Review article
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Review article
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Need for national guidance regarding proactive care of infants born at 22–23 weeks' gestation
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):53-61. Published online November 13, 2024
-

With advancements in neonatal intensive care, the limit of viability has shifted to 22–23 weeks' gestation, whose survival rates vary across countries and institutions. These rates are not static and can be improved through the proactive and centralized care guided by national protocols, including maternal transfer to high-activity regions with better neonatal intensive care practices before delivery.
- Endocrinology
- A review of vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D receptor polymorphisms in endocrine-related disorders
- Nur Faten Hafizah Rosli, Noor Shafina Mohd Nor, Rose Adzrianee Adnan, Siti Hamimah Sheikh Abdul Kadir
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):30-52. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency is high among children and adolescents and mainly attributed to changes in environmental factors.
· Vitamin D hormone-like properties are associated with many endocrine-related disorders.
· The effect of vitamin D is modulated by the vitamin D receptor, polymorphisms of which are reportedly associated with an increased risk of disease development in children and adolescents.
- Other
- Global trends in importance of 24-hour movement behaviors to pediatric health: implications for South Korea
- Eun-Young Lee, Reyana Jayawardena, Seiyeong Park, Justin Y Jeon, Yeon-Soo Kim, Mark S. Tremblay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):16-29. Published online November 11, 2024
-

