Funded articles
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Funded articles
- Funded articles
-
- National Research Foundation of Korea (33)
- Ministry of Science and ICT (15)
- Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (12)
- Ministry of Education (8)
- Chungnam National University (5)
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (5)
- Soonchunhyang University (5)
- Korean Pediatric Society (4)
- Ministry of Health and Welfare (4)
- Korea Health Industry Development Institute (3)
- Ministry of Environment (3)
- Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (3)
- Chonnam National University (2)
- Chulalongkorn University (2)
- Eulji University (2)
- Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital (2)
- Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University (2)
- Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Islam Indonesia (2)
- Hanyang University (2)
- Inha University (2)
- National Institutes of Health (2)
- Pusan National University (2)
- Tehran University of Medical Sciences and Health Services (2)
- Arak University of Medical Sciences (1)
- Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (1)
- Cairo University (1)
- Chonnam National University Hospital (1)
- Chung-Ang University (1)
- Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (1)
- Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (1)
- Duhok General Directorate of Health (1)
- Durham, North Carolina (1)
- e Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (1)
- Environmental Health Center for Hazardous Chemical Exposure (1)
- European Commission-European Research Executive Agency (1)
- Faculty of Medicine, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University (1)
- Faculty of Medicine, South Valley University (1)
- Gyeongsang National University (1)
- Gyeongsang National University Hospital (1)
- Hamadan University (1)
- Hankuk University of Foreign Studies (1)
- ICMR MD/MS Thesis Research Grant (1)
- Ilsung Research Award of Korean Academy Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease (1)
- Indonesia Endowment Fund for Education (1)
- Inha University Hospital (1)
- Inje University (1)
- Institute of Medical Science, Daegu Catholic University (1)
- JSPS KAKENHI (1)
- Kangwon National University (1)
- Kementerian Riset, Teknologi dan Pendidikan Tinggi (1)
- Khon Kaen University (1)
- Korea Childhood Leukemia Foundation (1)
- Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (1)
- Korea Environmental Industry and Technology Insitute (1)
- Korea Environmental Industry and Technology Institute (1)
- Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences (1)
- Korea National Institute of Health (1)
- Korea University Anam Hospital (1)
- Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease (1)
- Korean Society of Breastfeeding Medicine (1)
- Kunhee Lee Child Cancer & Rare Disease Project (1)
- Kurdistan University of Medical Science (1)
- Kyung Hee University (1)
- Kyungpook National University Hospital (1)
- Luzhou Municipal People’s Government-Southwest Medical University Science and Technology strategic cooperation (1)
- Manipal Academy of Higher Education (1)
- Manipal Research grant (1)
- Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (1)
- Ministry of Finance of Indonesia (1)
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (1)
- Ministry of Higher Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan (1)
- Ministry of Science and Technology (1)
- Ministry of Science, Information and Communication Technology, and Future Planning (1)
- Mundipharma Pharmaceutical Sdn. Bhd (1)
- Namseoul University (1)
- National Cancer Center (1)
- National Center for Child Health and Development (1)
- National Center for Mental Health (1)
- National Health Insurance Ilsan Hospital (1)
- National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital (1)
- National Institute of Medical Research Development (1)
- National IT Industry Promotion Agency (1)
- Navajbhai Ratan Tata trust - Health (1)
- Nazarbayev University (1)
- PEER/USAID (1)
- Probiotics International Ltd (1)
- Pusan National University Hospital (1)
- Pusan National University School of Medicine and Biomedical Research Institute (1)
- Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital (1)
- Ramathibodi Research Fund (1)
- Ratchadapisek Sompoch Endowment Fund (1)
- Research of Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (1)
- Samsung Medical Center (1)
- Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (1)
- Seoul National University Hospital (1)
- Severance Children’s Hospital (1)
- Severance Hospital Research Fund for Clinical Excellence (1)
- Sichuan Science and Technology Program (1)
- Soonchunhyang University Research Fund (1)
- Thailand Science Research and Innovation Fund Chulalongkorn University (1)
- The Health System Research Institute, Ministry of Public Health (1)
- Union Grants Commission (1)
- Universitas Indonesia (1)
- Universiti Teknologi MARA (1)
- Uttarakhand State Council for Science and Technology (1)
- WPLab, Inc. (1)
- Yonsei University College of Medicine (1)
- Zeist Foundation (1)
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Impact of obesity on pulmonary function of preschool children: an impulse oscillometry study
- Anuvat Klubdaeng, Kanokporn Udomittipong, Apinya Palamit, Pawinee Charoensittisup, Khunphon Mahoran
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):319-325. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: Does obesity in preschool children affect lung function, and which obesity indices can predict such alterations?
Finding: Preschool children with obesity exhibit impaired lung function characterized by elevated total and peripheral airway resistance. Waist-to-height ratio was the strongest predictor of such changes.
Meaning: Early obesity prevention and treatment are needed. Monitoring waist-to-height ratio, body weight, and body mass index may help identify children at risk of altered lung function.
- Neurology
- Occurrence of stroke in children and young adults in Indonesia: a multicenter private hospital study
- Jeanne Leman, Veli Sungono, Yosua Timotius Haryono, Muhammad Adam Mudzakir, Dewi Lestari Rahmawati, Callistus Bruce Henfry Sulay, Gilbert Sterling Octavius
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):303-310. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: What is the occurrence of pediatric stroke in Indonesia?
Finding: This multicenter study identified 1,074 stroke cases, predominantly hemorrhagic (83.4%), with males and older children at higher risk. Accidents were the primary cause (73.2%).
Meaning: Pediatric stroke in Indonesia shows critical epidemiological trends, highlighting the need for targeted prevention efforts, particularly for high-risk groups like males and accident victims.
