Most cited
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most cited
Most-cited articles are from the articles published during the last two years (2024 ~ ).
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Protecting our future: environmental hazards and children’s health in the face of environmental threats: a comprehensive overview
- Jungha Lee, Hyo-Bin Kim, Hun-Jong Jung, Myunghee Chung, So Eun Park, Kon-Hee Lee, Won Seop Kim, Jin-Hwa Moon, Jung Won Lee, Jae Won Shim, Sang Soo Lee, Yunkoo Kang, Young Yoo; The Environmental Health Committee of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):589-598. Published online October 31, 2024
-

· Exposure to air pollutants cause allergic and respiratory diseases as well as chronic kidney disease.
· Adequate physical activity and proper nutrition are essential for children to maintain good health.
· We must educate people about the harmful effects of noise, blue light, heavy metals and smoke.
· Government and society must actively decrease environ-mental hazards.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: from diagnosis to management
- Eujin Park, Hee Gyung Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):17-25. Published online June 14, 2023
-
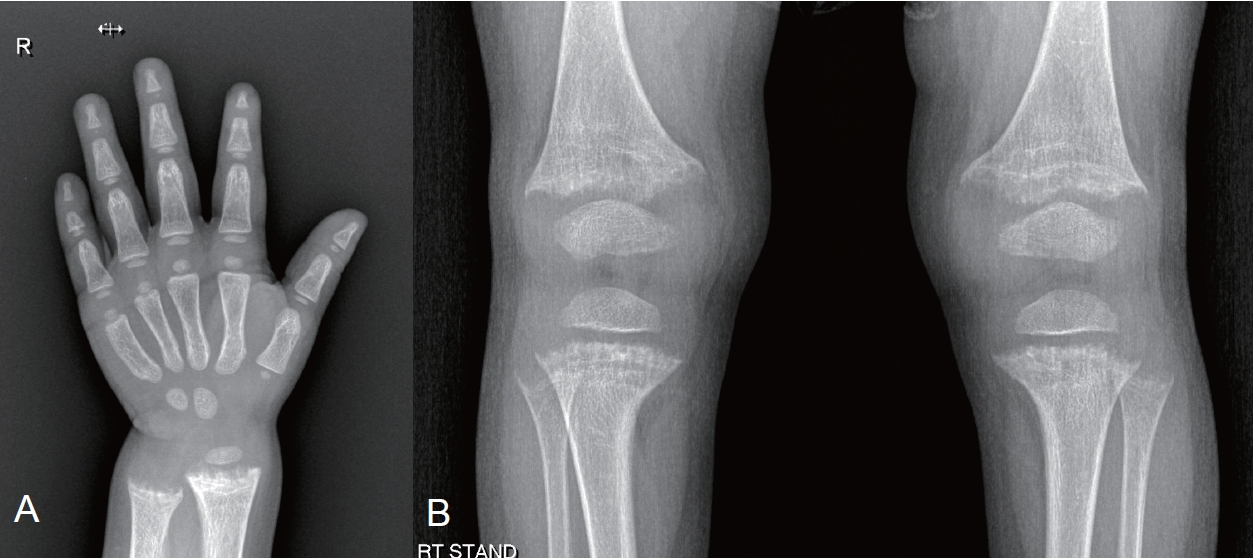
· X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH), the most common cause of hypophosphatemic rickets, affects 1/20,000 people.
· XLH is caused by a loss-of-function mutation of the PHEX gene.
· Its main pathogenesis is elevated fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23) level.
· Burosumab, an FGF23 inhibitor, was developed in the early 2000s.
· Burosumab was approved in Korea in 2020 for XLH patients aged 1+ years with radiographic evidence of bone disease.
- Original Article
- Adolescence Medicine
- Relationship between inflammatory biomarkers and insulin resistance in excess-weight Latin children
- Mariano Nicolás Aleman, María Constanza Luciardi, Emilce Romina Albornoz, María Cristina Bazán, Adela Victoria Abregú
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):37-45. Published online December 21, 2023
-
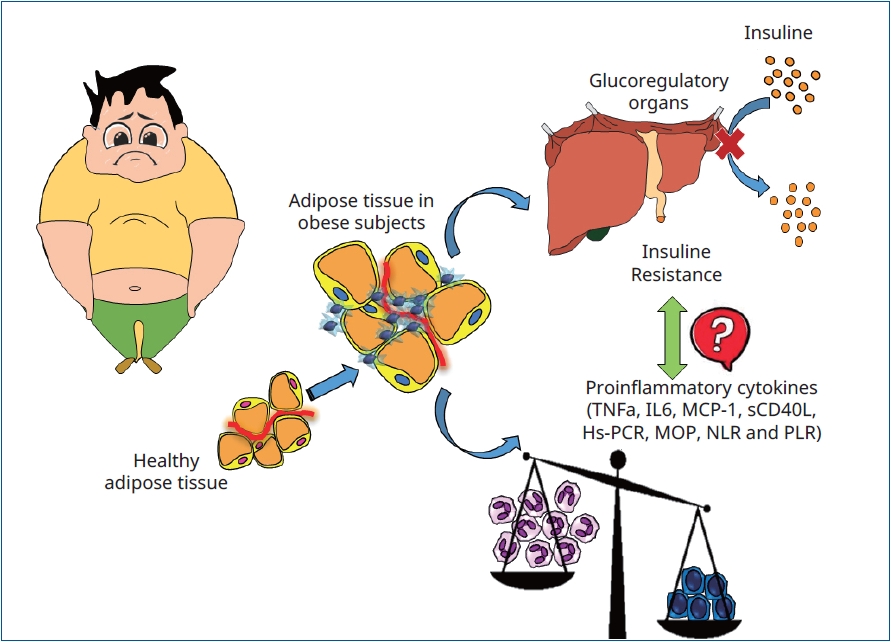
Question: What is the prevalence of insulin resistance (IR) in excess-weight Latin children, and can proinflammatory biomarkers predict it?
