Topics
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- TOPICS
- Topics
- Topics
-
- Adolescence Medicine (4)
- Allergy (64)
- Cardiology (81)
- Critical Care Medicine (15)
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine (24)
- Emergency Medicine (5)
- Endocrinology (65)
- Gastroenterology (76)
- General Pediatrics (58)
- Genetics and Metabolism (26)
- Hematology (20)
- Immunology (16)
- Infection (82)
- Neonatology (Perinatology) (127)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary) (54)
- Neurology (96)
- Nutrition (33)
- Oncology (19)
- Neurobehavior (12)
- Pulmonology (35)
- Rheumatology (4)
- Other (44)
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Inferior vena cava to aorta ratio in dehydrated pediatric patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Gilbert Sterling Octavius, Michelle Imanuelly, Johan Wibowo, Nadia Khoirunnisa Heryadi, Melanie Widjaja
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):477-484. Published online June 14, 2023
-
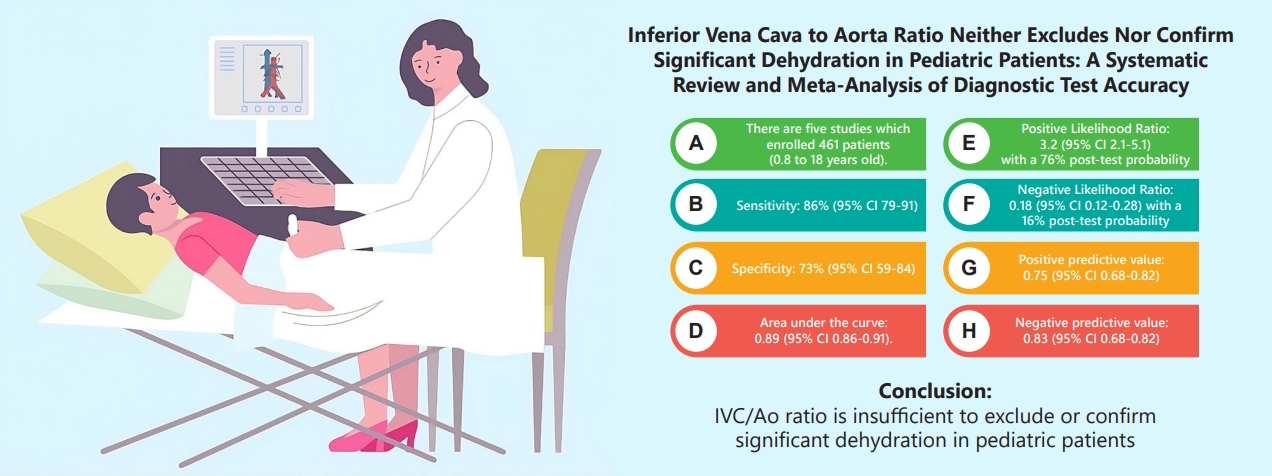
Question: The inferior vena cava to aorta (IVC/Ao) ratio measured via ultrasound has been touted as a promising noninvasive technique to assess clinically significant dehydration in pediatric patients.
Finding: Our meta-analysis found that IVC/Ao ratio had a positive likelihood ratio of 3.2 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.1–5.1) and negative likelihood ratio of 0.18 (95% CI, 0.12–0.28).
Meaning: Hence, IVC/Ao ratio is insufficient to exclude or confirm significant dehydration in pediatric patients.
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Noninvasive and simple, but accurate? Meta-analysis of evidence-based point-of-care ultrasound for assessing dehydration in children
- Jin-Hee Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):475-476. Published online July 11, 2023
-
· Point-of-care ultrasound imaging, including measurement of the inferior vena cava/aorta ratio, is powerful for evaluating the hemodynamic status of pediatric patients.
· Owing to the limited feasibility of randomized clinical trials and insufficient data in children, imaging tools require validation.
· Objective validity meta-analyses of imaging studies can affect clinical decision-making and serve as a cornerstone for evidence-based practice in pediatrics.
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- Long COVID in children and adolescents: prevalence, clinical manifestations, and management strategies
- Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):465-474. Published online June 19, 2023
-
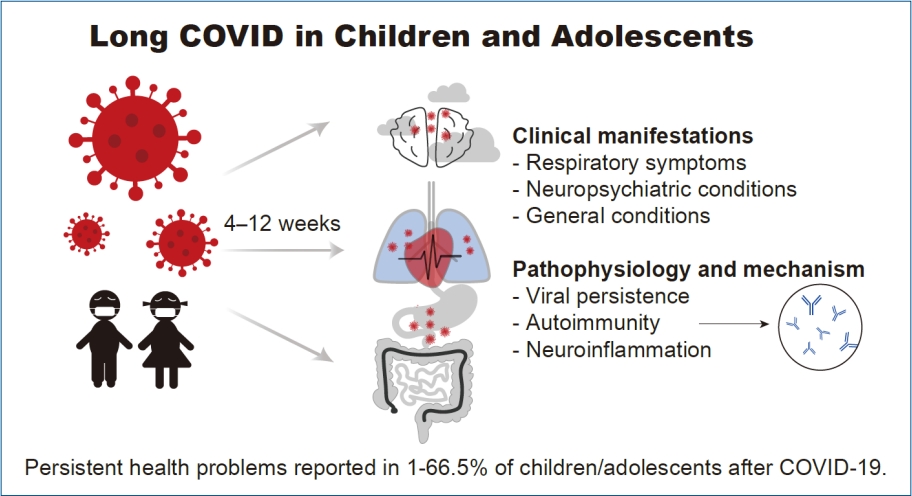
· Current definitions of long coronavirus disease (COVID) in children and adolescents vary in duration, ranging from 4 to 12 weeks or more.
· The clinical spectrum of long COVID in children and adolescents comprises a wide range of symptoms and might be a multisystem disorder.
· Persistent health problems with a prevalence of 1%–66.5% were reported in children and adolescents after COVID-19, with a higher incidence of persistent single or multiple symptoms.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Spontaneous movements as prognostic tool of neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants: a narrative review
- Hyun Iee Shin, Myung Woo Park, Woo Hyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):458-464. Published online May 16, 2023
-
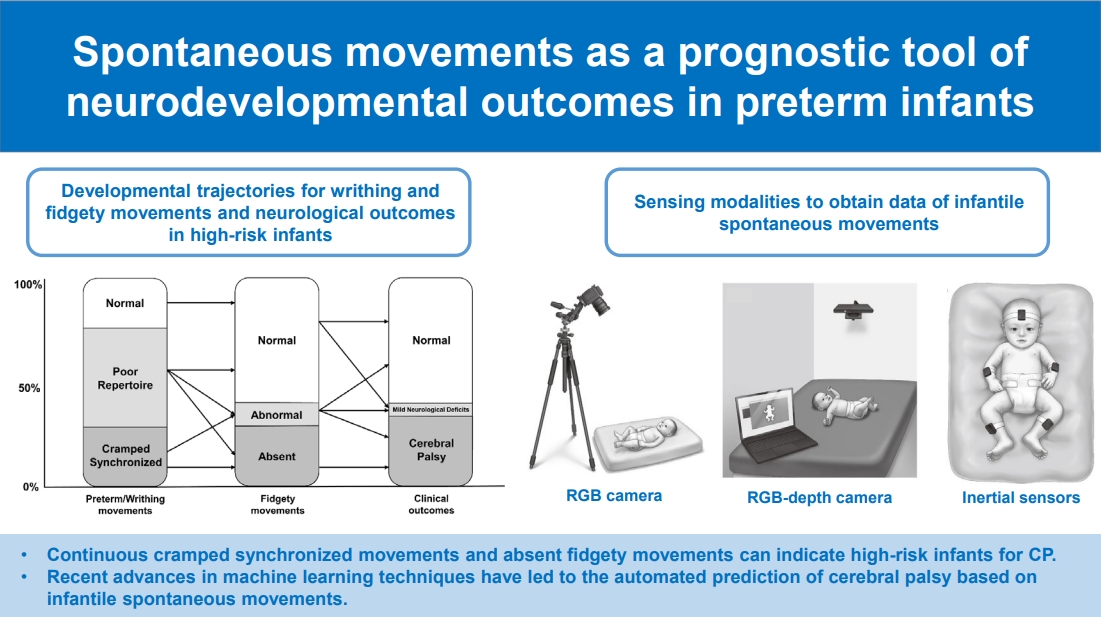
· Spontaneous movements can be useful to evaluate neuronal integrity in preterm infants.
