Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last six months.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Efficacy of leuprolide acetate versus triptorelin pamoate administered every 3 months for treatment of central precocious puberty (35 times)
- Thanaporn Thaneetrakool, Suphab Aroonparkmongkol, Nattakarn Numsriskulrat, Vichit Supornsilchai, Suttipong Wacharasindhu, Khomsak Srilanchakon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):91-96. Published online November 6, 2024
-

Question: What are the differences in efficacy between leuprolide acetate and triptorelin pamoate administered every 3 months for the treatment of central precocious puberty (CPP)?
Finding: There were no significant intergroup differences in luteinizing hormone suppression or predicted adult height at the end of treatment in girls with CPP.
Meaning: Leuprolide acetate and triptorelin pamoate have comparable efficacy for treating CPP.
- Editorial
- Other
- Further research on impact of microplastics on children's health is essential to protecting future generations (34 times)
- Jongin Lee, Dong-Wook Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):359-361. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· The ecological impacts of microplastics have been documented. It was recently recognized that they can directly or indirectly cause diseases in humans.
· There are few established methods for assessing human exposure to microplastics.
· Standardization of exposure assessments and large-scale epidemiological studies are required to explore the human effects of microplastics.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Efficacy and safety of carbon dioxide versus room-air insufflation in pediatric colonoscopy: a randomized controlled trial (34 times)
- Ajay Aravind, Ujjal Poddar, Anshu Srivastava, Moinak Sen Sarma
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):594-600. Published online March 11, 2025
-
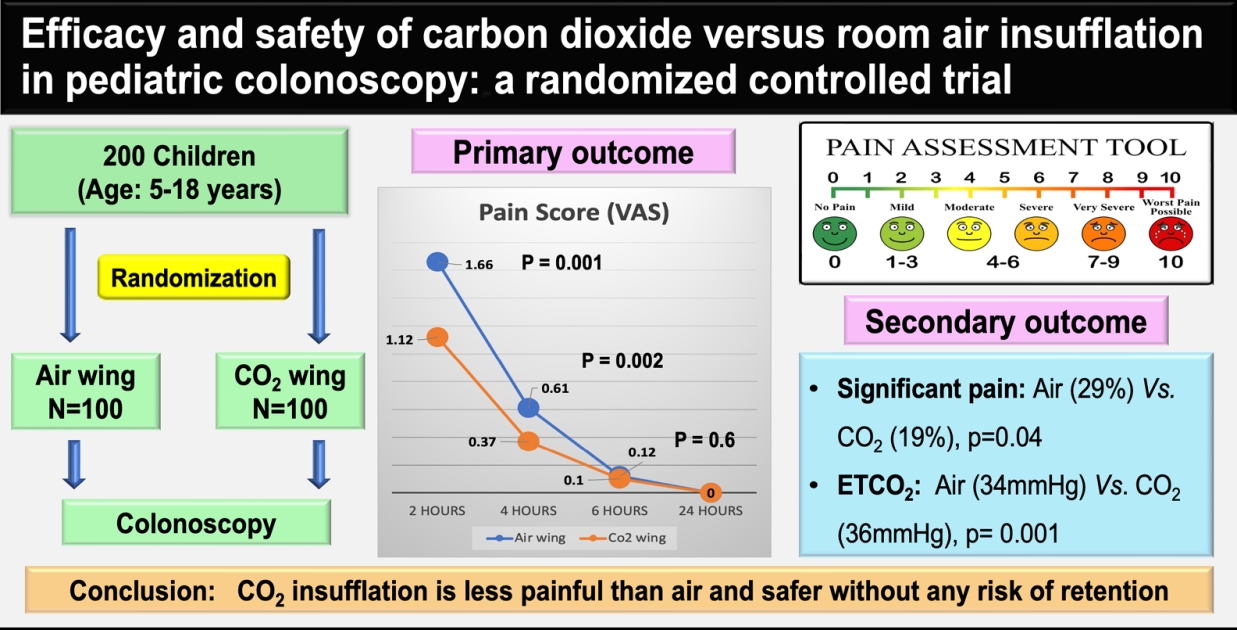
CO2 insufflation has been used instead of air insufflation to reduce postprocedure pain and discomfort in adults; however, adequately powered studies in children are scarce. This randomized controlled trial of 200 children showed that CO2 insufflation reduces postprocedure pain and discomfort during pediatric colonoscopy with no signs of CO2 retention. CO2 insufflation is safe and causes less pain in children.
- Editorial
- Infection
- Beyond COVID-19: meeting the challenge of evolving pediatric invasive group A streptococcal disease (34 times)
- Han Wool Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):971-973. Published online November 26, 2025
-
Pediatric for invasive group A Streptococcus has resurged globally with increasing severity and toxin-mediated presentations. Beta-lactams remain the first-line treatment, but linezolid has emerged as a safe alternative in cases refractory to β-lactams. Early intravenous immunoglobulin use may improve outcomes in severe streptococcal toxic shock syndrome cases, while C-reactive protein and procalcitonin aid early risk stratification. Integrating global surveillance and individualized therapy is crucial in the postpandemic era.
