Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last six months.
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- The predetermined future: tackling South Korea’s total fertility rate crisis (82 times)
- Jin Kyu Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):225-227. Published online November 6, 2024
-
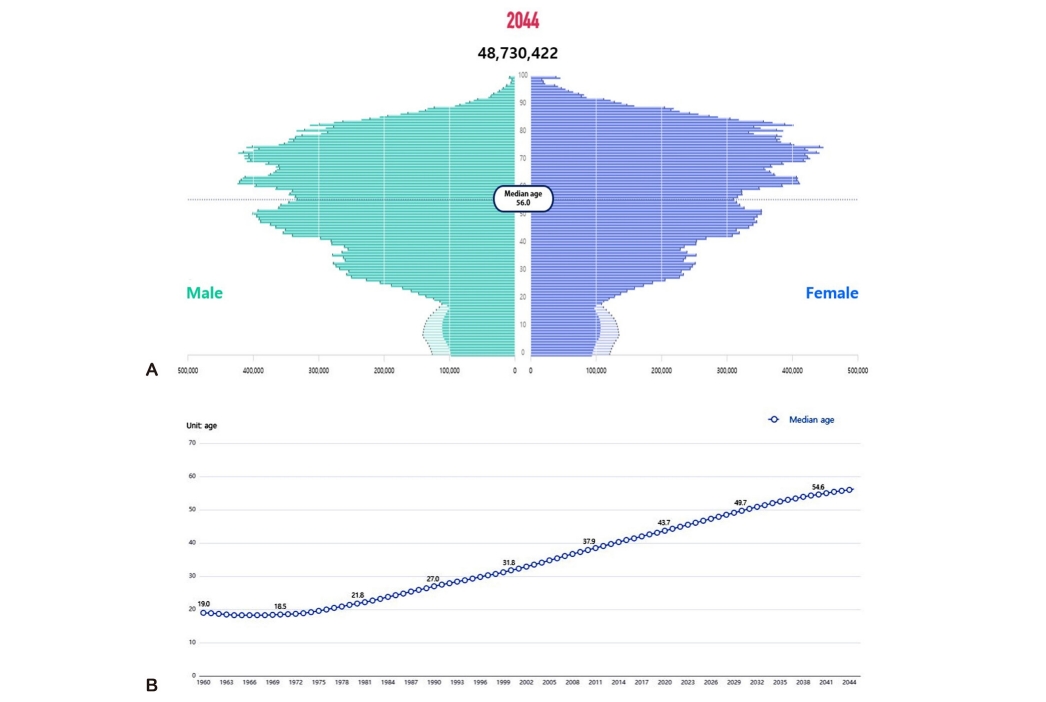
· South Korea faces a severe demographic crisis with the lowest global fertility rate. Despite significant investments, the total fertility rate continues to decline.
· It is necessary to fully mobilize national capabilities and execute comprehensive strategies that focus on both intangible and tangible values.
· Immediate and decisive action is essential to addressing these challenges effectively.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding dengue vaccine: a baseline study of community members and health providers in Indonesia (82 times)
- Abdul Wahab, Ida Safitri Laksanawati, Retna Siwi Padmawati, Asal Wahyuni Erlin Mulyadi, Wahyu Triadmajani, Jarir At Thobari
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):228-237. Published online November 13, 2024
-
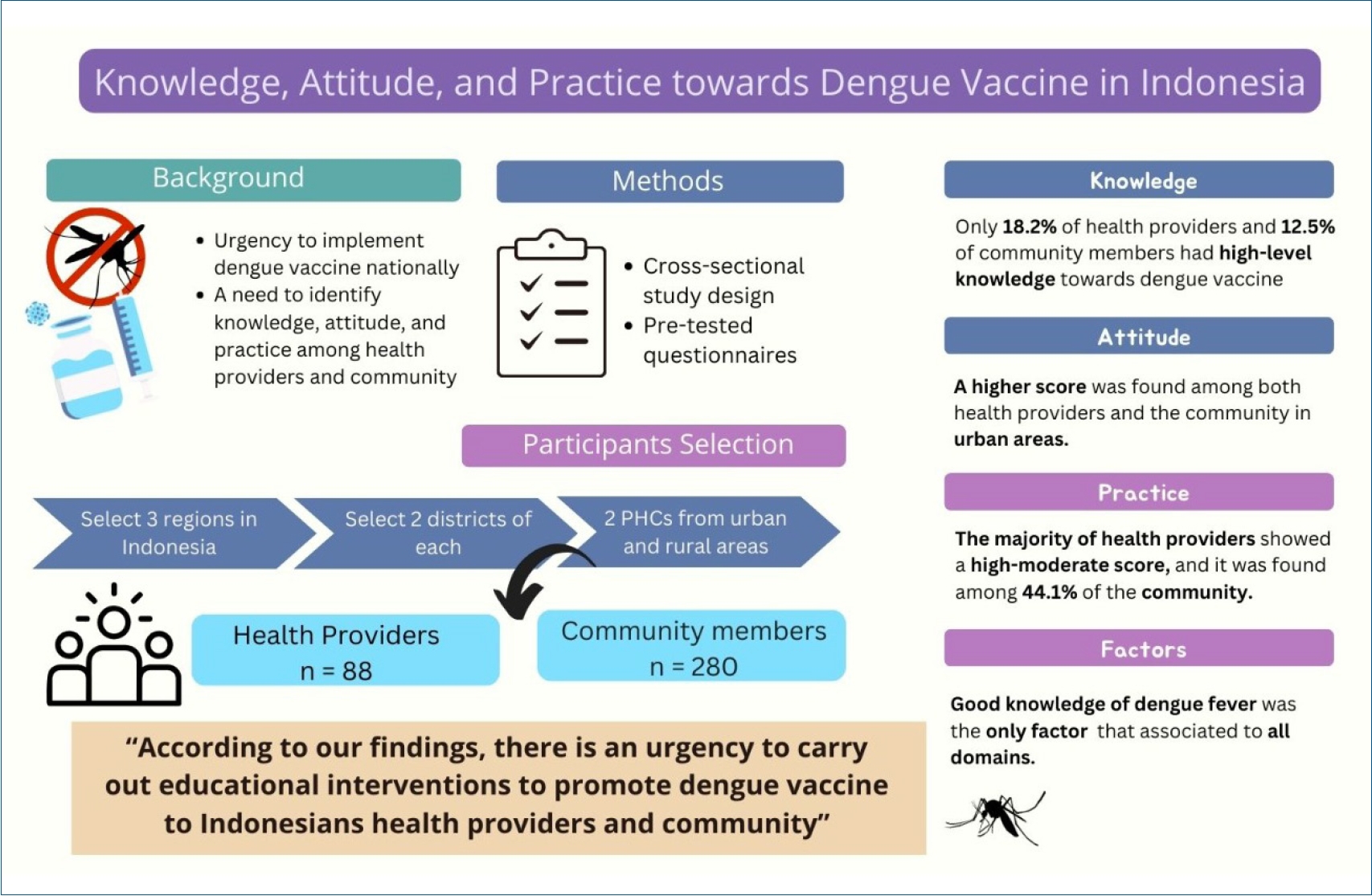
Question: Do community members and health providers show different level of knowledge, attitude, and practice towards dengue vaccine?