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Cerebral organoid research for pediatric patients with neurological disorders
- Jin Eun, Jung Eun Lee, Seung Ho Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):269-277. Published online November 28, 2024
-

Cerebral organoids obtained from human induced pluripotent stem cells are transforming the study of pediatric neurological diseases by providing more accurate models of human brain development and pathology. These advancements have improved pathology modeling and the potential for novel therapeutic approaches despite existing challenges such as reproducibility and vascularization.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Outcome of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease in Asian children: a multinational 1-year follow-up study
- Pornthep Tanpowpong, Suporn Treepongkaruna, James Guoxian Huang, Kee Seang Chew, Karen Sophia Calixto Mercado, Almida Reodica, Shaman Rajindrajith, Wathsala Hathagoda, Yoko Kin Yoke Wong, Way Seah Lee, Marion Margaret Aw
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):247-256. Published online November 13, 2024
-
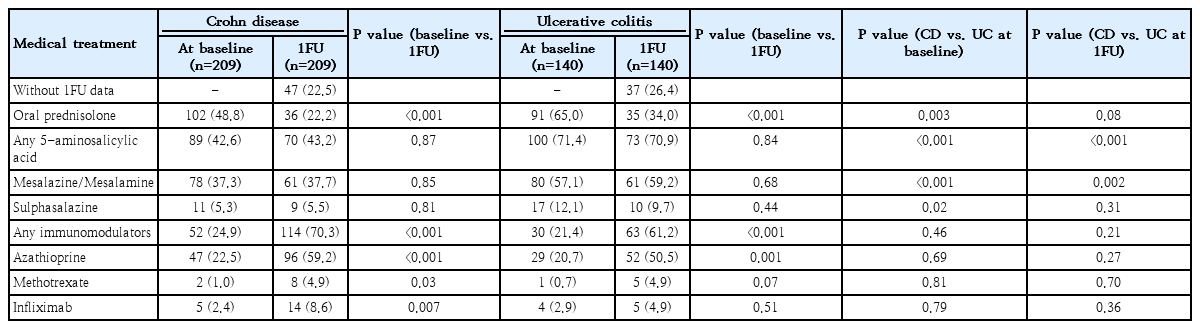
Question: Short-term (1-year) follow-up data in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), especially in Southeast Asian countries, are limited.
Finding/Meaning: Abdominal pain and pallor rates remained high at 1 year after IBD diagnosis. Three independent factors of 1-year clinical remission for Crohn disease were oral prednisolone, antibiotic, and immunomodulator use at 1-year follow-up. A history of weight loss at diagnosis was the only independent risk factor of IBD flare.
- Endocrinology
- Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone score changes in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency
- Pattara Wiromrat, Yutapong Raruenrom, Phanpaphorn Namphaisan, Nantaporn Wongsurawat, Ouyporn Panamonta, Chatlert Pongchaiyakul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):238-246. Published online November 13, 2024
-
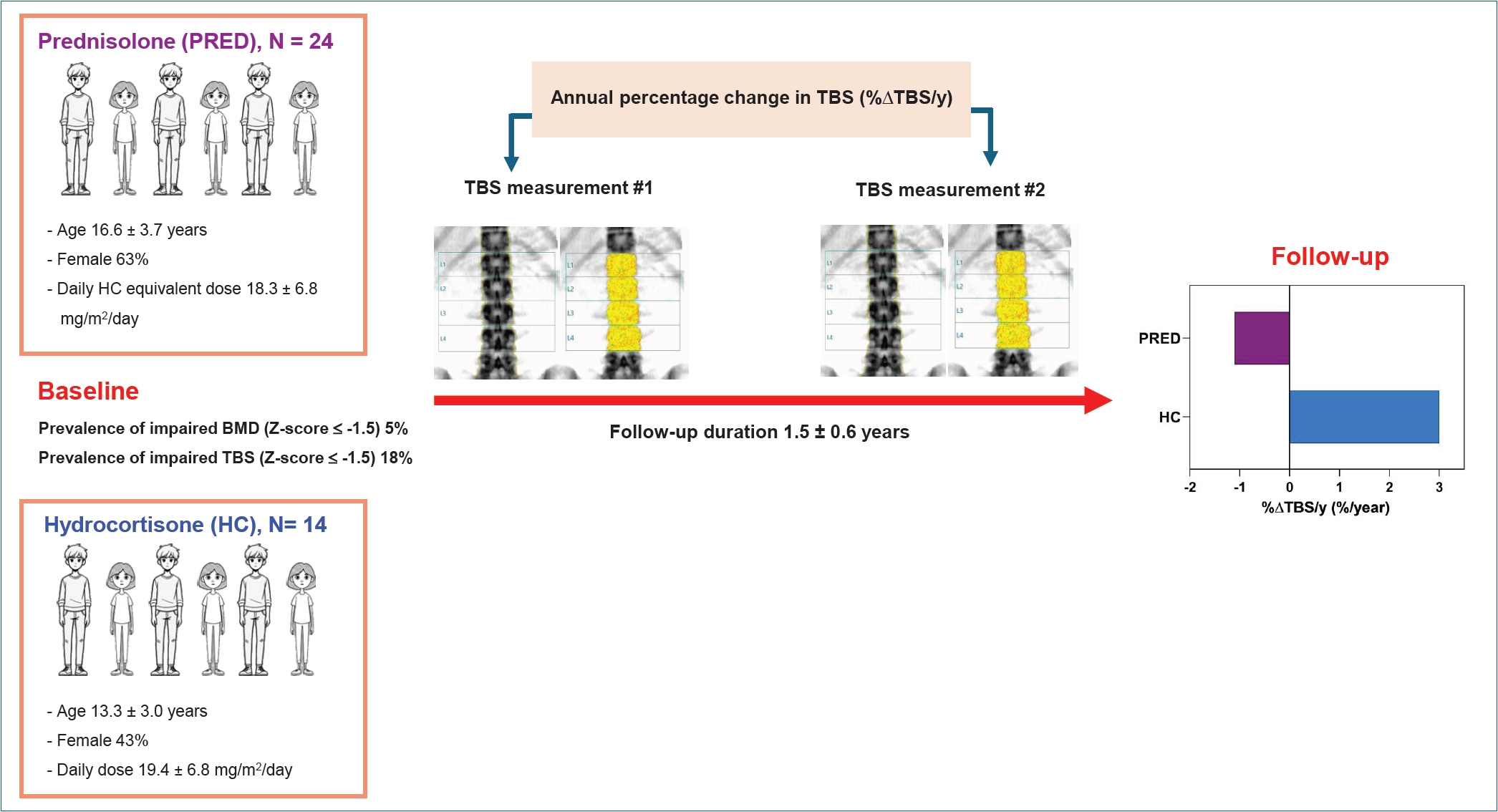
Question: What is the prevalence of an impaired trabecular bone score (TBS), a measure of bone microarchitecture, in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency (21OHD)? Do prednisolone and hydrocortisone affect TBS differently in this patient population?
