Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last six months.
- Original Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cytokine profile of Post–cardiopulmonary bypass in children (48 times)
- Kantara Saelim, Kanokpan Ruangnapa, Jirayut Jarutach, Pongsanae Duangpakdee, Smonrapat Surasombatpattana, Pharsai prasertsan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):1015-1022. Published online September 19, 2025
-

Question: Can cytokine levels predict low cardiac output syndrome (LCOS) in children post–cardiopulmonary bypass?
Finding: Elevated interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor-α levels were associated with LCOS, with an increase in IL-8 of >56 pg/mL from baseline to immediately postoperative being the strongest predictor.
Meaning: Monitoring immediately postoperative IL-8 levels may help identify pediatric patients at risk of LCOS, enabling timely interventions to improve outcomes.
- Gastroenterology
- Adenosine deaminase and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist genetic polymorphisms among obese children with versus without metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (48 times)
- Hala M. Sakhr, Mohammed H. Hassan, Azza Mohamed Taha, Ali Helmi Bakri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):808-818. Published online May 29, 2025
-
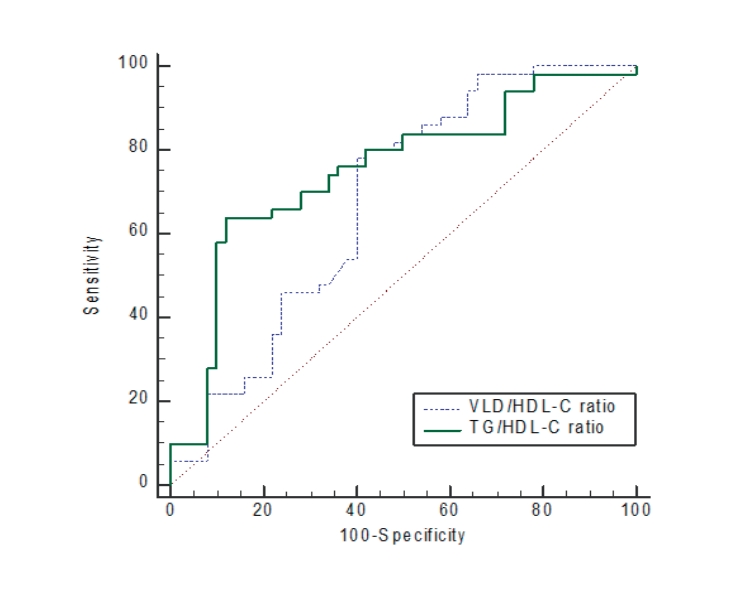
Question: Is there an association between adenosine deaminase (ADA) G22A and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RN) genetic polymorphisms and pediatric metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)?
Finding: The GG genotype and G allele of ADA G22A were significantly associated with obesity but not pediatric MAFLD, while the *1/*2 genotype of the IL-1RN gene was significantly associated with obesity and pediatric MAFLD.
Meaning: The IL-1RN gene may contribute to pediatric MAFLD.
- Infection
- Association between vitamin D polymorphisms and binding protein and COVID-19 risk and severity in children (47 times)
- Victoria Giatraki, Helen Dimitriou, Georgia Martimianaki, Christos Tsatsanis, Emmanouil Galanakis, Chrysoula Perdikogianni
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):998-1006. Published online October 22, 2025
-
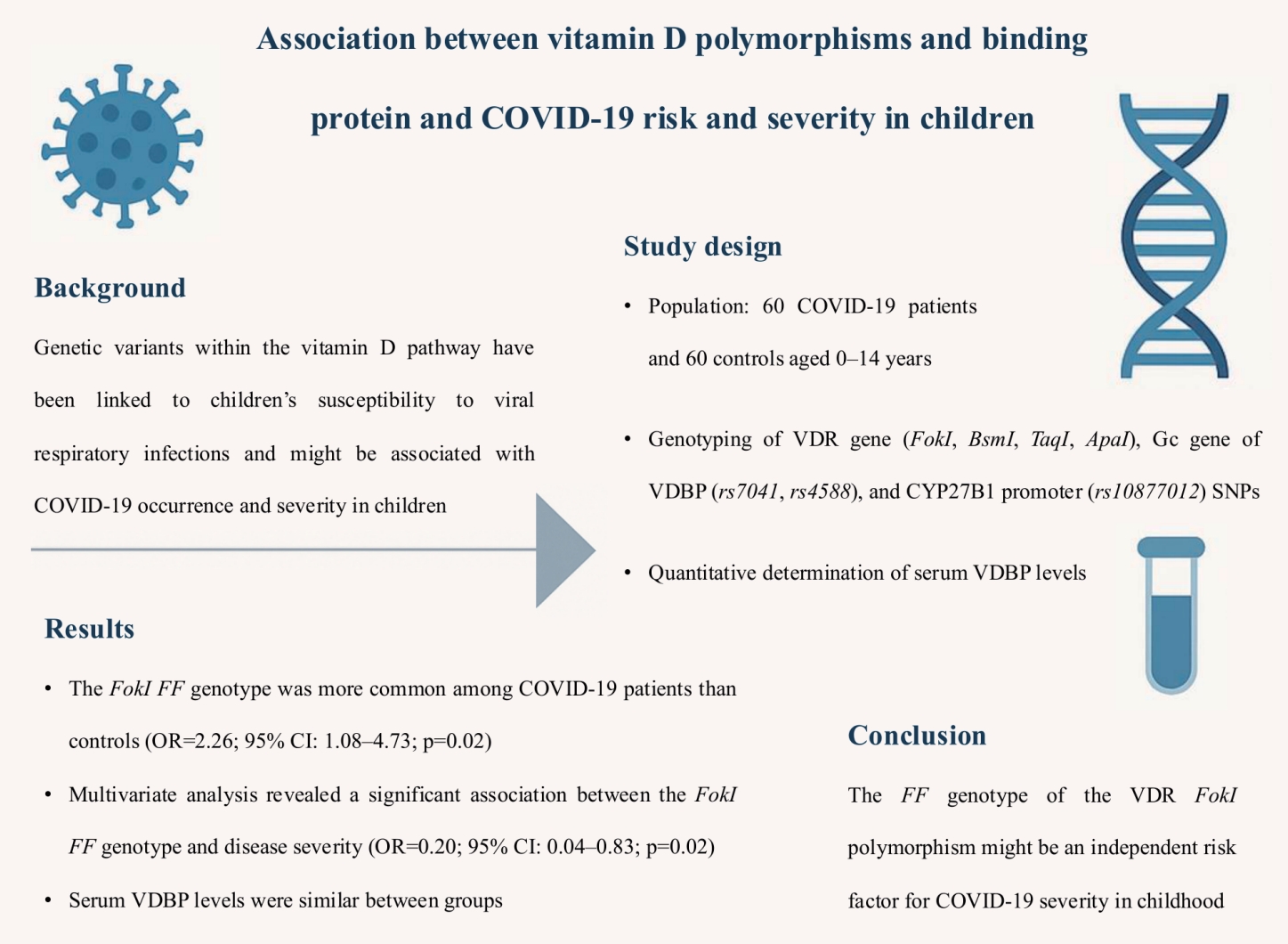
Question: Addressing crucial genetic variants within the vitamin D pathway and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) susceptibility, the vitamin D receptor, vitamin D binding protein, and CYP27B1-1260 polmorphisms might be associated with COVID-19 occurrence and severity in children.
Finding: The FokI FF genotype might be an independent risk factor for COVID-19 severity in childhood.
Meaning: This research may further elucidate genetic susceptibility to multisystem viral infections and establish genetic markers for severe clinical outcomes.
- Rheumatology
- Recurrent immunoglobulin A vasculitis in children and adolescents: prevalence and associated risk factors (46 times)