Finding: These 2 groups only differed in practice component, while the knowledge and attitude constituents were relatively low for both.
Meaning: There is an urgent need to deliver educational interventions to raise awareness of community members and health providers regarding dengue vaccination.
- Review Article
- Other
- Cost-effectiveness of newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency: a systematic review (80 times)
- Rezwanul Rana, Syed Afroz Keramat, Moin Ahmed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):628-640. Published online April 16, 2025
-

Universal newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) demonstrates robust cost-effectiveness across diverse high-income healthcare systems, both from healthcare and societal standpoints. Early detection yields substantial savings. While uncertainties persist, impacting precise cost-effectiveness, the overall finding is positive. Future research must prioritize enhanced data collection and statistical rigor to refine our understanding of SCID's economic impact within the Australian context.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Long-term epidemiological insights into rickets: a nationwide population-based retrospective study (80 times)
- Chun-Hao Chu, Ying-Chuan Chen, Pei-Yao Liu, Chun-Chieh Hu, Yu-Lung Lin, Feng-Chih Kuo, Chieh-Hua Lu, Tzu-Ju Hsu, Yu-Tung Hung, Fuu-Jen Tsai, Chien-Ming Lin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):879-891. Published online August 20, 2025
-

Question: What are the nationwide trends and mortality risk factors of nutritional versus hereditary rickets among children in Asia?
Finding: In 2012–2018, the incidence of rickets steadily increased, whereas mortality rates declined. Mortality is associated with a low household income, anemia, chronic kidney disease, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and a prolonged hospital stay.
Meaning: Early diagnosis and targeted interventions addressing social and medical vulnerabilities are critical to reducing ricket-related mortality.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Less invasive surfactant administration versus intubation-surfactant-extubation: a single-center retrospective study (80 times)
- C.S. Jithin, A. Nalina, A. Shashidhar, P.N. Suman Rao
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):991-997. Published online October 2, 2025
-
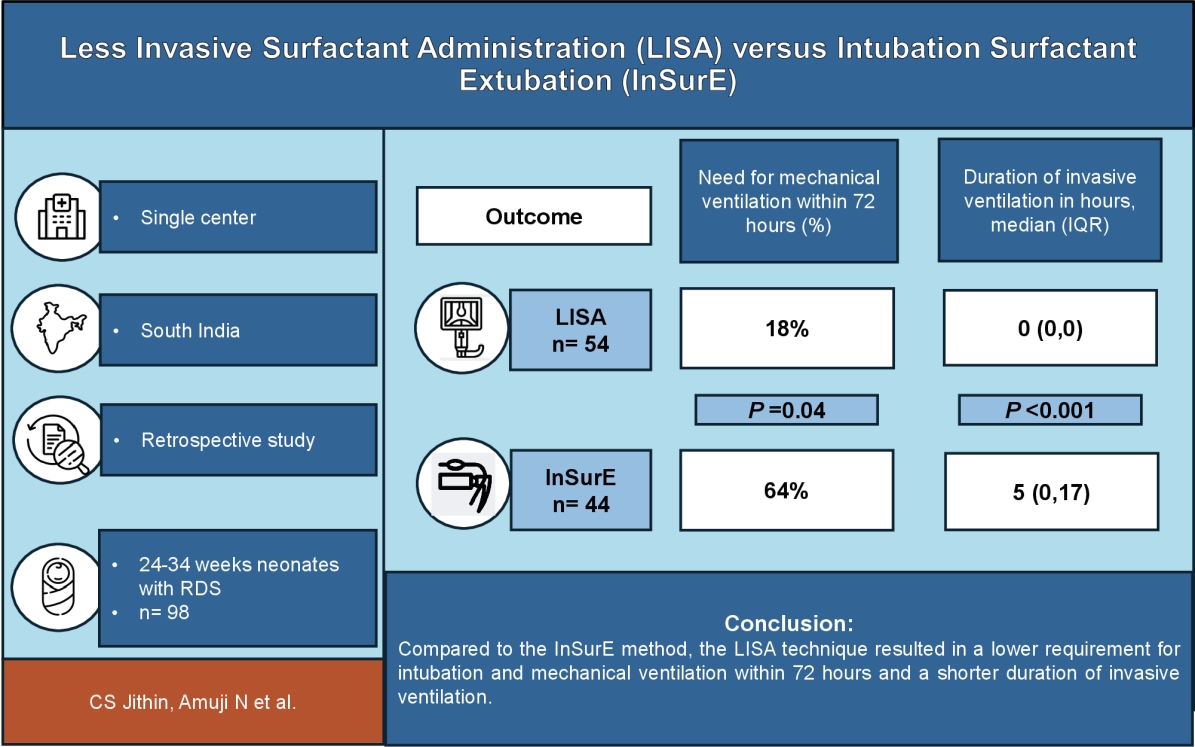
Question: Does less invasive surfactant administration (LISA) (vs. intubation-surfactant-extubation) improve clinical outcomes in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome?