Finding: IR prevalence was elevated and tumor necrosis factor- α, interleukin-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein- 1, soluble CD40 ligand, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels were increased in excess-weight Latin children. However, none predicted IR status.
Meaning: These inflammatory biomarkers were unable to predict IR status. Therefore, further investigations are necessary.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin levels can predict allergic disease development and atopic march in children
- Zak Callaway, Chang-Keun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):398-405. Published online February 3, 2025
-
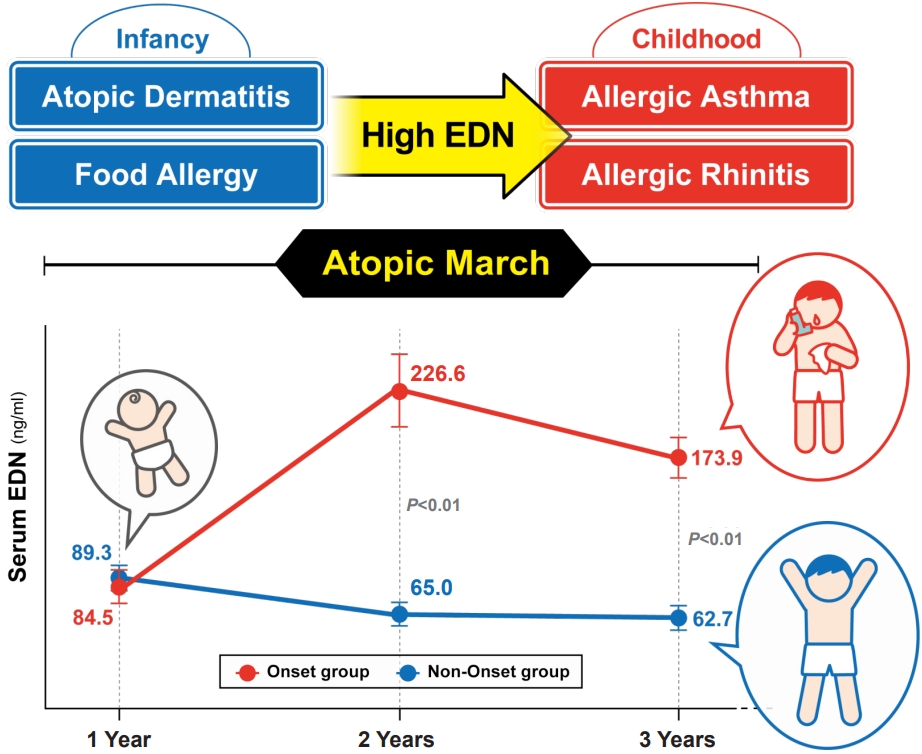
· Allergic march occurs in a subset of children, beginning with atopic dermatitis and progressing to food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and/or asthma. Its early diagnosis is important to slowing its progression.
· Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN), an excellent biomarker of eosinophil activity, is often elevated in allergic diseases.
· EDN levels have been used to predict allergic disease development and diagnose, treat, and monitor allergic diseases.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Outcome of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease in Asian children: a multinational 1-year follow-up study
- Pornthep Tanpowpong, Suporn Treepongkaruna, James Guoxian Huang, Kee Seang Chew, Karen Sophia Calixto Mercado, Almida Reodica, Shaman Rajindrajith, Wathsala Hathagoda, Yoko Kin Yoke Wong, Way Seah Lee, Marion Margaret Aw
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):247-256. Published online November 13, 2024
-
Question: Short-term (1-year) follow-up data in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), especially in Southeast Asian countries, are limited.
Finding/Meaning: Abdominal pain and pallor rates remained high at 1 year after IBD diagnosis. Three independent factors of 1-year clinical remission for Crohn disease were oral prednisolone, antibiotic, and immunomodulator use at 1-year follow-up. A history of weight loss at diagnosis was the only independent risk factor of IBD flare.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Neonatal risk factors associated with autism spectrum disorders: an umbrella review
- Amir Mohammad Salehi, Erfan Ayubi, Salman Khazaei, Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Zohreh Salimi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):459-464. Published online July 19, 2024
-

Question: What are the neonatal risk factors for autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Findings: Significant effect sizes were observed for congenital heart disease (odds ratio [OR], 1.35), macrosomia (OR, 1.11), low birth weight (OR, 1.63), very low birth weight (OR, 2.25), small for gestational age (OR, 1.17), jaundice (OR, 1.74), male sex (OR, 1.47), and Apgar score (OR, 1.40).
