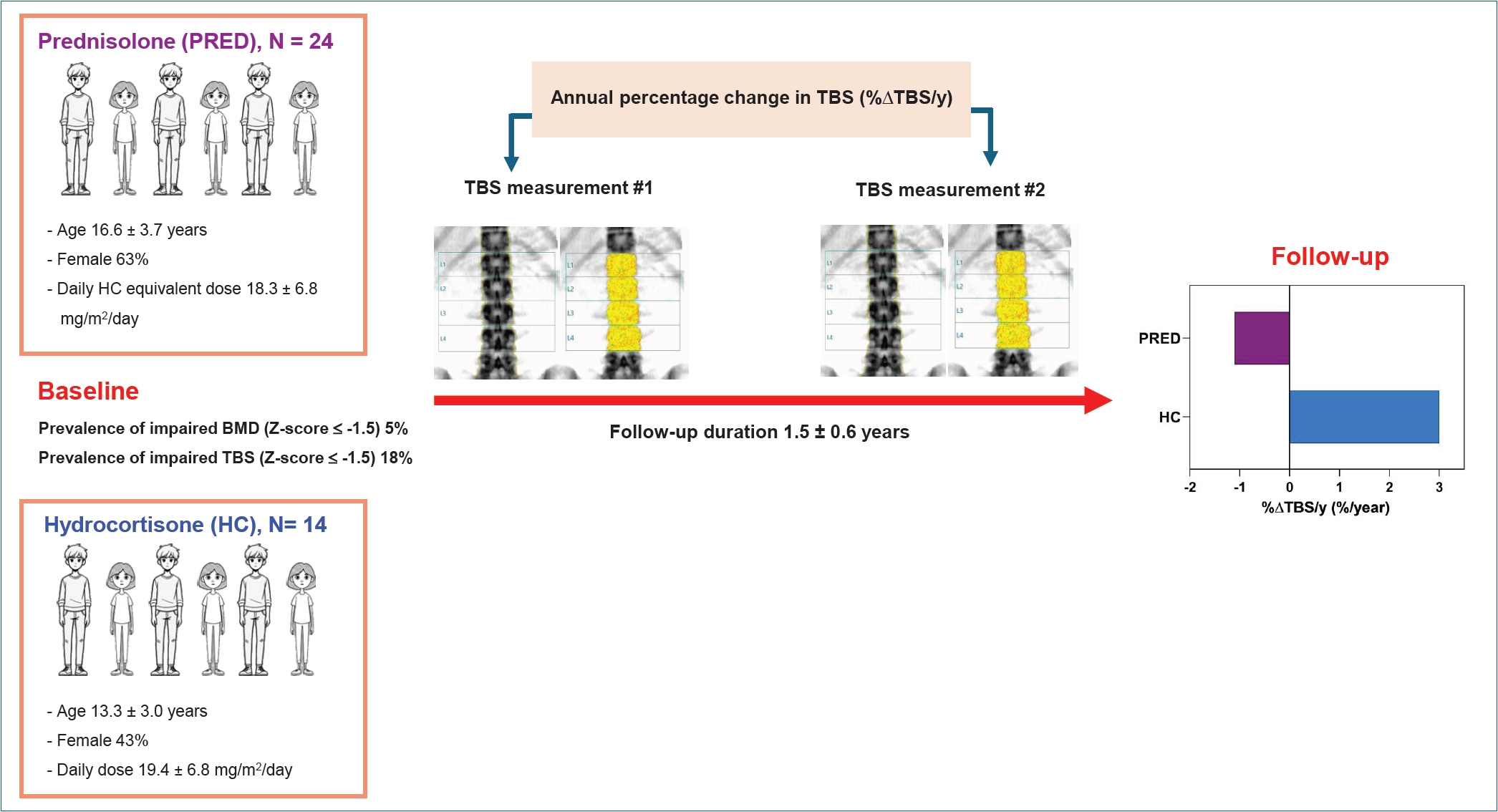
Question: What is the prevalence of an impaired trabecular bone score (TBS), a measure of bone microarchitecture, in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency (21OHD)? Do prednisolone and hydrocortisone affect TBS differently in this patient population?
Finding: Impaired TBS was observed in 18% of participants. Prednisolone use negatively impacted TBS change.
