Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last six months.
- Review Article
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Development of orphan drugs for rare diseases (122 times)
- Han-Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):315-327. Published online June 28, 2023
-
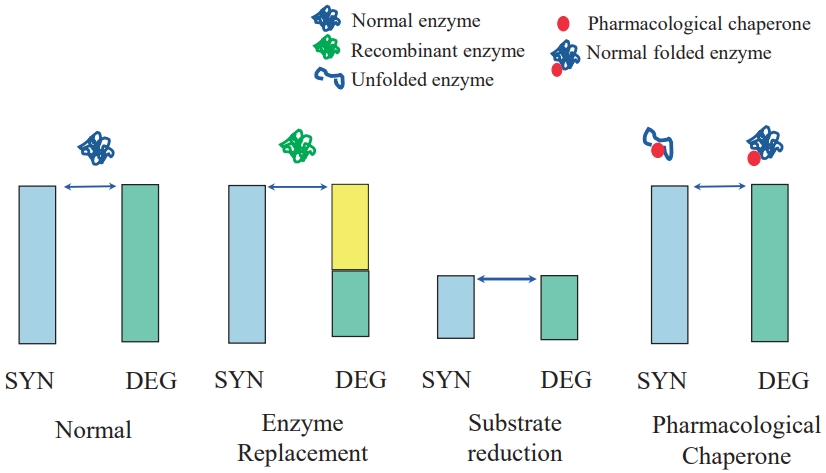
· Orphan disease is a rare disease, primarily affecting newborn and children. Vast majority of orphan diseases has genetic background.
· Orphan disease is individually rare. But as a whole, it is not rare, becoming a great socioeconomic burden.
· The diagnosis of rare genetic disease has been problematic, but recent progress of genome analysis technologies makes it faster and more precise.
· There are many unmet needs as to the curative treatment. However, the number of treatable rare diseases is growingly increasing owing to the development of biotechnology.
· Most orphan drugs are extremely expensive because of numer ous hurdles during the process of drug development as well as small number of patients.
- Gastroenterology
- High-resolution anorectal manometry in children (116 times)
- Yogesh Waikar
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):57-63. Published online June 14, 2023
-
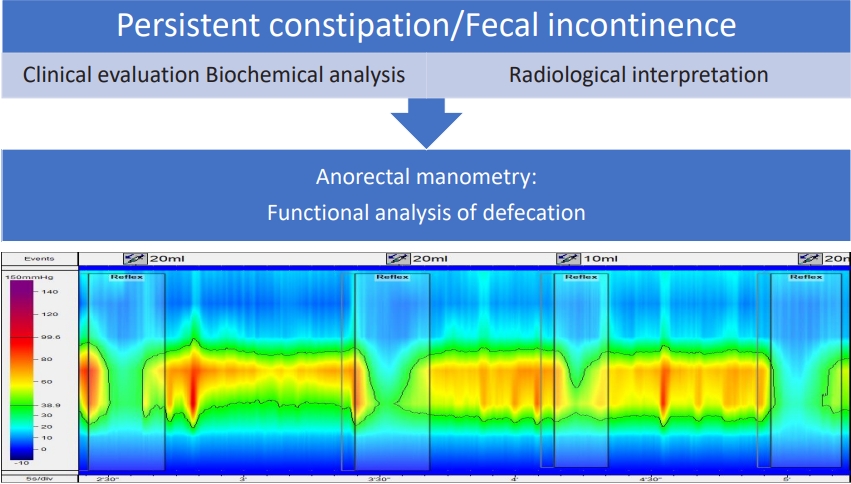
· Anorectal manometry is safe in children.
· Defecation Dyssynergia is one of the commonest cause of chronic constipation.
· Positive Rectoanal inhibiory reflex rules out Hirschsprung's Disease
- Allergy
- Comparison and review of international guidelines for treating asthma in children (111 times)
- Eui Jeong Roh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):447-455. Published online August 20, 2024
-

Asthma is the most common chronic disease among children. Although asthma in children may spontaneously improve, it continues into adulthood in many cases. Therefore, appropriate disease management and medication are essential. Consistent and objective guidelines are needed to manage pediatric asthma and related adverse reactions.
- Original Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Serum amyloid A and proadrenomedullin as early markers in critically ill children with sepsis (111 times)
- Nagwan Y. Saleh, Wafaa M. Abo El Fotoh, Mona S. Habib, Salem E. Deraz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):578-586. Published online February 26, 2025
-
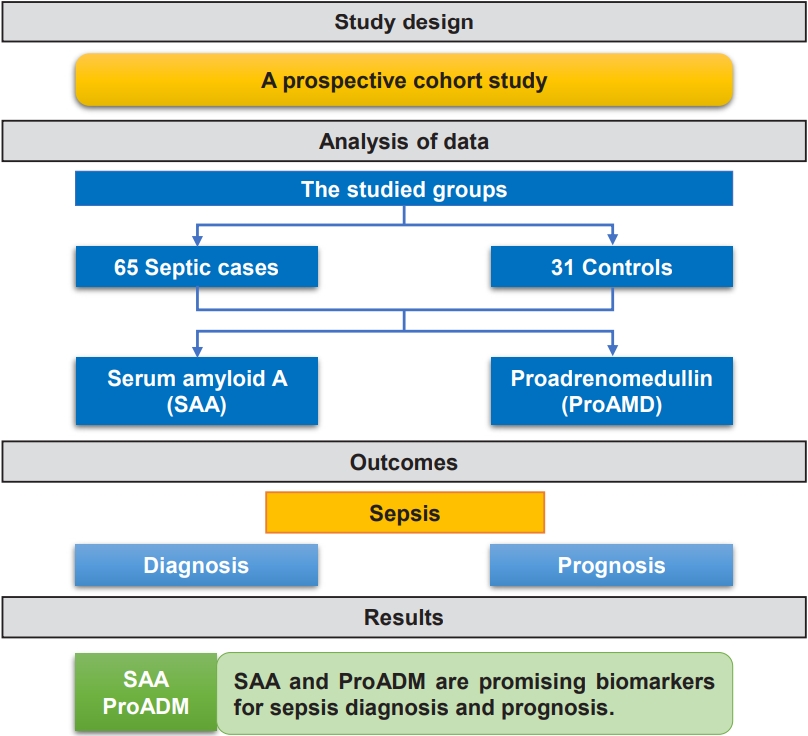
Question: Are serum amyloid A (SAA) and proadrenomedullin (proADM) levels early markers in critically ill children with sepsis?