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Assessment of natural killer cell subpopulations in pediatric patients with transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia major (34 times)
- Fathia Ibrahim Elbassal, Mohamed Abdel Rehim Soliman, Nourhan Hossam Eldin Mohamed, Mai El-Sayad Abd El-Hamid, Hanan Hassan El-Sheity
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):981-990. Published online September 12, 2025
-
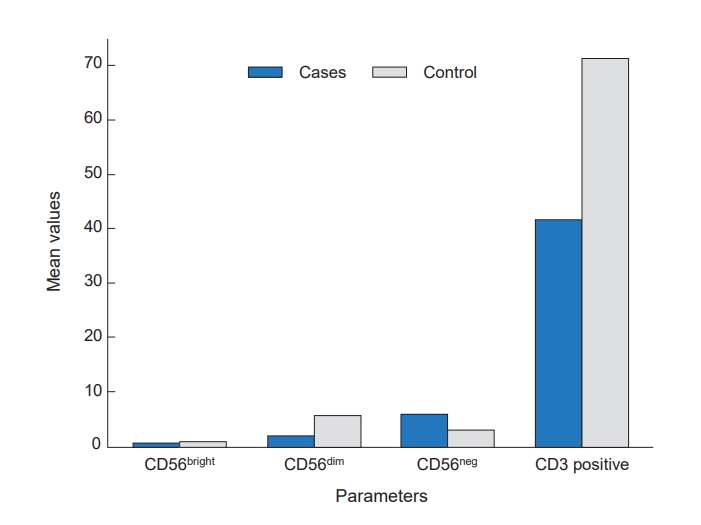
Question: How does iron overload affect immunity in pediatric patients with transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia major?
Finding: Iron overload in these patients is associated with disrupted natural killer (NK) cell subpopulations, reflecting impaired innate immunity.
Meaning: This highlights the need to monitor immune profile alongside iron status during thalassemia management.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Influence of infant microbiome on health and development (33 times)
- Noelle Younge
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):224-231. Published online August 21, 2023
-

· The infant gut microbiome is highly dynamic and individualized.
· Microbes are vertically transmitted from mother to infant during delivery and throughout infancy.
· Delivery mode, gestational age, diet, and antibiotic use influence infant microbiome composition and function.
· In animal studies, the microbiome played critical roles in the structural and functional development of the infant gastrointestinal and immune systems.
· Microbiome-targeted therapies have great potential to reduce infant morbidity and mortality.
- Neurology
- Role of nonpharmacological concussion management in children: systematic review of randomized controlled trials (33 times)
- Andre Marolop Pangihutan Siahaan, Alvin Ivander, Rr. Suzy Indharty, Steven Tandean, Anastasia Grace Milenia Ginting, Masrini Ginting, Felix Khosasi, Elbert
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):569-579. Published online October 28, 2024
-

The long-term effects of concussion for pediatric patient remains unclear. Children and teenagers do not experience or recover from concussion in the same manner as adults do. Concussions can cause a variety of anatomical and functional alterations. Nonpharmacological approach in pediatric concussion management is an understudied field of research with significant ability to affect prognosis and quality of life. Active rehabilitation and occupational therapy were especially promising.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Clinical characteristics and associated factors of pediatric acute necrotizing encephalopathy: a retrospective study (33 times)
- Huiling Zhang, Yilong Wang, Qianyun Ding, Xuekun Li, Sheng Ye
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):153-162. Published online November 11, 2024
-
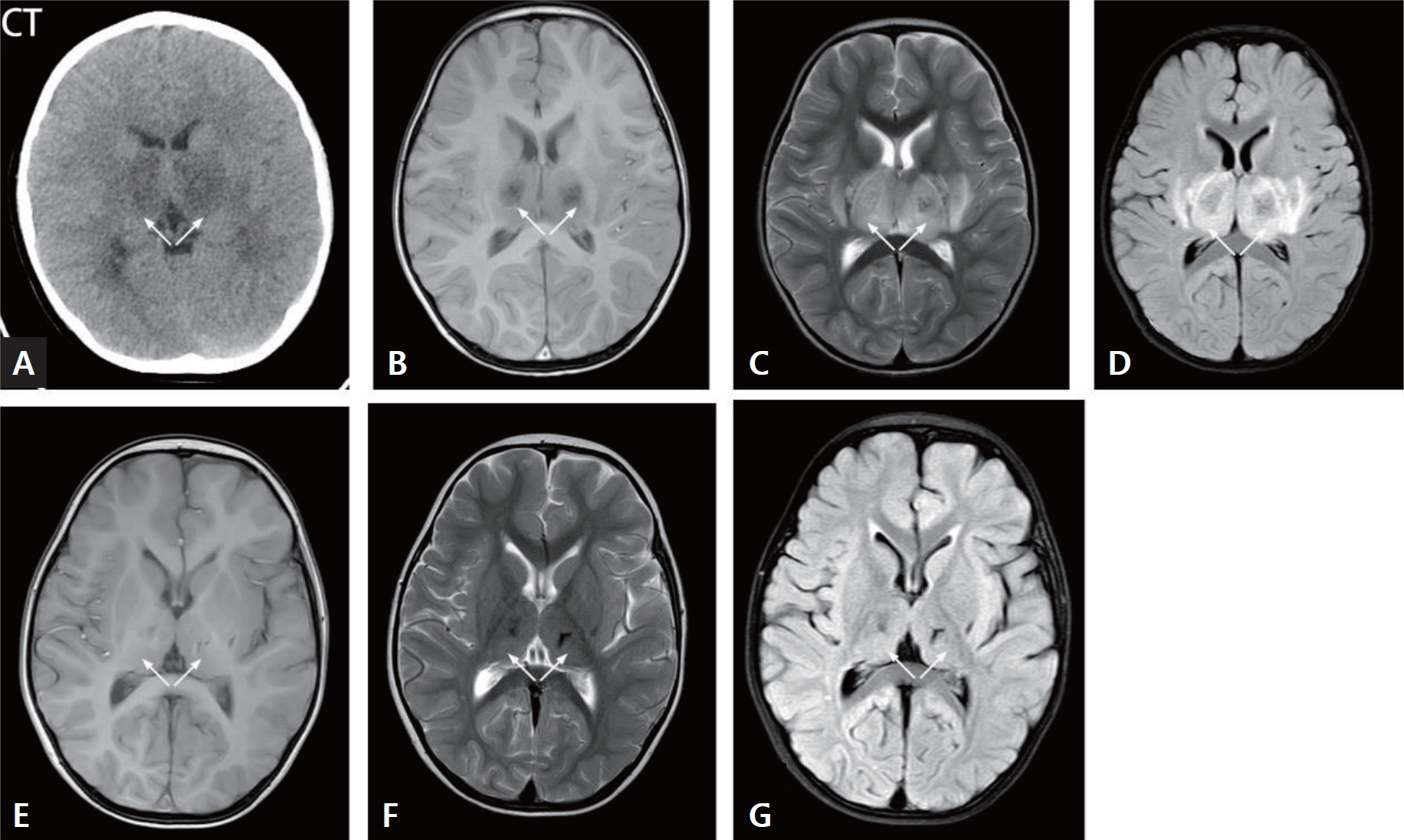
· The mortality rate of acute necrotizing encephalopathy was high.