Meaning: Impaired TBS is prevalent among adolescents with 21OHD. Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone microarchitecture development.
- General Pediatrics
- Knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding dengue vaccine: a baseline study of community members and health providers in Indonesia
- Abdul Wahab, Ida Safitri Laksanawati, Retna Siwi Padmawati, Asal Wahyuni Erlin Mulyadi, Wahyu Triadmajani, Jarir At Thobari
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):228-237. Published online November 13, 2024
-
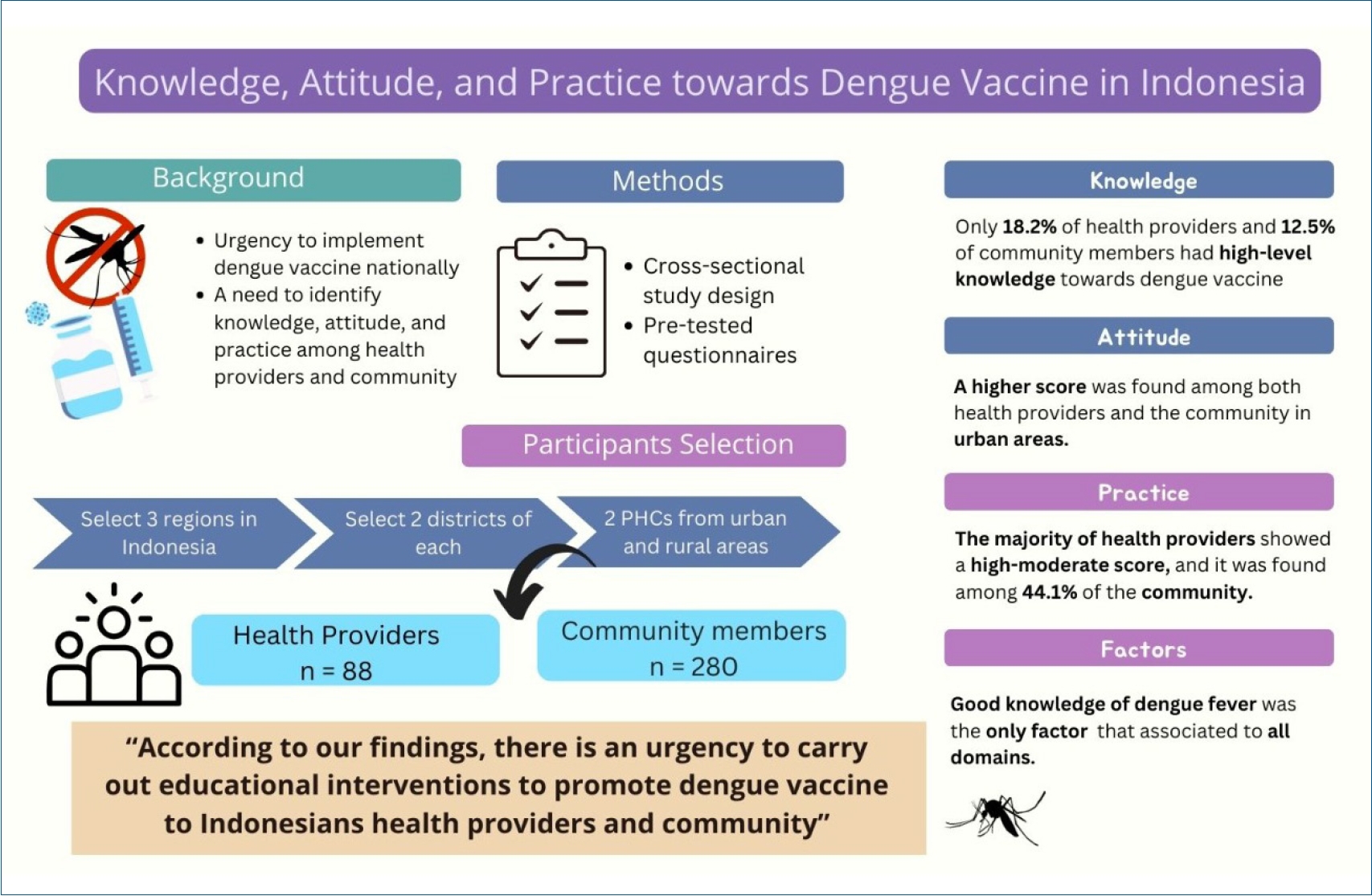
Question: Do community members and health providers show different level of knowledge, attitude, and practice towards dengue vaccine?
