Most cited
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most cited
Most-cited articles are from the articles published during the last two years (2024 ~ ).
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Hidden link between endocrine-disrupting chemicals and pediatric obesity
- Min Won Shin, Shin-Hye Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):199-222. Published online November 28, 2024
-
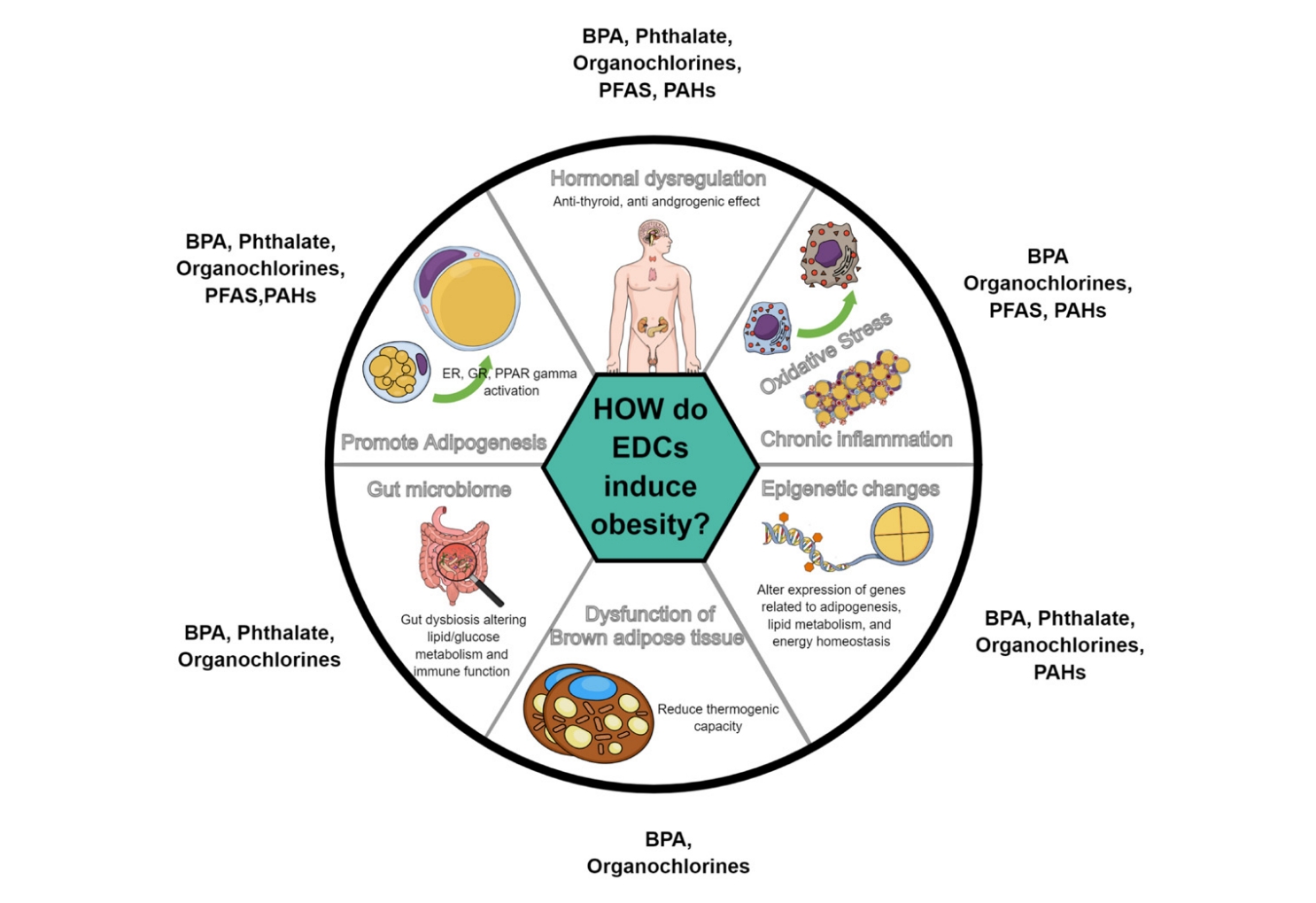
Studies indicate potential connections between exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and childhood obesity. Variations in the impact of EDCs in epidemiological studies may result from differences in exposure concentrations and timing, measurement methods, and interactive effects of multiple EDCs. Longitudinal studies on exposure to multiple EDCs are crucial to elucidating their contribution to pediatric obesity and minimize the adverse health consequences of EDC exposure.