Finding: This prospective case-control study included 65 critically ill children with sepsis admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit and 31 controls. SAA and proADM levels were significantly higher in patients versus controls.
Meaning: SAA and proADM are promising biomarkers for diagnosing and predicting outcomes in pediatric sepsis.
- Cardiology
- Vasovagal syncope and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in adolescents: transcranial doppler versus autonomic function test results (111 times)
- Dong Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):673-679. Published online August 6, 2025
-

Question: Vasovagal syncope (VVS) and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) are representative forms of neurally mediated syncope. What influences the occurrence of each?
Finding: Autonomic function test results did not differ, but cerebral blood flow during diastole on transcranial doppler differed between VVS and POTS.
Meaning: Differences in diastolic cerebral blood flow velocity play an important role in VVS and POTS.
- Editorial
- Nutrition
- Zinc as a treatment modality for acute infectious diarrhea in children (107 times)
- Ji Sook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):223-224. Published online October 31, 2024
-
· Prevention and management of dehydration is the major goal of treatment in acute infectious diarrhea in children.
· Zinc could be effective as an adjuvant therapy in reducing the duration of acute infectious diarrhea in malnourished children.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Dual-strain probiotics Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactobacillus acidophilus reverse gut dysbiosis in preterm neonates: a randomized controlled trial (107 times)
- Setthawut Sittiwong, Pornthep Tanpowpong, Pisut Pongchaikul, Pracha Nuntnarumit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):763-771. Published online August 6, 2025
-
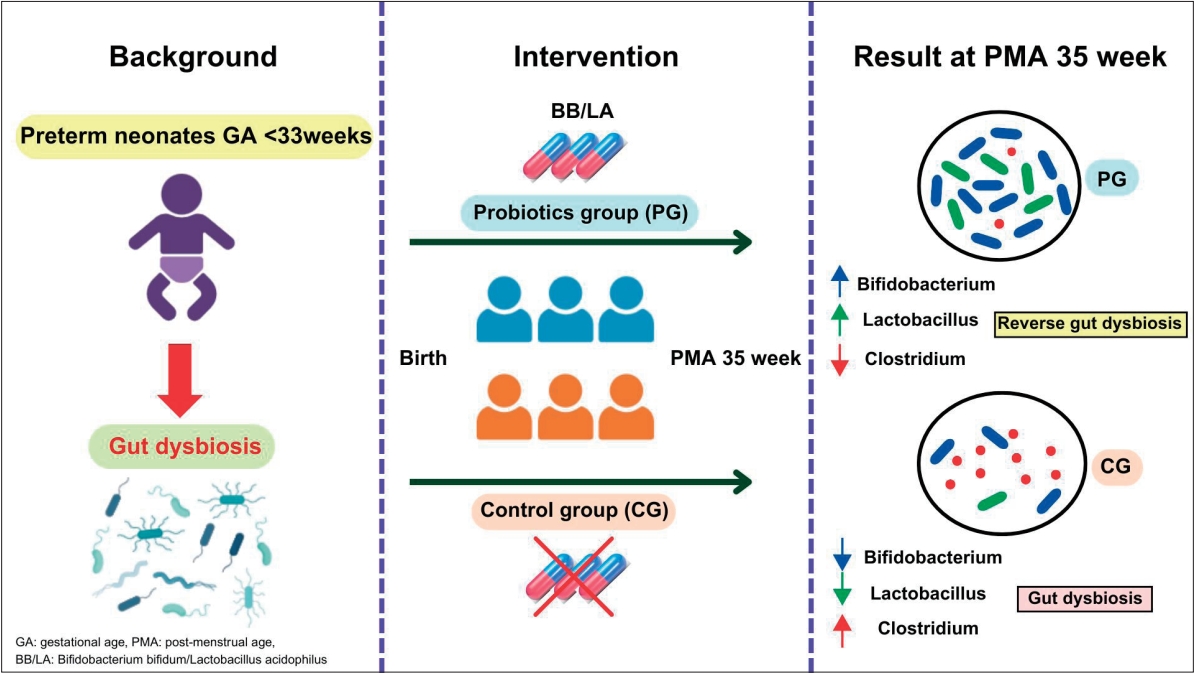
Question: Can probiotics BB/LA reverse gut dysbiosis in preterm neonates?