· Laboratory tests revealed that the fatal group had higher creatinine, lactate, activated partial thromboplastin time, thrombin time, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, creatine kinase, and D-dimer than survivors.
· The fatal group displayed lower Glasgow Coma Scale scores and arterial pH.
- Review Article
- Other
- Global trends in importance of 24-hour movement behaviors to pediatric health: implications for South Korea (33 times)
- Eun-Young Lee, Reyana Jayawardena, Seiyeong Park, Justin Y Jeon, Yeon-Soo Kim, Mark S. Tremblay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):16-29. Published online November 11, 2024
-

· The 24-hour movement behavior paradigm provides an important framework for future pediatric health promotion efforts.
· Policy priorities should include advancing surveillance and monitoring assessments related to 24-hour movement behaviors, evaluating their implementation in school and government policies, and building preparedness for future pandemics and natural disasters, including climate change, by promoting healthy 24-hour movement behaviors.
· Future research should advocate for the promotion of 24- hour movement behaviors.
- Editorial
- General Pediatrics
- Global breastfeeding efforts: a long way to go (33 times)
- Hye-Jung Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):300-302. Published online November 13, 2024
-

· Despite much effort, breastfeeding practices remain unsatisfactory worldwide.
· Effective breastfeeding-promoting interventions are needed that are appropriate for age, culture, and social environment.
· Interventions can promote breastfeeding, especially in younger populations such as adolescent mothers.
- Original Article
- Oncology
- Prognostic role of mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin in predicting infection in pediatric cancer with febrile neutropenia (32 times)
- Seham M. Ragab, Sara Mahmoud El-Deeb, Ahmed Saeed, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):445-453. Published online January 13, 2025
-

· Infection remains a leading cause of death in febrile neutropenia (FN).
· Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-ProADM) levels are higher among patients with FN and a bacterial infection.
· A longer FN duration and hospital stay length as well as elevated C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and MR-ProADM levels are significant risk factors for mortality.
- Editorial
- Basic Research
- Stem cell mining: urine cells to biobanking (32 times)
- Yong Joo Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):761-762. Published online September 24, 2025
-
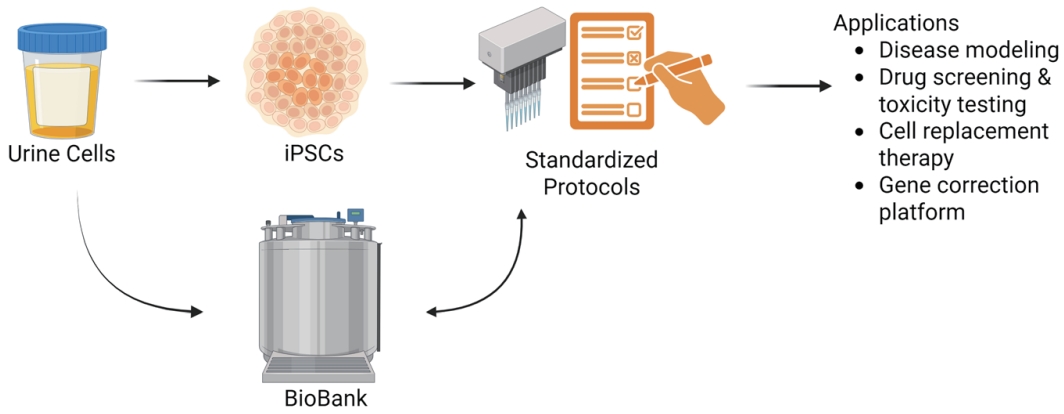
· A safe and accessible source of somatic cell generating induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) in pediatric neurogenic disorders
· A noninvasive and simple method for isolating urine cells, which can effectively reprogram into pluripotent stem cells using episomal vectors
· Establishing a urine-derived iPSC bank as a reliable and scalable resource for disease modeling, therapeutic testing, and personalized medicine in pediatric neurogenic disorders.
- Original Article
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Interleukin (IL)-1B and IL-1 receptor antagonist gene polymorphisms in children with primary immune thrombocytopenia (31 times)
- Seham Mohamed Ragab, Wafaa Moustafa Abo ElFotoh, Mahmoud Ahmed El-Hawy, Eman Abdelfatah Badr, Saara Khairat Ali Mostafa, Mai El-Sayad Abd El-Hamid
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):465-473. Published online July 24, 2024
-

· Polymorphisms in interleukin (IL)-1B and IL-1 receptor (IL-1R) antagonists may significantly affect the pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP).