Finding: LISA significantly reduced intubation and invasive mechanical ventilation needs within the first 72 hours and shortened the overall invasive respiratory support duration without increasing other morbidities.
Meaning: LISA is a less invasive and safer surfactant delivery alternative. Larger multicenter trials are needed to confirm its long-term safety and efficacy, especially in low- and middle-income countries.
- General Pediatrics
- Effect of online infant care training and postpartum counseling based on Meleis' transition theory on mothers' readiness for care and breastfeeding: a randomized controlled trial (78 times)
- Fatma Şule Bilgiç, Gülçin Bozkurt
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):521-530. Published online September 27, 2024
-

Question: Do interventions based on Meleis' transition theory affect mothers' readiness for baby care and breastfeeding?
Findings: We found a statistically significant difference between the intervention and control groups in mothers' readiness for newborn care and breastfeeding (P<0.001).
Meaning: This intervention increased breastfeeding rates while ensuring that mothers were ready to care for their babies and prepared for the role of motherhood.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Metabolic complications of obesity in children and adolescents (77 times)
- Hyunjin Park, Jung Eun Choi, Seunghee Jun, Hyelim Lee, Hae Soon Kim, Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):347-355. Published online November 16, 2023
-
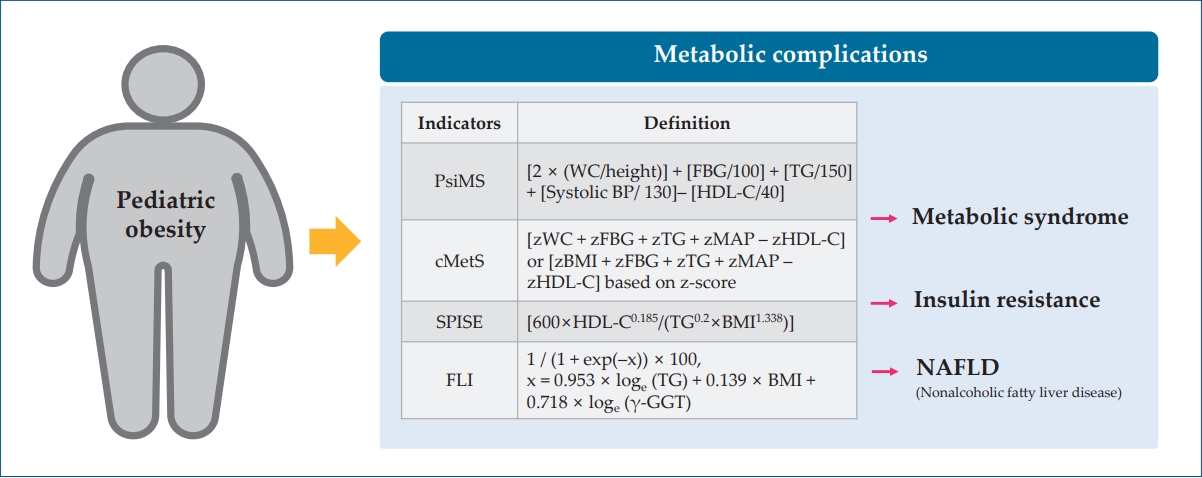
· Pediatric obesity increases the risk of metabolic complications (insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease) and long-term cardiovascular diseases.
· A new obesity definition and various indicators (continuous metabolic syndrome score, pediatric simple metabolic syndrome score, fatty liver index) have been proposed to evaluate children’s susceptibility to metabolic disorders.
· Laboratory and body composition tests in pediatric screenings can identify groups at high risk of metabolic complications of obesity.