Finding: Impaired TBS was observed in 18% of participants. Prednisolone use negatively impacted TBS change.
Meaning: Impaired TBS is prevalent among adolescents with 21OHD. Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone microarchitecture development.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effect of high-frequency oscillatory ventilation with intermittent sigh breaths on carbon dioxide levels in neonates
- Kulthida Baingam, Anucha Thatrimontrichai, Manapat Praditaukrit, Gunlawadee Maneenil, Supaporn Dissaneevate
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):178-184. Published online November 13, 2024
-
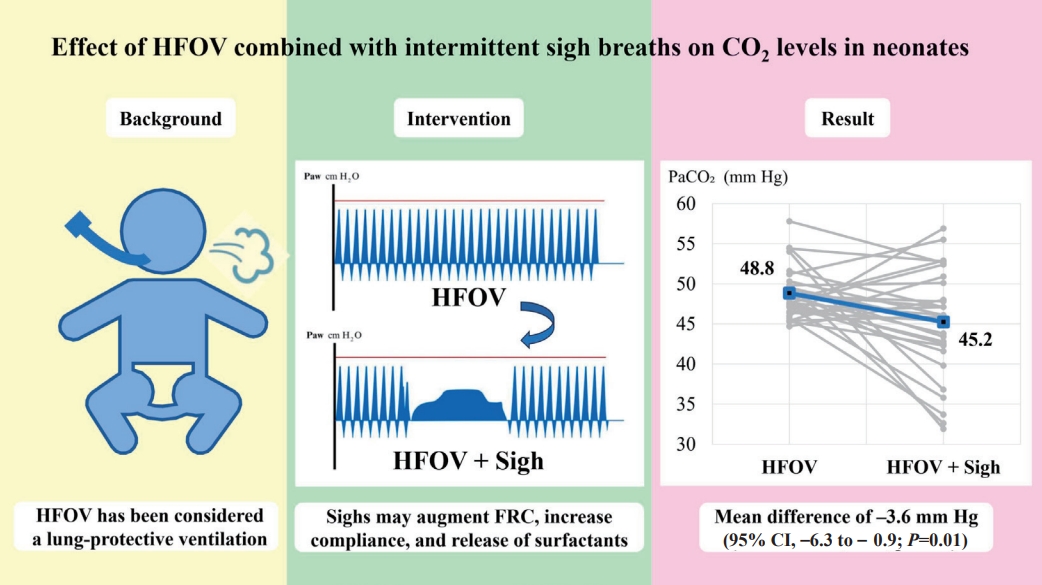
Question: Can sigh breaths (Sighs) application during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV) decrease partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) levels?
Finding: The mean PaCO2 level after Sighs during HFOV was significantly decreased compared to that after HFOV alone (mean difference, -3.6 mmHg).
Meaning: HFOV plus Sighs functionality can reduce PaCO2 levels. However, further studies are required to conclusively determine the effects of Sighs.