· IL-1B and IL-1R antagonist gene polymorphisms are correlated with severity and susceptibility to primary ITP in children.
- Long-term follow-up of neurocognitive function in patients with citrin deficiency and cholestasis (31 times)
- Meng-Ju Melody Tsai, Jung-Chi Chang, Heng-Yu Lu, Susan Shur-Fen Gau, Yin-Hsiu Chien, Wuh-Liang Hwu, Yen-Hsuan Ni, Huey-Ling Chen, Ni-Chung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):257-265. Published online November 28, 2024
-
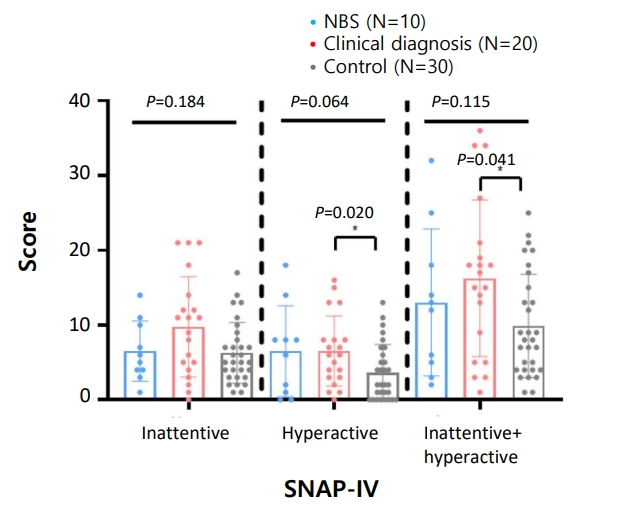
Question: Do transient metabolic disturbances in early childhood due to citrin deficiency have lasting effects on neurocognitive function?
Finding: Children with citrin deficiency have a higher prevalence of ADHD compared to the general population, with elevated ammonia levels in infancy associated with increased hyperactivity-impulsivity risk.
Meaning: Metabolic disturbances in early childhood due to citrin deficiency may contribute to long-term neurocognitive impacts, particularly ADHD, while IQ and life outcomes generally remain normal.
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Advancements and challenges in neonatal resuscitation: embracing laryngeal mask airways for improved outcomes (31 times)
- Jang Hoon Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):298-299. Published online November 28, 2024
-
Positive pressure ventilation (PPV) is the most critical intervention provided during delivery room resuscitation. In the new guidelines, this recommendation has been expanded to suggest the use of laryngeal mask airyway (LMA) versus face masks for PPV. Evidence-based information and hands-on training related to this practice will help more healthcare providers become familiar with and appropriately use LMA during delivery room resuscitations.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Role of miRNA-146a and miRNA-125b in Helicobacter pylori (31 times)
- Nashwa Farouk Mohamed, Ola G.A. Behairy, Manal S. EL-Defrawy, Mona Mahmoud Elsayed, Naglaa F. Alhusseini
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):781-789. Published online April 1, 2025
-
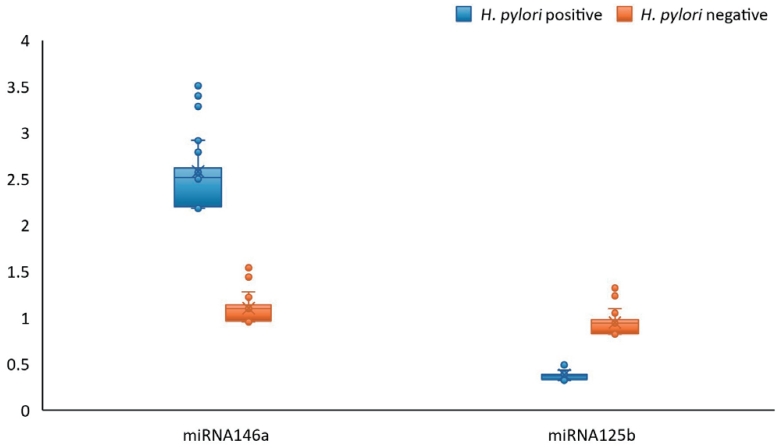
Question: Why is the early detection of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis in children important?
Finding: The early detection of H. pylori-related gastritis is crucial for its effective management, especially in pediatric patients with dyspepsia.
Meaning: The use of miRNA signatures could detect early gastritis, enabling timely H. pylori eradication treatment to mitigate growth delays and cancer risk.