- General Pediatrics
- Prevalence of childhood overweight and obesity in Malaysia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ker Yang Chua, Ker Yung Chua, Karuthan Chinna, Chooi Ling Lim, Maheeka Seneviwickrama
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):115-126. Published online November 13, 2024
-
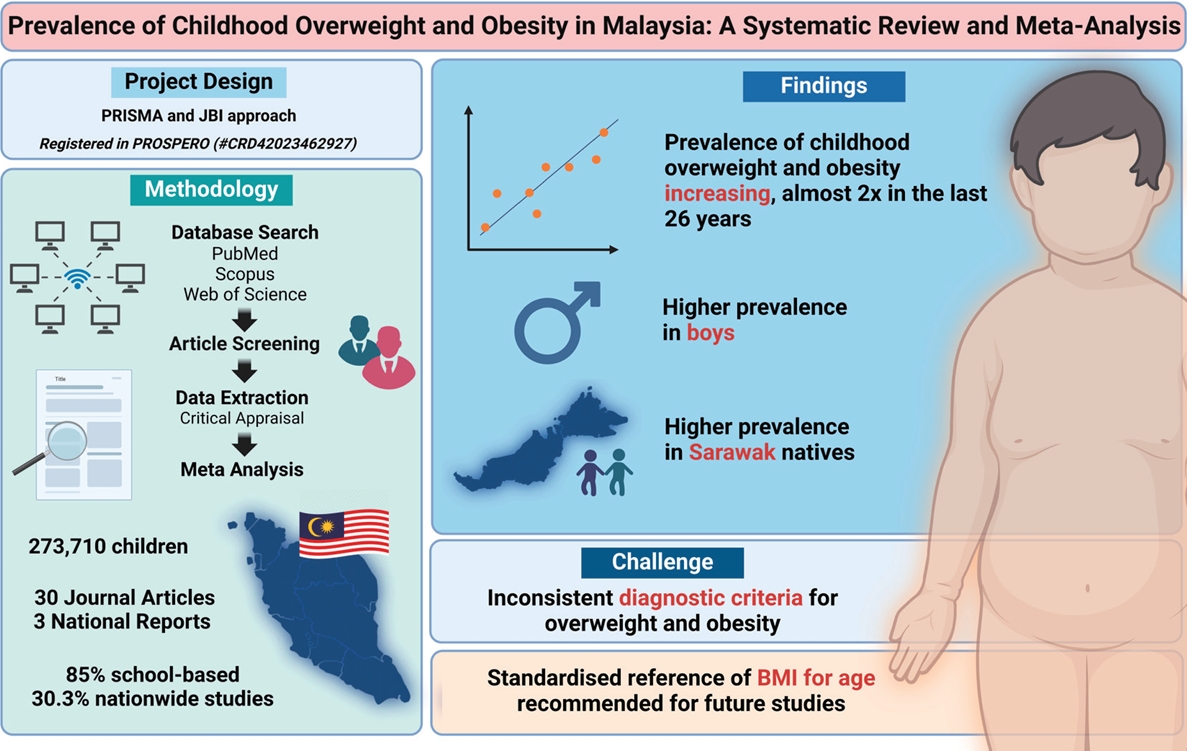
The incidence of childhood obesity is increasing worldwide. National surveys in Malaysia have shown similar trends. This review aimed to increase our understanding of the prevalence and associated factors of childhood overweight, obesity, and excess weight in Malaysia. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted of studies reporting the prevalence of overweight and obesity in Malaysian children aged <18 years....
- Original Article
- Infection
- Evolving treatment strategies for invasive Streptococcus pyogenes in children in the postpandemic era
- Laura Buricchi, Giuseppe Indolfi, Marco Renni, Elisabetta Venturini, Luisa Galli, Elena Chiappini
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):921-931. Published online August 11, 2025
-

Question: What are the roles of linezolid, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), and corticosteroids in pediatric invasive group A streptococcal infection (iGAS)? Can any improve outcomes beyond beta-lactams and clindamycin?
Finding: Two of 46 patients with iGAS died. Nearly all received beta-lactams plus clindamycin. Linezolid was effective in refractory cases. IVIG and corticosteroids had variable efficacies.
Meaning: Linezolid may be valuable in refractory cases. IVIG may be considered in severe presentations. The role of corticosteroids remains less clearly defined.
- Role of miRNA-146a and miRNA-125b in Helicobacter pylori
- Nashwa Farouk Mohamed, Ola G.A. Behairy, Manal S. EL-Defrawy, Mona Mahmoud Elsayed, Naglaa F. Alhusseini
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):781-789. Published online April 1, 2025
-
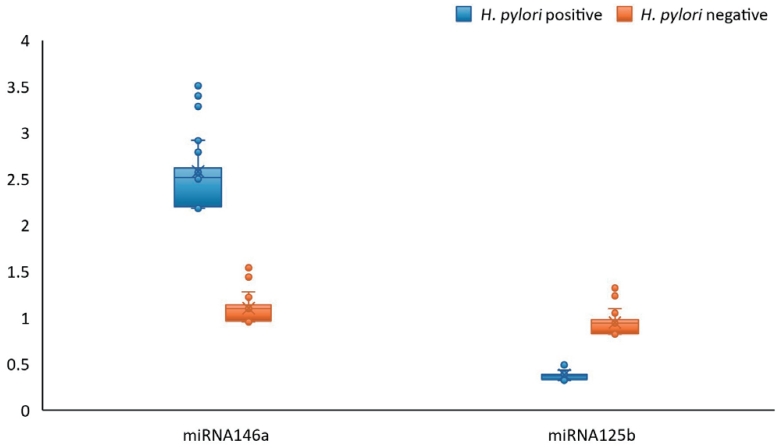
Question: Why is the early detection of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis in children important?
Finding: The early detection of H. pylori-related gastritis is crucial for its effective management, especially in pediatric patients with dyspepsia.
Meaning: The use of miRNA signatures could detect early gastritis, enabling timely H. pylori eradication treatment to mitigate growth delays and cancer risk.