- Original Article
- Oncology
- HLA‒B*58:01 and skin reactions in pediatric hematology and oncology patients treated with allopurinol (76 times)
- Parisa Maneechai, Cholada Ratanatharathron, Jassada Buaboonam, Kleebsabai Sanpakit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):974-980. Published online October 2, 2025
-
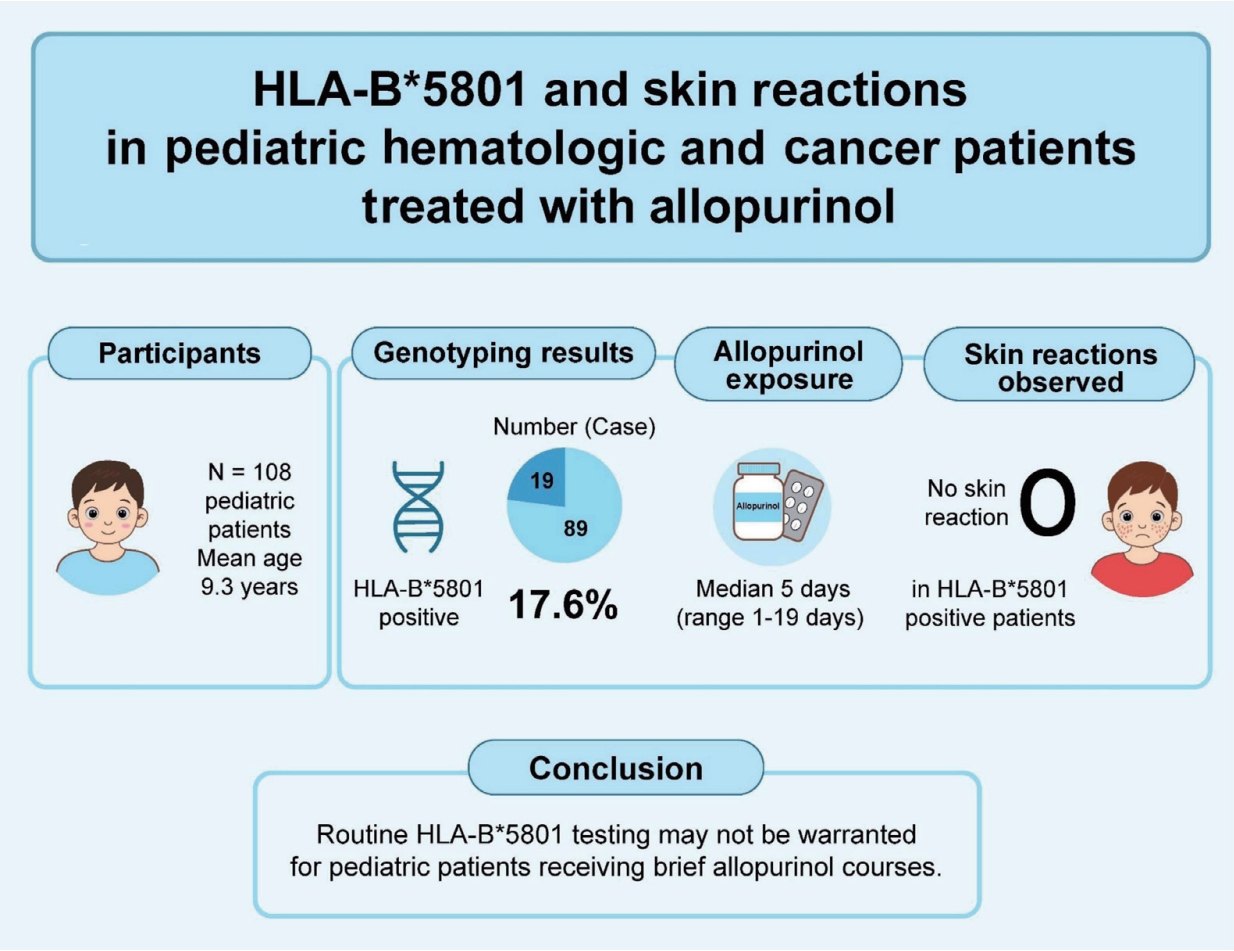
Question: Does human leukocyte antigen (HLA)–B*58:01 increase the risk of cutaneous reactions in pediatric patients with hematological and oncological diseases receiving allopurinol?
Finding: : Of 108 patients, 17.6% carried HLA–B*58:01 but none developed skin reactions. The only rash occurred in an HLA-B*58:01–negative patient.
Meaning: Short-duration allopurinol may mitigate severe cutaneous adverse reaction risk regardless of genotype. Routine HLA-B*58:01 screening may be unnecessary in pediatric patients with hematological and oncological diseases briefly receiving allopurinol.
- Gastroenterology
- Gut microbiota and metabolomic alterations in newborns of mothers with gestational diabetes mellitus (76 times)
- Wan-Hsin Su, Yi-Wei Wang, Chien-Chang Chen, Ming-Wei Lai, Hsun-Chin Chao, Ming-Chou Chiang, Ren-Huei Fu, Pai-Jui Yeh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):26-35. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Question: Does maternal gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) affect newborn gut microbiota and metabolomic profiles?
Finding: Neonates born to mothers with diet-controlled GDM exhibited reduced gut microbiota α-diversity, altered β-diversity, and metabolic shifts, including changes in fumarate and succinate levels, with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor and adipocytokine signaling pathway activation.
Meaning: Maternal GDM affects early microbial colonization and metabolism in newborns and may have long-term health implications.
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- Evidence-based management guidelines for noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis in children and adolescents (74 times)
- Eun Lee, Kyunghoon Kim, You Hoon Jeon, In Suk Sol, Jong Deok Kim, Taek Ki Min, Yoon Ha Hwang, Hyun-Ju Cho, Dong In Suh, Hwan Soo Kim, Yoon Hee Kim, Sung-Il Woo, Yong Ju Lee, Sungsu Jung, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Gwang Cheon Jang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):418-426. Published online January 23, 2024
-

· We suggest offering long-term macrolides to children with noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis with frequent exacerbations (conditional recommendation, moderate quality of evidence).
· We do not recommend the routine use of mucolytic agents, inhaled corticosteroids, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent exacerbation of bronchiectasis in children (inconclusive, very low quality of evidence).
· We recommend the use of nebulized hypertonic saline to prevent exacerbations and improve the lung function of children with noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis (weak recommendation, moderate quality of evidence).