- Letter to the Editor
- General Pediatrics
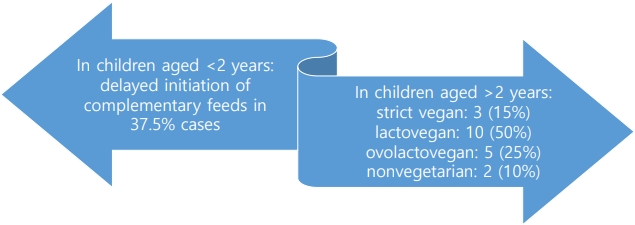
- Vitamin B12 deficiency in anemic children before versus after age 2 years: a form of hidden hunger in India (30 times)
- Sahil Goel, Ruchika Bhatnagar, Anita Kumari, Brig Prem Lochan Prasad, Lahar Sahai
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):116-118. Published online January 24, 2024
-
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Evaluation of pediatric migraine triggers: a single-center study (30 times)
- Hey-Joon Son, Joo-Ok Jin, Kon-Hee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):163-169. Published online November 11, 2024
-
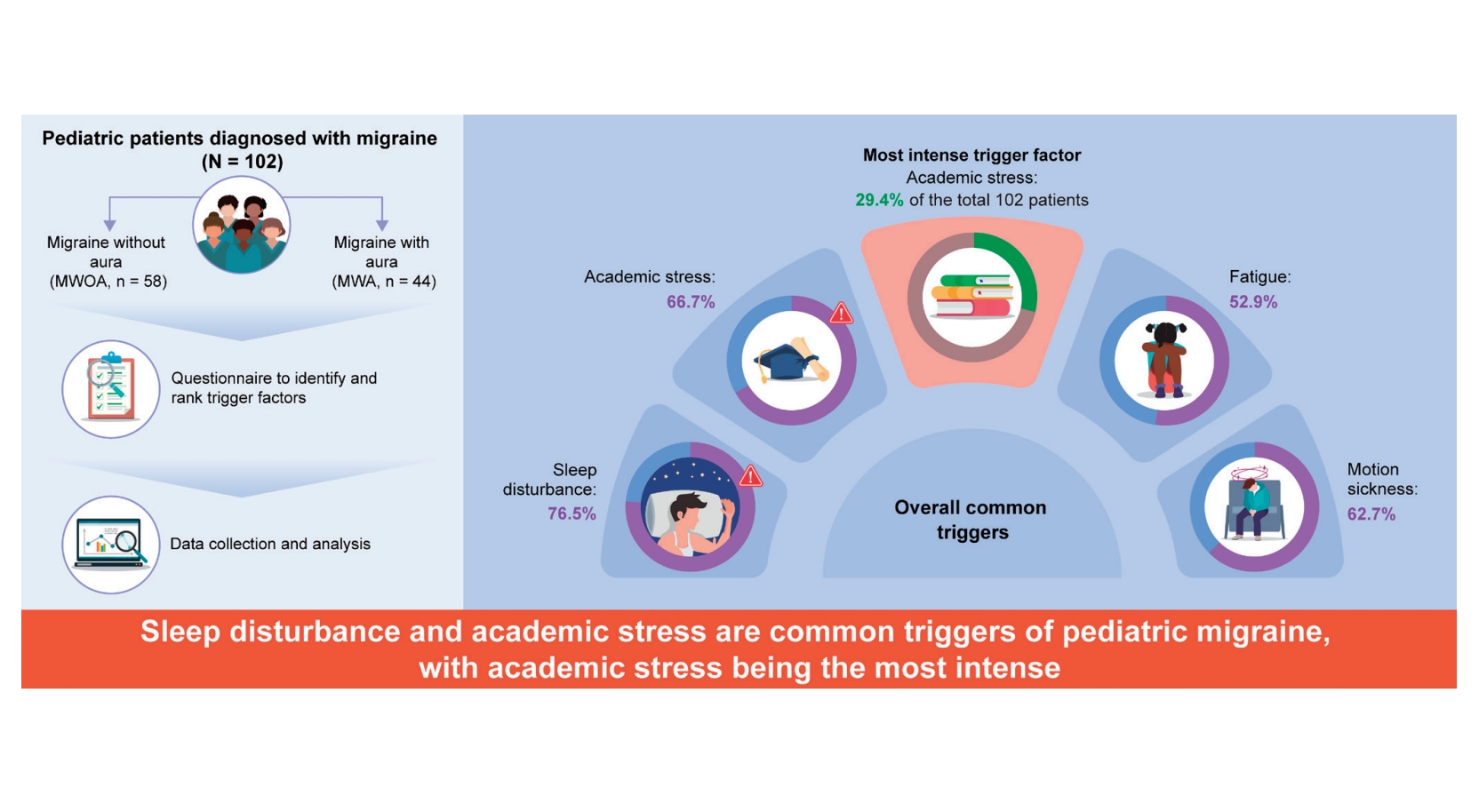
Question: What are the primary triggers for pediatric migraines, and how do they impact clinical management?
Finding: Common triggers for pediatric migraines include sleep disturbances, academic stress, and motion sickness, with academic stress identified as the most intense.
Meaning: Recognizing and addressing specific triggers like sleep disturbance and academic stress is crucial to effectively managing pediatric migraines with emphasis on personalized care to improve outcomes.
- Endocrinology
- Kisspeptin and DLK1 levels for monitoring treatment of girls with central precocious puberty (29 times)
- Witchuwan Onsoi, Nattakarn Numsriskulrat, Suphab Aroonparkmongkol, Vichit Supornsilchai, Khomsak Srilanchakon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):296-302. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Questions: Can the serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 be potential biomarkers for monitoring the treatments for central precocious puberty (CPP)?
Findings: There were no significant differences in the baseline serum kisspeptin and DLK1 levels in CPP girls compared to girls with premature thelarche (PT). After 6 months of GnRH analogue treatment in CPP girls, median serum kisspeptin levels decreased, while median serum DLK1 levels increased compared to baseline.
Meanings: Serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 may serve as novel biomarkers for monitoring the efficacy of treatments for CPP.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Mortality of very low birth weight infants by neonatal intensive care unit workload and regional group status (29 times)
- Sung-Hoon Chung, Chae Young Kim, Yong-Sung Choi, Myung Hee Lee, Jae Woo Lim, Byong Sop Lee, Ki-Soo Kim; the Korean Neonatal Network
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):619-627. Published online September 12, 2024
-

Question: How do structural and staffing characteristics of neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) influence the mortality rates of very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs)?
Findings: NICUs with higher staffing levels, particularly with more neonatologists, and those offering advanced care levels were associated with lower mortality rates. Additionally, regional disparities were observed, with some areas demon-strating significantly higher survival rates.