· The 24-hour movement behavior paradigm provides an important framework for future pediatric health promotion efforts.
· Policy priorities should include advancing surveillance and monitoring assessments related to 24-hour movement behaviors, evaluating their implementation in school and government policies, and building preparedness for future pandemics and natural disasters, including climate change, by promoting healthy 24-hour movement behaviors.
· Future research should advocate for the promotion of 24- hour movement behaviors.
- Microplastic and human health with focus on pediatric well-being: a comprehensive review and call for future studies
- Rogers Wainkwa Chia, Ntegang Venant Atem, Jin-Yong Lee, Jihye Cha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):1-15. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· Milk and formula are common sources of microplastic in infants.
· Water and air are the most common sources of microplastic pollution from infancy to adolescence.
· Microplastic use by children of all ages can cause cell damage and affect their health.
· Microplastics present in children can be quantified using a stereomicroscope and characterized using micro- Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy.
- Adolescence Medicine
- Diet-related behaviors affecting health and substance use among children and adolescents
- Ji-Hyun Seo, Sochung Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):664-671. Published online October 31, 2024
-
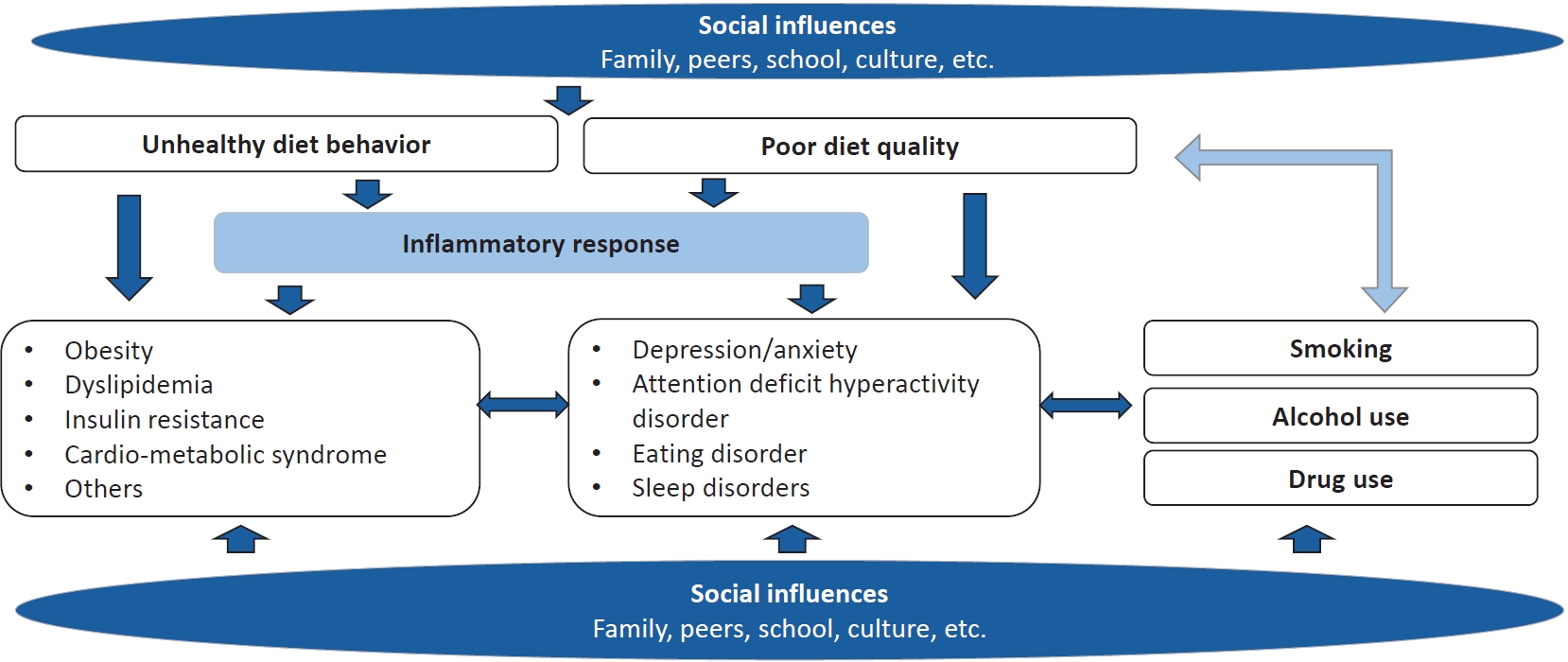
· Diet behaviors in children and adolescents are influenced by environmental and sociocultural factors.
· Unhealthy diet behaviors and poor diet quality are the main contributing factors to noncommunicable diseases and mental health problems during childhood and adolescence.
· Smoking and alcohol drinking in children and adolescents may be associated with unhealthy diet behavior or poor diet quality.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Strategies to support language development in neonatal intensive care unit: a narrative review
- Ju Sun Heo, Ee-Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):651-663. Published online November 6, 2024
-
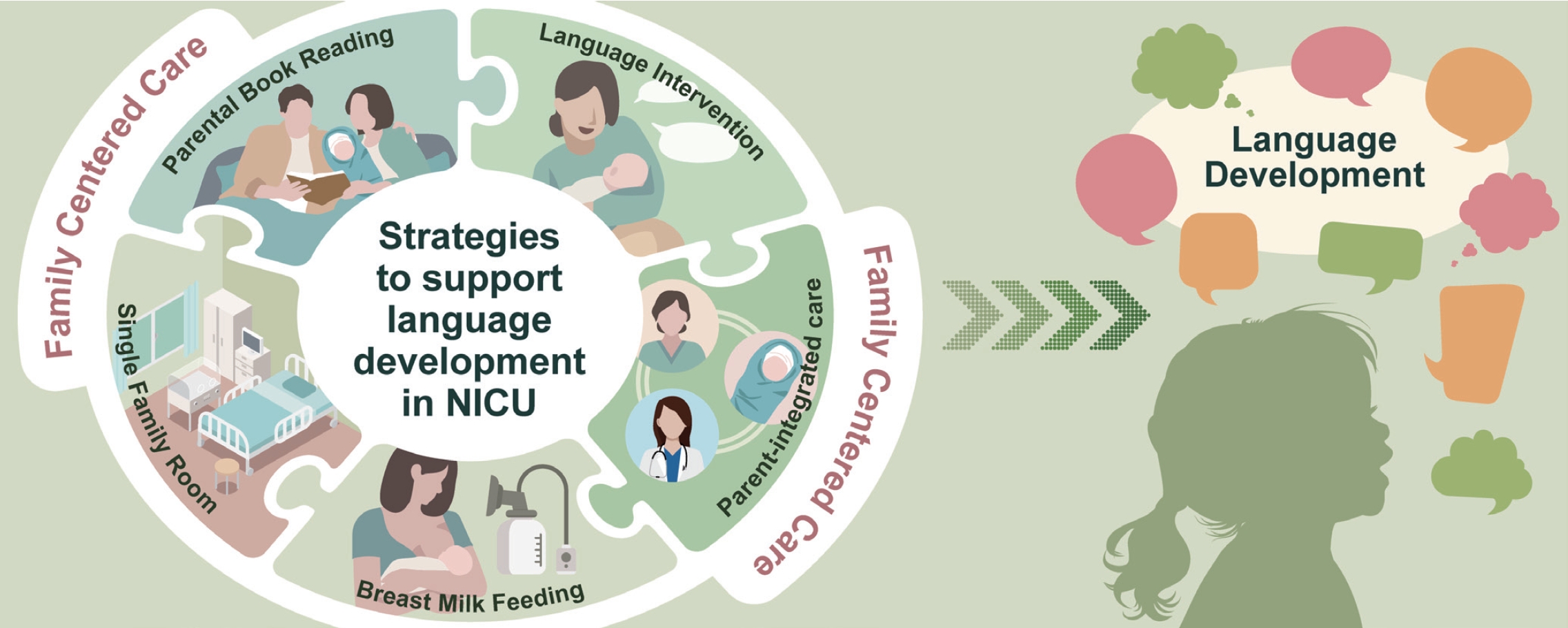
· Preterm infants often experience speech and language development delays during early childhood, impacting children's ultimate outcomes.