Meaning: These factors were identified as risk factors for ASD.
- Review Article
- Other
- Acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible babies and children: no valid rationale for controversy
- Lisa Zhao, John P. Jones, Lauren G. Anderson, Zacharoula Konsoula, Cynthia D. Nevison, Kathryn J. Reissner, William Parker
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):126-139. Published online June 14, 2023
-

Despite worldwide acceptance of acetaminophen (paracetamol) in pediatric medicine, careful examination reveals no valid objections to the conclusion that early exposure to acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible babies and children. Nevertheless, debate that early exposure to acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury has centered around the prenatal period, evidence of which is relatively limited compared to that in the postnatal period, which is the time of greatest absolute and relative risk.
- Allergy
- Practical issues of oral immunotherapy for egg or milk allergy
- Sukyung Kim, Kangmo Ahn, Jihyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):140-148. Published online June 19, 2023
-
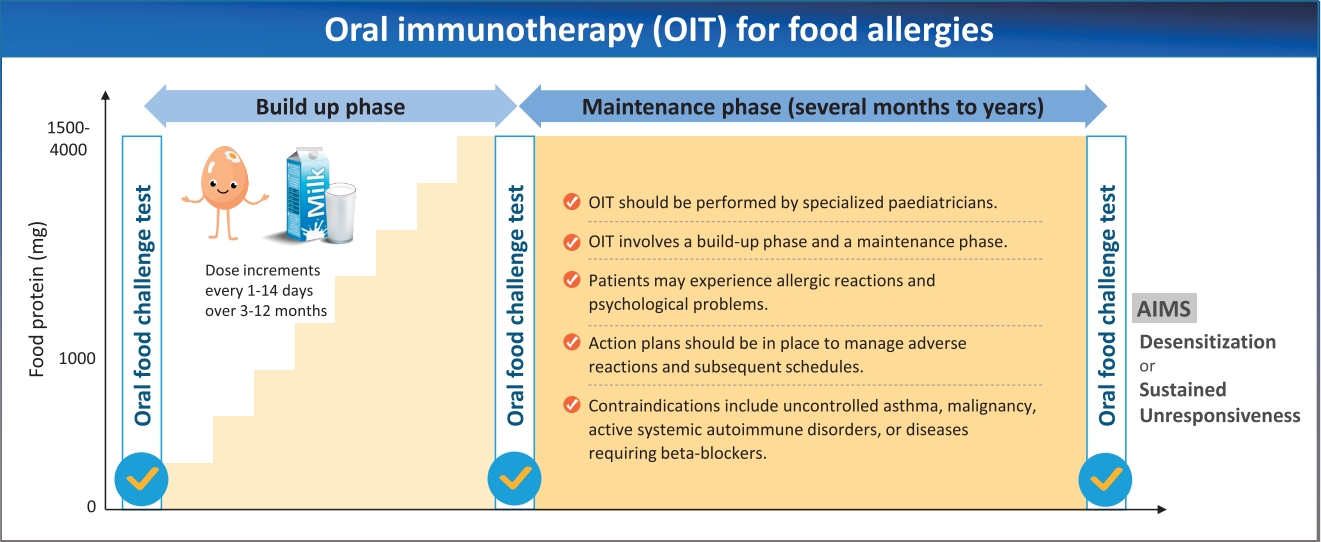
· Oral immunotherapy should be supervised by pediatricians with experience administering oral food challenge tests and managing allergic reactions.
· Food allergen intake is gradually increased and maintained for years.
· Patients may experience allergic reactions and psychological problems.
· Adjunctive therapies (biologics, antihistamines, and leukotriene receptor antagonists) may improve efficacy and safety.
· Contraindications include uncontrolled asthma, malignancy, active autoimmune disorders, and beta-blocker usage.
- Moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children: focus on systemic Th2 cytokine receptor antagonists and Janus kinase inhibitors
- Jeong Hee Kim, Mona Salem Samra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):64-79. Published online June 14, 2023
-
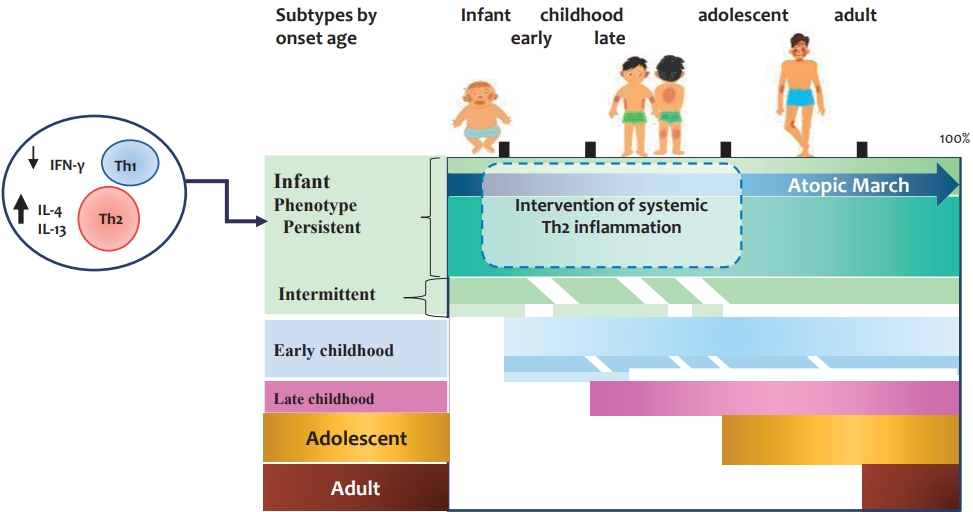
· Atopic dermatitis (AD) is characterized by a strong T helper (Th)2 response, although the extents of Th22, Th17/ interleukin (IL)-23, and Th1 responses vary among disease subtypes.