- Hematology
- Hyperhomocysteinemia in pediatric β-thalassemia: links to vitamin cofactor deficiencies and oxidative stress
- Arzu Dadashova, Gunay Aliyeva, Rana Rahimova, Gulnara Azizova, Khayala Mammadova
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):819-830. Published online July 8, 2025
-
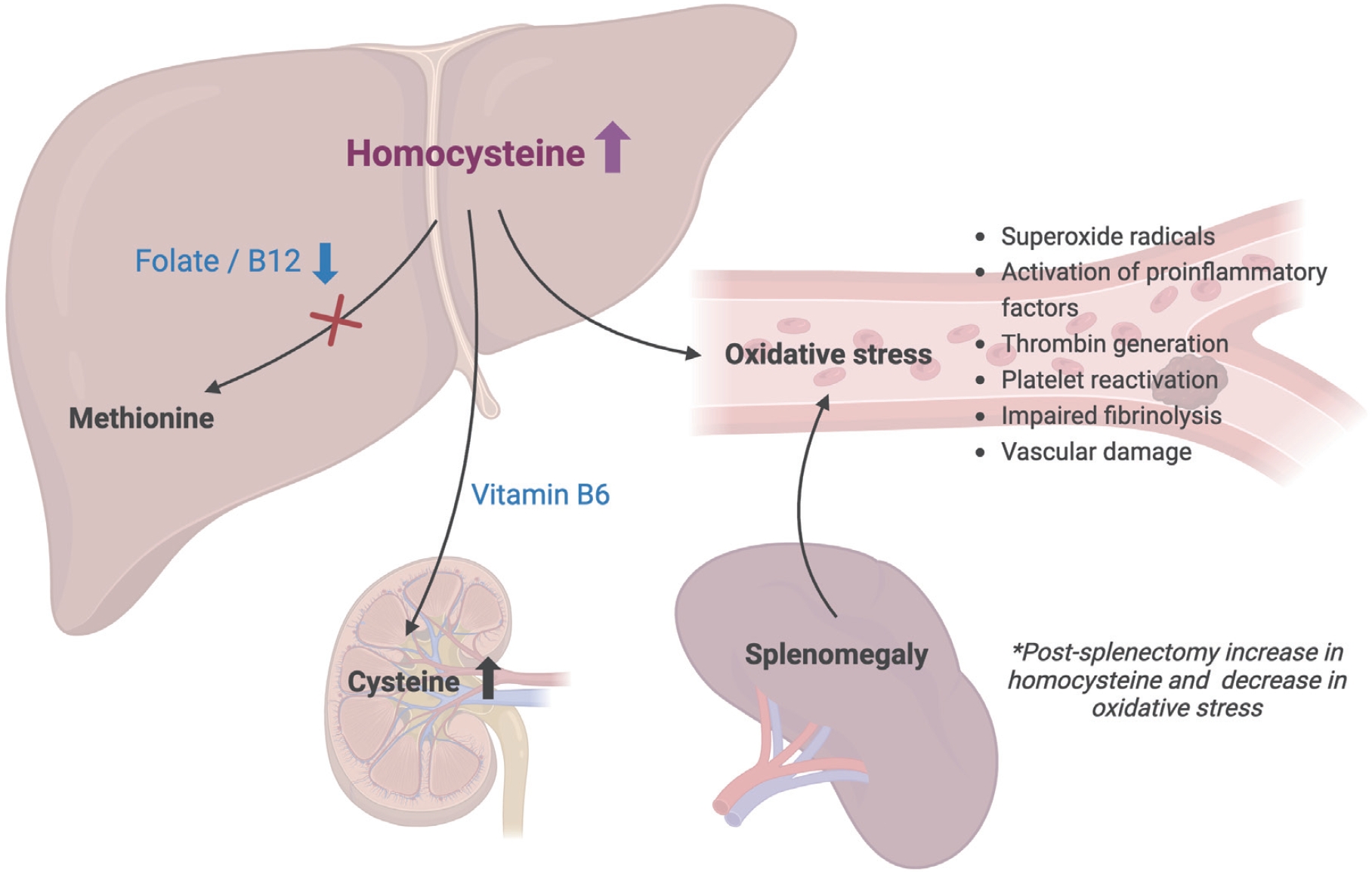
Question: What are the biochemical and clinical correlates of hyperhomocysteinemia in pediatric β-thalassemia, and how does it relate to vitamin status, oxidative stress, and splenectomy?
Finding: Most pediatric β-thalassemia patients exhibited severe hyperhomocysteinemia, which was strongly associated with folate and B12 deficiencies and influenced oxidative stress patterns, particularly in splenectomized individuals.
Meaning: These findings suggest that routine monitoring and correction of B-vitamin deficiencies may mitigate hyperhomocysteinemia-related risks in pediatric thalassemia.
- Infection
- Carbapenem resistance in gram-negative pathogens in an Iranian hospital: high prevalence of OXA-type carbapenemase genes
- Setareh Mamishi, Reihaneh Hosseinpour Sadeghi, Sadaf Sajedi Moghaddam, Babak Pourakbari, Shiva Poormohammadi, Maryam Sotoudeh Anvari, Shima Mahmoudi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):65-72. Published online October 31, 2024
-

Question: What is the prevalence of carbapenem resistance in gram-negative bacteria and associated carbapenemase genes?
Findings: This study identified a notable prevalence of carbapenem-resistant gram-negative isolates, with Escherichia coli being the predominant contributor, follow ed by Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, while bla OXA48 was the most prevalent carbapenemase gene.
Meaning: These findings highlight the urgent need for proactive measures including the rapid detection of carbapenemase- producing isolates and effective infection control.
- Editorial
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Advancing orphan drug development for rare diseases
- Jung Min Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):356-357. Published online November 17, 2023
-
· Rare diseases present unique challenges and unmet needs for which the development of orphan drugs tailored to them offers hope.
· Despite the hurdles posed by limited patient populations, orphan drug designations from regulatory agencies provide incentives, such as extended market exclusivity and tax credits, that ignite transformative advances.
· Scientific progress in genomics, personalized medicine, and analytics empowers precise interventions by decoding genetic anomalies and encouraging effective treatments.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effectiveness of online responsive teaching in young children with developmental disabilities: a pilot study
- Jung Sook Yeom, Jeongmee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):303-311. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Question: Does online responsive teaching (RT) impact children's and parents’ emotions and behaviors, and do parents find it satisfactory?
Finding: Online RT significantly improved children's pivotal and problem behaviors, decreased parenting stress, and enhanced parental interactive styles with high satisfaction.
Meaning: This pilot study's findings suggest that online RT can enhance child outcomes, offering accessible interventions amid challenges such as limited access and pandemics.
- Review Article
- Other
- Children’s health affected by parent’s behavioral characteristics: a review
- Sung Eun Kim, Jongin Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):232-239. Published online August 21, 2023
-

· Parents’ occupational hazards, long working hours, and smoking behaviors should be modified adequately to minimize adverse health effects on their children.