- Gastroenterology
- Differences in immune cells and gene expression in human milk by parity on integrated scRNA sequencing
- Dae Yong Yi, Hong-Jai Park, Min Sun Shin, Hyoungsu Kim, Sang Jin Lee, Insoo Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):141-152. Published online January 10, 2025
-
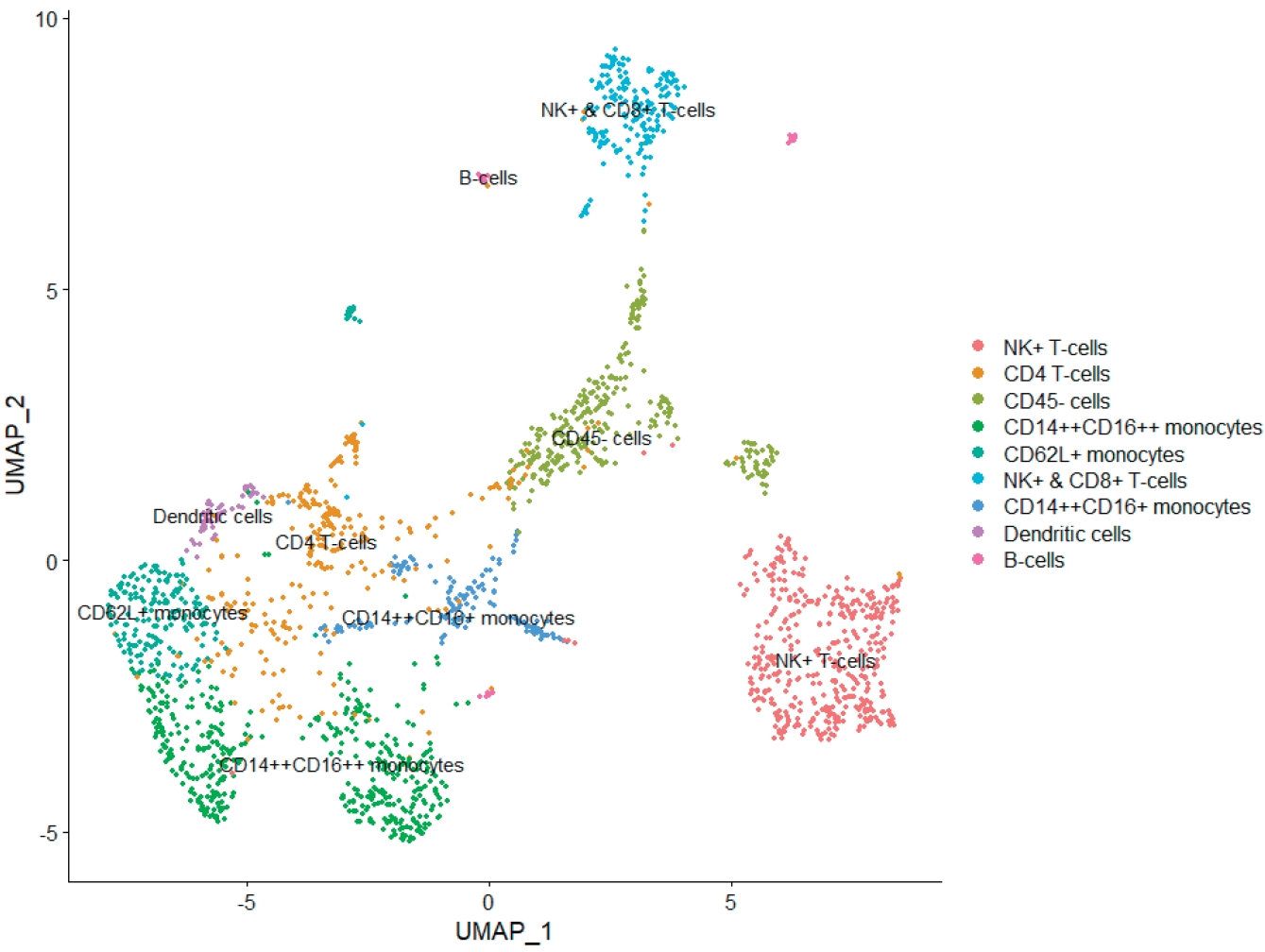
Question: Is there a difference in immune cells in human breast milk by parity?
Finding: There were higher proportions of monocytes and T/B cells in the primiparous and multiparous group, respectively. The expression of genes with a direct role in the infant immune system and immune response-related genes were highest in the primiparous group
Meaning: There were parity-dependent differences in the expression of genes between innate and adaptive immune cells.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Value of transabdominal ultrasonography for diagnosing functional constipation in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Duc Long Tran, Phu Nguyen Trong Tran, Paweena Susantitaphong, Phichayut Phinyo, Palittiya Sintusek
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):127-135. Published online November 13, 2024
-
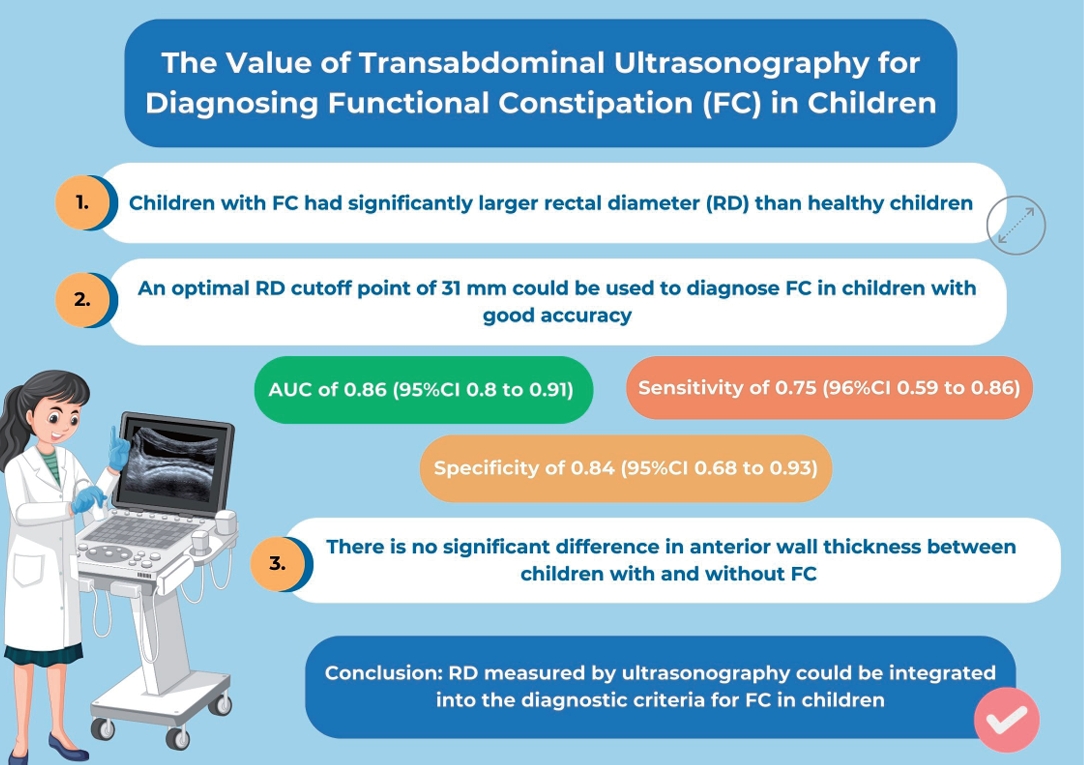
Transabdominal ultrasonography is increasingly used as a novel modality for detecting pediatric functional constipation (FC). This systematic review and metaanalysis aimed to assess the diagnostic parameters of FC including rectal diameter (RD) and anterior rectal wall thickness. A systematic search was conducted of the Ovid MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, and PubMed databases through September 29, 2023, to identify studies comparing RD...