- Nootsara Atchariyaphuk, Maynart Sukharomana, Thanaporn Chaiyapak, Sirirat Charuvanij
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):46-55. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Question: What can predict immunoglobulin A vasculitis (IgAV) recurrence, and when does it occur? How do childhood- and adolescent-onset IgAV compare?
Finding: The IgAV recurrence rate was 35.6%. It usually occurred within 12 months and was associated with corticosteroids treatment.
Meaning: Childhood-onset IgAV more commonly featured gastrointestinal and musculoskeletal manifestations and required hospitalization. Adolescent-onset IgAV more commonly featured renal involvement. Vigilant monitoring for recurrence is necessary, particularly with corticosteroids treatment.
- Other
- Comparing ethyl chloride and 10% lignocaine spray for pediatric intravenous cannulation pain relief (46 times)
- Susmitha Vellanki, Malavika Kulkarni, H.D. Arun Kumar, Deepali Shetty, Nikhil Karthik B, Mathew Tom
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):65-72. Published online November 21, 2025
-

Background: Intravenous cannulation (IVC) is a routine yet distressing procedure in pediatric patients, often provoking significant anxiety and procedural pain. Although eutectic mixtures such as eutectic mixture of local anesthetic cream are widely used, their delayed onset limits their applicability in time-sensitive settings. Ethyl chloride vapocoolant spray and 10% lignocaine spray have been proposed as rapid-onset alternatives, yet direct comparative...
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Action-plan and as-needed therapy in allergic rhinitis (45 times)
- Hyeon-Jong Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):267-273. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· The guidelines may not work in the real world.
· An action-plan reflecting patient’s severity and variable of symptoms, values and preferences as well as the benefits and harms of treatment, may be a useful alternative.
· The action plan and as-needed therapy must include the following elements: when, what, how, and why.
· Action plan and as-needed therapy can help patients manage their symptoms more effectively.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Recent updates on systemic treatment of atopic dermatitis (44 times)
- Jiyoung Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):580-588. Published online November 1, 2024
-
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a complex disease with multifactorial pathogenesis and variable clinical presentation. Up to one-fifth of patients with AD develop moderate to severe disease that is often refractory to classical therapies and can compromise quality of life. This review summarizes recent clinical evidence on biological agents and small-molecule immunotherapies for the treatment of AD.