· In General Movements Assessment, continuous cramped synchronized movements and absent fidgety movements can indicate high-risk infants for cerebral palsy.
· Recent advances in machine learning techniques have led to the automated prediction of cerebral palsy based on infantile spontaneous movements.
- Letter to the Editor
- Allergy
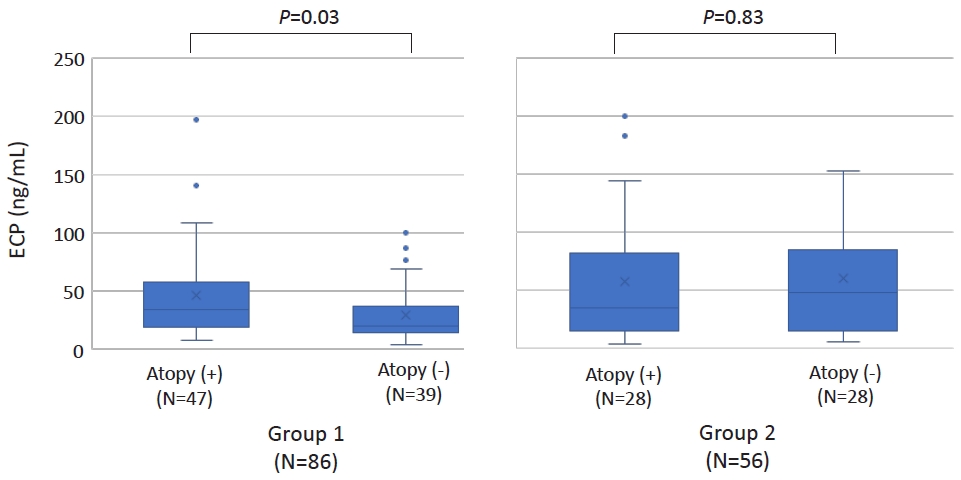
- Increased serum eosinophilic cationic protein in children with nonspecific chronic cough
- Young Hwan Kim, Yoon Young Jang, Jieun Jeong, Hai Lee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):455-457. Published online September 14, 2023
-
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Impact of short and intensive art-based intervention on symptomatology and social interactions among children with autism spectrum disorder
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Bayar Mohammed Omar Abdulla, Pranee Liamputtong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):447-454. Published online September 14, 2023
-

Question: Does a short and intensive art-based intervention affect symptoms and social interactions among children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Finding: The short and intensive art-based intervention did not affect symptoms in children with ASD level 2 or 3, including social awareness, social cognition, social communication, social motivation, and autistic mannerisms.
Meaning: The short and intensive art-based intervention did not improve the symptoms of patients with ASD.
- Neonatal risk factors associated with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: an umbrella review
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Erfan Ayubi, Sajjad Farashi, Saeid Bashirian, Fereshteh Mehri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):441-446. Published online July 14, 2023
-
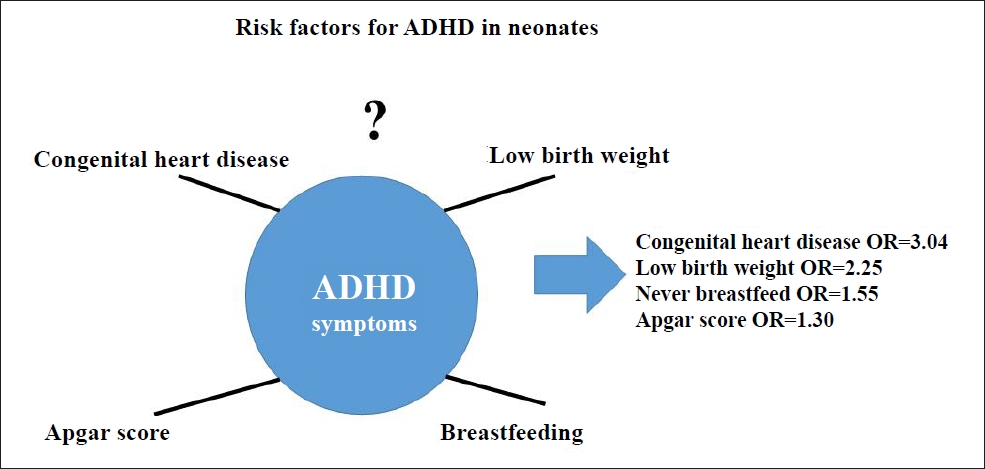
Question: The risk factors for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), such as breastfeeding, congenital heart disease, and low birth weight, in neonates are not well understood.
Finding: This umbrella review obtained significant effect sizes for ADHD for congenital heart disease (odds ratio [OR], 3.04), low birth weight (OR, 2.25), never breastfed (OR, 1.55), and Apgar score (OR, 1.30).
Meaning: Congenital heart disease, low birth weight, lack of breastfeeding, and Apgar scores were significant factors for ADHD.
- Editorial
- Immunology
- Systemic autoinflammatory disorders: autoinflammatory and autoimmune disorders
- Young Dae Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):439-440. Published online July 4, 2023
-
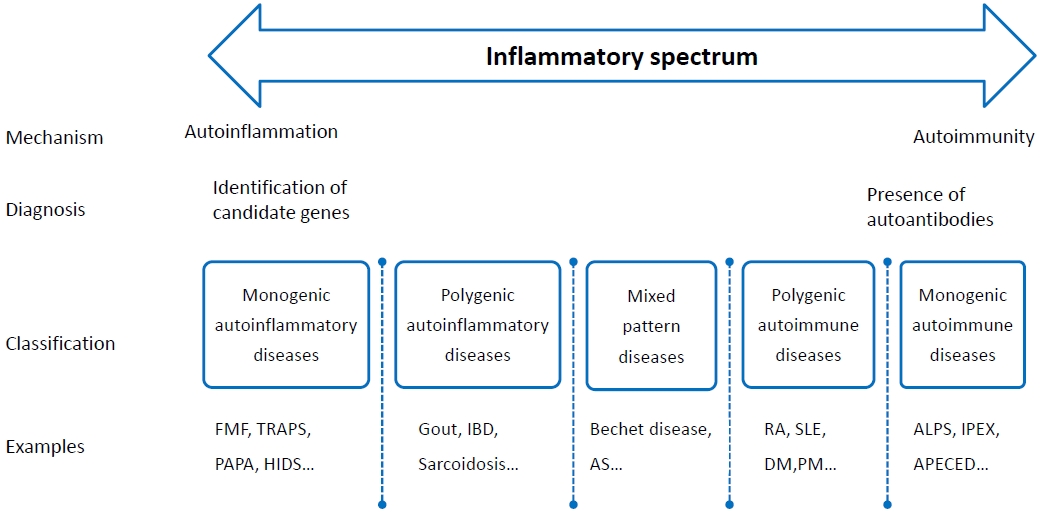
· Systemic autoinflammatory disorders (SAIDs) typically have an early onset in life, and may have close relatives may have similar disease.