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Instability of revised Korean Developmental Screening Test classification in first year of life
- Ji Eun Jeong, You Min Kim, Na Won Lee, Gyeong Nam Kim, Jisuk Bae, Jin Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):97-103. Published online November 11, 2024
-

Question: How stable are the revised Korean Developmental Screening Test score classifications in early infancy?
Finding: A significant number of infants improved into the peer and high-level group (≥-1 standard deviations), especially in the gross motor area.
Meaning: The early detection of developmental delay requires a comprehensive medical history, physical and neurological examinations, and repeated developmental screenings.
- Infection
- Carbapenem resistance in gram-negative pathogens in an Iranian hospital: high prevalence of OXA-type carbapenemase genes
- Setareh Mamishi, Reihaneh Hosseinpour Sadeghi, Sadaf Sajedi Moghaddam, Babak Pourakbari, Shiva Poormohammadi, Maryam Sotoudeh Anvari, Shima Mahmoudi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):65-72. Published online October 31, 2024
-

Question: What is the prevalence of carbapenem resistance in gram-negative bacteria and associated carbapenemase genes?
Findings: This study identified a notable prevalence of carbapenem-resistant gram-negative isolates, with Escherichia coli being the predominant contributor, follow ed by Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, while bla OXA48 was the most prevalent carbapenemase gene.
Meaning: These findings highlight the urgent need for proactive measures including the rapid detection of carbapenemase- producing isolates and effective infection control.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Need for national guidance regarding proactive care of infants born at 22–23 weeks' gestation
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):53-61. Published online November 13, 2024
-

With advancements in neonatal intensive care, the limit of viability has shifted to 22–23 weeks' gestation, whose survival rates vary across countries and institutions. These rates are not static and can be improved through the proactive and centralized care guided by national protocols, including maternal transfer to high-activity regions with better neonatal intensive care practices before delivery.
- Endocrinology
- A review of vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D receptor polymorphisms in endocrine-related disorders
- Nur Faten Hafizah Rosli, Noor Shafina Mohd Nor, Rose Adzrianee Adnan, Siti Hamimah Sheikh Abdul Kadir
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):30-52. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency is high among children and adolescents and mainly attributed to changes in environmental factors.
· Vitamin D hormone-like properties are associated with many endocrine-related disorders.
· The effect of vitamin D is modulated by the vitamin D receptor, polymorphisms of which are reportedly associated with an increased risk of disease development in children and adolescents.
- Other
- Microplastic and human health with focus on pediatric well-being: a comprehensive review and call for future studies
- Rogers Wainkwa Chia, Ntegang Venant Atem, Jin-Yong Lee, Jihye Cha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):1-15. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· Milk and formula are common sources of microplastic in infants.
· Water and air are the most common sources of microplastic pollution from infancy to adolescence.
· Microplastic use by children of all ages can cause cell damage and affect their health.
· Microplastics present in children can be quantified using a stereomicroscope and characterized using micro- Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Clinical, biochemical, and genetic study of TACE/TNF-α/ACE signaling pathway in pediatric COVID-19 infection
- Ahmed El-Abd Ahmed, Sawsan M.A. Abuhamdah, Mohammed H. Hassan, Nagwan I. Rashwan, Eman A. Abd-Elmawgood, Haggagy Mansour, Hoda S. Sherkawy, Shymaa G. Rizk
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):704-717. Published online November 27, 2024
-
Question: Is the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathway (TNF-α-converting enzyme [TACE]/TNF-α/angiotensin converting enzyme [ACE]) involved in pediatric coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection?
Finding: Significantly increased circulating TACE/TNF-α and decreased ACE2 levels were noted. TNF-α-308G/A plays a significant role in susceptibility to COVID-19 infection among children. The ACE (I/D) (rs4646994) and ACE2 (rs2285666) single nucleotide polymorphisms lack significant associations with pediatric COVID-19 infection.
Meaning: The TNF signaling pathway participates in pediatric COVID-19 infection.
- General Pediatrics
- Role of proper postnatal care in continued exclusive breastfeeding among young Indonesian mothers
- Wahyu Triadmajani, Shinta Prawitasari, Abdul Wahab
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):686-693. Published online September 12, 2024
-
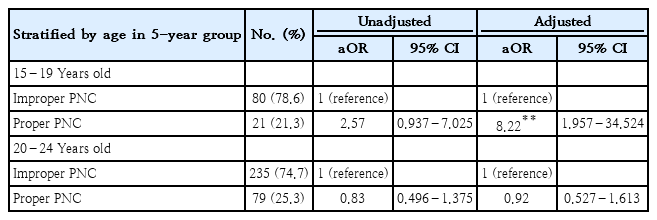
Question: Is proper postnatal care (PNC) associated with exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) practice among young Indonesian mothers?