· Children with moderate to severe AD may require early systemic therapy to reduce the systemic inflammation caused by increased Th2 cytokine levels.
· Dupilumab, which blocks IL-4/IL-13 receptor, has equivalent efficacy for extrinsic and intrinsic AD and a favorable safety profile in infants and children aged 6 months and older.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents
- Hae Sang Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):90-91. Published online January 24, 2024
-
· With the increase in childhood obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become a concern in recent years.
· NAFLD is strongly associated with insulin resistance.
· Lifestyle modifications are the mainstay treatment for NAFLD.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents: prevalence and associated factors
- Jee-Seon Shim, Jeong Mi Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):531-539. Published online September 24, 2024
-

Question: How prevalent is energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents and what are the associated factors?
Findings: The prevalence of energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents increased from 3.2% in 2014 to 12.2% in 2019. Energy drink consumption varies according to sociode-mographic and individual factors.
Meaning: Policies and educational strategies are needed to reduce energy drink consumption in adolescents.
- General Pediatrics
- Effect of online infant care training and postpartum counseling based on Meleis' transition theory on mothers' readiness for care and breastfeeding: a randomized controlled trial
- Fatma Şule Bilgiç, Gülçin Bozkurt
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):521-530. Published online September 27, 2024
-

Question: Do interventions based on Meleis' transition theory affect mothers' readiness for baby care and breastfeeding?
Findings: We found a statistically significant difference between the intervention and control groups in mothers' readiness for newborn care and breastfeeding (P<0.001).
Meaning: This intervention increased breastfeeding rates while ensuring that mothers were ready to care for their babies and prepared for the role of motherhood.
- Review Article
- Other
- Artificial intelligence in pediatric healthcare: current applications, potential, and implementation considerations
- Taejin Park, In-Hee Lee, Seung Wook Lee, Sek Won Kong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):641-651. Published online June 25, 2025
-

Artificial intelligence (AI) offers potential benefits in pediatric care, but its real-world adoption requires clinician literacy, ethical and legal safeguards, and cautious implementation. Large language models are emerging across healthcare, but their use in pediatric clinical practice remains premature. Thus, the cautious and accountable implementation of AI is crucial to preventing unintended harm and realizing its potential.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Characterization of gut microbiota in very low birth weight infants with versus without bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Anucha Thatrimontrichai, Manapat Praditaukrit, Gunlawadee Maneenil, Supaporn Dissaneevate, Kamonnut Singkhamanan, Komwit Surachat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):503-511. Published online February 26, 2025
-

Question: Does the gut microbiota differ between very low birth weight (VLBW) infants with versus without bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)?
Finding: Common respiratory pathogens were notably elevated in the BPD group, whereas anaerobic and butyrate-producing taxa, key components of postbiotics, were dominant in the non-BPD group.
Meaning: In gut-lung communication, the interplay between the intestinal and respiratory systems may implicate pro- and postbiotics in VLBW infants with BPD.
- Editorial
- Hematology
- Absolute versus functional iron deficiency
- Hye Lim Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):138-140. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· Iron deficiency (ID), the most common cause of anemia, can be classified into absolute and functional types. Absolute ID is a state of low total body iron, while functional ID is a state of imbalance between iron demand and iron availability due to inflammation and/or infection.
· ID is diagnosed by serum ferritin and transferrin saturation levels.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- A review of vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D receptor polymorphisms in endocrine-related disorders
- Nur Faten Hafizah Rosli, Noor Shafina Mohd Nor, Rose Adzrianee Adnan, Siti Hamimah Sheikh Abdul Kadir
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):30-52. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency is high among children and adolescents and mainly attributed to changes in environmental factors.
· Vitamin D hormone-like properties are associated with many endocrine-related disorders.
· The effect of vitamin D is modulated by the vitamin D receptor, polymorphisms of which are reportedly associated with an increased risk of disease development in children and adolescents.
- Allergy
- Action-plan and as-needed therapy in allergic rhinitis
- Hyeon-Jong Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):267-273. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· The guidelines may not work in the real world.
· An action-plan reflecting patient’s severity and variable of symptoms, values and preferences as well as the benefits and harms of treatment, may be a useful alternative.
· The action plan and as-needed therapy must include the following elements: when, what, how, and why.
· Action plan and as-needed therapy can help patients manage their symptoms more effectively.
