Original article
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Original article
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Polysomnographic features of children with obesity: body mass index predict severe obstructive sleep apnea in obese children?
- Rungrat Sukharom, Prakarn Tovichien, Kanokporn Udomittipong, Pinyapach Tiamduangtawan, Wattanachai Chotinaiwattarakul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):80-90. Published online November 6, 2024
-

Question: How Common is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in obese children? OSA is common in obese children, even without habitual snoring.
Finding: Among the subjects, 60.6% had positional OSA, 40.2% had rapid eye movement-related OSA, 59.8% had desaturation, 20.5% had sleep-related hypoventilation, and 5.0% had obesity hypoventilation syndrome. Body mass index (BMI) and neck and waist circumferences were significantly associated with severe OSA.
Meaning: We recommend screening obese children (BMI > 29.2 kg/m2) for OSA.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Short-term outcomes of oropharyngeal administration of colostrum in preterm neonates: a double-blind placebocontrolled randomized trial
- Ameneh Lamsehchi, Maryam Shokouhi Solgi, Mohammad Kazem Sabzehei, Behnaz Basiri, Elahe Talebi Ghane, Kiana Kimiaei Asadi, Sina Azadnajafabad
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):73-79. Published online October 31, 2024
-

Question: What are the short-term outcomes of oropharyngeal administration of colostrum (OAC) in preterm neonates?
Finding: This study demonstrated the significantly lower rates of necrotizing enterocolitis, clinically suspected sepsis, shorter hospital stay, period to full enteral feeding, and antibiotic therapy period in the OAC group.
Meaning: This trial may further expand the clinical application of OAC in premature infants to reduce their length of hospital stay and complications.
- Infection
- Carbapenem resistance in gram-negative pathogens in an Iranian hospital: high prevalence of OXA-type carbapenemase genes
- Setareh Mamishi, Reihaneh Hosseinpour Sadeghi, Sadaf Sajedi Moghaddam, Babak Pourakbari, Shiva Poormohammadi, Maryam Sotoudeh Anvari, Shima Mahmoudi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):65-72. Published online October 31, 2024
-

Question: What is the prevalence of carbapenem resistance in gram-negative bacteria and associated carbapenemase genes?
Findings: This study identified a notable prevalence of carbapenem-resistant gram-negative isolates, with Escherichia coli being the predominant contributor, follow ed by Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, while bla OXA48 was the most prevalent carbapenemase gene.
Meaning: These findings highlight the urgent need for proactive measures including the rapid detection of carbapenemase- producing isolates and effective infection control.
- Other
- Balance assessment with decreased base of support for children with disabilities
- Guilherme M. Cesar, Madison Giebler, Thad W. Buster, Judith M. Burnfield
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):718-724. Published online November 11, 2024
-
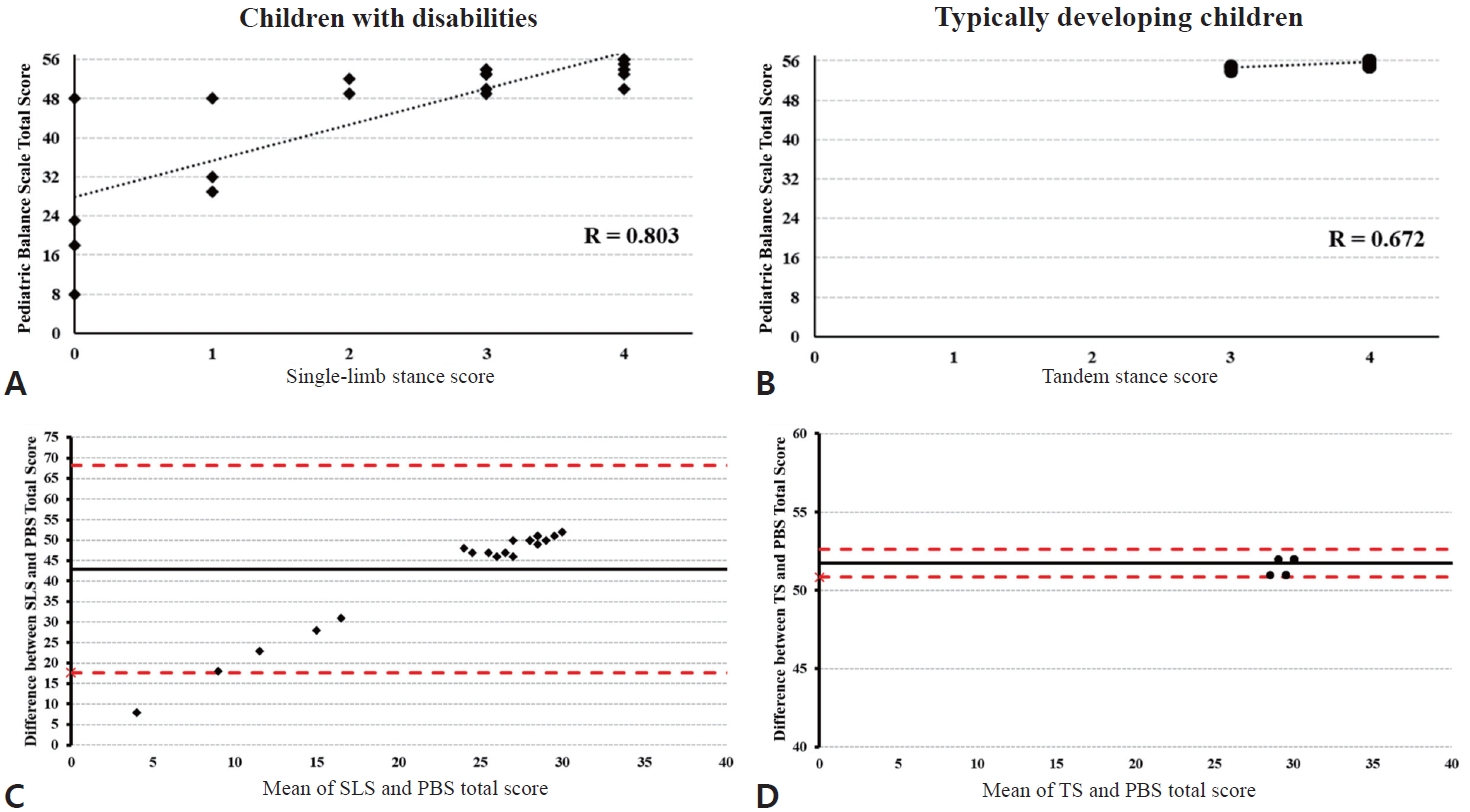
Question: Can a balance task with narrowed base of support indicate overall functional balance control in children with disabilities?