Finding: Proper PNC elevates the likelihood of EBF among Indonesian adolescent mothers aged 15–19 years.
Meaning: Breastfeeding services should be provided during the early postnatal period to support EBF practice among adolescent mothers. High-quality PNC is a tailored intervention for vulnerable populations.
- Nonpharmacological interventions for managing postoperative pain and anxiety in children: a randomized controlled trial
- Edlin Glane Mathias, Mamatha Shivananda Pai, Vijay Kumar, Dinesh Narayanakurup, Malavika Kulkarni, Vasudeva Guddattu, Ann-Cathrine Bramhagen, Baby S Nayak, Anice George
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):677-685. Published online October 31, 2024
-
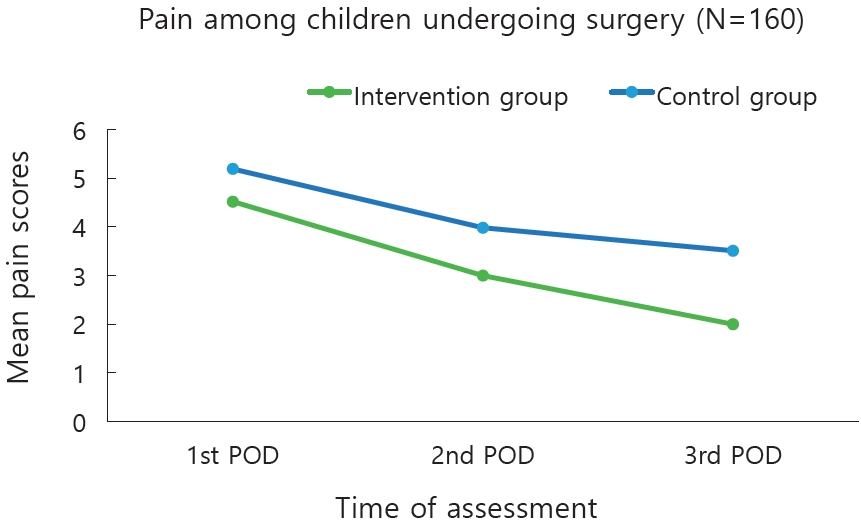
Question: What is the effect of nonpharmacological interventions on postoperative pain and anxiety among children.
Finding: Nurse-provided distraction interventions reduce pain and anxiety among pediatric surgical patients.
Meaning: The findings suggest that nonpharmacological interventions provided postoperatively to children reduce their pain and anxiety levels.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Advancements in food allergen immunotherapy: improving quality of life and reducing risks
- Jihyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):672-674. Published online July 31, 2024
-
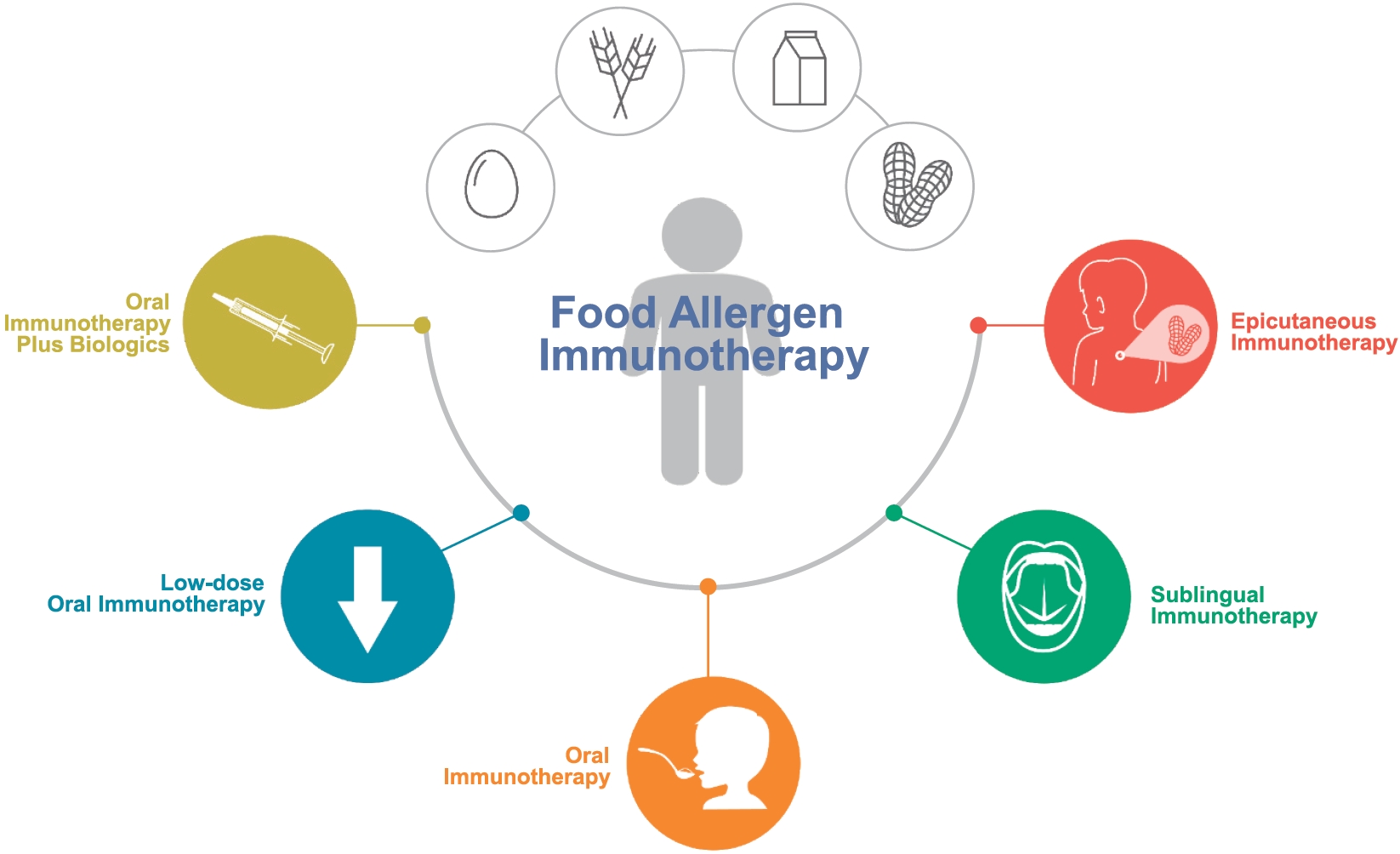
· Pediatric food allergies considerably impair patient and family quality of life, particularly those with persistent allergies to common food allergens.