Finding: These 2 groups only differed in practice component, while the knowledge and attitude constituents were relatively low for both.
Meaning: There is an urgent need to deliver educational interventions to raise awareness of community members and health providers regarding dengue vaccination.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effect of high-frequency oscillatory ventilation with intermittent sigh breaths on carbon dioxide levels in neonates
- Kulthida Baingam, Anucha Thatrimontrichai, Manapat Praditaukrit, Gunlawadee Maneenil, Supaporn Dissaneevate
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):178-184. Published online November 13, 2024
-
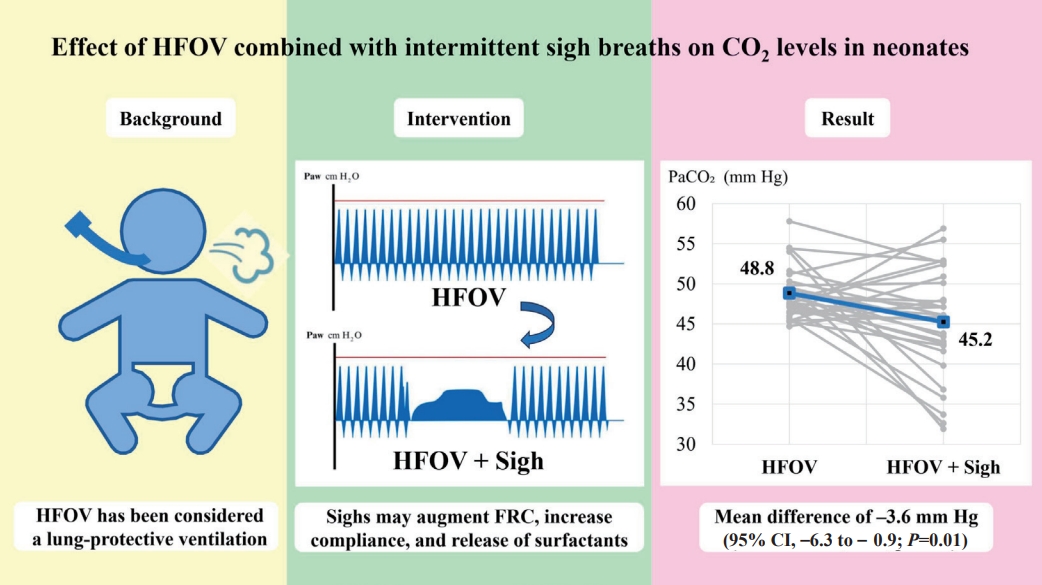
Question: Can sigh breaths (Sighs) application during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV) decrease partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) levels?
Finding: The mean PaCO2 level after Sighs during HFOV was significantly decreased compared to that after HFOV alone (mean difference, -3.6 mmHg).