Meaning: Adequate staffing and equitable regional distribution of medical resources are crucial for improving survival outcomes in VLBWIs. Efforts to enhance NICU staffing and address regional healthcare disparities are essential for optimizing care quality and reducing mortality in this vulnerable population.
- Gastroenterology
- Differences in immune cells and gene expression in human milk by parity on integrated scRNA sequencing (29 times)
- Dae Yong Yi, Hong-Jai Park, Min Sun Shin, Hyoungsu Kim, Sang Jin Lee, Insoo Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):141-152. Published online January 10, 2025
-
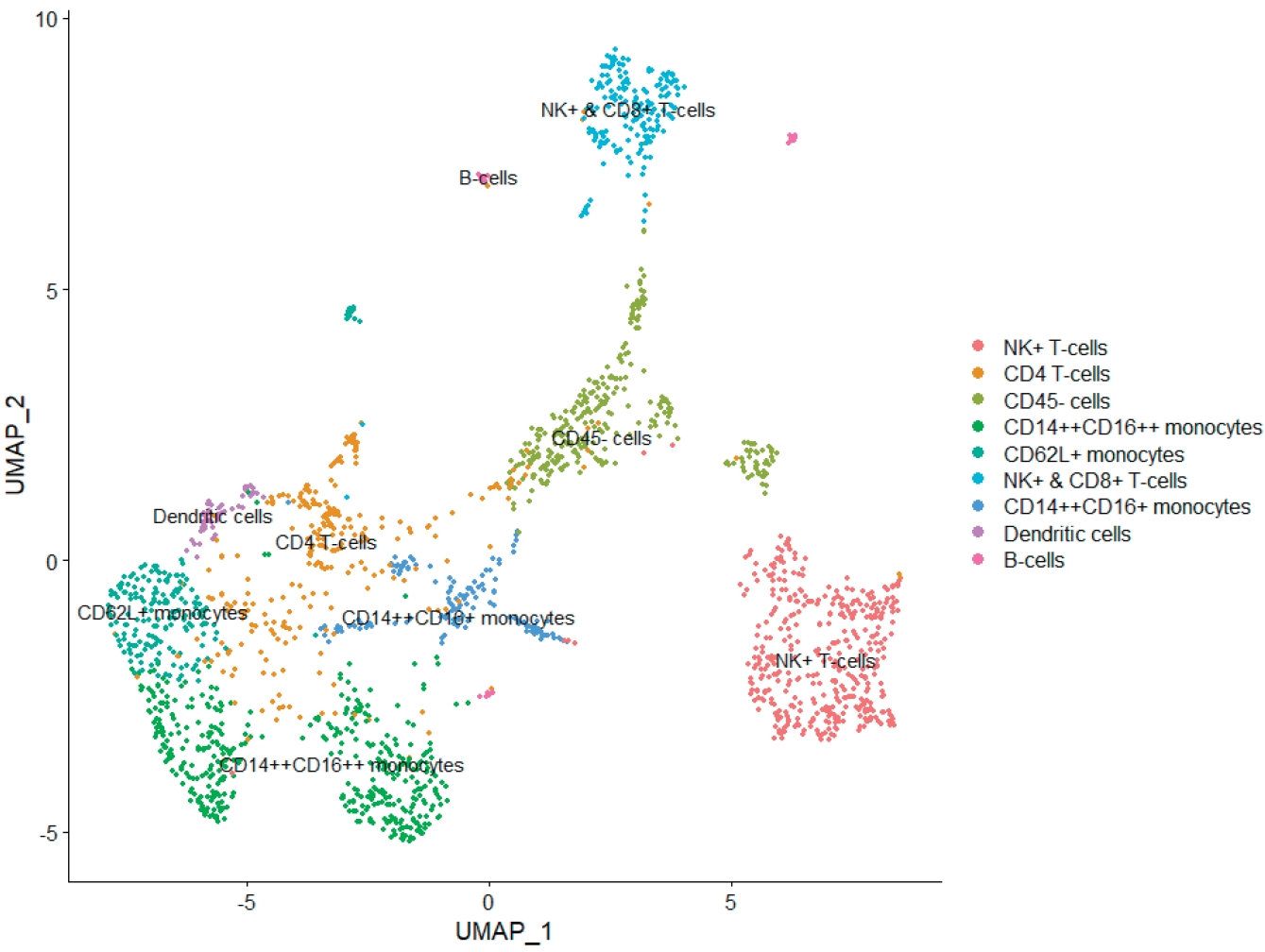
Question: Is there a difference in immune cells in human breast milk by parity?
Finding: There were higher proportions of monocytes and T/B cells in the primiparous and multiparous group, respectively. The expression of genes with a direct role in the infant immune system and immune response-related genes were highest in the primiparous group
Meaning: There were parity-dependent differences in the expression of genes between innate and adaptive immune cells.
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Role of microRNA-498 and microRNA-410 in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (29 times)
- Eman Salah Eldeen Arafat, Hasnaa Hesham Abotaleb, Dina Abdel Razek Midan, Abdel Hamid Abdo Ismail, Zeinab Sabri Abouzouna
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):512-521. Published online February 26, 2025
-

Question: Is it role of microRNA-410 (miRNA-410) and microRNA-498 (miRNA-498) in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)?
Findings: miRNA-498 and miRNA-410 can be auxiliary diagnostic and prognostic tools for neonatal HIE.
Meaning: we can use miRNA-498 and miRNA-410 as markers and indicator for HIE.