· Recent research has focused on developing diverse approaches to food allergen immunotherapy, showing promising outcomes of oral, sublingual, and epicutaneous immuno therapies.
· Critical considerations in immunotherapy candidate selection underscore the need for personalized approaches and reliable biomarkers in future studies to improve treatment outcomes.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Screen time among preschoolers: exploring individual, familial, and environmental factors
- Sangha Lee, Donghee Kim, Yunmi Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):641-650. Published online September 12, 2024
-
This systematic review examined the correlation between screen time and various factors in preschoolers. Findings suggest that media parenting, including setting appropriate media limits, is crucial in protecting against excessive screen exposure. However, limited research has been done on the impact of family and personal factors, particularly with the increasing use of portable devices among young children.
- Rheumatology
- Double-negative T cells in pediatric rheumatic diseases
- Dimitri Poddighe, Tilektes Maulenkul, Kuanysh Dossybayeva, Gulsamal Zhubanova, Zaure Mukusheva, Lyudmila Akhmaltdinova
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):632-640. Published online September 12, 2024
-
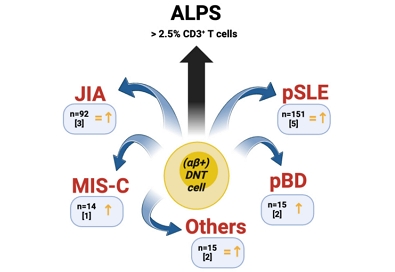
Double-negative T (DNT) cells appear to be increased in several pediatric rheumatic diseases and this finding may be correlated with disease activity to some extent. However, due to significant heterogeneity in several methodological aspects, further investigations in rheumatic children are needed to assess the potential relevance of DNT cells as biomarkers and clarify their immunopathological role.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Mortality of very low birth weight infants by neonatal intensive care unit workload and regional group status
- Sung-Hoon Chung, Chae Young Kim, Yong-Sung Choi, Myung Hee Lee, Jae Woo Lim, Byong Sop Lee, Ki-Soo Kim; the Korean Neonatal Network
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):619-627. Published online September 12, 2024
-

Question: How do structural and staffing characteristics of neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) influence the mortality rates of very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs)?
Findings: NICUs with higher staffing levels, particularly with more neonatologists, and those offering advanced care levels were associated with lower mortality rates. Additionally, regional disparities were observed, with some areas demon-strating significantly higher survival rates.
Meaning: Adequate staffing and equitable regional distribution of medical resources are crucial for improving survival outcomes in VLBWIs. Efforts to enhance NICU staffing and address regional healthcare disparities are essential for optimizing care quality and reducing mortality in this vulnerable population.
- Pulmonology
- Efficacies of different treatment strategies for infants hospitalized with acute bronchiolitis
- Hyeri Jeong, Dawon Park, Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Jeewon Shin, Hey-Sung Baek, Hyunsoo Hwang, Youn Ho Shin, Hye Mi Jee, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):608-618. Published online October 28, 2024
-

· This study analyzed 45 randomized controlled trials (5,061 participants, 13 interventions) of the comparative efficacies of treatments for acute bronchiolitis in infants.
· Inhalation therapy with epinephrine and hypertonic saline significantly reduced the length of hospital stay compared with normal saline.
· Hypertonic saline had the greatest ability to improve the clinical severity score of bronchiolitis in infants younger than 2 years of age.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Lifelong medical challenges and immunogenetics of Turner syndrome
- Won Kyoung Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):560-568. Published online July 31, 2024
-
· This summary emphasizes the importance of the early diagnosis of Turner syndrome (TS) and presents a multidisciplinary approach to its prevention and management, high-lighting the need for customized care.
· Advancements in immunogenetic research may improve our understanding of TS and improve its outcomes.
· TS encompasses a wide array of medical challenges, including cardiovascular, endocrine, autoimmune, and mental health issues, as well as a heightened cancer risk.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents: prevalence and associated factors
- Jee-Seon Shim, Jeong Mi Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):531-539. Published online September 24, 2024
-

Question: How prevalent is energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents and what are the associated factors?
Findings: The prevalence of energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents increased from 3.2% in 2014 to 12.2% in 2019. Energy drink consumption varies according to sociode-mographic and individual factors.