- Gastroenterology
- Practical concepts and strategies for early diagnosis and management of eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders in East-Asian children (43 times)
- Byung-Ho Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):185-198. Published online November 13, 2024
-
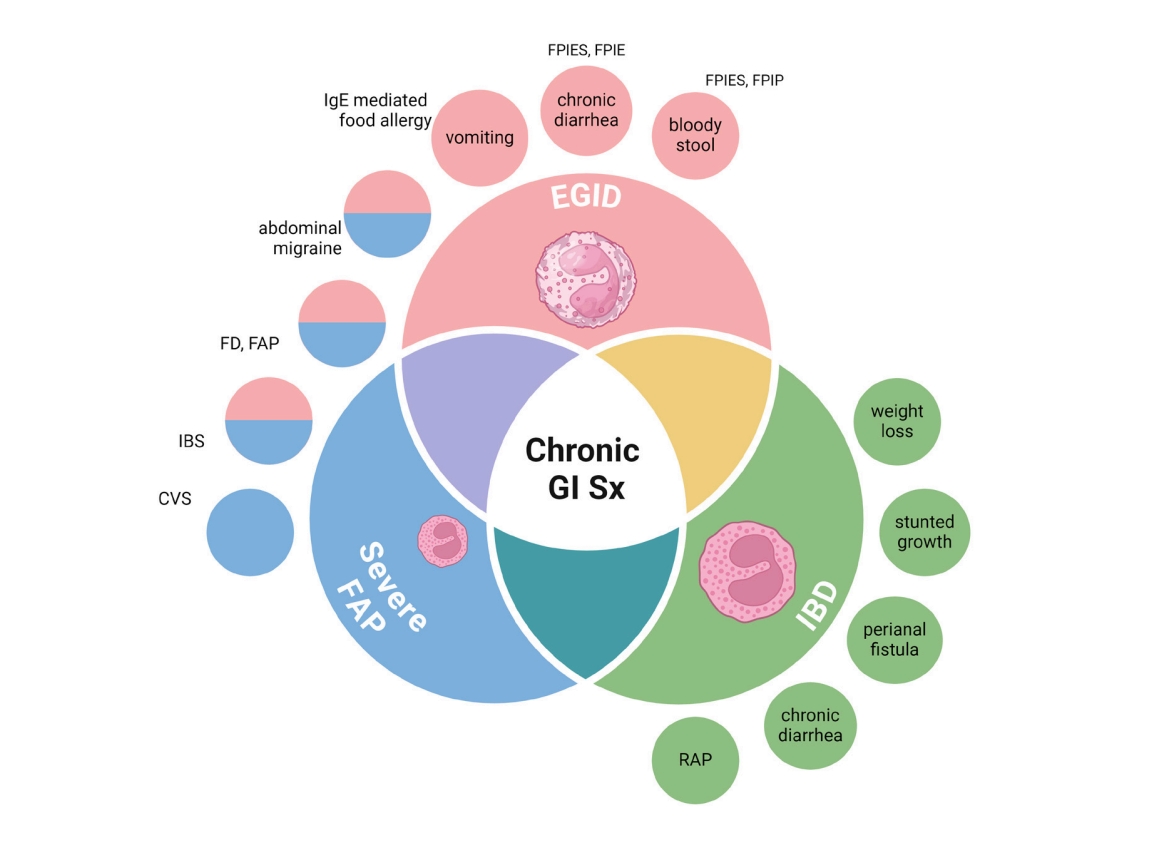
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs) often coexist with functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) and other IgE or non-IgE mediated GI diseases. Diagnosing EGIDs requires a high index of suspicion and a comprehensive approach to differentiate them from conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. Tests such as fecal calprotectin and biopsies aid in severe cases. Maintaining a food diary helps identify triggers for long-term elimination. Awareness and education are key to effective management.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Impact of obesity on pulmonary function of preschool children: an impulse oscillometry study (43 times)
- Anuvat Klubdaeng, Kanokporn Udomittipong, Apinya Palamit, Pawinee Charoensittisup, Khunphon Mahoran
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):319-325. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: Does obesity in preschool children affect lung function, and which obesity indices can predict such alterations?
Finding: Preschool children with obesity exhibit impaired lung function characterized by elevated total and peripheral airway resistance. Waist-to-height ratio was the strongest predictor of such changes.
Meaning: Early obesity prevention and treatment are needed. Monitoring waist-to-height ratio, body weight, and body mass index may help identify children at risk of altered lung function.
- Clinical Note
- General Pediatrics
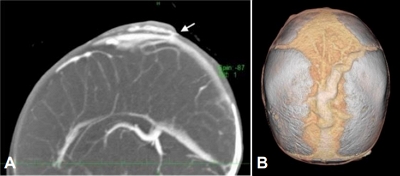
- Aplasia cutis congenita with unique vascular malformation and cranial hypoplasia: a case in a preterm infant (43 times)
- Yasufumi Sakata, Natsumi Fujii, Sadahiro Nomura, Yoshihiro Azuma, Hiroki Hamano, Hidenobu Kaneyasu, Seigo Okada, Kazumasa Takahashi, Shunji Hasegawa
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):472-474. Published online March 11, 2025
-
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Nonlinear association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and asthma in children and adolescents in the United States: a cross-sectional study (43 times)
- Chuhan Cheng, Liyan Zhang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):489-496. Published online March 11, 2025
-

Question: Is there a nonlinear relationship between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and asthma in children and adolescents?
Finding: NLR showed a nonlinear association with asthma, with an NLR threshold of 2.23 identifying individuals at higher risk.