Finding: While single-limb standing could explain overall balance control for children with disabilities, it was unrelated with balance control for typically developing children.
Meaning: One balance task with narrowed base of support can be used as practical assessment of balance abilities for children with disabilities when allocated session time is of concern.
- Infection
- Clinical, biochemical, and genetic study of TACE/TNF-α/ACE signaling pathway in pediatric COVID-19 infection
- Ahmed El-Abd Ahmed, Sawsan M.A. Abuhamdah, Mohammed H. Hassan, Nagwan I. Rashwan, Eman A. Abd-Elmawgood, Haggagy Mansour, Hoda S. Sherkawy, Shymaa G. Rizk
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):704-717. Published online November 27, 2024
-
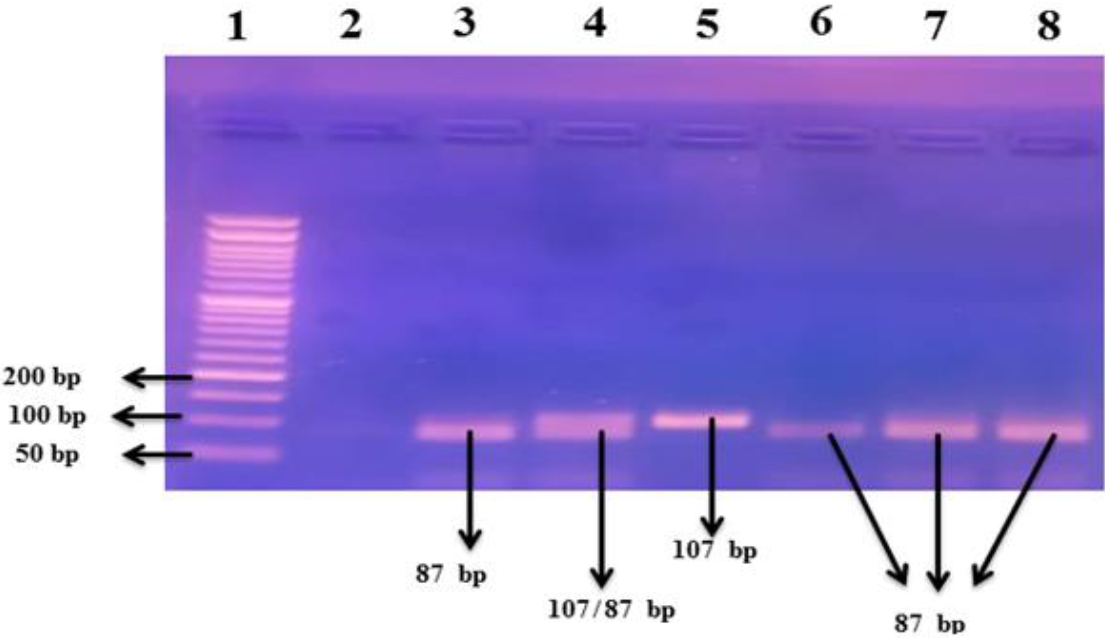
Question: Is the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathway (TNF-α-converting enzyme [TACE]/TNF-α/angiotensin converting enzyme [ACE]) involved in pediatric coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection?
Finding: Significantly increased circulating TACE/TNF-α and decreased ACE2 levels were noted. TNF-α-308G/A plays a significant role in susceptibility to COVID-19 infection among children. The ACE (I/D) (rs4646994) and ACE2 (rs2285666) single nucleotide polymorphisms lack significant associations with pediatric COVID-19 infection.
Meaning: The TNF signaling pathway participates in pediatric COVID-19 infection.
- Cardiology
- Comparative analysis of adolescent hypertension definitions for predicting early adulthood carotid artery intima-media thickness: Tehran lipid and glucose study
- Maryam Barzin, Shirin Yaghoobpoor, Maryam Mahdavi, Behnaz Abiri, Majid Valizadeh, Fereidoun Azizi, Pooneh Dehghan, Farhad Hosseinpanah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):694-703. Published online September 12, 2024
-
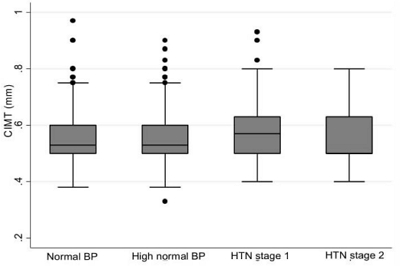
Question: What is the prevalence of HTN among adolescents enrolled in the TLGS according to 3 different accepted definitions (4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG). Also, what is the ability of each of these definitions in predicting early adulthood CIMT, as a surrogate for cardiovascular disease events?
Finding: The highest and lowest prevalence of stage 1 HTN was observed with the AAP-CPG (17.7%) and ESH (8.8%), respectively. Similarly, the highest and lowest prevalence of stage 2 HTN was noted with the AAP-CPG (1.5%) and ESH (0.8%), respectively. The highest to lowest predictive abilities belonged to the 4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG, respectively.
Meaning: Among the various definitions of pediatric HTN, the 4th report offered the best ability to predict a high CIMT during early adulthood, followed by the ESH and AAP-CPG.
- General Pediatrics
- Role of proper postnatal care in continued exclusive breastfeeding among young Indonesian mothers
- Wahyu Triadmajani, Shinta Prawitasari, Abdul Wahab
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):686-693. Published online September 12, 2024
-
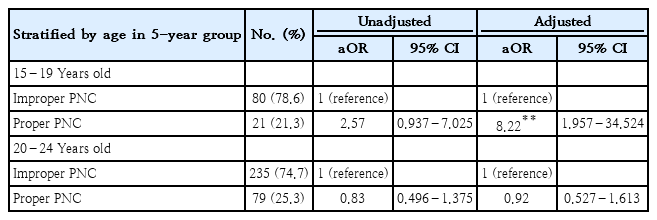
Question: Is proper postnatal care (PNC) associated with exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) practice among young Indonesian mothers?