Finding: BB/LA supplementation induced more diverse beta diversity and increased relative abundances of Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus and decreased relative abundance Clostridium.
Meaning: Early BB/LA supplementation could reverse gut dysbiosis in preterm neonates.
- Review Article
- Other
- Microplastic and human health with focus on pediatric well-being: a comprehensive review and call for future studies (106 times)
- Rogers Wainkwa Chia, Ntegang Venant Atem, Jin-Yong Lee, Jihye Cha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):1-15. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· Milk and formula are common sources of microplastic in infants.
· Water and air are the most common sources of microplastic pollution from infancy to adolescence.
· Microplastic use by children of all ages can cause cell damage and affect their health.
· Microplastics present in children can be quantified using a stereomicroscope and characterized using micro- Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy.
- Original Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- C3 glomerulopathy in children: experience at a resource-limited center (106 times)
- Soumya Reddy, Abhishek Ghante, Mahesha Vankalakunti, Anil Vasudevan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):311-318. Published online November 28, 2024
-

Question: What are the clinicopathological features and outcomes of pediatric C3 glomerulopathy (C3G) in resource-limited settings?
Finding: Children with C3G in resource-limited settings have significant morbidities, and most experience kidney sequelae despite treatment. Electron microscopy was performed in only 50% of our patients, while none received complement assays or genetic testing.
Meaning: Pediatric C3G presentation, management, and kidney outcomes vary. Its thorough evaluation and management are challenging in resource-limited settings.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Anxiety disorders presenting as gastrointestinal symptoms in children – a scoping review (105 times)
- Anjali Kumar, Pramodh Vallabhaneni
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):344-351. Published online January 13, 2025
-

A positive bidirectional relationship between gastrointestinal disorders and anxiety, but with no clear aetiology, was identified. Factors such as somatisation and pain catastrophising resulted in poorer pain-related outcomes in children. Further studies are required to understand this relationship in order to have targeted treatments and ensure better long term outcomes.
- General Pediatrics
- Bridging the gap: autism spectrum disorder in children in the United States and worldwide: a narrative review (105 times)
- Sandhya J. Kadam, Malika Goel
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):852-857. Published online October 2, 2025
-

The prevalence of autism is increasing worldwide. The United States has the highest numbers, likely due to the availability of better treatment options. However, global disparities exist, especially in low-resource settings in which stigma, underdiagnosis, and limited services hinder care. A coordinated international approach emphasizing early screening, inclusive policies, and culturally sensitive support systems can bridge this gap and improve the outcomes for children with autism and their families worldwide.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Strategies to support language development in neonatal intensive care unit: a narrative review (104 times)
- Ju Sun Heo, Ee-Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):651-663. Published online November 6, 2024
-
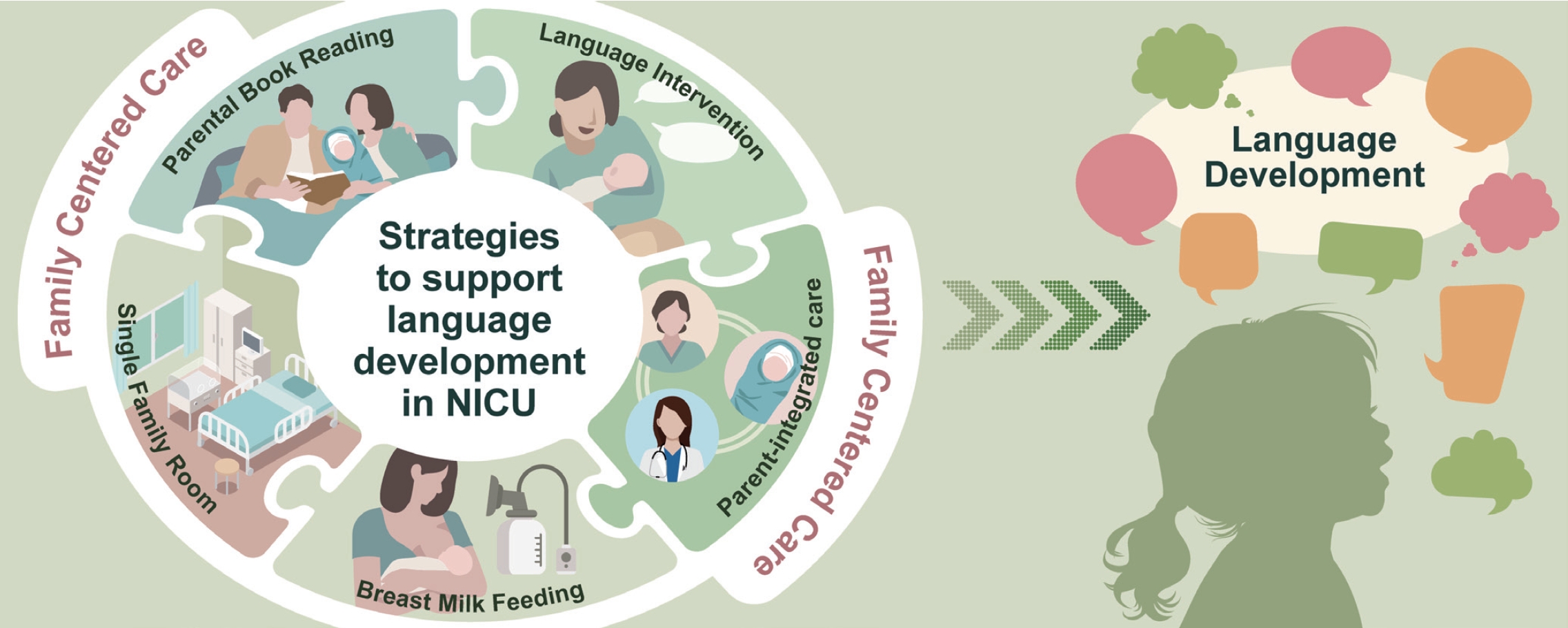
· Preterm infants often experience speech and language development delays during early childhood, impacting children's ultimate outcomes.