Meaning: An NLR<2.23 may serve as a potential biomarker for asthma risk assessment and management in pediatric populations, thereby offering a simple tool for the early identification of at-risk individuals.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Protecting our future: environmental hazards and children’s health in the face of environmental threats: a comprehensive overview (42 times)
- Jungha Lee, Hyo-Bin Kim, Hun-Jong Jung, Myunghee Chung, So Eun Park, Kon-Hee Lee, Won Seop Kim, Jin-Hwa Moon, Jung Won Lee, Jae Won Shim, Sang Soo Lee, Yunkoo Kang, Young Yoo; The Environmental Health Committee of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):589-598. Published online October 31, 2024
-

· Exposure to air pollutants cause allergic and respiratory diseases as well as chronic kidney disease.
· Adequate physical activity and proper nutrition are essential for children to maintain good health.
· We must educate people about the harmful effects of noise, blue light, heavy metals and smoke.
· Government and society must actively decrease environ-mental hazards.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Outcome of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease in Asian children: a multinational 1-year follow-up study (42 times)
- Pornthep Tanpowpong, Suporn Treepongkaruna, James Guoxian Huang, Kee Seang Chew, Karen Sophia Calixto Mercado, Almida Reodica, Shaman Rajindrajith, Wathsala Hathagoda, Yoko Kin Yoke Wong, Way Seah Lee, Marion Margaret Aw
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):247-256. Published online November 13, 2024
-
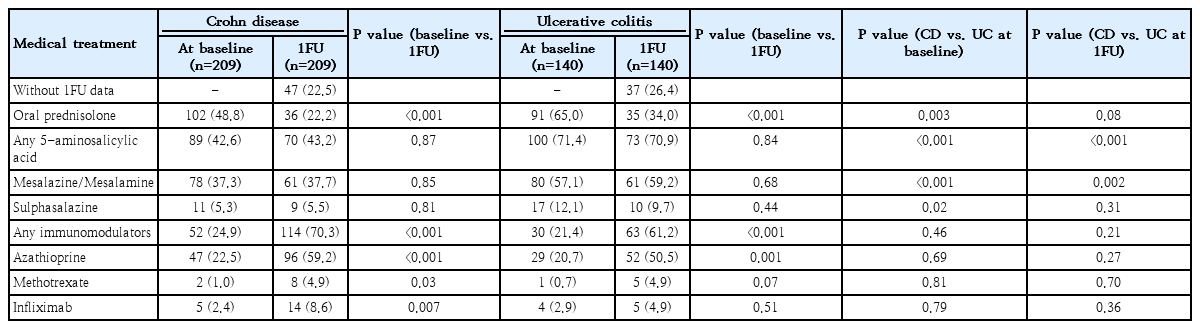
Question: Short-term (1-year) follow-up data in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), especially in Southeast Asian countries, are limited.
Finding/Meaning: Abdominal pain and pallor rates remained high at 1 year after IBD diagnosis. Three independent factors of 1-year clinical remission for Crohn disease were oral prednisolone, antibiotic, and immunomodulator use at 1-year follow-up. A history of weight loss at diagnosis was the only independent risk factor of IBD flare.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Differential roles of interleukin-6 and adrenomedullin in early diagnosis and mortality predictions in late-onset neonatal sepsis (42 times)
- Emilly Henrique dos Santos, Gabriel Acca Barreira, Mariana Okay Saippa, Maria Carolina Pires Cruz, Karen Alessandra Rodrigues, Ronaldo Arkader, Thelma Suely Okay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):463-471. Published online December 23, 2024
-

Question: Can adrenomedullin (ADM) or interleukin-6 (IL-6) detect late-onset neonatal sepsis (LOS) at admission (area under the curve [AUC]>0.90) as an early diagnostic marker?
Finding: Only IL-6 consistently distinguished survivors from nonsurvivors (AUC>0.90) on admission and antibiotic treatment days 3 and 7. C-reactive protein level identified infections from day 3 but failed to predict outcomes (AUC<0.70).
Meaning: IL-6 level can improve LOS diagnosis and prognosis.
- Infection
- Construction and validation of predictive models for intravenous immunoglobulin–resistant Kawasaki disease using an interpretable machine learning approach (41 times)
- Linfan Deng, Jian Zhao, Ting Wang, Bin Liu, Jun Jiang, Peng Jia, Dong Liu, Gang Li
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):405-414. Published online July 23, 2024
-

Question: Is there a reliable model to predict intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)-resistant Kawasaki disease (KD)?
Finding: We constructed 5 machine learning models to predict IVIG-resistant KD. Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) model was superior to logistic, support vector machine, light gradient boosting machine and multiple layers perception models. The SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) value interpreted the contribution of each feature in XGBoost model.