Finding: Proper PNC elevates the likelihood of EBF among Indonesian adolescent mothers aged 15–19 years.
Meaning: Breastfeeding services should be provided during the early postnatal period to support EBF practice among adolescent mothers. High-quality PNC is a tailored intervention for vulnerable populations.
- Nonpharmacological interventions for managing postoperative pain and anxiety in children: a randomized controlled trial
- Edlin Glane Mathias, Mamatha Shivananda Pai, Vijay Kumar, Dinesh Narayanakurup, Malavika Kulkarni, Vasudeva Guddattu, Ann-Cathrine Bramhagen, Baby S Nayak, Anice George
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):677-685. Published online October 31, 2024
-
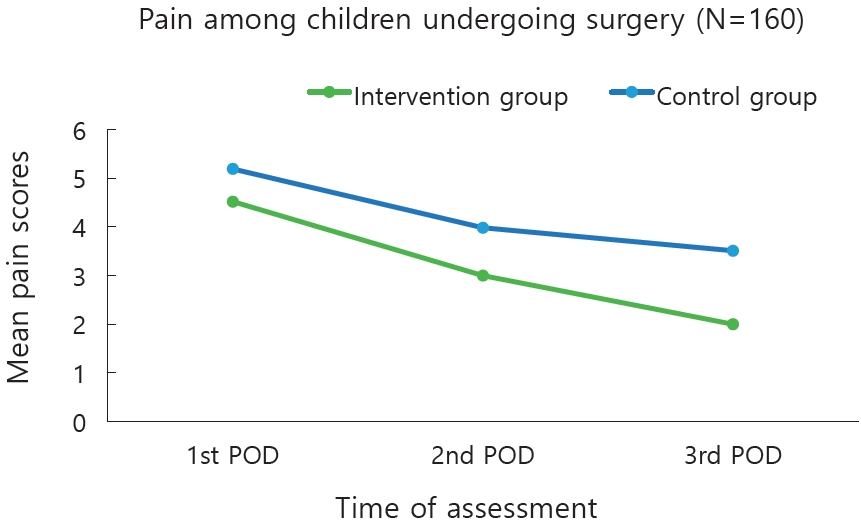
Question: What is the effect of nonpharmacological interventions on postoperative pain and anxiety among children.
Finding: Nurse-provided distraction interventions reduce pain and anxiety among pediatric surgical patients.
Meaning: The findings suggest that nonpharmacological interventions provided postoperatively to children reduce their pain and anxiety levels.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Mortality of very low birth weight infants by neonatal intensive care unit workload and regional group status
- Sung-Hoon Chung, Chae Young Kim, Yong-Sung Choi, Myung Hee Lee, Jae Woo Lim, Byong Sop Lee, Ki-Soo Kim; the Korean Neonatal Network
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):619-627. Published online September 12, 2024
-

Question: How do structural and staffing characteristics of neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) influence the mortality rates of very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs)?
Findings: NICUs with higher staffing levels, particularly with more neonatologists, and those offering advanced care levels were associated with lower mortality rates. Additionally, regional disparities were observed, with some areas demon-strating significantly higher survival rates.
Meaning: Adequate staffing and equitable regional distribution of medical resources are crucial for improving survival outcomes in VLBWIs. Efforts to enhance NICU staffing and address regional healthcare disparities are essential for optimizing care quality and reducing mortality in this vulnerable population.
- Pulmonology
- Efficacies of different treatment strategies for infants hospitalized with acute bronchiolitis
- Hyeri Jeong, Dawon Park, Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Jeewon Shin, Hey-Sung Baek, Hyunsoo Hwang, Youn Ho Shin, Hye Mi Jee, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):608-618. Published online October 28, 2024
-

· This study analyzed 45 randomized controlled trials (5,061 participants, 13 interventions) of the comparative efficacies of treatments for acute bronchiolitis in infants.
· Inhalation therapy with epinephrine and hypertonic saline significantly reduced the length of hospital stay compared with normal saline.
· Hypertonic saline had the greatest ability to improve the clinical severity score of bronchiolitis in infants younger than 2 years of age.
- Allergy
- Regional differences in diagnosis and management of cow's milk allergy
- Fabian Hendricx, Emma Robert, Jaime A. Ramirez-Mayans, Karen Rubi Ignorosa Arellano, Erick M. Toro Monjaraz, Yvan Vandenplas
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):601-607. Published online October 28, 2024
-

· Although there is broad consensus on many aspects regarding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of cow's milk allergy, the impact of geographical, cultural, and socioeconomic factors remains unestablished.
· Availability and cost of formula for the management of cow's milk allergy have a major impact on the therapeutic choice.
· Region-specific guidelines for the treatment of cow's milk allergy are required.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Protective effect of recombinant interleukin-10 on newborn rat lungs exposed to short-term sublethal hyperoxia
- Hyeon-Soo Lee, Young-Joon Ryu, Min-Jae Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):540-549. Published online September 27, 2024
-

Lung injury is generated from the early stage of hyperoxia through the biologic effects of cell death and inflammatory response, which eventually leads to evolution of bronchopul-monary dysplasia. Therefore, a protective measure against hyperoxia-induced lung injury is needed. The present study observed that anti-inflammatory cytokine, interleukin-10 had protective effects on newborn rat lungs from injury induced at the early stage of hyperoxia, by preventing cell death and down-regulating inflammatory response.
- Nutrition
- Energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents: prevalence and associated factors
- Jee-Seon Shim, Jeong Mi Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):531-539. Published online September 24, 2024
-

Question: How prevalent is energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents and what are the associated factors?
Findings: The prevalence of energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents increased from 3.2% in 2014 to 12.2% in 2019. Energy drink consumption varies according to sociode-mographic and individual factors.
Meaning: Policies and educational strategies are needed to reduce energy drink consumption in adolescents.
- General Pediatrics
- Effect of online infant care training and postpartum counseling based on Meleis' transition theory on mothers' readiness for care and breastfeeding: a randomized controlled trial
- Fatma Şule Bilgiç, Gülçin Bozkurt
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):521-530. Published online September 27, 2024
-

Question: Do interventions based on Meleis' transition theory affect mothers' readiness for baby care and breastfeeding?