· Promoting breastfeeding, increasing parent-infant interactions in a single-family room, promoting a nurturing language environment by parental book reading and language interventions, and parent-integrated interventions in the neonatal intensive care unit could potentially enhance children's language development.
· Integrating these strategies through family-centered care is essential.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Screen time among preschoolers: exploring individual, familial, and environmental factors
- Sangha Lee, Donghee Kim, Yunmi Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):641-650. Published online September 12, 2024
-
This systematic review examined the correlation between screen time and various factors in preschoolers. Findings suggest that media parenting, including setting appropriate media limits, is crucial in protecting against excessive screen exposure. However, limited research has been done on the impact of family and personal factors, particularly with the increasing use of portable devices among young children.
- Rheumatology
- Double-negative T cells in pediatric rheumatic diseases
- Dimitri Poddighe, Tilektes Maulenkul, Kuanysh Dossybayeva, Gulsamal Zhubanova, Zaure Mukusheva, Lyudmila Akhmaltdinova
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):632-640. Published online September 12, 2024
-
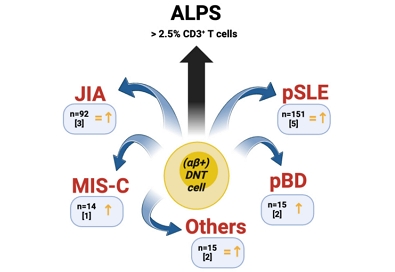
Double-negative T (DNT) cells appear to be increased in several pediatric rheumatic diseases and this finding may be correlated with disease activity to some extent. However, due to significant heterogeneity in several methodological aspects, further investigations in rheumatic children are needed to assess the potential relevance of DNT cells as biomarkers and clarify their immunopathological role.
- General Pediatrics
- Protecting our future: environmental hazards and children’s health in the face of environmental threats: a comprehensive overview
- Jungha Lee, Hyo-Bin Kim, Hun-Jong Jung, Myunghee Chung, So Eun Park, Kon-Hee Lee, Won Seop Kim, Jin-Hwa Moon, Jung Won Lee, Jae Won Shim, Sang Soo Lee, Yunkoo Kang, Young Yoo; The Environmental Health Committee of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):589-598. Published online October 31, 2024
-