- Rheumatology
- Double-negative T cells in pediatric rheumatic diseases
- Dimitri Poddighe, Tilektes Maulenkul, Kuanysh Dossybayeva, Gulsamal Zhubanova, Zaure Mukusheva, Lyudmila Akhmaltdinova
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):632-640. Published online September 12, 2024
-
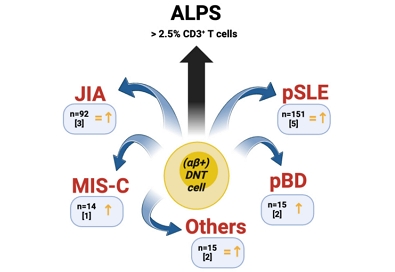
Double-negative T (DNT) cells appear to be increased in several pediatric rheumatic diseases and this finding may be correlated with disease activity to some extent. However, due to significant heterogeneity in several methodological aspects, further investigations in rheumatic children are needed to assess the potential relevance of DNT cells as biomarkers and clarify their immunopathological role.
- Endocrinology
- Lifelong medical challenges and immunogenetics of Turner syndrome
- Won Kyoung Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):560-568. Published online July 31, 2024
-
· This summary emphasizes the importance of the early diagnosis of Turner syndrome (TS) and presents a multidisciplinary approach to its prevention and management, high-lighting the need for customized care.
· Advancements in immunogenetic research may improve our understanding of TS and improve its outcomes.
· TS encompasses a wide array of medical challenges, including cardiovascular, endocrine, autoimmune, and mental health issues, as well as a heightened cancer risk.
- Original Article
- Basic Research
- Linezolid mitigates tissue injury in experimental model of pediatric testicular torsion: TLR-4/MAPK/NF-κB involvement
- Moein Ghasemi, Abolfazl Basiri, Houman Kazemzadeh, Mohammad Amin Manavi, Seyed Mohammad Tavangar, Ahmad Reza Dehpour, Hamed Shafaroodi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):700-711. Published online August 26, 2025
-

Question: What pharmacological strategies can limit ischemia-reperfusion injury in pediatric patients with testicular torsion?
Finding: In a rat model of testicular torsion, linezolid reduced oxidative stress, inflammation, and tissue injury via the Toll-like receptor 4/mitogen-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor kappa beta pathway.
Meaning: Linezolid may offer a pharmacological approach to attenuate testicular damage in pediatric patients with testicular torsion, warranting further clinical investigation.
- Hematology
- Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in pediatric patients with type VI mucopolysaccharidosis
- Vedat Uygun, Koray Yalçın, Hayriye Daloğlu, Seda Öztürkmen, Suna Çelen, Suleimen Zhumatayev, Gülsün Karasu, Akif Yeşilipek
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):601-607. Published online March 11, 2025
-
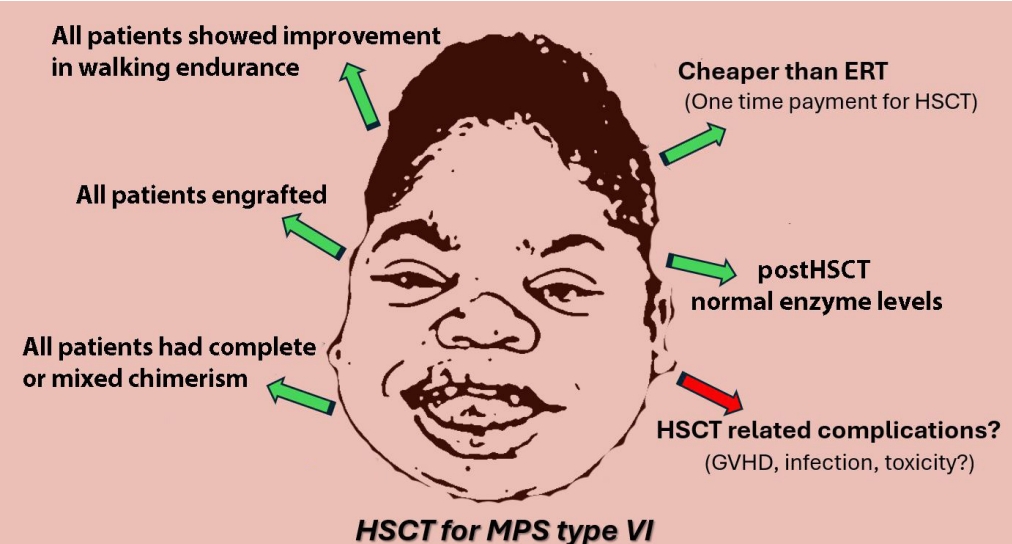
Question: Could hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) be an alternative to enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) for type VI mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS VI)?
Finding: HSCT is generally not offered due to reports of high toxicity and mortality. However, we detected fewer complications and graft-versus-host disease cases and no deaths with HSCT.
Meaning: HSCT is both less expensive than ERT and permanent; thus, it should be considered an alternative treatment for MPS VI.