Findings: We found a statistically significant difference between the intervention and control groups in mothers' readiness for newborn care and breastfeeding (P<0.001).
Meaning: This intervention increased breastfeeding rates while ensuring that mothers were ready to care for their babies and prepared for the role of motherhood.
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Interleukin (IL)-1B and IL-1 receptor antagonist gene polymorphisms in children with primary immune thrombocytopenia
- Seham Mohamed Ragab, Wafaa Moustafa Abo ElFotoh, Mahmoud Ahmed El-Hawy, Eman Abdelfatah Badr, Saara Khairat Ali Mostafa, Mai El-Sayad Abd El-Hamid
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):465-473. Published online July 24, 2024
-

· Polymorphisms in interleukin (IL)-1B and IL-1 receptor (IL-1R) antagonists may significantly affect the pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP).
· IL-1B and IL-1R antagonist gene polymorphisms are correlated with severity and susceptibility to primary ITP in children.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Neonatal risk factors associated with autism spectrum disorders: an umbrella review
- Amir Mohammad Salehi, Erfan Ayubi, Salman Khazaei, Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Zohreh Salimi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):459-464. Published online July 19, 2024
-

Question: What are the neonatal risk factors for autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Findings: Significant effect sizes were observed for congenital heart disease (odds ratio [OR], 1.35), macrosomia (OR, 1.11), low birth weight (OR, 1.63), very low birth weight (OR, 2.25), small for gestational age (OR, 1.17), jaundice (OR, 1.74), male sex (OR, 1.47), and Apgar score (OR, 1.40).
Meaning: These factors were identified as risk factors for ASD.
- Infection
- Construction and validation of predictive models for intravenous immunoglobulin–resistant Kawasaki disease using an interpretable machine learning approach
- Linfan Deng, Jian Zhao, Ting Wang, Bin Liu, Jun Jiang, Peng Jia, Dong Liu, Gang Li
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):405-414. Published online July 23, 2024
-

Question: Is there a reliable model to predict intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)-resistant Kawasaki disease (KD)?
Finding: We constructed 5 machine learning models to predict IVIG-resistant KD. Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) model was superior to logistic, support vector machine, light gradient boosting machine and multiple layers perception models. The SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) value interpreted the contribution of each feature in XGBoost model.
Meaning: XGBoost model showed the excellent performance to predict IVIG-resistant KD with explainable and visualizable machine learning algorithm.
- Nutrition
- Parental support and exclusive breastfeeding at 3 months in West Java, Indonesia: a mixed-methods approach
- Ratu Ayu Dewi Sartika, Fadila Wirawan, Wawan Gunawan, Primasti Nuryandari Putri, Nurul Husna Mohd Shukri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):358-367. Published online June 21, 2024
-
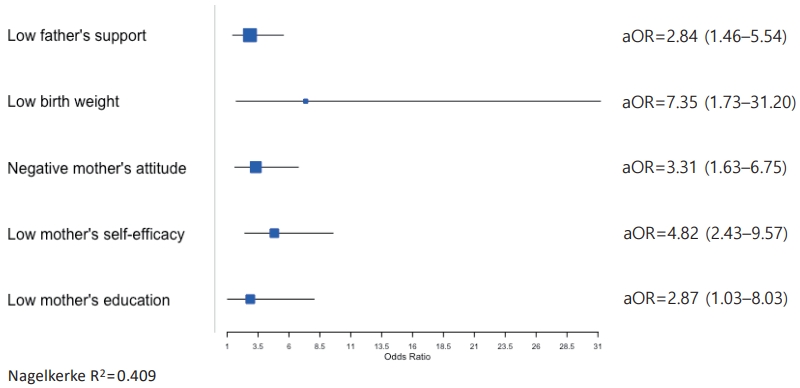
Question: Does paternal support affect exclusive breastfeeding failure?
Finding: Exclusive breastfeeding failure by 3 months was affected by paternal support.
Meaning: Fathers should be included in breastfeeding education and antenatal care.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effectiveness of online responsive teaching in young children with developmental disabilities: a pilot study
- Jung Sook Yeom, Jeongmee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):303-311. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Question: Does online responsive teaching (RT) impact children's and parents’ emotions and behaviors, and do parents find it satisfactory?
Finding: Online RT significantly improved children's pivotal and problem behaviors, decreased parenting stress, and enhanced parental interactive styles with high satisfaction.
Meaning: This pilot study's findings suggest that online RT can enhance child outcomes, offering accessible interventions amid challenges such as limited access and pandemics.
- Endocrinology
- Kisspeptin and DLK1 levels for monitoring treatment of girls with central precocious puberty
- Witchuwan Onsoi, Nattakarn Numsriskulrat, Suphab Aroonparkmongkol, Vichit Supornsilchai, Khomsak Srilanchakon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):296-302. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Questions: Can the serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 be potential biomarkers for monitoring the treatments for central precocious puberty (CPP)?
Findings: There were no significant differences in the baseline serum kisspeptin and DLK1 levels in CPP girls compared to girls with premature thelarche (PT). After 6 months of GnRH analogue treatment in CPP girls, median serum kisspeptin levels decreased, while median serum DLK1 levels increased compared to baseline.
Meanings: Serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 may serve as novel biomarkers for monitoring the efficacy of treatments for CPP.
- Pulmonology
- Oligohydramnios affects pulmonary functional/structural abnormalities in school-aged children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Jeong Eun Shin, Soon Min Lee, Mi-Jung Lee, Jungho Han, Joohee Lim, Haerin Jang, Ho Seon Eun, Min Soo Park, Soo Yeon Kim, Myung Hyun Sohn, Ji Ye Jung, Kyung Won Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):257-266. Published online April 16, 2024
-

Question: Is bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) associated with functional/structural abnormalities later in life?
Finding: School-aged children with severe BPD had abnormalities on pulmonary function tests and lung computed tomography despite no subjective respiratory symptoms; however, only prenatal oligohydramnios and prolonged ventilator use were associated with abnormal lung function.