· Promoting breastfeeding, increasing parent-infant interactions in a single-family room, promoting a nurturing language environment by parental book reading and language interventions, and parent-integrated interventions in the neonatal intensive care unit could potentially enhance children's language development.
· Integrating these strategies through family-centered care is essential.
- Editorial
- Hematology
- Absolute versus functional iron deficiency (103 times)
- Hye Lim Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):138-140. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· Iron deficiency (ID), the most common cause of anemia, can be classified into absolute and functional types. Absolute ID is a state of low total body iron, while functional ID is a state of imbalance between iron demand and iron availability due to inflammation and/or infection.
· ID is diagnosed by serum ferritin and transferrin saturation levels.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Neonatal ichthyosis-sclerosing cholangitis syndrome caused by a novel CLDN1 mutation: a case report and literature review (102 times)
- Upasana Ghosh, Ankit Agrawal, Varunvenkat M. Srinivasan, Rani Manisha, Umesh Shukla, Vikas Jain, Mayank Nilay, Harish Kumar
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):858-867. Published online October 2, 2025
-

· Neonatal ichthyosis-sclerosing cholangitis (NISCH) syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by cholestasis and manifestations such as generalized ichthyosis, alopecia, and dental anomalies.
· The clinical features of NISCH syndrome are distinct and necessitate an early genetic diagnosis.
· The disease phenotype can vary significantly, ranging from no liver involvement and transient neonatal cholestasis to end-stage liver disease.
· Management requires a multidisciplinary approach with long-term follow-up.
- Endocrinology
- Continuous glucose monitoring in Korean pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes: current landscape and clinical implications (101 times)
- Hwa Young Kim, Jaehyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):842-851. Published online October 2, 2025
-

Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has transformed pediatric type 1 diabetes care by facilitating tighter glycemic control, reducing hypoglycemia, and improving quality of life.
Recent advances in CGM technology and the expansion of insurance coverage in Korea have led to its broader adoption.
Emerging metrics such as time in tight range offer refined tools for individualized glycemic assessment, highlighting CGM’s evolving role in personalized pediatric diabetes management.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Comparative analysis of goal attainment for helmet therapy versus conservative management for positional plagiocephaly in infants (100 times)
- Bjoern Vogt, Ariane Deutschle, Georg Gosheger, Adrien Frommer, Andrea Laufer, Henning Tretow, Robert Roedl, Gregor Toporowski
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):892-900. Published online October 2, 2025
-

Question: Is helmet therapy more effective than conservative management in treating positional plagiocephaly?
Finding: Both approaches reduced cranial asymmetry with comparable correction speed. Helmet therapy showed a trend toward greater severity reduction.
Meaning: Early treatment initiation was the strongest predictor of improvement. Helmet therapy may offer additional benefit in more severe cases.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal family-centered care: evidence and practice models (99 times)
- Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):171-177. Published online June 14, 2023
-
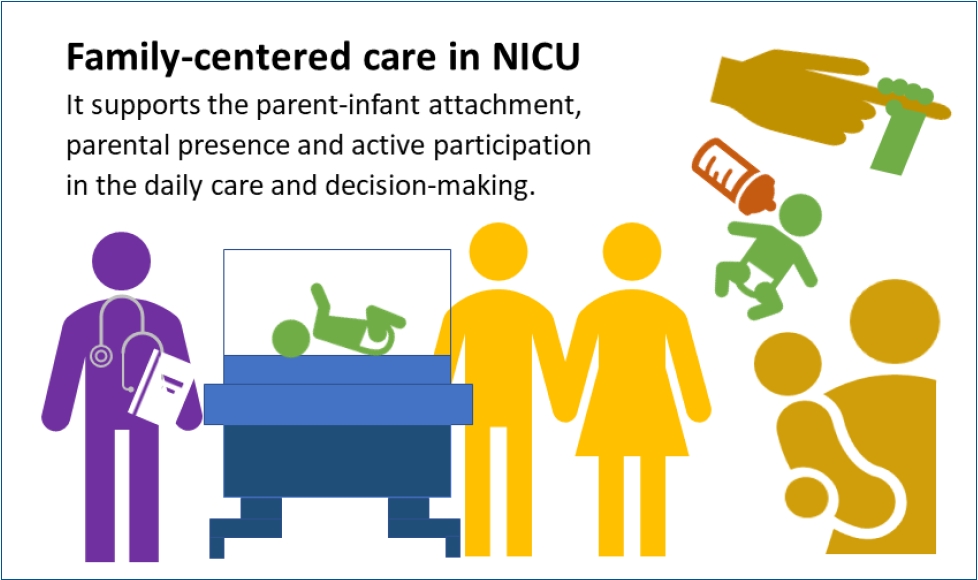
· Concrete evidence exists of early parent-infant attachment supported by family-centered care (FCC) in the neonatal intensive care unit.