· Exposure to air pollutants cause allergic and respiratory diseases as well as chronic kidney disease.
· Adequate physical activity and proper nutrition are essential for children to maintain good health.
· We must educate people about the harmful effects of noise, blue light, heavy metals and smoke.
· Government and society must actively decrease environ-mental hazards.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Recent updates on systemic treatment of atopic dermatitis
- Jiyoung Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):580-588. Published online November 1, 2024
-
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a complex disease with multifactorial pathogenesis and variable clinical presentation. Up to one-fifth of patients with AD develop moderate to severe disease that is often refractory to classical therapies and can compromise quality of life. This review summarizes recent clinical evidence on biological agents and small-molecule immunotherapies for the treatment of AD.
- Neurology
- Role of nonpharmacological concussion management in children: systematic review of randomized controlled trials
- Andre Marolop Pangihutan Siahaan, Alvin Ivander, Rr. Suzy Indharty, Steven Tandean, Anastasia Grace Milenia Ginting, Masrini Ginting, Felix Khosasi, Elbert
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):569-579. Published online October 28, 2024
-

The long-term effects of concussion for pediatric patient remains unclear. Children and teenagers do not experience or recover from concussion in the same manner as adults do. Concussions can cause a variety of anatomical and functional alterations. Nonpharmacological approach in pediatric concussion management is an understudied field of research with significant ability to affect prognosis and quality of life. Active rehabilitation and occupational therapy were especially promising.
- Endocrinology
- Lifelong medical challenges and immunogenetics of Turner syndrome
- Won Kyoung Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):560-568. Published online July 31, 2024
-
· This summary emphasizes the importance of the early diagnosis of Turner syndrome (TS) and presents a multidisciplinary approach to its prevention and management, high-lighting the need for customized care.
· Advancements in immunogenetic research may improve our understanding of TS and improve its outcomes.
· TS encompasses a wide array of medical challenges, including cardiovascular, endocrine, autoimmune, and mental health issues, as well as a heightened cancer risk.
- Growth plate closure and therapeutic interventions
- Ja Hyang Cho, Hae Woon Jung, Kye Shik Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):553-559. Published online October 28, 2024
-

Height gains result from longitudinal bone growth. Upon adequate growth, growth plate closure limits longitudinal bone growth. To date, gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs, aromatase inhibitors, C-type natriuretic peptide analogs, and fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 inhibitors have been studied or used as therapeutic interventions to delay growth plate closure and increase human height. The development of more effective therapeutic modalities for short stature, precocious puberty, and skeletal dysplasia is anticipated.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effect of pesticide exposure on stunting incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Yaltafit Abror Jeem, Muhammad Fathi Banna Al Faruqi, Mahdea Kasyiva, Vita Widyasari, Kuswati Kuswati, Nur Aini Djunet, Muflihah Rizkawati, Ety Sari Handayani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):510-518. Published online September 24, 2024
-

This review aimed to determine whether pesticide exposure is associated with stunting in children. The 13 included studies agree that pesticide exposure is not correlated with stunting incidence regardless of substance type (organophosphate and pyrethroid). Heterogeneity appeared with age covariate as potential confounding. The evidence of this study is challeng-ing, as the adverse effects of pesticides grossly occurred. The protection of children is warranted for preventing future neurodevelopment issues.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Demographic transition in South Korea: implications of falling birth rates
- Chae Young Kim, Sung-Hoon Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):498-509. Published online June 27, 2024
-

· Since 1960, South Korea's TFR decreased from 6.33 to 0.78 in 2022, below the 2.1 replacement level since 1983, with women's average age at first marriage rising to 31.3 in 2022.
· Policies needed: financial incentives, longer parental leave, better childcare.
· The U.S. (15.3% immigrants) and Germany (18.8%) use immigration to maintain demographic stability, a strategy South Korea is considering.
- Endocrinology
- Two- versus one-bag fluid delivery in pediatric and adolescent diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Maya L. Nasser, Joseph Nasr, Reem B. Zalloum, Nathanael Q.E. Yap, Natalie E. Bourdakos, Shahid Miangul, Tara A. Betts, Hayato Nakanishi, Christian A. Than, Serge Jabbour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):486-497. Published online June 27, 2024
-

· The safety and efficacy of the two-bag versus one-bag system for treating patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) < 21 years remains unestablished.
· Our meta-analysis demonstrated similar safety outcomes but sooner DKA resolution and shorter mean response time for intravenous fluid changes for the two-bag system.
· This preliminary evidence suggests that the two-bag system has some advantages in efficacy, but further studies are needed to evaluate their extent.
- Allergy
- Skin and oral intervention for food allergy prevention based on dual allergen exposure hypothesis
- Kiwako Yamamoto-Hanada, Yukihiro Ohya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):477-485. Published online June 14, 2023
-