· As of 2023, several diseases from fetal exposure to occupational hazards can be compensated with Industrial Accident Compensation Insurance in South Korea.
· A directed acyclic graph is recommended for medical research to control the effects of parents’ behaviors on children’s health.
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Changes in frequency of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis and their viral causes before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single-center study
- Hyejin Na, Sanghoon Lee, Seo Hee Kim, Young Ok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):213-220. Published online March 19, 2024
-
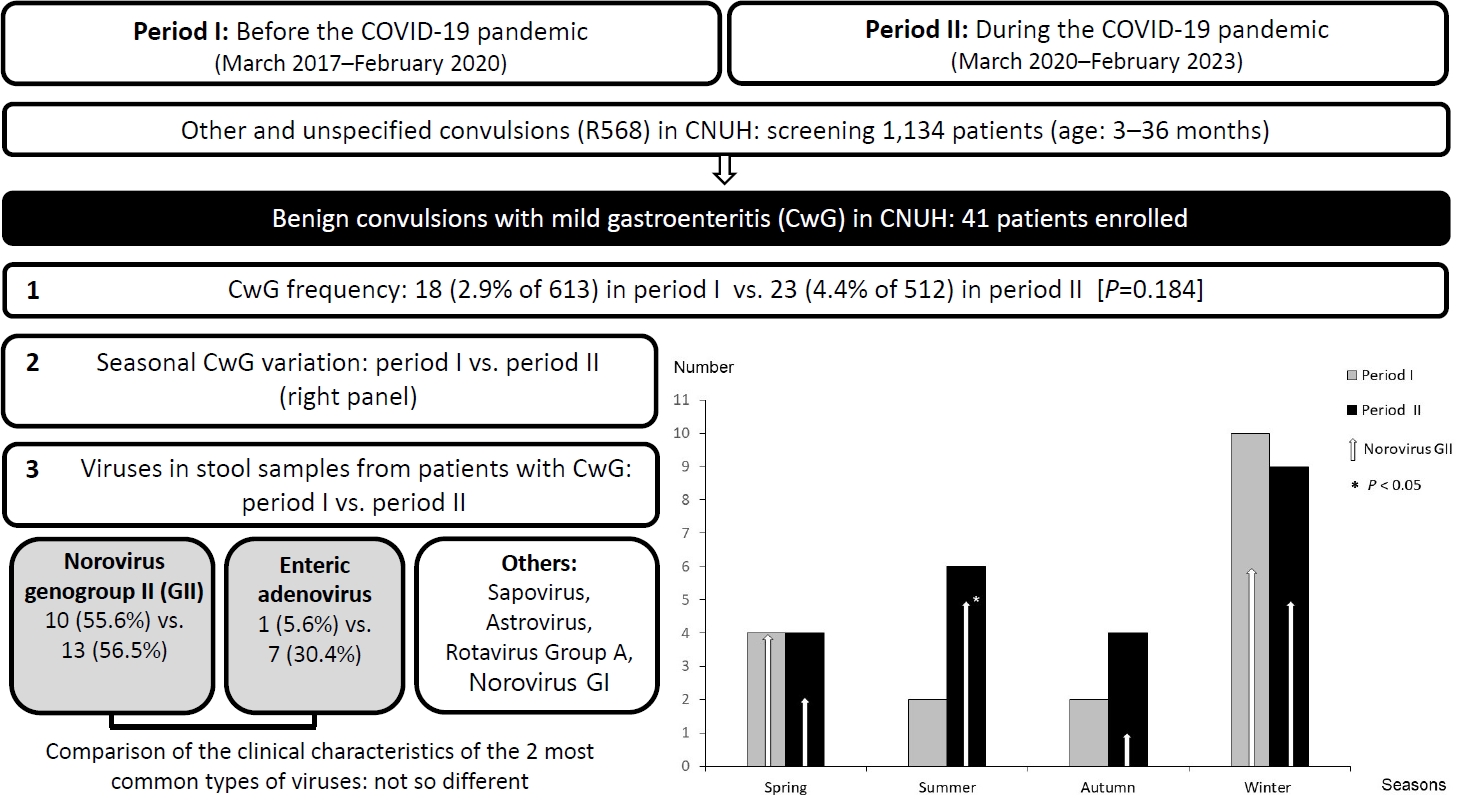
Question: Did coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) affect the frequency, seasonal variation, or virus type of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (CwG)?
Findings: We compared 41 cases of CwG before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. After March 2020, frequency did not change significantly (18 patients vs. 23 patients), seasonal variation was lost, and number of cases of enteric adenovirus-associated CwG increased (1 cases vs. 7 cases).
Meaning: The COVID-19 pandemic affected CwG.
- General Pediatrics
- Nonpharmacological interventions for managing postoperative pain and anxiety in children: a randomized controlled trial
- Edlin Glane Mathias, Mamatha Shivananda Pai, Vijay Kumar, Dinesh Narayanakurup, Malavika Kulkarni, Vasudeva Guddattu, Ann-Cathrine Bramhagen, Baby S Nayak, Anice George
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):677-685. Published online October 31, 2024
-
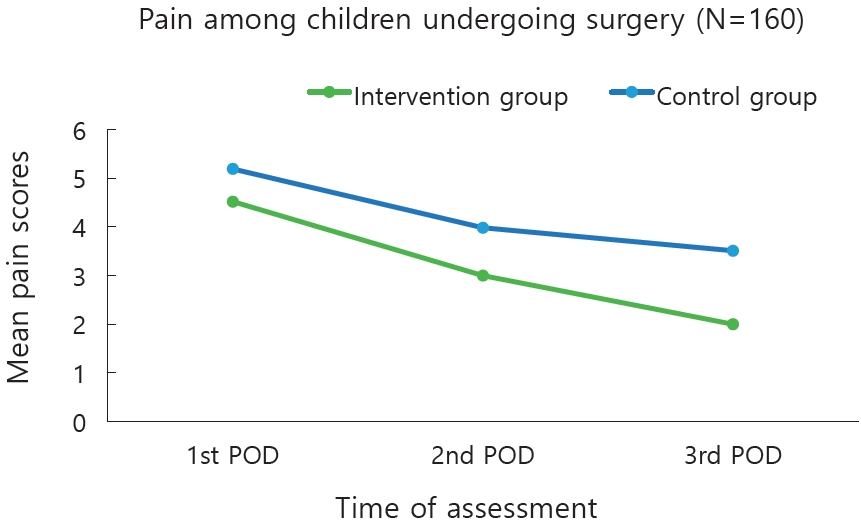
Question: What is the effect of nonpharmacological interventions on postoperative pain and anxiety among children.