· FCC involves the parents’ presence and participation in the infant’s care and decision-making.
· A private and comfortable space should be provided. A single-family room is ideal; however, a quiet space with a recliner can be a good alternative.
· Care culture changes and staff training are required.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Screen time among preschoolers: exploring individual, familial, and environmental factors (96 times)
- Sangha Lee, Donghee Kim, Yunmi Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):641-650. Published online September 12, 2024
-
This systematic review examined the correlation between screen time and various factors in preschoolers. Findings suggest that media parenting, including setting appropriate media limits, is crucial in protecting against excessive screen exposure. However, limited research has been done on the impact of family and personal factors, particularly with the increasing use of portable devices among young children.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Trends and determinants in breastfeeding among Korean infants (2007–2021): a nationwide study using the National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children (95 times)
- Minwoong Kang, Eui Kyung Choi, Jeung Min Lee, Hye-Jung Shin, Woo Ryoung Lee, Son Moon Shin; Korean Society of Breastfeeding Medicine
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):772-780. Published online July 4, 2025
-
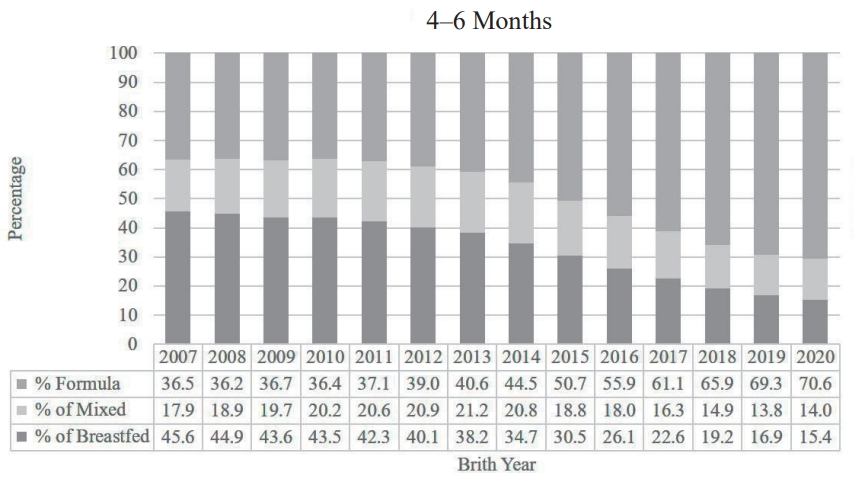
Question: What are the recent trends and determinants of breastfeeding in South Korea?
Finding: Breastfeeding rates in South Korea declined significantly from 2007 to 2021, with lower rates observed in preterm, low-birthweight, and multiple-birth infants as well as rural or lower-income households.
Meaning: Targeted interventions, including prenatal education, postnatal support, and community-based programs, are required to address disparities and improve breastfeeding rates.
- Letter to the Editor
- General Pediatrics
- Debate around and impact of digital screen time and media parenting on children’s development (94 times)
- Gowda Parameshwara Prashanth
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):551-553. Published online March 11, 2025
-

- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Impact of screen exposure during pediatric ages including multifaceted aggravating factors: a literature review (93 times)
- Daniel González-Pérez, David Sebastián Huertas-Moreno, Manuela Granados-Pinilla, Sofía Hernandez-Rojas, Laura González-Rincon, Geraldine Hurtado-Garcia, Simón Grisales-Calle, María José González-Mariño, Luz Dary Gutierrez-Castañeda, Jhon Camacho-Cruz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):751-760. Published online September 24, 2025
-
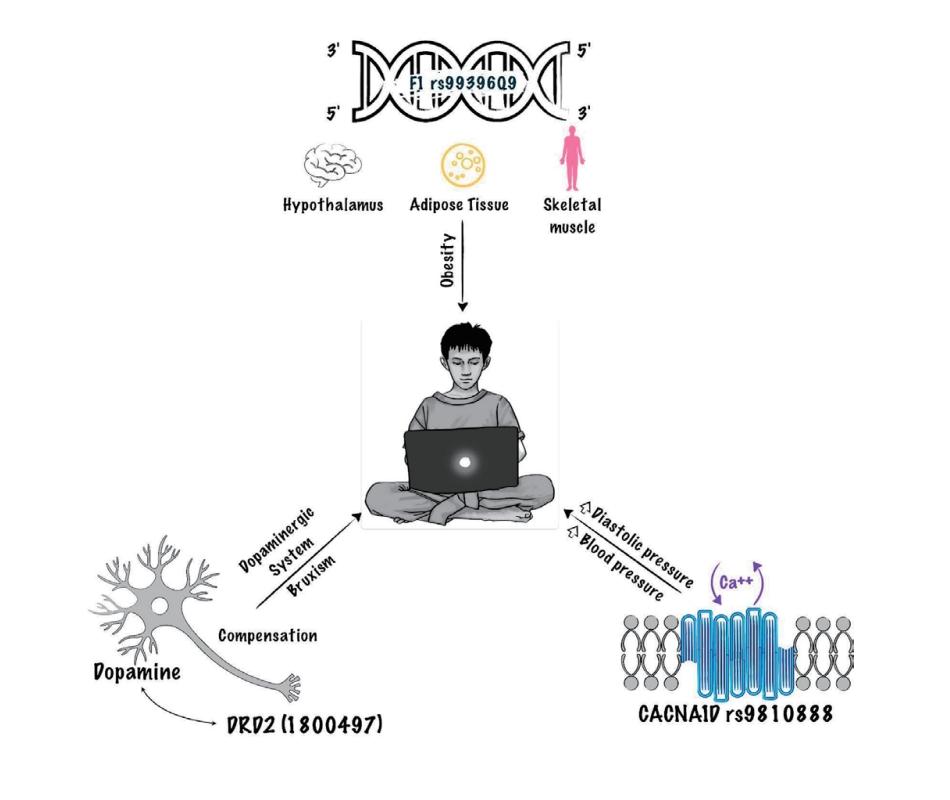
Excessive screen time in children is linked to obesity, overweight, sedentary behavior, depression and mood disorders, myopia, behavioral changes, sleep disturbances, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, among others. Polymorphisms in genes like FTO, CACNA1D, and DRD2 could further increase these risks. Implementing strategies such as limiting screen use, creating screen-free zones, and monitoring content is essential to mitigate adverse physical and mental health effects in the pediatric population.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Success rates of conservative treatment and optimal surgical timing for pediatric chylothorax (93 times)
- Pakwan Kaewchusen, Narumon Densupsoontorn, Supaluck Kanjanauthai, Puthita Saengpanit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):871-878. Published online August 6, 2025
-

Question: What is the success rate of conservative treatment for pediatric chylothorax, and when should surgical intervention be employed?