To prevent food allergy in infants, based on the dual allergen exposure hypothesis, we recommend a personalized approach consisting of both skin intervention (eczema treatment to achieve early remission and well-controlled skin without eczema to prevent percutaneous immunoglobulin E sensitization) and oral intervention (early allergenic food introduction).
- Comparison and review of international guidelines for treating asthma in children
- Eui Jeong Roh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):447-455. Published online August 20, 2024
-

Asthma is the most common chronic disease among children. Although asthma in children may spontaneously improve, it continues into adulthood in many cases. Therefore, appropriate disease management and medication are essential. Consistent and objective guidelines are needed to manage pediatric asthma and related adverse reactions.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Comprehensive evaluation of the child with global developmental delays or intellectual disability
- Abdullah Nasser Aldosari, T. Saeed Aldosari
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):435-446. Published online May 29, 2024
-

· A detailed history and comprehensive physical examination remain the cornerstones for establishing a diagnosis of global developmental delay/intellectual disability (GDD/ID).
· Comprehensive surveillance and screening programs play a significant role in the early detection of GDD.
· Whole-exome sequencing is highly recommended as first- or second-line testing for individuals with idiopathic GDD/ID.
· Early intervention by a well-versed multidisciplinary team can significantly improve the outcomes and prognosis of GDD/ID.
- Infection
- Incidence, causative organisms, and risk factors of bloodstream infections in pediatric liver transplant patients: a systematic review
- Mohamad Shieb, Rand Hasanain, Zara Arshad, Faisal A. Nawaz, Rahul Kashyap, Eric J. Stern
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):427-434. Published online April 5, 2024
-

The overall incidence of bloodstream infections was 23.5%. Gram-negative organisms occur at a much higher rate in pediatric liver transplant recipients then that the general pediatric population. However, when comparing pediatric and adult liver transplant recipients Gram-positive organisms occur with a much higher rate in the pediatric population highlighting the importance of early and broad spectrum antimicrobial coverage when bloodstream infections are suspected.
- Pulmonology
- Evidence-based management guidelines for noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis in children and adolescents
- Eun Lee, Kyunghoon Kim, You Hoon Jeon, In Suk Sol, Jong Deok Kim, Taek Ki Min, Yoon Ha Hwang, Hyun-Ju Cho, Dong In Suh, Hwan Soo Kim, Yoon Hee Kim, Sung-Il Woo, Yong Ju Lee, Sungsu Jung, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Gwang Cheon Jang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):418-426. Published online January 23, 2024
-

· We suggest offering long-term macrolides to children with noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis with frequent exacerbations (conditional recommendation, moderate quality of evidence).
· We do not recommend the routine use of mucolytic agents, inhaled corticosteroids, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent exacerbation of bronchiectasis in children (inconclusive, very low quality of evidence).
· We recommend the use of nebulized hypertonic saline to prevent exacerbations and improve the lung function of children with noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis (weak recommendation, moderate quality of evidence).
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Effects of diethylene glycol contamination of pharmaceutical products on unexplained acute kidney injury in children: a systematic review
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Muhammad Luthfi Adnan, Hilmi Ardian Sudiarto, Satria Bintang Mahathma, Alya Ayu Tazkia, Hana Afifah Firdaus, Alfreda Amelia Khotijah, Miranti Dewi Pramaningtyas, Emi Azmi Choironi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):395-402. Published online January 4, 2024
-

A recent unexplained acute kidney injury (AKI) outbreak due to pharmaceutical product contamination with diethylene glycol (DEG) raises public attention. Our study revealed that DEG-contaminated paracetamol causes unexplained AKI in children. However, paracetamol is not the only contaminated drug. Other drugs, such as cough expectorants, antihistamines, and sedatives, can also be affected. Other chemicals, such as ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, can also contribute to poisonings.
- Allergy
- Recent advances in food allergen immunotherapy
- You Hoon Jeon, Edwin H. Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):386-394. Published online December 7, 2023
-