Meaning: XGBoost model showed the excellent performance to predict IVIG-resistant KD with explainable and visualizable machine learning algorithm.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children: focus on systemic Th2 cytokine receptor antagonists and Janus kinase inhibitors (41 times)
- Jeong Hee Kim, Mona Salem Samra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):64-79. Published online June 14, 2023
-
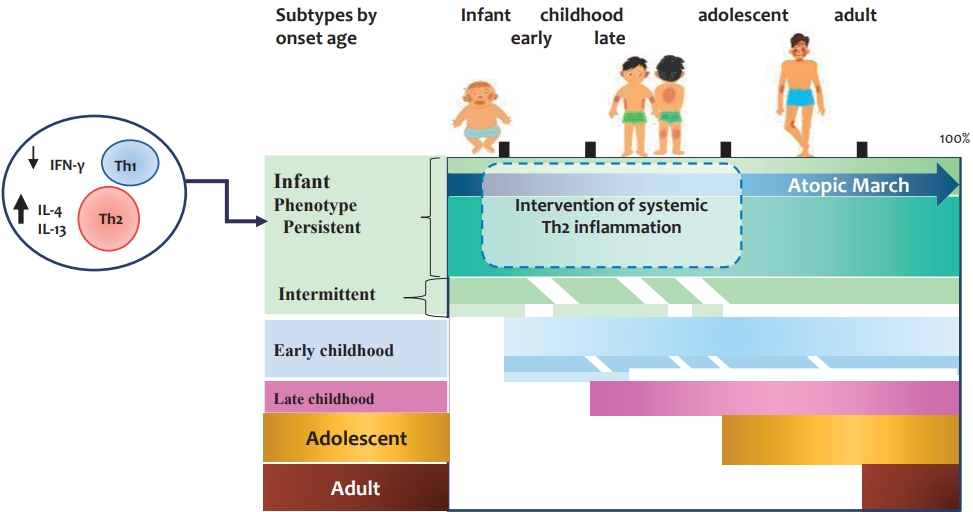
· Atopic dermatitis (AD) is characterized by a strong T helper (Th)2 response, although the extents of Th22, Th17/ interleukin (IL)-23, and Th1 responses vary among disease subtypes.
· Children with moderate to severe AD may require early systemic therapy to reduce the systemic inflammation caused by increased Th2 cytokine levels.
· Dupilumab, which blocks IL-4/IL-13 receptor, has equivalent efficacy for extrinsic and intrinsic AD and a favorable safety profile in infants and children aged 6 months and older.
- Gastroenterology
- Value of transabdominal ultrasonography for diagnosing functional constipation in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis (41 times)
- Duc Long Tran, Phu Nguyen Trong Tran, Paweena Susantitaphong, Phichayut Phinyo, Palittiya Sintusek
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):127-135. Published online November 13, 2024
-
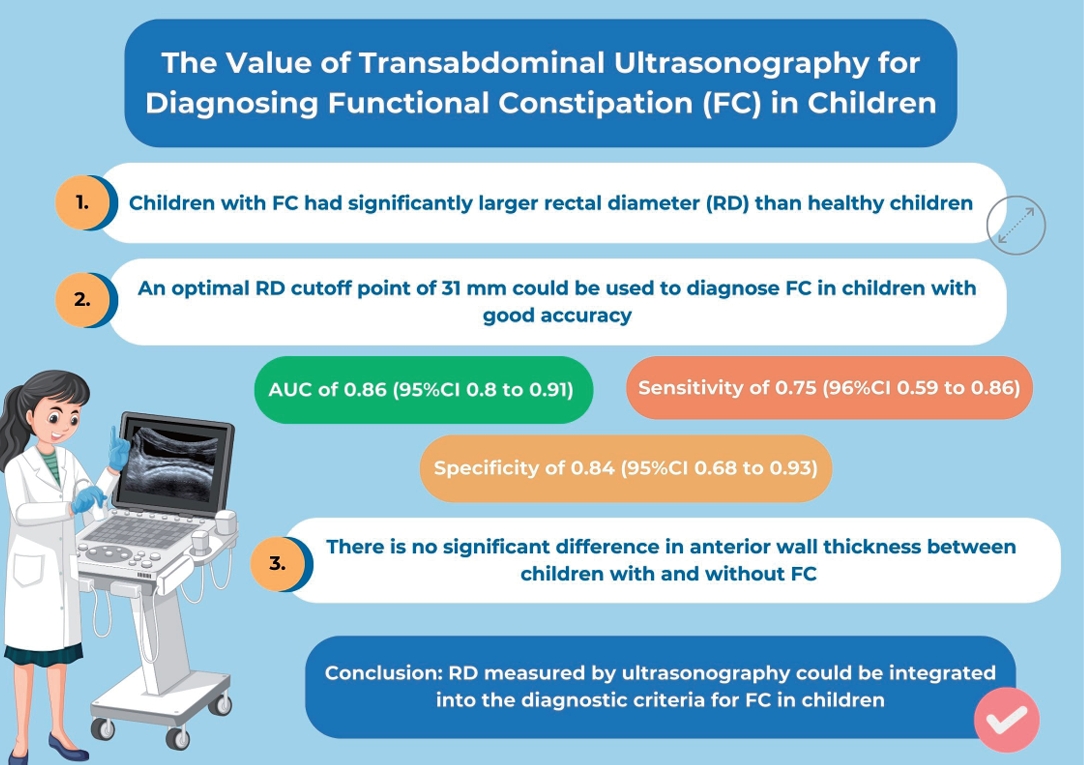
Transabdominal ultrasonography is increasingly used as a novel modality for detecting pediatric functional constipation (FC). This systematic review and metaanalysis aimed to assess the diagnostic parameters of FC including rectal diameter (RD) and anterior rectal wall thickness. A systematic search was conducted of the Ovid MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, and PubMed databases through September 29, 2023, to identify studies comparing RD...