Finding: Nurse-provided distraction interventions reduce pain and anxiety among pediatric surgical patients.
Meaning: The findings suggest that nonpharmacological interventions provided postoperatively to children reduce their pain and anxiety levels.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Growth plate closure and therapeutic interventions
- Ja Hyang Cho, Hae Woon Jung, Kye Shik Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):553-559. Published online October 28, 2024
-

Height gains result from longitudinal bone growth. Upon adequate growth, growth plate closure limits longitudinal bone growth. To date, gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs, aromatase inhibitors, C-type natriuretic peptide analogs, and fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 inhibitors have been studied or used as therapeutic interventions to delay growth plate closure and increase human height. The development of more effective therapeutic modalities for short stature, precocious puberty, and skeletal dysplasia is anticipated.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Recent updates on systemic treatment of atopic dermatitis
- Jiyoung Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):580-588. Published online November 1, 2024
-
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a complex disease with multifactorial pathogenesis and variable clinical presentation. Up to one-fifth of patients with AD develop moderate to severe disease that is often refractory to classical therapies and can compromise quality of life. This review summarizes recent clinical evidence on biological agents and small-molecule immunotherapies for the treatment of AD.
- Endocrinology
- Two- versus one-bag fluid delivery in pediatric and adolescent diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Maya L. Nasser, Joseph Nasr, Reem B. Zalloum, Nathanael Q.E. Yap, Natalie E. Bourdakos, Shahid Miangul, Tara A. Betts, Hayato Nakanishi, Christian A. Than, Serge Jabbour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):486-497. Published online June 27, 2024
-

· The safety and efficacy of the two-bag versus one-bag system for treating patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) < 21 years remains unestablished.
· Our meta-analysis demonstrated similar safety outcomes but sooner DKA resolution and shorter mean response time for intravenous fluid changes for the two-bag system.
· This preliminary evidence suggests that the two-bag system has some advantages in efficacy, but further studies are needed to evaluate their extent.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Association of macrophage migration-inhibitory factor gene and growth differentiation factor 15 gene polymorphisms and their circulating levels with respiratory distress syndrome among preterm neonates
- Ali Helmi Bakri, Mohammed H. Hassan, Khaled Abdalla Abd-Elbaseer, Mahmoud Abo-Alhassan Sayed, Ahmed Alamir Mahmoud Abdallah, Eman Ahmed Abd-Elmawgood
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):680-689. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: Do macrophage migration-inhibitory factor (MIF) and growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) levels and their gene polymorphisms affect RDS among preterm babies?
Finding: Significantly higher serum MIF and GDF-15 levels were observed in patients with severe respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). The mutant G- and C-alleles of GDF-15 rs4808793 C>G single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and MIF rs755622 G>C SNP were present at significantly higher frequencies in preterm neonates with RDS.
Meaning: MIF and GDF-15 play a significant role in neonatal RDS and its severity.
- Cardiology
- Vasovagal syncope and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in adolescents: transcranial doppler versus autonomic function test results
- Dong Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):673-679. Published online August 6, 2025
-

Question: Vasovagal syncope (VVS) and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) are representative forms of neurally mediated syncope. What influences the occurrence of each?
Finding: Autonomic function test results did not differ, but cerebral blood flow during diastole on transcranial doppler differed between VVS and POTS.
Meaning: Differences in diastolic cerebral blood flow velocity play an important role in VVS and POTS.