Meaning: Long-term monitoring of preterm infants’ lung health is essential, especially for those with prenatal oligohydramnios or prolonged ventilator use.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effect of vitamin E supplementation on bilirubin levels in infants with hyperbilirubinemia: a double-blind randomized clinical trial
- Mojtaba Cheraghi, Maziar Nikouei, Majid Mansouri, Siros Hemmatpour, Yousef Moradi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):249-256. Published online March 26, 2024
-
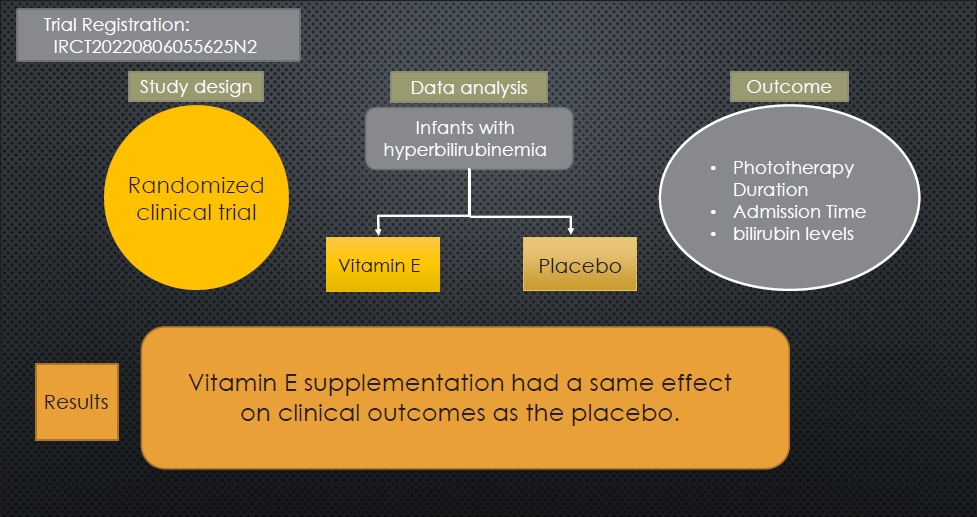
Question: Is vitamin E a viable therapeutic option for managing neonatal hyperbilirubinemia?
Finding: This randomized clinical trial examined the effects of oral vitamin E supplementation on bilirubin reduction (primary outcome), phototherapy duration, and length of hospital stay (secondary outcome) in 138 infants.
Meaning: Infants administered vitamin E versus placebo demonstrated similar reductions in bilirubin levels and length of hospital stay.
- Neurology
- Changes in frequency of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis and their viral causes before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single-center study
- Hyejin Na, Sanghoon Lee, Seo Hee Kim, Young Ok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):213-220. Published online March 19, 2024
-
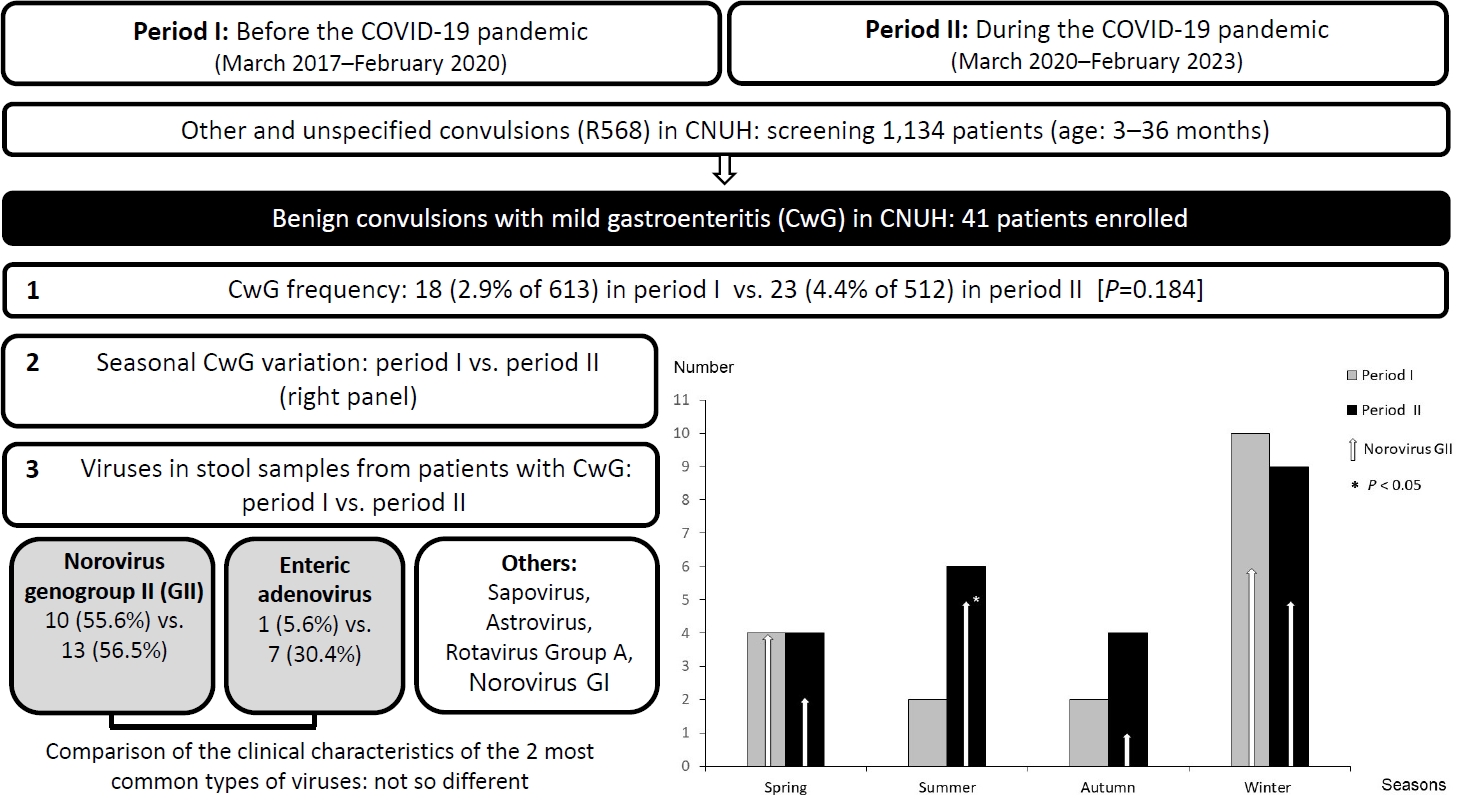
Question: Did coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) affect the frequency, seasonal variation, or virus type of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (CwG)?