Meaning: Policies and educational strategies are needed to reduce energy drink consumption in adolescents.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effect of pesticide exposure on stunting incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Yaltafit Abror Jeem, Muhammad Fathi Banna Al Faruqi, Mahdea Kasyiva, Vita Widyasari, Kuswati Kuswati, Nur Aini Djunet, Muflihah Rizkawati, Ety Sari Handayani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):510-518. Published online September 24, 2024
-

This review aimed to determine whether pesticide exposure is associated with stunting in children. The 13 included studies agree that pesticide exposure is not correlated with stunting incidence regardless of substance type (organophosphate and pyrethroid). Heterogeneity appeared with age covariate as potential confounding. The evidence of this study is challeng-ing, as the adverse effects of pesticides grossly occurred. The protection of children is warranted for preventing future neurodevelopment issues.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Demographic transition in South Korea: implications of falling birth rates
- Chae Young Kim, Sung-Hoon Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):498-509. Published online June 27, 2024
-

· Since 1960, South Korea's TFR decreased from 6.33 to 0.78 in 2022, below the 2.1 replacement level since 1983, with women's average age at first marriage rising to 31.3 in 2022.
· Policies needed: financial incentives, longer parental leave, better childcare.
· The U.S. (15.3% immigrants) and Germany (18.8%) use immigration to maintain demographic stability, a strategy South Korea is considering.
- Allergy
- Skin and oral intervention for food allergy prevention based on dual allergen exposure hypothesis
- Kiwako Yamamoto-Hanada, Yukihiro Ohya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):477-485. Published online June 14, 2023
-

To prevent food allergy in infants, based on the dual allergen exposure hypothesis, we recommend a personalized approach consisting of both skin intervention (eczema treatment to achieve early remission and well-controlled skin without eczema to prevent percutaneous immunoglobulin E sensitization) and oral intervention (early allergenic food introduction).
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Neonatal risk factors associated with autism spectrum disorders: an umbrella review
- Amir Mohammad Salehi, Erfan Ayubi, Salman Khazaei, Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Zohreh Salimi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):459-464. Published online July 19, 2024
-

Question: What are the neonatal risk factors for autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Findings: Significant effect sizes were observed for congenital heart disease (odds ratio [OR], 1.35), macrosomia (OR, 1.11), low birth weight (OR, 1.63), very low birth weight (OR, 2.25), small for gestational age (OR, 1.17), jaundice (OR, 1.74), male sex (OR, 1.47), and Apgar score (OR, 1.40).
Meaning: These factors were identified as risk factors for ASD.
- Infection
- Construction and validation of predictive models for intravenous immunoglobulin–resistant Kawasaki disease using an interpretable machine learning approach
- Linfan Deng, Jian Zhao, Ting Wang, Bin Liu, Jun Jiang, Peng Jia, Dong Liu, Gang Li
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):405-414. Published online July 23, 2024
-

Question: Is there a reliable model to predict intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)-resistant Kawasaki disease (KD)?
Finding: We constructed 5 machine learning models to predict IVIG-resistant KD. Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) model was superior to logistic, support vector machine, light gradient boosting machine and multiple layers perception models. The SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) value interpreted the contribution of each feature in XGBoost model.
Meaning: XGBoost model showed the excellent performance to predict IVIG-resistant KD with explainable and visualizable machine learning algorithm.
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Effects of diethylene glycol contamination of pharmaceutical products on unexplained acute kidney injury in children: a systematic review
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Muhammad Luthfi Adnan, Hilmi Ardian Sudiarto, Satria Bintang Mahathma, Alya Ayu Tazkia, Hana Afifah Firdaus, Alfreda Amelia Khotijah, Miranti Dewi Pramaningtyas, Emi Azmi Choironi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):395-402. Published online January 4, 2024
-

A recent unexplained acute kidney injury (AKI) outbreak due to pharmaceutical product contamination with diethylene glycol (DEG) raises public attention. Our study revealed that DEG-contaminated paracetamol causes unexplained AKI in children. However, paracetamol is not the only contaminated drug. Other drugs, such as cough expectorants, antihistamines, and sedatives, can also be affected. Other chemicals, such as ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, can also contribute to poisonings.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Parental support and exclusive breastfeeding at 3 months in West Java, Indonesia: a mixed-methods approach
- Ratu Ayu Dewi Sartika, Fadila Wirawan, Wawan Gunawan, Primasti Nuryandari Putri, Nurul Husna Mohd Shukri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):358-367. Published online June 21, 2024
-
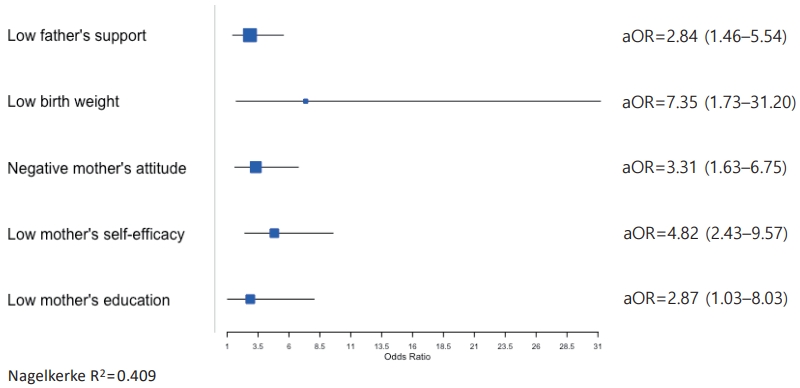
Question: Does paternal support affect exclusive breastfeeding failure?
Finding: Exclusive breastfeeding failure by 3 months was affected by paternal support.
Meaning: Fathers should be included in breastfeeding education and antenatal care.
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