· SAIDs should be suspected in any patient, especially children, who experience persistent or recurrent inflammatory episodes that fail to fit the pattern of other established diseases.
· Advancements in the understanding of autoinflammation will provide novel diagnostic and therapeutic options for SAIDs patients.
- Review Article
- Immunology
- Systemic autoinflammatory disorders
- Dae Chul Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):432-438. Published online June 14, 2023
-
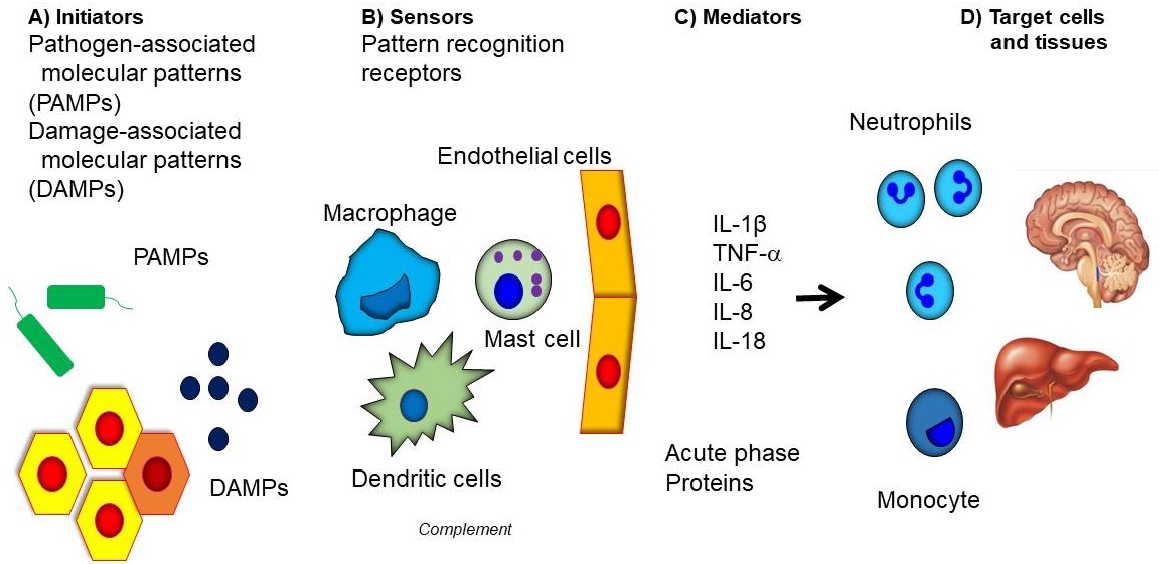
· Systemic autoinflammatory disorders (SAID) are disorders caused by dysregulation of the innate immunity with genetic background, leading to recurrent episodes of systemic inflammation.
· SAID is characterized by recurrent acute inflammatory responses including fever or skin manifestations, unrelated with infection or malignancy.
· Diagnosis is based on family and long-term history with detailed clinical and laboratory manifestations during febrile periods.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Kidney complications associated with COVID-19 infection and vaccination in children and adolescents: a brief review
- Hee Sun Baek, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):424-431. Published online June 28, 2023
-
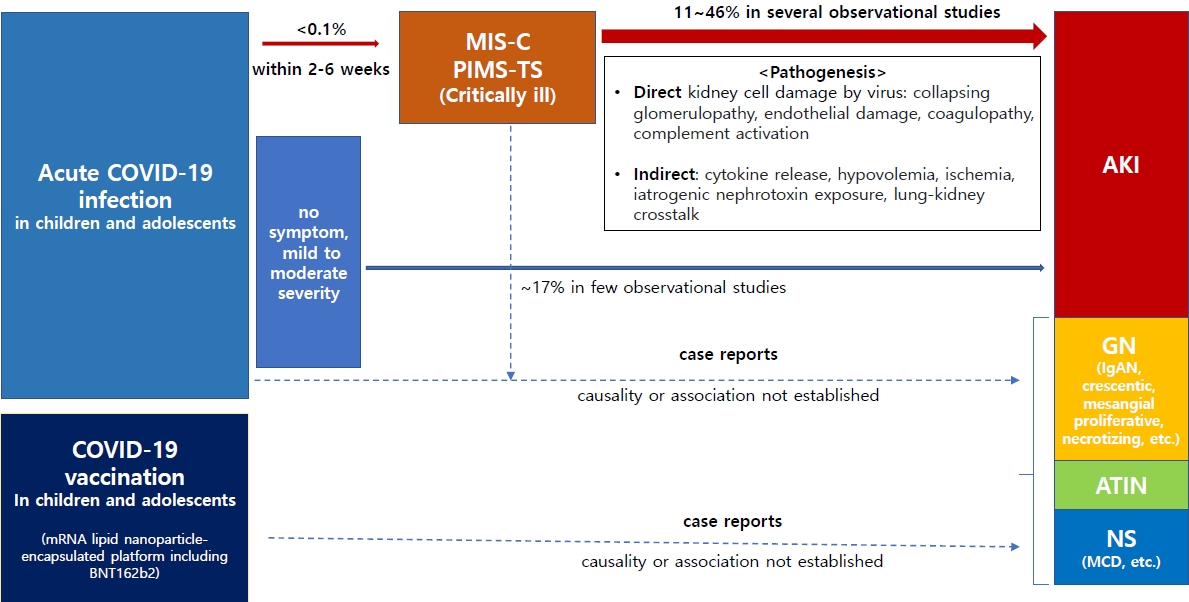
Several observational studies have shown that acute kidney injury affects up to 46% of children and adolescents who develop severe postinflammatory responses, such as multisystem inflammatory syndrome in childhood, due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Although causality has not been established, some cases of glomerulopathy or nephrotic syndrome occurring after COVID-19 infection or vaccination have been reported. Therefore, kidney complications associated with these conditions in children and adolescents warrant attention.