Finding: Overall success rate of conservative treatment was 83.3%. Surgically related etiologies and lower peak pleural fluid drainage rates were significantly associated with successful conservative management of pediatric chylothorax.
Meaning: If chylous drainage persists at ≥10 mL/kg/day beyond 2 weeks of optimal conservative treatment, surgical intervention should be considered.
- Review Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Protocolized sedation may reduce ventilation and sedation requirements in the pediatric intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis (90 times)
- Ambrus Szemere, Alíz Fazekas, Anna Réka Sebestyén, Rani Ezzeddine, Veronika Upor, Marie Anne Engh, Péter Hegyi, Zsolt Molnár, Klára Horváth
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):406-416. Published online February 19, 2025
-
Protocolized sedation may reduce ventilation requirements, pediatric intensive care unit length of stay, and sedative exposure. However, it may increase the likelihood of unplanned extubation, highlighting the importance of incorporating preventive measures to mitigate this risk.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Factors associated with thiamin deficiency in pediatric patients with heart disease and receiving diuretics: a single-center study (90 times)
- Phakwan Laohathai, Rathaporn Sumboonnanonda, Puthita Saengpanit, Chodchanok Vijarnsorn, Chatchawan Srisawat, Kwanjai Chotipanang, Sarawut Junnu, Supawan Kunnangja, Hathaichanok Rukprayoon, Phakkanan Phuangphan, Sompong Liammongkolkul, Arthima Phaokong, Narumon Densupsoontorn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):666-672. Published online April 16, 2025
-

Question: Are pediatric patients with heart disease who are receiving diuretics at risk of thiamin deficiency (TD)?
Finding: Fifteen percent of the patients had TD. TD was associated with inadequate dietary thiamin intake and increasing age.
Meaning: The thiamin pyrophosphate effect should be assessed in those with high risk of TD. Dietary counseling should be emphasized to ensure adequate dietary thiamin intake.
- Hematology
- Treatment and clinical outcomes of pediatric autoimmune hemolytic anemia: real-world single-center data from Korea (89 times)
- Young Dai Kwon, Eun Sun Jung, Yeon Jung Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):522-529. Published online April 16, 2025
-

Question: Can pediatric autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) be effectively managed using first-line steroids?
Finding: In this single-center study, pediatric patients with AIHA achieved normal hemoglobin levels within 16.5 days (range, 9.0–22.0 days) of first-line steroid treatment and maintained effective responses for 2 months.
Meaning: These outcomes highlight the efficacy of steroid treatment in pediatric versus adult AIHA and underscore the need for multicenter trials to establish standardized treatment guidelines.
- Infection
- Enteric pathogens implicated in acute infectious diarrhea among young children in resource-limited region with rapidly growing population: a hospital-based cross-sectional study (88 times)
- Aseel Mahmood Ibrahim Al-Mashahedah, Randa Mohammed Dhahi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):379-387. Published online December 23, 2024
-

Question: What are the most common enteric pathogens in acute diarrhea among children younger than 5 years of age, and which age group is most susceptible?
Finding: Bacteria were the most common causative microorganisms of diarrhea, followed by viruses, parasites, and fungi. The 1–2-year age group was the most commonly affected.
Meaning: There is a need to formulate preventive strategies targeting children exposed to enteric pathogens to limit diarrhea.
- Gastroenterology
- Fecal microbiome profiles in infants with biliary atresia versus nonbiliary atresia cholestasis: a pilot study (84 times)
- Nur Azizah, Fadilah Fadilah, Silvia Werdhy Lestari, Muzal Kadim, Fithriyah Sjatha, Hanifah Oswari
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):932-943. Published online August 20, 2025
-

Question: How does the gut microbiota profile of infants with biliary atresia (BA) differ from that of infants with non-BA cholestasis and healthy infants in the Indonesian population?
Finding: The unique fecal microbiome composition of the BA group differed significantly from that of the other 2 groups.