- Correspondence
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Authors' reply: a commentary on “COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus” (29 times)
- Karnchanit Sausukpaiboon, Nuanpan Penboon, Pornpimol Rianthavorn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):626-627. Published online July 18, 2025
-
- Guideline
- Infection
- Recommendation for use of 15- and 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines in Korean infants and children (29 times)
- Ki Wook Yun, Dong Hyun Kim, Jong Gyun Ahn, Byung-Wook Eun, Jin Lee, Jina Lee, Taek-Jin Lee, Hyunju Lee, Dae Sun Jo, Eun Young Cho, Hye-Kyung Cho, Soo-Han Choi, Young June Choe, Ui Yoon Choi, Yun-Kyung Kim; The Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):76-83. Published online December 30, 2025
-
Compared to PCV13, PCV15 includes 2 (22F and 33F), and PCV20 includes 7 (8, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B, 22F, and 33F) additional serotypes. The vaccination schedule remains the same: primary doses at 2, 4, and 6 months, and a booster at 12–15 months. If PCV13 was administered in the primary series, PCV15 and PCV20 may be used to complete it or as a booster.
- Review Article
- Nutrition
- Macronutrients modified dietary intervention in the management of overweight/obese children and adolescents: a systematic review (28 times)
- Jihyun Park, Oh Yoen Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):191-200. Published online July 11, 2023
-
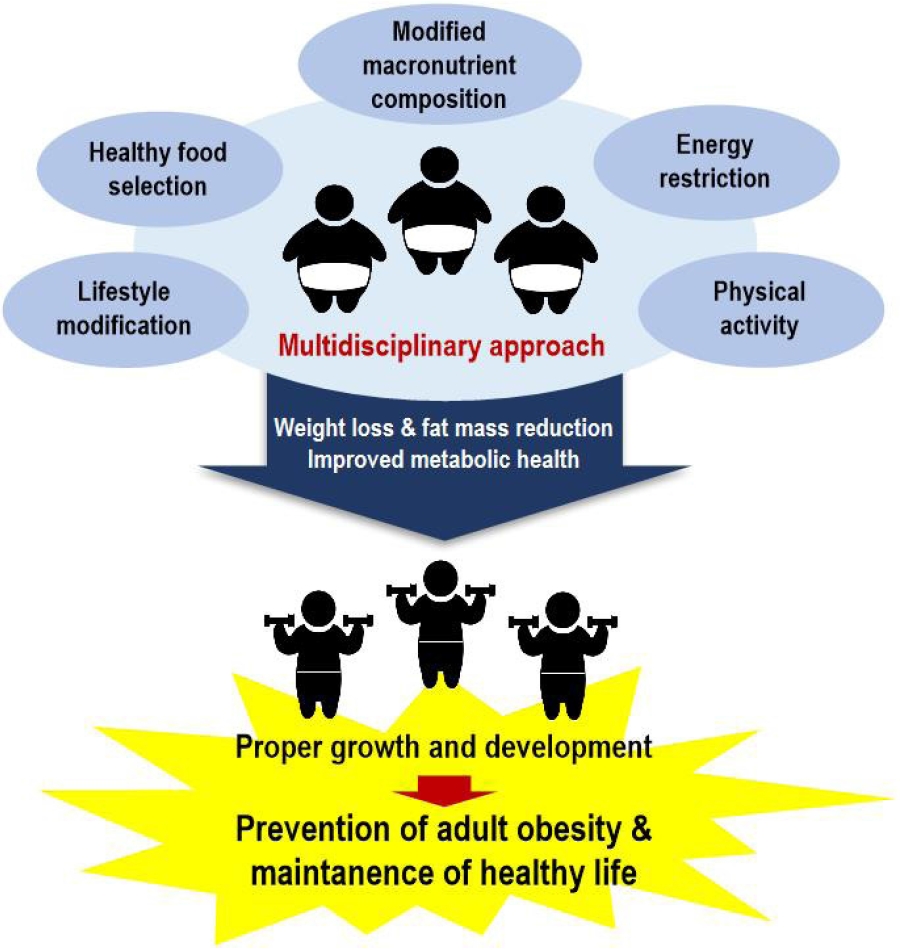
· Dietary macronutrient modifications affect the body composition of and metabolic markers in children and adolescents.
· Hypocaloric diets, regardless of macronutrient composition, are reportedly effective for weight loss in obese children.
· Future interventional studies with meta-analyses that include Korean children and adolescents are needed to provide basic information applicable to this population.
- Neurology
- Cerebral organoid research for pediatric patients with neurological disorders (28 times)
- Jin Eun, Jung Eun Lee, Seung Ho Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):269-277. Published online November 28, 2024
-

Cerebral organoids obtained from human induced pluripotent stem cells are transforming the study of pediatric neurological diseases by providing more accurate models of human brain development and pathology. These advancements have improved pathology modeling and the potential for novel therapeutic approaches despite existing challenges such as reproducibility and vascularization.
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- What we should know about pediatric heart failure: children are not small adults (28 times)
- Ja-Kyoung Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):62-64. Published online November 6, 2024
-
· Pediatric heart failure (PHF) features high morbidity and mortality rates.
· Although adults and children can share a common diagnosis of heart failure, the underlying causes can differ significantly and require distinct therapeutic approaches.
· Treatments designed for adults are often applied to PHF despite the fundamental physiological and developmental differences between them.
· Child-specific data are vital for the development of tailored treatments to meet the unique needs of patients with PHF.
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Instability of revised Korean Developmental Screening Test classification in first year of life (28 times)
- Ji Eun Jeong, You Min Kim, Na Won Lee, Gyeong Nam Kim, Jisuk Bae, Jin Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):97-103. Published online November 11, 2024
-

Question: How stable are the revised Korean Developmental Screening Test score classifications in early infancy?