Meaning: HFOV plus Sighs functionality can reduce PaCO2 levels. However, further studies are required to conclusively determine the effects of Sighs.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Characteristics of temper tantrums in 1–6-year-old children and impact on caregivers
- Warangkana Prutipaisan, Issarapa Chunsuwan, Tippawan Hansakunachai, Paskorn Sritipsukho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):170-177. Published online November 13, 2024
-
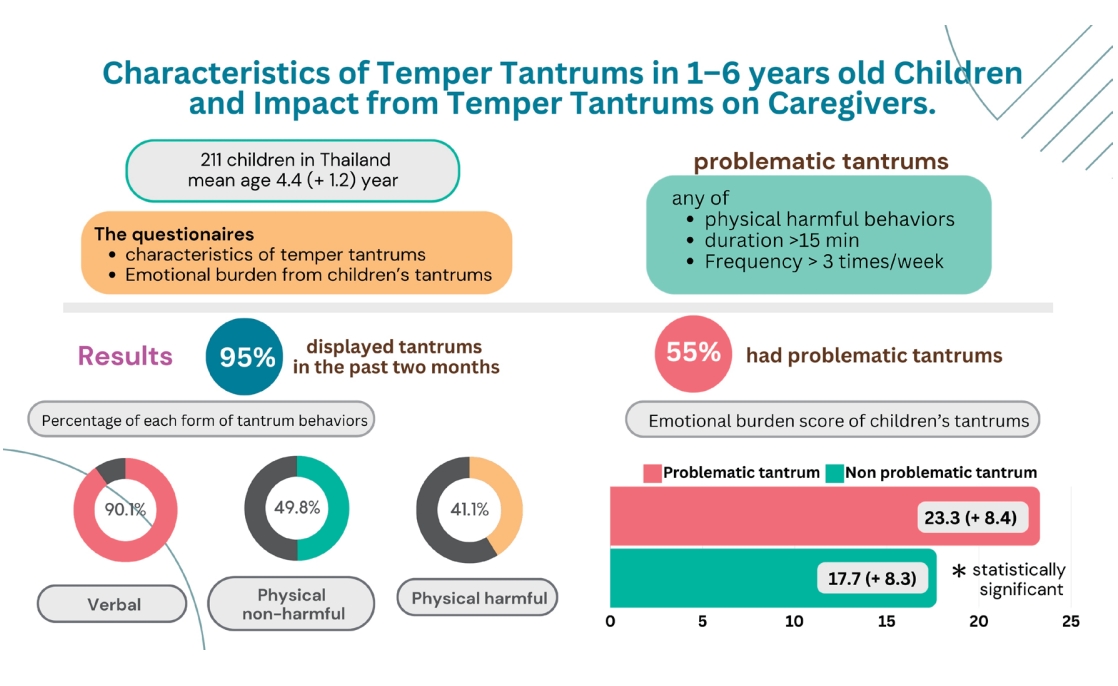
Question: What are common tantrum behaviors in preschool children, and how frequently are problematic behaviors observed? Do problematic tantrums have a different emotional impact on caregivers compared to typical tantrums?
Finding: Temper tantrums are common in preschool children, and verbal tantrums are the most common type.
Meaning: Problematic tantrums, defined as tantrums exhibiting aggressive physical behavior, long duration (>15 minutes), or frequent occurrence (>3 days/wk), significantly affected caregivers’ emotions.
- Neurology
- Evaluation of pediatric migraine triggers: a single-center study
- Hey-Joon Son, Joo-Ok Jin, Kon-Hee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):163-169. Published online November 11, 2024