- Clinical Note
- Gastroenterology
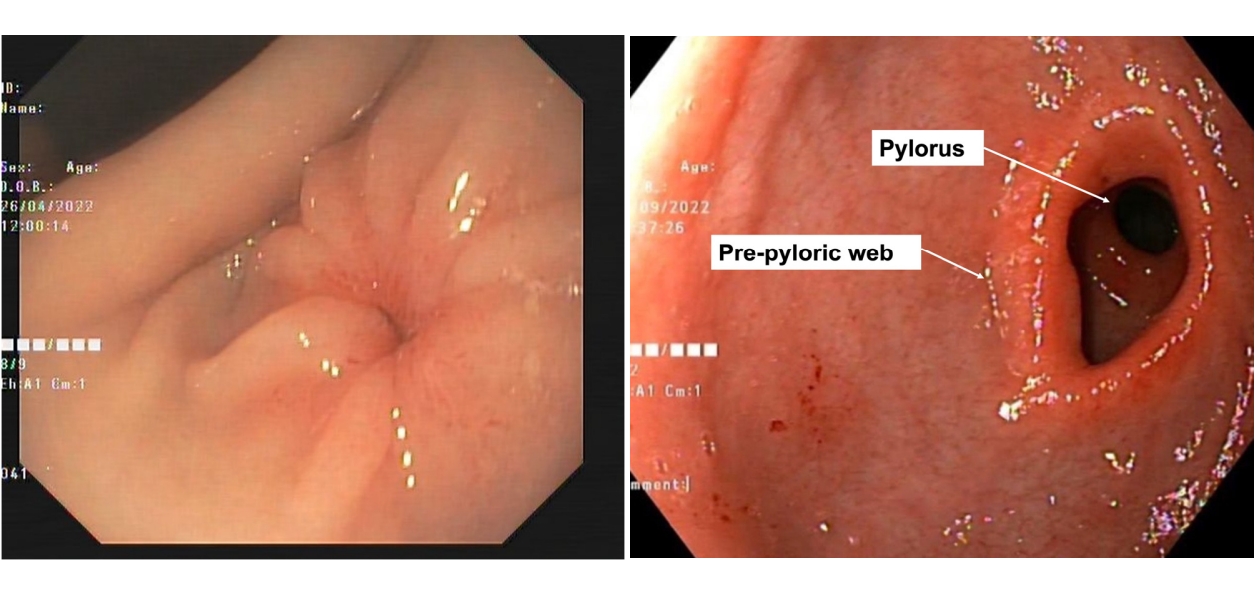
- Congenital antral web: rare cause of gastric outlet obstruction successfully managed with endoscopic balloon dilatation (41 times)
- Upasana Ghosh, Ujjal Poddar, Srinivas Srinidhi Vadlapudi, Moinak Sen Sarma, Anshu Srivastava
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):266-268. Published online January 13, 2025
-
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Impact of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on growth outcomes in mucopolysaccharidosis: a systematic review (41 times)
- Farzaneh Abbasi, Asal Khalili Dehkordi, Reihaneh Mohsenipour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):417-427. Published online March 11, 2025
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) enhances the growth outcomes of pediatric patients with mucopolysaccharidosis, with early intervention leading to improved height, weight, and body mass index. However, achieving a standard adult height remains uncommon among these patients, even in cases of early HSCT. Growth hormone therapy provides short-term benefits but does not address long-term height deficits. Pubertal development is generally normal; however, precocious puberty and pubertal arrest may occur.
- Allergy
- Skin and oral intervention for food allergy prevention based on dual allergen exposure hypothesis (40 times)
- Kiwako Yamamoto-Hanada, Yukihiro Ohya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):477-485. Published online June 14, 2023
-

To prevent food allergy in infants, based on the dual allergen exposure hypothesis, we recommend a personalized approach consisting of both skin intervention (eczema treatment to achieve early remission and well-controlled skin without eczema to prevent percutaneous immunoglobulin E sensitization) and oral intervention (early allergenic food introduction).
- Perspective
- Other
- Telemedicine in pediatrics: things to consider (40 times)
- Sandhya J. Kadam, Archana Reddy Bongurala
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):326-328. Published online February 3, 2025
-

This article highlights the benefits, challenges, and current significance of telemedicine. Future research is needed, primarily to address the challenges of optimizing the implementation of telehealth. To use telemedicine effectively and efficiently for the timely diagnosis and management of patients, an evaluation of current telemedicine practice is needed. Analysis of shortcomings and advantages can help enhance healthcare delivery to pediatric patients, making it more accessible for future use.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Polysomnographic features of children with obesity: body mass index predict severe obstructive sleep apnea in obese children? (40 times)
- Rungrat Sukharom, Prakarn Tovichien, Kanokporn Udomittipong, Pinyapach Tiamduangtawan, Wattanachai Chotinaiwattarakul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):80-90. Published online November 6, 2024
-

Question: How Common is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in obese children? OSA is common in obese children, even without habitual snoring.
Finding: Among the subjects, 60.6% had positional OSA, 40.2% had rapid eye movement-related OSA, 59.8% had desaturation, 20.5% had sleep-related hypoventilation, and 5.0% had obesity hypoventilation syndrome. Body mass index (BMI) and neck and waist circumferences were significantly associated with severe OSA.
Meaning: We recommend screening obese children (BMI > 29.2 kg/m2) for OSA.