- Infection
- Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccines: February 26, 2021, To June 4, 2022, Republic of Korea
- Yeon-Kyeng Lee, Yunhyung Kwon, Yesul Heo, Eun Kyoung Kim, Seung Yun Kim, Hoon Cho, Seontae Kim, Mijeong Ko, Dosang Lim, Soon-Young Seo, Enhi Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):415-423. Published online June 13, 2023
-
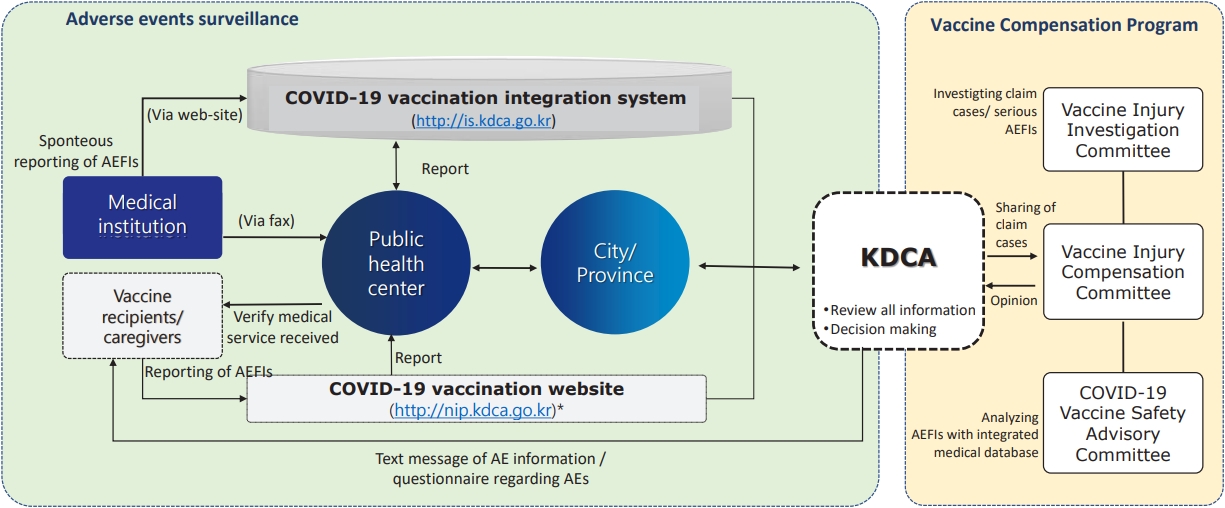
· Enhanced safety monitoring system of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines were implemented to detect signals rapidly as part of the national COVID-19 vaccination program.
· As of June 4, 2023, reported adverse events after COVID-19 vaccination was 0.38% among 125,107,883 doses of COVID- 19 vaccines administered.
· Most reported adverse reactions after COVID-19 vaccinations have shown nonserious and mild intensity.
- Correspondence
- Cardiology
- The authors reply: Age-, sex-, and height-based blood pressure reference charts, Yazd children 6–18 years, Iran
- Seyedeh Mahdieh Namayandeh, Nastran Ahmadi, Seyed Mahmood Sadr
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):414-414. Published online June 14, 2023
-
- General Pediatrics
- Letter to the editor: Age-, sex-, and height-based blood pressure reference charts, Yazd children 6-18 years, Iran
- Amar Taksande
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):412-413. Published online October 27, 2021
-
- Original Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Timing of parenteral nutrition initiation in critically ill children: a randomized clinical trial
- Nagwan Y. Saleh, Hesham M. Aboelghar, Nehad B. Abdelaty, Mohamed I. Garib, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):403-411. Published online June 14, 2023
-
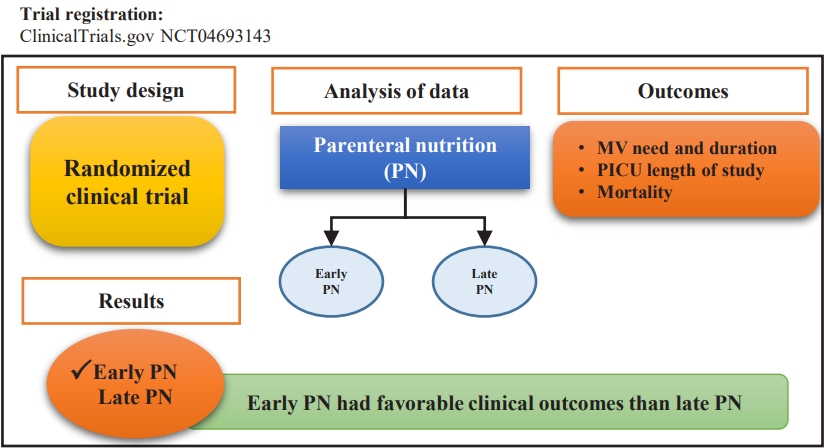
Question: What is the ideal initiation timing of parenteral nutrition for critically ill children?
Finding: This randomized clinical trial of 140 children examined the effects of an early or late start of parenteral nutrition on mechanical ventilation need (primary outcome) and length of stay and mortality (secondary outcomes).
Meaning: Children who received early versus late parenteral nutrition had lower mechanical ventilation need and duration.
- Gastroenterology
- Relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hyperandrogenemia in adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome
- Ozlem Kara, Hanife Aysegul Arsoy, Murat Keskin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):395-402. Published online June 14, 2023
-

Question: Is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) a risk factor for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in adolescents?
Finding: The frequency of NAFLD did not increase in adolescents with PCOS. However, hyperandrogenemia was a risk factor for NAFLD.
Meaning: Adolescents with PCOS and hyperandrogenemia should be closely monitored for hepatic steatosis.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Treatment of congenital cytomegalovirus infection
- Gyu Hong Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):384-394. Published online December 28, 2022
-
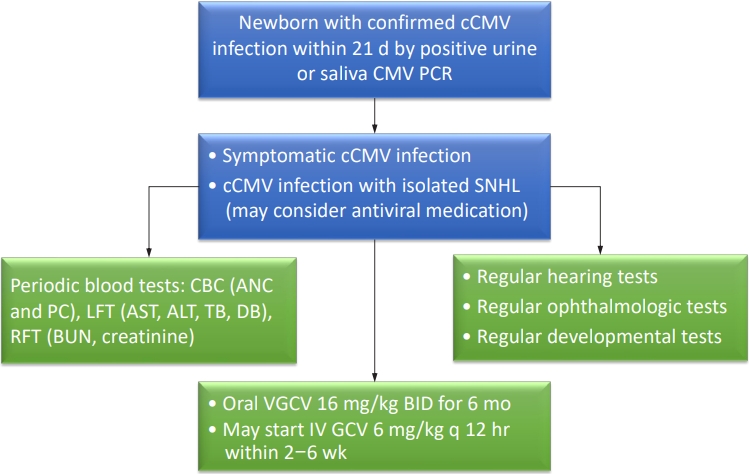
· Congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is among the most common causes of nongenetic sensorineural hearing loss.
· Congenital CMV is initially treated with intravenous ganciclovir for 2–6 weeks and switched to oral valganciclovir, or with oral valganciclovir for the entire 6-month period.
· Infants with congenital CMV require periodic monitoring of absolute neutrophil count, platelet count, and blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, liver function tests, audiological, ophthalmological, and developmental tests during antiviral medication.