· To enhance the safety of food allergen immunotherapy, alternative approaches such as sublingual immunotherapy, epicutaneous immunotherapy, low-dose oral immunotherapy (OIT), and omalizumab with OIT are being explored.
· Factors such as causative allergen type, natural outgrowth, symptom severity, and patient age should be considered.
· Individualized food allergen immunotherapy plans should be established to determine the most beneficial treatment for each patient.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Quantifying myelin in neonates using magnetic resonance imaging: a systematic literature review
- Nabila Hanem Arshad, Hasyma Abu Hassan, Nur Farhayu Omar, Zurina Zainudin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):371-385. Published online December 6, 2023
-

Question: This systematic review attempts to discover the best magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique for myelin quantification in neonates by evaluating various MRI parameters and their reproducibility.
Finding: Since the benefits of using synthetic MRI for quantifying myelin in neonates outweigh the very minor draw- backs, it is recommended.
Meaning: The findings suggest the importance of identifying noninvasive MRI techniques available to assess myelin tissue in neonates, which aid in diagnosing neurodevelopmental disorders.
- General Pediatrics
- Metabolic complications of obesity in children and adolescents
- Hyunjin Park, Jung Eun Choi, Seunghee Jun, Hyelim Lee, Hae Soon Kim, Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):347-355. Published online November 16, 2023
-
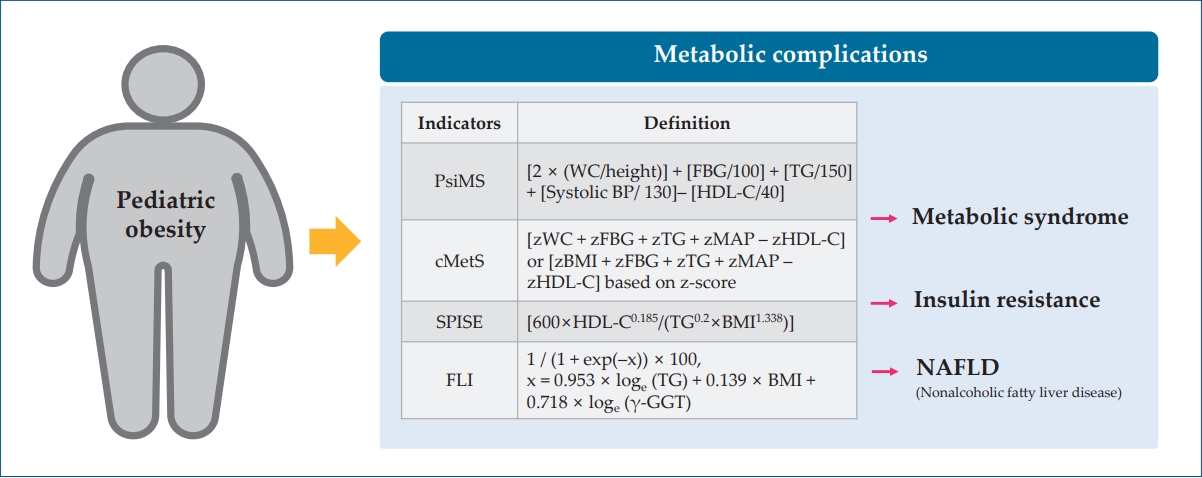
· Pediatric obesity increases the risk of metabolic complications (insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease) and long-term cardiovascular diseases.
· A new obesity definition and various indicators (continuous metabolic syndrome score, pediatric simple metabolic syndrome score, fatty liver index) have been proposed to evaluate children’s susceptibility to metabolic disorders.