- Review Article
- Other
- Use of virtual reality in children in a broad range of medical settings: a systematic narrative review of recent meta-analyses (39 times)
- Emily Antonovics, Grammatina Boitsios, Thomas Saliba
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):274-282. Published online May 21, 2024
-
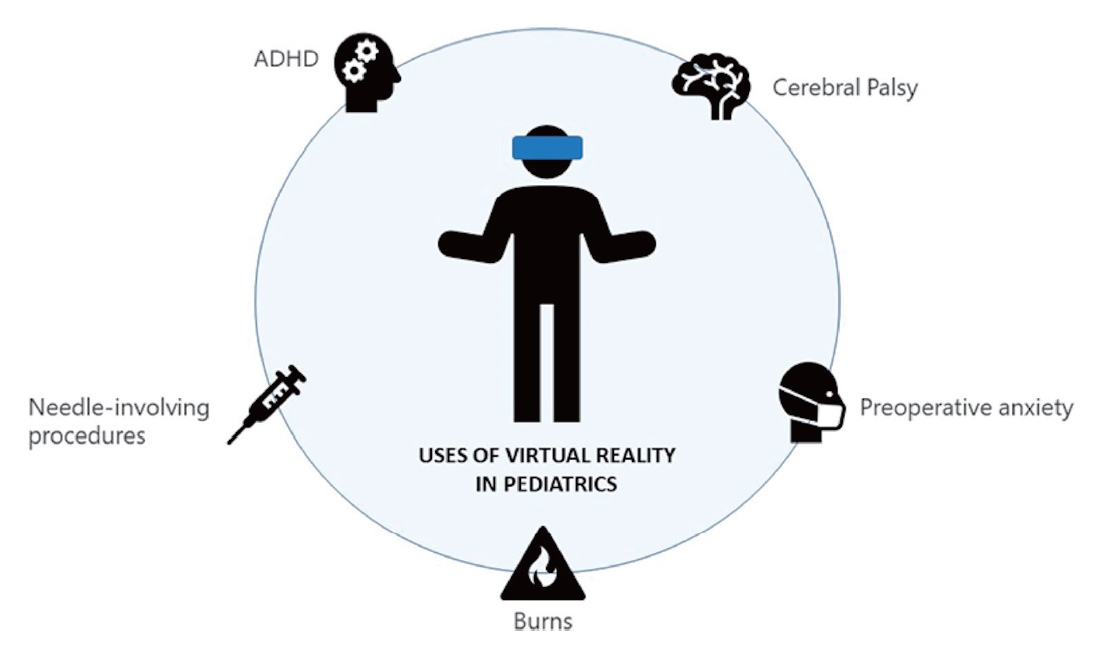
· Virtual reality (VR) is becoming increasingly common for entertainment and in medical settings.
· VR is useful for treating children with cerebral palsy.
· VR can help with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms.
· VR can decrease pain perception in children undergoing burn wound care.
· VR can reduce preoperative anxiety.
· VR can reduce fear and pain during needle-involving procedures.
- Rheumatology
- Double-negative T cells in pediatric rheumatic diseases (39 times)
- Dimitri Poddighe, Tilektes Maulenkul, Kuanysh Dossybayeva, Gulsamal Zhubanova, Zaure Mukusheva, Lyudmila Akhmaltdinova
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):632-640. Published online September 12, 2024
-
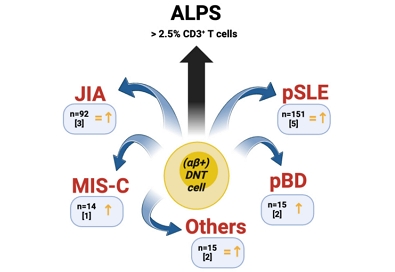
Double-negative T (DNT) cells appear to be increased in several pediatric rheumatic diseases and this finding may be correlated with disease activity to some extent. However, due to significant heterogeneity in several methodological aspects, further investigations in rheumatic children are needed to assess the potential relevance of DNT cells as biomarkers and clarify their immunopathological role.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Ciclesonide shows a lung-protective effect in neonatal hyperoxia-exposed rats (38 times)
- Victoria Mielgo, Miguel A. Gomez-Solaetxe, Lara Olazar, Begoña Loureiro, Carmen Rey-Santano
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):1023-1030. Published online October 2, 2025
-
Question: Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is the most prevalent chronic lung disease of prematurity. Numerous nonpharmacological/pharmacological interventions have been investigated without clear consensus. Can ciclesonide, a new synthetic glucocorticoid, effectively treat BPD?
Finding: Ciclesonide mitigated hyperoxia-induced lung injury and right ventricular hypertrophy in newborn rats.
Meaning: These findings suggest that postnatal ciclesonide may be an alternative to existing corticosteroids for the treatment of BPD.
- General Pediatrics
- Role of proper postnatal care in continued exclusive breastfeeding among young Indonesian mothers (37 times)
- Wahyu Triadmajani, Shinta Prawitasari, Abdul Wahab
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):686-693. Published online September 12, 2024
-
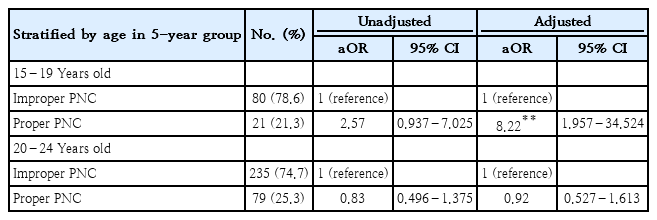
Question: Is proper postnatal care (PNC) associated with exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) practice among young Indonesian mothers?