- Oncology
- Breaking the barrier: a guidelines-based review of antiangiogenesis drug resistance in pediatric cancer therapy (74 times)
- Nader Shakibazad, Mahdi Shahriari, Mani Ramzi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):952-962. Published online November 24, 2025
-
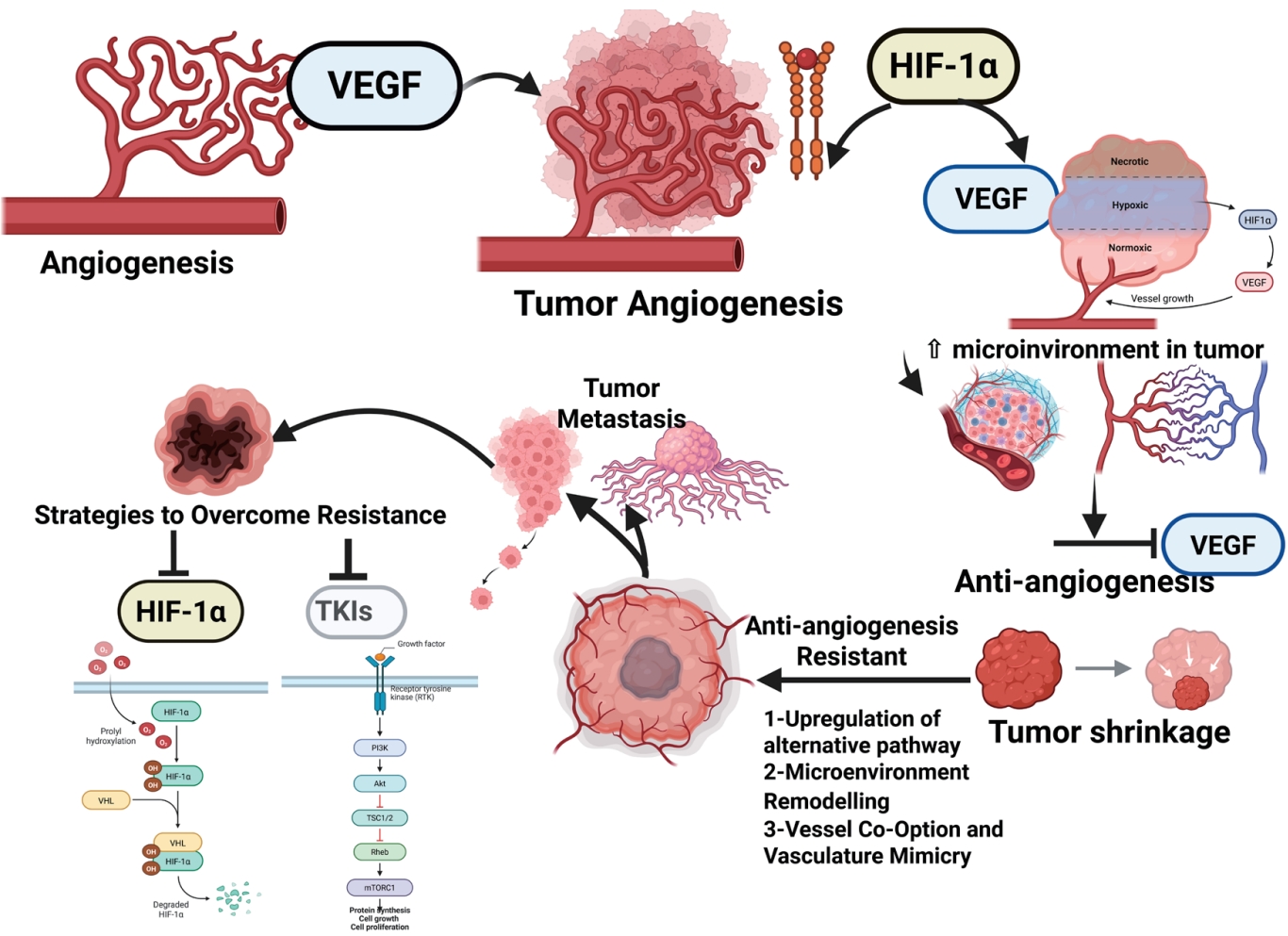
Antiangiogenic therapy resistance in pediatric cancers involves alternative angiogenic pathways, microenvironmental support, hypoxia-driven signaling, metabolic reprogramming, and structural adaptations such as vascular co-option. Metabolic adaptation highlights tumor plasticity. Effective treatments combine immunotherapy with biomarkers. To address vascular endothelial growth factor limitations, emerging targets include hypoxia-inducible factor-2α, endoglin, CXCR4, angiopoietin/Tie2, and bispecific antibodies. In resource-constrained settings, the guidelines recommend low-dose chemotherapy plus oral multiantiangiogenic agents to ensure improved accessibility and treatment outcomes.