· Laboratory and body composition tests in pediatric screenings can identify groups at high risk of metabolic complications of obesity.
- Endocrinology
- Association between pre- and postnatal exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals and birth and neurodevelopmental outcomes: an extensive review
- Ozge Yesildemir, Mensure Nur Celik
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):328-346. Published online November 16, 2023
-
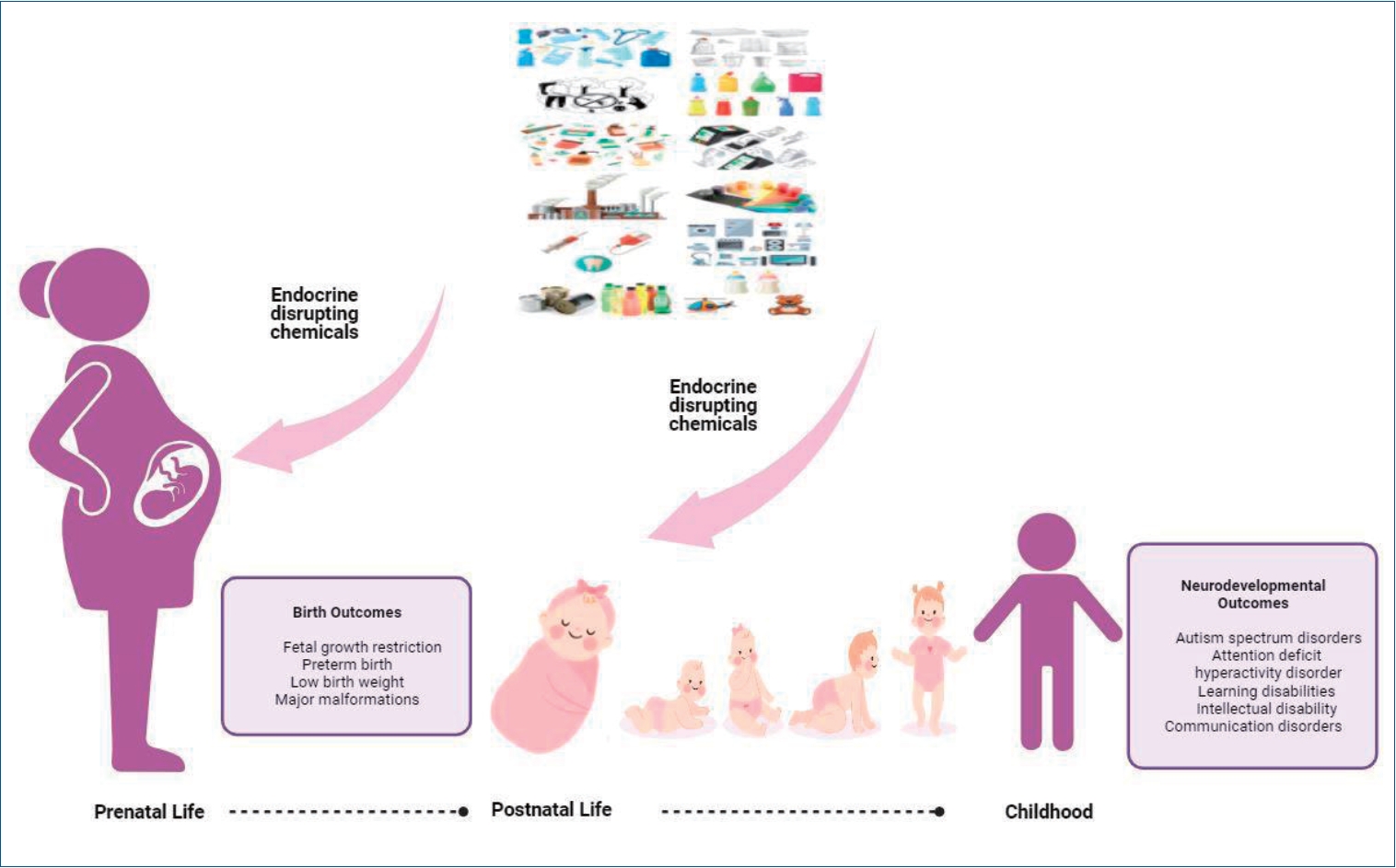
· Sensitivity to endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC) exposure increases during critical developmental periods (in embryos, fetuses, and neonates).
· Pre- and postnatal exposure to EDCs is associated with fetal growth restriction, preterm birth, and low birth weight.
· Exposure to EDCs during fetal and early postnatal life can have lasting and lifelong neurodevelopmental outcomes, including autism spectrum, attention deficit hyperactivity, and other cognitive and behavioral disorders.
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Development of orphan drugs for rare diseases
- Han-Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):315-327. Published online June 28, 2023
-
· Orphan disease is a rare disease, primarily affecting newborn and children. Vast majority of orphan diseases has genetic background.
· Orphan disease is individually rare. But as a whole, it is not rare, becoming a great socioeconomic burden.
· The diagnosis of rare genetic disease has been problematic, but recent progress of genome analysis technologies makes it faster and more precise.
· There are many unmet needs as to the curative treatment. However, the number of treatable rare diseases is growingly increasing owing to the development of biotechnology.
· Most orphan drugs are extremely expensive because of numer ous hurdles during the process of drug development as well as small number of patients.