- Gastroenterology
- Prevalence, risk factors, and treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in children
- Yu Kyung Cho, Jin Lee, Chang Nyol Paik
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):377-383. Published online August 21, 2023
-
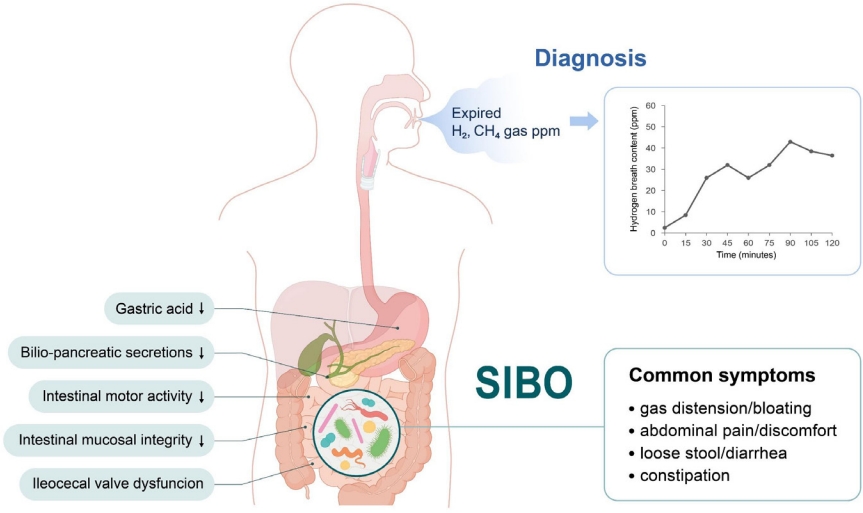
· Pediatric small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) manifestations range from nonspecific abdominal symptoms to malabsorption or malnutrition.
· SIBO is prevalent in children and adolescents with functional abdominal pain disorders.
· Predisposing factors include disturbed intestinal motility, altered anatomy, and/or abnormal body defense systems against intestinal bacteria.
· Breath tests are safe and noninvasive.
· Treatment principles include managing predisposing conditions, nutritional support, symptom control, and antibiotics.
- Other
- Hearing loss in neonates and infants
- Goun Choe, Su-Kyoung Park, Bong Jik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):369-376. Published online January 9, 2023
-
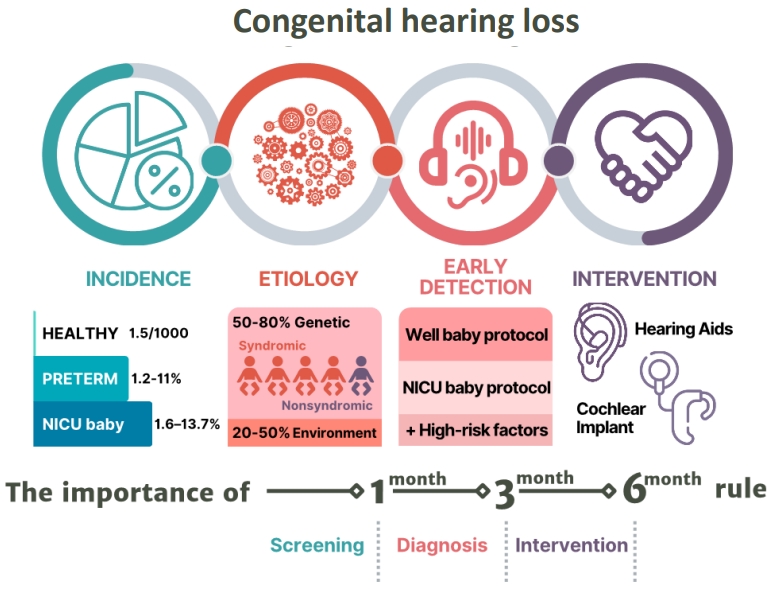
· Congenital hearing loss is common, with an approximate incidence of 1.5 per 1,000 newborns and affecting 1.2%–11% of preterm and 1.6%–13.7% of neonatal intensive care unit neonates.
· Etiologies vary, and up to 80% of cases are genetic.
· Newborn hearing screenings follow the 1-3-6 rule, and babies at high risk of hearing loss should be referred to otolaryngology for early detection and timely intervention.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
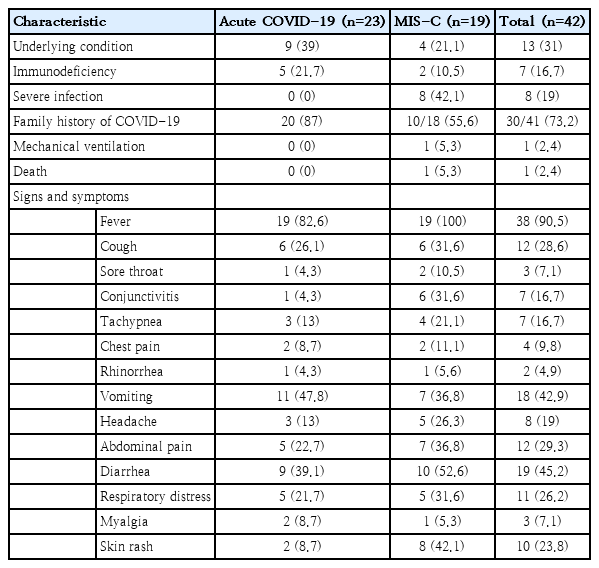
- SARS-CoV-2 fecal shedding pattern in pediatric patients with acute COVID-19 or COVID-19-associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome
- Setareh Mamishi, Fatemeh Jalali, Sepideh Benvari, Babak Pourakbari, Mohammad Reza Abdolsalehi, Reihaneh Hosseinpour Sadeghi, Mohammad Shahbabaie, Amene Navaeian, Shima Mahmoudi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):366-368. Published online June 14, 2023
-
- Original Article
- Allergy
- Association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children: a systematic review and multicenter cohort study using a common data model
- Ji Eun Lim, Hye Min Kim, Ju Hee Kim, Hey Sung Baek, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):357-365. Published online June 14, 2023
-
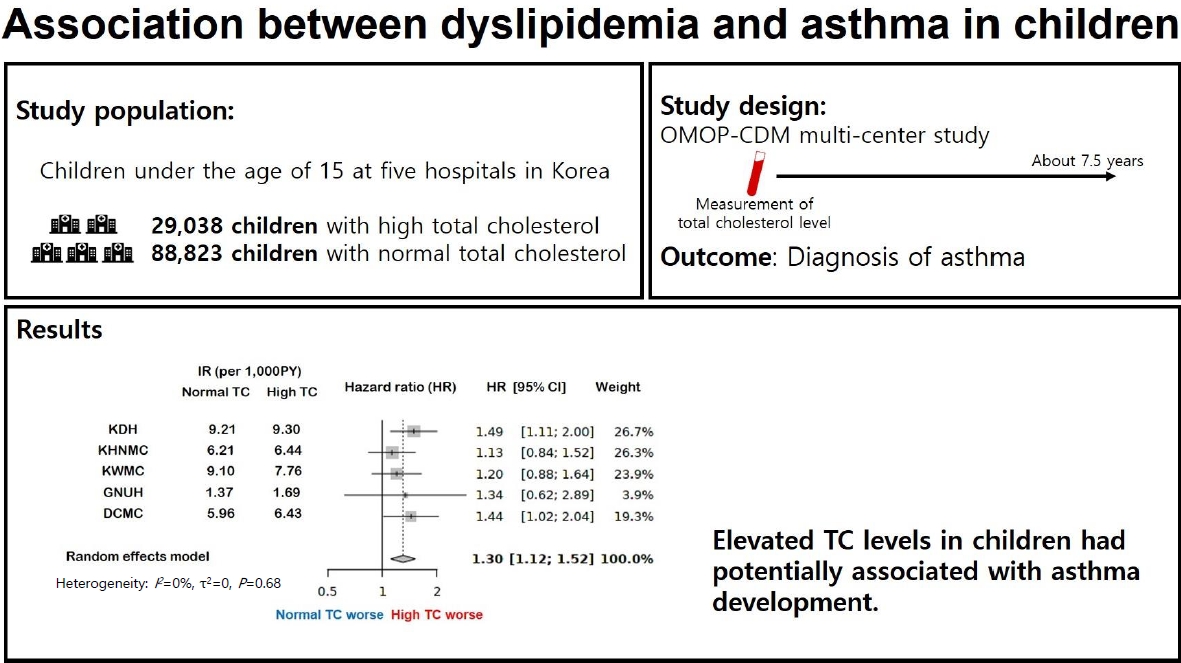
Question: Is dyslipidemia a risk factor for asthma in children?