- Gastroenterology
- Ingestion of foreign bodies and caustic substances in children: a narrative review on clinical evaluation and management update (73 times)
- Maria Rogalidou
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):11-21. Published online December 10, 2025
-

Foreign body and caustic substance ingestion in children aged 1–5 years can feature to severe and, sometimes life-threatening complications. High-risk items include batteries, magnets, and corrosive chemicals. Severity depends on object type, location, and ingestion timing. Prompt diagnosis and early endoscopic intervention are crucial. Individualized management, high clinical suspicion, and parental education are essential to improving outcomes and preventing immediate and long-term complications affecting a child’s quality of life.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Comorbidities of allergic rhinitis in children (72 times)
- Yong Ju Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):675-676. Published online July 31, 2024
-
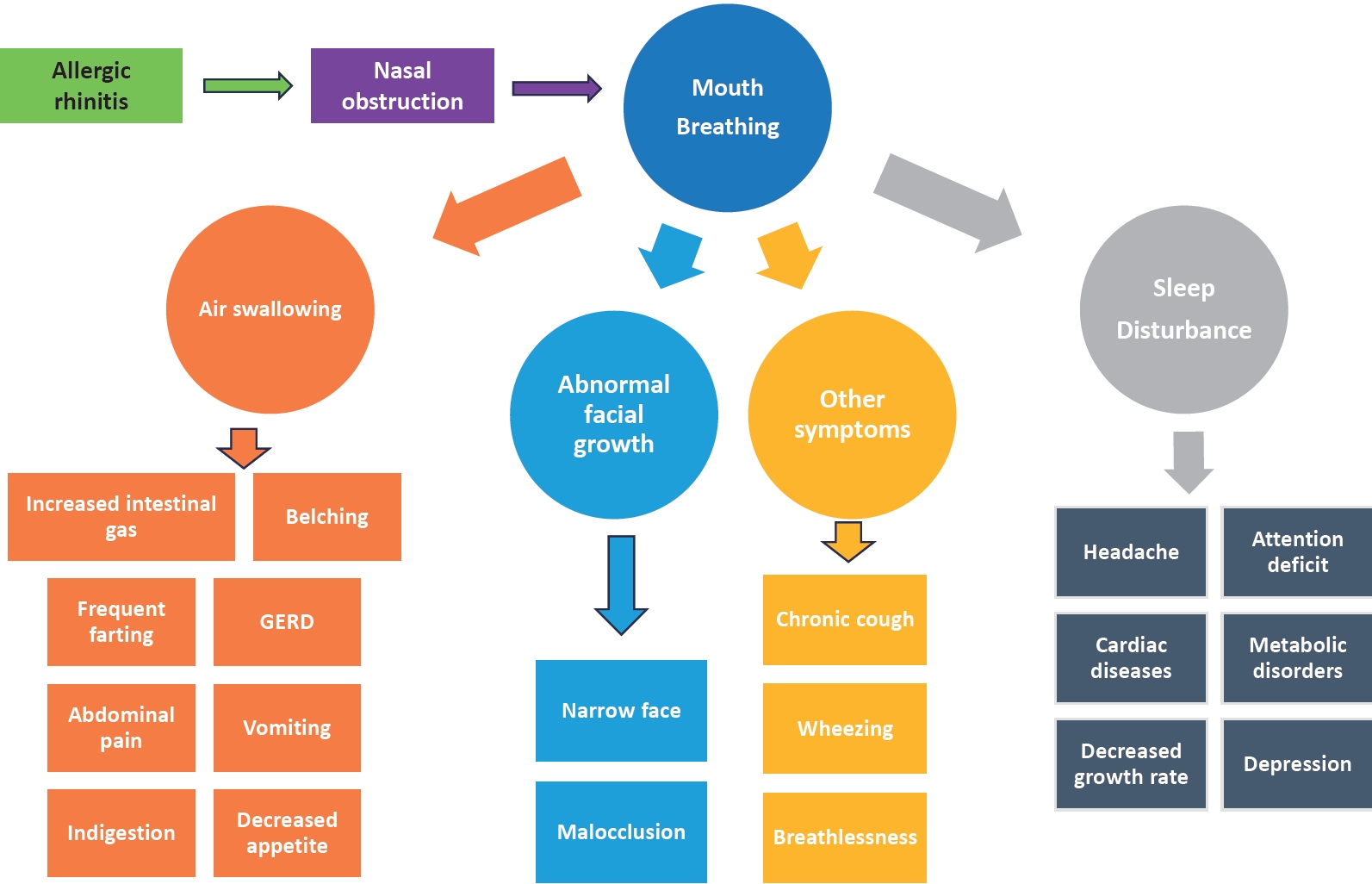
· Allergic rhinitis in children often goes undiagnosed or untreated, with significant systemic complications like sleep disorders, growth issues, and gastrointestinal symptoms linked to nasal obstruction.
· A patient-centered action plan that considers symptom severity, preferences, and comprehensive management of associated complications is essential for effective treatment.
- Neurology
- Screen time and neurodevelopment in preschoolers: addressing a growing concern in pediatric practice (72 times)
- Soongang Park, Hyewon Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):434-436. Published online January 13, 2025
-
· Excessive screen time in preschoolers is associated with neurodevelopmental delays, particularly during the early years of life.
· Parental supervision and national guidelines are critical in mitigating the negative impacts of excessive screen time and fostering healthy media habits in preschoolers.
- Review Article
- Hematology
- Iron deficiency in children with a focus on inflammatory conditions (70 times)
- Na Hee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):283-293. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· Iron deficiency has important effects on neurodevelopment and the immune system in children.
· Hepcidine plays an important role in iron homeostasis.
· Diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency in chronic inflammatory disease are important for patients' quality of life and disease course.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Evaluation of total serum bilirubin thresholds for discontinuing phototherapy in jaundiced neonates: a randomized study (69 times)
- Ajay Kumar, Nidhi Jain
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):539-545. Published online February 26, 2025
-

Question: What are the outcomes of jaundiced neonates when phototherapy is discontinued at 2 different total serum bilirubin (TSB) thresholds?
Findings: The study involved 80 neonates, comparing a recommended TSB threshold and a lower threshold for phototherapy discontinuation. Results showed a 14.3% reinstitution rate of treatment, with no adverse outcomes.
Meaning: Careful posttreatment monitoring is essential when discontinuing phototherapy, and future research should consider updated guidelines like those from the American Academy of Pediatrics.