- Review Article
- Other
- Myopia: a review of current concepts, association with nonophthalmological conditions, and treatment strategy in children and adolescents
- Yeon Woong Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):554-565. Published online April 1, 2025
-
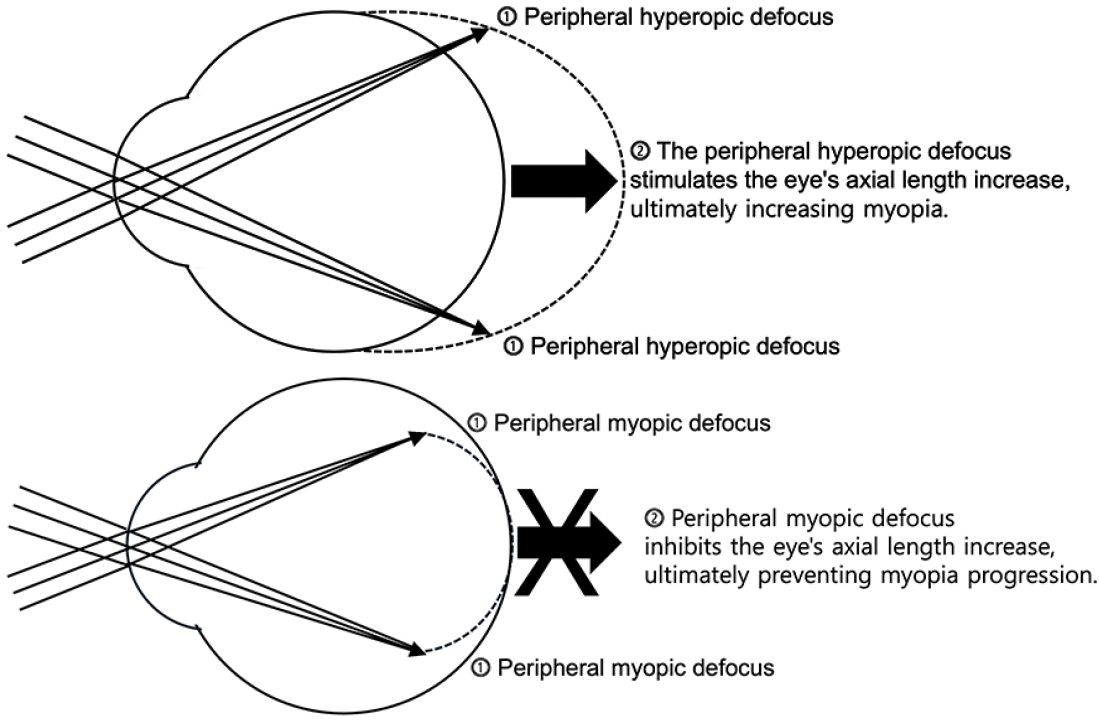
Myopia is a major ophthalmological disorder with increasing prevalence worldwide, particularly in East Asia. Evidence indicates that its development involves complex interactions between genetic and environmental factors. Body stature, sleep patterns, and nutritional status significantly influence the progression of myopia during childhood and adolescence. Its treatment and prevention strategies include optical correction, atropine therapy, increased outdoor activity, decreased near work, and regular retinal monitoring.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Nonlinear association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and asthma in children and adolescents in the United States: a cross-sectional study
- Chuhan Cheng, Liyan Zhang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):489-496. Published online March 11, 2025
-

Question: Is there a nonlinear relationship between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and asthma in children and adolescents?
Finding: NLR showed a nonlinear association with asthma, with an NLR threshold of 2.23 identifying individuals at higher risk.
Meaning: An NLR<2.23 may serve as a potential biomarker for asthma risk assessment and management in pediatric populations, thereby offering a simple tool for the early identification of at-risk individuals.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Differential roles of interleukin-6 and adrenomedullin in early diagnosis and mortality predictions in late-onset neonatal sepsis
- Emilly Henrique dos Santos, Gabriel Acca Barreira, Mariana Okay Saippa, Maria Carolina Pires Cruz, Karen Alessandra Rodrigues, Ronaldo Arkader, Thelma Suely Okay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):463-471. Published online December 23, 2024
-

Question: Can adrenomedullin (ADM) or interleukin-6 (IL-6) detect late-onset neonatal sepsis (LOS) at admission (area under the curve [AUC]>0.90) as an early diagnostic marker?
Finding: Only IL-6 consistently distinguished survivors from nonsurvivors (AUC>0.90) on admission and antibiotic treatment days 3 and 7. C-reactive protein level identified infections from day 3 but failed to predict outcomes (AUC<0.70).
Meaning: IL-6 level can improve LOS diagnosis and prognosis.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus
- Karnchanit Sausukpaiboon, Nuanpan Penboon, Pornpimol Rianthavorn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):454-462. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: What is the acceptance rate for coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
Finding: One-third of parents were hesitant to vaccinate their child. Parental willingness to vaccinate themselves, older patient age, and belief in the vaccine's potency were associated with vaccine acceptance.
Meaning: These findings highlight the need for targeted interventions to improve vaccine acceptance among parents of children with SLE.
- Editorial
- General Pediatrics
- Global breastfeeding efforts: a long way to go
- Hye-Jung Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):300-302. Published online November 13, 2024
-

· Despite much effort, breastfeeding practices remain unsatisfactory worldwide.
· Effective breastfeeding-promoting interventions are needed that are appropriate for age, culture, and social environment.
· Interventions can promote breastfeeding, especially in younger populations such as adolescent mothers.