Finding: A significant number of infants improved into the peer and high-level group (≥-1 standard deviations), especially in the gross motor area.
Meaning: The early detection of developmental delay requires a comprehensive medical history, physical and neurological examinations, and repeated developmental screenings.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effect of pesticide exposure on stunting incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis (27 times)
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Yaltafit Abror Jeem, Muhammad Fathi Banna Al Faruqi, Mahdea Kasyiva, Vita Widyasari, Kuswati Kuswati, Nur Aini Djunet, Muflihah Rizkawati, Ety Sari Handayani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):510-518. Published online September 24, 2024
-

This review aimed to determine whether pesticide exposure is associated with stunting in children. The 13 included studies agree that pesticide exposure is not correlated with stunting incidence regardless of substance type (organophosphate and pyrethroid). Heterogeneity appeared with age covariate as potential confounding. The evidence of this study is challeng-ing, as the adverse effects of pesticides grossly occurred. The protection of children is warranted for preventing future neurodevelopment issues.
- Endocrinology
- Hidden link between endocrine-disrupting chemicals and pediatric obesity (27 times)
- Min Won Shin, Shin-Hye Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):199-222. Published online November 28, 2024
-
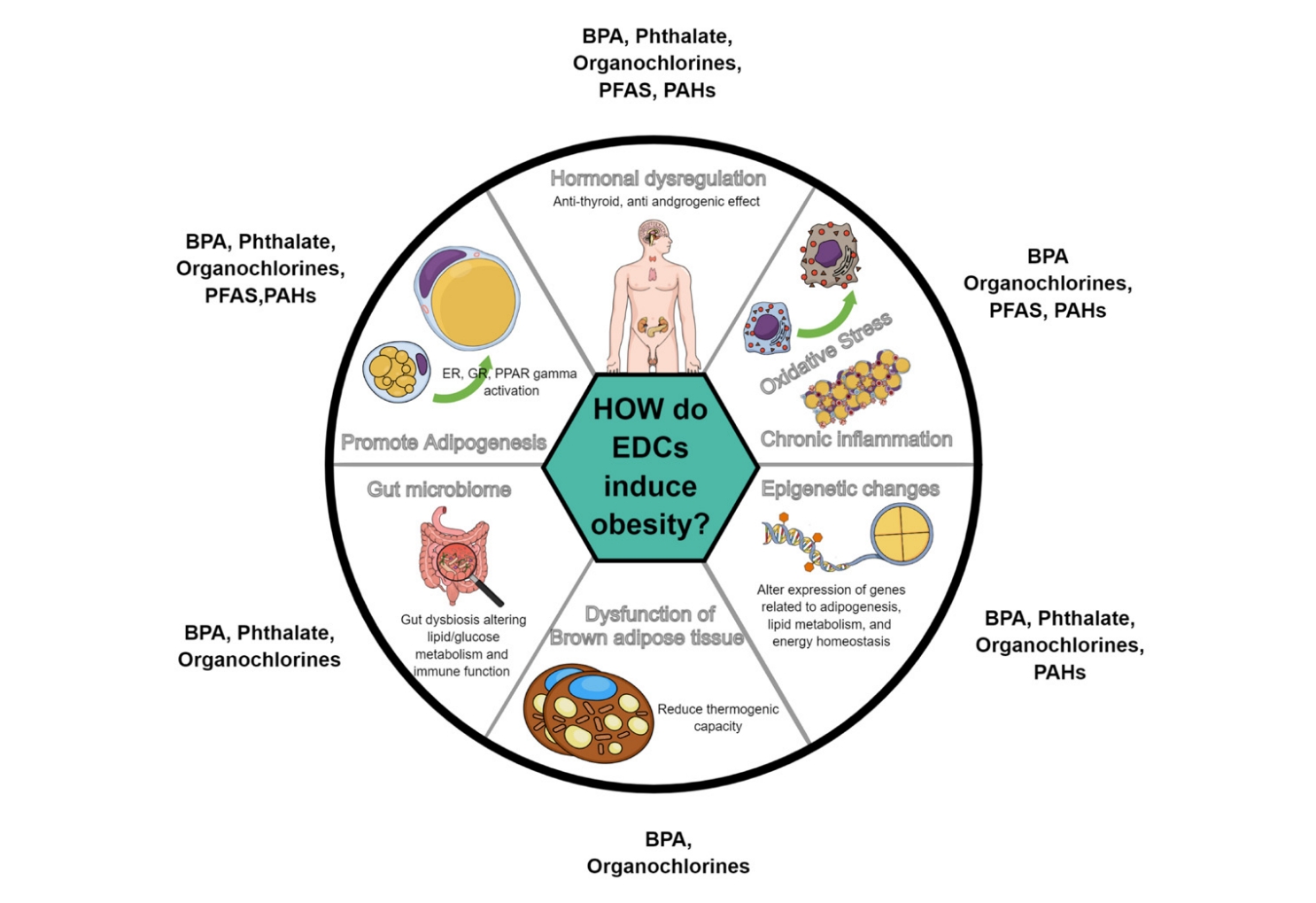
Studies indicate potential connections between exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and childhood obesity. Variations in the impact of EDCs in epidemiological studies may result from differences in exposure concentrations and timing, measurement methods, and interactive effects of multiple EDCs. Longitudinal studies on exposure to multiple EDCs are crucial to elucidating their contribution to pediatric obesity and minimize the adverse health consequences of EDC exposure.
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