-
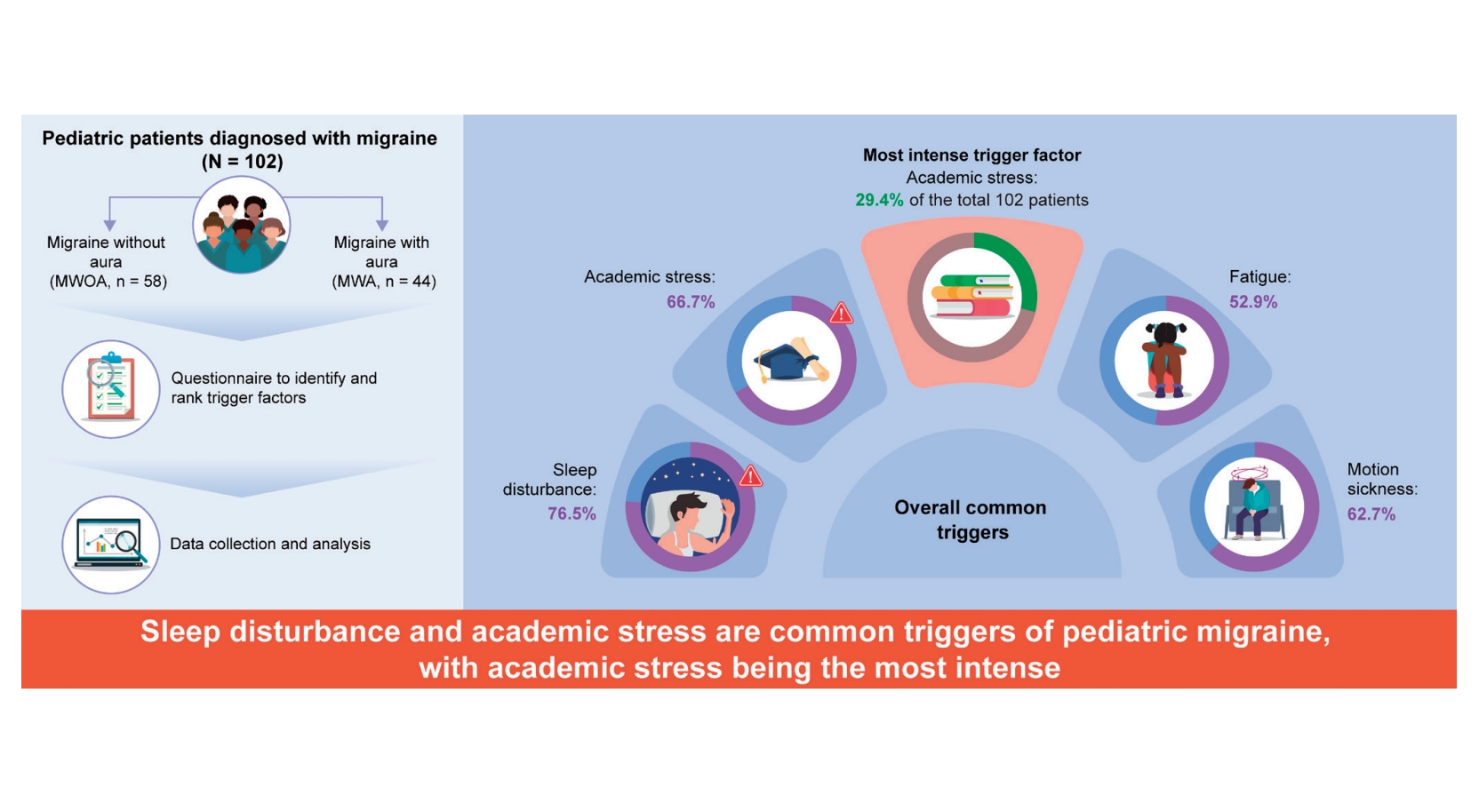
Question: What are the primary triggers for pediatric migraines, and how do they impact clinical management?
Finding: Common triggers for pediatric migraines include sleep disturbances, academic stress, and motion sickness, with academic stress identified as the most intense.
Meaning: Recognizing and addressing specific triggers like sleep disturbance and academic stress is crucial to effectively managing pediatric migraines with emphasis on personalized care to improve outcomes.
- Infection
- Clinical characteristics and associated factors of pediatric acute necrotizing encephalopathy: a retrospective study
- Huiling Zhang, Yilong Wang, Qianyun Ding, Xuekun Li, Sheng Ye
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):153-162. Published online November 11, 2024
-
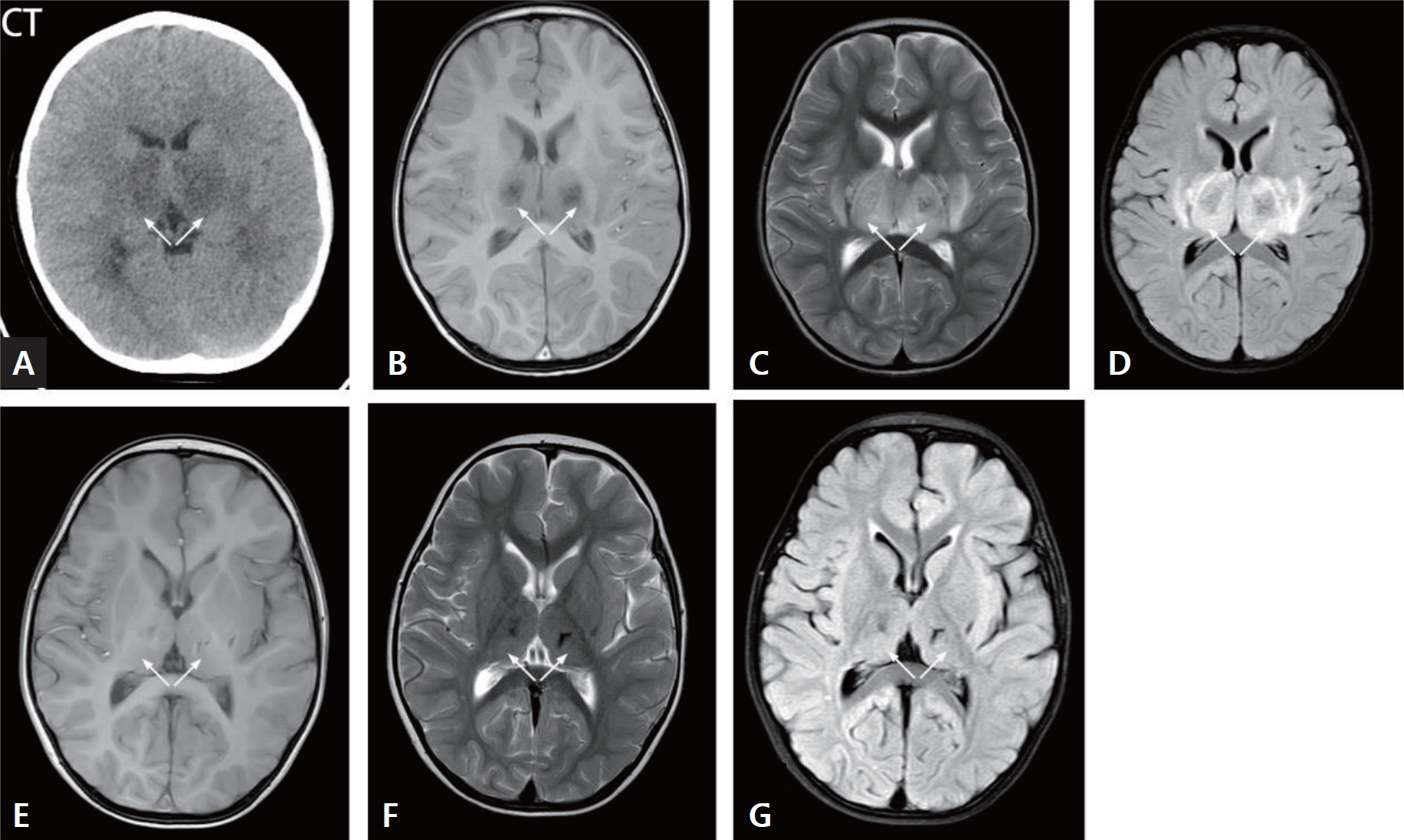
· The mortality rate of acute necrotizing encephalopathy was high.
· Laboratory tests revealed that the fatal group had higher creatinine, lactate, activated partial thromboplastin time, thrombin time, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, creatine kinase, and D-dimer than survivors.