Meaning: There is an urgent need to improve dysbiosis in BA and non-BA cholestasis to prevent worsening liver injury in cholestasis.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Practical issues of oral immunotherapy for egg or milk allergy (83 times)
- Sukyung Kim, Kangmo Ahn, Jihyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):140-148. Published online June 19, 2023
-
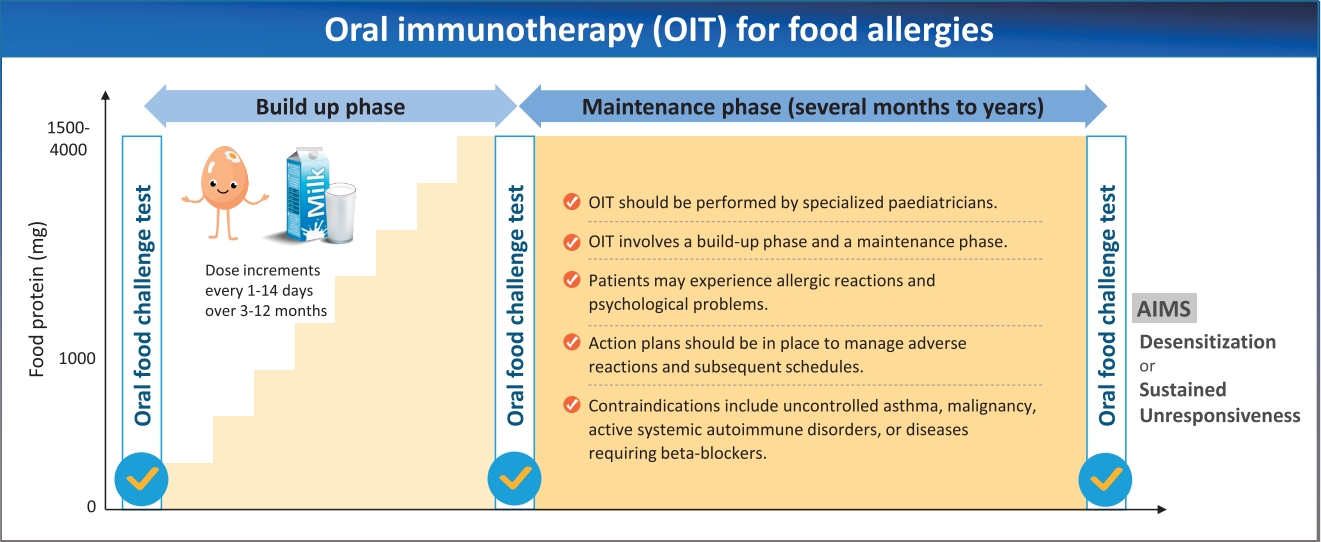
· Oral immunotherapy should be supervised by pediatricians with experience administering oral food challenge tests and managing allergic reactions.
· Food allergen intake is gradually increased and maintained for years.
· Patients may experience allergic reactions and psychological problems.
· Adjunctive therapies (biologics, antihistamines, and leukotriene receptor antagonists) may improve efficacy and safety.
· Contraindications include uncontrolled asthma, malignancy, active autoimmune disorders, and beta-blocker usage.
- Endocrinology
- Association between pre- and postnatal exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals and birth and neurodevelopmental outcomes: an extensive review (83 times)
- Ozge Yesildemir, Mensure Nur Celik
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):328-346. Published online November 16, 2023
-
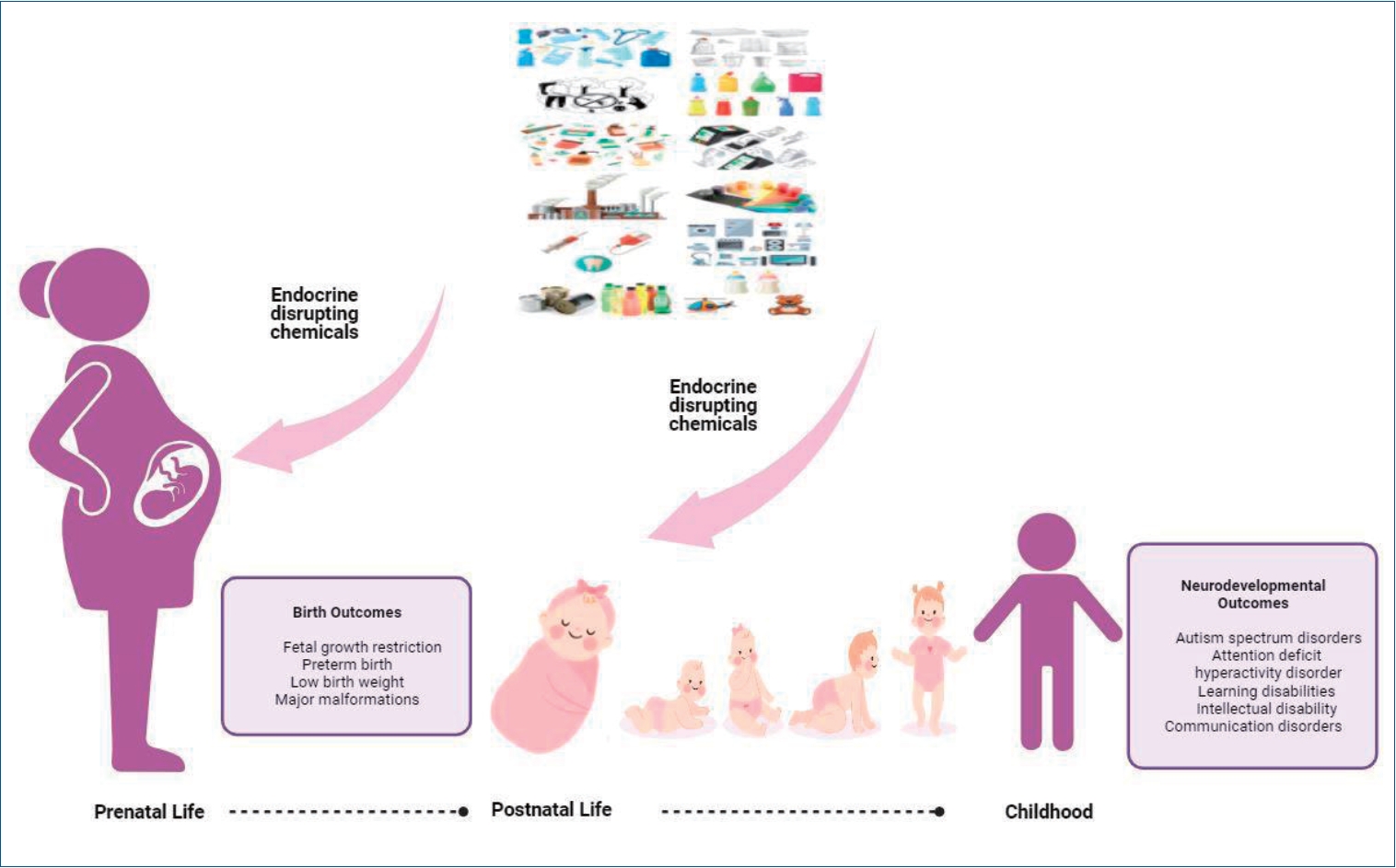