Finding: This was a comprehensive systematic review and retrospective multicenter study of the association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children. In a multicenter cohort analysis using the Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership Common Data Model, elevated total cholesterol levels were associated with increased risk of asthma development.
Meaning: These findings suggest an association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children.
- Neurology
- Need for palliative care from birth to infancy in pediatric patients with neurological diseases
- Raffaele Falsaperla, Silvia Marino, Carla Moscheo, Lucia Giovanna Tardino, Simona Domenica Marino, Concetta Sciuto, Piero Pavone, Giovanna Vitaliti, Federica Sullo, Martino Ruggieri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):350-356. Published online June 14, 2023
-
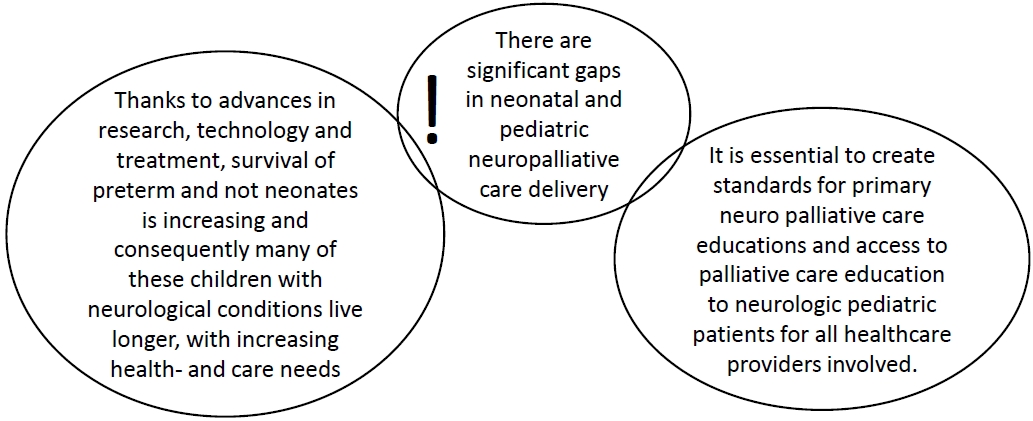
Question: What are the current palliative care protocols, palliative course, and implementable palliative care programs for hospitalized pediatric patients with neurological diseases in Italy?
Finding: We studied 34 newborns with nervous system diseases, all of whom had a poor prognosis.
Meaning: Despite current legislation in Italy, no palliative care network has been implemented. Given the vast number of patients with neurological conditions, standardized palliative care guidelines and protocols are required.
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- Arrhythmias in pediatric patients with COVID-19
- Ji-Eun Ban
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):348-349. Published online June 14, 2023
-
· Childrens with coronavirus disease 2019 less commonly display life-threatening arrhythmias, including premature atrial or ventricular beats, or conduction disturbances such as first-degree atrioventricular blocks.
· Life-threatening arrhythmias (e.g., nonsustained or sustained ventricular tachycardia, atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, complete atrioventricular block) occur in children with sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection suffering from myocarditis or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C).
· Monitoring clinical status and assessing and managing arrhythmias are crucial in MIS-C.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Trends of vitamin D in asthma in the pediatric population for two decades: a systematic review
- Myongsoon Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):339-347. Published online June 14, 2023
-
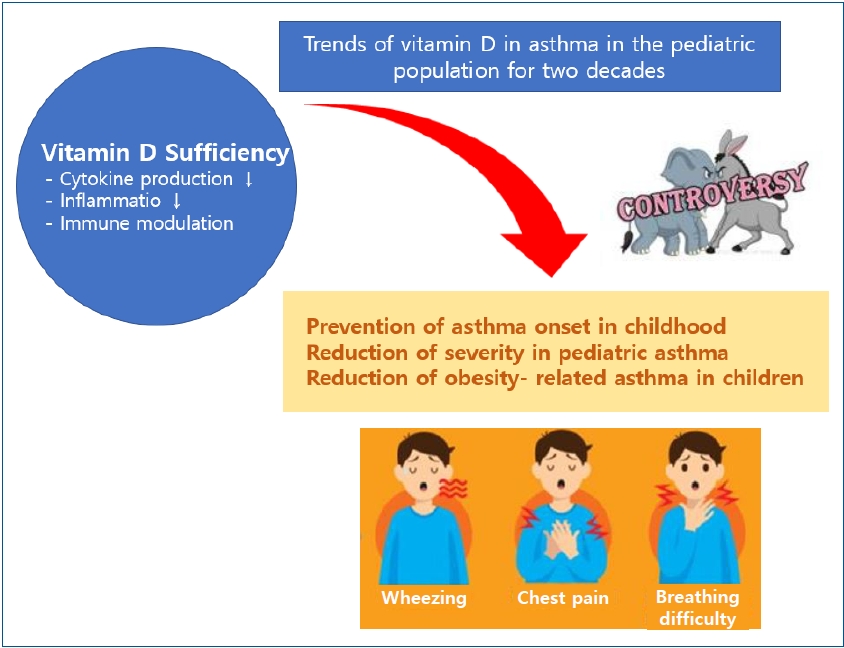
· Vitamin D may affect asthma via multiple mechanisms, including lung and optimal immune system functions.
· Many clinical trials have demonstrated the beneficial effects of vitamin D on asthma onset and aggravation. However, definitive clinical trials are lacking, and reports have detailed contradictory effects of vitamin D in children with asthma.
· Some exciting reports stated that obesity and vitamin D deficiency are associated with increased asthma symptoms in the pediatric population.
- Cardiology
- Environmental changes surrounding congenital heart disease
- Eun-Young Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):332-338. Published online January 2, 2023
-
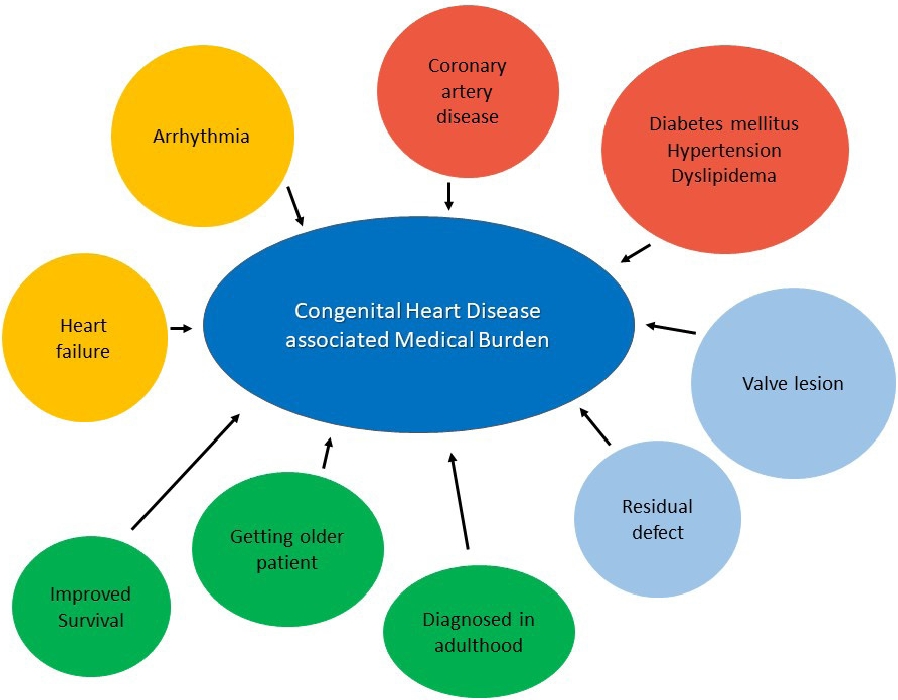
· As the number of patients with congenital heart disease increases, the medical burden increases.