- Hematology
- Iron deficiency in children with a focus on inflammatory conditions
- Na Hee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):283-293. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· Iron deficiency has important effects on neurodevelopment and the immune system in children.
· Hepcidine plays an important role in iron homeostasis.
· Diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency in chronic inflammatory disease are important for patients' quality of life and disease course.
- Other
- Use of virtual reality in children in a broad range of medical settings: a systematic narrative review of recent meta-analyses
- Emily Antonovics, Grammatina Boitsios, Thomas Saliba
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):274-282. Published online May 21, 2024
-
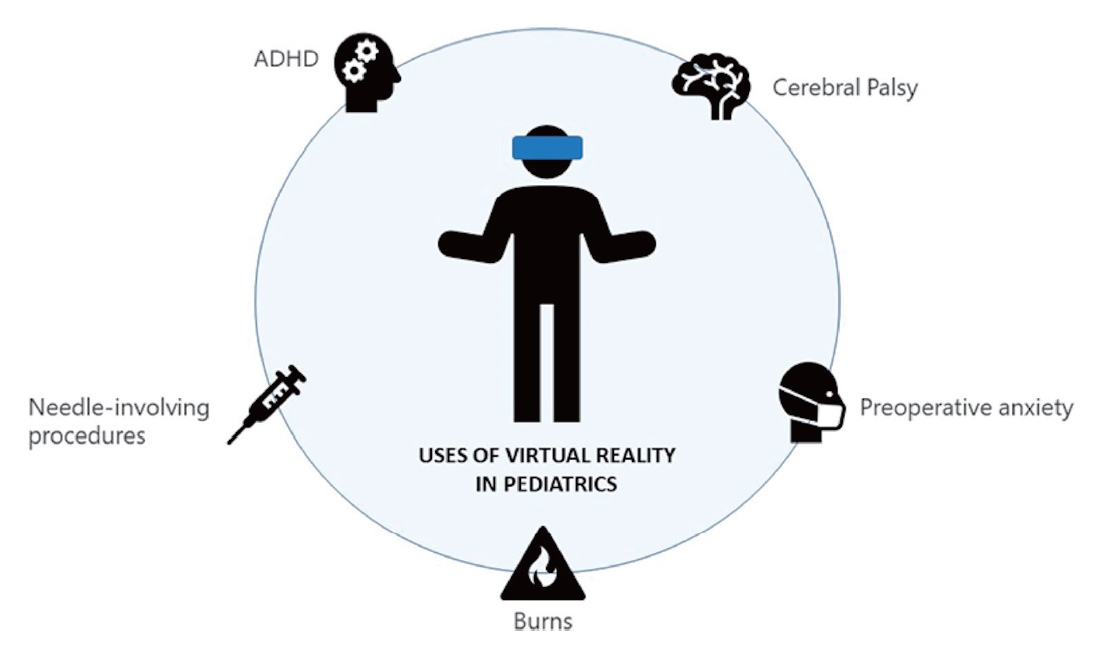
· Virtual reality (VR) is becoming increasingly common for entertainment and in medical settings.
· VR is useful for treating children with cerebral palsy.
· VR can help with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms.
· VR can decrease pain perception in children undergoing burn wound care.
· VR can reduce preoperative anxiety.
· VR can reduce fear and pain during needle-involving procedures.
- Allergy
- Action-plan and as-needed therapy in allergic rhinitis
- Hyeon-Jong Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):267-273. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· The guidelines may not work in the real world.
· An action-plan reflecting patient’s severity and variable of symptoms, values and preferences as well as the benefits and harms of treatment, may be a useful alternative.
· The action plan and as-needed therapy must include the following elements: when, what, how, and why.
· Action plan and as-needed therapy can help patients manage their symptoms more effectively.
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