· Sensitivity to endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC) exposure increases during critical developmental periods (in embryos, fetuses, and neonates).
· Pre- and postnatal exposure to EDCs is associated with fetal growth restriction, preterm birth, and low birth weight.
· Exposure to EDCs during fetal and early postnatal life can have lasting and lifelong neurodevelopmental outcomes, including autism spectrum, attention deficit hyperactivity, and other cognitive and behavioral disorders.
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Effectiveness of Helmet therapy for infants with moderate to severe positional plagiocephaly (83 times)
- Jeongho Kim, Jina Kim, Kyu Young Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):46-53. Published online December 5, 2023
-
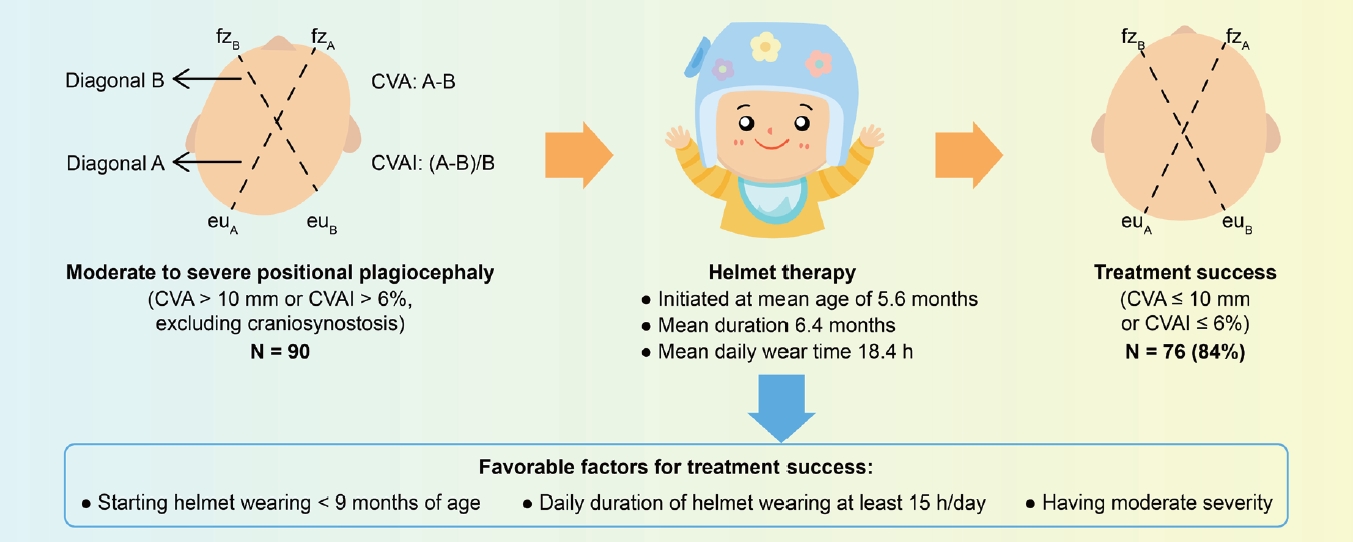
Question: Is helmet therapy effective for positional plagiocephaly? What factors influence helmet therapy efficacy for positional plagiocephaly?
Finding: Helmet therapy is effective for infants with moderate to severe positional plagiocephaly, and its effectiveness is influenced by age at treatment initiation, severity of head asymmetry, and daily duration of helmet wear.
Meaning: Pediatricians should initiate helmet therapy for positional plagiocephaly sooner, ideally before 9 months of age, to maximize treatment efficacy.
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