· Various fusion imaging techniques using percutaneous procedures have been introduced.
· With advances in technology, convenient ambulatory devices have been introduced.
· A well-organized team approach is required to resolve advanced heart failure in patients with congenital heart disease.
- Nutrition
- Protein substitutions as new-generation pharmanutrition approach to managing phenylketonuria
- Fatma Nur Keskin, Teslime Özge Şahin, Raffaele Capasso, Duygu Ağagündüz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):320-331. Published online November 1, 2022
-
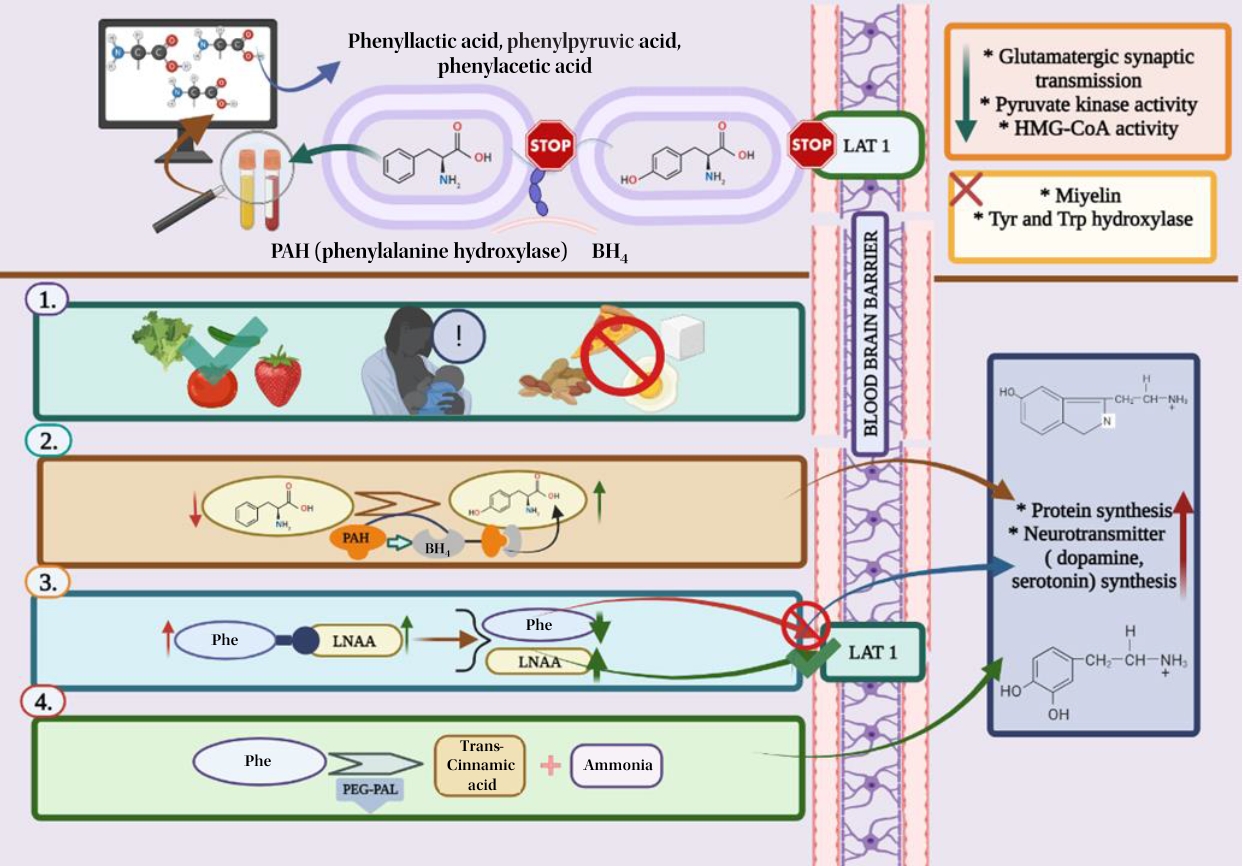
Phenylketonuria, an autosomal recessive disease that results from the inability to metabolize phenylalanine, is currently treated with medical nutrition therapy. New treatment approaches such as tetrahydrobiopterin, glycomacropeptide, large neutral amino acids, pegvaliase, and gene therapy significantly impact disease management and dietary enrichment. This article also reviews animal and human studies that have evaluated the efficacy and safety of these new protein substitutes.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
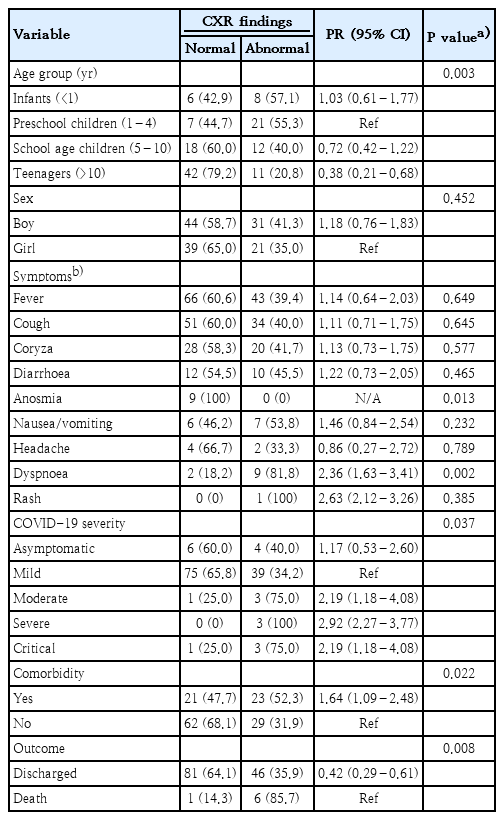
- Chest x-ray findings in children with COVID-19: lesson learned from referral hospitals in Medan, North Sumatera, Indonesia
- Andrew Limavady, Eka Airlangga, Ririe Fachrina Malisie, Ayodhia Pitaloka Pasaribu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):317-319. Published online May 16, 2023
-
- Original Article
- Infection
- Seroprevalence of maternal peripartum human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the Nigerian literature
- Abdulrasheed Usman, Muhammad Hamis Musa, Bukhari Isah Shuaib, Olayemi Balogun, Mukhtar Adeiza
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):307-316. Published online December 22, 2022
-
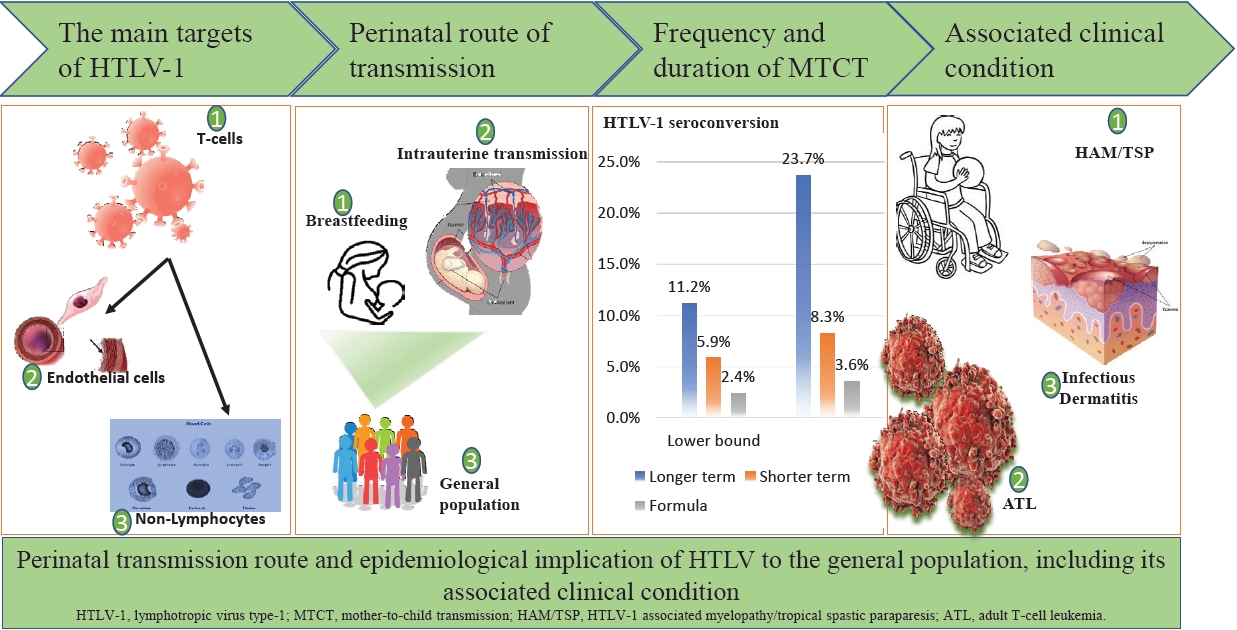
The peripartum period is an important transmission time for human T-cell lymphotropic virus-1 (HTLV-1) infection, mainly via breastfeeding and partly through the placental tissues of carrier mothers. Although most HTLV-1–infected individuals are asymptomatic, fetal and childhood infections often result in several diseases with disappointing treatment outcomes. An estimated HTLV-1 burden in Nigeria among perinatal women must be determined to enable rational planning of a comprehensive health care intervention.
- Gastroenterology
- Assessing indicators and clinical differences between functional and organic childhood constipation: a retrospective study in pediatric gastroenterology clinics