· The fatal group displayed lower Glasgow Coma Scale scores and arterial pH.
- Gastroenterology
- Differences in immune cells and gene expression in human milk by parity on integrated scRNA sequencing
- Dae Yong Yi, Hong-Jai Park, Min Sun Shin, Hyoungsu Kim, Sang Jin Lee, Insoo Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):141-152. Published online January 10, 2025
-
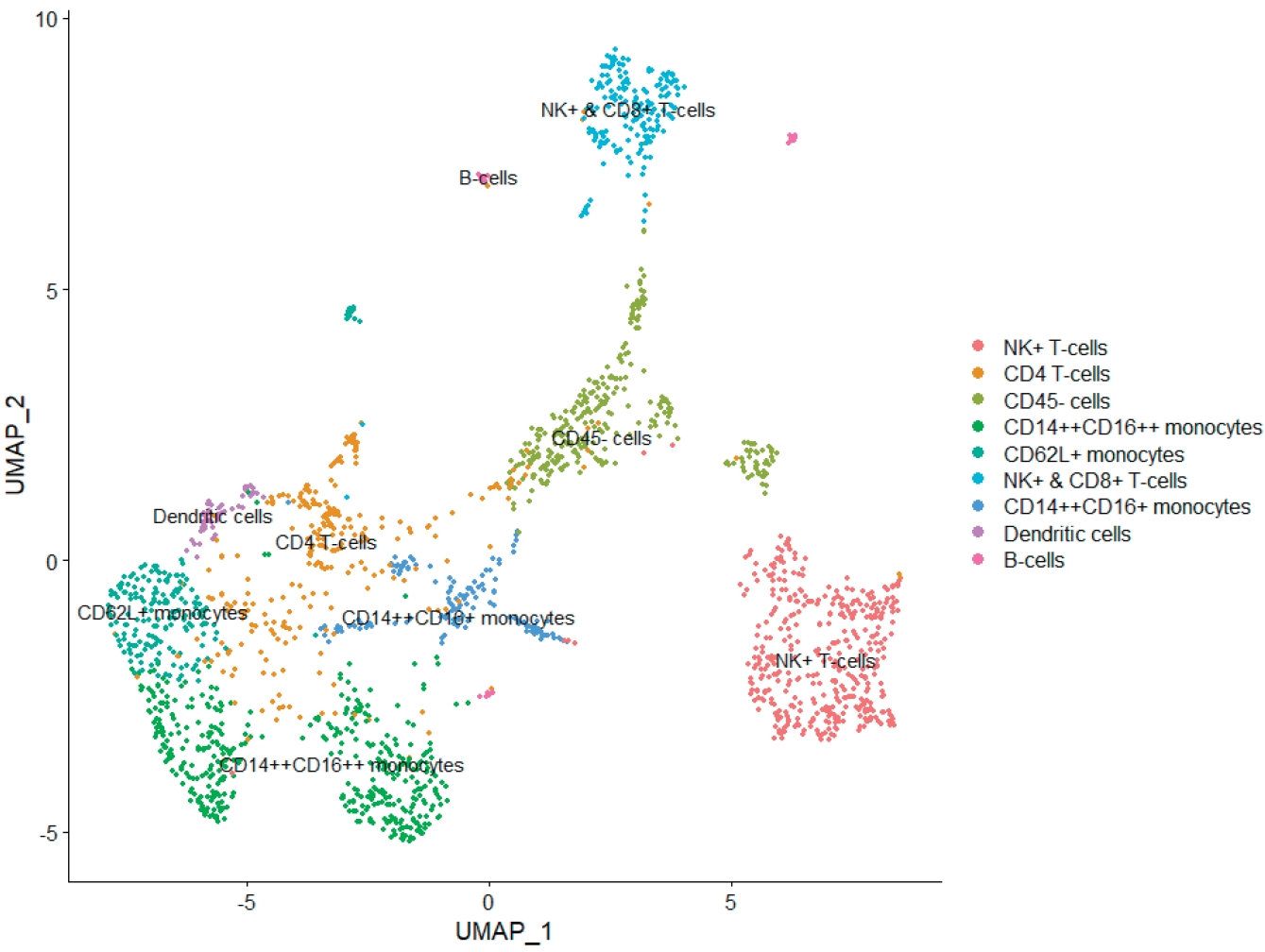
Question: Is there a difference in immune cells in human breast milk by parity?
Finding: There were higher proportions of monocytes and T/B cells in the primiparous and multiparous group, respectively. The expression of genes with a direct role in the infant immune system and immune response-related genes were highest in the primiparous group
Meaning: There were parity-dependent differences in the expression of genes between innate and adaptive immune cells.
- Neurology
- Instability of revised Korean Developmental Screening Test classification in first year of life
- Ji Eun Jeong, You Min Kim, Na Won Lee, Gyeong Nam Kim, Jisuk Bae, Jin Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):97-103. Published online November 11, 2024
-

Question: How stable are the revised Korean Developmental Screening Test score classifications in early infancy?
Finding: A significant number of infants improved into the peer and high-level group (≥-1 standard deviations), especially in the gross motor area.
Meaning: The early detection of developmental delay requires a comprehensive medical history, physical and neurological examinations, and repeated developmental screenings.
- Endocrinology
- Efficacy of leuprolide acetate versus triptorelin pamoate administered every 3 months for treatment of central precocious puberty
- Thanaporn Thaneetrakool, Suphab Aroonparkmongkol, Nattakarn Numsriskulrat, Vichit Supornsilchai, Suttipong Wacharasindhu, Khomsak Srilanchakon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):91-96. Published online November 6, 2024
-

Question: What are the differences in efficacy between leuprolide acetate and triptorelin pamoate administered every 3 months for the treatment of central precocious puberty (CPP)?
Finding: There were no significant intergroup differences in luteinizing hormone suppression or predicted adult height at the end of treatment in girls with CPP.
Meaning: Leuprolide acetate and triptorelin pamoate have comparable efficacy for treating CPP.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