- Neurology
- Establishing an induced pluripotent stem cell bank using urine cells from pediatric patients with neurogenetic diseases
- Hien Bao Dieu Thai, WonWoo Jung, Sol Choi, Woo Joong Kim, JangSup Moon, ByungChan Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):569-577. Published online April 1, 2025
-
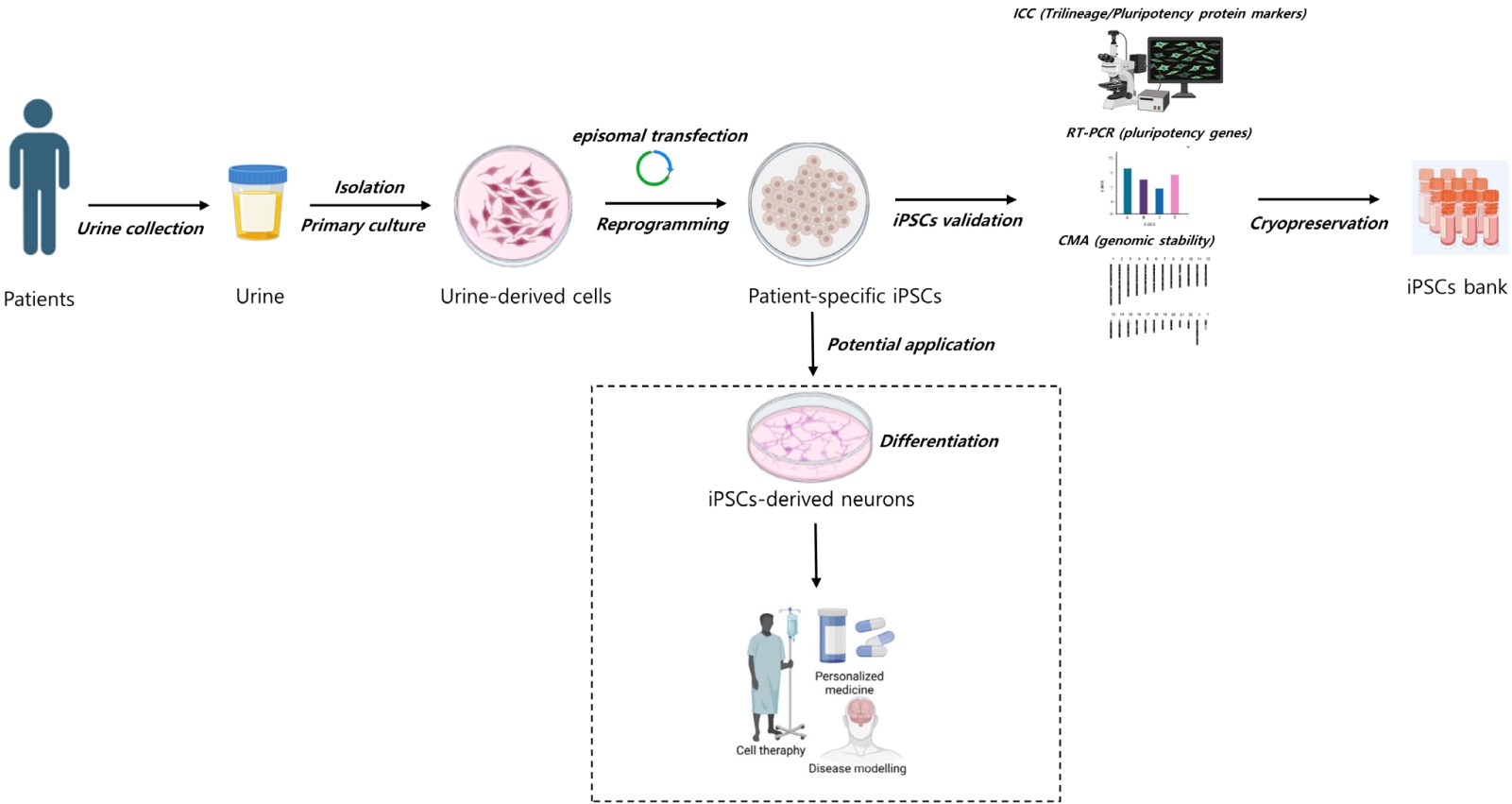
Question: What can be used to create a reliable supply of somatic cells for induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) generation and standardize procedures for building an iPSC bank for researching pediatric neurogenetic disorders?
Findings: Noninvasively acquired urine cells are a desirable cell source for iPSC reprogramming.
Meaning: An iPSC bank can be created from diverse patient cell sources and offer a useful resource for translating research results into clinical therapy for pediatric neurogenetic disorders.
- General Pediatrics
- Liposomal SunActive versus conventional iron for treatment of iron-deficiency anemia in children aged 2–12 years: a prospective randomized controlled trial
- Wael A. Bahbah, Yasmin A.H.S. Younis, Hanan Salama Elbelouny, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):608-615. Published online July 18, 2025
-
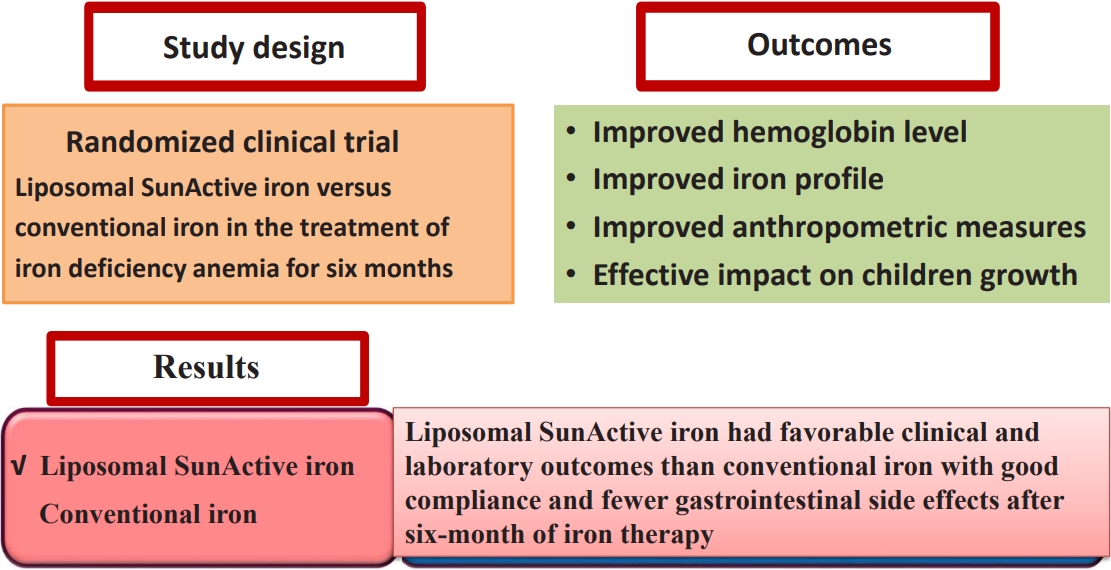
Background: Liposomal iron, a novel oral formulation of ferric pyrophosphate that demonstrates improved gastrointestinal absorption and bioavailability with fewer side effects than conventional iron, represents a significant advancement in the treatment of iron-deficiency anemia (IDA).