- Hasan M. Isa, Fatema A. Alkharsi, Fatema A. Salman, Maryam S. Ali, Zahra K. Abdulnabibi, Afaf M. Mohamed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):296-306. Published online June 14, 2023
-
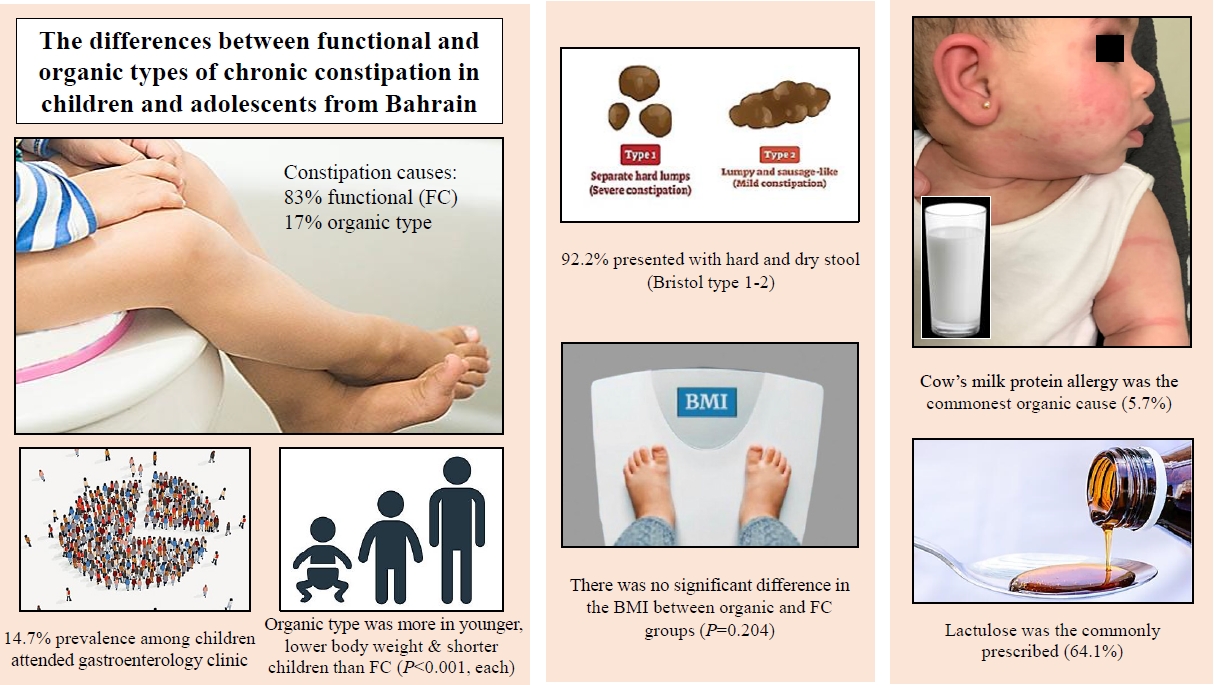
Question: What causes childhood constipation, and what can predict organic constipation?
Finding: Constipation represents 14.7% of gastroenterology visits. Functional constipation is more common among constipation types, while organic constipation is more common in young children and those with a low body weight, stunted growth, mucus in the stool, and associated diseases.
Meaning: Younger children and those with lower growth or mucus in the stool should be assessed for underlying organic causes of constipation.
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Gut microbiota’s impact on obesity
- Sujin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):294-295. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· An imbalance of the gut microbiota with a relative increase in Firmicutes versus Bacteroidetes is associated with the pathogenesis of obesity.
· Dysbiosis is associated with microbial genes associated with short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) production and increased colonic SCFA levels. SCFAs have also been shown to regulate appetite and satiety hormones, which can affect food intake and energy balance.
· A dietary high-fat intake is reportedly associated with increased plasma lipopolysaccharide. Altered Toll-like receptor-4 signaling leads to propagating the cascade of further inflammation and promoting insulin resistance.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST): development, applications, and implications for future early childhood development interventions
- Dooyoung Kim, Young June Choe, Bilal Aurang Zeb Durrani, EunYoung Kim, Junghye Byeon, Baik-Lin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):288-293. Published online December 22, 2022
-

· This review discusses the development and application of the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST) for ensuring early childhood development.
· Various studies have demonstrated the integral role of the K-DST in facilitating the detection of developmental delays and delivery of timely interventions.
· The tailoring of the K-DST to Korean infants and children suggests that other countries may further translate and adapt it.
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