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Lifelong impact of elevated blood pressure from childhood to adulthood
- Junhyun Kwon, Eunji Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):278-286. Published online November 28, 2024
-

· Childhood blood pressure (BP) is significantly associated with adult hypertension and cardiovascular disease.
· Despite ongoing debate regarding the need for regular BP screening and early pharmacotherapy in children, the benefits of optimizing BP throughout childhood are clear.
· Childhood presents a critical window for normalizing BP through lifestyle modifications such as reducing sodium intake and increasing physical activity to promote lifelong cardiovascular health and prevent longterm complications.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Recent advances in understanding pathophysiology of non-nutritional stunting in very preterm infants
- Eduardo Cuestas, Alina Rizzotti
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):287-297. Published online December 23, 2024
-

· Previous reviews of extrauterine growth restriction focused mainly on weight growth restriction caused by nutritional factors or pathological conditions.
· This review summarizes recent developments in the pathophysiology of nonnutritional length growth restriction in very preterm infants with focus on the impact of sustained neonatal inflammation on their short- and long-term outcomes.
· Further research is needed to investigate optimal strategies to improve length growth restriction in very preterm infants.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding dengue vaccine: a baseline study of community members and health providers in Indonesia
- Abdul Wahab, Ida Safitri Laksanawati, Retna Siwi Padmawati, Asal Wahyuni Erlin Mulyadi, Wahyu Triadmajani, Jarir At Thobari
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):228-237. Published online November 13, 2024
-
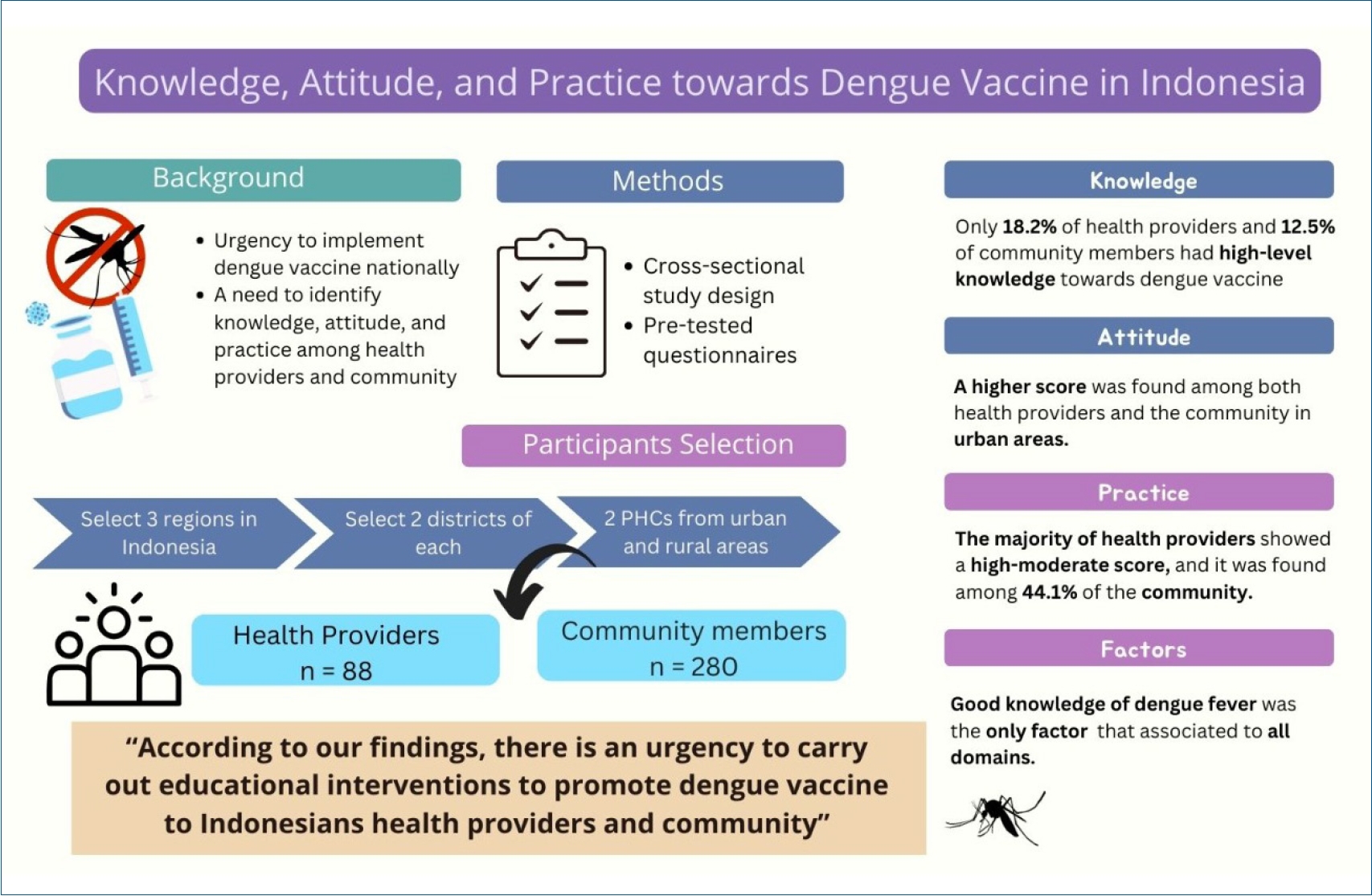
Question: Do community members and health providers show different level of knowledge, attitude, and practice towards dengue vaccine?