- Incidence of neural tube defects in tertiary care university hospital in Bangladesh (68 times)
- Ismat Jahan, Arif Hossain, Shah Nizam Uddin Shaon, Sadeka Choudhury Moni, Mohammad Kamrul Hassan Shabuj, Sanjoy Kumer Dey, Mohammad Abdul Mannan, Mohammod Shahidullah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):530-538. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: What is the burden of neural tube defects (NTDs) in a tertiary care neonatal intensive care unit in Bangladesh?
Finding: The overall incidence of NTD was 6.4 (range, 4.59–11.2) per 1,000 live births, and the meningomyelocele complex was the most frequent location.
Meaning: The high incidence of NTD found in a leading tertiary care multidisciplinary referral hospital in Bangladesh may not reflect that of the wider population.
- Pulmonology
- Clinical course of children with postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans with versus without comorbid bronchopulmonary dysplasia (67 times)
- Lamia Medghoul, Julien Grosjean, Christophe Marguet, Hortense Petat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):497-502. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: Postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans (PIBO) is a chronic respiratory disease that typically develops in children after a severe respiratory infection. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is often comorbid in patients with PIBO.
Finding: Corticosteroid pulse therapy effectively manages PIBO with or without comorbid BPD, significantly reducing exacerbations and decreasing the daily requirement for inhaled corticosteroids.
Meaning: Therapeutic effects of corticosteroid pulses are rapid and sustained over time, in both groups.
- Cardiology
- Unsustainable and overworked: unpacking the challenges faced by pediatric cardiologists and cardiac surgeons in Korea (67 times)
- Soo In Jeong, GI Beom Kim, Sung Hye Kim, Jae Yoon Na, Hong Ju Shin, Sin Weon Yun, Lucy Youngmin Eun, Sang Yun Lee, Chang-Ha Lee, Kwang Ho Choi, Seul Gi Cha, Mi Young Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):732-741. Published online August 6, 2025
-

Question: What are the key challenges affecting pediatric cardiologists and cardiac surgeons in Korea?
Finding: Excessive workloads, low procedural volumes, and legal risks contribute to high burnout. Regional disparities limit skill maintenance and threaten workforce sustainability.
Meaning: Targeted policies ensuring fair workloads, legal protections, and regional support are essential to stabilizing the pediatric cardiac workforce and maintaining high-quality care.
- General Pediatrics
- Effectiveness of Kinder Lebensqualität Fragebogen (KINDL) and Children’s Somatic Symptom Inventory-24 (CSSI-24) for measuring postacute sequelae of COVID-19 in children: a diagnostic validation study (66 times)
- Lawrence Shih-Hsin Wu, Pei-Chi Chen, Xiao-Ling Liu, Shu-Tsen Liu, Chi-Hung Wei, Yu-Lung Hsu, Kai-Sheng Hsieh, Huan-Cheng Lai, Chien-Heng Lin, Chieh-Ho Chen, An-Chyi Chen, I-Ching Chou, Wen-Jue Soong, Hui-Ju Tsai, Chung-Ying Lin, Jiu-Yao Wang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):944-951. Published online September 12, 2025
-

Question: Although children with postacute sequelae of coronavirus disease 2019 (PASC) may experience persistent symptoms that affect their quality of life (QoL), a screening tool for identifying high-risk children is lacking.
Finding: Kinder Lebensqualität fragebogen (KINDL) and Children's Somatic Symptom Inventory-24 (CSSI-24) were significantly correlated. An optimal KINDL cutoff score (74.75) detected those at high risk of a reduced QoL.
Meaning: Integrating KINDL and CSSI-24 into routine pediatric outpatient care may enable timely identification and interventions for children at risk of PASC-related impairments.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Pubertal induction in prepubertal males with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: testosterone or gonadotropins? (65 times)
- Paolo Cavarzere, Riccardo Battiston, Valentina Lupieri, Valentina Mancioppi, Claudio Maffeis
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):1-10. Published online December 18, 2025
-

The pubertal induction process in males still poses a challenge for pediatric endocrinologists. The existing literature is limited, and it is not yet possible to make definitive recommendations. We described the various treatment for this condition and tried to analyze the unresolved questions to address the question posed in the title of our manuscript.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Rickets prevalence and treatment outcome: real-world data from Taiwan (64 times)
- Young Suk Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):868-870. Published online October 23, 2025
-
Rickets should be recognized as a significant public health concern during infancy and childhood. Recent studies from Taiwan have demonstrated a steady increase in the prevalence of nutritional rickets, and a similar trend is likely to emerge in Korea. Therefore, comprehensive clinical evaluation and appropriate biochemical assessment are essential to prevent long-term skeletal and systemic complications. Prompt diagnosis and timely initiation of appropriate treatment are crucial.
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Effects of diethylene glycol contamination of pharmaceutical products on unexplained acute kidney injury in children: a systematic review (63 times)
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Muhammad Luthfi Adnan, Hilmi Ardian Sudiarto, Satria Bintang Mahathma, Alya Ayu Tazkia, Hana Afifah Firdaus, Alfreda Amelia Khotijah, Miranti Dewi Pramaningtyas, Emi Azmi Choironi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):395-402. Published online January 4, 2024
-

A recent unexplained acute kidney injury (AKI) outbreak due to pharmaceutical product contamination with diethylene glycol (DEG) raises public attention. Our study revealed that DEG-contaminated paracetamol causes unexplained AKI in children. However, paracetamol is not the only contaminated drug. Other drugs, such as cough expectorants, antihistamines, and sedatives, can also be affected. Other chemicals, such as ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, can also contribute to poisonings.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Recent advances in understanding pathophysiology of non-nutritional stunting in very preterm infants (62 times)
- Eduardo Cuestas, Alina Rizzotti
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):287-297. Published online December 23, 2024
-

· Previous reviews of extrauterine growth restriction focused mainly on weight growth restriction caused by nutritional factors or pathological conditions.