Purpose: To conduct an in-depth comparative study of liposomal SunActive and conventional iron supplements (iron polymaltose complex) for treating IDA in children aged 2–12 years Methods: This...
- Letter to the Editor
- General Pediatrics
- Debate around and impact of digital screen time and media parenting on children’s development
- Gowda Parameshwara Prashanth
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):551-553. Published online March 11, 2025
-

- Review Article
- Immunology
- NLRP3 inflammasome: a key player in neonatal brain injury
- Cagla Kiser, Ilkcan Ercan, Defne Engur, Sermin Genc
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):475-485. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is the major cause of neonatal brain injury. NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome activation leads to neuroinflammation, which significantly affects newborn mortality. The establishment of preventive and therapeutic strategies against brain damage requires a thorough understanding of the mechanisms underlying neuroinflammation and inflammasome activation in the neonatal brain.
- Perspective
- Gastroenterology
- Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in children: a practical update based on Indian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ISPGHAN) 2024 guidelines
- Ankit Agrawal, Arghya Samanta
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):546-550. Published online May 12, 2025
-

- Original Article
- Oncology
- Prognostic role of mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin in predicting infection in pediatric cancer with febrile neutropenia
- Seham M. Ragab, Sara Mahmoud El-Deeb, Ahmed Saeed, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):445-453. Published online January 13, 2025
-

· Infection remains a leading cause of death in febrile neutropenia (FN).
· Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-ProADM) levels are higher among patients with FN and a bacterial infection.
· A longer FN duration and hospital stay length as well as elevated C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and MR-ProADM levels are significant risk factors for mortality.
- Editorial
- Other
- Further research on impact of microplastics on children's health is essential to protecting future generations
- Jongin Lee, Dong-Wook Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):359-361. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· The ecological impacts of microplastics have been documented. It was recently recognized that they can directly or indirectly cause diseases in humans.
· There are few established methods for assessing human exposure to microplastics.
· Standardization of exposure assessments and large-scale epidemiological studies are required to explore the human effects of microplastics.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- The role of serum zinc and selenium levels in etiology of febrile seizures
- Yavuz Ataş, Hatice Gamze Poyrazoğlu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):388-394. Published online January 13, 2025
-

Zinc may play a key role in preventing febrile seizures by increasing the seizure threshold and reducing oxidative stress. Incorporating zinc supplements into treatment could help protect children from the adverse effects of febrile seizures and improve their overall outcomes.
- Neurology
- Occurrence of stroke in children and young adults in Indonesia: a multicenter private hospital study
- Jeanne Leman, Veli Sungono, Yosua Timotius Haryono, Muhammad Adam Mudzakir, Dewi Lestari Rahmawati, Callistus Bruce Henfry Sulay, Gilbert Sterling Octavius
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):303-310. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: What is the occurrence of pediatric stroke in Indonesia?
Finding: This multicenter study identified 1,074 stroke cases, predominantly hemorrhagic (83.4%), with males and older children at higher risk. Accidents were the primary cause (73.2%).
Meaning: Pediatric stroke in Indonesia shows critical epidemiological trends, highlighting the need for targeted prevention efforts, particularly for high-risk groups like males and accident victims.
- Pulmonology
- Impact of obesity on pulmonary function of preschool children: an impulse oscillometry study
- Anuvat Klubdaeng, Kanokporn Udomittipong, Apinya Palamit, Pawinee Charoensittisup, Khunphon Mahoran
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):319-325. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: Does obesity in preschool children affect lung function, and which obesity indices can predict such alterations?
Finding: Preschool children with obesity exhibit impaired lung function characterized by elevated total and peripheral airway resistance. Waist-to-height ratio was the strongest predictor of such changes.
Meaning: Early obesity prevention and treatment are needed. Monitoring waist-to-height ratio, body weight, and body mass index may help identify children at risk of altered lung function.
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Cerebral organoid research for pediatric patients with neurological disorders
- Jin Eun, Jung Eun Lee, Seung Ho Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):269-277. Published online November 28, 2024
-

Cerebral organoids obtained from human induced pluripotent stem cells are transforming the study of pediatric neurological diseases by providing more accurate models of human brain development and pathology. These advancements have improved pathology modeling and the potential for novel therapeutic approaches despite existing challenges such as reproducibility and vascularization.
- Original Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- C3 glomerulopathy in children: experience at a resource-limited center
- Soumya Reddy, Abhishek Ghante, Mahesha Vankalakunti, Anil Vasudevan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):311-318. Published online November 28, 2024
-

Question: What are the clinicopathological features and outcomes of pediatric C3 glomerulopathy (C3G) in resource-limited settings?
Finding: Children with C3G in resource-limited settings have significant morbidities, and most experience kidney sequelae despite treatment. Electron microscopy was performed in only 50% of our patients, while none received complement assays or genetic testing.
Meaning: Pediatric C3G presentation, management, and kidney outcomes vary. Its thorough evaluation and management are challenging in resource-limited settings.