Findings: We compared 41 cases of CwG before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. After March 2020, frequency did not change significantly (18 patients vs. 23 patients), seasonal variation was lost, and number of cases of enteric adenovirus-associated CwG increased (1 cases vs. 7 cases).
Meaning: The COVID-19 pandemic affected CwG.
- Nutrition
- Effect of probiotics plus zinc supplementation on clinical outcomes of infants and children with acute infectious diarrhea: a randomized controlled trial
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Saad Jbraeil Sulaiman, Zaid Waad Ahmed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):203-212. Published online February 19, 2024
-

Question: Does zinc supplementation along with probiotics affect disease severity or clinical outcomes of children with acute diarrhea?
Findings: This study indicated that zinc supplementation and probiotics had no effect on clinical improvement or disease severity among pediatric patients with acute diarrhea.
Meaning: Children who received probiotics plus zinc recovered faster than those who received probiotics only.
- Cardiology
- Effect of face mask on pulmonary artery pressure during echocardiography in children and adolescents
- Alireza Ahmadi, Mohammad Reza Sabri, Zohreh Sadat Navabi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):161-167. Published online January 23, 2024
-
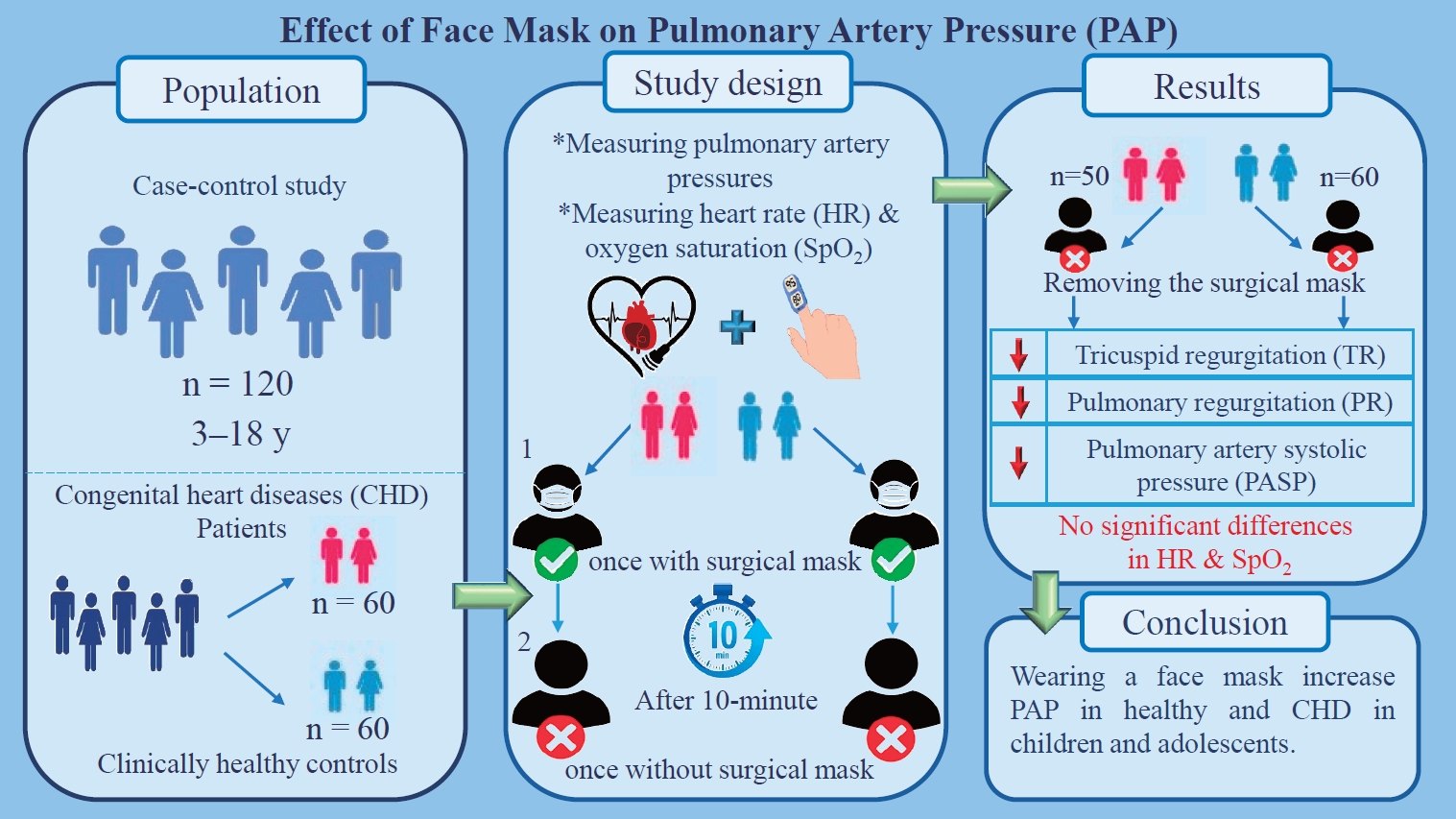
Question: Can face masks alter pulmonary pressure in children and adolescents with and without congenital heart disease?
Findings: Mask removal during echocardiography (ECHO) reduced pulmonary pressure.