· This review summarizes recent developments in the pathophysiology of nonnutritional length growth restriction in very preterm infants with focus on the impact of sustained neonatal inflammation on their short- and long-term outcomes.
· Further research is needed to investigate optimal strategies to improve length growth restriction in very preterm infants.
- Original Article
- Oncology
- Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation following chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for treatment of relapsed/refractory hematologic malignancy in children and young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis (62 times)
- Ghea Mangkuliguna, Edi Setiawan Tehuteru, Reganedgary Jonlean, Nicholas Adrianto, Stella Kallista
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):712-721. Published online July 4, 2025
-

Question: Does consolidative allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) after chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy improve outcomes of children and young adult patients with relapsed/refractory hematologic malignancies?
Finding: The meta-analysis showed reduced relapse rates and favorable survival trends with allo-SCT despite low evidence quality.
Meaning: Consolidative allo-SCT after CAR T-cell therapy may enhance survival; however, further clinical studies are needed.
- Gastroenterology
- Treatment targeting pediatric inflammatory bowel disease-associated anemia: experience from a single tertiary center (62 times)
- Ana S.C. Fernandes, Sara Azevedo, Ana Rita Martins, Ana Isabel Lopes
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):722-731. Published online June 10, 2025
-

Question: Does treating iron deficiency (ID) using intravenous iron in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) feature long-term safety and efficacy?
Finding: Intravenous iron supplementation was safe and effective. However, the ID recurrence rate was higher than expected.
Meaning: Proactive screening and treatment of ID in pediatric IBD are essential. The Ganzoni formula likely underestimates the iron requirements of pediatric patients. Prospective trials are needed to optimize iron treatment dosing.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- A review of vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D receptor polymorphisms in endocrine-related disorders (61 times)
- Nur Faten Hafizah Rosli, Noor Shafina Mohd Nor, Rose Adzrianee Adnan, Siti Hamimah Sheikh Abdul Kadir
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):30-52. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency is high among children and adolescents and mainly attributed to changes in environmental factors.
· Vitamin D hormone-like properties are associated with many endocrine-related disorders.
· The effect of vitamin D is modulated by the vitamin D receptor, polymorphisms of which are reportedly associated with an increased risk of disease development in children and adolescents.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- The role of serum zinc and selenium levels in etiology of febrile seizures (61 times)
- Yavuz Ataş, Hatice Gamze Poyrazoğlu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):388-394. Published online January 13, 2025
-

Zinc may play a key role in preventing febrile seizures by increasing the seizure threshold and reducing oxidative stress. Incorporating zinc supplements into treatment could help protect children from the adverse effects of febrile seizures and improve their overall outcomes.
- Hematology
- Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in pediatric patients with type VI mucopolysaccharidosis (61 times)
- Vedat Uygun, Koray Yalçın, Hayriye Daloğlu, Seda Öztürkmen, Suna Çelen, Suleimen Zhumatayev, Gülsün Karasu, Akif Yeşilipek
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):601-607. Published online March 11, 2025
-
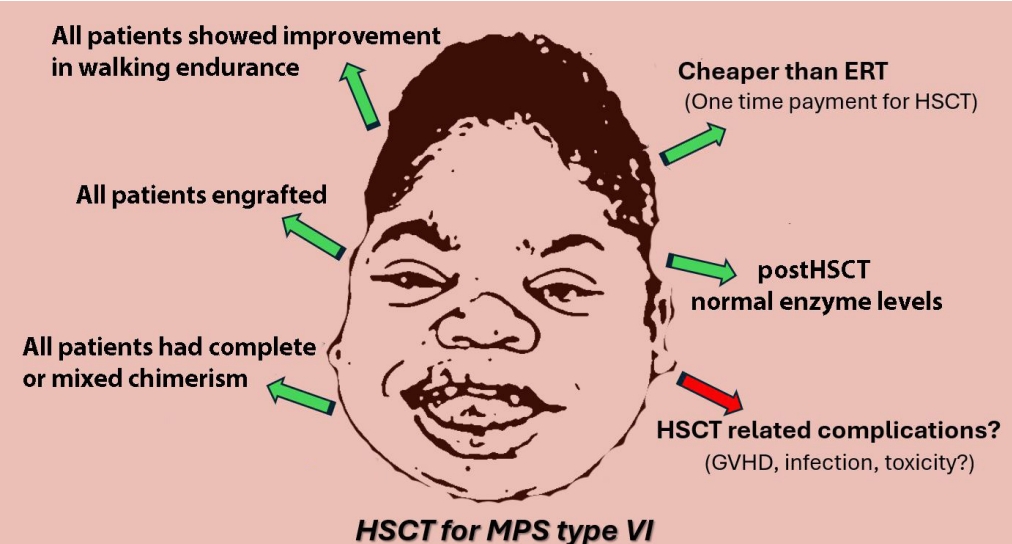
Question: Could hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) be an alternative to enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) for type VI mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS VI)?
Finding: HSCT is generally not offered due to reports of high toxicity and mortality. However, we detected fewer complications and graft-versus-host disease cases and no deaths with HSCT.
Meaning: HSCT is both less expensive than ERT and permanent; thus, it should be considered an alternative treatment for MPS VI.
- Perspective
- General Pediatrics
- Navigating the complex behavioral landscape of children in foster care and adopted families (61 times)
- Anisha Choi, Sandhya J. Kadam
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):620-623. Published online May 12, 2025
-
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