Finding: Proper PNC elevates the likelihood of EBF among Indonesian adolescent mothers aged 15–19 years.
Meaning: Breastfeeding services should be provided during the early postnatal period to support EBF practice among adolescent mothers. High-quality PNC is a tailored intervention for vulnerable populations.
- Other
- Virtual, augmented, and mixed reality: potential clinical and training applications in pediatrics (37 times)
- Suyoung Yoo, Meong Hi Son
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):92-103. Published online May 24, 2023
-
· Review of articles that investigated the applications of virtual, augmented, or mixed reality in pediatric clinical settings and in the training of pediatric medical professionals was conducted.
· A total of 89 studies were retrieved, with 36 randomized controlled trials.
· In most studies, intervention using the novel technology was at least as effective or more effective than the traditional method.
· Use of virtual, augmented, and mixed reality has potential in pediatrics.
- Nutrition
- Differential effects of dietary and physical activity interventions on adiposity of children with obesity (37 times)
- Anekchoke Tangtongsoong, Chonnikant Visuthranukul, Yuda Chongpison, Sirinuch Chomtho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):370-378. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: How do dietary intake and physical activity affect body mass index (BMI) z scores and adiposity among children with obesity?
Finding: Higher dietary protein and fiber intakes were significantly associated with a decrease in BMI z scores and adiposity among children with obesity.
Meaning: Optimizing dietary interventions by focusing on protein and fiber intakes could be an effective strategy for managing childhood obesity.
- Clinical Note
- Gastroenterology
- Abdominal pain in a young girl: a twist in the tale (36 times)
- Upasana Ghosh, Ankit Agrawal, Umesh Shukla, Vikas Jain, Deeksha Bhalla
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):395-397. Published online March 11, 2025
-
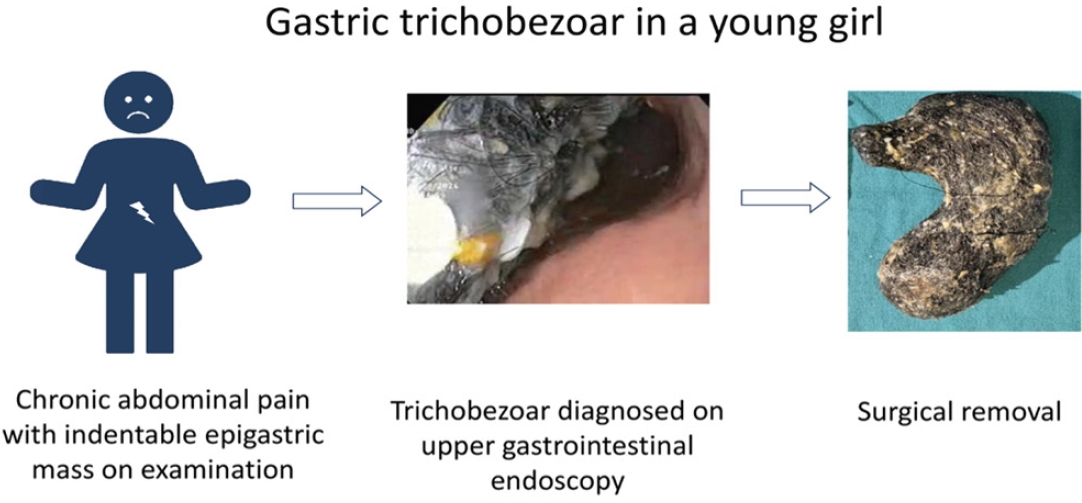
· Chronic abdominal pain caused by a gastric trichobezoar is extremely rare among children.
· An indentable epigastric mass is characteristic and upper gastrointestinal endoscopy is diagnostic of a gastric trichobezoar.
· Symptomatic large trichobezoars usually require surgery.
· Neuropsychiatric disorders are often associated with gastric trichobezoar, making a psychiatric evaluation of paramount importance.
- Review Article
- Nutrition
- The Korea Infant Physical Growth Examination Survey (KIPGroS): a study protocol (35 times)
- Jong Woo Hahn, MinSoo Shin, Jin Gyu Lim, Yoon-Joo Kim, Ki Soo Kang, Narae Lee, Seong Hee Jeong, Mun Hui Jeong, Yeoun Joo Lee, Eui Kyung Choi, Jung Ok Shim, Jee Yoon Park, Chan-Wook Park, Joo Young Kim, Su Jin Jeong, Young Hwa Jung, Jaehyun Kim, Chang Won Choi, Ju Whi Kim, Seung Han Shin, Yun Jeong Lee, Young Ah Lee, Choong-Ho Shin, Seung-sik Hwang, Young Eun Kim, Youn Ha Kang, Kyungwon Oh, Sungha Yun, Jae Sung Ko, Jin Soo Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):352-358. Published online February 13, 2025
-
The suitability of World Health Organization (WHO) growth charts for assessing the growth of children under 3 years of age in all countries remains controversial, and their applicability must be evaluated based on country-specific growth data. The Korea Infant Physical Growth Examination Survey evaluated the suitability of WHO growth charts to contribute to the next revision of growth charts in Korea.
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