Meaning: These findings suggest that face masks should be removed during ECHO in children and adolescents.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Oral administration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates intestinal injury in necrotizing enterocolitis
- Yeong Seok Lee, Yong Hoon Jun, Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):152-160. Published online February 19, 2024
-
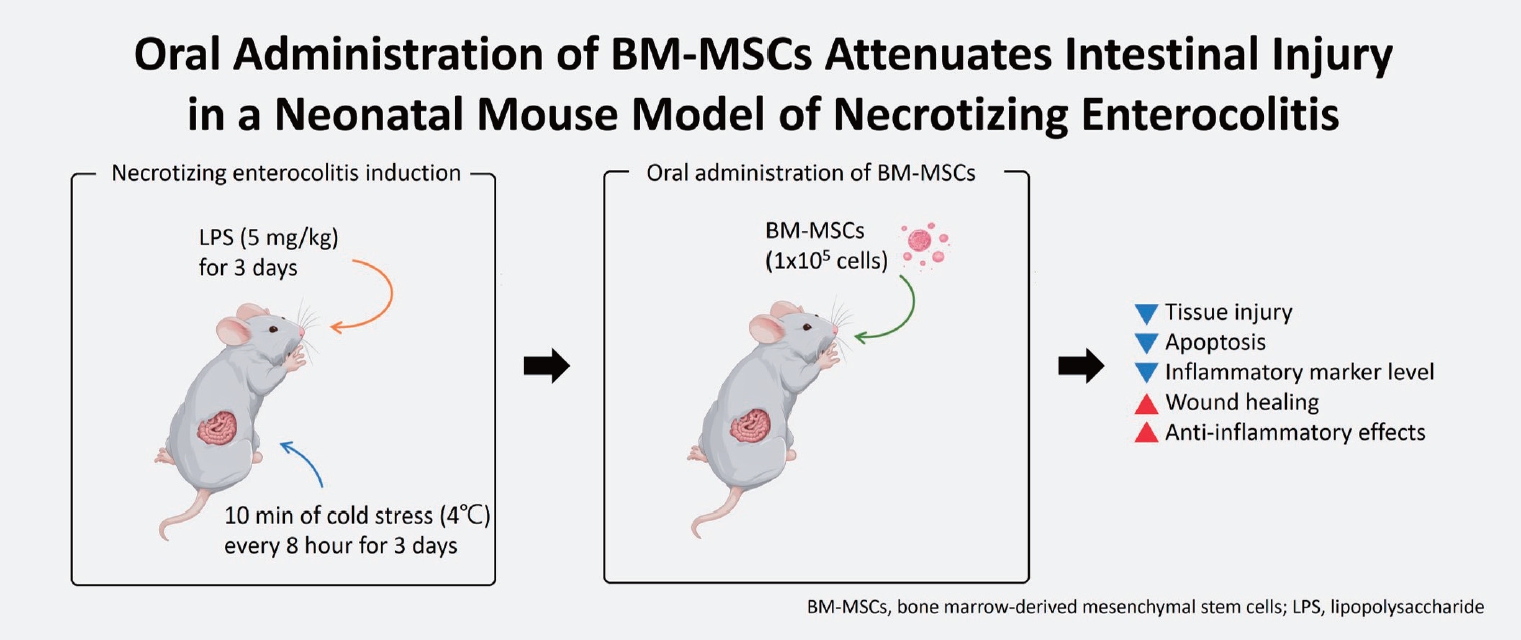
Question: What is the optimal dose of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) for treating necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), and is orally administered BM-MSC effective?
Findings: High (1×106 cells) or multiple BM-MSC doses showed similar effects as low (1×105 cells) doses of intraperitoneally administered BM-MSCs. Furthermore, orally administered BM-MSCs were as effective as intraperitoneally administered BM-MSCs.
Meaning: Orally administered low-dose BM-MSCs are a potential treatment for NEC.
- Prevalence of anxiety, depression, and stress among parents of neonates admitted to neonatal intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Asha P. Shetty, Kurvatteppa Halemani, Alwin Issac, Latha Thimmappa, Sanjay Dhiraaj, Radha K, Prabhaker Mishra, Vijai Datta Upadhyaya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):104-115. Published online November 14, 2023
-
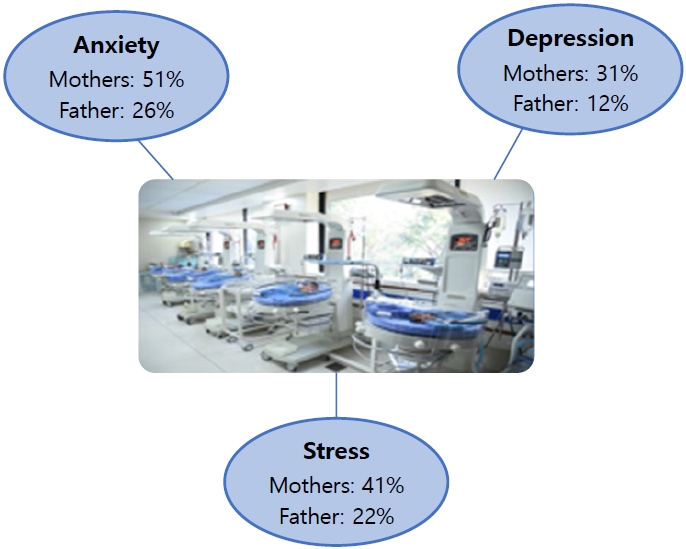
Question: What emotions do parents experience when their newborns are admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)?
Finding: Mothers experienced more anxiety (51%), depression (31%), and stress (41%) symptoms than fathers (26%, 12%, and 22%, respectively).
Meaning: Parents often experience anxiety, stress, and depression following NICU admission. Healthcare workers are responsible for providing regular parental counseling.
- Other
- Virtual, augmented, and mixed reality: potential clinical and training applications in pediatrics
- Suyoung Yoo, Meong Hi Son
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):92-103. Published online May 24, 2023
-
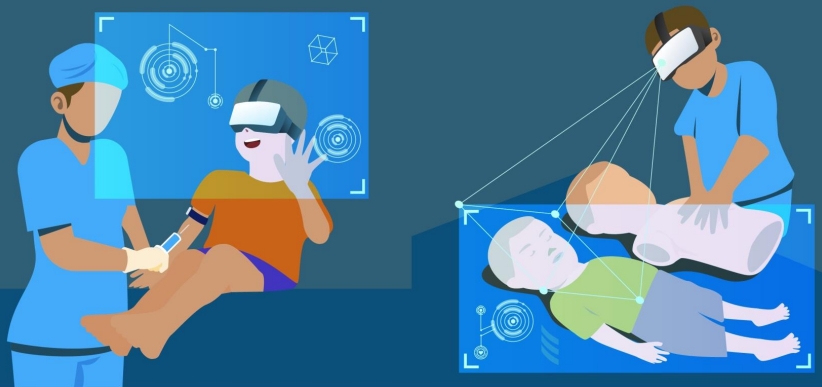
· Review of articles that investigated the applications of virtual, augmented, or mixed reality in pediatric clinical settings and in the training of pediatric medical professionals was conducted.