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- The predetermined future: tackling South Korea’s total fertility rate crisis
- Jin Kyu Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):225-227. Published online November 6, 2024
-
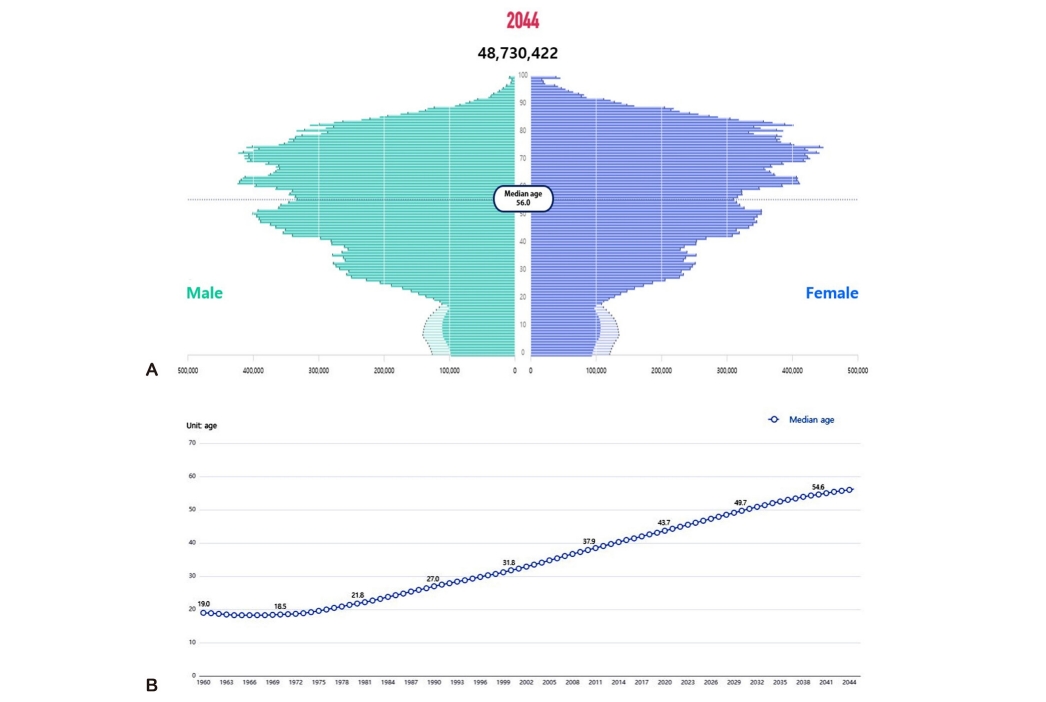
· South Korea faces a severe demographic crisis with the lowest global fertility rate. Despite significant investments, the total fertility rate continues to decline.
· It is necessary to fully mobilize national capabilities and execute comprehensive strategies that focus on both intangible and tangible values.
· Immediate and decisive action is essential to addressing these challenges effectively.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Practical concepts and strategies for early diagnosis and management of eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders in East-Asian children
- Byung-Ho Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):185-198. Published online November 13, 2024
-
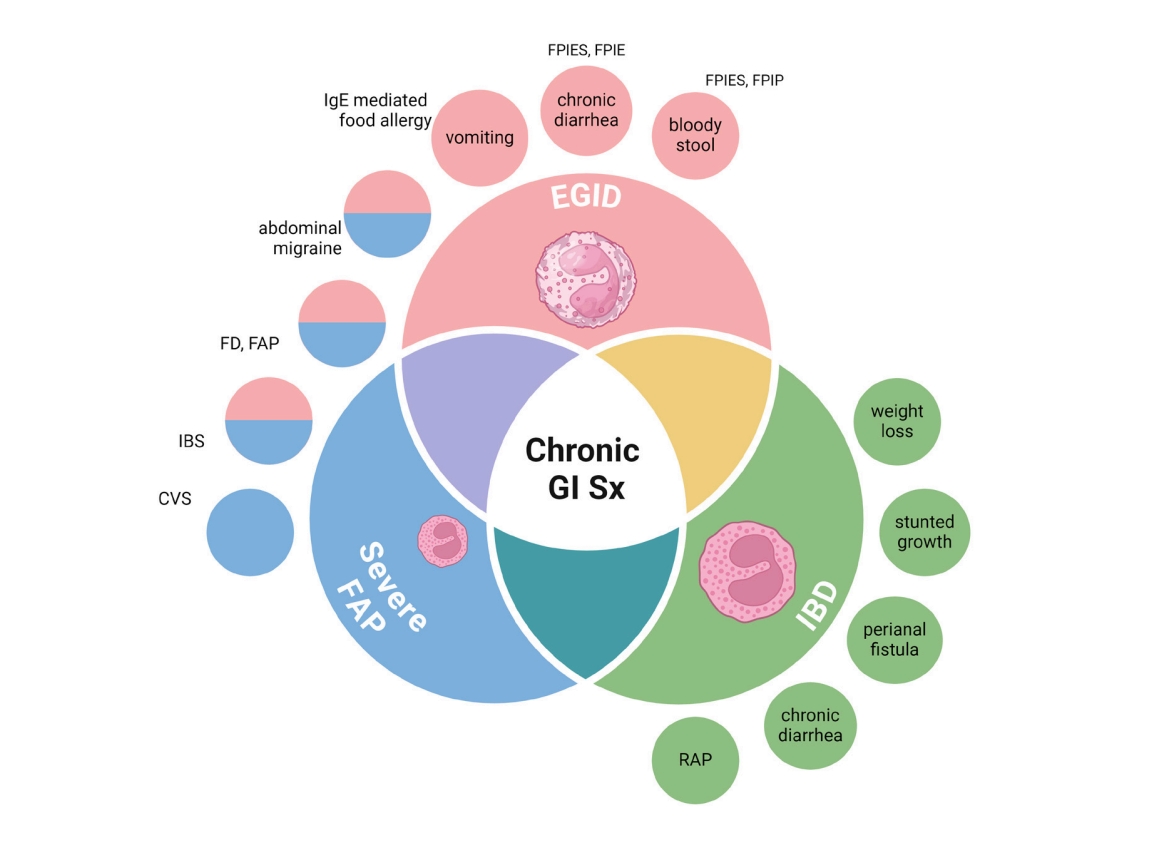
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs) often coexist with functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) and other IgE or non-IgE mediated GI diseases. Diagnosing EGIDs requires a high index of suspicion and a comprehensive approach to differentiate them from conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. Tests such as fecal calprotectin and biopsies aid in severe cases. Maintaining a food diary helps identify triggers for long-term elimination. Awareness and education are key to effective management.
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.