Finding: These 2 groups only differed in practice component, while the knowledge and attitude constituents were relatively low for both.
Meaning: There is an urgent need to deliver educational interventions to raise awareness of community members and health providers regarding dengue vaccination.
- Endocrinology
- Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone score changes in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency
- Pattara Wiromrat, Yutapong Raruenrom, Phanpaphorn Namphaisan, Nantaporn Wongsurawat, Ouyporn Panamonta, Chatlert Pongchaiyakul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):238-246. Published online November 13, 2024
-
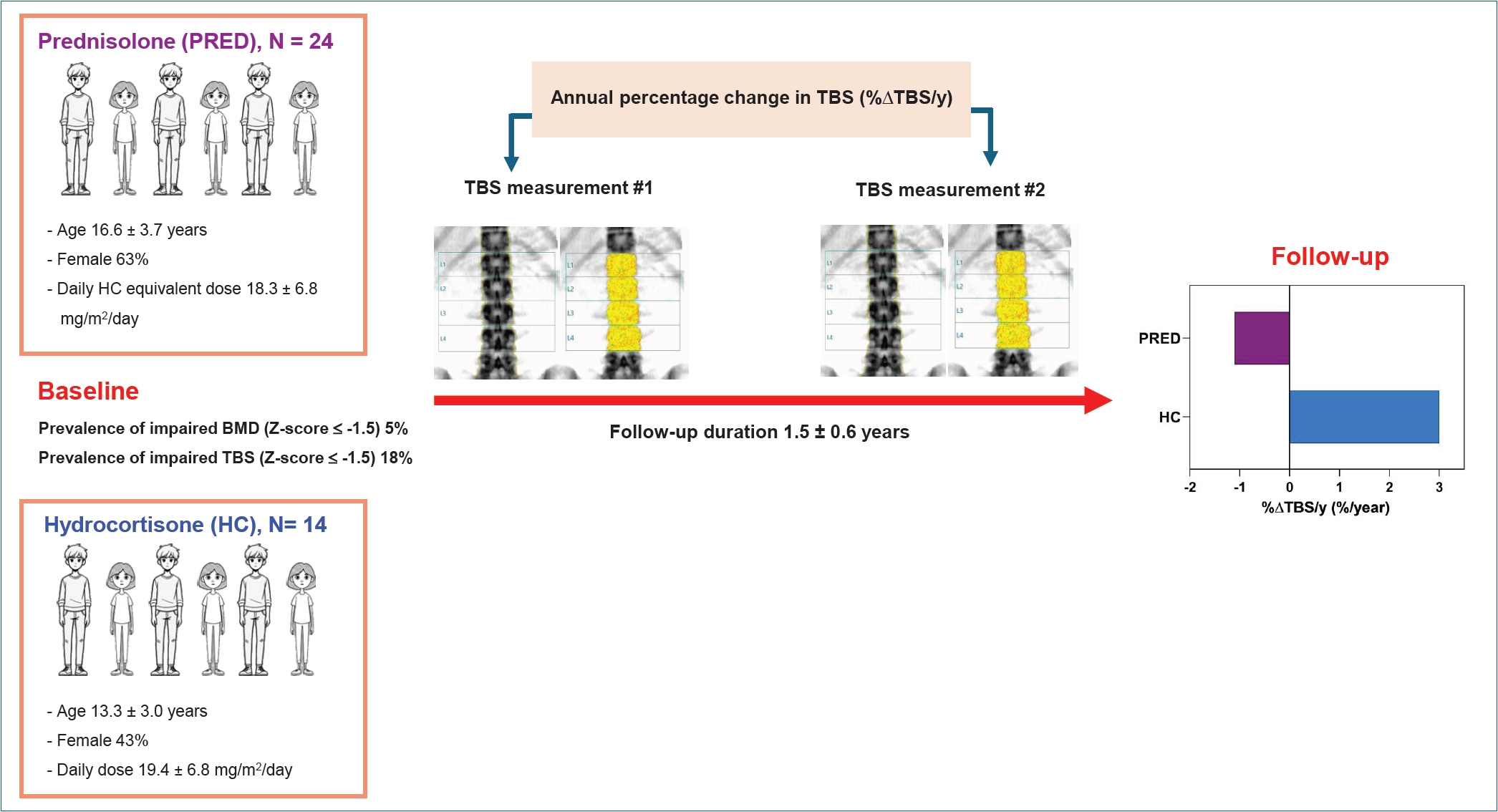
Question: What is the prevalence of an impaired trabecular bone score (TBS), a measure of bone microarchitecture, in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency (21OHD)? Do prednisolone and hydrocortisone affect TBS differently in this patient population?
Finding: Impaired TBS was observed in 18% of participants. Prednisolone use negatively impacted TBS change.
Meaning: Impaired TBS is prevalent among adolescents with 21OHD. Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone microarchitecture development.
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.