· A total of 89 studies were retrieved, with 36 randomized controlled trials.
· In most studies, intervention using the novel technology was at least as effective or more effective than the traditional method.
· Use of virtual, augmented, and mixed reality has potential in pediatrics.
- Neurology
- Effectiveness of Helmet therapy for infants with moderate to severe positional plagiocephaly
- Jeongho Kim, Jina Kim, Kyu Young Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):46-53. Published online December 5, 2023
-
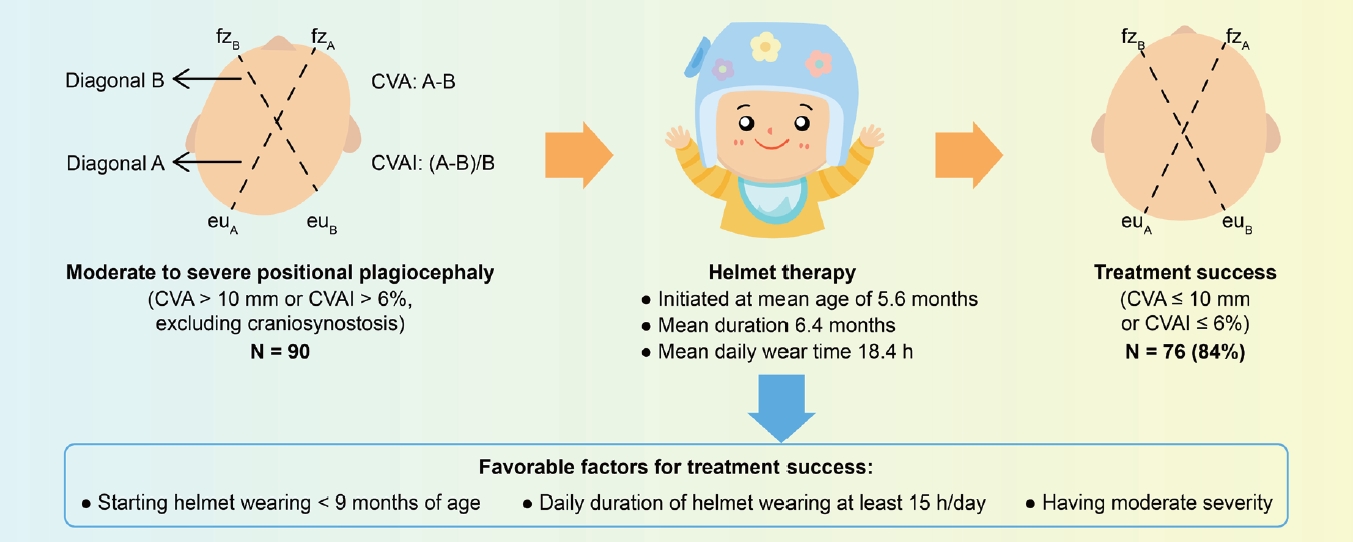
Question: Is helmet therapy effective for positional plagiocephaly? What factors influence helmet therapy efficacy for positional plagiocephaly?
Finding: Helmet therapy is effective for infants with moderate to severe positional plagiocephaly, and its effectiveness is influenced by age at treatment initiation, severity of head asymmetry, and daily duration of helmet wear.
Meaning: Pediatricians should initiate helmet therapy for positional plagiocephaly sooner, ideally before 9 months of age, to maximize treatment efficacy.
- Adolescence Medicine
- Relationship between inflammatory biomarkers and insulin resistance in excess-weight Latin children
- Mariano Nicolás Aleman, María Constanza Luciardi, Emilce Romina Albornoz, María Cristina Bazán, Adela Victoria Abregú
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):37-45. Published online December 21, 2023
-
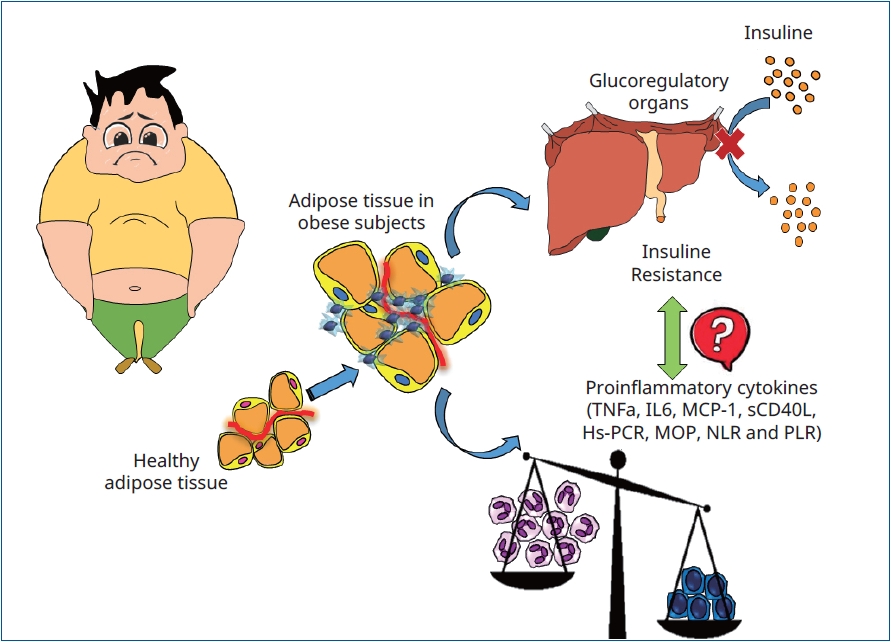
Question: What is the prevalence of insulin resistance (IR) in excess-weight Latin children, and can proinflammatory biomarkers predict it?
Finding: IR prevalence was elevated and tumor necrosis factor- α, interleukin-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein- 1, soluble CD40 ligand, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels were increased in excess-weight Latin children. However, none predicted IR status.
Meaning: These inflammatory biomarkers were unable to predict IR status. Therefore, further investigations are necessary.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











